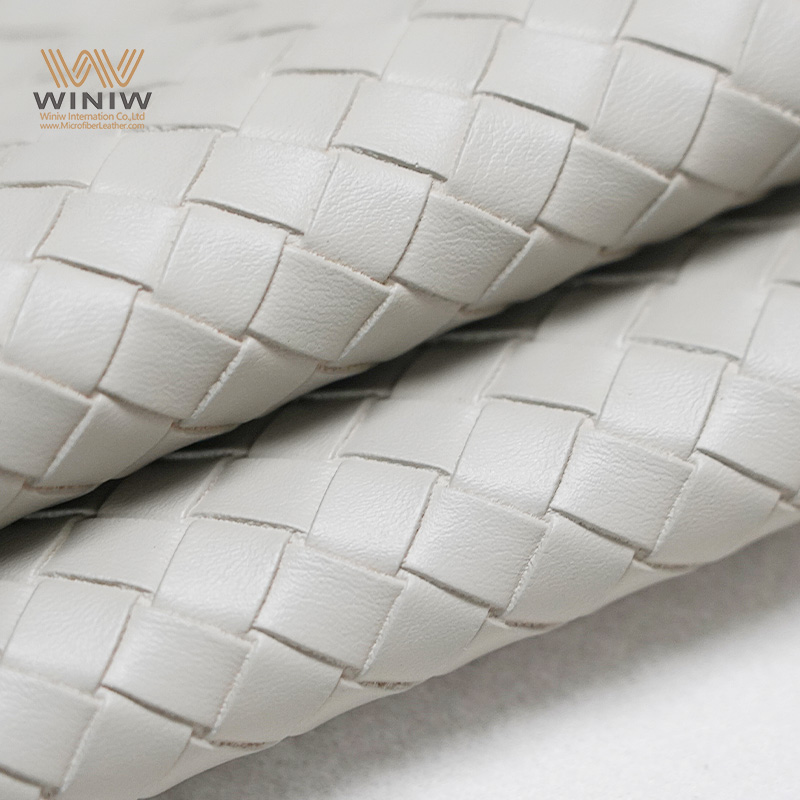
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for recycled leather vs bonded leather
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing sustainable materials like recycled leather and bonded leather presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As the demand for eco-friendly alternatives continues to rise, understanding the nuances between these two materials is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the characteristics, applications, and sourcing strategies of recycled leather and bonded leather, offering insights that cater specifically to the needs of businesses operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Vietnam.
Throughout this guide, we will explore various types of recycled and bonded leather, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and practical applications across different industries. We will also discuss essential criteria for vetting suppliers, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable partners who align with their sustainability goals. Additionally, cost considerations will be analyzed, equipping decision-makers with the knowledge necessary to balance quality and budget constraints effectively.
By providing a well-rounded understanding of recycled leather and bonded leather, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of the global market confidently. Whether your focus is on fashion, automotive, or furniture industries, our insights will help you make strategic choices that enhance your product offerings while promoting environmental responsibility.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Recycled Leather Vs Bonded Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Understanding recycled leather vs bonded leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of recycled leather vs bonded leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘recycled leather vs bonded leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘recycled leather vs bonded leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for recycled leather vs bonded leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing recycled leather vs bonded leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the recycled leather vs bonded leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding recycled leather vs bonded leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Leather | Made from pre-consumer and post-consumer leather waste; often mechanically processed. | Fashion, automotive interiors, furniture | Pros: Sustainable, reduced waste; Cons: Variable quality; may require careful sourcing. |
| Bonded Leather | Composed of leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex; often has a synthetic feel. | Upholstery, accessories, low-cost goods | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Less durable than genuine leather, potential environmental concerns. |
| Vegetable-Tanned Recycled Leather | Uses natural tanning agents; biodegradable and eco-friendly. | Eco-conscious fashion brands, luxury goods | Pros: Sustainable, high-quality finish; Cons: Limited availability, often higher cost. |
| Chrome-Tanned Recycled Leather | Processed with toxic chemicals; can be recycled but with environmental impact. | Mass-market products, casual wear | Pros: Widely available, lower cost; Cons: Environmental concerns, potential health risks. |
| PU Leather (Bonded) | Made with a polyurethane coating over a fabric base; mimics leather appearance. | Fashion, furniture, temporary goods | Pros: Vegan-friendly, easy to clean; Cons: Limited recyclability, less durable than real leather. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Recycled Leather?
