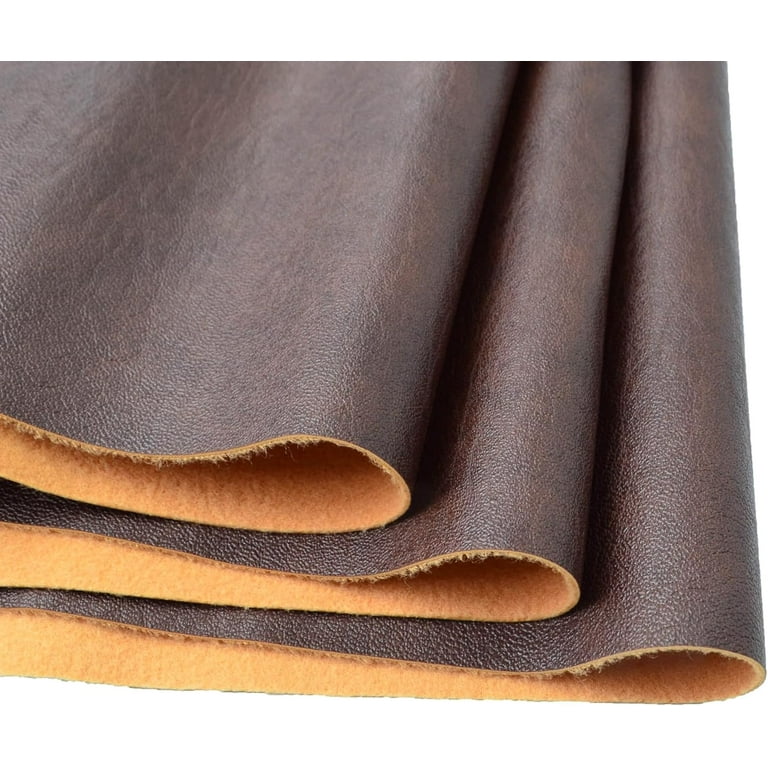
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is sueded
In the competitive landscape of global sourcing, understanding what is sueded can significantly impact your procurement strategies. As an international B2B buyer, whether you’re operating in Nigeria, Brazil, or across Europe, navigating the nuances of suede material is essential for making informed decisions that align with market demands. Suede, known for its luxurious texture and aesthetic appeal, presents unique challenges in sourcing, including quality assessment, supplier reliability, and cost management.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of suede, including genuine leather and synthetic alternatives, while highlighting their applications across diverse industries, such as fashion, automotive, and home decor. Additionally, we will provide insights on effective supplier vetting processes, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers who meet quality and ethical standards. The guide will also explore cost factors associated with suede procurement, helping you to negotiate better deals and optimize your budget.
By equipping yourself with the knowledge contained within this guide, you will be empowered to make strategic purchasing decisions that not only enhance your product offerings but also support sustainable and ethical sourcing practices. Embrace the opportunity to elevate your business with a thorough understanding of suede, ensuring that your company remains competitive in the global marketplace.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 What Is Sueded Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is sueded
- Understanding what is sueded Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is sueded
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is sueded’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is sueded
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is sueded
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is sueded’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is sueded Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is sueded With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is sueded
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is sueded Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is sueded
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is sueded
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what is sueded Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Suede | Made from the underside of animal hides; soft, napped finish | Fashion (apparel, accessories), upholstery | Pros: Luxurious feel, breathable; Cons: Less durable, stains easily, requires professional cleaning. |
| Synthetic Suede | Crafted from polyester or nylon; mimics the look and feel of natural suede | Footwear, furniture, automotive interiors | Pros: More durable, easier to clean; Cons: Less breathable, may lack the luxury appeal of natural suede. |
| Camurça de microfibra | A type of synthetic suede made from finely woven polyester fibers | Apparel, upholstery, sports gear | Pros: High durability, water-resistant; Cons: Can be less soft than natural suede, may not have the same aesthetic appeal. |
| Faux Suede | Made from various synthetic materials; designed to replicate suede’s texture | Fashion, home decor, accessories | Pros: Cost-effective, animal-friendly; Cons: May not offer the same texture and feel as genuine suede. |
| Eco-Friendly Suede | Produced from recycled materials or sustainable sources | Fashion, eco-conscious products | Pros: Appeals to environmentally conscious consumers; Cons: Availability may be limited, potentially higher costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Natural Suede and Its B2B Suitability?
Natural suede is derived from the underside of animal hides, offering a soft and luxurious feel that makes it popular in high-end fashion and upholstery. Its unique texture provides a high-quality aesthetic, making it suitable for apparel, accessories, and premium furniture. However, buyers should consider its lower durability compared to other leather types and the need for professional cleaning, which can increase maintenance costs.
How Does Synthetic Suede Compare in B2B Applications?
Synthetic suede, typically made from polyester or nylon, replicates the appearance and feel of natural suede while offering enhanced durability and ease of maintenance. This type is widely used in footwear and automotive interiors, where resilience against wear and tear is crucial. Buyers appreciate the lower cost and practicality but should note that synthetic options may lack the luxurious appeal that some consumers seek.
