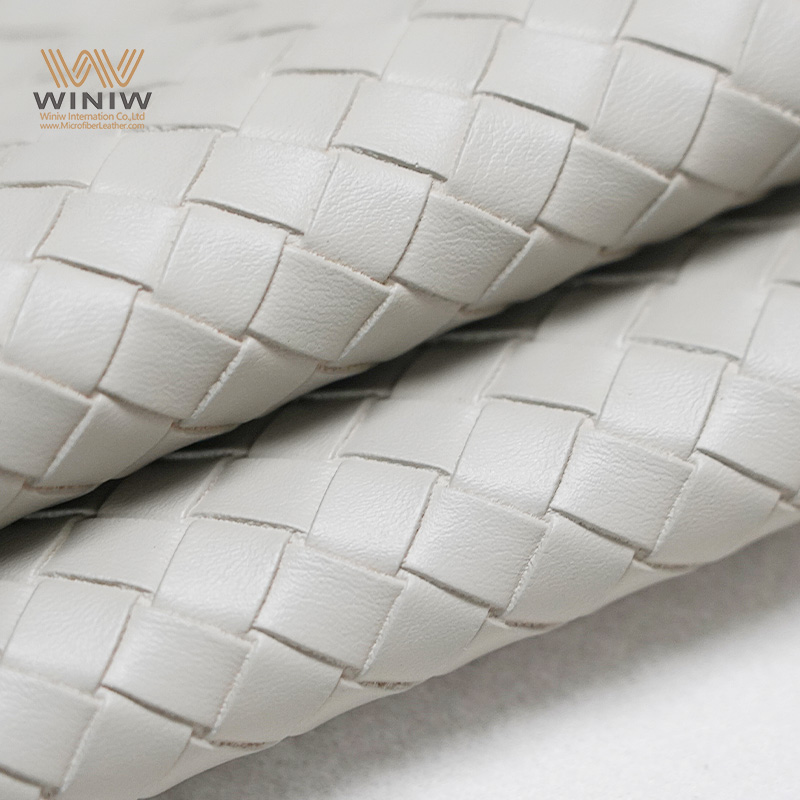
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather grades
Navigating the complexities of leather grades can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing materials that meet both quality standards and market demands. Understanding the nuances between various types of leather—such as full grain, top grain, and corrected grain—can directly impact your product’s durability, aesthetic appeal, and ultimately, your bottom line. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets such as Germany and Brazil, by demystifying the leather grading system.
In the following sections, we will explore the different grades of leather, their applications across various industries, and offer insights on effective supplier vetting processes. Additionally, we will provide an overview of cost considerations associated with each grade, enabling you to make informed purchasing decisions. By equipping you with actionable knowledge about leather grades, this guide aims to enhance your procurement strategy, ensuring that you select the right materials that align with your quality expectations and market needs. Whether you’re looking to source leather for fashion, furniture, or automotive applications, a deeper understanding of leather grades will help you navigate the global market with confidence.
Table Of Contents
- Top 7 Leather Grades Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather grades
- Understanding leather grades Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of leather grades
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather grades’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather grades
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather grades
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather grades’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather grades Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather grades With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather grades
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather grades Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather grades
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather grades
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
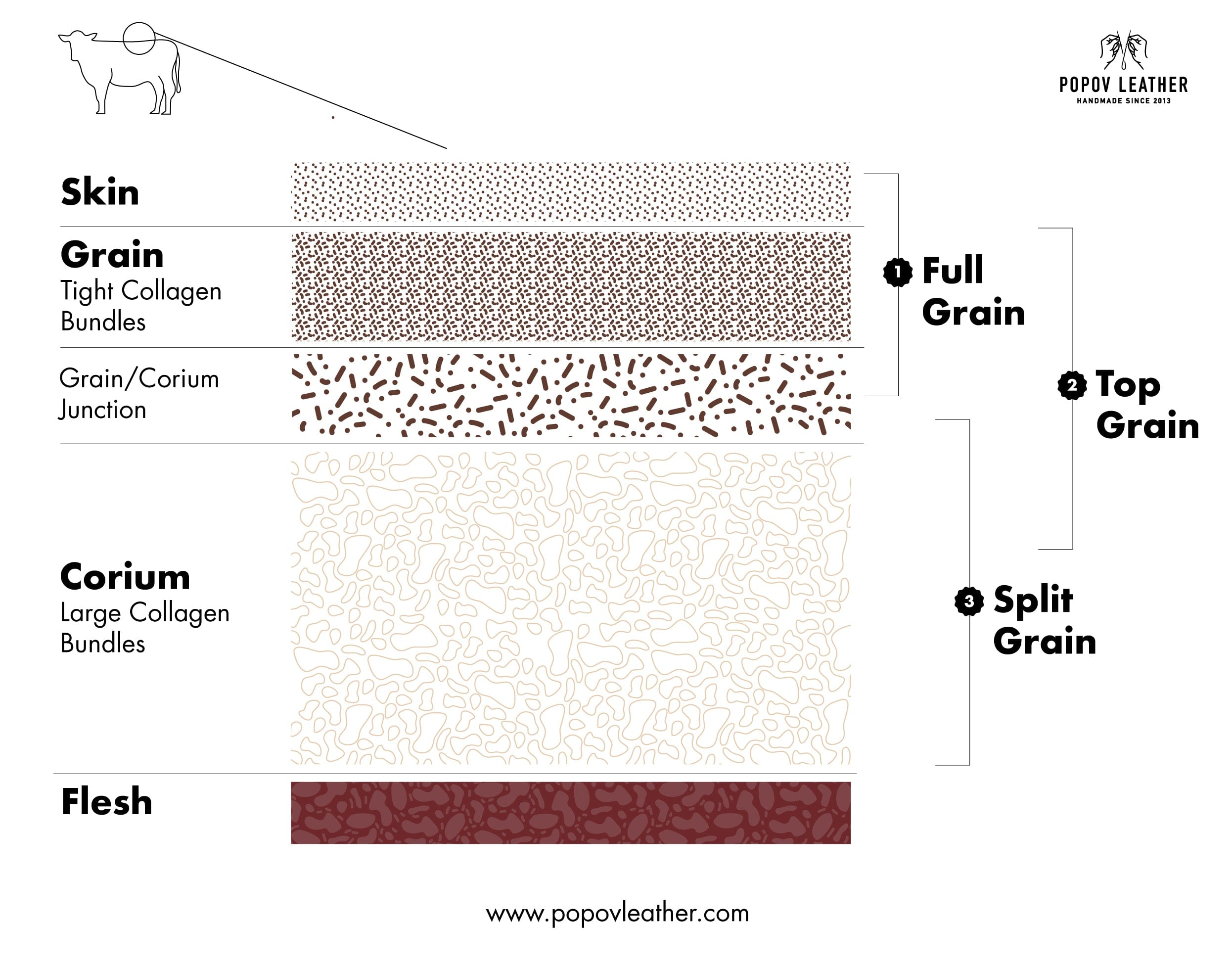
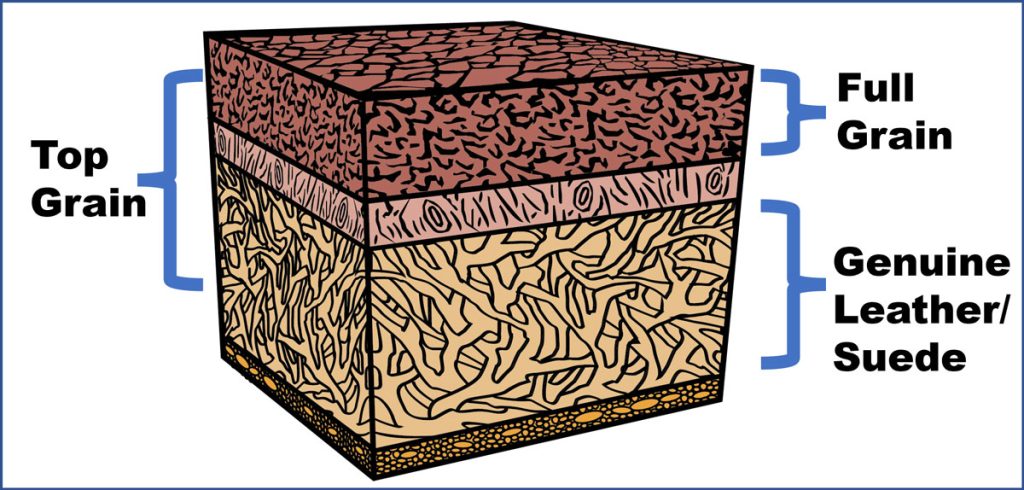
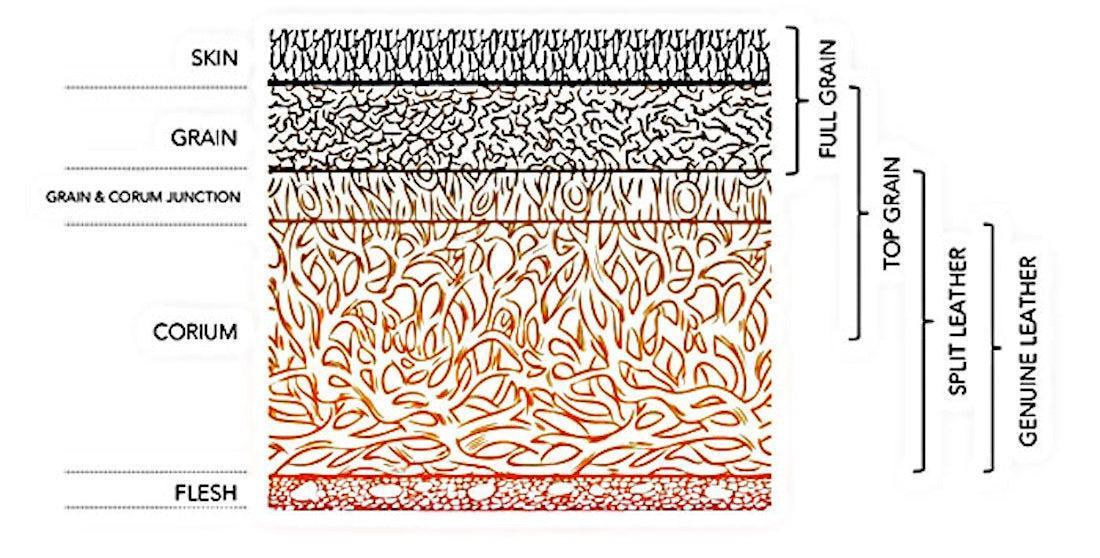
