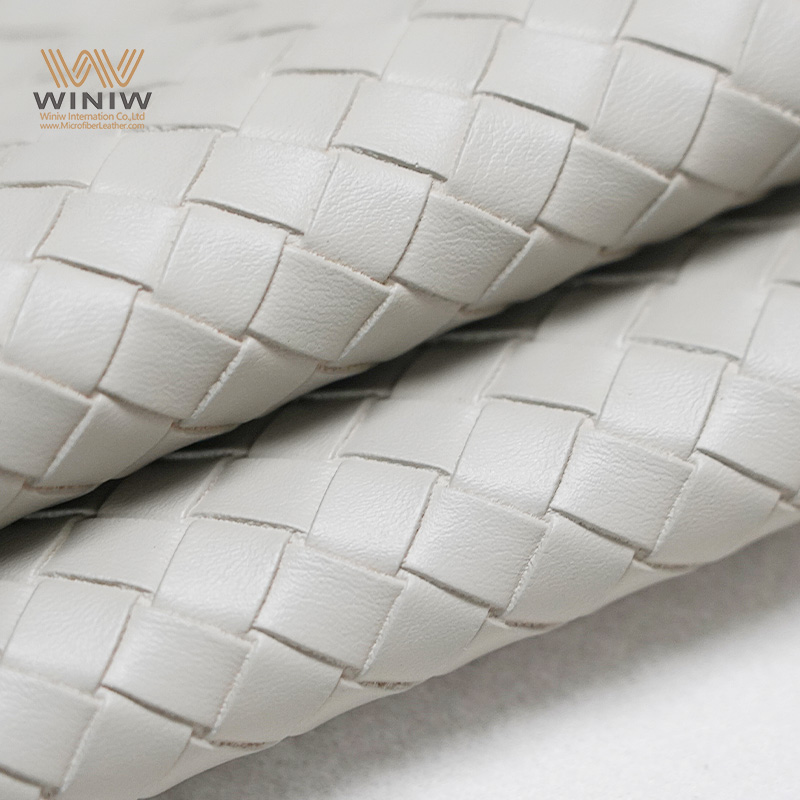
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for make leather
Navigating the complexities of the global market for make leather can present significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to sourcing high-quality materials that meet both aesthetic and functional needs. As the demand for leather goods continues to rise across various sectors, from fashion to automotive, understanding the nuances of leather types, applications, and production processes becomes essential for informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide aims to equip international buyers—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Nigeria—with the knowledge they need to navigate this intricate landscape.
Within these pages, we delve into the various types of leather, exploring their unique properties and best uses, and provide insights into supplier vetting processes to ensure quality and reliability. Furthermore, we analyze cost factors, enabling buyers to make competitive yet sustainable purchasing decisions. By addressing these critical aspects, this guide empowers B2B professionals to confidently approach the make leather market, fostering partnerships that enhance product offerings and meet consumer demands. Whether you are a seasoned buyer or new to the leather industry, this resource is designed to support your strategic sourcing endeavors and drive business growth in a dynamic global marketplace.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 Make Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for make leather
- Understanding make leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of make leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘make leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for make leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for make leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘make leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for make leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing make leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for make leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the make leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of make leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for make leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding make leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chrome Tanned Leather | Quick tanning process, vibrant colors, water-resistant | Upholstery, fashion accessories, footwear | Pros: Fast production; Cons: Less eco-friendly due to chemicals used. |
| Vegetable Tanned Leather | Natural tanning using plant materials, retains natural look | Belts, saddlery, high-end fashion items | Pros: Eco-friendly; Cons: Longer production time and less uniformity. |
| Camurça | Soft, napped finish, lightweight | Apparel, accessories, automotive interiors | Pros: Luxurious feel; Cons: Less durable, prone to stains. |
| Nubuck | Sanded top layer for a velvety finish | Luxury goods, shoes, and bags | Pros: Durable and soft; Cons: Requires careful maintenance. |
| Bonded Leather | Made from leftover leather scraps, cost-effective | Budget-friendly products, furniture | Pros: Affordable; Cons: Lower quality and durability compared to full-grain leather. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Chrome Tanned Leather?
Chrome tanned leather is characterized by its rapid tanning process, which typically takes just a few hours. This leather type is known for its vibrant colors and water resistance, making it a popular choice in various industries. B2B buyers looking for quick production times and a wide range of color options will find chrome tanned leather suitable for upholstery, fashion accessories, and footwear. However, the chemical process involved raises environmental concerns, which buyers should consider when sourcing.
How Does Vegetable Tanned Leather Compare in Suitability?
Vegetable tanned leather is distinguished by its use of natural tannins derived from plant materials. This method results in a leather that retains a natural look and feel, making it ideal for products like belts, saddlery, and high-end fashion items. While it is more environmentally friendly than chrome tanned leather, the tanning process is slower, resulting in longer lead times for B2B buyers. Companies focused on sustainability and artisanal craftsmanship may prioritize vegetable tanned leather despite the longer production times.
What Advantages Does Suede Offer for B2B Buyers?
Suede is known for its soft, napped finish, which gives it a luxurious feel. This lightweight leather is commonly used in apparel, accessories, and automotive interiors. B2B buyers seeking to enhance their product offerings with a premium feel may find suede appealing. However, it is less durable than other leather types and can be prone to stains, necessitating careful maintenance. Buyers should weigh the aesthetic benefits against the practical limitations of suede.
What Makes Nubuck a Preferred Choice for Luxury Goods?
Nubuck leather features a sanded top layer that creates a velvety finish, providing both durability and softness. It is often used in luxury goods, shoes, and bags, appealing to B2B buyers in the high-end market. While nubuck is more resistant to wear than suede, it requires careful maintenance to keep it looking its best. Buyers should consider the balance between luxury appeal and maintenance requirements when selecting nubuck for their products.
Why Consider Bonded Leather for Cost-Effective Solutions?
Bonded leather is made from leftover leather scraps that are bonded together, making it a cost-effective option for B2B buyers. It is commonly used in budget-friendly products and furniture. While it offers an affordable alternative to full-grain leather, it is important to note that bonded leather typically has lower quality and durability. Buyers should assess their target market’s expectations and product longevity when considering bonded leather as a viable option.
Key Industrial Applications of make leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of make leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Leather garments and accessories | High durability and aesthetic appeal | Quality of leather, sourcing certifications, and ethical production practices |
| Automotive | Upholstery and interior components | Enhanced comfort and luxury feel | Compatibility with existing designs and regulations, availability of specific grades of leather |
| Furniture & Upholstery | Sofas, chairs, and decorative items | Long-lasting materials with luxury finishes | Color matching, texture preferences, and fire-retardant treatments |
| Sporting Goods | Footwear and protective gear | Performance enhancement and durability | Weight considerations, breathability, and compliance with safety standards |
| Industrial Applications | Belts, straps, and harnesses | Strength and reliability for heavy-duty use | Load capacity, resistance to environmental factors, and customization options |
How is ‘make leather’ utilized in the fashion and apparel industry?
