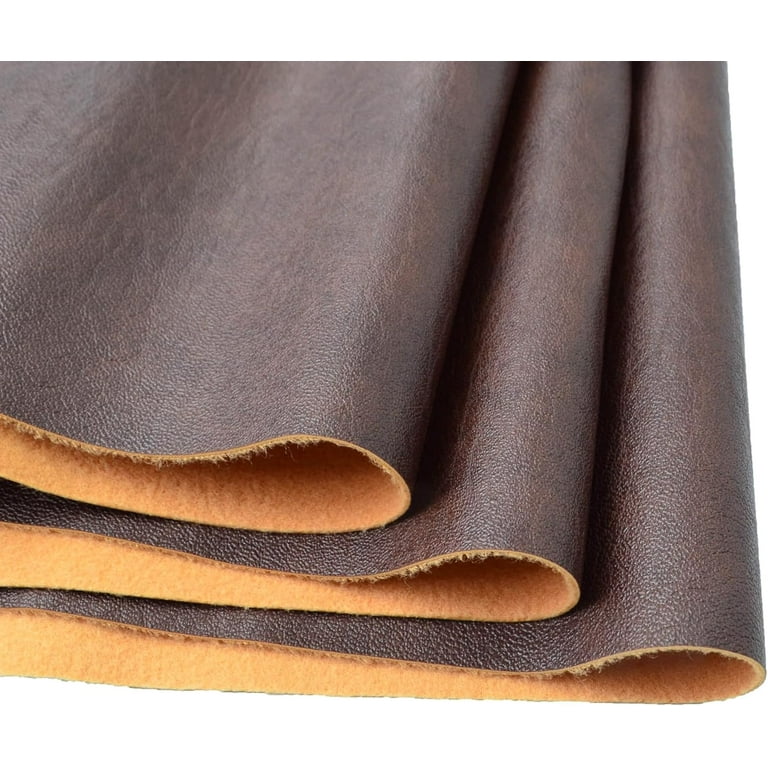
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is suede leather
In the competitive landscape of leather goods, understanding what suede leather is and how to effectively source it can be a game-changer for international B2B buyers. Suede, characterized by its soft texture and unique aesthetic, presents both opportunities and challenges in sourcing high-quality materials for various applications, from fashion accessories to upholstery. As businesses expand their reach into diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for reliable, durable suede leather continues to grow.
This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of suede leather, including its types, sourcing strategies, applications, and the factors influencing cost. We will explore the differences between suede and traditional leather, examine the best practices for vetting suppliers, and provide insights on market trends that could impact your purchasing decisions. With a clear focus on empowering B2B buyers, this guide will equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions that align with your business goals.
By understanding the intricacies of suede leather, including its production processes and quality indicators, you can confidently navigate the global market and establish lasting relationships with reputable suppliers. This guide serves as your roadmap to sourcing premium suede leather that not only meets your specifications but also enhances your product offerings in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 What Is Suede Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is suede leather
- Understanding what is suede leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is suede leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is suede leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is suede leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is suede leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is suede leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is suede leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is suede leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is suede leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is suede leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is suede leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is suede leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what is suede leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sheepskin Suede | Soft, lightweight, smooth nap | Fashion apparel, luxury goods | Pros: Luxurious feel, lightweight; Cons: Less durable, prone to staining. |
| Cowhide Suede | Thicker, rougher texture, more durable | Upholstery, rugged footwear | Pros: Durable, versatile; Cons: Heavier, less soft than other suedes. |
| Pigskin Suede | Soft, strong, and somewhat water-resistant | Workwear, casual footwear | Pros: Resilient, good for outdoor use; Cons: Limited availability, can be thicker. |
| Nubuck | Similar to suede but made from the outer hide | High-end footwear, luxury bags | Pros: Durable, rich texture; Cons: Requires special care, more expensive. |
| Deerskin Suede | Exceptionally soft, flexible, and lightweight | High-quality garments, accessories | Pros: Soft and supple, excellent for clothing; Cons: Less durable than cowhide. |
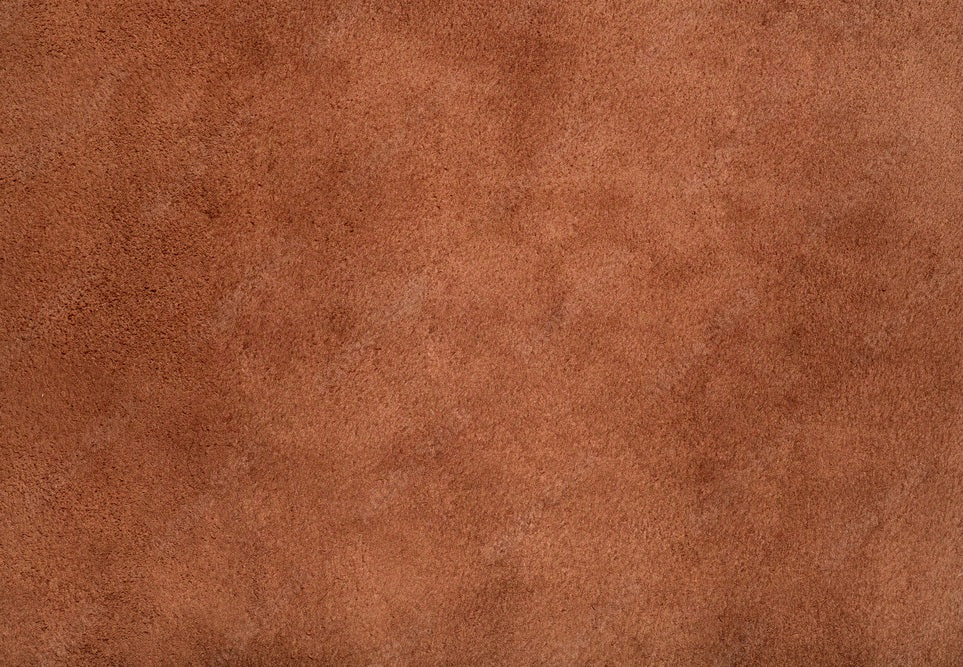
What are the Characteristics of Sheepskin Suede?
Sheepskin suede is renowned for its exceptionally soft texture and lightweight feel, making it a popular choice in the fashion industry for items like jackets, shoes, and luxury accessories. Its smooth nap provides a delicate appearance, appealing to high-end markets. B2B buyers should consider its suitability for products that require a luxurious touch, though they must also be aware that it is less durable and more susceptible to staining compared to other types of suede.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
