Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is pu leather mean
In today’s competitive landscape, understanding the intricacies of PU leather—its composition, applications, and market implications—is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to source sustainable and cost-effective materials. PU leather, a synthetic alternative to genuine leather, offers a unique blend of affordability and versatility, but it also presents challenges related to durability and environmental impact. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of PU leather, their applications across industries, and essential considerations for supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Nigeria and Brazil, can make informed purchasing decisions.
Throughout this guide, we will explore critical factors such as the manufacturing processes behind PU leather, its sustainability credentials, and the long-term value it can provide. By addressing these elements, we aim to equip B2B buyers with actionable insights that enhance their sourcing strategies. From understanding the differences between PU leather and other materials to evaluating costs and potential health implications, this resource is designed to empower businesses with the knowledge they need to navigate the global market effectively. With an informed approach, you can ensure that your purchases align with both your budget and your brand’s commitment to sustainability and quality.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 What Is Pu Leather Mean Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is pu leather mean
- Understanding what is pu leather mean Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is pu leather mean
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is pu leather mean’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is pu leather mean
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is pu leather mean
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is pu leather mean’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is pu leather mean Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is pu leather mean With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is pu leather mean
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is pu leather mean Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is pu leather mean
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is pu leather mean
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
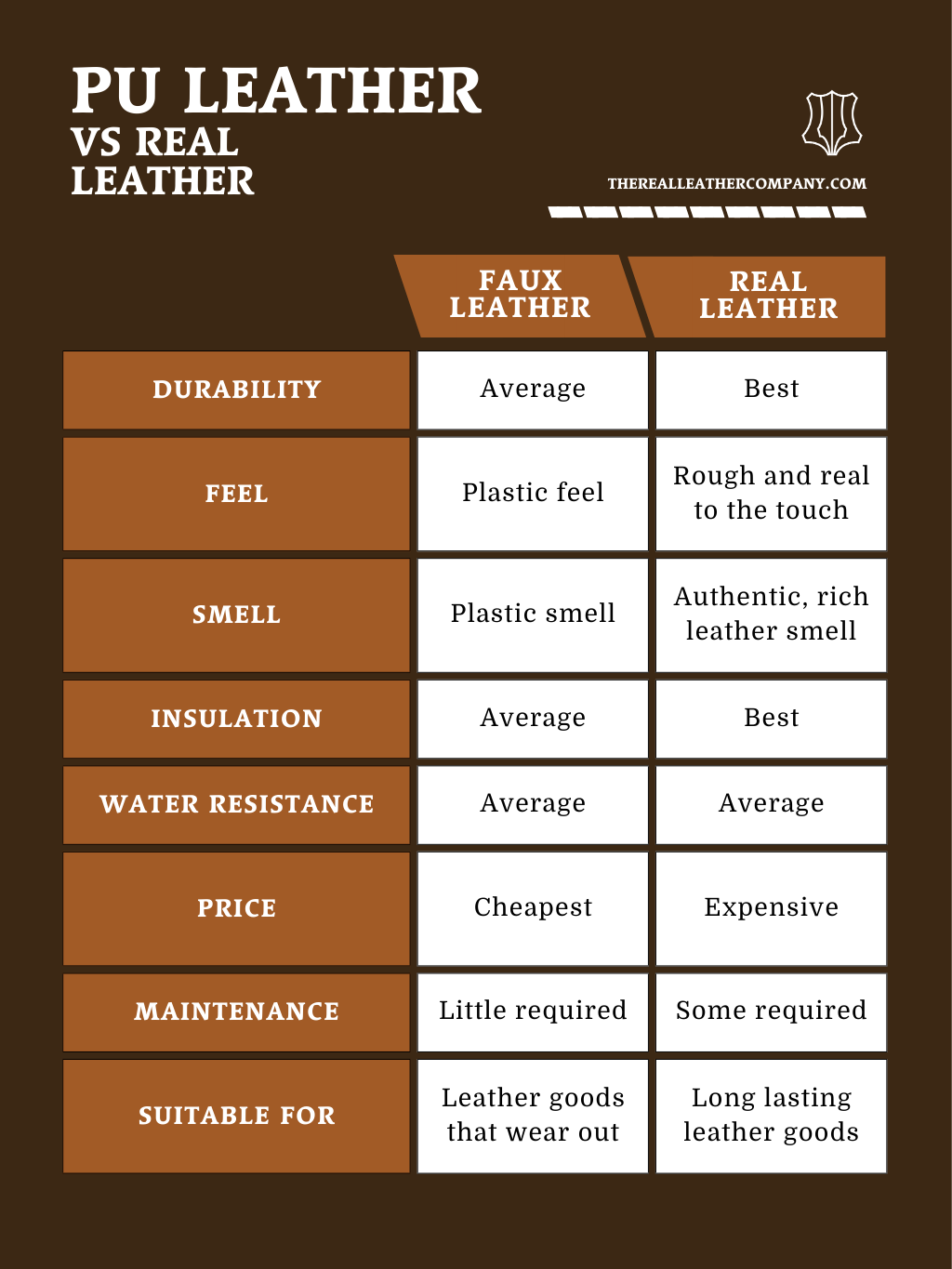
Understanding what is pu leather mean Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coated PU Leather | Fabric backing coated with polyurethane; resembles real leather | Fashion accessories, upholstery | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Less durable, may peel over time. |
| Microfiber PU Leather | Made from ultra-fine polyester fibers; softer and more durable | Automotive interiors, high-end fashion | Pros: More durable than standard PU; Cons: Higher cost, still synthetic. |
| Eco-Friendly PU Leather | Made with water-based adhesives; reduced environmental impact | Sustainable fashion, eco-conscious brands | Pros: Lower environmental footprint; Cons: May not match durability of genuine leather. |
| Vegan PU Leather | Completely animal-free; often marketed as a cruelty-free option | Vegan fashion brands, animal welfare markets | Pros: Appeals to ethical consumers; Cons: Quality can vary significantly. |
| Printed PU Leather | Features printed designs; customizable appearances | Promotional items, custom accessories | Pros: Highly customizable; Cons: Durability may be compromised depending on print quality. |
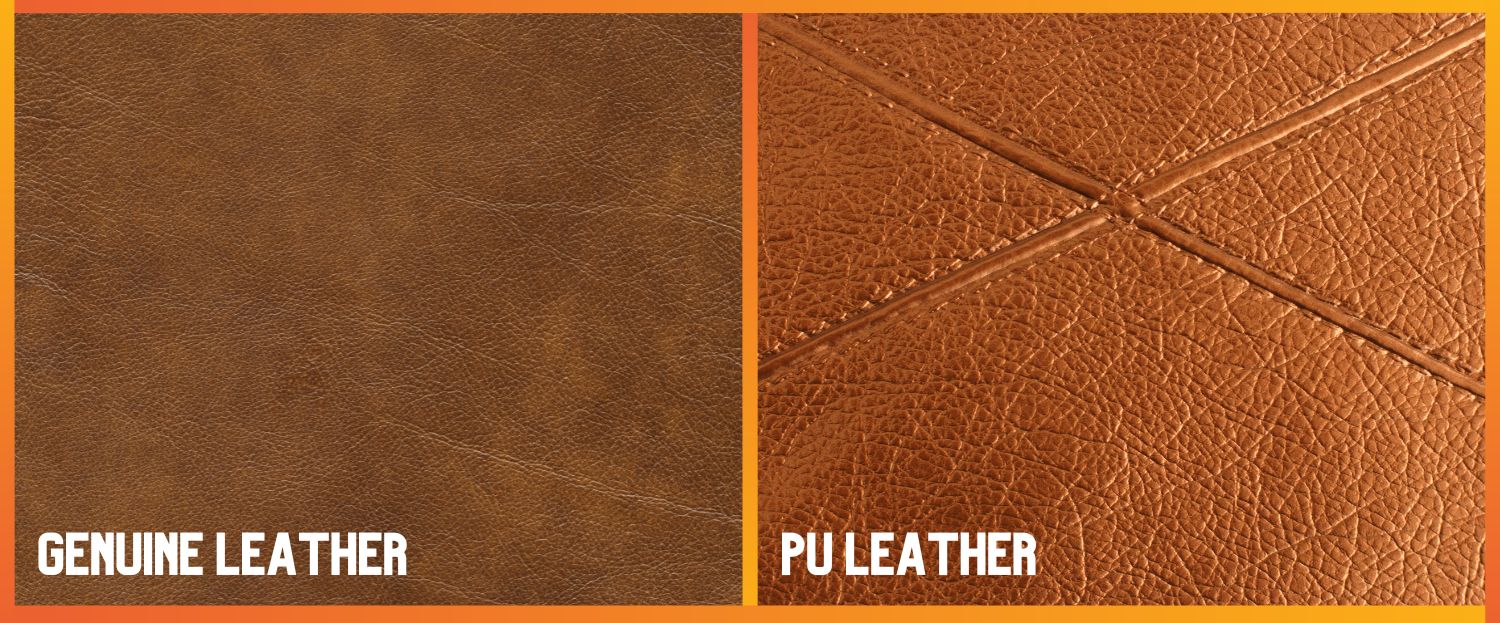