Recycled leather is primarily derived from leather waste, either from production processes or discarded consumer products. It is processed through mechanical or chemical methods to create a new material that retains some qualities of genuine leather. This type of leather is increasingly favored in industries focused on sustainability, including fashion and automotive sectors. B2B buyers should consider the sourcing of recycled leather, as its quality can vary significantly based on the initial materials and processing methods used.
How Does Bonded Leather Compare to Recycled Leather?
Bonded leather, on the other hand, is a composite material made from leather scraps that are bonded together with adhesives. While it is more affordable and versatile, it often lacks the durability and luxurious feel of genuine leather. This makes it suitable for mass-market applications such as upholstery and accessories. B2B buyers should evaluate the intended use carefully, as the lower durability may necessitate more frequent replacements, impacting long-term cost-effectiveness.
Why Choose Vegetable-Tanned Recycled Leather for Eco-Conscious Brands?
Vegetable-tanned recycled leather is noted for its environmentally friendly properties, utilizing natural tannins instead of harmful chemicals. This type of leather is biodegradable and appeals to high-end fashion brands looking to enhance their sustainability credentials. While it offers an attractive finish and durability, the higher cost and limited availability can pose challenges for bulk purchases. B2B buyers in this space must weigh the benefits of sustainability against budget constraints.
What Are the Implications of Using Chrome-Tanned Recycled Leather?
Chrome-tanned recycled leather is processed using chemicals that can pose environmental risks. Although it is widely available and cost-effective, B2B buyers should be cautious about the potential health and environmental implications associated with its production and disposal. This type of leather is often found in mass-market products, where cost is a significant factor. Companies should consider the long-term impact of using such materials on their brand image and sustainability goals.
How Does PU Leather Fit into the Landscape of Bonded Leather Options?
PU leather, a type of bonded leather, is crafted with a polyurethane coating that mimics the look of genuine leather while being vegan-friendly. Although it is easy to clean and maintain, its recyclability is limited, which can be a drawback for environmentally conscious buyers. In B2B contexts, PU leather is often used for fashion items and temporary goods, making it important for buyers to assess the lifecycle and disposal implications of their purchases.
Key Industrial Applications of recycled leather vs bonded leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of recycled leather vs bonded leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion and Apparel | Sustainable clothing lines using recycled leather | Enhances brand image as eco-friendly, attracts conscious consumers | Quality of recycled leather, certifications, and sourcing location |
| Automotive | Interior upholstery and trims made from bonded leather | Cost-effective solution with aesthetic appeal | Durability, compliance with safety standards, and sourcing reliability |
| Furniture | Upholstery for sofas and chairs using recycled leather | Unique selling point in sustainability-focused markets | Material quality, fire resistance, and design versatility |
| Accessories | Bags, wallets, and belts using bonded leather | Affordable luxury appeal, broad market reach | Consistency in texture, color options, and ethical sourcing |
| Footwear | Shoe linings and components made from recycled leather | Lightweight, breathable, and sustainable options | Performance characteristics, environmental impact, and supplier certifications |
How is Recycled Leather Used in the Fashion and Apparel Industry?
In the fashion sector, recycled leather is increasingly utilized in sustainable clothing lines. This application allows brands to differentiate themselves in a crowded market by promoting eco-friendliness. International buyers, particularly from Europe and South America, are keen on sourcing recycled leather that meets quality standards and certifications. By using recycled leather, businesses can reduce waste and appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers, enhancing their overall brand image.
What Are the Benefits of Bonded Leather in the Automotive Sector?
Bonded leather finds significant applications in the automotive industry, particularly for interior upholstery and trims. This material offers a cost-effective solution while maintaining an aesthetic appeal that enhances the vehicle’s luxury feel. Buyers from Africa and the Middle East should focus on durability and compliance with safety standards when sourcing bonded leather for automotive applications. The lightweight nature of bonded leather also contributes to fuel efficiency, making it an attractive choice for manufacturers.
How is Recycled Leather Transforming the Furniture Sector?
In the furniture industry, recycled leather is used for upholstery on sofas and chairs, providing a unique selling point in markets that prioritize sustainability. This application not only reduces environmental impact but also caters to consumers looking for stylish yet responsible choices. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East must consider material quality and fire resistance when sourcing recycled leather for furniture. The versatility in design options allows businesses to cater to diverse consumer tastes.
Why Choose Bonded Leather for Accessories?
Bonded leather is widely used in the production of accessories such as bags, wallets, and belts. This application offers an affordable luxury appeal, making it accessible to a broader market segment. International B2B buyers should prioritize consistency in texture and color options when sourcing bonded leather for accessories, as these factors significantly influence consumer perception. Ethical sourcing practices are also critical to align with growing consumer demands for responsible production.