In the fashion and apparel sector, ‘make leather’ is predominantly used for crafting high-quality garments and accessories, such as jackets, bags, and belts. The inherent durability and timeless aesthetic of leather make it a preferred choice among designers and consumers alike. International buyers, especially from Europe and the Middle East, often seek leather that meets specific quality standards and ethical sourcing practices. They must consider the leather’s origin, tanning methods, and environmental impact to align with consumer preferences for sustainability.

Illustrative image related to make leather
What role does ‘make leather’ play in the automotive industry?
In the automotive industry, ‘make leather’ is essential for upholstery and interior components, offering a blend of luxury and comfort. Leather is used for seats, dashboards, and steering wheels, enhancing the overall driving experience. B2B buyers in this sector must focus on compatibility with vehicle designs and compliance with industry regulations, particularly regarding safety and environmental standards. Sourcing leather that meets these criteria ensures a premium product that resonates with customers seeking quality and sophistication in their vehicles.
How is ‘make leather’ applied in furniture and upholstery?
The furniture and upholstery industry extensively uses ‘make leather’ for creating sofas, chairs, and decorative items. Leather provides a luxurious finish and significant durability, making it ideal for high-end furniture. Buyers need to pay attention to factors like color matching, texture preferences, and fire-retardant treatments, especially when sourcing for international markets. Ensuring the leather meets local regulations and customer expectations can enhance marketability and customer satisfaction.
In what ways does ‘make leather’ contribute to sporting goods?
In the sporting goods sector, ‘make leather’ is commonly used for footwear and protective gear, where performance and durability are paramount. Leather enhances breathability and comfort, making it suitable for athletic applications. Buyers need to consider factors such as weight, breathability, and compliance with safety standards when sourcing leather for sports products. This focus on quality not only improves athlete performance but also reinforces brand reputation in a competitive market.
What are the industrial applications of ‘make leather’ in heavy-duty products?
In industrial applications, ‘make leather’ is utilized for manufacturing belts, straps, and harnesses that require high strength and reliability. These products are essential in various sectors, including construction and manufacturing, where durability is critical. B2B buyers must evaluate the load capacity and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring the leather meets the specific requirements of heavy-duty use. Customization options can also be a significant consideration, allowing businesses to tailor products to their operational needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘make leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Leather Materials for Production
The Problem: One significant challenge B2B buyers face in the leather industry is sourcing high-quality leather that meets their specific production needs. Buyers often encounter inconsistent quality, limited availability, or high costs when dealing with various suppliers. This inconsistency can lead to production delays, increased waste, and ultimately, dissatisfied customers. Additionally, navigating the differences between chrome-tanned and vegetable-tanned leather can complicate decision-making, especially when specific attributes are required for certain applications, such as durability for upholstery or softness for garments.
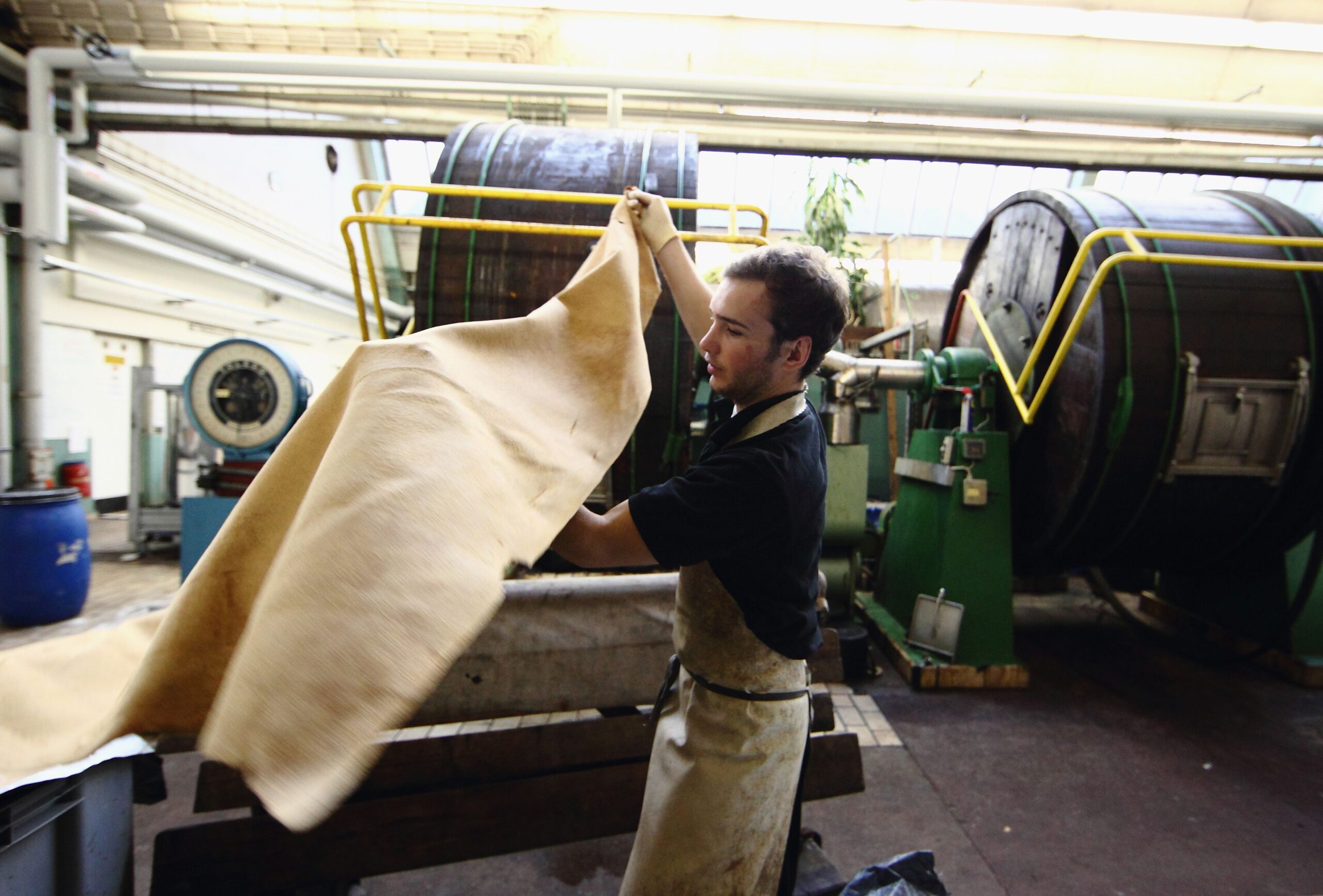

Illustrative image related to make leather
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, B2B buyers should establish long-term relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in leather. Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that have a solid reputation for consistency and quality. Request samples to evaluate the leather’s characteristics, such as thickness, texture, and finish, which will help ensure it meets your production standards. Furthermore, consider leveraging technology to streamline your supply chain; platforms that connect buyers with vetted suppliers can enhance transparency and reliability. When specifying your needs, be clear about the end-use of the leather, as this will guide the supplier in providing the most appropriate type of leather. Establishing a quality assurance process within your procurement strategy can also help maintain standards and mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
Scenario 2: Navigating Environmental Regulations in Leather Production
The Problem: Environmental regulations concerning leather production can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in regions where stricter sustainability practices are being enforced. Many countries are increasingly scrutinizing tanning processes and the use of chemicals, which can lead to compliance risks and potential fines. Buyers may struggle to find tanneries that utilize sustainable practices while still providing the desired quality and characteristics of leather, creating a dilemma between quality and compliance.
