Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vegan leather material
In an increasingly eco-conscious market, navigating the global landscape for vegan leather material presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. As the demand for sustainable alternatives to traditional leather surges, sourcing high-quality vegan leather that meets diverse industry needs—from fashion to automotive—can be daunting. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of vegan leather, exploring various types, applications, and emerging innovations. It offers a comprehensive framework for evaluating suppliers, understanding cost structures, and assessing the environmental impact of materials.
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly in regions like Saudi Arabia and Germany, making informed purchasing decisions is paramount. The guide empowers businesses to identify reliable sources of vegan leather, ensuring that they meet both ethical standards and customer expectations. By addressing critical factors such as product durability, sourcing practices, and market trends, this resource equips decision-makers with the insights necessary to confidently integrate vegan leather into their offerings. As the market evolves, staying informed will not only enhance product lines but also align with the growing consumer demand for sustainable solutions.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Vegan Leather Material Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vegan leather material
- Understanding vegan leather material Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of vegan leather material
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vegan leather material’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vegan leather material
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vegan leather material
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vegan leather material’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vegan leather material Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vegan leather material With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vegan leather material
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vegan leather material Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vegan leather material
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vegan leather material
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
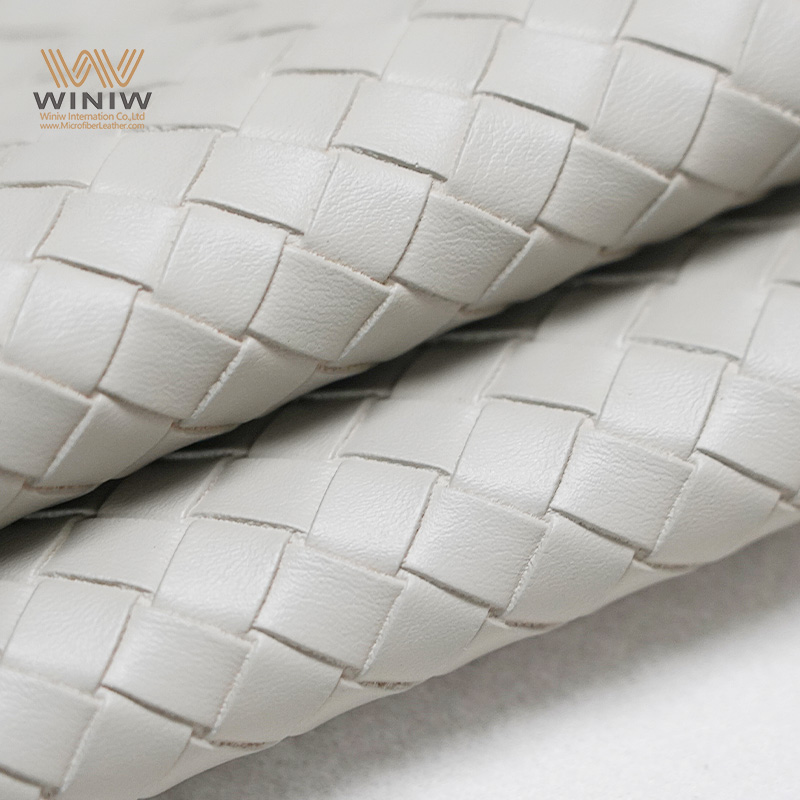
Understanding vegan leather material Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cuero PU | Made from polyurethane, softer and more flexible | Fashion, upholstery, automotive interiors | Pros: More eco-friendly than PVC; versatile. Cons: Less durable than real leather; potential for wear. |
| Cuero PVC | Made from polyvinyl chloride, highly durable | Affordable fashion items, accessories | Pros: Cost-effective; widely available. Cons: Environmental concerns; less breathable. |
| Plant-Based Leather | Derived from natural materials like pineapple leaves, mushrooms, or cactus | High-end fashion, luxury goods, eco-conscious brands | Pros: Sustainable; unique aesthetics. Cons: Higher production costs; limited availability. |
| Piel de microfibra | Synthetic fibers mimicking leather, soft touch | Fashion, upholstery, automotive interiors | Pros: Soft, durable, stain-resistant. Cons: May not be as eco-friendly as plant-based alternatives. |
| Apple Leather | Made from apple waste, biodegradable | Fashion accessories, bags, footwear | Pros: Sustainable; unique texture. Cons: Higher cost; may not match durability of traditional leather. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of PU Leather for B2B Buyers?
PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is a popular choice due to its softness and flexibility. It mimics the look and feel of genuine leather while being more environmentally friendly compared to PVC. For B2B buyers, PU leather is ideal for fashion and upholstery applications, particularly in markets focused on ethical sourcing. Buyers should consider the balance between cost and durability, as PU leather typically lasts 2-5 years, making it suitable for fast fashion but potentially less appealing for long-term investments.
How Does PVC Leather Stand Out in the Market?