What Makes Microfiber Suede an Attractive Option for Businesses?
Microfiber suede is a subtype of synthetic suede, constructed from finely woven polyester fibers. It is highly durable and often water-resistant, making it ideal for various applications, including sports gear and upholstery. B2B buyers benefit from its longevity and ease of cleaning, although they may find it slightly less soft than traditional suede, which could affect consumer preferences in certain markets.
Why Choose Faux Suede for Cost-Effective Solutions?
Faux suede, made from various synthetic materials, aims to mimic the texture of genuine suede while being more affordable. It is commonly used in fashion and home decor, appealing to budget-conscious consumers and businesses. While it offers a cost-effective alternative, buyers should be aware that it may not provide the same tactile experience as real suede, which could influence customer satisfaction.
How Does Eco-Friendly Suede Address Sustainability in B2B Markets?
Eco-friendly suede is crafted from recycled materials or sourced sustainably, catering to the growing demand for environmentally responsible products. This type is increasingly popular in the fashion industry, especially among brands targeting eco-conscious consumers. While it may come at a premium price and limited availability, its appeal lies in aligning with corporate social responsibility goals, making it a worthwhile investment for brands looking to enhance their sustainability profile.
Key Industrial Applications of what is sueded
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is sueded | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Suede jackets and footwear | High-end appeal, softness, and comfort | Quality of suede, sourcing from reputable suppliers, and compliance with ethical standards. |
| Automotive | Upholstery for luxury vehicles | Enhanced aesthetics and comfort | Durability against wear and tear, ease of maintenance, and compatibility with existing materials. |
| Home Furnishings | Suede upholstery for furniture | Luxury feel and aesthetic appeal | Color options, fabric durability, and cleaning requirements. |
| Accessories | Suede bags and wallets | Stylish appearance and tactile experience | Material authenticity, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness. |
| Sporting Goods | Suede grips for sports equipment | Improved grip and comfort | Performance specifications, sourcing from specialized manufacturers, and environmental considerations. |
How is Suede Used in the Fashion & Apparel Industry?
In the fashion and apparel industry, suede is predominantly utilized for high-quality jackets, shoes, and accessories. Its soft texture and luxurious appearance cater to the premium market segment, attracting consumers seeking comfort and style. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize sourcing suede that meets ethical standards and is produced by reputable suppliers to ensure product quality and brand integrity.
What Role Does Suede Play in the Automotive Sector?
Suede is widely used in luxury vehicle upholstery, providing an elegant touch that enhances the overall aesthetic appeal of the interior. Its soft feel contributes to passenger comfort, making it a preferred choice for high-end automobiles. Buyers in this sector must consider the durability of suede against wear and tear, as well as its maintenance requirements, ensuring that the material can withstand the rigors of everyday use while maintaining its luxurious appearance.
Why is Suede Popular in Home Furnishings?
In the home furnishings sector, suede is favored for upholstery on sofas, chairs, and other furniture pieces due to its plush texture and visual appeal. It offers a sophisticated look that can elevate the ambiance of any living space. When sourcing suede for home furnishings, international buyers need to consider the color options available, the durability of the fabric, and the cleaning requirements, as suede can be challenging to maintain.
How is Suede Utilized in Accessories?
Suede is a popular choice for making stylish bags, wallets, and belts, appealing to consumers looking for a combination of fashion and functionality. The tactile experience of suede adds value to accessories, making them more desirable. Buyers should focus on the authenticity of the suede and the reliability of their suppliers to ensure they are providing high-quality products that meet consumer expectations while also being cost-effective.
What Benefits Does Suede Offer in Sporting Goods?
In the sporting goods industry, suede is often used for grips on equipment such as tennis rackets and golf clubs. Its texture provides an enhanced grip and comfort, which can improve performance. Buyers should seek suppliers who specialize in suede for sporting applications, ensuring that the material meets specific performance specifications and environmental considerations, especially in regions with varying climates.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is sueded’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Durability of Suede in Diverse Markets
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the perception of suede’s durability, particularly when sourcing materials for high-demand industries like fashion or automotive. In regions such as Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary significantly, buyers may be concerned about how suede will withstand humidity, heat, or even dust. The misconception that suede is inherently weak or unsuitable for certain applications can lead to hesitance in placing orders, impacting business relationships and profitability.
The Solution: To address durability concerns, buyers should consider sourcing suede treated with advanced protective coatings, such as Scotchgard or silicone-based sprays, which enhance water and stain resistance. When specifying orders, it’s crucial to communicate the intended use and environmental conditions to suppliers. Additionally, exploring synthetic alternatives like Ultrasuede can provide a more durable option while still offering the luxurious appearance of natural suede. Educating clients about proper care and maintenance, such as regular brushing and professional cleaning, can also alleviate durability concerns, ensuring that suede products retain their appeal over time.