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should prioritize partnerships with tanneries that are certified in sustainable practices, such as those adhering to ISO 14001 standards or the Leather Working Group’s environmental audits. This not only ensures compliance with regulations but also enhances the brand’s reputation in a market that increasingly values sustainability. Additionally, buyers can engage in proactive communication with suppliers regarding their environmental practices and certifications. Implementing a sustainability audit process within your supply chain can help identify potential risks and areas for improvement. Training your procurement team on environmental regulations and sustainable sourcing practices can also empower them to make informed decisions and mitigate compliance risks effectively.
Scenario 3: Understanding the Leather Processing Steps for Product Development
The Problem: Many B2B buyers entering the leather goods market may lack a comprehensive understanding of the various steps involved in leather processing, which can lead to misalignment between product development and market expectations. This gap in knowledge can result in choosing inappropriate materials or processing methods, leading to subpar products that do not meet customer demands. Furthermore, buyers may find it challenging to communicate their specifications effectively to suppliers, resulting in delays and increased costs.
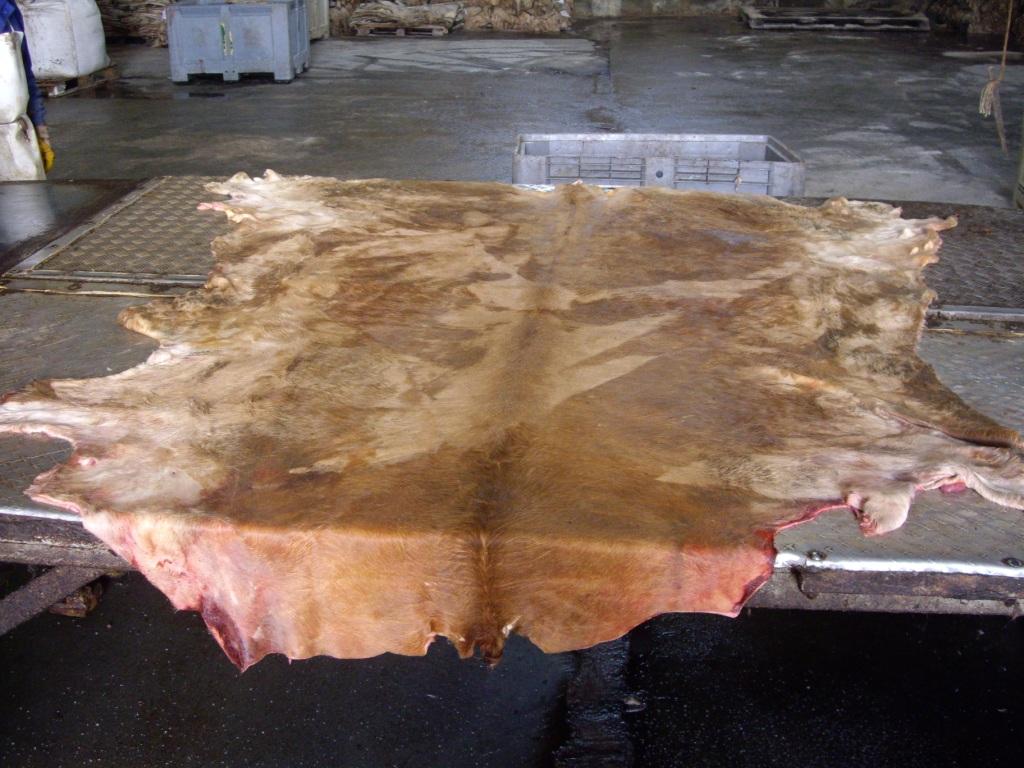

Illustrative image related to make leather
The Solution: To bridge this knowledge gap, buyers should invest in training and resources that educate them on the leather-making process, from hide preparation to finishing techniques. Engaging in workshops or industry conferences can provide valuable insights into best practices and the latest trends in leather processing. Additionally, creating a collaborative relationship with suppliers can facilitate open communication about the technical aspects of leather production, enabling buyers to articulate their needs more effectively. Documenting the entire leather processing workflow, including timelines and quality checks, can help in managing expectations and ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned throughout the product development process. Utilizing digital tools such as product lifecycle management software can also enhance visibility and collaboration, streamlining the development process and improving final product quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for make leather
What Are the Key Materials Used in Leather Production?
When selecting materials for leather production, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each option is crucial for B2B buyers. The following analysis covers four common materials used in the leather-making process: cowhide, sheepskin, synthetic leather, and vegetable-tanned leather.
How Does Cowhide Perform in Leather Production?
Cowhide is the most widely used material in leather production, primarily due to its durability and versatility. It has excellent tensile strength and can withstand significant wear and tear, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including upholstery, footwear, and accessories. The temperature resistance of cowhide is substantial, allowing it to perform well in various environmental conditions.
Pros: Cowhide is durable, offers a high-quality finish, and can be treated for water resistance. Its natural grain provides aesthetic appeal, making it a preferred choice for luxury products.
Cons: The processing of cowhide can be complex and costly, particularly when considering the tanning and finishing stages. Additionally, it may not be suitable for all climates, as extreme humidity can lead to mold growth.
Impact on Application: Cowhide’s robustness makes it compatible with a wide range of products, but it may require specific treatments for moisture-rich environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, especially for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should also consider the ethical sourcing of hides, which may affect brand reputation.
What Are the Benefits of Sheepskin in Leather Goods?
Sheepskin is another popular material, known for its softness and lightweight properties. It offers good thermal insulation, making it ideal for garments and accessories that require comfort and warmth.
Pros: The softness and flexibility of sheepskin make it comfortable against the skin. It is also relatively lightweight, which is advantageous for fashion items.
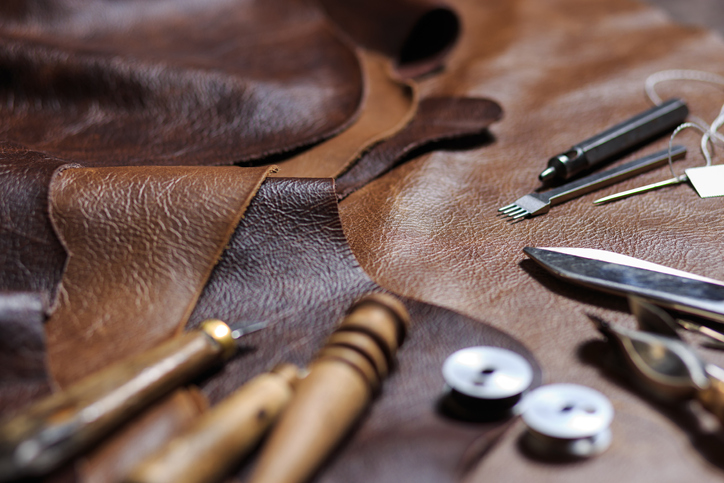

Illustrative image related to make leather
Cons: Sheepskin is less durable than cowhide and may not withstand heavy wear. It is also more susceptible to staining and damage from water.
