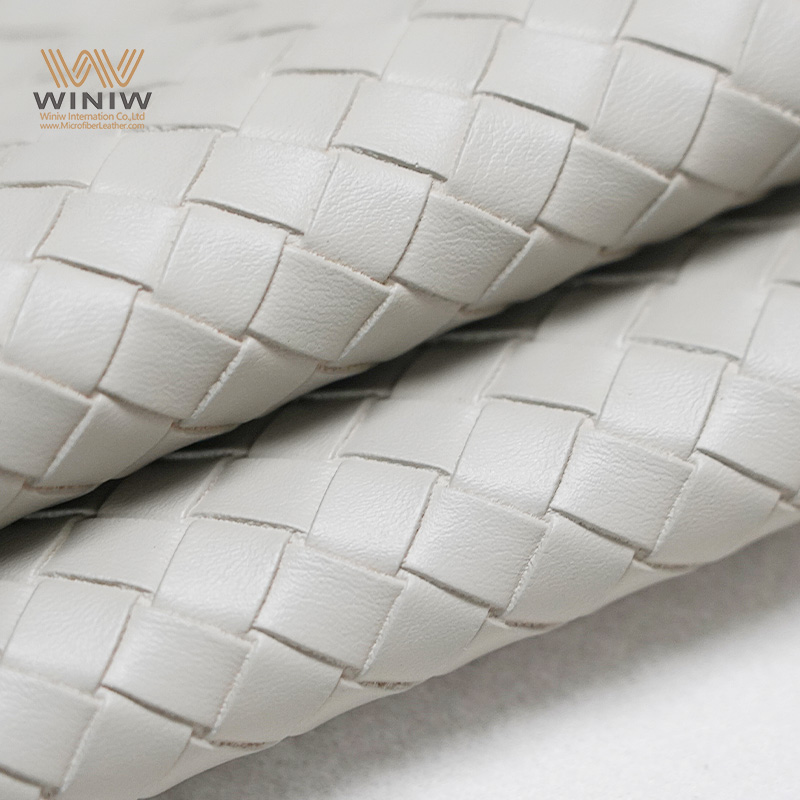
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather manufacturing
Navigating the complexities of the global leather manufacturing market can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers seeking high-quality materials. Whether you are sourcing durable leather for automotive interiors or luxurious handbags, understanding the intricacies of leather production is essential. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the leather manufacturing process, from the initial sourcing of hides to the final finishing techniques. It delves into the various types of leather available, their applications across different industries, and the critical steps involved in supplier vetting.
In an era where sustainability is paramount, this guide also emphasizes the importance of responsible sourcing practices, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Germany. By equipping you with actionable insights on cost considerations, quality benchmarks, and ethical sourcing, we empower you to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business values.
Navigating the global leather market requires not only knowledge of the production process but also an understanding of the broader supply chain dynamics. This guide serves as a vital resource for B2B buyers aiming to enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring that you can confidently select leather products that meet your quality standards and sustainability goals.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Leather Manufacturing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather manufacturing
- Understanding leather manufacturing Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of leather manufacturing
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather manufacturing’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather manufacturing
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather manufacturing
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather manufacturing’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather manufacturing Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather manufacturing With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather manufacturing
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather manufacturing Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather manufacturing
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather manufacturing
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding leather manufacturing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Grain Leather | Made from the top layer of hide; retains natural grain | High-end fashion, luxury goods, upholstery | Pros: Durable, breathable, ages beautifully. Cons: Higher cost, may require special care. |
| Top Grain Leather | Sanded and refinished top layer; more uniform appearance | Footwear, handbags, automotive interiors | Pros: Less expensive than full grain, durable. Cons: Less breathability, may not age as well. |
| Camurça | Made from the underside of the hide; soft texture | Fashion apparel, accessories, upholstery | Pros: Soft and flexible, unique aesthetics. Cons: Less durable, susceptible to stains. |
| Nubuck | Top grain leather that is sanded for a velvety feel | High-end footwear, luxury bags | Pros: Soft, luxurious appearance, durable. Cons: Requires regular maintenance, can be pricey. |
| Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Tanned using natural tannins; eco-friendly | Eco-conscious products, artisanal goods | Pros: Biodegradable, unique character. Cons: Longer production time, can be stiff initially. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Full Grain Leather?
Full grain leather is celebrated for its authenticity, made from the top layer of hide that retains the natural grain and imperfections. This type of leather is highly durable and develops a rich patina over time, making it ideal for luxury goods and high-end upholstery. B2B buyers should consider sourcing full grain leather for products that demand longevity and aesthetic appeal, although they should be prepared for a higher price point and the need for proper care to maintain its quality.
How Does Top Grain Leather Differ from Other Types?
Top grain leather is derived from the second layer of hide, where the surface is sanded down to create a more uniform look. It is less expensive than full grain leather while still offering good durability and resistance to wear. Common applications include footwear and automotive interiors. Buyers should weigh the benefits of cost savings against potential drawbacks, such as reduced breathability and the possibility of not developing the same character over time as full grain leather.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
Why Choose Suede for Fashion and Accessories?
Suede, made from the underside of the hide, is known for its soft texture and flexibility, making it a popular choice for fashion apparel and accessories. Its unique aesthetic can add a touch of luxury to products. However, B2B buyers should be mindful of its lower durability and susceptibility to stains, which may necessitate specific care instructions for end consumers.
What Makes Nubuck a Preferred Choice in Luxury Markets?
Nubuck leather is similar to suede but is made from the top grain that has been sanded to create a velvety finish. This gives nubuck a luxurious feel and appearance, making it suitable for high-end footwear and bags. While it offers durability and a premium look, buyers should consider the ongoing maintenance required to keep nubuck looking its best, as well as its generally higher price point compared to other leather types.
Why Consider Vegetable-Tanned Leather for Eco-Conscious Products?
Vegetable-tanned leather is processed using natural tannins, making it a sustainable choice for eco-conscious brands. This leather type is biodegradable and develops a unique character over time, appealing to artisanal and environmentally friendly product lines. However, buyers should be aware of longer production times and the initial stiffness that may require breaking in before use.
Key Industrial Applications of leather manufacturing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Leather Manufacturing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Upholstery for seats and interiors | Enhances luxury appeal and durability | Sourcing eco-friendly leather options, compliance with automotive standards, and availability of specific colors and textures. |
| Fashion & Apparel | Leather garments and accessories | Offers style, durability, and brand prestige | Preference for sustainable sourcing, traceability of materials, and compliance with fashion industry regulations. |
| Furniture | Leather upholstery for sofas and chairs | Provides comfort, luxury, and aesthetic value | Focus on quality, sourcing from reputable tanneries, and availability of various finishes and colors. |
| Footwear | Leather shoes and boots | Durability, comfort, and style | Need for specific leather types (full-grain, nubuck), sourcing from tanneries with ethical practices, and customization options. |
| Sporting Goods | Leather goods for sports equipment | Enhances performance and durability | Consideration for specific leather treatments, compliance with sporting regulations, and sourcing from specialized manufacturers. |
How is Leather Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, leather is predominantly used for upholstery in seats, dashboards, and steering wheels. Its application enhances the luxury feel of vehicles, appealing to consumers who seek comfort and style. The durability of leather also addresses concerns about wear and tear, making it a preferred choice for high-end models. International buyers should consider sourcing leather that meets automotive safety and environmental standards, ensuring that it is both functional and sustainable.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
What Role Does Leather Play in Fashion and Apparel?
Leather plays a significant role in the fashion and apparel industry, where it is used to create garments, handbags, and accessories. Its unique texture and ability to age beautifully add value to fashion items, contributing to brand prestige. For international buyers, it is essential to prioritize sustainable sourcing and transparency in the supply chain, as consumers increasingly demand ethically produced materials. Compliance with fashion industry standards and trends can also impact purchasing decisions.
Why is Leather Important in Furniture Manufacturing?
In furniture manufacturing, leather is commonly used for upholstery on sofas, chairs, and other seating solutions. It offers a combination of comfort, luxury, and durability, making it an attractive option for both residential and commercial applications. Buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality leather that meets their aesthetic and functional requirements. Additionally, understanding the availability of different finishes and colors can help businesses create unique offerings that stand out in the competitive market.
How is Leather Utilized in Footwear Production?
Leather is a fundamental material in the footwear industry, used to manufacture shoes and boots that provide durability, comfort, and style. The choice of leather type, such as full-grain or nubuck, can significantly affect the performance and appeal of the footwear. For international buyers, sourcing from tanneries that adhere to ethical practices and offer customization options is crucial. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements for different types of footwear can aid in selecting the right leather for the intended application.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
What is the Application of Leather in Sporting Goods?
Leather is often used in the production of sporting goods, such as balls, gloves, and protective gear. Its durability and performance characteristics make it an ideal choice for items that undergo significant wear. For businesses in this sector, sourcing leather that meets specific treatment and quality standards is essential. Buyers should also consider compliance with sporting regulations and the potential for innovative leather treatments that enhance performance and longevity in athletic applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather manufacturing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Sustainable Leather in a Competitive Market
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing sustainable leather that meets both ethical standards and their specific product requirements. With increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, businesses face pressure to align their sourcing practices with sustainability goals. However, the lack of transparency in the leather supply chain can lead to confusion and difficulties in identifying responsible suppliers. This can result in reputational risks if the sourced leather does not align with the buyer’s sustainability commitments.
The Solution: To effectively source sustainable leather, buyers should prioritize working with tanneries that are certified by recognized organizations focused on environmental stewardship. Conduct thorough research to understand the tannery’s practices regarding waste management, water usage, and chemical treatments. Buyers can also request documentation that outlines the environmental impact of the leather production process. Building long-term relationships with a select group of reputable suppliers can enhance transparency and reliability. Additionally, consider leveraging technology such as blockchain to track the leather’s journey from raw hide to finished product, ensuring compliance with sustainability standards.
Scenario 2: Navigating Quality Control in Leather Production
The Problem: Quality control in leather manufacturing is a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly when dealing with international suppliers. Variability in leather quality can stem from differences in tanning processes, raw material sourcing, and finishing techniques. This inconsistency can lead to delays in production, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction if the final products do not meet expected standards.
The Solution: Implementing a robust quality assurance program is essential for mitigating quality-related issues in leather production. Buyers should develop clear specifications and standards that outline desired characteristics such as grain quality, thickness, and color consistency. Regular communication with suppliers is crucial; schedule routine audits and quality checks at various stages of the manufacturing process. Additionally, consider establishing a third-party inspection service that specializes in leather products to ensure compliance with your quality standards before shipment. This proactive approach can help maintain product consistency and enhance overall satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions in Leather Manufacturing
The Problem: The leather manufacturing industry is susceptible to supply chain disruptions due to factors such as geopolitical issues, trade regulations, and environmental factors impacting livestock availability. B2B buyers may find themselves in a precarious situation where delays in leather supply can halt production lines, leading to significant financial losses and missed market opportunities.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of supply chain disruptions, buyers should adopt a diversified sourcing strategy. This involves identifying multiple suppliers across different regions to create a buffer against localized disruptions. Establishing long-term contracts with key suppliers can also provide stability in pricing and availability. Additionally, buyers should invest in inventory management systems that allow for real-time tracking of stock levels and lead times. By maintaining a safety stock of critical leather materials, businesses can better navigate unforeseen disruptions while ensuring continuous production flow. Implementing contingency plans that outline alternative sourcing options can further enhance resilience in the face of supply chain challenges.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather manufacturing
What Are the Key Materials Used in Leather Manufacturing?
In the leather manufacturing industry, the selection of materials is crucial for ensuring product performance, sustainability, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in leather production, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Chrome-Tanned Leather
Key Properties: Chrome-tanned leather is known for its durability and resistance to water and heat. It typically has a temperature rating that can withstand moderate environmental stress, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: One of the main advantages of chrome-tanned leather is its quick tanning process, which can be completed in a matter of days. This results in lower production costs and faster turnaround times. However, the environmental impact of chromium, a toxic metal, raises concerns, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
Impact on Application: Chrome-tanned leather is widely used in automotive interiors, footwear, and fashion goods due to its flexibility and aesthetic appeal. However, it may not be suitable for applications requiring high breathability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Europe and North America should ensure compliance with REACH regulations, which restrict the use of certain chemicals, including chromium. Understanding local regulations in Africa and South America is also essential, as these may differ significantly.
2. Vegetable-Tanned Leather
Key Properties: Vegetable-tanned leather is made using natural tannins from plant sources. It is biodegradable and exhibits good breathability, making it ideal for high-end leather goods.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of vegetable-tanned leather is its eco-friendliness and the unique patina it develops over time, adding character to the product. However, the tanning process is slower and can be more expensive than chrome tanning, which may deter some manufacturers.
Impact on Application: This type of leather is often used for luxury items such as wallets, belts, and high-quality bags. Its natural properties make it suitable for applications where aesthetics and sustainability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for certifications like the Leather Working Group (LWG) rating to ensure sustainable sourcing. Compliance with ASTM standards for leather quality may also be necessary, especially in European markets.
3. Synthetic Leather (PU and PVC)
Key Properties: Synthetic leather, made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers a high degree of customization in texture and color. It is generally resistant to moisture and easy to clean.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of synthetic leather is its lower cost and the ability to mimic the appearance of genuine leather without animal products. However, it lacks the durability and breathability of natural leather, which may limit its application in high-performance products.
Impact on Application: Synthetic leather is commonly used in fashion accessories, upholstery, and budget-friendly footwear. Its water resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications, but it may not perform well in high-temperature environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that synthetic leathers comply with international standards such as ISO and ASTM for safety and quality. Additionally, awareness of the growing consumer preference for sustainable materials is crucial.
4. Suede Leather
Key Properties: Suede, made from the underside of animal hides, is known for its soft texture and luxurious feel. It typically has good breathability but is less resistant to water and stains compared to other leathers.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
Pros & Cons: The softness and aesthetic appeal of suede make it highly desirable for fashion applications. However, its vulnerability to damage from moisture and dirt can be a significant drawback, requiring special care and maintenance.
Impact on Application: Suede is often used in high-end footwear, jackets, and accessories. Its unique texture adds a premium feel, but its limited durability in harsh conditions can restrict its use.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of cleaning and care products for suede, especially in regions where such products are not readily accessible. Compliance with local quality standards is also essential to ensure product longevity.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for leather manufacturing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chrome-Tanned Leather | Automotive interiors, footwear, fashion goods | Quick tanning process, durable | Environmental concerns with chromium | Medium |
| Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Luxury wallets, belts, high-quality bags | Eco-friendly, develops unique patina | Slower tanning process, higher cost | Elevado |
| Couro sintético | Fashion accessories, upholstery, budget footwear | Lower cost, customizable appearance | Less durable, lacks breathability | Low |
| Suede Leather | High-end footwear, jackets, accessories | Soft texture, luxurious feel | Vulnerable to moisture and dirt | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers looking to navigate the complexities of leather manufacturing and make informed decisions that align with their business goals.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
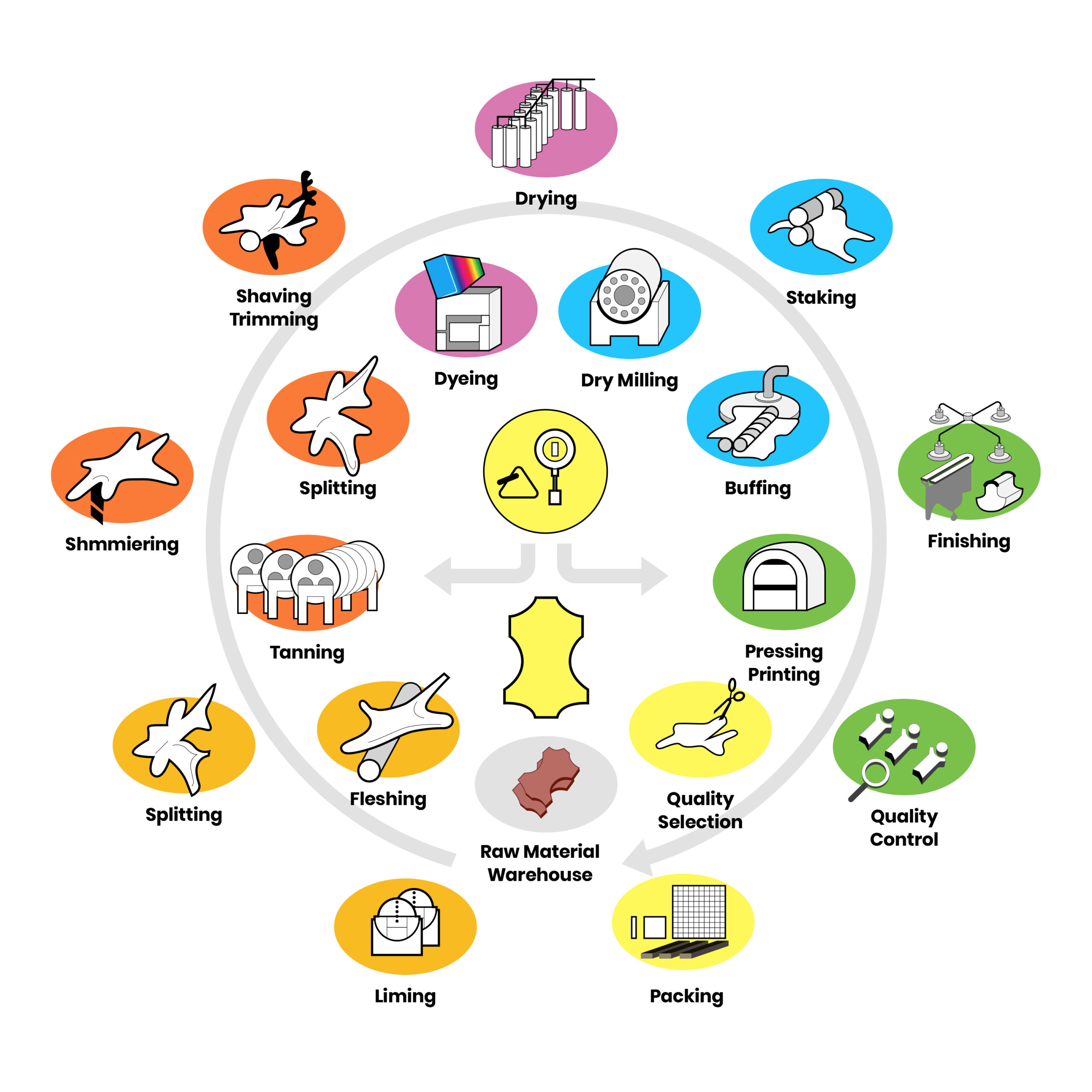
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather manufacturing
What Are the Main Stages in Leather Manufacturing?
Leather manufacturing is a complex process that involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final quality of the leather product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers who want to ensure they are sourcing high-quality leather.
1. Material Preparation: How Are Raw Hides Processed?
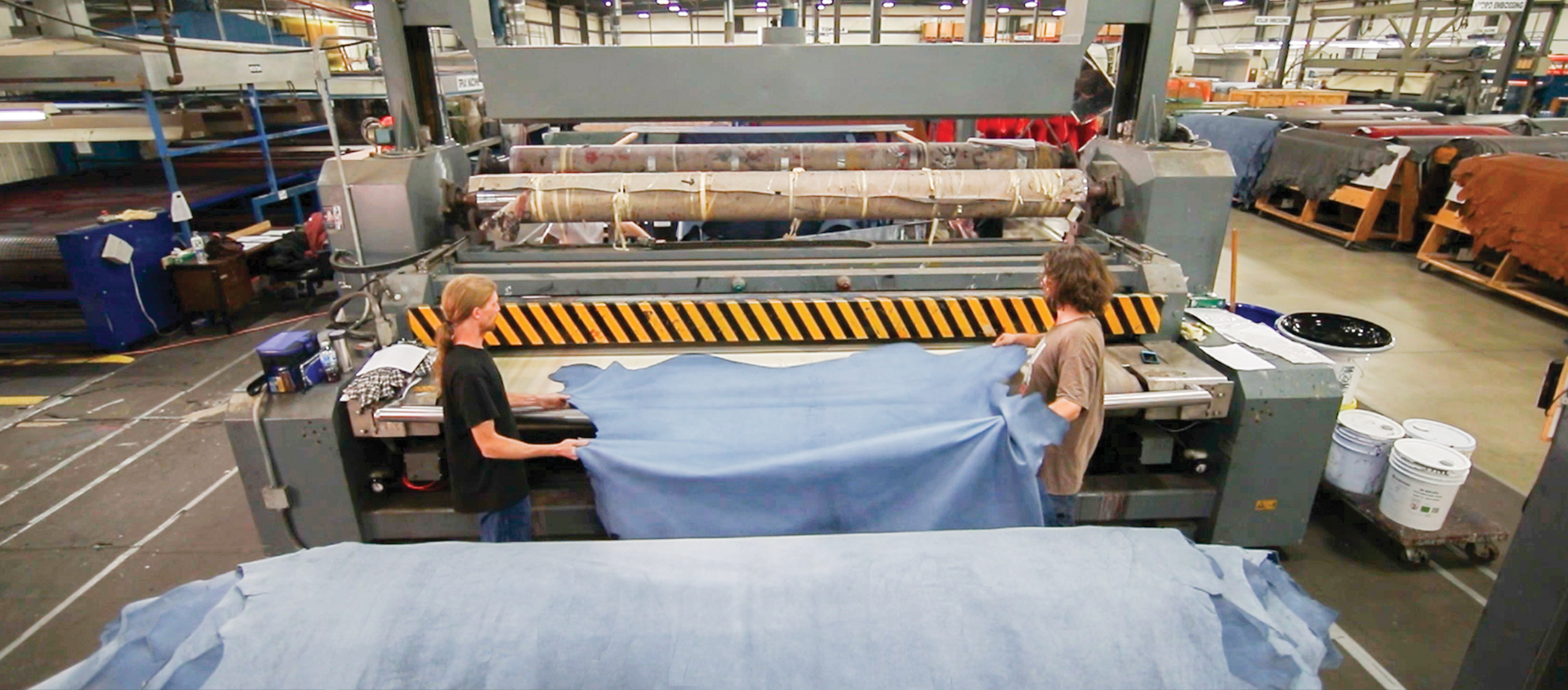
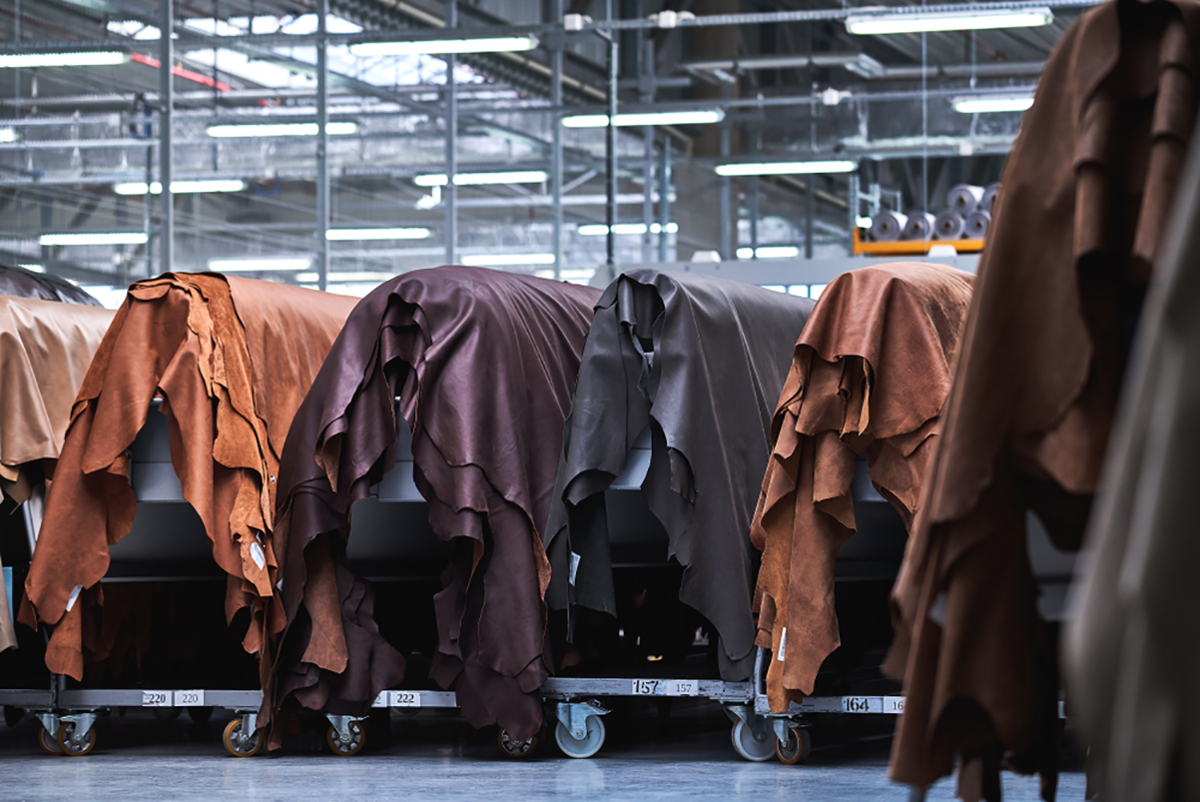
The journey of leather begins with the sourcing of raw hides, primarily a by-product of the meat industry. Preservation is the first step, which often involves salting or refrigeration to prevent decomposition during transportation to the tannery. Once the hides arrive, they undergo a cleaning process known as beamhouse operations. This phase removes impurities such as dirt, salt, and hair, preparing the hides for tanning.
In this stage, the hides may be split into layers, allowing manufacturers to create different types of leather, such as full grain or suede. The thickness of the leather is adjusted based on the end product’s requirements, with thicker hides used for durable items like boots and thinner hides for garments.
2. How Does Tanning Stabilize the Leather?
Tanning is the process that converts raw hides into leather by stabilizing the protein structure, making it durable and resistant to decay. The main methods of tanning include chrome tanning, vegetable tanning, and chrome-free alternatives. Each method imparts distinct characteristics to the leather. For example, chrome-tanned leather is known for its softness and durability, while vegetable-tanned leather is often valued for its eco-friendliness and rich patina.
After tanning, the leather may be referred to as ‘wet-blue’ or ‘wet-white’ depending on the tanning method used. This stage is crucial as it lays the foundation for the leather’s future applications in various industries, including fashion, automotive, and furniture.
3. What Is the Role of Retanning in Leather Quality?
Retanning is a specialized process that refines the leather’s properties by adding color and enhancing its tactile qualities. This step often includes fatliquoring, which introduces oils that soften the leather and improve its feel. The retanning process allows manufacturers to tailor the leather’s characteristics to specific applications, such as creating the ideal texture for luxury handbags or durable upholstery.
Once this phase is complete, the leather is labeled as ‘crust’ and is ready for further processing, including milling and finishing.
4. How Does Milling Enhance Leather Texture?
Milling involves tumbling the leather in dry drums to soften it further and accentuate its natural grain. This technique creates a desirable, soft handle that is often sought after in high-quality leather products. Tumbled leather is recognized for its unique appearance and feel, making it suitable for various applications, from clothing to accessories.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
5. What Are the Finishing Techniques Applied to Leather?
The final stage in the leather manufacturing process is finishing. This involves applying various surface treatments to enhance the leather’s durability, appearance, and functionality. Techniques may include dyeing, embossing, and coating with protective layers. The finishing process not only affects the aesthetic appeal but also the leather’s resistance to wear and environmental factors.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Important in Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a crucial aspect of leather manufacturing, ensuring that the final products meet international standards and buyer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding these quality control measures is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
1. What International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
International standards, such as ISO 9001, provide a framework for quality management systems in manufacturing. Compliance with these standards indicates a commitment to quality, consistency, and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for products sold in Europe or API standards for certain applications can further assure buyers of product quality.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in leather manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw hides upon arrival at the tannery to ensure they meet predefined quality specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the tanning and finishing stages, regular inspections are conducted to ensure adherence to quality standards and detect any deviations early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the finishing process, a comprehensive inspection assesses the final product’s quality, including appearance, texture, and durability.
These checkpoints help maintain quality throughout the production cycle, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.
Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
3. How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their quality management practices and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and the final product.
4. What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to understand the nuances of quality control in leather manufacturing. Different regions may have varying standards and practices, affecting product quality. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and market expectations to ensure compliance and satisfaction.
Moreover, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear guidelines and expectations upfront can mitigate misunderstandings and foster a successful partnership.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Leather Manufacturing
Navigating the complexities of leather manufacturing and quality assurance requires diligence and understanding. By familiarizing themselves with the manufacturing processes, relevant international standards, and quality control measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful sourcing of high-quality leather products. This knowledge not only enhances buyer confidence but also strengthens supplier relationships, ultimately contributing to long-term business success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather manufacturing’
When sourcing leather for manufacturing, it’s essential to navigate the complexities of the supply chain effectively. This checklist will guide B2B buyers through the critical steps to ensure they procure high-quality, sustainable leather that meets their specific needs.
Step 1: Identify Your Leather Requirements
Before engaging suppliers, clearly define the type of leather you need. Consider factors such as the intended use (e.g., footwear, upholstery, automotive), required durability, and aesthetic preferences. Understanding these requirements helps you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensures they can meet your specifications.
Step 2: Research Sustainable Sourcing Practices
Given the environmental impact of leather production, prioritize suppliers that practice sustainable sourcing. Look for those that utilize by-products from the meat industry and follow eco-friendly tanning methods, such as vegetable tanning. This not only supports ethical manufacturing but also enhances your brand’s reputation in environmentally conscious markets.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Certifications are critical indicators of a supplier’s commitment to quality and sustainability. Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or Leather Working Group (LWG) certification for responsible leather production. These credentials provide assurance that the supplier adheres to industry standards.
Step 4: Conduct Supplier Audits
Before finalizing your choice, conduct thorough audits of potential suppliers. This includes factory visits, reviewing their operational processes, and assessing their compliance with health and safety regulations. Observing their production environment and practices firsthand can reveal insights into their quality control measures and ethical standards.
Step 5: Request Samples and Technical Specifications
Always request samples of the leather and detailed technical specifications. This step allows you to evaluate the quality, texture, and color of the leather firsthand. Ensure that the samples meet your requirements for thickness, finish, and durability, as these factors are crucial for the final product’s performance.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is vital for successful procurement. Establish clear channels for discussing specifications, timelines, and any potential issues. Regular updates and open lines of communication with your supplier can help prevent misunderstandings and ensure that the production process runs smoothly.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate terms that protect your interests. Discuss pricing, delivery timelines, and quality assurance protocols. Make sure to include clear terms regarding returns or replacements in case the leather does not meet the agreed-upon standards. Establishing favorable terms can mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the leather sourcing process, ensuring they select the right suppliers that align with their quality, sustainability, and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather manufacturing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure in leather manufacturing is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The bulk of costs arises from raw materials, specifically animal hides, which are predominantly by-products from the meat industry. The quality and source of these hides can significantly influence pricing. Additionally, tanning agents (chrome, vegetable tannins, etc.) and finishing chemicals contribute to the material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial throughout the leather manufacturing process, from cleaning and tanning to finishing. Labor costs can vary by region, influenced by local wage standards and expertise levels. In countries with a strong tradition of leather craftsmanship, such as Italy or Germany, labor costs may be higher due to the specialized skills required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production facilities with modern equipment tend to have lower overhead costs, which can lead to competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools and machinery for processes like dyeing and finishing is necessary. The initial investment can be substantial, but it is amortized over time, affecting the per-unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the final product meets specified standards incurs additional costs. This includes testing materials and finished goods, which is critical for maintaining quality and compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary significantly based on the distance from the tannery to the buyer, transportation mode, and logistics provider. These costs can escalate quickly, especially for international shipments.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a margin to cover risks and ensure profitability. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the buyer’s negotiation power.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Leather Manufacturing Costs?
Several factors influence leather pricing, making it essential for buyers to understand their implications:

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that benefit both parties.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to additional processing and material requirements. Buyers should balance customization needs with cost implications.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials typically command higher prices. Certifications (e.g., eco-friendly tanning) may also influence costs, as they often require additional processing.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly impact the total landed cost. Buyers should consider who bears the risk and responsibility at various stages of the shipping process.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for B2B Buyers?
To maximize value and minimize costs, buyers should consider the following negotiation tips:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also logistics, quality control, and potential waste. A lower initial price may not always represent the best overall value.
-
Leverage Market Knowledge: Research prevailing market prices and trends to strengthen your negotiation position. Being informed about competitors can help you push for better deals.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms over time. Loyalty can often be rewarded with discounts or priority service.
-
Be Flexible with Specifications: If possible, be open to alternative materials or processes that may reduce costs while still meeting your quality standards.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific pricing nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be prepared for changes in exchange rates that can impact costs significantly.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Understand the import regulations and associated costs in your country, as these can add significantly to the total price.
-
Cultural Differences in Negotiation Styles: Different regions have varying approaches to negotiation. Familiarizing yourself with these can lead to more effective discussions.
Disclaimer
Pricing in the leather manufacturing industry can fluctuate due to various factors, including market demand, raw material availability, and geopolitical influences. The insights provided here are indicative and should be further researched and verified based on specific purchasing scenarios.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather manufacturing With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Leather Manufacturing
In the quest for sustainable and innovative materials, businesses are increasingly exploring alternatives to traditional leather manufacturing. While leather, derived from animal hides, has long been valued for its durability and aesthetic appeal, emerging materials and technologies offer different advantages. This analysis compares leather manufacturing with two viable alternatives: synthetic leather and bio-based materials. Each solution presents unique benefits and challenges, making it crucial for B2B buyers to understand their options.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Leather Manufacturing | Couro sintético | Bio-Based Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability, naturally breathable | Varies; can mimic leather but less breathable | Typically less durable than leather, but can be engineered for specific uses |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on type | Generally lower, but quality varies | Can be cost-effective, but premium options may be higher |
| Ease of Implementation | Established processes, requires skilled labor | Easier to mass-produce; less labor-intensive | Production processes are evolving; may require new equipment |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning and care | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Maintenance depends on material; some may require special care |
| Best Use Case | Fashion, automotive, and high-end goods | Fashion, accessories, and budget-friendly products | Eco-conscious brands, furniture, and packaging |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Synthetic Leather: Pros and Cons
Synthetic leather, often made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyurethane (PU), offers a lower-cost alternative to traditional leather. Its primary advantage lies in its ability to mimic the look and feel of leather without the use of animal products. Synthetic leather is easier to clean and maintain, making it a popular choice for fashion and accessories. However, it lacks the breathability and longevity of genuine leather, and its production process can be associated with environmental concerns due to plastic use. B2B buyers looking for cost-effective and cruelty-free options may find synthetic leather suitable, but should consider the long-term durability and environmental impact.
Bio-Based Materials: Pros and Cons
Bio-based materials are derived from renewable biological resources and include options like mycelium leather (made from fungi), pineapple leather (from pineapple leaves), and apple leather (from apple waste). These materials are celebrated for their sustainability and reduced environmental footprint. They can offer comparable aesthetics to leather while appealing to eco-conscious consumers. However, bio-based materials may not yet match leather’s durability and longevity. As production technologies improve, these alternatives are becoming more viable for various applications, particularly for brands focused on sustainability. B2B buyers should assess the performance characteristics of bio-based materials in relation to their specific needs and market demands.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between leather manufacturing and its alternatives, B2B buyers must consider multiple factors, including performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance. Each option has its unique strengths and weaknesses, making it essential to align the choice with the target market and product requirements. For businesses prioritizing sustainability, bio-based materials may offer an attractive option, while those looking for cost efficiency might lean towards synthetic leather. Ultimately, understanding the specific needs of their customers and the environmental impact of their choices will guide buyers in making informed decisions that resonate with their brand values and market expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather manufacturing
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Leather Manufacturing?
In leather manufacturing, understanding the critical specifications of leather is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the most important technical properties:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality classification of leather based on its origin, tanning method, and finishing. Higher grades, such as full-grain leather, retain the natural texture and durability of the hide, while lower grades may involve more processing and synthetic additives. For B2B buyers, selecting the right grade ensures that the leather meets product specifications and end-user expectations, particularly in high-end markets.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the acceptable variations in the thickness and dimensions of leather. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.5mm in thickness may be required for specific applications, such as automotive upholstery. Understanding tolerance levels is crucial for manufacturers to ensure consistent quality and fit in their products, minimizing waste and rework.
3. Water Resistance
Water resistance measures the leather’s ability to repel moisture, which is vital for products exposed to the elements, such as footwear and outdoor gear. A higher water resistance rating indicates better performance in wet conditions. Buyers must consider this property when sourcing leather for products that require durability and longevity in challenging environments.
4. Breathability
Breathability refers to the leather’s capacity to allow air and moisture vapor to pass through it. This property is particularly important for apparel and footwear, as it affects comfort and wearability. B2B buyers should prioritize breathable leather to enhance consumer satisfaction and product performance.
5. Colorfastness
Colorfastness indicates how well the leather retains its color when exposed to light, water, and friction. A high colorfastness rating is essential for ensuring that the leather maintains its aesthetic appeal over time. Buyers should pay attention to this property, especially when sourcing leather for fashion and luxury goods.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Leather Manufacturing?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon is crucial for B2B buyers in leather manufacturing. Here are some common terms that can facilitate better communication and negotiations:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces goods that are marketed by another company under its brand. In leather manufacturing, OEMs often supply leather products to brands that focus on design and marketing. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers secure high-quality products while minimizing production costs.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum quantity of leather that a supplier requires for a single order. This term is significant for buyers, as it impacts inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases effectively, ensuring they do not overstock or miss opportunities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for a price quote for specific goods or services. In the leather industry, an RFQ helps buyers obtain competitive pricing and terms from various suppliers. Crafting a clear and detailed RFQ can lead to better negotiation outcomes and cost savings.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers to clarify shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, reducing the risk of disputes and ensuring smooth transactions.
5. Crust Leather
Crust leather is leather that has been tanned but not yet finished. It has undergone the retanning process, which enhances its quality but lacks surface treatments. Buyers may seek crust leather for further processing or customization, allowing for flexibility in product development.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in the leather manufacturing industry can make more informed decisions, foster better supplier relationships, and ultimately enhance their product offerings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather manufacturing Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Leather Manufacturing?
The leather manufacturing sector is currently experiencing significant shifts driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. International B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking high-quality leather products that meet both functional and aesthetic demands. One key trend is the integration of digital technologies in the supply chain, including AI-driven inventory management and blockchain for traceability, which enhances transparency and efficiency. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is reshaping how manufacturers and buyers connect, enabling direct sourcing and reducing reliance on traditional distribution channels.
Another notable market dynamic is the shift towards customization and personalization. B2B buyers are now looking for manufacturers who can offer bespoke solutions tailored to specific market needs, such as unique textures, colors, and finishes. This trend is particularly prevalent in sectors like fashion and automotive, where brand differentiation is paramount. Moreover, the ongoing global push for sustainability is influencing sourcing decisions, as buyers prioritize suppliers who adhere to environmentally friendly practices and demonstrate a commitment to ethical production.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Leather Manufacturing Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are critical components for B2B buyers in the leather manufacturing sector. The environmental impact of traditional tanning processes, which often involve harmful chemicals, has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly interested in sourcing leather from tanneries that utilize vegetable tanning methods or chrome-free alternatives, which are less harmful to both the environment and human health.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. B2B buyers are seeking suppliers who ensure fair labor practices and animal welfare standards throughout the production process. Certifications such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) and Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) play a vital role in providing assurance regarding sustainability claims. By prioritizing suppliers with recognized ‘green’ certifications, buyers can mitigate risks associated with reputational damage and align their procurement strategies with consumer demand for responsible products.

Illustrative image related to leather manufacturing
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Leather Manufacturing Sector Relevant to Today’s B2B Buyers?
The leather manufacturing sector has evolved significantly over the centuries, transitioning from artisanal craftsmanship to a more industrialized approach. Historically, leather was produced through labor-intensive methods that varied greatly by region and culture. Today, advancements in technology have streamlined production processes, allowing for greater efficiency and consistency in product quality.
The modern era has also introduced a heightened awareness of environmental and ethical issues within the leather supply chain. As a result, there has been a marked shift towards sustainable practices and transparency. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers, as understanding the historical context of leather production can inform better sourcing decisions and foster relationships with suppliers who are committed to ethical standards and innovation. As the market continues to adapt, staying informed about these trends will be crucial for buyers aiming to remain competitive in the global leather landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather manufacturing
-
How do I choose a reliable leather supplier for my business?
To select a dependable leather supplier, begin by researching their industry reputation and customer reviews. Verify their certifications, such as ISO or environmental sustainability standards, to ensure quality compliance. Attend trade shows or exhibitions to meet suppliers face-to-face and assess their product range. Request samples to evaluate the leather quality and discuss their production capabilities, including minimum order quantities (MOQs) and customization options. Establish clear communication regarding lead times, payment terms, and logistics to avoid potential issues during the procurement process. -
What types of leather are best suited for different applications?
The best type of leather depends on the intended application. Full-grain leather is ideal for high-quality goods like luxury handbags and footwear, while top-grain leather offers a balance of quality and cost-effectiveness, suitable for everyday items. Suede is perfect for fashion accessories but less durable, while vegetable-tanned leather is preferred for eco-conscious products. For automotive applications, consider chrome-tanned leather for its durability and resistance. Understanding these characteristics helps in making informed purchasing decisions tailored to specific needs. -
What are the common payment terms in leather manufacturing?
Payment terms can vary widely in leather manufacturing. Standard practices often include a deposit of 30-50% upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or after quality inspection. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms for established relationships. It’s essential to clarify payment methods (e.g., bank transfer, letter of credit) and any penalties for late payments. Negotiating favorable terms can enhance cash flow management, especially for international transactions, where currency exchange rates and fees may apply. -
How can I ensure the leather quality meets my standards?
To ensure leather quality, establish clear specifications before placing an order. Request samples and conduct quality assurance checks upon delivery. Collaborate with suppliers to understand their quality control processes, including testing for durability, colorfastness, and environmental compliance. Implement a standardized inspection process for each shipment, and consider third-party testing for added assurance. Building a strong partnership with your supplier can facilitate better quality management and compliance with your specific requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing leather internationally?
When sourcing leather internationally, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties. Evaluate the total landed cost, which includes shipping, insurance, and tariffs, to determine the true cost of procurement. Work with logistics partners experienced in handling leather goods to avoid potential damage during transit. Ensure that the supplier provides proper documentation for customs clearance, including certificates of origin and compliance with international trade standards. Timely communication with all parties involved can streamline the logistics process. -
What customization options are available for leather products?
Many leather suppliers offer customization options, including color, texture, and finish. You can request specific tanning methods or treatments to achieve desired properties, such as water resistance or softness. Embossing, printing, or dyeing can create unique designs tailored to your brand. Discuss your customization needs early in the negotiation process, as some suppliers may have limitations based on their production capabilities or lead times. Be clear about your expectations to ensure the final product aligns with your vision. -
How do I verify the sustainability practices of a leather manufacturer?
To verify a leather manufacturer’s sustainability practices, request documentation of their sourcing and production processes. Look for certifications like the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or Leather Working Group (LWG) that indicate adherence to environmental standards. Engage in discussions about waste management, water usage, and chemical treatments used in tanning. Transparency in their supply chain is crucial; inquire about their suppliers and whether they prioritize ethical sourcing of raw materials. Conducting site visits can provide firsthand insight into their operations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for leather products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for leather products can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 500 square meters for bulk orders, but smaller quantities may be available for custom products. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their flexibility regarding MOQs. Some manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for first-time buyers or sample orders, allowing you to test the market without committing to large quantities.
Top 5 Leather Manufacturing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Nera Tanning – Leather Production Process
Domain: neratanning.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: The leather making process involves five key steps: 1. Preservation – allows transport and storage of raw material. 2. Preparatory operations (beamhouse) – cleaning hides, opening collagen structure, fleshing, and processing with base chemicals. 3. Tanning – transforming collagen into leather using various agents like Zeology, chrome, or vegetable extracts. 4. Post-tannage (Wet-end) – applying syn…
2. Steel Horse Leather – Premium Leather Bags
Domain: steelhorseleather.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: The Dagny Weekender | Large Leather Duffle Bag – $349.00 (was $399.00), The Endre Weekender | Vintage Leather Duffle Bag – $289.00 (was $329.00), The Welch Briefcase | Vintage Leather Messenger Bag – $249.00 (was $279.00), The Hagen Backpack | Vintage Leather Backpack – $249.00 (was $299.00).
3. Love Your Leather – High-Quality Leather Production
Domain: loveyourleather.ca
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Leather production involves 23 detailed steps, starting from curing hides to final measurement. The process includes soaking, liming, fleshing, tanning with minerals, oils, or vegetables, dyeing, fatliquoring, and finishing. Each step is crucial for transforming raw animal hides into high-quality leather, which is known for its durability and flexibility. The entire process takes an average of 10 …
4. Spinneybeck – Full Grain Leathers
Domain: spinneybeck.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Spinneybeck produces full grain leathers at a tannery in Arzignano, Italy. The leather manufacturing process involves six phases: raw material preparation, tanning, retanning, and final inspection. The raw material is sourced from Europe, particularly Italy, Southern Germany, and Denmark, ensuring high-quality hides. The hides undergo a series of treatments including desalting, soaking, defleshing…
5. Ahlstrom – Leather Production Process
Domain: ahlstrom.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: This company, Ahlstrom – Leather Production Process, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather manufacturing
In the realm of leather manufacturing, strategic sourcing stands as a cornerstone for success. By understanding the intricate processes involved—from preservation and cleaning to tanning and finishing—international buyers can make informed decisions that align with sustainability goals and market demands. Leather, primarily a by-product of the food industry, presents a unique opportunity for businesses to engage in a circular economy, ensuring that resources are utilized efficiently and responsibly.
Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize partnerships with tanneries that emphasize sustainable practices and quality craftsmanship. This not only enhances product longevity but also meets the growing consumer demand for ethically sourced materials. By leveraging insights into the supply chain, businesses can optimize their procurement strategies, reduce costs, and improve product offerings.
As we look toward the future, the leather industry is poised for innovation, driven by advancements in sustainable technologies and changing consumer preferences. Embrace this opportunity to source responsibly and position your brand at the forefront of the market. Connect with reliable suppliers and stay informed on best practices to ensure your leather products meet both quality standards and ethical expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.