Scenario 2: Navigating the Cleaning and Maintenance of Suede Products
The Problem: One of the most significant pain points for B2B buyers is the cleaning and maintenance of suede, which is notoriously challenging. In markets where customers expect easy-care fabrics, such as in the fashion industry or luxury goods, buyers may worry that the upkeep of suede products will deter consumers. This hesitation can complicate inventory decisions, as buyers may opt for alternative materials that require less maintenance, potentially sacrificing quality and appeal.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should prioritize sourcing suede that has been treated for easier cleaning and maintenance. Offering a range of products, including suede care kits that contain brushes, erasers, and protective sprays, can empower retailers to educate their customers on proper care techniques. Furthermore, consider partnering with suppliers who provide guidance on professional cleaning services, allowing customers to maintain the integrity of their suede items without hassle. By positioning suede as a luxury product that can be easily cared for, buyers can enhance customer satisfaction and drive sales.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
Scenario 3: Sourcing Ethical and Sustainable Suede Alternatives
The Problem: In today’s market, B2B buyers face increasing pressure to source sustainable and ethically produced materials. This is particularly true in regions such as Europe, where consumers are more environmentally conscious. Traditional suede production often raises concerns about animal welfare and environmental impact, making it challenging for buyers to align their purchasing decisions with their corporate social responsibility goals.
The Solution: Buyers should explore and prioritize suppliers who offer ethically sourced suede, such as those that use by-products from the meat industry or implement sustainable farming practices. Additionally, consider integrating synthetic suede options into product lines, which can provide a similar aesthetic without the ethical dilemmas associated with animal-derived materials. Engaging with suppliers that hold certifications for sustainability can further enhance credibility and appeal to eco-conscious consumers. By transparently communicating the sourcing practices to customers, businesses can differentiate themselves in a competitive market and build trust with their clientele.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is sueded
What Are the Key Properties of Common Sueded Materials?
When selecting materials for sueded applications, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials used in sueded products: genuine suede leather, synthetic suede (such as microfiber), faux suede, and suede-like textiles.
How Does Genuine Suede Leather Perform in Applications?
Genuine suede leather is derived from the underside of animal hides, typically lamb or calf. It possesses a soft, napped texture that is appealing for high-end fashion and luxury goods. Key properties include low breathability and high heat retention, making it suitable for colder climates but less ideal for hot, humid environments.
Pros: Genuine suede offers exceptional comfort and a luxurious feel, which can enhance the perceived value of products. It is also durable when properly cared for and can last many years.
Cons: The material is susceptible to water damage and staining, requiring professional cleaning. Additionally, it has a higher cost due to sourcing and processing animal hides, which may not align with budget constraints for some buyers.
What Advantages Does Synthetic Suede Offer?
Synthetic suede, often made from polyester or nylon microfibers, mimics the appearance and feel of genuine suede. It is more resistant to water and stains and can be produced at a lower cost.
Pros: Synthetic suede is easier to clean and maintain, making it a practical choice for everyday applications. It also provides consistent quality and can be manufactured in various colors and textures.
Cons: While synthetic suede is durable, it may not offer the same luxurious feel or breathability as genuine suede. Some buyers may perceive it as less prestigious, which can impact brand image.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
Why Choose Faux Suede for Cost-Effective Solutions?
Faux suede is another alternative, often made from recycled materials or blended fabrics that simulate the look of suede. It is lightweight and can be produced in bulk, making it appealing for mass-market products.
Pros: Faux suede is cost-effective and environmentally friendly, appealing to conscious consumers. It is also versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications, from clothing to upholstery.
Cons: However, faux suede may lack the durability of genuine suede and can wear out more quickly. It also may not provide the same level of comfort, particularly in high-end applications.
What Are the Benefits of Suede-Like Textiles?
Suede-like textiles encompass a broad category of materials designed to mimic suede’s appearance and texture. These can include cotton blends and other synthetic fabrics treated to achieve a napped finish.
Pros: These textiles are often lightweight and cost-effective, making them suitable for various applications, including fashion and home decor. They can also be produced in a variety of colors and patterns, offering flexibility for designers.
Cons: The main limitation is that suede-like textiles may not provide the same level of luxury or durability as genuine suede. They can also be less resistant to wear and tear, which could impact long-term performance in high-use applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Sueded Applications
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is sueded | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genuine Suede Leather | High-end fashion items, luxury goods | Luxurious feel and comfort | Susceptible to water and staining | Elevado |
| Synthetic Suede | Everyday apparel, accessories | Easy to clean and maintain | May lack prestige and breathability | Medium |
| Faux Suede | Mass-market clothing, upholstery | Cost-effective and eco-friendly | Less durable than genuine suede | Low |
| Suede-like Textiles | Fashion, home decor | Versatile and lightweight | May not provide luxury feel or durability | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the materials available for sueded applications, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is sueded
What Are the Main Stages of Suede Manufacturing?
The manufacturing process of suede involves several critical stages, each ensuring that the final product meets the desired quality and aesthetic standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the quality of suede products from various suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for Suede Production?