What Are the Characteristics of Coated PU Leather?
Coated PU leather is a widely used synthetic material characterized by a fabric backing that is coated with a layer of polyurethane. This gives it a leather-like appearance and feel, making it popular in fashion accessories and upholstery. However, its durability is a concern; frequent use can lead to cracking and peeling. B2B buyers should consider the lifecycle cost, as products made from coated PU leather may require more frequent replacement compared to genuine leather.
How Does Microfiber PU Leather Compare in Durability?
Microfiber PU leather is crafted from ultra-fine polyester fibers, resulting in a softer and more durable alternative to traditional PU leather. It is commonly used in automotive interiors and high-end fashion items, where a premium feel is desired. While it offers better durability than standard PU leather, it comes at a higher price point. B2B buyers should weigh the cost against the longevity and aesthetic appeal, especially in sectors that prioritize quality.
What Makes Eco-Friendly PU Leather a Sustainable Choice?
Eco-friendly PU leather is produced using water-based adhesives and processes that minimize environmental impact. This type of PU leather is increasingly favored by sustainable fashion brands looking to appeal to eco-conscious consumers. While it offers a more sustainable option, its durability may not match that of genuine leather. B2B buyers focused on sustainability should assess the certifications and sourcing practices of suppliers to ensure alignment with their brand values.
Why Is Vegan PU Leather Gaining Popularity?
Vegan PU leather is entirely animal-free and is often marketed as a cruelty-free alternative to traditional leather. This type appeals to ethical consumers and is commonly found in vegan fashion brands. However, the quality of vegan PU leather can vary widely, so B2B buyers should conduct thorough quality checks and consider the supplier’s reputation in the market. This ensures that the products meet consumer expectations for both ethics and performance.
Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
How Can Printed PU Leather Enhance Customization?
Printed PU leather offers unique customization options with various designs and patterns, making it suitable for promotional items and custom accessories. While this type allows for creative branding opportunities, its durability may be compromised based on the quality of the print. B2B buyers should evaluate the printing techniques used and consider the end-use of the products to ensure they meet both aesthetic and functional requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of what is pu leather mean
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is pu leather mean | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Accessories | Handbags and wallets | Cost-effective alternative to genuine leather with aesthetic appeal | Ensure ethical production and verify chemical safety standards |
| Automotive | Upholstery for seats and interiors | Lightweight and water-resistant, enhancing vehicle aesthetics | Look for durability and resistance to wear and tear |
| Muebles | Upholstered furniture | Versatile design options and easy maintenance | Assess environmental impact and sourcing transparency |
| Footwear | Shoes and boots | Affordable and stylish, catering to fast fashion demands | Check for comfort, breathability, and long-term performance |
| Sports Equipment | Protective gear and bags | Lightweight and resistant to weather conditions | Verify compliance with safety standards and material performance |
How is PU Leather Used in the Fashion and Accessories Industry?