How Does Cowhide Suede Differ from Other Types?
Cowhide suede is characterized by its thicker and rougher texture, which contributes to its durability and versatility. This type is often utilized in upholstery and rugged footwear, appealing to industries that demand robust materials. B2B buyers should note that while cowhide suede offers excellent longevity, its heavier weight and less soft feel may not suit all applications, especially those requiring a refined aesthetic.
What are the Advantages of Pigskin Suede?
Pigskin suede stands out for its combination of softness and strength, often regarded as somewhat water-resistant. This makes it ideal for workwear and casual footwear, where durability is crucial. For B2B buyers, the resilience of pigskin suede can be a significant selling point, particularly in outdoor or industrial applications. However, its availability can be limited, and its thickness may not be suitable for every design requirement.
Why is Nubuck Considered a Premium Option?
Nubuck, while similar to suede, is made from the outer layer of the hide, resulting in a more durable and rich texture. It is often used in high-end footwear and luxury bags, attracting B2B buyers looking for premium materials. However, nubuck requires special care to maintain its appearance, and its higher price point may deter some buyers. Understanding the balance between quality and maintenance is essential for businesses considering nubuck for their product lines.
What Makes Deerskin Suede Unique?
Deerskin suede is celebrated for its exceptional softness, flexibility, and lightweight nature. It is particularly favored in high-quality garments and accessories, where a soft touch is paramount. B2B buyers should consider deerskin for clothing that prioritizes comfort and luxury, though they should be mindful of its lower durability compared to cowhide. This makes it less suitable for heavy-duty applications, emphasizing the need for careful selection based on intended use.
Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
Key Industrial Applications of what is suede leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is suede leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion and Apparel | Suede jackets and outerwear | Enhances brand image through luxury appeal | Ensure quality and texture consistency; consider local climate needs |
| Footwear | Casual and formal shoes | Offers a unique aesthetic that differentiates products | Source from reputable tanneries; check for durability and maintenance needs |
| Automotive | Upholstery for luxury vehicles | Provides a premium feel, enhancing customer experience | Focus on durability and stain resistance; compliance with automotive standards |
| Furniture and Interiors | Upholstered furniture and home accessories | Adds a touch of elegance and comfort to interiors | Assess fire-retardant treatments; consider sustainability certifications |
| Sporting Goods | Equipment and apparel for outdoor activities | Offers lightweight, breathable options for comfort | Evaluate wear resistance and ease of cleaning; check for eco-friendly sourcing |
How is Suede Leather Used in Fashion and Apparel?
In the fashion and apparel industry, suede leather is predominantly used for jackets and outerwear. Its soft, textured surface provides a luxurious feel that appeals to consumers looking for high-end fashion items. By incorporating suede into their collections, brands can elevate their image and attract a discerning clientele. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing high-quality suede that maintains consistency in texture and color, particularly in regions with varying climates, such as the Middle East and Europe, where seasonal collections may require different suede weights.