The first step in suede production is material preparation, where the raw animal hides, typically sourced from lamb, goat, or calf, are selected. The hides undergo a process known as liming, where a natural chemical is used to remove hair follicles. This step is crucial as it prepares the hide for tanning, making it suitable for further processing.
Once the hair is removed, the hides are treated with tannins, which preserve the material and prevent decomposition. This tanning process transforms the raw hide into leather, setting the stage for the suede to be created.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming and Finishing Suede?
After tanning, the leather is thinned and split to achieve the napped texture characteristic of suede. This is done through specialized machinery that ensures the leather retains its softness while achieving the desired thickness.
Finishing techniques include applying a mixture of salts, oils, and natural compounds that enhance durability and softness. Some manufacturers may opt for synthetic treatments to improve performance characteristics, such as stain resistance. The final step in this stage is a texturing process that gives suede its signature fuzzy finish.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Suede Production?
Quality assurance in suede manufacturing is vital for ensuring that the final products meet international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these standards can assist in evaluating potential suppliers.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Adherence to this standard indicates that a supplier has established processes for consistent quality control throughout the manufacturing process.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in the European market and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for specialized applications are crucial. These certifications assure buyers that the products have undergone rigorous testing and meet safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Suede Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the suede manufacturing process, ensuring that defects are caught early and that the final product meets customer expectations.
What Are the Main QC Checkpoints?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials such as animal hides are inspected for defects, ensuring that only quality materials enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are performed to monitor the processes and ensure compliance with quality standards. This includes checking the thickness of the leather, the effectiveness of the tanning process, and the consistency of the napped finish.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the suede is completed, the final product undergoes comprehensive inspections for visual and functional defects. This includes checking for color consistency, texture uniformity, and overall appearance.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Suede Quality?
To maintain high-quality standards, various testing methods are employed throughout the manufacturing process.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier QC Processes?
B2B buyers can verify the quality control processes of their suppliers through several means:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of the supplier’s facilities can provide insight into their quality management practices and adherence to international standards.
-
Inspection Reports: Requesting detailed inspection reports can help buyers understand the frequency and type of quality checks performed during production.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s adherence to quality standards. This is particularly important for international buyers, as it helps mitigate risks associated with cross-border transactions.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality assurance in suede manufacturing is critical.
How Do Regional Differences Affect Quality Assurance?
Cultural and regulatory differences may impact the quality assurance practices of suppliers in different regions. For example, suppliers in Europe may have stricter adherence to environmental regulations compared to those in other regions.
Additionally, language barriers and differences in business practices can lead to misunderstandings regarding quality expectations. Therefore, establishing clear communication and expectations upfront is essential for successful partnerships.
What Are the Best Practices for Ensuring Quality in International Transactions?
-
Clear Specifications: Provide detailed product specifications and quality expectations to suppliers to minimize misunderstandings.
-
Building Relationships: Developing strong relationships with suppliers can enhance collaboration and facilitate better quality control.
-
Regular Follow-ups: Establish a routine for follow-ups and feedback to address any quality concerns promptly.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in suede production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality products that meet their market demands.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is sueded’
Introdução
This sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in understanding and procuring sueded materials effectively. Suede, known for its soft texture and luxurious appeal, is widely used in various applications, from fashion to interior design. By following this checklist, you can ensure that your sourcing process is thorough and aligns with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear specifications for the type of suede you require. This includes the thickness, texture, and finish of the suede, as well as the intended application—be it footwear, apparel, or upholstery. Understanding these technical aspects helps in communicating effectively with suppliers and ensures you receive the right product.
- Consider material composition: Decide between genuine leather suede and synthetic alternatives based on your budget and sustainability goals.
- Identify color and pattern needs: Specify if you need custom colors or patterns, as this can influence sourcing options.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in suede. Look for companies with a strong reputation and expertise in the specific type of suede you are interested in. This step is crucial to ensure quality and reliability.
- Utilize online platforms: Explore B2B marketplaces and trade directories to find suppliers that meet your criteria.
- Check industry reviews: Read customer testimonials and case studies to gauge supplier performance and reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify that potential suppliers hold the necessary certifications. This ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations, particularly regarding sustainability and ethical sourcing practices.
- Look for environmental certifications: Certifications such as ISO 14001 can indicate a commitment to environmentally responsible practices.
- Check for quality certifications: Ensure that suppliers adhere to quality management standards like ISO 9001.
Step 4: Request Samples
Always request samples of the suede materials before making a bulk purchase. This allows you to assess the quality, texture, and color firsthand, ensuring it meets your expectations.