In the fashion and accessories sector, PU leather is widely used for creating handbags and wallets. This synthetic material offers a visually appealing alternative to genuine leather at a fraction of the cost. For B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing PU leather products means balancing aesthetics with ethical production. It’s crucial to verify that suppliers adhere to safety standards, avoiding toxic chemicals during manufacturing, which can impact consumer health and brand reputation.
What Role Does PU Leather Play in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, PU leather is utilized for upholstery in vehicle interiors, including seats and door panels. Its lightweight nature contributes to improved fuel efficiency, while its water-resistant properties enhance durability against spills. For international buyers, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, it’s essential to consider the material’s longevity and resistance to wear, ensuring that it meets automotive standards for safety and comfort. Buyers should also assess the environmental implications of sourcing PU leather to align with sustainability goals.
Why is PU Leather Popular in the Furniture Sector?
PU leather is commonly employed in upholstered furniture, offering versatile design options and ease of maintenance. This synthetic material allows manufacturers to create stylish products that are often more affordable than genuine leather. B2B buyers in the furniture industry should focus on sourcing PU leather that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also durable and resistant to stains. Environmental impact should also be a key consideration, as buyers are increasingly looking for sustainable materials that align with consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
How is PU Leather Applied in the Footwear Industry?
In the footwear industry, PU leather is favored for its affordability and stylish appeal, making it a popular choice for shoes and boots. This material allows manufacturers to produce trendy designs that cater to fast fashion consumers. For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Nigeria and Brazil, it’s vital to ensure that the PU leather used is comfortable and breathable to meet consumer expectations. Long-term performance and wear resistance are also critical factors, as these attributes influence customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
What are the Advantages of PU Leather in Sports Equipment?
PU leather finds application in the production of protective gear and sports bags, valued for its lightweight properties and resistance to various weather conditions. This makes it an ideal choice for athletes and outdoor enthusiasts. B2B buyers in the sports equipment sector must prioritize compliance with safety standards and the performance characteristics of PU leather to ensure that the products meet the rigorous demands of sports activities. Additionally, sourcing from manufacturers that emphasize sustainability can enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is pu leather mean’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding PU Leather’s Quality and Durability
The Problem:
B2B buyers, particularly those in the furniture and fashion industries, often encounter confusion regarding the quality and durability of PU leather. Many suppliers market PU leather as a cost-effective alternative to genuine leather, leading buyers to assume they are purchasing a product with comparable longevity and performance. Unfortunately, this misunderstanding can result in significant financial losses due to high replacement rates when the material starts to crack and peel after just a few months of use.
The Solution:
To mitigate this risk, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on the specific PU leather products they intend to purchase. Request detailed specifications and performance data from suppliers, including expected lifespan and care instructions. It’s also beneficial to seek samples before committing to bulk orders. Testing these samples in real-world conditions can help gauge their durability and suitability for your application. Additionally, consider sourcing PU leather from manufacturers who provide transparent information about their production processes, including the quality of the polymers used, to ensure you are making an informed investment.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
Scenario 2: Environmental Concerns Regarding PU Leather
The Problem:
International buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of the materials they choose. PU leather, being a petroleum-based synthetic product, raises concerns regarding its biodegradability and the chemicals involved in its production. This can put companies at risk of negative publicity or backlash from eco-conscious consumers, particularly in markets in Europe and South America where sustainability is a critical purchasing factor.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who are committed to sustainable practices in their production of PU leather. Inquire about the environmental certifications of the materials used and the processes involved in manufacturing. Additionally, consider alternative materials such as vegetable-tanned leather or recycled synthetic options that may offer a lower environmental impact. Developing a sustainable sourcing strategy not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with global trends towards eco-friendly products. Engaging in partnerships with suppliers who share these values can lead to mutual benefits and innovative product offerings.
Scenario 3: Navigating Misleading Marketing Claims
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges due to misleading marketing terms such as “genuine leather” or “leather-like” that are sometimes used to describe PU leather. This can lead to confusion and poor purchasing decisions, especially when the product does not meet the quality or performance expectations associated with genuine leather. Such misrepresentation can damage a company’s reputation if the products fail to perform as promised.
The Solution:
To navigate these misleading claims, B2B buyers should develop a clear understanding of terminology related to leather products. Educate your procurement team on the distinctions between various types of leather, including PU leather, genuine leather, and faux leather. When sourcing, always ask for clarity on product descriptions and insist on detailed product specifications that include material composition. Establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers who provide honest and transparent information will ensure that your purchasing decisions are well-informed. Additionally, utilizing a checklist of required product attributes can help streamline the evaluation process and reduce the risk of miscommunication.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is pu leather mean
What Are the Key Materials Related to PU Leather?
When considering the use of PU leather in various applications, it is essential to analyze the materials involved in its production and their implications for performance, durability, and environmental impact. Below, we will explore the primary materials associated with PU leather, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
What is PU Leather Made Of? Analyzing Polyurethane
PU leather is primarily composed of polyurethane, a synthetic polymer that is formed through a chemical reaction between diisocyanates and polyols. This material is designed to mimic the appearance and feel of genuine leather while offering a more cost-effective alternative.
- Key Properties: PU leather is generally flexible, lightweight, and can be made to be water-resistant. However, it has a limited temperature resistance and can degrade under prolonged exposure to UV light.