PVC leather is recognized for its durability and cost-effectiveness, making it a staple in the fashion and accessories sectors. Its widespread availability allows businesses to meet consumer demand for affordable alternatives to genuine leather. However, B2B buyers should weigh the environmental impact of PVC production, which raises concerns about sustainability. While it serves well for short-term applications, brands aiming for eco-friendly positioning may find PVC less desirable.
What Makes Plant-Based Leather an Attractive Option?
Plant-based leathers, derived from materials like pineapple leaves or mushrooms, are rapidly gaining traction in the luxury market. These alternatives appeal to eco-conscious brands seeking to differentiate their products with sustainable options. B2B buyers should note that while plant-based leathers offer unique aesthetics and a lower environmental footprint, they often come with higher production costs and may have limited availability. This makes them suitable for niche markets focused on sustainability.
Why Choose Microfiber Leather for Your Business?
Microfiber leather is crafted from synthetic fibers designed to replicate the softness and durability of traditional leather. It is particularly valued in the fashion and automotive industries due to its stain resistance and ease of maintenance. For B2B buyers, microfiber leather offers a balance of quality and affordability, though it may not provide the same eco-credentials as plant-based alternatives. When considering microfiber, businesses should evaluate their target market’s preferences for sustainability versus practicality.
What Are the Advantages of Using Apple Leather?
Apple leather, made from the waste of apple processing, presents a unique sustainable option for fashion and accessories. Its biodegradable nature aligns well with the increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. B2B buyers should consider the distinct texture and story behind apple leather, which can enhance brand appeal. However, the higher production costs and potential durability concerns compared to traditional leather may influence purchasing decisions, making it more suitable for premium markets.
Key Industrial Applications of vegan leather material
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vegan leather material | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Vegan leather garments and accessories | Aligns with consumer demand for sustainable fashion | Ensure compliance with eco-certifications and quality standards. |
| Automotive | Vegan leather upholstery for vehicles | Enhances brand image with eco-friendly offerings | Focus on durability and resistance to wear in high-traffic areas. |
| Furniture & Upholstery | Vegan leather for sofas and chairs | Provides a stylish, ethical alternative to traditional leather | Assess material flexibility and stain resistance properties. |
| Sports Equipment | Vegan leather in sports gear (balls, gloves) | Appeals to eco-conscious athletes and teams | Consider performance characteristics and longevity under stress. |
| Electronics & Accessories | Vegan leather cases and covers for devices | Differentiates products in a competitive market | Evaluate sourcing for durability and aesthetic finish. |
How is Vegan Leather Material Used in the Fashion & Apparel Industry?
In the fashion sector, vegan leather is increasingly utilized for garments, bags, and accessories, appealing to consumers who prioritize sustainability. Brands like Stella McCartney have successfully integrated vegan leather into their collections, demonstrating its aesthetic and functional qualities. For international B2B buyers, sourcing vegan leather requires attention to certifications that guarantee eco-friendliness and ethical production methods, ensuring the final product aligns with consumer expectations in diverse markets.
What Role Does Vegan Leather Play in the Automotive Sector?
The automotive industry is embracing vegan leather for vehicle interiors, including seats and dashboards. This shift not only caters to eco-conscious consumers but also enhances brand reputation. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing materials that meet durability standards and can withstand wear and tear in high-traffic areas. Additionally, understanding regional preferences for aesthetics can help manufacturers better cater to markets in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
How is Vegan Leather Transforming Furniture & Upholstery?
Vegan leather is revolutionizing the furniture industry by offering an ethical and stylish alternative for upholstery. It is used in sofas, chairs, and other furnishings, providing durability and ease of maintenance. For B2B buyers, selecting vegan leather for upholstery requires a focus on material flexibility and stain resistance, crucial for longevity in high-use environments. Understanding local trends in design can also influence successful product offerings in various international markets.
In What Ways is Vegan Leather Applied in Sports Equipment?
In sports, vegan leather finds applications in items such as gloves and balls, appealing to athletes who seek environmentally friendly options. This material’s versatility and performance characteristics make it suitable for high-impact use. Buyers must consider the balance between durability and comfort, ensuring that the sourced vegan leather can withstand rigorous activity. International buyers should also keep in mind the varying standards and preferences in sports equipment across regions.
Why is Vegan Leather Important for Electronics & Accessories?
Vegan leather is increasingly used in protective cases and covers for electronic devices, providing a premium look while appealing to eco-conscious consumers. The unique selling proposition for businesses lies in differentiating their products in a saturated market. When sourcing vegan leather for electronics, it is essential to assess its durability and aesthetic finish, ensuring that it meets the demands of both functionality and style for diverse international consumers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vegan leather material’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Concerns with Vegan Leather Durability
The Problem: A B2B buyer sourcing vegan leather for high-end fashion products is often faced with the challenge of durability. Many vegan leather materials, particularly those made from PVC and lower-quality PU, are prone to wear and tear, leading to dissatisfaction among consumers who expect longevity from their purchases. This situation can result in costly returns, damaged brand reputation, and decreased customer loyalty, especially in competitive markets like Europe and the Middle East where quality is paramount.