Impact on Application: Sheepskin is ideal for luxury fashion items and interior applications, but its limitations in durability may restrict its use in high-wear products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that sheepskin meets relevant quality standards and consider the potential for higher costs due to sourcing and processing.
How Does Synthetic Leather Compare in Terms of Cost and Performance?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), has gained popularity due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility. It mimics the appearance of natural leather while offering a range of finishes and colors.

Illustrative image related to make leather
Pros: Synthetic leather is generally less expensive than natural leather and is easier to clean. It is also resistant to moisture and stains, making it suitable for various applications.
Cons: While synthetic leather can be durable, it often lacks the breathability and longevity of natural leather. It may also be less environmentally friendly due to the use of petroleum-based materials.
Impact on Application: Synthetic leather is widely used in fashion, upholstery, and automotive applications, but its performance may vary based on the manufacturing process.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of environmental regulations related to synthetic materials, particularly in Europe, where sustainability is increasingly prioritized.
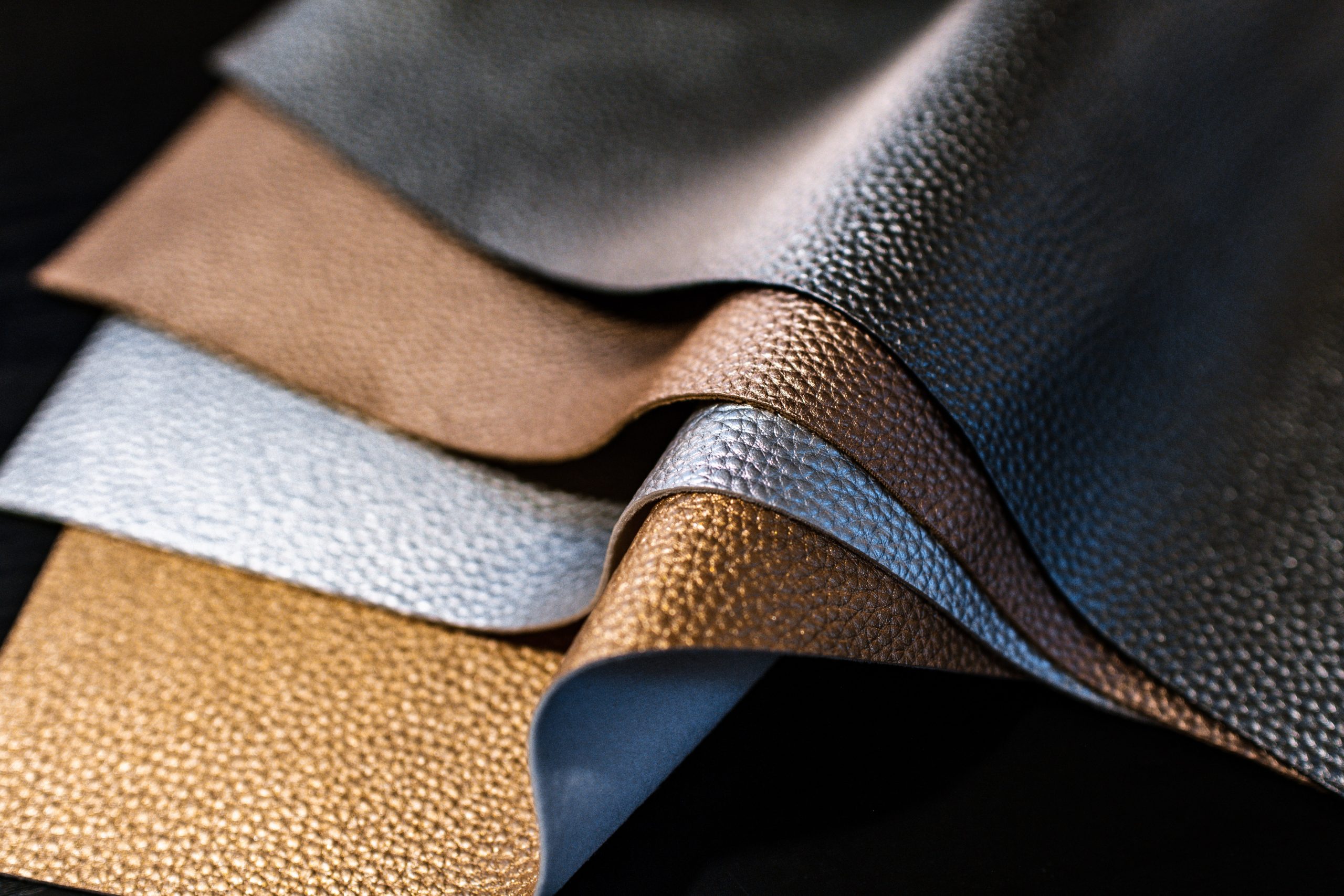

Illustrative image related to make leather
What Makes Vegetable-Tanned Leather a Sustainable Choice?
Vegetable-tanned leather is made using natural tannins from plant sources, making it a sustainable option for environmentally conscious buyers. It is known for its unique aging process, which enhances its character over time.
Pros: This type of leather is biodegradable and free from harmful chemicals, appealing to eco-friendly brands. It also develops a rich patina, adding to its aesthetic value.
Cons: Vegetable-tanned leather is generally stiffer and may require more maintenance to keep it in good condition. The tanning process can also be time-consuming, leading to higher costs.
Impact on Application: Ideal for high-end goods such as belts, wallets, and bags, vegetable-tanned leather is particularly suited for products that benefit from a unique appearance over time.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with eco-certifications is crucial for buyers in Europe and North America. Understanding local regulations concerning natural materials will also aid in sourcing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Leather Production
| Material | Typical Use Case for make leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cowhide | Upholstery, footwear, accessories | High durability and aesthetic appeal | Complex processing, climate sensitivity | Elevado |
| Sheepskin | Luxury garments, accessories | Softness and comfort | Less durable, susceptible to stains | Medium |
| Couro sintético | Fashion, upholstery, automotive | Cost-effective, easy to clean | Less breathable, environmental concerns | Low |
| Vegetable-Tanned Leather | High-end goods, belts, wallets | Eco-friendly, unique aging | Stiffer, requires maintenance | Medium to High |
This guide provides essential insights into material selection for leather production, equipping international B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions tailored to their specific market needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for make leather
What Are the Key Stages in Leather Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of leather involves a series of well-defined stages that transform raw hides into finished leather products. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers, as it allows them to assess quality and suitability for their specific needs.