- Pros & Cons: The main advantage of PU leather is its affordability and ease of maintenance. It can be wiped clean and does not require conditioning like real leather. However, it is less durable, often cracking and peeling after 1-2 years of use, making it unsuitable for high-wear applications.
- Impact on Application: PU leather is often used in fashion accessories, upholstery, and automotive interiors. Its compatibility with various media is limited due to its chemical composition, which may not withstand harsh environmental conditions.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local climate conditions that may affect PU leather’s longevity. Compliance with local environmental regulations regarding VOC emissions and waste management is also crucial.
What Other Materials Are Used in PU Leather Production?
In addition to polyurethane, the backing materials used in PU leather production play a significant role in its overall performance.
Analyzing Fabric Backing Materials
The backing for PU leather is typically made from woven or non-woven fabrics, which provide structural integrity and support.
- Key Properties: The backing material can vary widely, with some fabrics offering enhanced breathability and moisture resistance. Common fabrics include polyester and cotton blends.
- Pros & Cons: Fabric backing can improve the overall strength of PU leather, but it can also increase manufacturing complexity and costs. While it can enhance comfort, the choice of backing material can significantly affect the final product’s durability.
- Impact on Application: The choice of backing material can determine the suitability of PU leather for specific applications, such as clothing versus upholstery.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local fabric standards and certifications, ensuring that the materials used comply with regulations in their respective markets.
What Are the Environmental Considerations of PU Leather?
The production of PU leather raises significant environmental concerns, particularly regarding its non-biodegradable nature and the chemicals used in its manufacturing process.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
- Key Properties: PU leather is derived from petroleum-based materials, which contribute to its carbon footprint. The presence of VOCs and other harmful chemicals during production poses risks to both human health and the environment.
- Pros & Cons: While PU leather is often marketed as a vegan alternative to animal leather, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Its short lifespan leads to increased waste, and the manufacturing process can be harmful to ecosystems.
- Impact on Application: The environmental implications of PU leather can affect brand perception and consumer preferences, particularly in markets with a growing demand for sustainable products.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the sustainability practices of their suppliers and seek certifications that demonstrate compliance with environmental standards, such as ISO 14001.
Summary Table of Materials Related to PU Leather
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is pu leather mean | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Fashion accessories, upholstery, automotive | Affordable and easy to maintain | Limited durability, prone to cracking and peeling | Low |
| Fabric Backing Materials | Clothing, upholstery | Enhances strength and comfort | Increases manufacturing complexity and cost | Medium |
| Chemical Additives | Moisture resistance, durability enhancement | Improves product performance | Potential health risks and environmental impact | Medium |
| Eco-friendly Alternatives | Sustainable fashion products | Reduced environmental impact | Generally higher cost and limited availability | Alta |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions regarding PU leather and its alternatives, particularly in diverse international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is pu leather mean
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of PU Leather?
The manufacturing process of PU leather involves several key stages, each critical to producing a quality product that meets market demands. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source PU leather effectively.
Material Preparation: What Goes Into PU Leather?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. PU leather is primarily made from polyurethane, a synthetic polymer derived from a reaction between diisocyanates and polyols. This process begins with the careful selection of high-quality raw materials to ensure the durability and aesthetic appeal of the final product.
Once the raw materials are selected, a backing material—usually a blend of fabric—is prepared. This backing provides structural integrity and support. The selection of the backing material can significantly influence the texture and feel of the PU leather, making it essential for manufacturers to choose wisely based on the intended application.
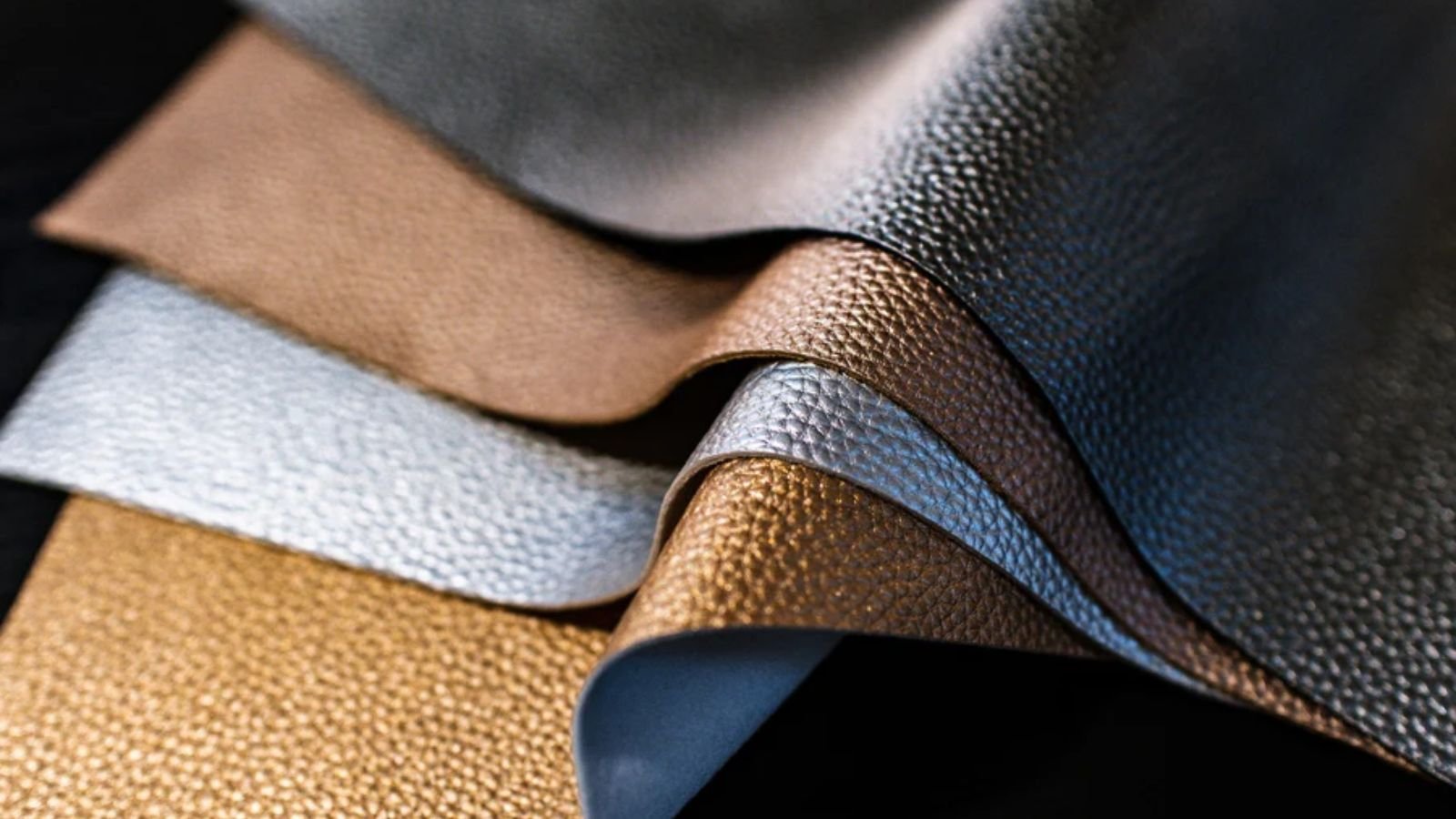
How Is PU Leather Formed?