Understanding leather grades Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Grain Leather | Complete grain intact, natural markings, high durability | Luxury goods, high-end furniture, accessories | Pros: Exceptional quality, breathability, develops patina; Cons: Higher cost, may have visible imperfections. |
| Corrected Grain Leather | Sanded surface, uniform appearance, less breathability | Apparel, footwear, upholstery | Pros: Consistent look, easier to clean; Cons: Less character, potential durability concerns. |
| Split Grain Leather | Lower quality, lacks the top grain, often less durable | Budget-friendly products, mass-market goods | Pros: Cost-effective, lightweight; Cons: Prone to wear, less aesthetically pleasing. |
| Bonded Leather | Made from leather scraps, synthetic backing | Low-end goods, promotional items | Pros: Very low cost, eco-friendly (recycling); Cons: Poor durability, lacks genuine leather feel. |
| Nubuck | Soft, suede-like finish, sanded top grain | Footwear, gloves, upholstery | Pros: Attractive appearance, hides scratches; Cons: Requires careful maintenance, can stain easily. |
What are the characteristics of Full Grain Leather and its suitability for B2B buyers?
Full Grain Leather retains the complete grain structure of the hide, showcasing natural markings and imperfections that enhance its aesthetic appeal. This type is renowned for its durability and breathability, making it ideal for luxury goods, high-end furniture, and premium accessories. For B2B buyers, investing in Full Grain Leather translates to long-lasting products that age beautifully, offering both quality and a unique character that can elevate brand prestige. However, the higher price point may require justification in cost-sensitive markets.
How does Corrected Grain Leather differ from Full Grain Leather?
Corrected Grain Leather undergoes a sanding process to remove surface imperfections, resulting in a more uniform appearance. This type is commonly used in apparel, footwear, and upholstery, where a consistent look is often prioritized. For B2B buyers, Corrected Grain Leather offers a balance between quality and affordability, making it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to maintain a professional appearance in their products. However, the potential reduction in breathability and character may be a trade-off for some buyers.
What are the implications of choosing Split Grain Leather for B2B applications?