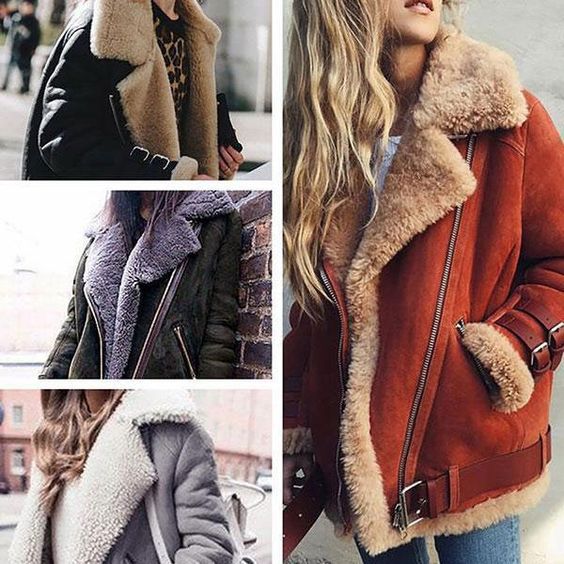

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
- Evaluate sample characteristics: Check for softness, flexibility, and finish to ensure it aligns with your specifications.
- Conduct durability tests: Assess how the suede performs under various conditions, especially if it will be used in high-wear applications.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, minimum order quantities, and delivery timelines. Establishing clear terms at this stage can prevent misunderstandings later.
- Discuss payment terms: Consider options that best suit your cash flow, such as upfront payments or installment plans.
- Clarify return policies: Understand the supplier’s policies on returns and exchanges in case the delivered goods do not meet your standards.
Step 6: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a quality control process to monitor the incoming suede materials. This step is vital to ensure that the products received match the agreed specifications and standards.
- Define inspection criteria: Set specific criteria for evaluating the quality of the suede, including texture, color consistency, and any defects.
- Incorporate feedback loops: Regularly communicate with suppliers to address any quality issues promptly and improve future orders.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, you can streamline your procurement process for sueded materials, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is sueded Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sueded Sourcing?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing sueded materials, several components contribute to the overall expense. The primary elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The cost of suede is influenced by the type of animal skin used, with lambskin typically being the most common. Higher-quality skins or those treated with specialized processes can significantly increase material costs. Additionally, synthetic alternatives, while generally less expensive, vary in quality and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in tanning, finishing, and processing suede. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can affect the quality of craftsmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can mitigate overhead costs, but they require an initial investment in technology and training.
-
Tooling: The initial setup costs for tooling can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider the potential for amortizing these costs over larger orders to improve cost efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high-quality suede involves rigorous QC processes, which add to the overall cost. Certifications for environmental sustainability or fair labor practices can also impact pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping expenses can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. International shipping can introduce tariffs and import duties that further increase costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin within their pricing structure, which can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the suede offered.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider When Sourcing Suede?
Several factors can influence the pricing of suede, particularly for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often benefit from economies of scale, resulting in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate to find the optimal order size that balances their needs with cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized suede products may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications upfront to avoid unexpected charges later.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The presence of certifications for quality, sustainability, or ethical sourcing can influence price. Buyers should weigh the benefits of sourcing certified materials against the potential for higher costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) can affect overall pricing and liability for shipping costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Suede Cost-Effectively?
International B2B buyers can employ several strategies to enhance cost efficiency when sourcing suede:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a strong relationship can lead to better deals and flexibility in future transactions.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider ongoing costs such as maintenance, cleaning, and durability. Higher-quality suede may have a higher upfront cost but can save money in the long run due to reduced replacement needs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import duties that could impact the total cost. Staying informed about these factors can aid in making more strategic purchasing decisions.