After material preparation, the next phase is forming. This involves applying a layer of polyurethane onto the backing material through a process known as coating. Manufacturers employ various techniques for this, including:

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
- Roll Coating: A method that ensures an even application of polyurethane over the entire surface of the backing fabric.
- Spray Coating: Used for more intricate designs, this technique allows for varying textures and finishes.
- Foam Coating: This method creates a thicker layer of polyurethane, providing additional cushioning and comfort.
The coating process typically includes embossing to replicate the look of natural leather, adding a layer of realism that appeals to consumers.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Once the PU leather is formed, the next stage is assembly. This step involves cutting the coated fabric into desired shapes and sizes, followed by stitching and bonding to create the final product, whether it be handbags, upholstery, or footwear.
Manufacturers may also incorporate additional materials during this phase, such as zippers, linings, and reinforcements, depending on the product specifications. Precision in this stage is vital to ensure the durability and functionality of the final product.
What Are the Finishing Techniques Used in PU Leather Production?
The finishing stage is crucial for enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of PU leather. This process can include:
- Surface Treatments: Applying additional coatings to improve water resistance, UV stability, or scratch resistance.
- Coloring and Dyeing: Using environmentally friendly dyes to achieve the desired color while maintaining the integrity of the material.
- Quality Control Measures: Ensuring that the finished product meets specific standards, both in terms of appearance and durability.
These finishing techniques not only contribute to the product’s visual appeal but also its longevity, making them essential for manufacturers aiming to meet consumer expectations.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
What Are the Key Quality Control Measures for PU Leather?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the PU leather manufacturing process. Implementing effective quality control (QC) measures helps ensure that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Apply to PU Leather Manufacturing?
B2B buyers should be aware of relevant international standards that govern the manufacturing of PU leather. The most notable include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system and is critical for ensuring consistent quality in production processes.
- CE Marking: Particularly important for products sold in the European Union, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Understanding these standards can help buyers assess the credibility and reliability of their suppliers.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
What Are the QC Checkpoints in PU Leather Production?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure the product meets established standards. These checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, IPQC checks for adherence to manufacturing standards and specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection occurs before the product is packaged and shipped. It ensures that the finished product meets all quality standards and is free from defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following verification methods:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into a supplier’s manufacturing practices and adherence to quality standards.
- Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed reports on quality control processes and results can help buyers assess supplier reliability.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of product quality and compliance with international standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have specific quality standards and regulations that suppliers must comply with. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regional requirements to ensure that the products they source meet local market demands.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
What Role Does Sustainability Play in Quality Control?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the manufacturing process of PU leather. B2B buyers should inquire about the environmental impact of the production processes and the materials used. Suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices often have more robust quality control measures in place, as they are committed to maintaining high standards across all aspects of their operations.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with PU leather, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing products. This knowledge not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also enhances the overall quality and sustainability of the products offered in the marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is pu leather mean’
To assist B2B buyers in understanding and sourcing PU leather, this practical guide outlines essential steps to consider during the procurement process. PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is a synthetic alternative to genuine leather, and while it offers various advantages, it also has significant limitations. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing PU leather effectively.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
Step 1: Understand the Material Composition
Before making a purchase, ensure you have a comprehensive understanding of what PU leather is made from. PU leather is typically a fabric coated with a layer of polyurethane, which can vary in quality. Knowing the composition helps in assessing durability and potential environmental impacts.
- Key Points:
- Look for suppliers who provide detailed specifications about the material.
- Inquire about the backing fabric and the thickness of the polyurethane layer.
Step 2: Assess the Quality Standards
Quality can vary significantly among suppliers. It’s vital to establish the quality standards you require for your products. High-quality PU leather should resist cracking and peeling over time.
- Key Points:
- Request samples to evaluate the feel, durability, and appearance.
- Verify if the supplier adheres to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Certifications can provide assurance regarding the safety and environmental impact of PU leather products. Look for suppliers with certifications that confirm compliance with health and environmental regulations.
- Key Points:
- Check for certifications like OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 or REACH compliance.
- Ensure that the supplier can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Step 4: Investigate the Manufacturing Process
Understanding how PU leather is produced can reveal potential health and environmental concerns. Some manufacturing processes may involve toxic chemicals that could affect your end-users.