What Role Does Recycled Leather Play in Footwear?
Recycled leather is increasingly being utilized in the footwear industry, particularly for shoe linings and components. This material is lightweight and breathable, making it an ideal choice for comfortable footwear. Buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should assess the performance characteristics of recycled leather to ensure it meets the demands of the footwear market. Sourcing from suppliers with environmental certifications can further enhance the sustainability profile of footwear brands.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘recycled leather vs bonded leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Differences in Leather Types
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with differentiating between recycled leather and bonded leather in terms of quality and durability. When sourcing materials for high-end products, such as furniture or luxury goods, the risk of choosing an inferior leather type can lead to dissatisfaction among clients or consumers. This concern is particularly pronounced in markets that emphasize sustainability, as buyers want to ensure that their materials not only meet aesthetic standards but also perform well over time.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, B2B buyers should establish a rigorous vetting process for suppliers. Start by requesting detailed specifications and certifications regarding the leather’s composition and manufacturing processes. Look for suppliers who can provide samples for physical testing, ensuring that the recycled leather meets your quality standards. Additionally, consider leveraging industry certifications that validate the environmental impact and quality of the leather products. By prioritizing transparency and quality assurance, buyers can confidently choose materials that align with their brand values and customer expectations.
Scenario 2: Understanding Environmental Impact and Supply Chain Transparency
The Problem: Buyers in regions such as Africa and South America are increasingly pressured to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability, yet they find it challenging to understand the environmental implications of recycled versus bonded leather. The confusion often stems from a lack of clear information regarding the sourcing, processing, and end-of-life disposal of these materials, which can hinder responsible purchasing decisions.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should engage directly with manufacturers and request a complete lifecycle assessment (LCA) of the leather products. An LCA will provide insights into the environmental impact from sourcing to disposal, helping you make informed decisions. Additionally, prioritize suppliers who practice transparency in their operations and can provide documentation on their recycling processes and materials used. Consider forming partnerships with brands that have a strong sustainability focus, as this not only enhances credibility but also aligns your products with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly options. Leveraging sustainability reports and third-party audits can further bolster your commitment to environmental responsibility.
Scenario 3: Sourcing Challenges in Emerging Markets
The Problem: In emerging markets, the availability of high-quality recycled leather may be limited, leading buyers to default to bonded leather, which is often more readily accessible but not as sustainable. This reliance can compromise the integrity of product offerings, particularly as consumers become more discerning about the origins and sustainability of the materials they purchase.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, buyers should consider diversifying their supplier base by exploring international partnerships that specialize in recycled leather. Utilize platforms that connect businesses with sustainable material suppliers, and attend trade shows focused on eco-friendly products. Establishing relationships with manufacturers who prioritize innovative recycling methods can also yield better quality materials. Additionally, consider investing in local initiatives that promote the recycling of leather within your region, which can help improve availability and reduce costs over time. By actively seeking out and fostering relationships with dedicated suppliers, businesses can enhance their product lines with sustainable leather options while supporting local economies.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for recycled leather vs bonded leather
When evaluating materials for recycled leather and bonded leather, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance characteristics, manufacturing complexities, and compliance with regional standards. Here, we analyze key materials used in these leather types, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for specific markets.
What Are the Key Properties of Recycled Leather?
Recycled leather is primarily made from post-consumer or post-industrial leather waste, which is processed into a usable material. This material retains some of the original leather’s properties, such as durability and aesthetic appeal. The production process often involves mechanical recycling methods, which can impact the material’s consistency and quality.
- Key Properties: Recycled leather typically exhibits moderate temperature resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 70°C. It is less resistant to moisture compared to bonded leather due to its fibrous nature.
- Pros: Environmentally friendly and sustainable, recycled leather offers good durability and can be produced at a lower cost than genuine leather.
- Cons: Variability in quality can be a concern, and the mechanical recycling process may result in lower tensile strength compared to original leather.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for fashion accessories, upholstery, and automotive interiors, recycled leather is suitable for applications where aesthetics are crucial but may not perform well under extreme conditions.
How Does Bonded Leather Compare in Terms of Performance?
Bonded leather is created by combining leather scraps with a polymer backing, resulting in a composite material. This process enhances the usability of leather waste while creating a product that mimics the look of genuine leather.
- Key Properties: Bonded leather typically has a higher moisture resistance and can endure temperatures up to 90°C. Its composite nature allows for greater flexibility in design and application.