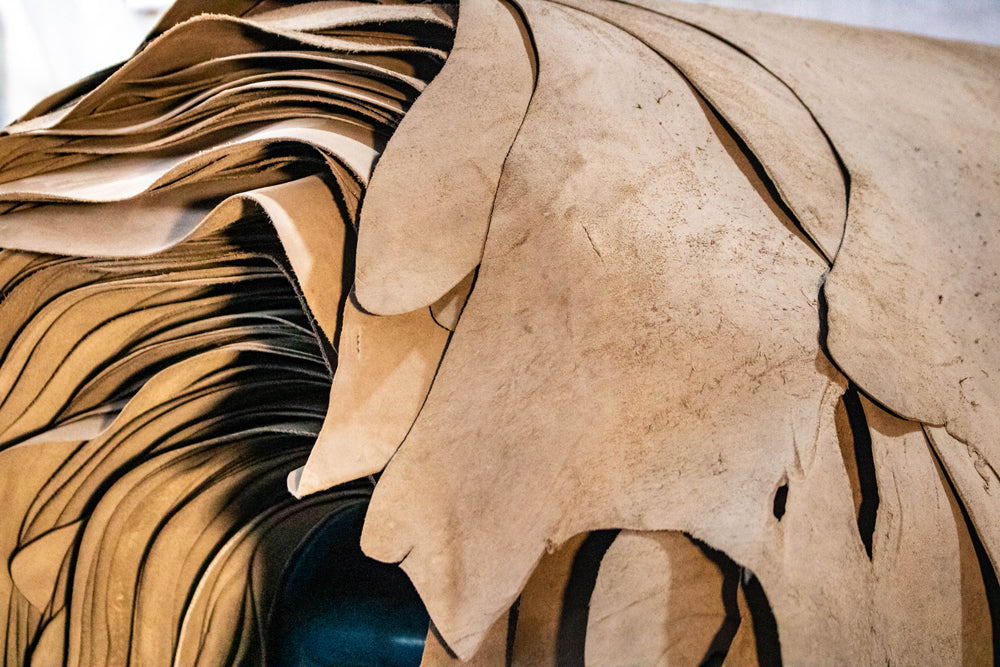
Material Preparation: How Are Hides Processed Before Tanning?
The first stage of leather production is material preparation. This involves several critical steps:
-
Fleshing: After the hide is removed from the animal, it is fleshed to eliminate any remaining meat and fat. This step is crucial to ensure a clean and viable raw material for tanning.
-
Hair Removal: The hair is removed through a chemical digestion process, typically using lime and sodium sulfide. This process is essential for preparing the hide for tanning.
-
Pickling: The hides are then pickled in a solution of water, salt, and acid. This step helps to maintain the hide’s integrity and prepares it for the tanning process.
By ensuring that these steps are conducted meticulously, manufacturers lay the groundwork for high-quality leather production.

Illustrative image related to make leather
What Are the Different Tanning Methods Used in Leather Production?
Tanning is the pivotal stage that converts raw hides into leather. There are several methods, each with unique characteristics:
-
Chrome Tanning: This method, which uses trivalent chrome salts, is prevalent due to its speed and effectiveness. It typically takes about eight hours for the chrome to penetrate the hide thoroughly. Chrome-tanned leather is known for its durability and resistance to wear, making it suitable for a wide range of products, including upholstery and footwear.
-
Vegetable Tanning: This slower method employs tannins derived from tree barks. It can take several days to complete but results in leather that is often more environmentally friendly and has a distinct aesthetic appeal. Vegetable-tanned leather is commonly used for products like belts and saddlery.
Understanding these tanning methods is crucial for B2B buyers as they dictate the leather’s characteristics, including flexibility, color, and texture.
How Are Leather Hides Split and Finished for Market Readiness?
After tanning, the hides undergo splitting and shaving:
-
Splitting: The hides are split into sheets of varying thickness depending on the intended use. This allows manufacturers to optimize their material usage and create products that meet specific requirements.
-
Finishing: This final stage involves applying protective coatings and surface treatments. Various techniques, such as embossing, dyeing, and polishing, are employed to enhance the leather’s appearance and durability. The finishing process not only affects the aesthetic qualities of the leather but also its functionality, such as water resistance and abrasion resistance.
These finishing techniques are vital for B2B buyers who require leather products to meet specific industry standards and customer expectations.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance is a critical component of leather manufacturing, ensuring that the final products meet both customer expectations and regulatory standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with several relevant international and industry-specific standards:

Illustrative image related to make leather
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system and is applicable to any organization looking to improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Leather manufacturers certified under ISO 9001 are likely to have established processes that enhance product quality.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Buyers should verify that their suppliers adhere to these regulations, particularly for items like leather goods used in consumer applications.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) offers standards relevant for leather used in oil and gas applications. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can meet these specific requirements if applicable.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Leather Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the leather manufacturing process, with several key checkpoints established to ensure product integrity:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw hides and materials before processing. Buyers should inquire about the IQC practices of their suppliers to ensure that only high-quality materials are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various checkpoints are established to monitor quality at different stages. This may include checks during tanning, splitting, and finishing to identify any defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the leather products are finished, a final inspection is conducted to ensure they meet specifications and standards. This can include visual inspections, physical tests, and compliance with applicable regulations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess a supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with standards. This hands-on approach provides valuable insights into the supplier’s operational capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their QC processes and outcomes. These reports should detail testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control practices. This can be particularly important for international buyers who may face challenges in conducting on-site audits.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding leather production and quality standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and craftsmanship can help buyers better communicate their expectations and assess supplier capabilities.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping and logistics can impact product quality. Buyers should consider how transportation methods and storage conditions may affect the leather’s condition upon arrival.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing leather products, ensuring they meet their business needs while maintaining high standards of quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘make leather’
To assist international B2B buyers in sourcing quality leather, this guide offers a practical checklist detailing essential steps in the procurement process. By adhering to this checklist, you can ensure that your sourcing decisions align with both your business requirements and sustainability goals.

Illustrative image related to make leather
Step 1: Identify Your Leather Needs
Understanding the specific type of leather required for your products is the first step in the sourcing process. Different applications, such as upholstery, footwear, or accessories, necessitate various leather types, such as chrome-tanned or vegetable-tanned leather. Clarifying your needs upfront can significantly streamline your sourcing process and help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in the type of leather you require. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of companies. Pay attention to supplier reviews and ratings to gauge their reputation in the market. A well-informed shortlist will help in making comparisons easier down the line.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, verify the certifications and compliance of your shortlisted suppliers. Look for international standards such as ISO certifications and environmental compliance, which indicate a commitment to quality and sustainability. This step is crucial as it ensures that the leather is sourced ethically and processed in a manner that meets industry standards.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Once you have narrowed down your supplier options, request samples to assess the quality of their leather products. Examine the samples for texture, durability, and finish. High-quality leather should meet your aesthetic and functional requirements, ensuring that it aligns with your brand’s standards.

Illustrative image related to make leather
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions regarding pricing, minimum order quantities, and payment terms. Understanding the total cost of procurement, including shipping and tariffs, is essential for budget planning. Negotiating favorable terms can lead to long-term partnerships that benefit both parties.
Step 6: Discuss Lead Times and Delivery Logistics
Confirm the lead times for production and delivery with your selected supplier. It’s vital to understand their capacity to meet your timeline, especially if you have specific project deadlines. Discuss logistics options to ensure timely delivery, considering factors like shipping routes and customs clearance.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to a successful supplier relationship. Set up a plan for regular updates regarding production status, potential issues, and any changes in demand. This will foster a transparent partnership and allow you to address concerns proactively, ensuring a smoother sourcing experience.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing leather more effectively, ensuring they partner with suppliers that meet their quality, ethical, and logistical requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for make leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Sourcing?