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality vegan leather alternatives that prioritize durability. Investigate suppliers who specialize in innovative materials, such as those made from plant-based sources like pineapple leaves, apples, or mushrooms. These materials not only offer a unique aesthetic but also tend to have improved durability compared to traditional synthetic options. Additionally, request samples and conduct thorough testing under realistic conditions to assess how the material holds up over time. Establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers who provide transparency about their production processes can also ensure that the materials meet the desired quality standards.
Scenario 2: Environmental Sustainability Misconceptions
The Problem: As the demand for sustainable products grows, B2B buyers often encounter conflicting information about the environmental impact of vegan leather. While marketed as eco-friendly, many options are derived from petroleum-based plastics like PVC and PU, raising concerns about microplastics and non-biodegradability. This ambiguity can lead to hesitancy among buyers committed to sustainability, potentially undermining their business objectives and brand values.
The Solution: To navigate these complexities, buyers should prioritize sourcing vegan leather from manufacturers that utilize genuinely sustainable practices and materials. Engage with suppliers who can provide certifications or documentation proving their vegan leather is made from biodegradable or recycled sources. Additionally, consider collaborating with brands that are transparent about their lifecycle assessments, showing how their products minimize environmental impact from production to disposal. By aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, B2B buyers can confidently promote their products as environmentally responsible, thereby enhancing their brand’s credibility in a competitive marketplace.
Scenario 3: Limited Design Versatility of Vegan Leather
The Problem: B2B buyers in the fashion and upholstery industries often struggle with the perceived limitations of vegan leather in terms of design versatility. Traditional vegan leathers can lack the rich textures and finishes that high-end consumers expect, leading to creative constraints when developing products. This challenge can hinder innovation and result in products that do not resonate with target audiences.
The Solution: To overcome this limitation, buyers should seek out cutting-edge vegan leather options that offer a wide range of textures, colors, and finishes. Collaborate with suppliers known for their commitment to innovation in material development, and explore alternatives like vegan leathers made from agricultural waste or bio-based polymers that can mimic the luxurious feel of traditional leather. Additionally, consider investing in custom design options, where manufacturers can tailor the materials to meet specific aesthetic requirements. Encouraging open dialogue with suppliers about design needs can lead to more creative solutions and ultimately result in products that stand out in the marketplace, appealing to discerning consumers who value both style and ethics.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vegan leather material
What Are the Key Materials Used in Vegan Leather?
Vegan leather is gaining traction as a sustainable alternative to traditional leather, and its composition varies significantly based on the source material. This section analyzes four common materials used in vegan leather, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Compare as a Vegan Leather Material?
Polyurethane (PU) is one of the most prevalent materials used in the production of vegan leather. It offers a good balance of flexibility, breathability, and aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for a variety of applications, from fashion to upholstery.
Pros: PU is relatively durable, water-resistant, and can be produced in a wide range of textures and colors. It is often more affordable than traditional leather, appealing to cost-sensitive markets.
Cons: Its environmental impact is a concern, as PU is a petroleum-based product that can take decades to biodegrade. Additionally, while PU can last several years, it generally has a shorter lifespan compared to high-quality animal leather.
Impact on Application: PU’s water resistance makes it suitable for products exposed to moisture, such as bags and shoes. However, its lower durability may limit its use in high-wear applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East may need to comply with stringent environmental regulations regarding the use of synthetic materials. Understanding local standards like DIN and ASTM is crucial for compliance.
What Role Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Play in Vegan Leather?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is another common synthetic material for vegan leather. It is known for its affordability and versatility, making it a popular choice in mass production.
Pros: PVC is inexpensive and can be produced in various colors and finishes, making it attractive for budget-conscious brands. It is also resistant to moisture and easy to clean.
Cons: PVC has a significant environmental footprint due to its production process, which involves harmful chemicals. Its durability is also lower than that of PU, with a tendency to crack over time, especially in extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: PVC is often used in lower-end products, such as inexpensive bags and accessories. Its lack of breathability can be a drawback in clothing applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the growing movement against PVC due to its environmental impact. Compliance with local regulations, especially in Europe, is critical as many countries are moving towards banning certain PVC products.
Are Natural Fibers Viable Alternatives for Vegan Leather?
Natural fibers such as pineapple leaves (Piñatex) and apple peels are emerging as innovative alternatives to synthetic vegan leather. These materials are derived from agricultural waste, making them more sustainable.
Pros: Natural fibers are biodegradable and often have a lower environmental impact compared to synthetic options. They offer unique textures and aesthetics that appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Cons: The production process can be more complex and costly compared to synthetic materials. Additionally, natural fibers may not offer the same level of durability or water resistance, limiting their application in certain sectors.