Split Grain Leather is derived from the lower layers of the hide, resulting in a product that is generally less durable and visually appealing compared to higher-grade leathers. It is often used for budget-friendly products and mass-market goods. While Split Grain Leather can be a cost-effective solution for B2B buyers, it is essential to consider the potential trade-offs in quality and longevity. Businesses targeting price-sensitive segments may find value in this option, but they should be prepared for the limitations it presents.
Why should B2B buyers be cautious with Bonded Leather?
Bonded Leather is created from leather scraps bonded together with synthetic materials, making it the least desirable option in terms of quality. It is typically used for low-end goods and promotional items. While it is very cost-effective and can appeal to eco-conscious brands looking to recycle materials, B2B buyers should be aware of its poor durability and lack of genuine leather characteristics. This type may serve short-term needs but is unlikely to satisfy customers seeking quality and longevity.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
What makes Nubuck a popular choice in the leather market?
Nubuck is characterized by its soft, suede-like texture achieved through sanding the top grain of the leather. It is commonly used in footwear, gloves, and upholstery, providing an attractive and luxurious feel. For B2B buyers, Nubuck can be appealing due to its ability to hide scratches and its aesthetic versatility. However, it requires careful maintenance to prevent staining and damage from moisture, which should be considered when evaluating its long-term suitability for various applications.
Key Industrial Applications of leather grades
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of leather grades | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | High-end footwear and accessories | Enhanced brand image and customer loyalty | Quality of leather, sourcing practices, and ethical standards |
| Automotive | Upholstery for luxury vehicles | Increased perceived value and comfort | Compliance with industry regulations and durability requirements |
| Furniture & Interior Design | Custom leather furniture | Unique aesthetics and durability | Availability of various leather grades and customization options |
| Sports Equipment | Leather goods for sporting activities | Performance enhancement and durability | Weight, flexibility, and moisture resistance of leather grades |
| Industrial Goods | Protective gear and workwear | Safety and longevity in demanding environments | Compliance with safety standards and wear resistance |
How are Different Leather Grades Utilized in the Fashion & Apparel Industry?
In the fashion and apparel sector, high-end footwear and accessories predominantly utilize full-grain and corrected-grain leather. These grades provide not only superior durability but also the ability to develop a unique patina, enhancing the product’s aesthetic appeal over time. This is crucial for brands aiming to establish a premium image, especially in competitive markets across Europe and South America. International buyers must consider the sourcing of ethically produced leather to align with consumer values and ensure compliance with regional regulations.
What Role Does Leather Play in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, leather is commonly used for upholstery in luxury vehicles. Full-grain leather is preferred for its durability and ability to withstand wear while providing a luxurious feel. This enhances the vehicle’s perceived value, making it more appealing to consumers. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should focus on sourcing from tanneries that adhere to environmental standards and offer materials that meet strict durability and maintenance requirements.
Why is Leather Important for Furniture & Interior Design?
Custom leather furniture pieces often incorporate high-quality leather grades like full grain and corrected grain due to their unique aesthetics and long-lasting properties. These materials can be tailored to match specific design themes, making them highly sought after in upscale markets. Buyers from Europe, particularly Germany, should ensure that the leather is sourced sustainably and offers customization options to meet diverse consumer preferences.
How is Leather Used in Sports Equipment?
In the sports equipment sector, leather grades are utilized in various products, from gloves to protective gear. Full-grain leather is favored for its flexibility and moisture resistance, which enhances performance during physical activities. International buyers must prioritize sourcing leather that meets specific weight and durability standards to ensure the longevity and functionality of the equipment, especially in regions with diverse climate conditions.
What Considerations are There for Industrial Leather Goods?
In industrial applications, leather is often used for protective gear and workwear, where safety and durability are paramount. Split grain and corrected grain leathers are commonly chosen for their resilience in demanding environments. Buyers need to ensure that their leather meets industry safety standards and offers wear resistance, particularly in regions where harsh working conditions are prevalent, such as in the Middle East and parts of Africa.
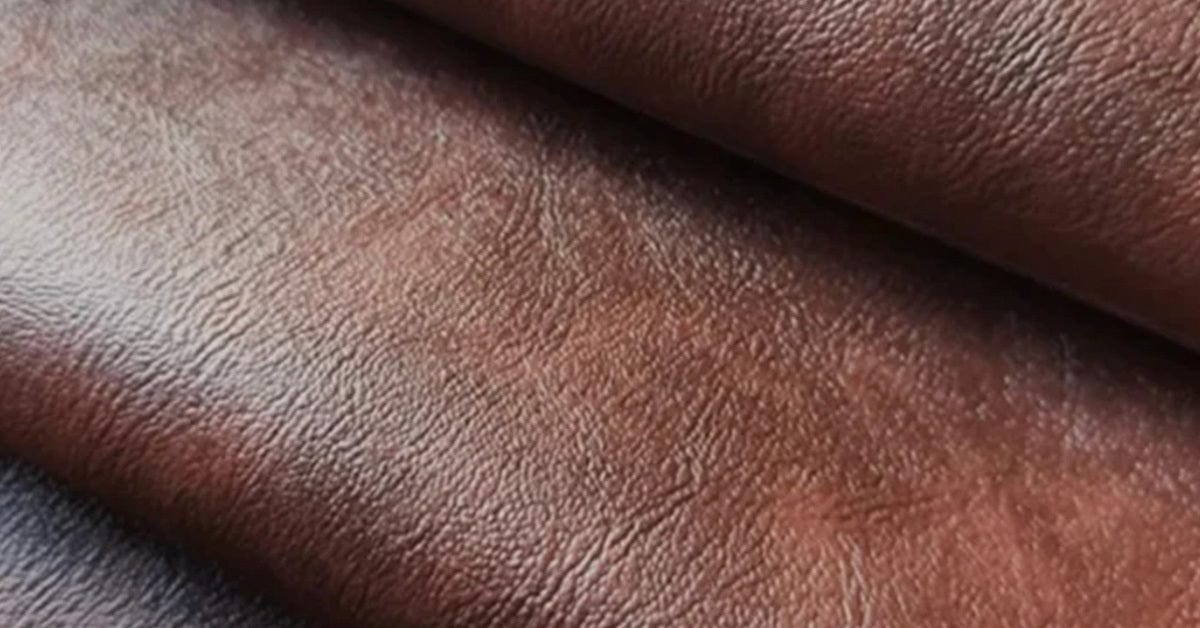
Illustrative image related to leather grades
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather grades’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Leather Grades and Quality
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion due to the lack of standardized grading systems across tanneries. This can lead to misinterpretations about the quality and suitability of various leather types. For example, a buyer may believe they are sourcing high-quality full-grain leather, only to find that the supplier has sent corrected grain leather, which may not meet their product standards. This not only affects the final product’s quality but can also lead to financial losses and damaged relationships with customers.