When sourcing leather, understanding the cost structure is vital for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
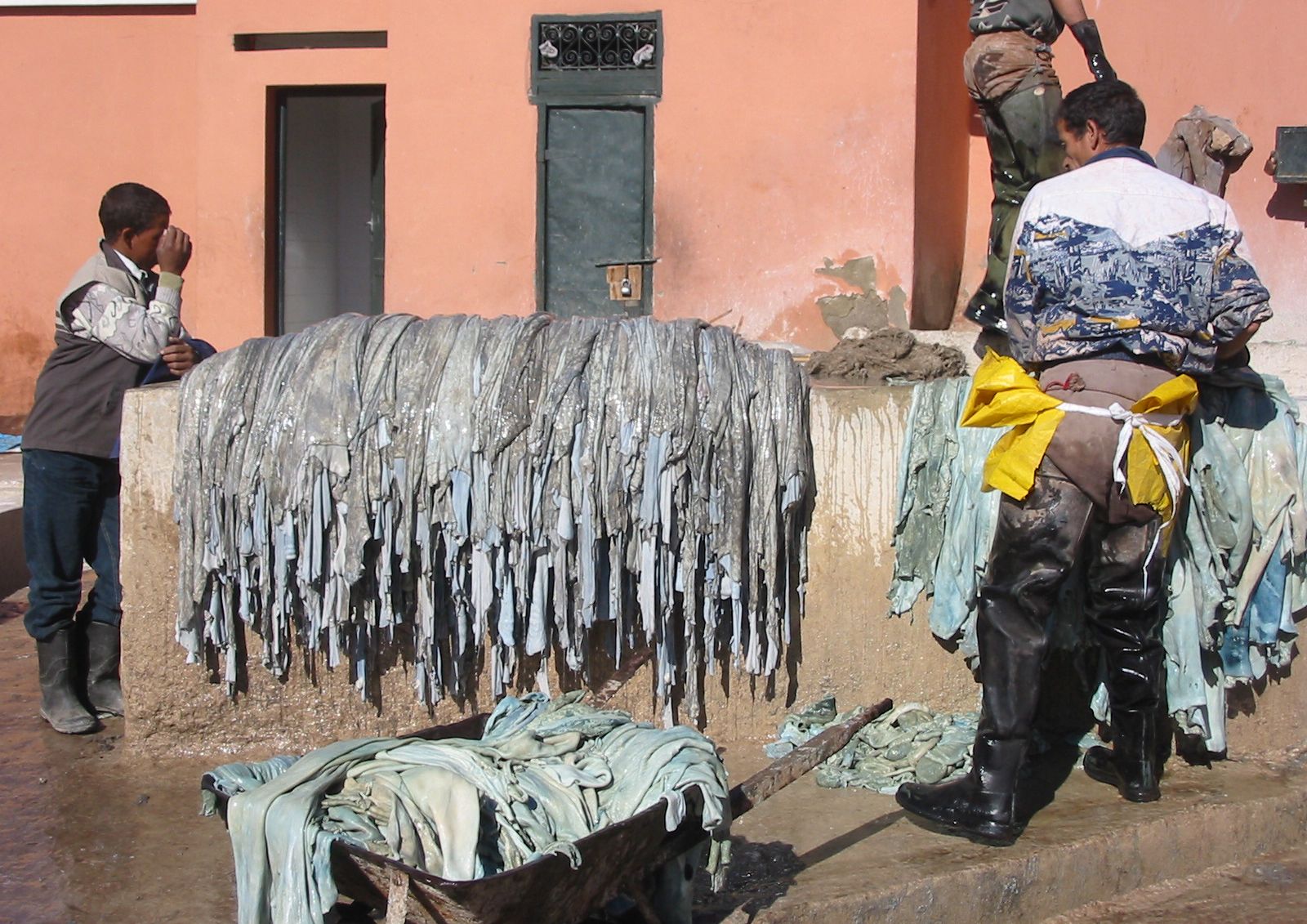

Illustrative image related to make leather
-
Materials: The primary input in leather production is the raw hides, predominantly sourced from cattle. The price can fluctuate based on market demand and supply. Additionally, tanning agents (chrome or vegetable) and finishing materials significantly contribute to the overall material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for processing hides. The tanning process, quality control, and finishing require experienced workers, which adds to the labor costs. Countries with high labor costs may impact pricing structures, making it crucial to consider sourcing from regions with competitive labor markets.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient management of these overheads can help keep overall costs in check.
-
Tooling: Investment in machinery and tools for processing leather can be substantial, particularly for specialized or custom projects. These costs are often amortized over production runs, making initial orders more expensive.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that leather meets specific standards involves rigorous QC processes. These additional steps, while increasing costs, are necessary for maintaining product quality and compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the origin of the hides and the destination market. International shipping, customs duties, and insurance add layers of complexity and cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their operational costs and profit margins. This can vary widely depending on the supplier’s business model and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Leather Sourcing Costs?
Several factors can influence leather pricing:
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in bulk often leads to lower per-unit prices due to economies of scale. However, minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary by supplier, affecting overall costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized leather products or specific quality requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality leather or certified sustainable practices can lead to premium pricing. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can also provide better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms is crucial. Incoterms dictate who bears responsibility for shipping costs, insurance, and customs clearance, which can significantly affect the total landed cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Leather Sourcing?
To maximize value in leather sourcing, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a long-term relationship can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as shipping, handling, and potential returns or defects to assess the true cost of sourcing leather.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local economic conditions, tariffs, and trade agreements. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to stay informed about these factors to make well-informed purchasing decisions.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Leather prices can be volatile. Keeping abreast of market trends, including supply chain disruptions or changes in consumer preferences, can help buyers anticipate price changes and adjust their sourcing strategies accordingly.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for leather sourcing can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors and are subject to change. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and supplier comparisons to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing make leather With Other Solutions
In the evolving landscape of materials used for crafting goods, “make leather” stands out as a traditional yet versatile option. However, as businesses look to innovate and optimize their product offerings, it becomes essential to explore alternative solutions. This analysis will compare “make leather” with synthetic leather and natural fabrics, providing B2B buyers with a clearer understanding of their options.
| Comparison Aspect | ‘Make Leather’ | Couro sintético | Natural Fabrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, high-quality, breathability | Generally water-resistant, less breathable | Varies widely; often less durable |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, long-term value | Lower initial cost, but may need replacing sooner | Varies; often lower than leather |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized skills and tools | Easy to source and work with | Generally easy, but depends on the material |
| Maintenance | Requires regular care and conditioning | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Varies; some require special care |
| Best Use Case | High-end products (bags, furniture, etc.) | Fashion items, upholstery, casual wear | Apparel, home textiles, eco-friendly products |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Synthetic Leather as an Alternative?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers a budget-friendly alternative to traditional leather. Its primary advantages include lower costs and ease of maintenance, making it ideal for mass-produced items. However, synthetic leather lacks the durability and breathability of genuine leather, which may lead to quicker wear and tear. Additionally, concerns regarding its environmental impact—stemming from plastic production—can deter eco-conscious businesses.