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regularly assess your suppliers for quality and compliance with standards. This ensures that you are receiving the best value for your investment and helps mitigate risks associated with low-quality materials.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for suede sourcing can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate and current pricing tailored to their specific needs.
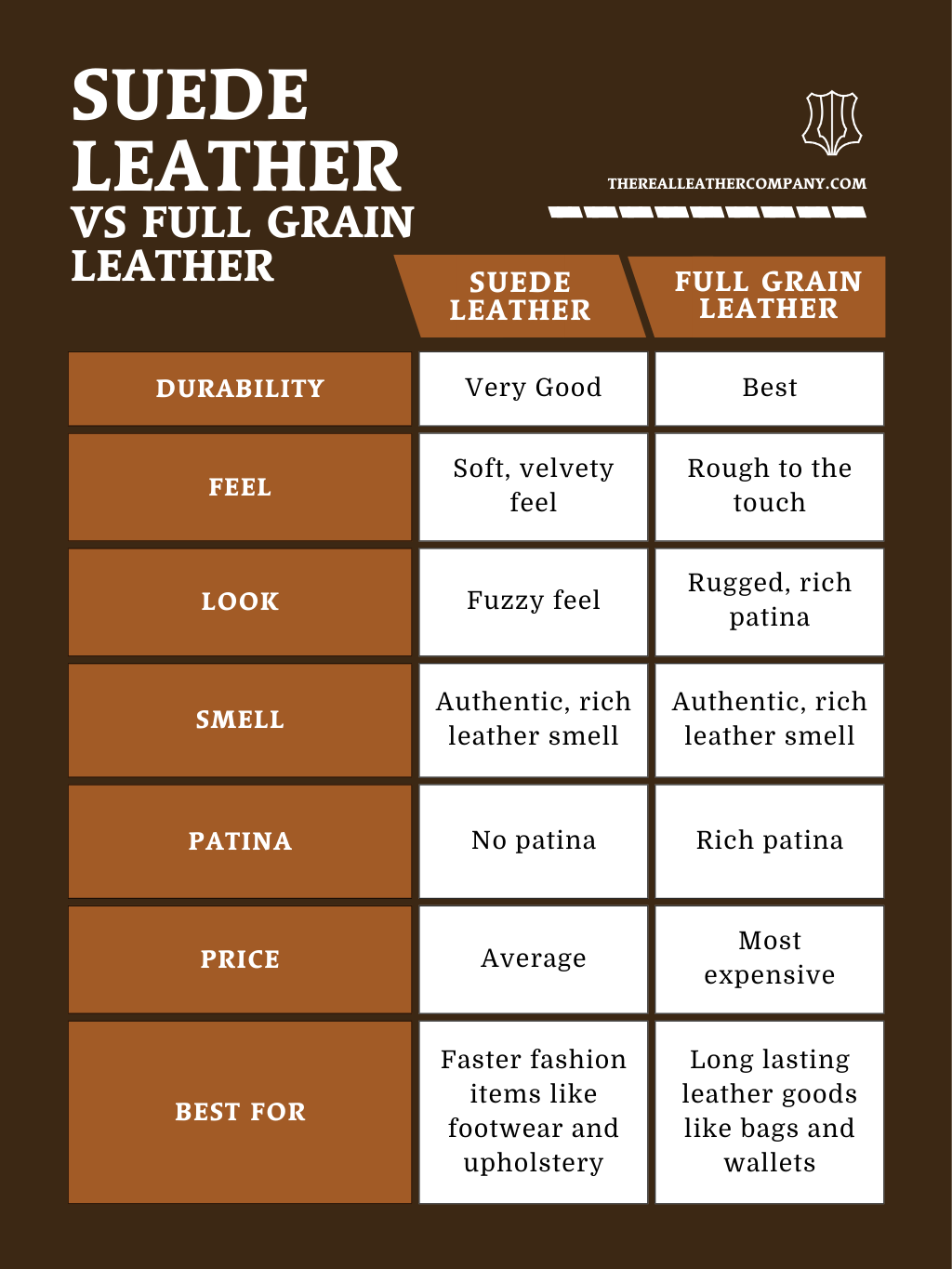
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is sueded With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Sueded Materials
When considering fabric options for various applications, businesses often evaluate suede against alternative materials. Suede is prized for its luxurious feel and aesthetic appeal, but it does have limitations in terms of durability and maintenance. Understanding the alternatives available can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | What Is Sueded | Alternative 1: Faux Suede | Alternative 2: Genuine Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Soft, luxurious feel; less durable; prone to stains | Similar aesthetic; more durable; less breathable | Highly durable; water-resistant; classic appearance |
| Cost | Higher due to animal sourcing and processing | Generally lower; cost-effective | Higher initial investment; varies by quality |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires special care; professional cleaning recommended | Easy to clean; machine washable | Requires regular conditioning and care |
| Maintenance | High; prone to staining; needs professional cleaning | Low; easy maintenance; resistant to stains | Moderate; needs regular care to maintain appearance |
| Best Use Case | Fashion items, luxury accessories | Casual apparel, budget-friendly alternatives | High-end products, durable goods |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Faux Suede
Faux suede, often made from polyester or nylon, mimics the look and feel of real suede without the drawbacks associated with animal-derived materials. Its primary advantage is durability; it is less prone to damage from water and stains, making it an excellent choice for casual apparel and accessories. Additionally, faux suede is typically more affordable, which can be a significant advantage for businesses looking to manage costs. However, it may lack the luxurious feel of genuine suede and can sometimes appear less authentic.
Genuine Leather
Genuine leather offers a classic alternative to suede, known for its exceptional durability and resistance to wear and tear. While it tends to be more expensive than both suede and faux suede, the investment can pay off in terms of longevity, making it ideal for high-end products such as luxury handbags and professional attire. Genuine leather also develops a unique patina over time, enhancing its aesthetic appeal. On the downside, it requires regular maintenance, including conditioning and cleaning, to keep it looking its best, which can be a consideration for businesses with limited resources.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right fabric for your business needs involves considering factors such as performance, cost, and maintenance. Suede is an excellent choice for high-end fashion and luxury items, where aesthetics are paramount. However, if durability and ease of care are more critical, faux suede or genuine leather may be preferable options. By assessing your specific application requirements and budget constraints, you can make a decision that balances quality with practicality, ensuring that your products meet both customer expectations and operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is sueded
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Sueded Materials?
1. Material Composition
Suede is primarily made from the underside of animal hides, commonly lambskin, although it can also be derived from calf, goat, or deer skins. Additionally, synthetic alternatives are available, made from polyester or nylon blends. Understanding the material composition is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects the durability, cost, and application of the suede in various products such as apparel, footwear, and accessories.