Impact on Application: These materials are well-suited for fashion and luxury goods, where sustainability is a key selling point. However, their lower durability may restrict their use in high-wear products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the growing consumer demand for sustainable products, especially in Europe and North America. Compliance with organic certification standards may also be necessary.
How Do Mushroom-Based Materials Fit into the Vegan Leather Landscape?
Mushroom-based materials, such as mycelium leather, are gaining attention as a sustainable alternative to both traditional and synthetic leathers.
Pros: These materials are biodegradable and can be produced with minimal environmental impact. They also offer unique textures and are customizable in terms of appearance.
Cons: The technology for mass production is still developing, which can lead to higher costs. Additionally, the durability of mushroom leather may not yet match that of traditional leather.
Impact on Application: Mushroom leather is ideal for niche markets focused on sustainability, such as high-end fashion and eco-friendly products. Its unique properties can serve as a strong marketing point.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should stay informed about the evolving regulations surrounding sustainable materials, particularly in regions with strict environmental standards like Germany.
Summary Table of Vegan Leather Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for vegan leather material | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Fashion items, upholstery | Flexible, water-resistant | Shorter lifespan than real leather | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Inexpensive bags, accessories | Affordable, easy to clean | Environmental concerns, less durable | Low |
| Natural Fibers (e.g., Piñatex) | Fashion, luxury goods | Biodegradable, unique textures | Higher production costs, less durable | Alta |
| Mushroom-Based Materials | Niche markets, eco-friendly products | Low environmental impact | Higher costs, developing technology | Alta |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the various materials used in vegan leather, enabling informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vegan leather material
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Vegan Leather?
The manufacturing of vegan leather involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final product’s quality and sustainability. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers more effectively.
How Are Materials Prepared for Vegan Leather Production?
The first step in manufacturing vegan leather is material preparation. This typically involves sourcing raw materials, which can include synthetic polymers like polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), as well as natural fibers derived from plants such as pineapple leaves, apple peels, or cactus.
Sourcing high-quality materials is crucial as it directly impacts the durability and appearance of the final product. Suppliers may use a combination of these materials to achieve specific properties, such as breathability and flexibility. Quality assurance begins at this stage, as manufacturers should ensure that all materials meet international standards for safety and environmental impact.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Vegan Leather?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming, which involves the application of various techniques to create the leather-like surface. Common methods include coating and lamination, where the chosen substrate is coated with a layer of PU or PVC.
Some manufacturers are also exploring innovative techniques like bio-based coatings that utilize natural materials, enhancing the eco-friendliness of vegan leather. The forming process can significantly affect the texture, feel, and overall quality of the vegan leather, making it essential for B2B buyers to inquire about the specific techniques used by potential suppliers.
How Is Vegan Leather Assembled and Finished?
After forming, the assembly stage involves cutting the vegan leather into desired shapes and sewing or bonding the pieces together. The finishing process often includes applying dyes, textures, or protective coatings to enhance the product’s aesthetic appeal and durability.
Finishing techniques may also involve treatments that improve water and stain resistance, key attributes for many applications in fashion, upholstery, and automotive industries. Buyers should look for suppliers who utilize advanced finishing technologies that comply with international regulations, ensuring that the products are safe and environmentally friendly.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Vegan Leather?
Quality control (QC) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, especially for B2B buyers who need assurance that the products they purchase meet their specifications and standards.
Which International Standards Apply to Vegan Leather Manufacturing?
For vegan leather manufacturers, adherence to international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for ensuring consistent quality and customer satisfaction. ISO 9001 outlines requirements for a quality management system, emphasizing a process-based approach to quality assurance.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in the European market and other certifications relevant to specific regions (like API in the U.S.) may also be necessary. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers maintain these certifications to mitigate risks associated with product quality and compliance.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Vegan Leather Production?
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process. Commonly, these include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint occurs when raw materials are received. Suppliers should check for defects or non-compliance with specifications before materials proceed to the next stage.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC involves monitoring the production process to identify and rectify any issues in real-time. This ensures that quality is maintained throughout the forming and assembly stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the product is completed, FQC checks the final output against predefined criteria. This includes assessing durability, aesthetics, and compliance with safety standards.
B2B buyers should ask suppliers about their specific QC processes and any documented evidence of compliance with these checkpoints.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Vegan Leather?
Testing methods play a vital role in ensuring the quality of vegan leather. Common tests include:
-
Tensile Strength Testing: Measures the material’s ability to withstand tension without breaking.
-
Water Resistance Testing: Assesses the material’s capacity to repel water, which is crucial for applications in fashion and upholstery.
-
Colorfastness Testing: Determines how well a material retains its color under various conditions, such as exposure to sunlight or washing.
-
Chemical Resistance Testing: Evaluates the material’s resistance to various chemicals, ensuring safety for consumers.