The Solution: To navigate this confusion, buyers should establish clear communication with their suppliers about specific leather grades. Before placing an order, ask for detailed descriptions and examples of the leather types being offered, including photographs and sample swatches. Additionally, implement a quality assurance process that includes checking the leather upon delivery. Develop a checklist based on the characteristics of the desired leather grade, such as grain pattern, thickness, and surface finish. Educating your procurement team on how to identify different leather grades can also empower them to make informed decisions, thereby reducing the risk of receiving subpar materials.
Scenario 2: Uncertainty About Durability and Longevity
The Problem: A common concern among B2B buyers is the uncertainty regarding the durability of different leather grades. For instance, a manufacturer sourcing leather for high-end handbags may worry that using corrected grain leather could compromise the product’s longevity, especially if they intend to position their brand in the luxury market. This concern is heightened by the misunderstanding that all leather from the top cut is of equal quality, leading to potential misalignment with brand values.
The Solution: To address durability concerns, it is crucial to conduct thorough research on the specific leather grades being considered. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide comprehensive information on the tanning processes and how they impact the leather’s durability. Request technical data sheets that outline the leather’s resistance to wear and tear, as well as its aging properties. It may also be beneficial to seek recommendations from industry experts or consult case studies that illustrate the long-term performance of various leather grades in similar applications. By aligning product quality with brand positioning, buyers can confidently choose leather that not only meets their durability standards but also enhances their brand reputation.
Scenario 3: Misalignment of Product Expectations and Actual Performance
The Problem: B2B buyers often experience misalignment between their expectations for leather products and the actual performance of the materials they source. For example, a furniture manufacturer may expect upholstery leather to provide a soft touch and luxurious appearance but finds that the split grain leather they received lacks the desired aesthetic and feel. This misalignment can lead to customer dissatisfaction and increased returns, impacting the bottom line.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should engage in a thorough vetting process when selecting leather grades for specific applications. It is advisable to create detailed product specifications that outline the desired characteristics, such as texture, finish, and intended use. In addition, establish a collaborative relationship with suppliers who can provide guidance on which leather grades will best meet your performance criteria. Consider testing samples in real-world conditions before finalizing large orders. This proactive approach will help ensure that the leather sourced aligns with customer expectations, thereby enhancing satisfaction and reducing return rates.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather grades
What Are the Key Properties of Full Grain Leather for B2B Buyers?
Full grain leather is renowned for its durability and natural beauty, making it a top choice for high-end products. Its key properties include excellent breathability, which allows moisture to escape, and a robust structure that can withstand significant wear and tear. Full grain leather is also known for its ability to develop a rich patina over time, enhancing its aesthetic appeal. For B2B buyers, particularly in markets like Europe and the Middle East, the ability to customize products with unique natural markings can be a significant selling point.
However, full grain leather comes with a higher price tag due to its premium quality and the intensive tanning processes required. Additionally, it may not be suitable for all applications, especially where a uniform appearance is critical. Buyers should consider the specific end-use of the leather products and whether the unique characteristics of full grain leather align with market expectations.
How Does Corrected Grain Leather Compare in Terms of Performance?
Corrected grain leather offers a balance between quality and cost, making it an appealing option for manufacturers targeting mid-range markets. This leather type is sanded and treated to remove imperfections, resulting in a more uniform appearance that is often preferred in fashion and upholstery. Its resistance to stains and spills is a key advantage, particularly for buyers in regions with varying climates, such as South America and Africa.
Illustrative image related to leather grades
On the downside, corrected grain leather may lack the breathability and natural feel of full grain leather, which can be a disadvantage for products that require a high level of comfort. Additionally, while it is generally durable, the corrective processes can sometimes compromise the leather’s long-term integrity. Buyers should weigh these factors against their target market’s preferences and the intended use of the final products.
What Are the Considerations for Split Grain Leather in Product Development?
Split grain leather, often considered a lower-quality option, is derived from the fibrous part of the hide that remains after the top grain has been removed. Its key properties include a softer texture and a lower cost, making it attractive for budget-conscious manufacturers. This type of leather is commonly used in products like bags and footwear, particularly in markets where price sensitivity is high.
However, split grain leather is generally less durable and may not withstand heavy use as well as higher-grade leathers. It is also more prone to wear and tear, which can affect the longevity of the end product. For B2B buyers, especially those in emerging markets, the cost savings must be balanced with the potential for increased returns or replacements due to product failure.
How Does Bonded Leather Fit into the B2B Landscape?
Bonded leather is made from leather scraps and fibers that are bonded together with adhesives, making it the most affordable option on the market. Its primary advantage is cost-effectiveness, which can be appealing for manufacturers targeting mass markets. Bonded leather can be visually appealing and is often used in budget-friendly furniture and accessories.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
However, the key disadvantage is its lack of durability and authenticity compared to genuine leather types. Bonded leather is susceptible to peeling and wear, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction and returns. For B2B buyers, especially those in competitive markets, it is crucial to consider the long-term implications of using bonded leather and how it aligns with brand values and customer expectations.
Summary Table of Leather Grades for B2B Buyers
| Material | Typical Use Case for leather grades | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Grain Leather | High-end bags, wallets, furniture | Exceptional durability and aesthetic appeal | Higher cost, may not suit all applications | Alta |
| Corrected Grain Leather | Apparel, upholstery, footwear | Uniform appearance, stain resistance | Less breathability, potential durability issues | Medium |
| Split Grain Leather | Budget-friendly bags, footwear | Cost-effective for mass production | Lower durability, prone to wear and tear | Low |
| Bonded Leather | Budget furniture, accessories | Highly affordable | Lacks durability, may peel over time | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the various leather grades, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific market needs and product requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather grades
What Are the Key Stages in the Leather Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing of leather grades involves several meticulous stages, each critical in determining the final product’s quality. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess suppliers and their capabilities effectively.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Hides Processed?
The journey begins with raw cowhides, which typically range between 6 to 10 mm in thickness. The first step is splitting the hides into usable sections, primarily the top and bottom cuts. This is often done using a splitter during the wet stage of processing to ensure uniform thickness. The top cut is further processed to produce high-quality leather grades like full grain and corrected grain, while the bottom cut is used for lower-grade options.