- Pros: Cost-effective and widely available, bonded leather can be produced in various textures and colors, making it appealing for diverse applications.
- Cons: The durability of bonded leather is generally lower than that of recycled leather, particularly in high-wear environments. It may also be less environmentally friendly due to the use of synthetic materials.
- Impact on Application: Commonly used in furniture, bookbinding, and fashion accessories, bonded leather is suitable for applications requiring a balance of aesthetics and functionality.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Selecting Materials?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various compliance and standardization challenges. For example, adherence to regional standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), DIN (German Institute for Standardization), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) is essential for ensuring product quality and safety.
- Specific Considerations: Buyers should be aware of the environmental regulations in their markets, as recycled leather may qualify for sustainability certifications, which can enhance brand reputation. Additionally, understanding local consumer preferences can guide material choices, as regions may favor eco-friendly options or traditional leather aesthetics.
Summary Table of Material Comparisons
| Material | Typical Use Case for recycled leather vs bonded leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Leather | Fashion accessories, upholstery, automotive interiors | Environmentally friendly and sustainable | Variability in quality and lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Bonded Leather | Furniture, bookbinding, fashion accessories | Cost-effective and versatile design | Lower durability in high-wear environments | Low |
In conclusion, both recycled leather and bonded leather present unique advantages and challenges for B2B buyers. Understanding the properties, applications, and market considerations will enable informed decisions that align with sustainability goals and consumer demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for recycled leather vs bonded leather
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather?
The manufacturing processes for recycled leather and bonded leather differ significantly due to the materials and techniques involved. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers seeking high-quality products that meet sustainability standards.
How Is Recycled Leather Manufactured?
-
Material Preparation:
– Collection: Recycled leather is primarily sourced from post-industrial and post-consumer waste. This includes scraps from manufacturing processes and discarded leather goods.
– Sorting and Cleaning: The collected leather is sorted based on type, quality, and condition. It undergoes a thorough cleaning process to remove contaminants and impurities. -
Forming:
– Mechanical Recycling: The cleaned leather is mechanically shredded into fine fibers. This process allows for the creation of a uniform material that can be reconstituted.
– Chemical Recycling: In some cases, leather may be subjected to chemical processes to break it down at the molecular level, extracting useful components for creating new leather products. -
Assembly:
– Reconstitution: The shredded leather fibers are mixed with adhesives and other binders to form sheets or panels. This step is crucial for ensuring the durability and quality of the final product.
– Molding and Cutting: The reconstituted leather is then molded or cut into the desired shapes for various applications, from fashion items to automotive interiors. -
Finishing:
– Surface Treatment: The final product may undergo various treatments such as dyeing, coating, or embossing to enhance aesthetics and durability. Eco-friendly finishes are often preferred in sustainable manufacturing practices.
What Is the Manufacturing Process for Bonded Leather?
-
Material Preparation:
– Sourcing: Bonded leather is primarily made from leather scraps and fibers, often sourced from tanneries and furniture manufacturers. The scraps are collected and sorted for quality.
– Shredding: Similar to recycled leather, the leather scraps are mechanically shredded into smaller pieces. -
Forming:
– Bonding: The shredded leather is mixed with synthetic materials, typically polyurethane (PU) or other adhesives. This blend is crucial for achieving the desired texture and appearance.
– Sheet Formation: The mixture is then compressed and formed into sheets, which can be further processed based on the intended use. -
Assembly:
– Cutting and Stitching: Once the sheets are formed, they are cut into specific patterns and stitched together to create finished products, such as bags, furniture, or upholstery. -
Finishing:
– Coating: Bonded leather often undergoes a surface coating process to enhance durability and resistance to wear. This may include applying a protective layer to improve the overall longevity of the product.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Recycled and Bonded Leather?
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring that both recycled leather and bonded leather meet international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Apply to Recycled and Bonded Leather?
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems. It ensures that manufacturers have processes in place to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for industries that require specific performance criteria, such as automotive or aviation sectors.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. For recycled leather, this may include assessing the quality of the sourced scraps.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to monitor the quality of the production. This includes verifying the consistency of the bonding process in bonded leather manufacturing.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are packaged and shipped, a final inspection is conducted to ensure they meet all quality specifications and standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
- Physical Testing: This includes tensile strength tests, abrasion resistance tests, and colorfastness tests. These ensure that the leather products can withstand regular use.
- Chemical Testing: For bonded leather, chemical analyses may be performed to ensure that the materials used are non-toxic and comply with environmental regulations.