B2B buyers should request test reports and certificates from suppliers to verify the results of these tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial.
What Steps Should Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess quality control measures. Buyers can request on-site visits to observe the manufacturing process and QC checkpoints firsthand. Additionally, conducting third-party inspections can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s compliance with quality standards.
How Can Buyers Ensure Compliance with International QC Standards?
Buyers should request documentation that demonstrates compliance with international standards, including quality management system certifications and testing reports. This documentation serves as a safeguard against potential quality issues and assures that the product meets the buyer’s specifications.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
Different regions may have varying regulations and standards for vegan leather products. For instance, European buyers may prioritize eco-labels and certifications that emphasize sustainability, while buyers in the Middle East might focus more on durability and performance.
Understanding these regional nuances can help B2B buyers select the right suppliers who align with their market demands and consumer preferences. Engaging with suppliers who are knowledgeable about these differences can also facilitate smoother transactions and greater product acceptance in diverse markets.
Conclusion
Navigating the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for vegan leather involves understanding the critical stages of production, the importance of international standards, and the specific QC measures that ensure product quality. By taking the time to evaluate suppliers thoroughly, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and consumer expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vegan leather material’
Introducción
In the evolving landscape of sustainable materials, vegan leather has gained significant traction among manufacturers and consumers alike. This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring vegan leather materials, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your ethical standards, quality requirements, and business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications for the vegan leather you wish to source is critical. This includes identifying the desired material type (e.g., PU, PVC, or plant-based alternatives) and understanding the physical properties needed for your products, such as durability, flexibility, and water resistance. Align these specifications with your end-use applications to ensure compatibility.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay updated on the latest trends and innovations in the vegan leather market. Knowledge of emerging materials, such as those derived from mushrooms, pineapples, or cacti, can provide your business with a competitive edge. Understanding market demand trends in your target regions, such as Africa or Europe, will also help tailor your offerings to meet consumer expectations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, including their production capabilities, certifications, and past client references. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in sustainable practices and those who can provide transparency regarding their supply chain.
- Considerations:
- Supplier certifications (e.g., ISO, GOTS).
- Experience in your specific industry or product category.
Step 4: Assess Quality Control Processes
Understanding a supplier’s quality control processes is vital to ensure that the vegan leather meets your standards. Inquire about their testing methods for durability, colorfastness, and environmental impact. Robust quality assurance practices can prevent costly returns and enhance your brand’s reputation.
Step 5: Verify Environmental and Ethical Standards
Confirm that your chosen supplier adheres to recognized environmental and ethical standards. This includes evaluating their sustainability practices, such as waste management and energy consumption, as well as their adherence to labor rights and fair trade principles. Aligning with suppliers who share your values can strengthen your brand’s commitment to ethical sourcing.
Step 6: Request Samples for Evaluation
Before finalizing an order, always request material samples. This allows you to assess the texture, appearance, and overall quality of the vegan leather. Use this opportunity to evaluate how the material performs under different conditions and how it meets your specifications.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Establish Clear Contracts
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate favorable terms that include pricing, delivery timelines, and payment conditions. Establish clear contracts that outline product specifications, quality expectations, and penalties for non-compliance. This ensures a mutual understanding and safeguards your business interests throughout the procurement process.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing of vegan leather materials, ensuring alignment with both ethical standards and business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vegan leather material Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Vegan Leather Material Sourcing?
When sourcing vegan leather, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the pricing. Common options like polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are generally less expensive than innovative alternatives like mushroom leather or cactus-based materials. While PU offers better flexibility and durability compared to PVC, the latter remains popular due to its lower cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the production location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer cheaper vegan leather, but this can come at the expense of quality. Investing in skilled labor often results in better finishing and adherence to quality standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with production facilities, machinery, and utilities. As the vegan leather market expands, manufacturers may invest in more advanced equipment, which can raise overhead costs but also improve product quality.
-
Tooling: The cost of molds and other tooling can be significant, especially for custom designs. Customization typically requires a higher initial investment but can lead to better product differentiation in the market.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the vegan leather meets specific standards. This may involve additional costs but is crucial for maintaining brand reputation, particularly in premium markets.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are vital considerations, especially for international trade. Shipping vegan leather across borders can incur tariffs and customs fees, impacting overall pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers will apply a markup to cover their operational costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the average margin in the vegan leather industry will help buyers gauge if a price is reasonable.
What Factors Influence Vegan Leather Pricing for International Buyers?
Several key factors can influence the pricing of vegan leather materials for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or eco-certifications often come with a premium price. Buyers should assess whether the added cost aligns with their brand values and target market.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, production capacity, and location can all influence pricing. Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers may yield better pricing and terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for determining who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transportation. This can significantly impact the total landed cost.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help B2B Buyers Secure Better Prices?
B2B buyers can employ several negotiation strategies to improve cost efficiency:
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing a strong rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms over time.