How Do Natural Fabrics Compare to ‘Make Leather’?
Natural fabrics, such as cotton, linen, or hemp, serve as another alternative to leather. They are often more affordable and easier to work with, making them popular for various applications, especially in clothing and eco-friendly products. However, their performance can be inconsistent; they may not offer the same durability or water resistance as leather. Additionally, natural fabrics might require specific care to maintain their quality over time, which can be a drawback for businesses aiming for low-maintenance solutions.
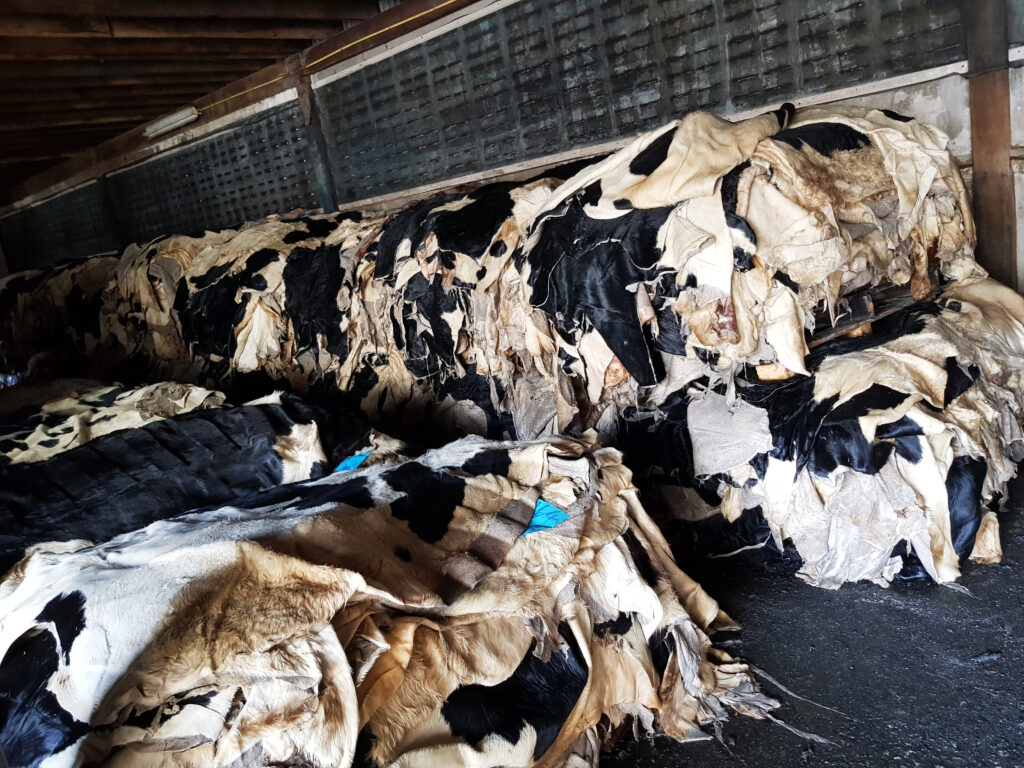

Illustrative image related to make leather
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between “make leather” and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including budget constraints, intended use, and target market preferences. For high-end products where durability and aesthetic appeal are paramount, traditional leather remains an excellent choice. Conversely, if cost-effectiveness and ease of production are more critical, synthetic leather or natural fabrics might be preferable. Ultimately, aligning the material choice with the brand’s values and customer expectations will lead to more successful product outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for make leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Leather for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical properties of leather is crucial for B2B buyers as these specifications directly impact product quality, durability, and suitability for various applications. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality classification of leather based on the hide’s origin, processing method, and appearance. Common grades include full-grain, top-grain, and corrected grain. For buyers, selecting the appropriate grade ensures the leather meets their specific quality requirements, affecting the end product’s appeal and longevity. -
Thickness (Weight)
Leather thickness is typically measured in ounces or millimeters. Different applications require varying thicknesses; for example, upholstery leather might range from 1.0 to 1.5 mm, while leather for belts may require 3.0 mm or more. Understanding thickness helps buyers choose the right leather for their products, balancing durability and flexibility. -
Tensile Strength
This property measures the leather’s ability to withstand pulling forces without breaking. High tensile strength is essential for applications like bags and footwear, where durability is paramount. Buyers should inquire about tensile strength specifications to ensure the leather can withstand the demands of its intended use. -
Water Resistance
Water resistance indicates how well leather can repel moisture. While all leather has some degree of water resistance, treated leather offers enhanced protection. For buyers in wet climates or those producing outdoor gear, knowing the water resistance level is critical to ensure the longevity and functionality of their products. -
Finish Type
The finish affects the leather’s appearance, texture, and durability. Common finishes include aniline, semi-aniline, and pigmented. Each finish type has unique properties and applications, and understanding these can help buyers select leather that aligns with their aesthetic and functional needs. -
Color Fastness
This property refers to the leather’s ability to retain its color when exposed to light, washing, or rubbing. High color fastness is essential for products that will be subjected to wear and tear. Buyers should prioritize this property to maintain the visual appeal of their leather goods over time.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand in the Leather Industry?
Navigating the leather industry requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Here are key terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components or products that are sold under another company’s brand. In leather, OEMs often create bespoke leather goods for brands. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers negotiate better terms and ensure product quality. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand as it can impact their purchasing strategy and inventory management. Knowing MOQs helps buyers assess their order size against their production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products or services. Buyers should utilize RFQs to ensure they receive competitive pricing and to clarify specifications and expectations with potential suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears shipping costs and risks at different stages of transportation. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for effective negotiation and logistics planning. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their production schedules and manage inventory effectively, minimizing disruptions in their supply chain. -
Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ISO or Leather Working Group (LWG) certifications, indicate compliance with environmental and quality benchmarks. Buyers should consider certification standards to ensure their suppliers meet industry norms, enhancing product credibility and sustainability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in the leather industry can make informed decisions that align with their business goals and customer expectations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the make leather Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Make Leather Sector?
The global leather market is poised for significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including fashion, automotive, and furniture. The rise of e-commerce platforms has transformed how B2B buyers source leather goods, facilitating direct connections with manufacturers and suppliers worldwide. Notably, countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are emerging as key players, with a growing interest in both traditional craftsmanship and innovative leather technologies.

Illustrative image related to make leather
One of the most notable trends is the increasing adoption of digital tools in sourcing processes. Platforms that offer virtual showrooms and AI-driven analytics are helping buyers make informed decisions based on real-time data. Furthermore, there is a noticeable shift towards customization and personalization, allowing businesses to cater to specific market niches, particularly in regions like Germany and Nigeria where consumer preferences are evolving rapidly.
Emerging markets are also witnessing a surge in local production capabilities, reducing reliance on imports and enhancing supply chain resilience. This trend is particularly significant for B2B buyers who seek to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions. As supply chains adapt, understanding local regulations and establishing strong relationships with local suppliers will be crucial for international buyers looking to navigate these dynamics effectively.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Make Leather Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of the leather industry, with growing awareness of environmental impacts and ethical sourcing practices. The traditional leather production process often involves significant water usage and chemical treatments, raising concerns about its ecological footprint. As a result, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices and transparency in their supply chains.