2. Breathability
Suede exhibits low breathability compared to other fabrics. This characteristic makes it less suitable for high-heat environments or activities that involve significant sweating. For B2B buyers in regions with high temperatures or humidity, this property is essential when selecting materials for apparel or upholstery, ensuring comfort for end-users.
3. Moisture Resistance
One of the notable drawbacks of suede is its low moisture resistance. Unlike traditional leather, suede is highly permeable, which can lead to staining and damage when exposed to water. For manufacturers and retailers, this means that products made from suede require special care instructions and may need additional treatments to enhance their water resistance, affecting product lifecycle and customer satisfaction.
4. Durability and Maintenance
While suede is known for its soft texture, it is less durable than other types of leather. This reduced durability necessitates professional cleaning and maintenance to preserve the material’s appearance and integrity. B2B buyers should consider the maintenance requirements when selecting suede products, as it impacts long-term costs and customer service considerations.
5. Thickness and Texture
Suede is typically thinner than traditional leather, contributing to its unique feel and flexibility. The napped surface gives it a luxurious appearance, but the thinness can affect the strength of the material. Buyers must evaluate the thickness required for specific applications, as this can influence product design and functionality.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Sueded Materials?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or products that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of suede, OEMs may be involved in producing suede components for fashion brands or automotive upholstery. Understanding OEM relationships can help B2B buyers identify reliable suppliers and streamline their supply chains.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For suede suppliers, MOQs can vary significantly depending on the type and quality of suede. B2B buyers must be aware of MOQ requirements to manage inventory effectively and ensure they are not overcommitting to products that may not sell.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process used to invite suppliers to bid on specific products or services. For buyers of suede materials, issuing an RFQ allows them to compare prices, quality, and delivery terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that are widely used in international commercial transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers when negotiating shipping and delivery terms for suede products, as they clarify responsibilities for transportation, insurance, and risk.
5. Tanning
Tanning is the process that transforms animal hides into leather, including suede. This term is essential for B2B buyers to understand, as it affects the quality, durability, and environmental impact of the suede. Buyers should inquire about the tanning methods used by suppliers to ensure compliance with quality standards and sustainability practices.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing suede products, ensuring they meet both quality and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is sueded Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting the Suede Sector?
The global suede market is currently experiencing a dynamic transformation, driven by several key factors that are essential for international B2B buyers to consider. With the rise of fast fashion and increasing consumer demand for luxury textiles, the suede sector is witnessing significant growth, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Emerging technologies in textile manufacturing, such as digital printing and automated cutting, are enhancing production efficiency, allowing suppliers to meet the rapid turnaround times expected by retailers.
Moreover, the increasing popularity of synthetic alternatives to traditional suede is reshaping sourcing strategies. These materials often offer better durability and lower maintenance needs, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Countries like China remain dominant in suede production and exportation, but suppliers in Africa and South America are gaining traction by focusing on unique regional designs and sustainable practices. B2B buyers are advised to stay informed about these trends to identify reliable suppliers who align with their business needs and consumer preferences.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Suede Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming non-negotiable standards in the suede industry. The environmental impact of animal leather production, including water usage and carbon emissions, has prompted many businesses to seek alternatives that minimize their ecological footprint. For B2B buyers, understanding these implications is crucial. Brands that prioritize sustainability often look for suppliers who can provide transparent supply chains and environmentally friendly materials, such as certified organic suede or recycled synthetics.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
Moreover, certifications such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification are gaining importance. These certifications assure buyers that the materials meet stringent environmental and social criteria. Ethical sourcing not only enhances brand reputation but also attracts a growing segment of consumers who are willing to pay a premium for sustainably produced goods. B2B buyers should focus on establishing partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices, ensuring long-term viability in a competitive market.
What Is the Historical Context of Suede’s Evolution for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the historical context of suede can provide valuable insights for B2B buyers. The term “suede” originates from the French phrase “gants de Suède,” referring to Swedish gloves made from the soft inner skin of animals. Initially, suede was primarily used for gloves, but its applications expanded over time as artisans recognized its potential for various textile products.
By the late 19th century, suede became synonymous with luxury, often used in clothing, footwear, and accessories. As production techniques evolved, the availability of suede broadened, making it accessible to a wider audience. Today, both genuine and synthetic suede are integral to fashion and upholstery industries, with manufacturers innovating to meet consumer demands for quality and sustainability. For B2B buyers, this historical perspective highlights the significance of suede as a premium product, encouraging informed sourcing decisions that resonate with market trends and consumer values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is sueded
1. What is suede and how is it different from other types of leather?
Suede is a type of leather made from the underside of animal hides, primarily lambskin, which gives it a soft, napped texture. Unlike traditional leather, which is derived from the outer layer and is more durable and water-resistant, suede is more permeable and prone to staining. This makes it ideal for applications where softness and comfort are prioritized, such as clothing and accessories. Understanding these differences is crucial for B2B buyers to assess the suitability of suede for their products.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
2. What are the main applications of suede in the B2B market?
Suede is commonly used in a variety of products including footwear, jackets, handbags, and upholstery. Its luxurious feel and aesthetic appeal make it a preferred choice in high-end fashion and interior design. B2B buyers should consider the specific applications they are targeting, as this will influence the type of suede they need, whether it be for fashion items or durable upholstery.