-
Leverage Market Trends: Being aware of market trends and competitor pricing can provide leverage during negotiations. Buyers should stay informed about fluctuations in material costs and demand.
-
Discuss Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focusing on TCO rather than just initial pricing can lead to better long-term value. Highlighting the benefits of quality products can justify higher upfront costs.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Conducting thorough market research can uncover alternative suppliers who may offer more competitive pricing or better quality products.
What Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Pricing Nuances?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific pricing nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can significantly impact pricing, so buyers should consider hedging strategies or fixed pricing agreements.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Understanding local regulations and potential tariffs can help avoid unexpected costs when importing vegan leather.
-
Cultural Differences: Negotiation styles and business practices can vary by region. Buyers should adapt their approach to align with the cultural context of their suppliers.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for vegan leather materials can vary widely based on market conditions, material choices, and supplier capabilities. This analysis provides a framework for understanding the cost structure and pricing influences but should not be viewed as a definitive pricing guide. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vegan leather material With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Vegan Leather: What Are the Best Options?
As the demand for sustainable and ethical materials grows, businesses are increasingly exploring alternatives to traditional vegan leather. Each alternative presents unique advantages and challenges. This section compares vegan leather material against two viable alternatives: natural leather and recycled materials.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Vegan Leather Material | Natural Leather | Recycled Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate durability (2-5 years), water-resistant | High durability (up to lifetime), develops patina | Varies widely, often less durable than leather |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Moderate to high | Varies, often lower cost but depends on source |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to produce, versatile | Requires skilled labor for tanning and processing | Depends on availability and sourcing complexity |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, prone to wear | Requires conditioning to maintain quality | Maintenance varies; some may require more care |
| Best Use Case | Fashion, upholstery, accessories | Luxury goods, high-end fashion | Casual goods, eco-friendly products |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Natural Leather?
Natural leather is a traditional material known for its durability and aesthetic appeal. Its lifespan can extend for decades, making it a sustainable choice in the long run. However, the tanning process often involves toxic chemicals, raising environmental concerns. Additionally, the higher cost and ethical issues surrounding animal rights can deter certain consumers. Nevertheless, for businesses targeting the luxury market, natural leather remains a strong contender due to its perceived value and quality.
How Do Recycled Materials Compare to Vegan Leather?
Recycled materials, such as repurposed plastics or fabric scraps, are gaining traction as a sustainable alternative. They typically have a lower environmental impact since they utilize existing materials, reducing waste. The cost can be lower compared to virgin materials, making it an economically attractive option. However, the performance and durability of recycled materials can vary significantly, and they may not offer the same quality as vegan leather or natural leather. Businesses focusing on eco-conscious consumers may find recycled materials appealing, especially for casual or lifestyle products.
Conclusion: Which Material Should B2B Buyers Choose?
When selecting the right material, B2B buyers must consider their target market, product application, and ethical values. Vegan leather offers a versatile and cost-effective solution, particularly for fashion and accessories. Natural leather excels in durability and luxury appeal but comes with higher costs and ethical considerations. Recycled materials provide an environmentally friendly option that can attract sustainability-focused consumers, although performance may vary. Ultimately, the choice will depend on aligning the material’s characteristics with the company’s brand identity and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vegan leather material
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Vegan Leather Material?
Vegan leather, while an innovative alternative to traditional leather, comes with a set of technical properties that are critical for B2B buyers in various industries. Understanding these specifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Composition
The primary materials used in vegan leather production include polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PU is generally considered more environmentally friendly and offers better flexibility and breathability compared to PVC. For B2B buyers, knowing the composition helps in assessing the suitability of vegan leather for specific applications, such as fashion, upholstery, or automotive interiors.
2. Durability and Lifespan
Vegan leather typically has a lifespan of 2 to 5 years, depending on its quality and care. This is considerably shorter than genuine leather, which can last a lifetime. Buyers must evaluate the durability based on the intended use—whether for high-traffic items like shoes or less-utilized products like decorative goods. Understanding durability directly impacts inventory turnover and customer satisfaction.
3. Water Resistance and Maintenance
Most vegan leathers possess inherent water resistance, which makes them easier to clean and maintain compared to traditional leather. This property is vital for industries such as automotive and furniture, where spills and stains are common. Buyers should consider this when assessing the total cost of ownership and customer care requirements for products made from vegan leather.
4. Thickness and Weight
Vegan leather can vary significantly in thickness, which affects its application. Thinner materials are often used for clothing and accessories, while thicker variants may be better suited for upholstery or automotive applications. Buyers need to specify the desired thickness to ensure the final product meets performance and aesthetic criteria.
5. Breathability
Breathability is a critical property, especially in fashion applications, where comfort is paramount. PU vegan leather generally offers better breathability than PVC. For B2B buyers, this can influence consumer acceptance and product performance, particularly in climates where heat retention can be an issue.