Ethical sourcing is not only a market differentiator but also a response to consumer demand for responsibly produced goods. Many suppliers are now pursuing certifications such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and the Leather Working Group (LWG), which assure buyers of compliance with environmental and social standards. These certifications can enhance brand reputation and build trust with consumers who are increasingly scrutinizing the origins of the products they purchase.
Moreover, the shift towards plant-based and alternative leather materials, such as mushroom leather and lab-grown leather, is gaining momentum. These innovations offer B2B buyers the opportunity to diversify their product offerings while aligning with sustainability goals. By embracing eco-friendly practices and materials, businesses can not only improve their environmental impact but also tap into a growing market segment that values sustainability.
How Has the Make Leather Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the leather sector is deeply intertwined with human history, dating back to prehistoric times when animal hides were used for clothing and shelter. The industrial revolution marked a significant turning point, introducing mechanized tanning processes that improved efficiency and quality. This era saw the rise of leather as a staple material in various industries, including fashion and automotive.
In recent decades, the leather industry has faced challenges related to environmental concerns and changing consumer preferences. The rise of synthetic alternatives initially posed a threat, but the unique qualities of leather, such as durability and aesthetic appeal, have ensured its continued relevance. Today, the industry is at a crossroads, balancing traditional craftsmanship with modern sustainability practices, making it an exciting time for B2B buyers to engage with innovative suppliers who respect both heritage and the environment.
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of the make leather sector requires a keen understanding of market dynamics, a commitment to sustainability, and a willingness to adapt to evolving consumer demands. B2B buyers who embrace these principles will be well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this vibrant industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of make leather
-
How is leather sourced and processed for international trade?
Leather is primarily sourced from cattle, which are raised for meat, making leather a by-product of the meat industry. The processing involves several steps: preparation, tanning (often using chrome or vegetable methods), splitting, shaving, setting, and finishing. For international trade, it’s essential to work with suppliers who adhere to quality and environmental standards, ensuring that the leather meets the necessary regulatory requirements for importation in your region. -
What are the main types of leather suitable for different applications?
The best type of leather depends on the intended application. For garments and upholstery, chrome-tanned leather is preferred due to its softness and durability. Vegetable-tanned leather is ideal for items requiring rigidity, such as belts and shoe soles. Understanding the characteristics of each type helps buyers select the right leather for their specific needs and ensures product quality aligns with consumer expectations. -
How can I vet suppliers of leather products effectively?
To vet suppliers, assess their reputation through online reviews and industry recommendations. Request samples to evaluate the quality of their leather and inspect their production processes for sustainability and ethical practices. Additionally, verify certifications, such as ISO or environmental compliance, and inquire about their experience in international trade, as this can affect shipping and customs processes. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQ) for leather products?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Typically, MOQs range from 50 to 500 square meters for bulk leather orders. Custom-made products may require higher MOQs due to increased production costs. Always clarify MOQs with potential suppliers early in negotiations to ensure they align with your purchasing capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing leather internationally?
Payment terms often vary based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include a deposit upfront (usually 30%) and the balance upon delivery or before shipping. Some suppliers may also offer letters of credit or trade financing options. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide a balance of security for both parties, particularly when dealing with large orders. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for leather products?
Quality assurance can be ensured by establishing clear specifications with your supplier, including desired leather grades, finishes, and performance characteristics. Conduct regular audits of the manufacturing process and consider third-party quality inspections before shipment. Additionally, implementing a return policy for defective products can provide an added layer of security for your investment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing leather?
When importing leather, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs specific to your region. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for large orders but takes longer. Engage a freight forwarder familiar with leather goods to navigate customs and ensure compliance with all import regulations, which can vary significantly by country. -
Can I customize leather products, and what should I know about the process?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options, including size, color, embossing, and stitching patterns. When customizing, be clear about your design requirements and any specific quality standards. Keep in mind that customized products often come with higher MOQs and longer lead times. Discussing your vision early in the process can help streamline production and ensure the final product meets your expectations.
Top 6 Make Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Gold Bark Leather – Leather Tanning Methods
Domain: goldbarkleather.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: The article discusses the process of making leather, highlighting two primary methods: Bark Tanning and Brain Tanning. Bark Tanning uses plant-based tannins to stabilize collagen in animal skins, resulting in stiff, water-resistant leather suitable for items like shoes and bags. Brain Tanning, on the other hand, uses fat and lecithin, often sourced from animal brains, to create soft, supple leathe…
2. Love Your Leather – Leather Production Process
Domain: loveyourleather.ca
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: The process of making leather involves 23 steps, taking an average of 10 working days. Key steps include: 1. Curing hides to prevent deterioration; 2. Soaking to rehydrate and remove excess salt/dirt; 3. Painting to remove wool; 4. Liming to remove hair; 5. Fleshing to remove tissue; 6. De-Liming to neutralize alkali; 7. Bating to relax the pelt; 8. Pickling to prepare for tanning; 9. De-Greasing …
3. WikiHow – Leather Making Process
Domain: wikihow.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Leather is a material made from the skin of an animal using tanning or similar processes. The process of making leather involves several steps: 1. Remove the hide and trim off any fat or flesh. 2. Apply salt to the skin side, fold the hide, and wait 24 hours. 3. Soak the hide in cool water for at least 1 day. 4. Remove the hair from the skin and hang it to dry. 5. Place the hide in a lime bath and…
4. Tandy Leather – Sneaker Starter Pack
Domain: tandyleather.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Tandy Leather – Sneaker Starter Pack, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Steel Horse Leather – Handmade Leather Bags
Domain: steelhorseleather.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Leather Bags, Leather Duffle Bags, Leather Backpacks, Leather Messenger Bags, Leather Tote Bags, Leather Work Bags, Leather Briefcases, Leather Laptop Bags, Leather Satchels, Leather Crossbody Bags, Leather Accessories, Leather Travel Bags, Leather Gifts, Handmade Leather Bags, Vintage Leather Bags, Men’s and Women’s Leather Bags, Various Styles and Sizes including Large, Mini, and Vintage options…
6. Reddit – Leather Making Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Leather Making Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for make leather
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Leather Supply Chain?
In the dynamic landscape of leather production, strategic sourcing stands as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers. By leveraging direct relationships with reputable tanneries and suppliers, buyers can ensure the procurement of high-quality leather that meets both environmental and ethical standards. Understanding the intricacies of the leather-making process—from preparation and tanning to finishing—enables businesses to make informed decisions that align with their product requirements and sustainability goals.

Illustrative image related to make leather
Furthermore, the by-product nature of leather production, primarily sourced from the meat industry, offers an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic materials. This factor is particularly relevant for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where sustainability is increasingly prioritized by consumers.
As we look ahead, the global leather market is poised for growth, driven by demand for premium leather goods across various sectors, including fashion, automotive, and upholstery. Now is the time for B2B buyers to forge strategic partnerships, embrace innovative sourcing practices, and explore new markets. By doing so, they will not only enhance their supply chains but also position themselves as leaders in a competitive industry. Engage with trusted suppliers today and secure your place in the evolving leather market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to make leather
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.