Once split, the hides undergo tanning, which can be vegetable-based or chrome-based. The choice of tanning affects the leather’s characteristics significantly. For example, vegetable-tanned leather is known for its eco-friendliness and ability to develop a rich patina over time, making it desirable for high-end products.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Leather Products?
After tanning, the leather is shaped into products through various forming techniques. Common methods include:
- Cutting: Hides are cut into specific shapes using dies or patterns. Precision is critical here to ensure minimal waste and optimal use of material.
- Stitching: High-quality stitching is essential for durability. Techniques vary from traditional hand-stitching to machine methods, depending on the product’s requirements.
- Molding: For items like bags or shoes, leather may be molded to achieve specific forms. This process involves heat and pressure to ensure the leather retains its shape.
Finishing: How Is Leather Treated for Appearance and Durability?
The finishing stage enhances the leather’s aesthetic and functional properties. This can involve processes like:
- Dyeing: Various methods, including aniline and semi-aniline dyeing, are used to achieve desired colors. Aniline dyes, for instance, allow the natural grain to show through, while semi-aniline provides a bit more protection.
- Coating: Applying a protective layer can improve water resistance and durability. This is especially important for items subjected to wear and tear, like footwear and upholstery.
- Polishing: A final polish can give the leather a rich luster, enhancing its visual appeal.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the leather industry to ensure that products meet international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be aware of the various QA measures that manufacturers implement.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
What International Standards Should Leather Manufacturers Follow?
One of the most recognized international quality management standards is ISO 9001. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has a robust quality management system in place. Other relevant certifications may include CE marking, which signifies conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards, and API standards, particularly for oil and gas applications.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Structured?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before production begins. It ensures that only high-quality hides are processed.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This stage involves continuous monitoring during production. Operators inspect leather for defects, ensuring adherence to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final products undergo rigorous inspection to verify that they meet predefined quality standards before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Leather Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure leather meets quality standards:
- Physical Testing: This includes assessing tensile strength, tear strength, and abrasion resistance. Such tests help determine the leather’s durability and suitability for specific applications.
- Chemical Testing: Leather is tested for harmful substances, such as heavy metals, to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
- Visual Inspection: Trained inspectors visually check for cosmetic defects, ensuring the leather’s appearance meets market expectations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify a supplier’s quality control practices. Here are some strategies:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the quality control processes in place. Buyers should look for adherence to international standards and best practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control measures, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results. These reports can offer valuable insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Independent inspections can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. Engaging a reputable third-party inspection service can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding QC nuances is essential. Different markets may have varying expectations regarding leather quality, and buyers should ensure that their suppliers can meet these demands. For example, European buyers might prioritize compliance with stricter environmental regulations, while Middle Eastern buyers may focus on durability for specific applications.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear lines of communication and setting expectations upfront can help mitigate these challenges.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the leather manufacturing process and quality assurance measures is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality leather products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather grades’
To successfully navigate the procurement of leather grades, B2B buyers need a structured approach. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to ensure that buyers make informed decisions when sourcing leather, whether for manufacturing, retail, or other applications.
Step 1: Identify Your Leather Requirements
Understanding your specific needs is crucial before approaching suppliers. Consider factors such as the intended use of the leather (e.g., upholstery, fashion, accessories) and the desired quality level (e.g., full grain vs. corrected grain). This clarity will guide your sourcing strategy and help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Different Leather Grades
Familiarize yourself with the various grades of leather. Knowing the differences between full grain, top grain, corrected grain, split grain, and bonded leather is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Each grade has unique characteristics and price points, so understanding these can help you select the right type for your application.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
Step 3: Define Your Technical Specifications
Create a detailed specification sheet that outlines your leather needs. This should include thickness, finish, color, and any specific treatments required (e.g., water resistance, stain resistance). Providing clear specifications helps suppliers understand your requirements and reduces the risk of receiving unsuitable products.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications for quality and sustainability. Look for certifications like ISO, REACH, or other industry-specific standards. This step is vital as it indicates that the supplier adheres to best practices in leather production, ensuring a consistent and high-quality product.
Step 5: Request Samples
Before making a large order, always request samples of the leather grades you are considering. Inspect the samples for quality, texture, and finish to ensure they meet your specifications. This hands-on evaluation allows you to verify the supplier’s claims and assess how the leather performs in real-world applications.
Step 6: Evaluate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified potential suppliers, compare their pricing structures and payment terms. Look for transparency in pricing to avoid hidden costs, and consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping and handling. Favor suppliers who offer flexible payment options and clear return policies.
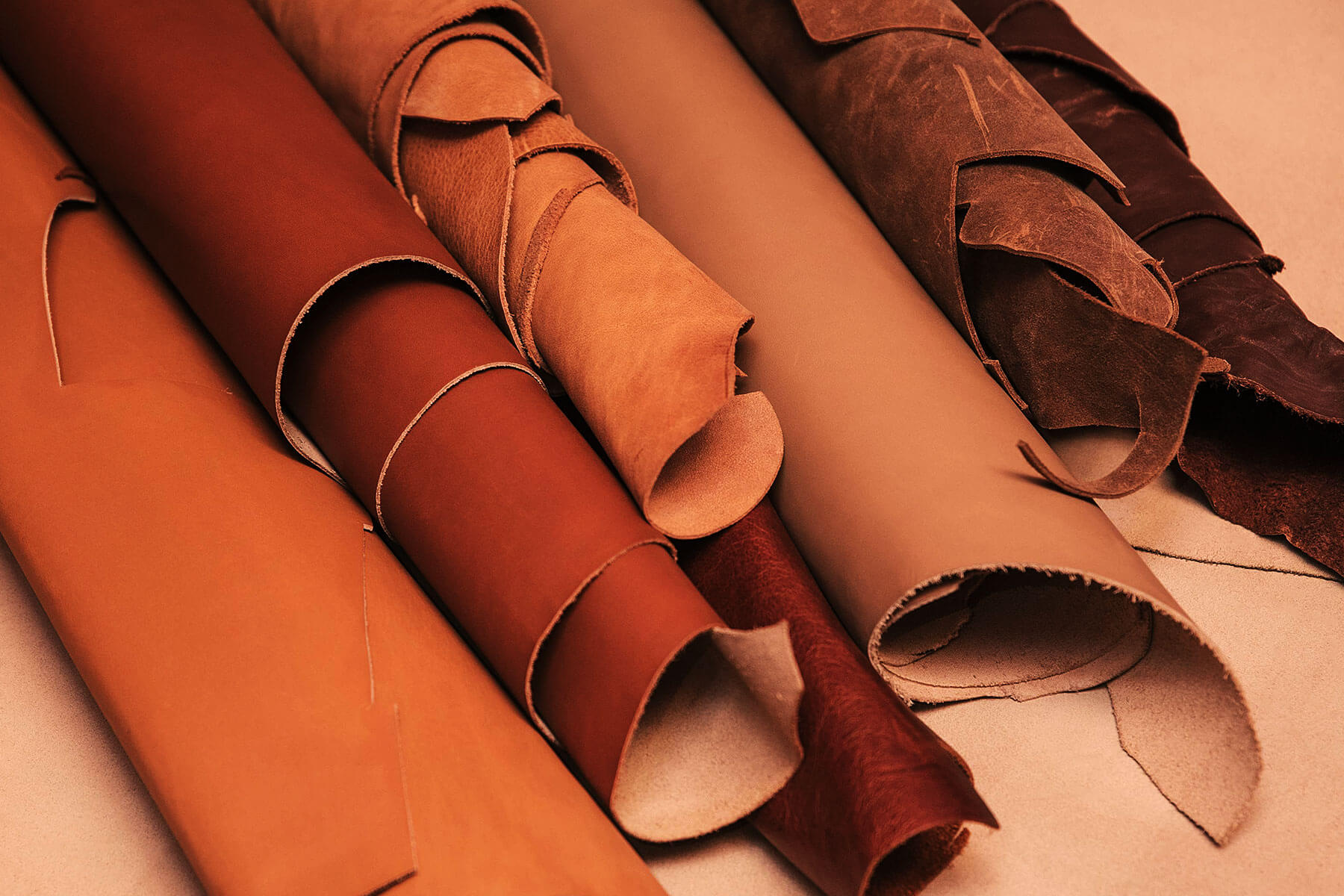

Illustrative image related to leather grades
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to a successful procurement process. Set up regular check-ins with your chosen supplier to discuss order statuses, delivery timelines, and any potential issues. Establishing a rapport can lead to better service and more favorable terms in future transactions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their leather sourcing process, ensuring they procure the right materials for their business needs while minimizing risks associated with quality and supplier reliability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather grades Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Grades Sourcing?
When sourcing leather grades, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of leather chosen significantly impacts cost. Full grain leather, known for its quality and durability, often commands a higher price compared to corrected or split grain leather. The sourcing of raw hides, which can vary by region, also influences material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled craftsmanship is essential in leather processing. Labor costs can vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the tanning and finishing processes. For instance, countries with a strong tradition in leather craftsmanship may have higher labor costs due to skilled artisans.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the facility, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Overheads can fluctuate based on the scale of production and the technology employed in processing leather.
-
Tooling: Custom molds or tooling for specific designs can add to the initial costs. For unique or specialized leather products, these upfront investments are necessary for quality assurance.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing strict QC measures ensures that the leather meets the desired standards. While this incurs additional costs, it ultimately protects the brand’s reputation and reduces returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary greatly depending on the distance from the supplier, the mode of transport, and the chosen Incoterms. For international buyers, understanding these logistics is vital for accurate cost estimations.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a markup to cover their operational costs and profit margins. This can vary widely, influenced by factors such as brand reputation and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Leather Grades Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of leather grades, making it essential for buyers to consider:

Illustrative image related to leather grades
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often attract discounts, which can significantly affect the overall cost per unit. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate terms that align with their purchase volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to additional processing and tooling. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Leather sourced from reputable suppliers with quality certifications may come at a premium. However, this investment often translates into better durability and customer satisfaction.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is crucial for managing shipping responsibilities and costs. Different terms can affect the final pricing, especially for international transactions.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Leather Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings. Here are some tips:
-
Research Market Prices: Before entering negotiations, gather information on market rates for different leather grades. This knowledge empowers buyers to negotiate from a position of strength.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Long-term relationships often yield more favorable conditions compared to one-off transactions.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, evaluate the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential waste. A higher initial investment in quality leather may result in lower TCO over time.
-
Be Clear on Specifications: Clearly outline your requirements to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to additional costs. Transparency in specifications helps streamline the production process and reduces the risk of costly errors.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to meet minimum quantities that trigger discounts. This strategy not only reduces per-unit costs but can also improve supplier relationships.
What Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Pricing Nuances?
International buyers must navigate various nuances when sourcing leather grades. Currency fluctuations can impact pricing, making it essential to lock in rates when possible. Additionally, understanding local tariffs and import duties is vital for accurate cost forecasting.
Lastly, be aware of cultural differences in negotiation styles. Buyers from different regions may have varying approaches to pricing discussions, which can influence the overall negotiation process.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
Disclaimer: Prices for leather grades can vary significantly based on market conditions, regional differences, and supplier-specific factors. Always conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather grades With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Leather Grades
When considering leather grades for B2B applications, it’s essential to evaluate various alternatives that can fulfill similar roles. Alternatives may offer unique advantages in terms of performance, cost, and environmental impact. In this section, we will compare leather grades against synthetic leather and high-quality textile solutions, providing a comprehensive overview to help international buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Leather Grades | Synthetic Leather (PU) | High-Quality Textiles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability, excellent patina | Good durability, less breathable | Varies widely, can be durable or delicate |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sourcing | Generally lower, mass-produced | Varies; premium textiles can be expensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled craftsmanship | Easy to manufacture and work with | Can be easy to implement, depending on type |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning | Easy to clean, resistant to stains | Maintenance depends on the fabric type |
| Best Use Case | Luxury goods, high-end applications | Affordable fashion, upholstery | Fashion, casual wear, and functional items |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Synthetic Leather?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU), serves as a popular alternative to traditional leather. One of its primary advantages is cost-effectiveness, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to reduce expenses without sacrificing quality. Synthetic leather is also easier to clean and maintain, which appeals to manufacturers in industries like fashion and automotive.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
However, there are notable downsides. While synthetic leather can mimic the appearance of genuine leather, it typically lacks the breathability and natural aging qualities of higher-grade leathers. Its durability varies, and it may not offer the same luxurious feel that many consumers expect from leather products. Additionally, environmental concerns regarding the production of synthetic materials can deter eco-conscious buyers.
How Do High-Quality Textiles Compare to Leather Grades?
High-quality textiles, such as cotton blends, wool, and advanced synthetic fabrics, can provide a versatile alternative to leather grades. These materials can be tailored for specific applications, offering a wide range of aesthetics and functionalities. For instance, some textiles are designed to be water-resistant or flame-retardant, making them suitable for specialized uses.
The primary advantage of high-quality textiles is their adaptability and often lower cost compared to leather. They can also be produced in various colors and patterns, appealing to diverse consumer preferences. However, the durability and long-term performance of textiles can vary significantly based on the material and weave. In many cases, textiles may not match the lifespan of high-grade leather, which is a crucial consideration for buyers investing in long-lasting products.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Selecting the appropriate material—whether it be leather grades, synthetic leather, or high-quality textiles—depends on several factors, including the intended application, budget constraints, and desired product longevity. For luxury items, leather grades remain the gold standard due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. In contrast, for more budget-conscious projects or where easy maintenance is paramount, synthetic leather or high-quality textiles could be more suitable.
Ultimately, buyers should weigh the performance, cost, and maintenance implications of each option against their specific needs and market demands. By conducting thorough research and considering these alternatives, businesses can make strategic decisions that align with their operational goals and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather grades
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Leather Grades?
Understanding the technical properties of leather grades is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when making sourcing decisions that impact quality, cost, and end-use performance. Here are some essential specifications:

Illustrative image related to leather grades
1. Material Grade
The material grade of leather indicates its quality based on the part of the hide used and the manufacturing process. Full grain leather represents the highest quality, retaining the complete grain structure, while corrected grain and split grain indicate lower quality due to processing methods. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is essential to ensure product durability and customer satisfaction.
2. Thickness
Leather thickness is typically measured in millimeters (mm), ranging from 1.2mm to 2.0mm for most applications. The thickness affects the leather’s strength, flexibility, and suitability for specific products like bags, wallets, or upholstery. Buyers must consider the required thickness to meet functional and aesthetic needs while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in the leather’s physical properties, such as thickness, weight, and color. High tolerance levels indicate consistent quality, which is vital for manufacturers who rely on uniformity in mass production. Inconsistent tolerances can lead to production delays and increased costs, making it essential for buyers to clarify tolerance levels during negotiations.
4. Breathability
Breathability is a property that affects the leather’s ability to allow air and moisture to pass through. Full grain leather tends to be more breathable, which is advantageous for products like footwear and upholstery. For B2B buyers, understanding breathability can help ensure the longevity and comfort of end products, particularly in climates with high humidity.
5. Finishing Process
The finishing process applied to leather impacts its appearance, texture, and functionality. This can include processes like dyeing, embossing, and applying protective coatings. Buyers should be aware of the finishing techniques used as they can significantly affect the leather’s durability, maintenance requirements, and overall aesthetic appeal.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Leather Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the leather market. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or products that are used in another company’s end product. In the leather industry, this could involve manufacturers that provide leather components for apparel, footwear, or accessories. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers streamline their sourcing processes and ensure compatibility with existing products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it influences inventory levels, cash flow, and production planning. Negotiating favorable MOQs can help businesses optimize their supply chains while minimizing excess stock.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. In the leather industry, an RFQ typically outlines the desired leather grade, quantity, and any special requirements. By issuing RFQs, buyers can compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, enabling informed purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, specifying who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border leather sourcing, as they can impact total landed costs and risk management.
5. Tannery
A tannery is a facility where raw hides are processed into leather through various tanning methods. The choice of tannery can influence the quality and characteristics of the leather produced. Buyers should consider the reputation and capabilities of tanneries when selecting suppliers to ensure high-quality outcomes.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the leather market more effectively, making informed choices that align with their business needs and customer expectations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather grades Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Impacting the Leather Grades Sector?
The leather grades sector is witnessing significant transformations driven by global economic shifts, evolving consumer preferences, and technological advancements. One of the primary market drivers is the increasing demand for high-quality leather products, particularly in emerging markets across Africa and South America. As disposable incomes rise in these regions, consumers are showing a preference for durable, premium products, making full-grain and top-grain leathers more desirable. In Europe, particularly in Germany, there is a strong inclination towards artisanal and bespoke leather goods, which further elevates the demand for superior leather grades.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
Technological advancements are reshaping sourcing practices in the leather industry. The adoption of digital platforms for procurement is on the rise, allowing international buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and streamline their sourcing processes. B2B tech solutions, such as blockchain for supply chain transparency and AI-driven analytics for market trends, are becoming crucial for buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, the trend towards customization is gaining momentum, with manufacturers increasingly offering tailored products that cater to specific market demands, driving the need for various leather grades.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing Leather Grades in B2B?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the leather industry, significantly impacting purchasing decisions among international B2B buyers. The environmental impact of leather production, particularly concerning water usage and chemical treatments, has led to a growing demand for sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and minimizing waste.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining traction. Buyers are looking for ‘green’ certifications, such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification, which indicates responsible sourcing and environmentally friendly practices. Furthermore, the use of alternative materials, such as plant-based leathers or recycled leather, is being explored as a viable option for eco-conscious buyers. These trends not only align with consumer values but also enhance brand reputation and market competitiveness.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
How Has the Leather Grades Sector Evolved Over Time?
The leather grades sector has undergone a significant evolution influenced by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. Historically, leather was primarily sourced and processed using traditional methods, which often resulted in high variability in quality. As industrialization progressed, mass production techniques emerged, leading to the classification of leather into various grades, such as full-grain, top-grain, and corrected grain.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards quality and sustainability. B2B buyers are increasingly educated about the differences in leather grades and their implications for product durability and aesthetics. This knowledge empowers them to make informed choices that align with both their business goals and ethical standards. Today, the leather industry is not just about functionality; it encompasses craftsmanship, sustainability, and a commitment to ethical practices that resonate with modern consumers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather grades
-
How do I determine the right leather grade for my products?
To select the appropriate leather grade, first consider the intended use of your product. Full grain leather offers durability and a unique aesthetic, making it ideal for high-end goods. Top grain leather is more consistent in appearance and easier to maintain, suitable for mass-produced items. If cost is a concern, corrected grain or split grain leather can be viable options, but be aware of potential quality compromises. Always request samples to assess texture, finish, and overall quality before finalizing your decision. -
What are the key differences between full grain and corrected grain leather?
Full grain leather retains the complete grain structure, showcasing natural markings and offering superior breathability and durability. It’s prized for its aesthetic qualities and ability to develop a rich patina over time. Corrected grain leather, on the other hand, undergoes processes to remove imperfections, resulting in a more uniform appearance. While it can be durable, it may lack the character of full grain leather and has reduced breathability. Your choice should align with the desired aesthetic and functional qualities of your final product. -
What should I consider when vetting leather suppliers internationally?