6. Eco-friendliness
While vegan leather is marketed as a sustainable alternative to animal leather, its environmental impact varies based on the production methods and materials used. Buyers should inquire about certifications and eco-friendly production processes to ensure that their sourcing aligns with sustainability goals.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in the Vegan Leather Industry?
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the vegan leather market. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that manufactures products based on the designs and specifications provided by another company. In the vegan leather sector, this could involve producing custom goods for fashion brands. Knowing whether a supplier operates as an OEM can help buyers manage product customization and branding effectively.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for B2B buyers to understand, as it affects inventory levels and cash flow. Suppliers may set MOQs based on production costs and material availability, so negotiating favorable terms can lead to more efficient purchasing.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting detailed price quotes for specific products or services. This process is vital for buyers looking to compare costs and make informed decisions. An effective RFQ should clearly outline specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities. For instance, “FOB” (Free on Board) indicates that the seller covers costs until the goods are loaded onto a vessel.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. This metric is crucial for inventory management and production planning. Buyers should always clarify lead times with suppliers to align their supply chain processes accordingly.
By grasping these essential properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the vegan leather market more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vegan leather material Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Vegan Leather Material Sector?
The vegan leather market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable and ethical alternatives to traditional leather. With a projected market value of $89.6 billion by 2025, B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should pay close attention to emerging trends. Notably, the rise of bio-based materials—such as those derived from cactus, pineapple, and mushrooms—presents new sourcing opportunities that align with eco-conscious consumer preferences. Additionally, the fashion and automotive industries are leading the charge, with brands like Tesla and Stella McCartney championing vegan leather in their product lines.
Technological advancements are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. Innovations in manufacturing processes are enhancing the quality and durability of vegan leather, making it a viable alternative for high-end applications. B2B buyers should consider integrating these innovative materials into their offerings to meet evolving market demands. Furthermore, the digitalization of supply chains is enabling greater transparency, allowing buyers to track the origin of materials and ensure compliance with sustainability standards. As such, leveraging technology in sourcing strategies can significantly enhance product credibility and appeal in a competitive marketplace.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Vegan Leather Supply Chain?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount in the vegan leather sector, particularly as consumers become increasingly aware of the environmental impacts associated with traditional leather production. The production of vegan leather from petroleum-based plastics like PVC and PU poses significant challenges, including high carbon emissions and the generation of microplastics. B2B buyers need to prioritize sourcing from suppliers who utilize eco-friendly materials and processes.
Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and OEKO-TEX® can serve as reliable indicators of sustainable practices. These certifications not only enhance the credibility of products but also resonate with ethically-minded consumers. Additionally, establishing partnerships with suppliers committed to transparency and ethical labor practices can further strengthen a company’s market position. By aligning with sustainable sourcing practices, businesses can not only mitigate environmental risks but also meet growing consumer expectations for responsible production.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Vegan Leather in the B2B Landscape?
The concept of vegan leather has evolved considerably since its inception in the 1920s, transitioning from basic synthetic alternatives to sophisticated bio-based materials. Initially dominated by PVC, the market faced criticism for environmental and health impacts. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sustainable options, such as polyurethane (PU) and plant-based alternatives that mimic the aesthetic and tactile qualities of real leather.
This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers, as the demand for high-quality, sustainable vegan leather continues to rise. The shift reflects broader consumer trends favoring ethical and eco-friendly products, compelling manufacturers and suppliers to innovate. By understanding the historical context and current advancements in vegan leather, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with both market trends and consumer values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vegan leather material
-
1. How do I solve the challenge of sourcing high-quality vegan leather?
To effectively source high-quality vegan leather, start by identifying reputable suppliers with a proven track record in sustainability and ethical practices. Conduct thorough research, including reading reviews and case studies, and request samples to evaluate material quality. Establish a clear communication channel with potential suppliers to discuss specifications, certifications, and production processes. Attend trade shows or industry events to meet suppliers face-to-face, which can help build trust and facilitate negotiations. -
2. What is the best type of vegan leather for fashion applications?
For fashion applications, polyurethane (PU) vegan leather is often considered the best option due to its superior flexibility, breathability, and aesthetic appeal. PU leather can mimic the texture and feel of animal leather while being more environmentally friendly than PVC. Additionally, exploring innovative materials like mushroom leather or cactus-based options can provide unique selling points and cater to eco-conscious consumers. Ultimately, the choice should align with your brand’s values and target market preferences. -
3. How can I vet suppliers of vegan leather materials?
Vetting suppliers requires a multi-faceted approach. Start by verifying their certifications, such as ISO or sustainability standards, to ensure they adhere to ethical practices. Request information about their production processes, sourcing of raw materials, and labor conditions. Conduct factory visits or audits if possible, and ask for references from other clients. Additionally, consider their responsiveness to inquiries and willingness to collaborate on customization, as these factors often indicate a supplier’s reliability and commitment to customer satisfaction. -
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for vegan leather?