- Durability Testing: Products are often subjected to wear-and-tear simulations to assess their longevity and performance under various conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This includes reviewing their adherence to international standards and their own internal QC measures.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand the quality metrics that are being tracked and the results of any testing conducted.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased view of the supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly important when sourcing from regions with less established quality assurance frameworks.
What QC Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of varying quality standards and practices across different markets.
- Local Regulations: Understanding local regulations regarding materials and safety standards is essential. For instance, European buyers may require stricter compliance with REACH regulations compared to other regions.
- Cultural Differences: Different markets may have varying expectations regarding product quality, sustainability practices, and ethical sourcing. Engaging in open communication with suppliers can help bridge these gaps.
- Sustainability Credentials: As sustainability becomes increasingly important, buyers should inquire about the environmental impact of the manufacturing processes and the certifications that suppliers hold.
By paying close attention to the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for both recycled leather and bonded leather, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals and sustainability commitments.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘recycled leather vs bonded leather’
To assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions when sourcing recycled leather versus bonded leather, this practical sourcing guide outlines key steps to consider throughout the procurement process. Understanding the nuances between these materials can significantly impact product quality, sustainability, and overall brand reputation.
Step 1: Identify Your Product Requirements
Before beginning your sourcing journey, clearly define the specifications for the leather products you intend to procure. Consider factors such as durability, intended use, aesthetic qualities, and sustainability goals. This clarity will help you narrow down which type of leather—recycled or bonded—best meets your needs.
Step 2: Research Material Properties
Understanding the properties of both recycled leather and bonded leather is crucial. Recycled leather is typically made from repurposed leather scraps, offering a more sustainable option with varying degrees of durability. In contrast, bonded leather combines leather fibers with adhesives, which may result in a less durable product. Evaluate the performance characteristics relevant to your industry to ensure the selected material aligns with your product’s requirements.
Step 3: Assess Environmental Impact
Sustainability is a growing concern for consumers and businesses alike. When sourcing, consider the environmental impact of each material. Recycled leather generally has a lower carbon footprint due to its repurposed nature, while bonded leather may involve more energy-intensive production processes. Review suppliers’ sustainability certifications and practices to ensure they align with your company’s environmental goals.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards. Look for certifications related to sustainability, quality assurance, and ethical sourcing practices. This step is essential to ensure that the products you receive are not only of high quality but also ethically produced.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before making bulk purchases, always request samples of both recycled and bonded leather products. Testing samples will allow you to evaluate the texture, durability, and overall quality firsthand. Ensure that the samples meet your specifications and perform well under typical use conditions.
Step 6: Examine Cost-Effectiveness
Analyze the cost implications of sourcing recycled leather versus bonded leather. While recycled leather may offer long-term savings due to its durability and sustainability benefits, bonded leather can sometimes be more affordable upfront. Calculate the total cost of ownership, including potential maintenance and replacement costs, to make a well-informed decision.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship with Suppliers
Building a strong relationship with your chosen supplier can lead to better pricing, product availability, and support. Engage in open communication about your needs and expectations, and consider establishing agreements that foster collaboration. A reliable supplier will be essential in ensuring consistent quality and responsiveness to market demands.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing recycled leather versus bonded leather, ensuring they make informed choices that align with their business objectives and sustainability initiatives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for recycled leather vs bonded leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Recycled Leather vs. Bonded Leather?
When sourcing materials like recycled leather and bonded leather, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: Recycled leather typically involves higher raw material costs due to the processes needed to recycle and prepare the leather. In contrast, bonded leather, made from leather scraps bonded with synthetic materials, tends to be less expensive. The environmental impact and sustainability of recycled leather can justify its higher cost for brands focused on eco-friendly practices.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly. Recycled leather processing may require skilled labor for quality control and handling, which can drive up costs. Bonded leather production often involves simpler manufacturing processes, potentially leading to lower labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: The overhead for recycled leather production can be higher due to specialized equipment and facilities needed for processing. Bonded leather facilities may be more standardized and efficient, leading to lower overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Investment in tooling for recycled leather can be substantial, especially if specialized machinery is required for different recycling methods. In contrast, bonded leather may require less investment in custom tooling, making it a more cost-effective option for manufacturers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Both types require rigorous QC, but the methods differ. Recycled leather may necessitate additional QC measures to ensure consistency and quality due to its varied sourcing. Bonded leather, having a more uniform composition, might incur lower QC costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation and logistics costs can impact both materials. The sourcing of recycled leather may involve longer transportation routes to collect waste materials, while bonded leather could be produced more locally, reducing logistics costs.