- Key Points:
- Ask suppliers about their production methods and whether they minimize the use of harmful substances.
- Inquire if they have measures in place to manage waste and emissions.
Step 5: Determine the Environmental Impact
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, assess the environmental footprint of the PU leather you plan to source. This includes understanding its biodegradability and the resources used in production.
- Key Points:
- Evaluate whether the supplier employs eco-friendly practices in their manufacturing process.
- Consider sourcing PU leather that is marketed as environmentally sustainable.
Step 6: Request Detailed Product Specifications
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, request detailed product specifications for the PU leather they offer. This documentation should include information on the expected lifespan, maintenance requirements, and warranty terms.
- Key Points:
- Ensure specifications detail the intended use cases to determine suitability for your needs.
- Pay attention to care instructions to inform your customers properly.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is crucial for a successful sourcing partnership. Ensure that you have clear channels for discussing specifications, timelines, and any potential issues.
- Key Points:
- Set up regular check-ins with your suppliers to discuss progress and feedback.
- Establish protocols for addressing concerns or quality issues promptly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing PU leather, ensuring they select products that meet their quality, environmental, and ethical standards.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is pu leather mean Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in PU Leather Sourcing?
When sourcing PU leather, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The primary raw material for PU leather is polyurethane, often combined with a backing fabric. Prices can vary significantly based on quality and supplier. High-quality polyurethane may command a premium, while lower-grade options are more affordable but may affect durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on the production location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Asia, may offer competitive pricing, whereas Europe and North America may incur higher labor costs due to stringent labor laws and wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running the production facility, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient factories may have lower overhead costs, which can be beneficial for pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for molds and specialized machinery can be significant, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider these costs in their total investment, particularly for lower volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing a robust QC process ensures that the PU leather meets specified standards. While this incurs additional costs, it can prevent losses from defective products and enhance customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the supplier’s location, order volume, and shipping method. Incoterms also play a crucial role in determining who bears the cost and risk during transportation.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can aid in negotiations.
What Influences Pricing for PU Leather Products?
Several factors can influence the pricing of PU leather beyond the basic cost components.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders usually lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific requirements (e.g., unique textures or colors) can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality PU leather or materials that meet specific environmental or health standards may come at a premium. Certifications can also affect pricing and should be discussed upfront.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their track record and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can affect the overall cost structure, as they dictate the responsibilities of the buyer and seller during shipping.
What Are Some Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings. Here are some actionable tips:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential replacements. This holistic view can help justify higher initial costs if the product offers better longevity.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs or negotiate for lower prices on larger quantities. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts for bulk purchases.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from several suppliers can provide leverage during negotiations. It allows you to compare prices and terms, helping you secure the best deal.
-
Be Clear About Specifications: Providing detailed specifications can prevent misunderstandings and unexpected costs. Ensure that all parties are aligned on what is being produced.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Understanding market trends and fluctuations in material costs can empower you during negotiations, enabling you to advocate for fair pricing.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing nuances associated with PU leather sourcing is crucial for international B2B buyers. By considering the various cost components and price influencers, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful partnerships and optimized purchasing strategies. Always remember to approach negotiations with a comprehensive understanding of the total cost of ownership to ensure the best value for your investment.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is pu leather mean With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to PU Leather: A Comparative Analysis
As businesses increasingly seek sustainable and durable materials, understanding alternatives to PU leather becomes crucial. PU leather, while popular for its affordability and resemblance to genuine leather, presents several drawbacks in terms of durability, environmental impact, and safety. This analysis compares PU leather with viable alternatives: vegetable-tanned leather and recycled materials, focusing on various performance aspects important for B2B buyers.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is PU Leather Mean | Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Recycled Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate durability; prone to cracking and peeling | High durability; develops a unique patina over time | Variable durability; depends on material quality and processing |
| Cost | Generally low-cost | Higher initial investment but cost-effective long-term | Cost varies; often lower than new materials but can be inconsistent |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to source; widely available | Requires specialized suppliers; longer lead times | Availability can be variable based on material sourcing |
| Maintenance | Minimal upkeep; wipe clean | Requires regular conditioning; more care needed | Maintenance depends on the specific material and processing |
| Best Use Case | Budget-friendly fashion items and accessories | High-quality products where longevity and aesthetics are prioritized | Eco-conscious products, promotional items, and casual wear |
Exploring Vegetable-Tanned Leather as an Alternative
Vegetable-tanned leather stands out as a premium alternative to PU leather. Sourced from natural plant materials, it boasts high durability and an attractive aging process that enhances its character over time. While the initial cost is higher than PU leather, the long-term value is significant due to its longevity and unique aesthetic appeal. However, sourcing can be more complex, requiring partnerships with specialized tanneries, which may lead to longer lead times for production.
Evaluating Recycled Materials for Eco-Friendly Solutions
Recycled materials present an innovative alternative to traditional leather options, including PU leather. This category encompasses a range of materials derived from post-consumer or post-industrial waste, offering a sustainable solution to material sourcing. The cost of recycled materials can vary widely, often being lower than new materials, yet the quality can be inconsistent. The ease of implementation depends on the availability of quality recycled materials, which can fluctuate. Additionally, while maintenance requirements vary, many recycled products are designed for low upkeep, appealing to eco-conscious brands looking to minimize their environmental footprint.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When deciding between PU leather and its alternatives, B2B buyers must consider their specific needs and the values of their target market. If durability and aesthetic appeal are paramount, vegetable-tanned leather may be the superior choice despite its higher initial cost. Conversely, for brands prioritizing sustainability and lower costs, recycled materials can offer a compelling solution. Understanding these nuances allows businesses to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and customer expectations, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and ethical product offering.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is pu leather mean
What are the Key Technical Properties of PU Leather?