Minimum order quantities for vegan leather can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of material. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 to 1,000 meters for bulk orders. However, some suppliers may offer smaller quantities for samples or trial orders, especially for new clients. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production requirements while ensuring cost-effectiveness. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing vegan leather internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region but typically involve an initial deposit ranging from 30% to 50% of the total order value, with the balance due upon delivery or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer flexible payment options, including letters of credit or installment payments based on production milestones. It’s crucial to clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
6. How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for vegan leather products?
To ensure quality assurance, establish a comprehensive QA process that includes setting clear specifications and standards for the vegan leather material. Collaborate with suppliers to conduct pre-production inspections and in-line quality checks during the manufacturing process. Implement a final inspection before shipping to verify that products meet your standards. Additionally, consider third-party quality audits to add an extra layer of assurance, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing vegan leather?
When importing vegan leather, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling textile imports to navigate potential challenges. Understand the customs duties and tariffs applicable to your region to factor these costs into your budgeting. It’s also essential to communicate with suppliers about shipping timelines to ensure timely delivery aligned with your production schedules. -
8. How does the environmental impact of vegan leather compare to traditional leather?
The environmental impact of vegan leather varies based on the materials used. While traditional leather production contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and often involves harmful chemicals, some vegan leathers, particularly those made from plant-based materials, offer a more sustainable alternative. However, many vegan leathers are still derived from petroleum-based sources like PU and PVC, which can contribute to microplastic pollution. Thus, selecting suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices and materials is critical for minimizing environmental impact.
Top 5 Vegan Leather Material Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carl Friedrik – Vegan Leather Collection
Domain: carlfriedrik.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Vegan leather is made from synthetic materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyurethane (PU), as well as natural fibers from sources like cactus plants, agave leaves, and pineapple leaves. It is characterized by being waterproof, thin, stain-resistant, and flexible, but has a shorter lifespan of 2-5 years compared to real leather, which can last a lifetime. Vegan leather is used in a variety…
2. WebMD – Vegan Leather
Domain: webmd.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Vegan leather is an eco-friendly alternative to animal leather made from plant-based or sustainable sources. It is artificial, synthetic, or ‘faux’ leather created from agricultural waste products and sustainable biomaterials. Common materials used include polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride, cork, cactus, kombucha cellulose, mushroom mycelium, pineapple leaf fibers (Pinatex), yeast collagen, silicon…
3. Buffalo Jackson – Vegan Leather Options
Domain: buffalojackson.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Vegan leather is a term used for faux leather, primarily made from polyurethane, with some options including cork, barkcloth, waxed cotton, and paper. While marketed as a vegan-friendly alternative, it is often less environmentally friendly than traditional leather sourced from sustainable ranches. The article suggests that if one is looking for a high-quality leather alternative, they should cons…
4. Alternative Leathers – Desserto® Cactus Leather
Domain: alternativeleathers.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: {“products”: [{“name”: “Desserto® Cactus Leather”, “price”: “$17.00”, “description”: “Unique and environmentally friendly material used by brands like Fossil, Adidas, and Mercedes, developed in Mexico.”}, {“name”: “Piñatex® Original Pineapple Leather”, “price”: “$24.00”, “description”: “Sustainable alternative developed in the 1990s, used by trusted brands worldwide.”}, {“name”: “Vegea® Grape Leat…
5. Good On You – Piñatex
Domain: goodonyou.eco
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Piñatex: A leather alternative made from pineapple leaf fibres, manufactured by Ananas Anam. It involves sun-drying long fibres from pineapple leaves and felting them with a corn-based polylactic acid (PLA) to create Piñafelt. Piñatex supports local farming communities by providing income from previously discarded materials. It is not 100% biodegradable; the PLA used is biodegradable under control…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vegan leather material
As the vegan leather market continues to evolve, strategic sourcing becomes a crucial factor for B2B buyers aiming to capitalize on this growing trend. Understanding the diverse materials that constitute vegan leather—ranging from synthetic options like PU and PVC to innovative organic alternatives—enables businesses to make informed decisions that align with sustainability goals and consumer demands. The anticipated market growth, projected to reach $89.6 billion by 2025, underscores the urgency for companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to invest in high-quality vegan leather solutions.
By prioritizing ethical sourcing and transparent supply chains, businesses can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the increasing consumer preference for sustainable products. As the industry faces challenges regarding the environmental impact of synthetic materials, ongoing innovation in vegan leather production presents a unique opportunity for B2B buyers to differentiate themselves in a competitive landscape.
Looking ahead, engaging with reliable suppliers and exploring cutting-edge alternatives will be key to leveraging the full potential of vegan leather. Now is the time to act—evaluate your sourcing strategies and align them with the future of sustainable materials in the fashion and upholstery markets.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.