-
Margin: The profit margin for suppliers of recycled leather is generally higher due to the perceived value and sustainability aspect. Bonded leather suppliers may operate on thinner margins due to competitive pricing pressures.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Recycled vs. Bonded Leather?
Several factors can influence the pricing of recycled and bonded leather, making it essential for international B2B buyers to consider these nuances.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders usually yield better pricing due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer significant discounts for minimum order quantities (MOQs), which can be crucial for budgeting.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or unique specifications can drive up costs for both materials. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The type of materials used and any relevant quality certifications can impact pricing. Recycled leather with eco-certifications may command a premium, while bonded leather might have fewer certification costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality assurance but at a higher cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. Costs associated with shipping, insurance, and tariffs can vary greatly depending on the agreed terms, impacting the total cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs Effectively?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating the complexities of pricing is critical.
-
Negotiation: Approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your needs and the market. Leverage bulk purchasing to negotiate better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just upfront pricing. Consider long-term sustainability benefits of recycled leather against the initial lower cost of bonded leather.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Familiarize yourself with local market conditions and the economic landscape of your suppliers. Currency fluctuations and geopolitical factors can affect pricing significantly.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: It’s important to note that prices can vary widely based on specific conditions, including supplier relationships, market demand, and production capabilities. Always request updated quotes to ensure accurate budgeting.
By understanding these key components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing recycled versus bonded leather, ultimately aligning their procurement strategies with their business goals.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing recycled leather vs bonded leather With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather: What Are Your Options?
In the quest for sustainable materials, B2B buyers are increasingly evaluating the merits of recycled leather and bonded leather against other viable alternatives. Understanding these options can help companies make informed decisions that align with both their environmental goals and product requirements. Below, we provide a comparative analysis of recycled leather and bonded leather against two noteworthy alternatives: synthetic leather and natural leather.
| Comparison Aspect | Recycled Leather Vs Bonded Leather | Couro sintético | Natural Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good durability, but varies by source | High durability, water-resistant | Excellent durability, breathability |
| Cost | Moderate, dependent on recycling process | Generally lower than natural leather | Higher due to sourcing and processing |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized recycling facilities | Easy to produce in bulk | Involves complex sourcing and processing |
| Maintenance | Low, but can vary by product type | Low, easy to clean | Moderate, requires conditioning |
| Best Use Case | Fashion, accessories, automotive interiors | Fashion, upholstery, bags | High-end fashion, furniture, luxury goods |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Synthetic Leather
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers a compelling alternative for many applications. Its performance is generally superior in terms of water resistance and ease of cleaning, making it suitable for various industries, including fashion and automotive. However, it is less environmentally friendly due to its petroleum-based origins and challenges in recycling. While the cost is typically lower than natural leather, the long-term environmental implications may deter eco-conscious buyers.
2. Natural Leather
Natural leather is revered for its durability, breathability, and luxurious feel, making it the preferred choice for high-end products. While it boasts excellent performance characteristics, its sourcing and processing can significantly drive up costs. Additionally, the environmental impact of traditional tanning processes raises concerns among sustainability-minded companies. Natural leather is best suited for luxury markets, where quality and brand prestige are paramount, but buyers must weigh the trade-offs in terms of cost and ecological footprint.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When considering recycled leather, bonded leather, or alternative materials, B2B buyers must assess their specific needs regarding performance, cost, sustainability, and ease of implementation. For companies focused on eco-friendliness, recycled leather presents a promising solution, albeit with varying quality depending on the source. On the other hand, those seeking durability and low maintenance might find synthetic leather more appealing. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on a balance between product requirements, market positioning, and corporate sustainability goals. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that not only meet their operational needs but also align with broader environmental objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for recycled leather vs bonded leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather?
When comparing recycled leather and bonded leather, several critical specifications must be understood to facilitate informed purchasing decisions in the B2B landscape. Here are some essential technical properties:
1. Material Composition
- Recycled Leather: Made from repurposed leather scraps, blended with adhesives and often other fibers to create a new material. This composition contributes to its eco-friendly appeal.
- Bonded Leather: Comprised of leather scraps that are bonded together with polyurethane or latex. The proportion of genuine leather in bonded leather can vary, impacting its overall quality and feel.
B2B Importance: Understanding material composition is crucial for buyers focused on sustainability and quality. Businesses looking to enhance their green credentials may prefer recycled leather, while those seeking lower-cost alternatives may opt for bonded leather.
2. Durability and Wear Resistance
- Recycled Leather: Generally offers good durability, although it may not match the longevity of full-grain leather. Its performance can depend on the recycling process and the quality of the original leather used.
- Bonded Leather: Typically less durable than recycled leather due to its synthetic bonding agents. It can show wear and tear more quickly, especially in high-use applications.
B2B Importance: Buyers in industries such as furniture and automotive manufacturing must consider the expected lifespan and durability of the materials to minimize replacement costs and ensure customer satisfaction.
3. Environmental Impact
- Recycled Leather: Provides an environmentally friendly option by reducing waste in the leather industry and minimizing the demand for new raw materials.
- Bonded Leather: While it utilizes waste material, the synthetic adhesives used can have a negative environmental impact during production and disposal.
B2B Importance: Companies committed to sustainability will find recycled leather aligns with their corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals. Understanding the environmental impact helps businesses build a positive brand image.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
- Recycled Leather: Often priced higher than bonded leather due to the recycling process and quality control, but can still be competitive compared to high-quality natural leather.
- Bonded Leather: Generally more affordable, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers.
B2B Importance: Price sensitivity varies by industry, and understanding the cost implications helps buyers align their product offerings with their target market’s expectations.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in Recycled and Bonded Leather Transactions?
Navigating the landscape of recycled and bonded leather requires familiarity with industry terminology. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or products that are used in another company’s final product. In the leather industry, OEMs may produce goods for fashion brands using either recycled or bonded leather.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to ensure they meet production requirements without overcommitting.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. An RFQ is critical for comparing costs between recycled and bonded leather options.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
A set of globally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps mitigate risks in cross-border transactions.
5. Tolerance
Refers to the allowable limits of variation in a material’s dimensions or properties. In the context of leather, understanding tolerance is vital for ensuring consistency and quality in manufacturing.
6. Certification
Refers to the official recognition that a product meets certain standards, such as sustainability or quality certifications. Certifications can enhance product credibility and appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
B2B Importance: Mastering these terms enables buyers to communicate effectively with suppliers, negotiate better deals, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the recycled leather vs bonded leather Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Impacting Recycled Leather vs. Bonded Leather?
The global leather industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by sustainability imperatives and changing consumer preferences. With approximately 8 million tons of leather waste generated annually, the demand for recycled leather is growing, particularly among environmentally-conscious consumers and businesses. Key trends include the increasing adoption of mechanical and chemical recycling processes, which are enhancing the quality and availability of recycled leather products. B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of the differences in recycling infrastructure across these areas. For instance, Europe leads in recycling facilities, while developing countries often rely on informal upcycling methods, presenting unique sourcing opportunities and challenges.
Emerging technologies in the recycling process are also reshaping the market. Innovations such as enzyme-assisted recycling and bio-recycling methods are gaining traction, promising to improve the quality of recycled materials. Furthermore, the rise of digital platforms for sourcing recycled materials allows international buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and products, streamlining procurement processes. As companies increasingly incorporate sustainability into their business models, understanding the dynamics of recycled versus bonded leather becomes essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Recycled Leather vs. Bonded Leather?
Sustainability is no longer just a trend; it is a fundamental aspect of B2B sourcing strategies. The environmental impact of leather production and disposal has led to a heightened focus on ethical sourcing practices. Recycled leather presents a more sustainable option, as it reduces waste and minimizes the carbon footprint associated with traditional leather production. In contrast, bonded leather, often made from scraps and synthetic materials, raises concerns regarding its long-term environmental effects, particularly as it is less recyclable and may contain harmful chemicals.
For B2B buyers, understanding certifications and standards for recycled leather is crucial. Look for materials that carry ‘green’ certifications, such as Global Recycled Standard (GRS) or OEKO-TEX, which indicate responsible sourcing practices. By prioritizing suppliers who adhere to these standards, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing consumer demand for ethically sourced products. This shift towards sustainable materials is not just beneficial for the environment; it can also drive customer loyalty and open new market opportunities.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Recycled and Bonded Leather?
The evolution of leather products has its roots in ancient practices, but the modern definitions of recycled and bonded leather emerged in the late 20th century. As environmental concerns rose in the 1980s and 1990s, the leather industry began to explore recycling methods as a solution to mounting waste. Recycled leather gained popularity as manufacturers sought to repurpose leather scraps and waste into new products, promoting sustainability.
Conversely, bonded leather was developed as a cost-effective alternative, combining leather fibers with synthetic materials. While initially marketed as a premium option, its composition has led to mixed perceptions regarding quality and sustainability. Today, the market is increasingly differentiating between these two materials, with recycled leather gaining favor among businesses committed to sustainable practices. Understanding this historical context can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of recycled leather vs bonded leather
-
1. How do I determine whether to source recycled leather or bonded leather for my products?
To make an informed decision between recycled leather and bonded leather, consider factors such as sustainability goals, product application, and target market preferences. Recycled leather is often regarded as more environmentally friendly, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and businesses. In contrast, bonded leather, while typically less expensive, may not offer the same durability or sustainability credentials. Evaluate your brand’s positioning and customer expectations to guide your choice. -
2. What are the key differences in quality between recycled leather and bonded leather?
Recycled leather generally boasts higher quality due to its composition, which includes genuine leather fibers, enhancing its durability and feel. In contrast, bonded leather consists of shredded leather scraps bonded with synthetic materials, leading to a less robust product that may wear out faster. For applications requiring longevity and premium aesthetics, recycled leather is the superior choice, while bonded leather may suffice for budget-sensitive projects. -
3. What customization options are available for recycled leather and bonded leather?
Both recycled and bonded leather can be customized in terms of color, texture, and finish. However, recycled leather may offer greater versatility for high-end designs due to its authentic leather characteristics. When sourcing, inquire about the supplier’s ability to provide samples and the range of customization options, including embossing or printing, to align with your brand’s requirements. -
4. What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing recycled leather and bonded leather?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and material type. Recycled leather suppliers may have higher MOQs due to the complexity of sourcing and processing materials. Bonded leather suppliers often have lower MOQs, making it more accessible for smaller businesses. Always clarify MOQs upfront to avoid complications in your procurement process. -
5. How can I ensure the quality of recycled leather or bonded leather products before purchasing?
Implement a rigorous supplier vetting process, including requesting samples to assess material quality, texture, and durability. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance protocols and certifications related to sustainable practices. Engaging in third-party audits or inspections can further validate the supplier’s claims and ensure the products meet your specifications. -
6. What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of recycled and bonded leather?
Payment terms can differ widely based on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness. Typically, you may encounter options such as upfront payment, net 30-60 days, or letters of credit for larger orders. It’s advisable to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow while ensuring that the supplier remains secure in their transaction. -
7. What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing recycled or bonded leather?
When importing, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your region. Recycled leather may require special documentation to verify its material composition for compliance with environmental standards. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in handling leather products can streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. -
8. How do sustainability practices in the production of recycled leather compare to those of bonded leather?
Recycled leather production generally emphasizes sustainability by repurposing waste from the leather industry, thereby reducing landfill contributions. In contrast, bonded leather production involves synthetic materials, which may not align with eco-friendly practices. When sourcing, prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable methods and can provide transparency regarding their sourcing and production processes.
Top 3 Recycled Leather Vs Bonded Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Gionar – Recycled Leather Solutions
Domain: gionar.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Recycled leather is a sustainable alternative to traditional leather, made from repurposed leather waste. The global leather industry produces approximately 8 million tons of waste annually, with only about 20% currently being recycled. Recycled leather differs from bonded leather in its composition and production process. The recycling process involves collecting and sorting leather, crushing it …
2. Manuel Dreesmann – Bonded Leather Insights
Domain: manuel-dreesmann.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: This company, Manuel Dreesmann – Bonded Leather Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. LeatherNeo – Bonded Leather
Domain: leatherneo.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Bonded leather is a composite leather made from ground leather fibers glued with a polyurethane combination and attached to a paper or fiber backing. It is a cheaper alternative to real leather, maintaining a similar look and feel. The composition can range from 10% to 90% real leather, with the surface often embossed to resemble genuine leather. Common applications include upholstery, bookbinding…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for recycled leather vs bonded leather
In evaluating the strategic sourcing of recycled leather versus bonded leather, it becomes clear that both materials offer unique advantages and challenges. Recycled leather stands out for its sustainability, utilizing waste from the leather industry and appealing to eco-conscious consumers. This not only reduces environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation. On the other hand, bonded leather, while often more affordable and widely available, may not align as closely with the growing demand for sustainable materials.
B2B buyers should consider the long-term value of integrating recycled leather into their product lines. As regulations tighten and consumer preferences shift towards sustainable options, sourcing recycled leather can provide a competitive edge in the marketplace. Furthermore, understanding the complexities of leather recycling methods and the challenges associated with bonded leather can inform better purchasing decisions.
Looking ahead, the demand for sustainable materials will only increase, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing strategic sourcing of recycled leather, international buyers can not only meet market demands but also contribute positively to the environment. Embrace this opportunity to lead in sustainable sourcing and differentiate your offerings in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.