When sourcing leather from international suppliers, prioritize their reputation and experience in the industry. Check for certifications that indicate adherence to environmental and ethical standards, such as ISO or Leather Working Group certifications. Request references and reviews from previous clients to gauge reliability. It’s also crucial to assess their production capabilities, lead times, and communication practices to ensure they align with your business needs. Conducting a factory visit, if feasible, can further enhance your understanding of their operations. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for leather grades?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for leather can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific leather grade. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 to 500 square meters for full grain or top grain leather, while split grain or bonded leather may have lower MOQs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for new customers or small businesses, so it’s worth negotiating based on your needs. Always clarify MOQs before placing an order to avoid unexpected costs or delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing leather?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation with the remaining balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer more favorable terms, such as net 30 or net 60 days, especially for established relationships. Ensure that payment methods are secure and traceable, such as bank transfers or letters of credit. It’s advisable to discuss and formalize payment terms in the contract to prevent misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my leather orders?
To ensure quality assurance for leather products, establish clear specifications and standards before placing an order. Request samples to evaluate the leather’s texture, color, and finish. It’s beneficial to conduct inspections at various stages of production, including pre-shipment inspections, to verify compliance with your standards. Engaging third-party quality control services can provide additional assurance, especially for larger orders or new suppliers. Documenting all QA processes will help mitigate risks and maintain product consistency. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing leather?
When importing leather, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your destination country. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments but requires longer transit times. Ensure your supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including certificates of origin and compliance. Additionally, be aware of tariffs and import duties that may apply to leather goods, which can impact overall costs. -
How can I customize leather products for my brand?
Customization options for leather products can include selecting specific grades, colors, finishes, and even embossing or debossing logos. Discuss your customization requirements with the supplier, as many are willing to work with clients to create unique products. Be prepared to provide design specifications and possibly pay additional costs for tooling or setup fees. Prototyping is essential to ensure that the final product meets your expectations, so request samples of customized items before proceeding with large orders.
Top 7 Leather Grades Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Popov Leather – Leather Quality Chart
Domain: popovleather.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Leather Quality Chart: Decoding the World of Leather Grades – Popov Leather®\n\n1. **Leather Grades**: The leather grades are classified into three common categories based on finishing and the section of cowhide used: Top Grain Leather, which includes Full Grain Leather, Corrected Grain Leather, Split Grain Leather (sometimes called ‘Genuine Leather’), and Bonded Leather.\n\n2. **Full Grain Leathe…
2. Reddit – Leather Grades Explained
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Grades of leather such as Full Grain, Top Grain, Genuine, and Bonded are not recognized as real grades by any authority. Full Grain leather means the outermost layer is unaltered, preserving its natural character. Top Grain refers to the top layer split from a hide, often sanded or embossed. Genuine Leather simply means real leather, similar to how ‘wood’ can refer to various qualities of wood pro…
3. Leather Edge Paint – Leather Grades Explained
Domain: blog.leatheredgepaint.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: 5 Leather Grades: 1. Full Grain Leather: Complete grain intact, most durable, lasts longer, includes vegetable tanned and distressed leather. 2. Top Grain Leather: Second highest quality, imperfections removed, thinner, commonly used in high-end products, sanded surface, less breathable. 3. Split Grain Leather: Lacks grain, includes suede, soft, less durable, porous. 4. Genuine Leather: Marketing …
4. Weaver Leather Supply – Leather Grades Explained
Domain: weaverleathersupply.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Leather grades are categorized as A, B, or C based on the number of defects. Grade A allows for 1-2 small defects in prime areas and 3-4 in non-prime areas. Grade B can have 3-4 defects in prime areas, 6-12 inches of damage, and small holes in non-prime areas. Grade C allows for more than 12 inches of damage and color variation. Weaver Leather Supply uses a tannery run (TR) method, consisting of 2…
5. Steel Horse Leather – Quality Leather Bags & Accessories
Domain: steelhorseleather.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Grades Of Leather – A Comprehensive Guide To Leather Qualities. Key product categories include: Leather Bags (Duffle Bags, Backpacks, Messenger Bags, Tote Bags, Work Bags, Briefcases, Laptop Bags, Satchels, Crossbody Bags), Accessories (Toiletry Bags, Wallets, Coin Purses, Tech Cases), Travel Bags (Travel Duffle Bags, Backpacks, Weekenders, Organizers), Gifts (Leather Gifts for Him and Her, Grooms…
6. Billy Tannery – Types of Leather
Domain: billytannery.co.uk
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Types of Leather: 1. Full Grain Leather – Highest quality, retains natural state, durable, unique marks, improves with age. 2. Top Grain Leather – Sanded for uniformity, softer finish, less durable. 3. Genuine Leather – Also known as corrected-grain leather, thinner and weaker, used for cheaper goods. 4. Split Leather – Uses corium section, fragile, low life expectancy. 5. Bonded Leather – Made fr…
7. Leathersofa – Alexandria Sectional
Domain: leathersofaco.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Alexandria Sectional (Left Arm Loveseat + Left Arm Right Chaise Sofa)’, ‘base_leather’: ‘Sooner Golden Tan’, ‘price’: ‘$9,200.00’, ‘description’: ‘Few designs offer a more perfect balance of style and comfort than the Alexandria. This contemporary off the floor silhouette features a beautifully sculpted frame and soft.’}, {‘name’: ‘Roma – Sofa with Power RA/LA Incliners & Power Headrest…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather grades
In the ever-evolving landscape of leather sourcing, understanding the nuances of leather grades is paramount for international buyers. Full grain and top grain leathers offer the highest quality and durability, making them ideal for premium products. Conversely, split grain and bonded leathers, while cost-effective, may compromise on longevity and aesthetic appeal. Buyers should prioritize strategic sourcing by partnering with reputable tanneries that uphold high standards in their grading systems and production processes.

Illustrative image related to leather grades
By integrating thorough market research and supplier evaluations, businesses can ensure they are investing in leather that not only meets their quality requirements but also enhances their brand reputation. As global demand for sustainable and ethically sourced materials continues to grow, embracing transparency in the supply chain will be crucial.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage their understanding of leather grades to make informed decisions that align with both market trends and consumer expectations. Engage with trusted suppliers and consider the long-term value of your leather investments to secure a competitive edge in your industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.