Understanding the technical properties of PU leather is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when evaluating it against alternative materials. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Composition
PU leather is primarily made from polyurethane, a polymer derived from a chemical reaction between diisocyanates and polyols. This composition allows PU leather to mimic the appearance of genuine leather while being more affordable. For B2B buyers, knowing the exact composition is vital for assessing the product’s quality and suitability for specific applications, whether in fashion, automotive, or furniture industries.
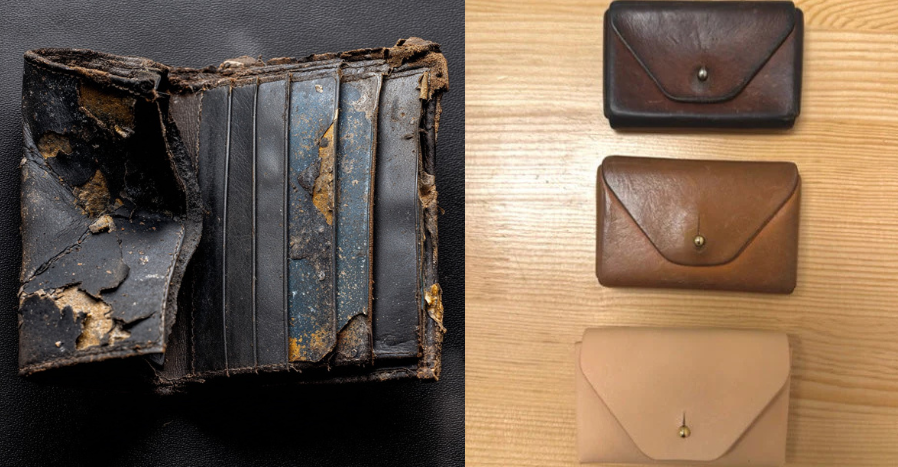
2. Durability and Lifespan
Typically, PU leather has a lifespan ranging from 6 to 24 months, significantly shorter than that of genuine leather, which can last over a decade. This durability factor is crucial for B2B buyers evaluating the long-term value of their investment. Products requiring frequent replacement can lead to increased costs and waste, impacting sustainability initiatives.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
3. Environmental Impact
PU leather is a petroleum-based product and is non-biodegradable, raising environmental concerns. Buyers should consider the lifecycle analysis of PU leather versus alternatives, as purchasing decisions can influence corporate sustainability goals. Understanding the environmental footprint can also affect branding and consumer perception.
4. Chemical Resistance and Safety
Some PU leather products may contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other potentially harmful chemicals. B2B buyers must ensure that the products meet safety regulations, particularly in industries like fashion and consumer goods. Certifications regarding chemical safety can be a deciding factor in procurement decisions.
5. Texture and Finish
The texture of PU leather is typically uniform and can be designed to resemble various types of leather finishes. This property is essential for product aesthetics, especially in fashion and luxury goods. Buyers need to assess the texture to ensure it aligns with their brand’s quality standards and consumer expectations.
6. Maintenance Requirements
PU leather is generally easy to clean, requiring only a wipe-down to maintain its appearance. For B2B buyers, understanding maintenance needs is crucial in determining product usability and customer satisfaction. Products that require less upkeep can be more attractive for bulk purchasing.
What are Common Trade Terms Used in the PU Leather Industry?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms related to PU leather:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or products that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of PU leather, an OEM might supply PU leather components for automotive interiors or fashion accessories. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers streamline their supply chains.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels and cash flow effectively. Suppliers often set MOQs based on production costs and logistics.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process wherein a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products. For PU leather, an RFQ can help buyers assess multiple suppliers and negotiate better terms, ensuring cost-effectiveness in procurement.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of international sales terms that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions involving PU leather, as they outline who bears the costs and risks at various stages of the shipping process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is critical for B2B buyers to plan their inventory and production schedules effectively, particularly when sourcing PU leather from international suppliers.
6. Certification Standards
These refer to various industry standards that guarantee the quality and safety of materials, including PU leather. Certifications such as OEKO-TEX or REACH compliance can indicate that the product meets specific environmental and safety criteria, aiding buyers in making informed decisions.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing PU leather, ensuring that they select products that align with their business goals and consumer expectations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is pu leather mean Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for PU Leather in the B2B Sector?
The PU leather market has experienced notable growth due to its affordability and versatility, making it a popular choice among manufacturers and international B2B buyers. Key drivers of this market include increasing demand for cost-effective materials in fashion, automotive, and furniture industries. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses are increasingly exploring PU leather as a substitute for genuine leather, especially in emerging markets where price sensitivity is high.

Illustrative image related to what is pu leather mean
Current trends indicate a rising interest in customization and design flexibility, as manufacturers look to differentiate their offerings. Technological advancements in the production of PU leather are enhancing its quality, making it more appealing for various applications. For example, innovations in coating techniques are yielding PU leather that mimics the texture and appearance of real leather more closely. Furthermore, the shift towards online marketplaces is facilitating easier sourcing for B2B buyers, allowing them to access a broader range of suppliers and products with comparative ease.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Changing PU Leather Supply Chains?
The environmental impact of PU leather production has become a pressing concern for international buyers. Traditional PU leather manufacturing involves the use of toxic chemicals and processes that can harm both human health and the environment. As a result, there is a growing demand for sustainable alternatives and ethical sourcing practices within the industry. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to environmentally friendly manufacturing processes and use non-toxic materials.
Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and OEKO-TEX® can help buyers identify products that meet sustainability criteria. Additionally, the rise of plant-based materials and innovative recycling methods is reshaping the landscape of PU leather. Buyers are encouraged to seek partnerships with manufacturers who not only focus on product quality but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, thereby enhancing their brand’s reputation and appeal in an eco-conscious market.