3. How do I evaluate the quality of suede when sourcing?
When sourcing suede, look for several quality indicators: the thickness of the material, the softness of the nap, and the absence of defects like pilling or uneven texture. Request samples from suppliers to assess these qualities firsthand. Additionally, inquire about the tanning process and any treatments applied to enhance durability and water resistance, as these factors significantly impact the longevity and performance of the suede.
4. What factors should I consider for international trade of suede products?
When engaging in international trade, consider import regulations, tariffs, and trade agreements specific to suede products in your target market. It’s essential to understand the legal requirements for animal-derived materials and ensure compliance with local laws in both the exporting and importing countries. Additionally, consider currency fluctuations and payment methods that minimize risk, such as letters of credit.
5. How do I vet potential suppliers for suede products?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their industry reputation through reviews and references from other businesses. Verify their production capabilities and quality assurance processes, ensuring they adhere to international standards. Conduct site visits if possible, and request certifications related to ethical sourcing and environmental impact. Establish clear communication channels to facilitate ongoing dialogue about product specifications and timelines.
6. What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for suede products?
Minimum order quantities for suede can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units, depending on the complexity of the item and the supplier’s production capabilities. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers upfront to negotiate favorable terms that align with your business model.
7. What payment terms should I negotiate when sourcing suede?
When negotiating payment terms, consider options like upfront deposits, milestone payments, or net payment terms based on delivery schedules. Common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining balance upon shipment. Be sure to clarify any additional costs, such as shipping and customs duties, to avoid unexpected expenses that could affect cash flow.
8. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for suede products?
To ensure quality assurance, establish clear specifications for the suede products you are sourcing, including texture, color, and durability requirements. Implement a QA process that includes pre-shipment inspections and random sampling of products. Collaborate with suppliers to develop a mutual understanding of quality standards and consider third-party quality assurance services for an independent assessment before shipment.
Top 5 What Is Sueded Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sewport – Suede Fabric
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“Fabric Name”: “Suede Fabric”, “Also Known As”: [“Fuzzy leather”, “Napped leather”, “Ultrasuede”], “Fabric Composition”: “The underside of animal skins or a similar synthetic material”, “Breathability”: “Low”, “Moisture-Wicking Abilities”: “Low”, “Heat Retention Abilities”: “High”, “Stretchability”: “Low”, “Prone to Pilling/Bubbling”: “Low”, “Country of Origin”: “Sweden”, “Biggest Exporting/Produ…
2. Merriam-Webster – Suede Definition
Domain: merriam-webster.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Suede is defined as leather with a napped surface or a fabric finished with a nap to simulate suede. The term ‘suede’ can also be used as a verb, meaning to give a suede finish or nap to a fabric or leather. The first known use of the word ‘suede’ as a noun was in 1883, and as a verb in 1921. The etymology traces back to the French term ‘gants de Suède’ meaning ‘Swedish gloves.’
3. MasterClass – Suede Leather
Domain: masterclass.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Suede is a high-quality form of leather made from the underside of animal hides, characterized by a soft, smooth surface. Commonly made from lambskin, it can also be produced from goats, pigs, calves, and deer. Suede is softer, thinner, and less strong than full-grain leather. It is popular for fashion items such as shoes, accessories, and jackets. Different types of suede include sheepskin suede …
4. Collins Dictionary – Sueded Definition
Domain: collinsdictionary.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Sueded is an adjective in American English that describes a material made to resemble suede.
5. Reddit – Sueded T-Shirts
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Sueded T-shirts are marketed as having a soft texture, different from regular cotton shirts. They are often made from brushed cotton, giving them a suede-like feel. Some users have noted that while they are softer than typical cotton, they do not feel exactly like real suede. The term ‘sueded’ refers to a specific level of brushing or abrasion applied to the fabric, which enhances its softness.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is sueded
Suede, a luxurious fabric derived from the underside of animal hides, presents unique opportunities for B2B buyers looking to enhance their product offerings. Its soft texture and aesthetic appeal make it a preferred choice in various applications, including footwear, apparel, and accessories. However, the distinctive properties of suede, such as its low durability and high maintenance needs, necessitate strategic sourcing to ensure quality and longevity in product lines.
International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality suede while adhering to sustainable practices. Emphasizing the importance of sourcing from established manufacturers can mitigate risks associated with inferior products, ensuring that your brand maintains its reputation for quality.
As the demand for suede continues to grow, particularly for fashion and luxury markets, staying informed on market trends and sourcing strategies will be crucial. Invest in building relationships with reputable suppliers and consider incorporating innovative synthetic alternatives to diversify your offerings. By taking these steps, your business can effectively capitalize on the enduring allure of suede while meeting the evolving needs of consumers.
Illustrative image related to what is sueded
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded