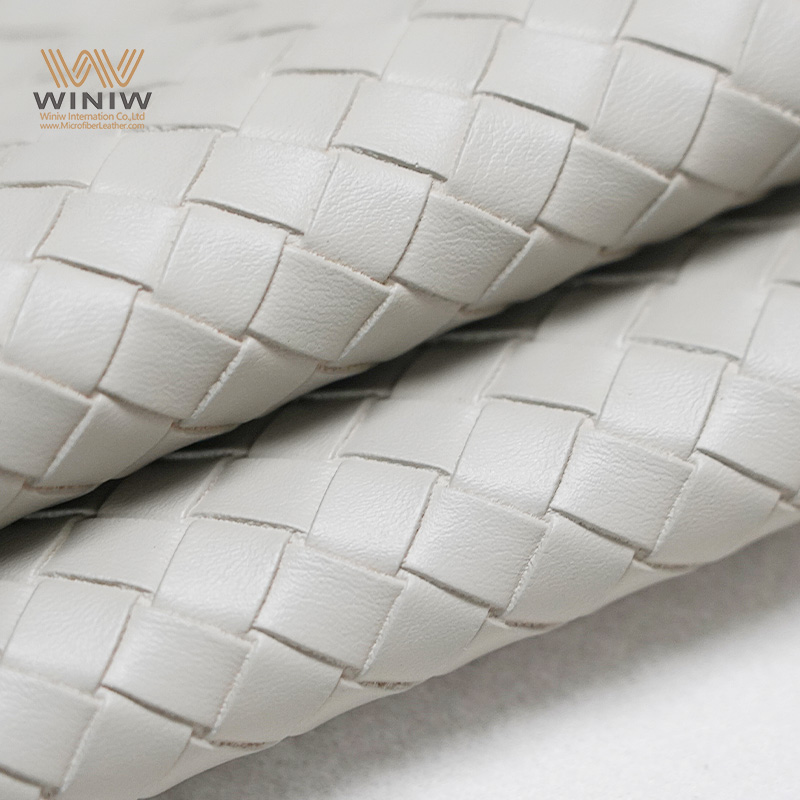
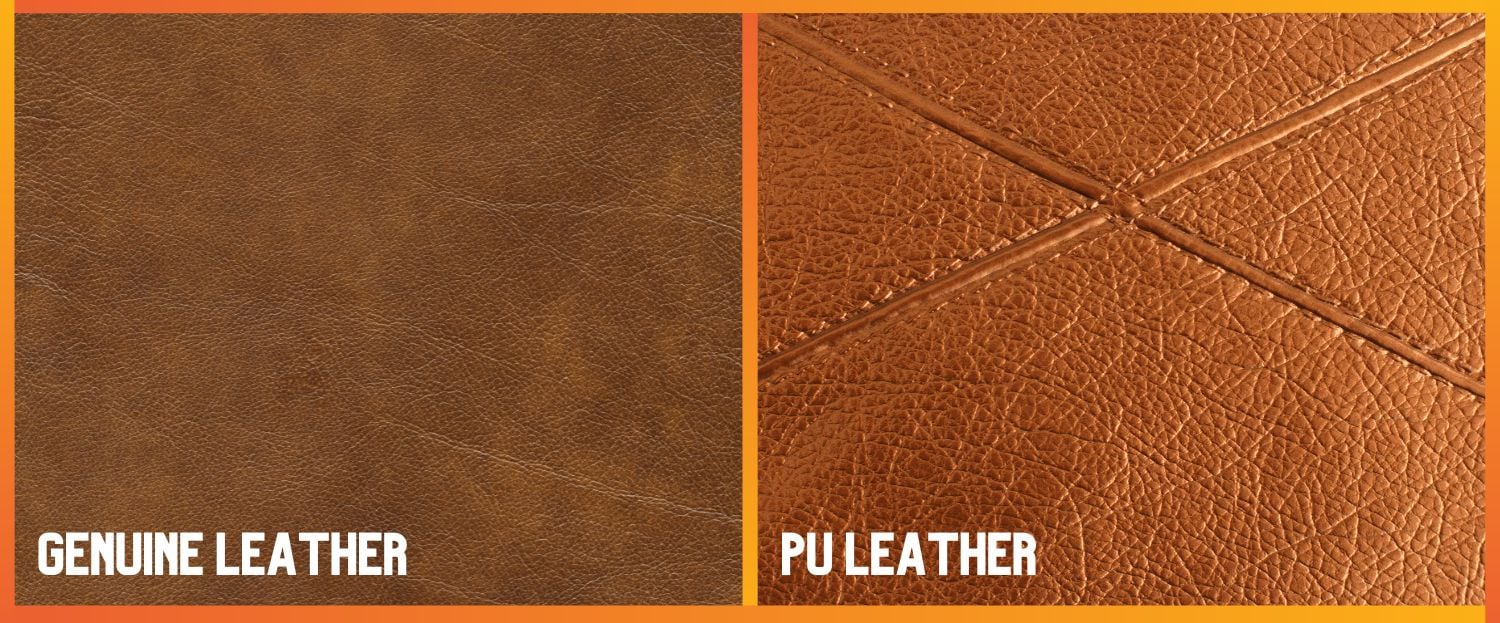
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pu leather defined
In the fast-evolving landscape of materials sourcing, understanding the nuances of PU leather is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their product offerings. As you explore options for integrating PU leather into your supply chain—whether for fashion, furniture, or automotive applications—navigating the complexities of this synthetic alternative to genuine leather can present challenges. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of PU leather, their applications across different industries, and critical factors for supplier vetting, including sustainability practices and cost considerations.
The guide is designed to empower B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Vietnam and Nigeria, enabling you to make informed purchasing decisions. By examining the characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks of PU leather, you will gain insights into how to effectively source this material while aligning with your business values and customer expectations. Furthermore, understanding the lifecycle and environmental impact of PU leather will equip you with the knowledge necessary to negotiate better terms and foster sustainable practices within your supply chain. Together, we will navigate the global market for PU leather, ensuring your investments yield long-term value and quality.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Pu Leather Defined Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pu leather defined
- Understanding pu leather defined Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of pu leather defined
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pu leather defined’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for pu leather defined
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pu leather defined
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pu leather defined’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pu leather defined Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pu leather defined With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pu leather defined
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pu leather defined Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pu leather defined
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pu leather defined
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding pu leather defined Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% PU Leather | Fully synthetic, vegan-friendly, available in various colors | Upholstery, fashion accessories | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to clean; Cons: Less durable, can crack over time. |
| Bicast Leather | Genuine leather base with a PU coating, offers a leather-like look | Furniture, automotive interiors | Pros: More affordable than full leather, retains some leather properties; Cons: Less breathable, can peel. |
| Split Leather | Made from the fibrous parts of genuine leather, coated with PU | Budget furniture, bags | Pros: Economical, retains some leather texture; Cons: Not as durable, prone to wear. |
| Couro vegan | Made entirely from synthetic materials, often marketed as eco-friendly | Eco-conscious brands, fashion | Pros: Animal-friendly, diverse designs; Cons: Environmental concerns due to plastic content. |
| Corrected Grain Leather | Leather that has been treated to remove imperfections and coated with PU | Upholstered goods, fashion items | Pros: Uniform appearance, cost-effective; Cons: Lacks the authenticity of natural leather, less durable. |
What Are the Characteristics of 100% PU Leather?
100% PU leather is a fully synthetic material, designed to mimic the appearance of genuine leather. It is often used in upholstery and fashion accessories due to its cost-effectiveness and availability in a wide range of colors. For B2B buyers, this type of PU leather is suitable for projects requiring a budget-friendly alternative without the ethical concerns associated with animal products. However, its durability is limited, making it essential to consider the intended use and lifespan of the products being manufactured.
How Does Bicast Leather Compare to Other Types?
Bicast leather combines genuine leather with a polyurethane coating, providing a more affordable option while maintaining some of the aesthetic qualities of real leather. It is commonly used in furniture and automotive interiors. B2B buyers should note that while bicast leather offers a good balance between price and appearance, it may not be as breathable or long-lasting as full-grain leather. Understanding the end-use application is crucial, as this material may not withstand heavy wear.
What Is Split Leather and Its Applications?
Split leather utilizes the fibrous remains of genuine leather, coated with a layer of PU to enhance its durability and appearance. This type is often seen in budget furniture and bags, appealing to cost-sensitive buyers. While it retains some leather characteristics, B2B purchasers should be aware that split leather may not endure the same level of wear and tear as higher-quality leather options. Evaluating the target market’s expectations for durability is vital when considering split leather.
What Are the Benefits of Vegan Leather for Eco-Conscious Brands?
Vegan leather is crafted from synthetic materials, marketed as an animal-friendly alternative. It is increasingly popular among eco-conscious brands and fashion lines seeking to minimize their environmental footprint. While B2B buyers appreciate the ethical aspect of vegan leather, they must also weigh the potential environmental impact of its plastic content. When sourcing vegan leather, it’s important to consider the supplier’s sustainability practices and the material’s overall lifecycle.
How Does Corrected Grain Leather Fit into the Market?
Corrected grain leather undergoes treatment to remove natural imperfections and is typically coated with PU for added durability. This type of leather is often utilized in upholstered goods and fashion items. For B2B buyers, corrected grain leather presents a cost-effective solution with a uniform appearance, though it lacks the authenticity of natural leather. Understanding the target demographic’s preferences for quality and authenticity will guide purchasing decisions effectively.
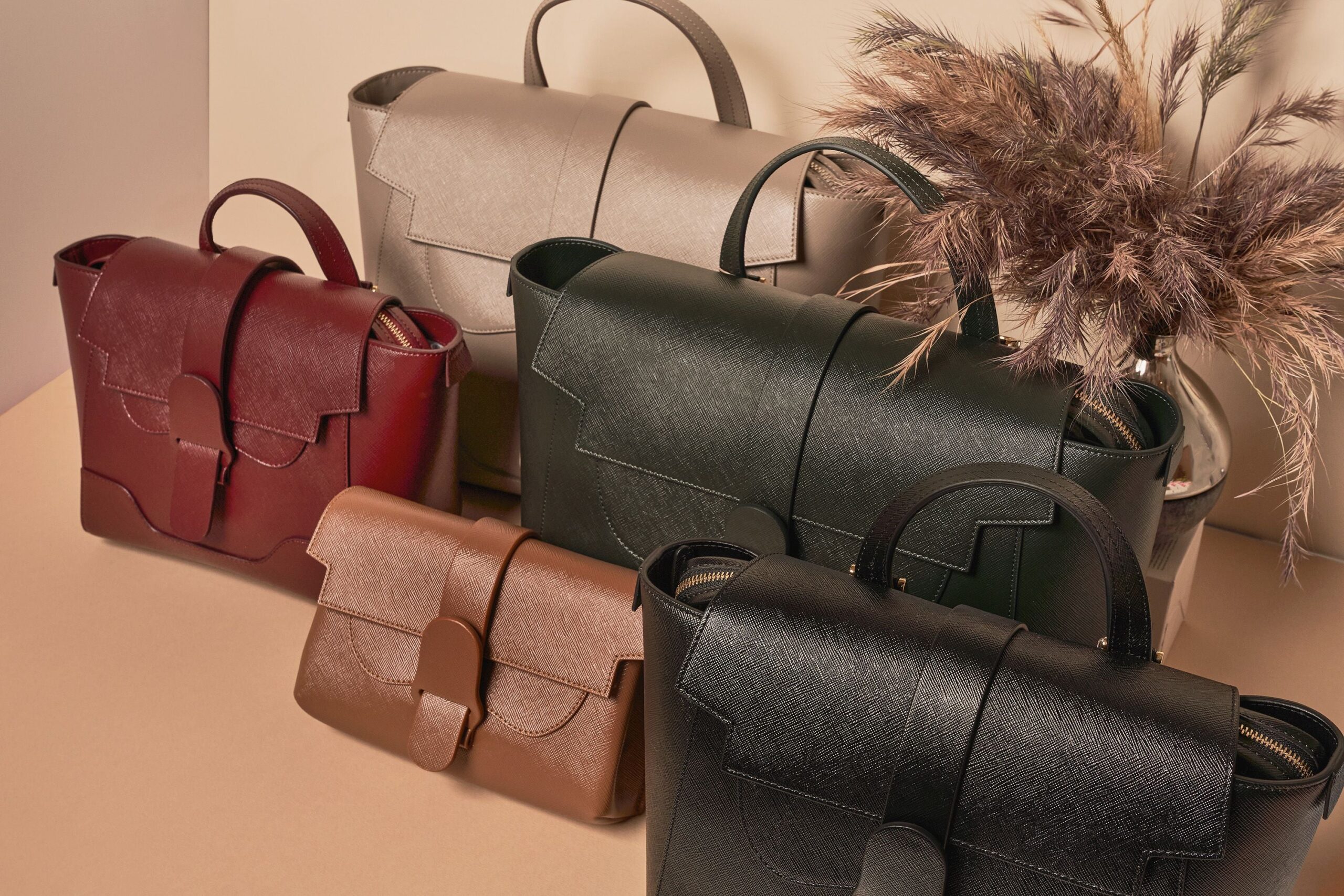
Key Industrial Applications of pu leather defined
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pu leather defined | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Upholstery for office and home furniture | Cost-effective, easy to maintain, and versatile | Ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards; check for durability ratings. |
| Fashion and Accessories | Handbags, wallets, and belts | Affordable alternative to genuine leather; wide variety of styles and colors | Verify the quality of materials; consider sustainability certifications. |
| Automotive | Interior seating and trim | Lightweight, water-resistant, and customizable | Assess material durability; ensure compliance with automotive industry standards. |
| Footwear | Shoes and boots | Lower production costs and diverse design options | Check for breathability and comfort; ensure adherence to safety regulations. |
| Home Décor | Decorative items and wall coverings | Aesthetic appeal at a lower cost; easy to clean | Look for eco-friendly options; assess colorfastness and texture quality. |
How is PU Leather Used in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing sector, PU leather is predominantly used for upholstery in both office and home environments. Its affordability makes it an attractive option for businesses looking to furnish spaces without compromising on style. PU leather solves the problem of high maintenance associated with real leather, as it is easy to clean and resistant to water. For international buyers, especially in Africa and South America, sourcing PU leather that meets safety and environmental standards is crucial, as regulations can vary significantly across regions.
What Role Does PU Leather Play in Fashion and Accessories?
In the fashion industry, PU leather is widely utilized for producing handbags, wallets, and belts. Its versatility allows designers to create a wide range of styles and colors, appealing to diverse consumer preferences. The primary advantage for businesses is the lower production cost compared to genuine leather, making it easier to offer competitive pricing. B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider the quality of PU leather and seek suppliers that provide sustainability certifications to meet growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Why is PU Leather Important in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry employs PU leather for interior seating and trim, given its lightweight nature and water resistance. This synthetic material allows for customization in design and color, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of vehicles. The key value for businesses lies in its durability and ease of maintenance, which can lead to higher customer satisfaction. Buyers from various regions, including Vietnam and Nigeria, must ensure that the PU leather sourced meets specific automotive industry standards for safety and longevity.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
How is PU Leather Utilized in Footwear Production?
In footwear manufacturing, PU leather is a popular choice for shoes and boots due to its lower production costs and diverse design capabilities. This material provides an alternative that can mimic the look and feel of genuine leather while being easier to care for. For B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets, ensuring that the sourced PU leather is breathable and comfortable is essential, as these factors significantly impact customer satisfaction and product longevity.
What are the Applications of PU Leather in Home Décor?
PU leather is increasingly used in home décor for decorative items and wall coverings, offering an aesthetic appeal at a fraction of the cost of genuine leather. Its ease of cleaning and maintenance makes it an attractive choice for businesses looking to provide stylish yet practical home solutions. For international buyers, particularly those in Europe, assessing the eco-friendliness of PU leather options is vital, as consumer preferences are shifting towards sustainable materials that do not compromise on style.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pu leather defined’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Concerns with PU Leather Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often face uncertainty regarding the quality of PU leather products. With various grades and types of PU leather available, distinguishing between high-quality options and subpar alternatives can be daunting. This confusion is compounded by misleading marketing terms like “genuine leather” or “leather-like,” which can lead to dissatisfaction and returns. Poor-quality PU leather can crack, peel, or emit unpleasant odors, negatively impacting brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this challenge, buyers should establish stringent quality criteria before sourcing PU leather. This includes requesting detailed specifications from suppliers, such as the material composition and production methods. Conducting thorough supplier audits and requesting product samples is also essential. Additionally, buyers should consider partnering with manufacturers that provide transparency in their sourcing and production processes. Certifications related to environmental impact and chemical safety can also serve as indicators of quality. Implementing a robust quality assurance process will help ensure that the PU leather sourced meets the expected standards, ultimately enhancing customer trust and satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
Scenario 2: Managing Environmental and Health Risks Associated with PU Leather
The Problem: As awareness of environmental issues grows, B2B buyers are increasingly concerned about the ecological impact and potential health risks associated with PU leather. The manufacturing process often involves volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other chemicals that can harm both the environment and human health. Buyers who prioritize sustainability face the challenge of selecting PU leather products that align with eco-friendly practices, while still meeting their performance and aesthetic needs.
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing PU leather from manufacturers who adhere to strict environmental and health regulations. This can be achieved by requiring suppliers to provide Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) or compliance certificates that confirm their products meet recognized sustainability standards. Additionally, seeking out PU leather that is free from harmful chemicals and produced using eco-friendly methods can significantly mitigate health risks. Engaging in dialogue with suppliers about their sustainability initiatives and asking for documentation can further ensure that the products align with the buyer’s environmental commitments, thus supporting a responsible supply chain.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Durability and Longevity of PU Leather Products
The Problem: A common frustration for B2B buyers is the perceived lack of durability in PU leather products compared to genuine leather. Many buyers report that their PU leather items wear out quickly, leading to additional costs associated with replacements and repairs. This concern is particularly relevant for businesses in industries such as hospitality and automotive, where product longevity is crucial for maintaining a professional image and controlling operational costs.
The Solution: To combat durability issues, buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality PU leather that is specifically designed for the intended application. This may involve selecting products with reinforced backing or higher-density polyurethane layers, which can enhance resilience. Furthermore, engaging with suppliers who offer warranties or guarantees on their PU leather products can provide added peace of mind. It is also beneficial to implement proper care and maintenance protocols to prolong the lifespan of PU leather items. Educating staff on cleaning methods and protective treatments can help maintain the integrity of the material, ensuring that the products remain visually appealing and functional for as long as possible.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pu leather defined
What Are the Key Materials Used in PU Leather Production?
In the production of PU leather, several key materials are utilized, each offering distinct properties and implications for B2B buyers. Understanding these materials is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, especially for international buyers who may face varying regulations and market preferences.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
1. Polyurethane (PU) Coating
Key Properties: Polyurethane is a thermoplastic polymer known for its flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion. It can withstand a range of temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PU coating is its cost-effectiveness compared to genuine leather. It is easy to clean and does not absorb water, which is beneficial in environments where spills are common. However, PU can crack and peel over time, leading to a shorter lifespan than genuine leather, which may not meet the durability expectations of certain applications.
Impact on Application: PU-coated fabrics are often used in furniture, automotive interiors, and fashion accessories. However, the synthetic nature of PU can lead to compatibility issues with certain adhesives or dyes, which may not bond well with plastic-based materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of potential VOC emissions during PU production, which may conflict with local environmental regulations. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN can also affect sourcing decisions.
2. Fabric Base Material
Key Properties: The base fabric for PU leather is typically made from polyester or cotton, providing structural integrity and flexibility. The choice of fabric influences the overall feel and durability of the final product.
Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
Pros & Cons: A fabric base can enhance the breathability of PU leather, making it more comfortable for end-users. However, the durability of the base fabric can vary significantly; lower-quality fabrics may compromise the overall lifespan of the PU leather.
Impact on Application: The type of fabric used can affect the usability of PU leather in high-stress environments, such as automotive seating or outdoor furniture. Buyers must consider the intended use when selecting a fabric base to ensure it meets performance expectations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Different regions may have preferences for specific fabric types based on climate and usage. For example, buyers in humid climates may prefer breathable cotton bases, while those in arid regions may opt for polyester for its moisture resistance.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
3. Adhesives and Backing Materials
Key Properties: Adhesives are crucial in the lamination process of PU leather, ensuring that the PU coating adheres properly to the base fabric. Common adhesives include water-based and solvent-based options, each with varying levels of durability and environmental impact.
Pros & Cons: Water-based adhesives are generally more environmentally friendly and safer for indoor use, but they may not provide the same level of bond strength as solvent-based adhesives. This can lead to delamination issues in high-use applications.
Impact on Application: The choice of adhesive can significantly impact the longevity and performance of PU leather products. For instance, products exposed to moisture or high temperatures may require stronger adhesives to maintain integrity over time.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international safety standards for adhesives is critical, particularly in markets with stringent regulations regarding VOC emissions. Buyers should also consider the end-use environment when selecting adhesives to ensure compatibility.
Summary Table of Key Materials for PU Leather
| Material | Typical Use Case for PU Leather Defined | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane Coating | Furniture, automotive interiors | Cost-effective, easy to clean | Prone to cracking and peeling | Low |
| Fabric Base Material | Fashion accessories, upholstery | Enhances breathability | Durability varies by fabric quality | Medium |
| Adhesives and Backing | Lamination in PU leather production | Environmentally friendly options | Potential delamination issues | Medium |
By understanding these materials and their implications, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing PU leather products, ensuring they meet both performance and regulatory standards in their respective markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pu leather defined
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of PU Leather?
The manufacturing of PU leather involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the desired quality and performance standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in producing PU leather is the preparation of the base material, typically a fabric substrate such as polyester or nylon. This fabric is often coated with a layer of polyurethane, which gives the material its leather-like appearance. The fabric is treated to enhance its strength and durability before the polyurethane coating is applied. This involves processes such as:

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
- Chemical Treatment: The base fabric is often subjected to chemical treatments that enhance adhesion and prepare it for the polyurethane coating.
- Surface Texturing: Techniques like embossing may be employed to create a texture that mimics the grain of real leather.
2. Forming
In this stage, the polyurethane is applied to the prepared substrate. This can be done using several techniques, including:
- Casting: Liquid polyurethane is poured onto the fabric and spread evenly.
- Coating: A spray or roll coating method may be used for a more controlled application.
- Lamination: In some cases, a lamination process is employed where a thin layer of PU is bonded to the fabric through heat and pressure.
Each method impacts the final texture, thickness, and durability of the PU leather.
3. Assembly
Once the PU leather has been formed, it is cut and assembled into the final product. This stage often involves:
- Cutting: Precision cutting tools are used to ensure that pieces fit together correctly.
- Sewing: High-quality stitching techniques are employed to enhance durability. This is particularly important for products like bags, furniture, and automotive interiors.
- Adhesive Bonding: In some applications, adhesives may be used to bond PU leather to other materials.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes are essential to achieve the desired aesthetic and functional properties. Common finishing techniques include:

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
- Surface Treatments: Additional coatings may be applied to enhance water resistance or to provide a specific texture.
- Coloring: Dyes or pigments are applied to give the PU leather its final color.
- Quality Inspection: Before the products are packaged, they undergo quality checks to ensure they meet the specified standards.
What Are the Quality Control Standards for PU Leather?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of PU leather manufacturing, ensuring that the products meet international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers must be aware of these standards to make informed purchasing decisions.
International Standards
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management standards that manufacturers of PU leather should adhere to. This standard focuses on:
- Process Management: Ensuring that all stages of production are well-documented and controlled.
- Customer Satisfaction: Emphasizing the importance of meeting customer requirements and expectations.
- Continuous Improvement: Encouraging manufacturers to continually assess and improve their processes.
Industry-Specific Certifications
In addition to ISO 9001, there are several industry-specific certifications that may be relevant:
- CE Marking: This indicates that the product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API (American Petroleum Institute): Relevant for PU leather used in automotive or industrial applications, ensuring that materials meet specific performance standards.
What Are the QC Checkpoints Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are crucial in ensuring that defects are caught early and do not affect the final product. The following checkpoints are typically implemented in the manufacturing process of PU leather:

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt. Suppliers should conduct tests to verify:
- Material Specifications: Ensuring that the substrate fabric and polyurethane meet the required standards.
- Chemical Composition: Testing for harmful substances, particularly volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During manufacturing, IPQC involves monitoring various stages of production to ensure adherence to specifications. This may include:
- Thickness Measurements: Ensuring the polyurethane layer is applied uniformly.
- Adhesion Tests: Verifying that the polyurethane adheres properly to the fabric substrate.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
Before products are shipped, FQC checks the finished items for:
- Aesthetic Quality: Inspecting for color consistency, texture, and overall appearance.
- Durability Testing: Performing tests to assess the lifespan of the PU leather, including scratch resistance and wear tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should implement strategies to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers:
Supplier Audits
Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and QC practices. This can include:

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
- On-Site Visits: Observing the production process and QC measures in action.
- Documentation Review: Examining quality manuals, inspection reports, and certification documents.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports that outline:
- Testing Methods: Information on the types of tests performed (e.g., tensile strength, colorfastness).
- Results: Historical data on product performance and defect rates.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. This includes:
- Pre-Shipment Inspections: Verifying that products meet specifications before shipment.
- Random Sampling: Testing a selection of products for compliance with quality standards.
What Are the Nuances in QC and Certification for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets, understanding the nuances in quality control and certification is vital:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding the use of chemicals in PU leather. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local laws.
- Sustainability Considerations: With growing concerns about environmental impact, buyers may prefer suppliers who demonstrate sustainable practices in their manufacturing and QC processes.
- Cultural Expectations: Understanding local standards and expectations for quality can help buyers negotiate better terms and ensure that they receive products that meet their needs.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing PU leather products, ensuring that they select suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pu leather defined’
To assist B2B buyers in sourcing PU leather effectively, this guide provides a practical checklist that outlines key steps in the procurement process. Understanding the nuances of PU leather and the suppliers involved is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific requirements for the PU leather you need. This includes the desired thickness, texture, color, and intended application (e.g., upholstery, fashion accessories, or automotive interiors). Having precise specifications helps streamline the sourcing process and ensures that suppliers can meet your needs.
Step 2: Research Supplier Reputation
Investigate potential suppliers’ reputations within the industry. Look for reviews, ratings, and testimonials from other businesses, especially those in your sector or geographical region. A supplier’s track record can provide insights into their reliability, product quality, and customer service.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Assess their experience with PU leather products to ensure they can deliver on your specifications.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have relevant certifications, such as ISO or environmental compliance standards. This is particularly important if you are concerned about sustainability or the use of harmful chemicals in the manufacturing process. Certifications can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and environmental responsibility.
Step 5: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Always request samples of the PU leather before making bulk purchases. This allows you to assess the material’s quality, feel, and durability firsthand. Pay attention to characteristics such as the texture, flexibility, and any odors that may indicate the presence of harmful chemicals.
Step 6: Inquire About Production Capabilities
Discuss the supplier’s production capacity and lead times. Understanding their ability to scale production to meet your demands is vital, especially if you foresee increased orders in the future. Ask about their production processes to gauge their efficiency and quality control measures.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate the terms of the purchase, including pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Ensure that all agreements are documented in a contract to protect your interests. Transparency in this phase can help avoid potential misunderstandings later on.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing PU leather, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business needs and values.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pu leather defined Sourcing
When considering sourcing PU leather, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section provides an in-depth analysis of the cost components, price influencers, and practical tips for optimizing procurement strategies.
What Are the Key Cost Components in PU Leather Sourcing?
The cost structure for PU leather typically encompasses several key components:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in PU leather production is the raw material itself—polyurethane and fabric substrates. Prices can vary significantly based on the quality and type of materials used, with higher-quality PU leather generally commanding a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the production location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Southeast Asia, can offer more competitive pricing. However, labor costs in Europe or North America may be higher due to wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with running production facilities, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overheads.
-
Tooling: Customization often requires specialized tooling, which can add to initial costs. Buyers should consider the amortization of these costs over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet specified standards incurs additional costs. Stringent QC processes are vital, especially for high-end applications, and can influence overall pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and fuel prices. Additionally, customs duties and tariffs may apply, affecting the total landed cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can be negotiated based on order size and relationship longevity.
How Do Price Influencers Affect PU Leather Costs?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of PU leather:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often yield better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it economically advantageous for buyers who can commit to higher volumes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products, such as specific colors or textures, can increase costs. Buyers should be clear about their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The use of premium materials or adherence to specific quality certifications (like ISO) can elevate costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capabilities, and location can all influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their reliability and experience.
-
Incoterms: The agreed Incoterms can affect the total cost. For instance, choosing FOB (Free on Board) can shift some shipping responsibilities and costs to the buyer, impacting overall pricing strategy.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing PU Leather?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume commitments and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing. Building rapport with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with durability, maintenance, and replacement frequency. PU leather may be cheaper upfront but could incur higher replacement costs due to its shorter lifespan.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions that can affect pricing. Engaging with local experts or consultants can provide invaluable insights.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is essential to note that pricing for PU leather can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always seek multiple quotations and conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any sourcing decision.
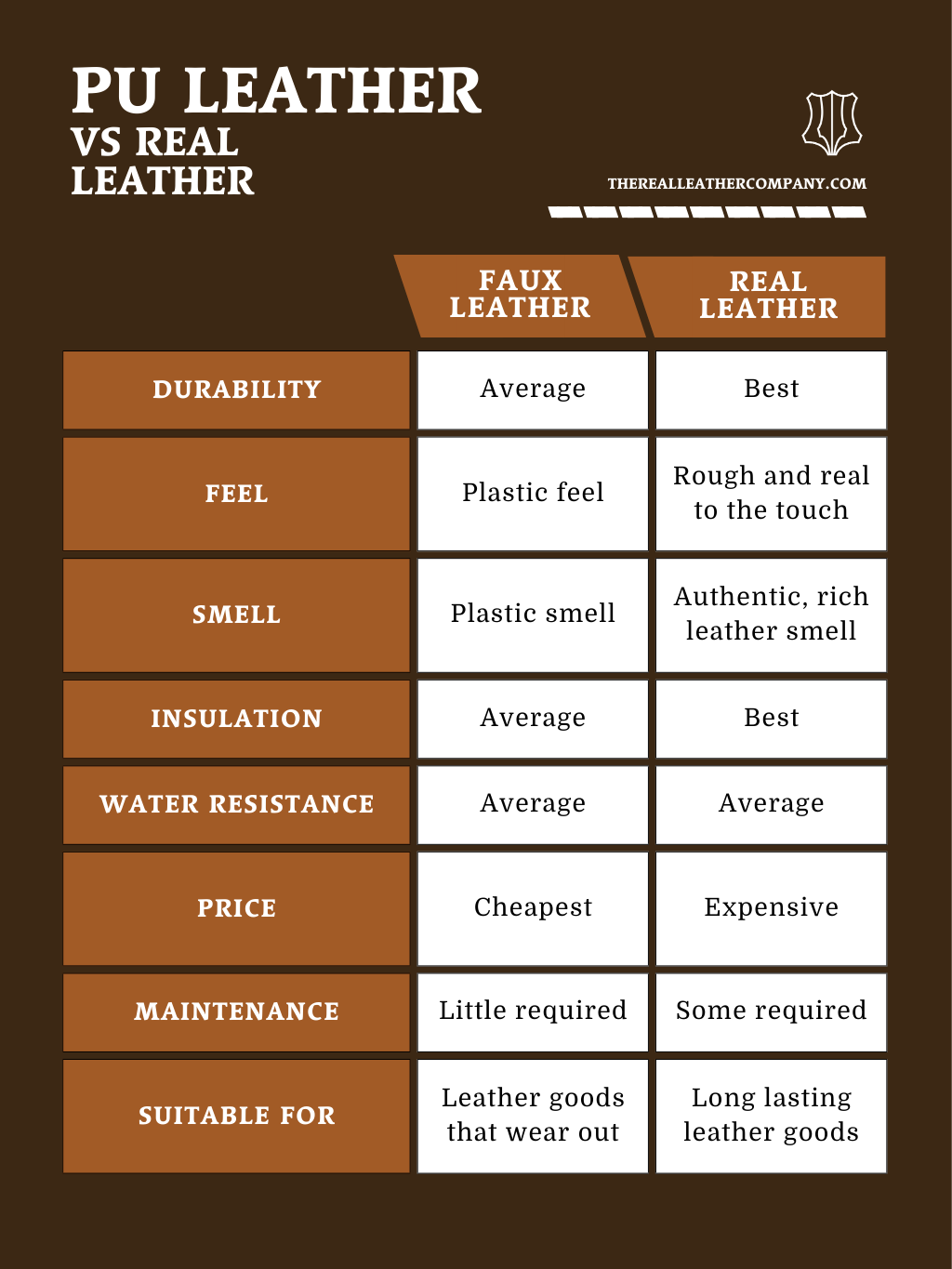
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pu leather defined With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to PU Leather: A Comparative Analysis
As B2B buyers seek cost-effective and sustainable materials, understanding the alternatives to PU leather becomes crucial. PU leather, while popular for its affordability and versatility, has significant drawbacks, including durability issues and environmental concerns. This analysis compares PU leather with two viable alternatives: genuine leather and vegetable-tanned leather, enabling buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
| Comparison Aspect | Pu Leather Defined | Genuine Leather | Vegetable-Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate durability; prone to cracking and peeling | High durability; ages well, develops patina | Excellent durability; environmentally friendly aging process |
| Cost | Low cost; typically more affordable than genuine leather | Higher cost; premium materials and craftsmanship | Moderate cost; higher than PU but lower than high-end genuine leather |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to produce and customize; widely available | Requires skilled craftsmanship; longer production time | Labor-intensive; requires skilled artisans for production |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean but may wear quickly | Requires regular conditioning; develops character over time | Needs occasional cleaning; ages beautifully with proper care |
| Best Use Case | Budget-conscious applications; fashion items | Luxury goods; high-end furniture | Eco-conscious products; artisanal goods |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Genuine Leather: The Premium Choice
Genuine leather is a timeless choice known for its durability and luxurious feel. It can last for decades when properly maintained, making it an excellent long-term investment. However, the higher cost may deter budget-sensitive buyers. Genuine leather also requires more care, including conditioning to prevent drying and cracking. For businesses looking to position themselves in the luxury market, genuine leather is an irreplaceable material that conveys quality and prestige.
Vegetable-Tanned Leather: The Eco-Friendly Option
Vegetable-tanned leather is processed using natural tannins from plant sources, making it a sustainable alternative to PU leather. This type of leather is known for its robustness and ability to develop a unique patina over time, enhancing its aesthetic appeal. While it is typically more expensive than PU leather, the environmental benefits and longevity make it a worthwhile investment for eco-conscious brands. The primary downside is the longer production time and the need for skilled artisans, which may complicate supply chain logistics.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Leather Solution for Your Business Needs
Selecting the right material for your products hinges on various factors, including budget, intended use, and sustainability goals. PU leather offers a low-cost and easy-to-manufacture solution, but its lack of durability and environmental concerns may not align with every brand’s values. Genuine leather stands out for its longevity and luxury, ideal for high-end markets, while vegetable-tanned leather appeals to those prioritizing sustainability. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, B2B buyers can align their material choices with their brand identity and customer expectations, ensuring a successful product offering.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pu leather defined
What Are the Key Technical Properties of PU Leather for B2B Buyers?
When evaluating PU leather for commercial applications, understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are some of the key specifications that can significantly impact product quality and performance.
1. Material Composition
PU leather is primarily composed of a thermoplastic polymer, specifically polyurethane. The quality of the PU leather can vary based on the thickness and density of the polymer layer applied over the base fabric. High-quality PU leather typically features a thicker polyurethane coating, enhancing durability and resistance to wear and tear, making it a more reliable choice for furniture and accessories.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength refers to the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that a material can withstand before breaking. For PU leather, a higher tensile strength indicates better durability and resistance to tearing. This is particularly important in high-usage environments, such as office furniture or automotive seating, where materials face significant stress.
3. Water Resistance
PU leather is generally water-resistant, meaning it does not absorb moisture like genuine leather. This property is crucial for applications in environments prone to spills or high humidity, as it simplifies maintenance and prolongs the lifespan of the product. B2B buyers should ensure that the specific PU leather they are sourcing meets the necessary water resistance standards for their intended use.
4. Chemical Resistance
The ability of PU leather to resist chemicals, including oils and solvents, is another important property. This is particularly relevant in industries such as automotive or healthcare, where exposure to various substances is common. A PU leather that exhibits high chemical resistance will maintain its appearance and integrity over time, reducing replacement costs.
5. Respirabilidade
While PU leather is less breathable than genuine leather, certain manufacturing processes can enhance its breathability. This property is vital for products like upholstery, where comfort is paramount. B2B buyers should consider the breathability of the material to ensure it meets consumer comfort expectations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to PU Leather?
Navigating the procurement of PU leather involves familiarity with industry jargon. Understanding these terms can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication with suppliers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of PU leather, an OEM may be responsible for creating PU leather products that are then branded and sold by another company. This relationship is critical for B2B buyers seeking custom solutions.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory levels and cash flow. Negotiating favorable MOQs can lead to better pricing and supply chain efficiency.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting pricing and other information from suppliers. B2B buyers typically use RFQs to obtain competitive quotes for PU leather products, ensuring they make cost-effective purchasing decisions while comparing various suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers in understanding shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities when sourcing PU leather from global suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes for a supplier to fulfill an order. For PU leather, this includes the time required for manufacturing, quality checks, and shipping. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their inventory and production schedules more effectively.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing PU leather, ensuring that they select products that meet their business needs and quality standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pu leather defined Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the PU Leather Sector?
The global PU leather market is experiencing significant growth driven by a combination of affordability, versatility, and an increasing demand for vegan alternatives. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly gravitating towards PU leather due to its lower price point compared to genuine leather. Emerging markets in countries such as Vietnam and Nigeria are witnessing a surge in demand for affordable, fashionable, and ethically produced materials, making PU leather an attractive option for manufacturers and retailers alike.
Current trends indicate a growing preference for customizable PU leather products, allowing businesses to meet specific consumer needs. Additionally, advances in technology are leading to improved production techniques that enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of PU leather. Innovations such as digital printing and eco-friendly coatings are making it possible to create high-quality finishes that mimic the look of genuine leather while reducing environmental impact. As buyers become more discerning, the demand for transparency in sourcing and manufacturing processes is also rising, with companies increasingly required to demonstrate their commitment to ethical practices.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the PU Leather Industry?
The environmental impact of PU leather production is a crucial consideration for B2B buyers. Traditional PU leather is made from petroleum-based polymers, raising concerns about its biodegradability and overall ecological footprint. However, a shift towards sustainable practices is evident, with manufacturers exploring eco-friendly materials and production processes. Buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers who offer ‘green’ certifications, such as Global Recycled Standard (GRS) or OEKO-TEX Standard 100, which can assure them of the product’s reduced environmental impact.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is becoming a paramount concern. Companies are increasingly held accountable for their supply chains, with stakeholders demanding transparency regarding labor practices and material sourcing. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to ethical standards, ensuring that their products are not only environmentally friendly but also socially responsible. By aligning with suppliers committed to ethical practices, businesses can enhance their brand image and meet the growing consumer demand for sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context of PU Leather in the B2B Marketplace?
PU leather emerged in the mid-20th century as an alternative to genuine leather, primarily due to its affordability and versatility. Initially developed for use in fashion and upholstery, PU leather quickly gained popularity across various industries, including automotive, furniture, and fashion accessories. Its ability to mimic the look and feel of real leather without the associated costs made it an attractive option for manufacturers and consumers alike.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
Over the years, advancements in technology have led to significant improvements in the quality and durability of PU leather, making it a viable option for a broader range of applications. As consumer preferences have evolved, so too has the focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing, prompting manufacturers to adapt their practices to meet modern demands. Today, PU leather represents a critical component of the global textile industry, balancing consumer needs for cost-effective and stylish materials with an increasing emphasis on environmental responsibility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pu leather defined
-
How do I determine the quality of PU leather for my products?
To assess the quality of PU leather, consider several factors: the thickness of the material, the texture, and the manufacturer’s reputation. High-quality PU leather should have a consistent texture and a smooth finish, without visible imperfections. Conduct a smell test; premium PU leather typically has a less pronounced plastic odor. Additionally, request samples to evaluate durability through tests like bending and scratching. Lastly, ensure the supplier provides certifications regarding the material’s composition and safety standards, which can further validate quality. -
What are the key differences between PU leather and genuine leather?
PU leather is a synthetic alternative made from plastic-coated fabrics, while genuine leather is derived from animal hides. The main differences lie in durability and maintenance; genuine leather ages beautifully and can last decades, developing a unique patina, whereas PU leather may crack and peel within a few years. PU leather is often more affordable and available in various colors but lacks breathability and the luxurious feel of real leather. For buyers, understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions based on product longevity and market positioning. -
What customization options are available for PU leather products?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for PU leather, including color choices, texture variations, and embossed designs. When sourcing, inquire about the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for custom designs, as these can vary significantly between suppliers. Additionally, consider whether the supplier can accommodate specific branding requirements, such as logo placements or unique patterns. Establishing a clear communication channel with the manufacturer will facilitate the customization process and ensure that the final product aligns with your brand’s aesthetic and functional needs. -
What are the typical payment terms for sourcing PU leather internationally?
Payment terms for international PU leather sourcing can vary widely based on supplier policies and buyer negotiations. Common arrangements include a deposit (usually 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to shipping. It’s advisable to discuss payment methods such as wire transfers, letters of credit, or PayPal for security. Always review the terms outlined in the purchase agreement, and consider establishing a payment schedule that aligns with production timelines to manage cash flow effectively. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing PU leather?
Implementing a robust QA process is essential when sourcing PU leather. Start by requesting detailed product specifications and certifications from your supplier to verify compliance with international standards. Conduct on-site inspections or audits to assess manufacturing practices and material quality. Additionally, establish a protocol for receiving samples before full production to evaluate the physical properties of the leather. Regular communication with your supplier during the production phase can help preemptively address any quality issues. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing PU leather?
When importing PU leather, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply. Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of air freight versus sea freight based on your timeline and budget. Ensure you have the necessary documentation, such as invoices and certificates of origin, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Collaborating with a reliable logistics partner can help navigate these complexities and ensure timely delivery of your products, minimizing potential disruptions in your supply chain. -
What are the environmental implications of using PU leather?
PU leather is often touted as a more sustainable alternative to genuine leather; however, it is essential to consider its environmental footprint. The production process involves petrochemicals, which contribute to pollution and are non-biodegradable. Additionally, some PU leather products may contain harmful VOCs. When sourcing, look for suppliers who utilize eco-friendly production practices or certifications that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. This not only aligns with global environmental standards but also resonates with increasingly eco-conscious consumers. -
How do I identify reliable suppliers for PU leather?
Identifying reliable suppliers for PU leather involves thorough research and due diligence. Start by assessing their industry reputation through reviews, case studies, and testimonials from previous clients. Request references and verify their production capabilities, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. Attending trade shows and industry events can also provide opportunities for direct interaction and relationship building. Lastly, consider starting with small trial orders to gauge the supplier’s reliability and product quality before committing to larger purchases.
Top 3 Pu Leather Defined Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Manuel Dreesmann – PU Leather Solutions
Domain: manuel-dreesmann.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: PU leather is a synthetic material that is often used as a substitute for genuine leather. It is made by applying a layer of polyurethane to a base material, usually polyester or cotton. While PU leather can be more affordable and easier to maintain than real leather, it is less durable and may not age as well. The article suggests avoiding PU leather due to its environmental impact, as it is not …
2. Rahui – PU Leather
Domain: rahui.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, Rahui – PU Leather, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Yorkshire Fabric Shop – PU Leather
Domain: yorkshirefabricshop.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: PU leather is synthetic leather made from polyurethane, a plastic that mimics the feel and appearance of real leather without using animal products. Faux leather, derived from upholstery fabric like polyester, offers a premium quality finish that resembles real leather, often featuring textures and finishes such as wax, dye, PVC, or polyurethane. Both materials are water-resistant, easy to clean, …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pu leather defined
In conclusion, understanding PU leather is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to make informed sourcing decisions. While PU leather offers affordability and a range of aesthetic options, its durability and environmental impact raise significant concerns. Buyers should weigh the benefits of cost-effectiveness against the potential need for frequent replacements and the implications of synthetic materials on sustainability.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in navigating these challenges. By selecting high-quality PU leather suppliers who adhere to ethical manufacturing practices, businesses can enhance their product offerings while aligning with sustainability goals. It is essential to conduct thorough supplier evaluations and demand transparency in sourcing materials, ensuring that the products align with both quality standards and environmental considerations.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for responsibly sourced materials like PU leather will only grow. Therefore, proactive engagement with suppliers, along with a commitment to sustainability, will position businesses favorably in a competitive landscape. Embrace this opportunity to refine your sourcing strategy and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to pu leather defined
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.