What Is the Historical Context of PU Leather Production?
PU leather emerged in the mid-20th century, driven by the need for affordable and accessible alternatives to genuine leather. The first synthetic leather was created from polyurethane, a polymer that was initially utilized for industrial applications. By the 1960s, manufacturers began experimenting with this material to produce consumer goods that mimicked the look and feel of leather.
Over the years, advancements in technology have improved the quality of PU leather, allowing it to compete more effectively with traditional leather. However, despite its popularity, the environmental implications of PU leather production have sparked a movement toward more sustainable and ethical practices. As buyers become more informed about the origins and impacts of their materials, the shift towards greener alternatives is likely to continue shaping the future of PU leather in the B2B sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is pu leather mean
-
1. What is PU leather and how is it made?
PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is a synthetic material designed to mimic the look and feel of real leather. It is produced by coating a backing fabric with a layer of polyurethane, which is then treated to enhance durability and appearance. The manufacturing process often involves adding textures and additional chemicals for moisture resistance. This material is popular for its affordability, but it lacks the longevity and character of genuine leather. -
2. How does PU leather compare to genuine leather in terms of durability?
PU leather typically lasts between 6 to 24 months with regular use, while genuine leather can endure for decades. PU leather is prone to cracking, peeling, and fading over time, especially under heavy wear conditions. In contrast, genuine leather develops a unique patina and becomes more supple with age, making it a better long-term investment for businesses looking for quality and durability in their products. -
3. What are the environmental implications of using PU leather?
PU leather is a petroleum-based product and non-biodegradable, contributing to environmental pollution. The production process can release harmful chemicals, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which pose health risks and environmental concerns. Businesses should consider these factors when sourcing materials and may want to explore eco-friendly alternatives like vegetable-tanned leather for a more sustainable choice. -
4. What should I consider when vetting PU leather suppliers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their transparency regarding the materials used and the manufacturing processes. Check for certifications that indicate eco-friendliness and compliance with safety standards. Additionally, assess their production capacity, quality assurance processes, and history of customer service. Request samples to evaluate the quality of their PU leather before making larger commitments. -
5. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for PU leather products?
MOQs for PU leather products can vary widely among suppliers, ranging from a few hundred to several thousand units. Factors influencing MOQ include the supplier’s production capabilities, material costs, and customization options. It’s crucial to communicate your needs clearly and negotiate terms that align with your business objectives while ensuring the supplier can meet your volume requirements. -
6. What payment terms are typically available for international PU leather purchases?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common options include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance payment upon shipment. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms, allowing buyers to pay within a specified period post-delivery. Always clarify terms before finalizing agreements to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
7. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for PU leather products?
To ensure QA, establish clear specifications for the PU leather products you require, including texture, durability, and finish. Request samples for evaluation before placing bulk orders, and consider implementing regular audits of the supplier’s production processes. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can facilitate better communication regarding quality control and adherence to your standards. -
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing PU leather?
When importing PU leather, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs in your target market. Ensure your supplier can provide necessary documentation, such as certificates of origin and compliance with local regulations. Factor in lead times for production and shipping to avoid delays, and work with logistics partners experienced in international trade to streamline the process.
Top 5 What Is Pu Leather Mean Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Manuel Dreesmann – PU Leather Alternatives
Domain: manuel-dreesmann.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: PU leather is a synthetic material made from polyurethane, often used as a cheaper alternative to genuine leather. It is important to avoid PU leather due to its environmental impact, lack of durability compared to real leather, and potential health risks from chemicals used in its production.
2. HowStuffWorks – PU Leather Guide
Domain: home.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: PU (Polyurethane) leather is an artificial leather made from polyurethane, a type of plastic. It is 100% vegan and does not contain animal skin. There are two types of PU leather: full-synthetic (totally vegan) and semi-synthetic (which has a natural leather base). PU leather is water-resistant, easy to clean, and available in a wide variety of colors. However, it lacks the authentic appearance an…
3. Prestige Leather Care – PU Leather Solutions
Domain: prestigeleathercare.co.uk
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: PU leather, also known as polyurethane leather, is an artificial type of leather made from thermoplastic polymers. It is often referred to by other names such as bicast leather, split leather, reconstituted leather, bonded leather, and corrected grain leather. PU leather can be cleaned with a suitable leather cleaner and brush. It is considered vegan only if it is 100% PU; otherwise, it may contai…
4. Senreve – PU Leather Handbags
Domain: senreve.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is an artificial leather made of thermoplastic polymer. It is 100% vegan and can be identified by various names such as Bicast Leather, Doublecast Leather, Split Leather, Bonded Leather, Reconstituted Leather, and Corrected Grain Leather. Pros of PU leather include water resistance, ease of cleaning, and a wider variety of colors. Cons include a plastic shine, …
5. Rahui – PU Leather Solutions
Domain: rahui.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, Rahui – PU Leather Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is pu leather mean
As businesses navigate the complexities of sourcing materials, understanding the implications of using PU leather is paramount. While PU leather offers an affordable alternative to genuine leather, its durability, environmental impact, and potential toxicity raise significant concerns. International B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets such as Nigeria and Brazil, should weigh these factors carefully against their procurement strategies.
Strategic sourcing involves not only cost considerations but also the long-term value and sustainability of materials. By opting for higher-quality alternatives, such as vegetable-tanned leather, businesses can ensure they are making a responsible choice that aligns with ethical and environmental standards. This approach not only enhances product quality but also bolsters brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Looking forward, it is essential for buyers to stay informed about material innovations and trends in sustainability. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize transparency and ethical practices can lead to stronger partnerships and a competitive edge. As you evaluate your sourcing decisions, consider the broader implications of your material choices—both for your business and the planet. Let’s work together toward a sustainable future in the leather goods industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.