What Role Does Suede Play in Footwear?
Suede is widely utilized in both casual and formal footwear, offering a distinctive aesthetic that sets products apart in a competitive market. The material’s unique texture and softness make it an attractive choice for shoe manufacturers aiming to provide comfort without sacrificing style. When sourcing suede for footwear, B2B buyers must ensure the material is durable enough to withstand daily wear and easy to maintain, especially in humid climates found in South America and parts of Africa.
Why is Suede Important in Automotive Upholstery?
In the automotive sector, suede leather is favored for its premium appearance and tactile quality, enhancing the overall customer experience in luxury vehicles. Its use in upholstery can significantly boost the perceived value of a car, attracting buyers looking for comfort and sophistication. When sourcing suede for automotive applications, businesses must consider factors like durability, stain resistance, and compliance with automotive safety standards to ensure long-lasting performance.
How is Suede Used in Furniture and Interiors?
Suede leather finds its place in the furniture industry, where it is used for upholstered furniture and home accessories. Its soft texture adds an element of elegance and comfort to interiors, making it a preferred choice for high-end furniture lines. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing suede that meets fire-retardant regulations and sustainability certifications, especially in markets like Europe where consumer awareness of eco-friendly products is growing.
What is the Application of Suede in Sporting Goods?
In the realm of sporting goods, suede leather is often used for equipment and apparel designed for outdoor activities. Its lightweight and breathable nature makes it an ideal choice for creating comfortable gear that doesn’t compromise on style. Buyers in this sector should evaluate the wear resistance of suede and consider ease of cleaning, particularly for products intended for rugged use in diverse environments, such as those found in Africa and South America.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is suede leather’ & Their Solutions
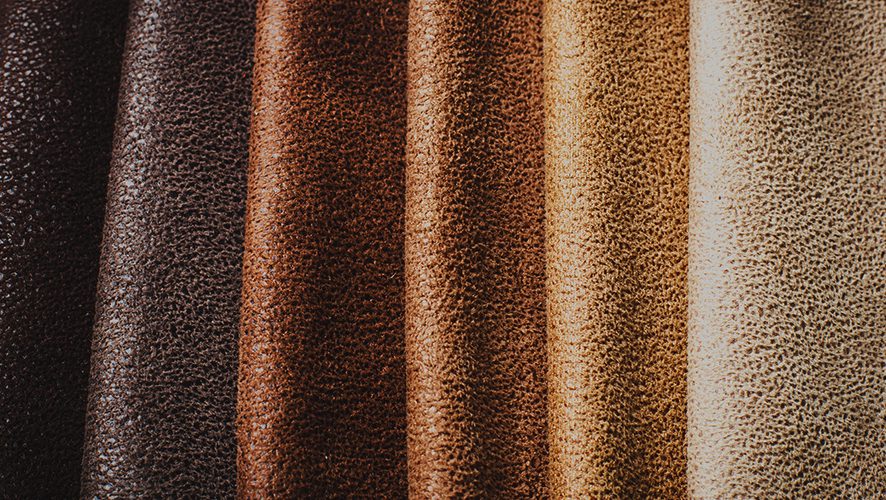
Scenario 1: Understanding Quality Variations in Suede Leather
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the challenge of differentiating between various grades of suede leather. This is particularly crucial when sourcing for high-end fashion items or upholstery. With multiple types of suede available—such as sheepskin, cowhide, and goat suede—buyers may find it difficult to determine which material best suits their product specifications. This lack of clarity can lead to costly mistakes, including purchasing inferior quality suede that does not meet customer expectations or industry standards.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
The Solution: To effectively navigate the complexities of suede quality, buyers should develop a clear set of criteria that outlines the specifications needed for their intended use. This could include factors such as softness, durability, and price point. Engaging with reputable suppliers who provide detailed information on their suede products is essential. Requesting samples of different suede types can help buyers assess the texture and quality firsthand. Additionally, leveraging certifications or industry standards can further ensure that the suede meets necessary quality benchmarks. Establishing a relationship with a knowledgeable supplier who understands the nuances of suede can also provide valuable insights into the best options available for specific applications.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Maintenance and Care Concerns with Suede Leather
The Problem: One common pain point for B2B buyers is the perceived difficulty in maintaining suede leather products. Unlike traditional leather, suede is more susceptible to stains and water damage, leading to concerns about its long-term durability and appearance. Buyers in fashion or upholstery industries often worry that their customers will be dissatisfied if the products require excessive upkeep or if they wear out quickly.
The Solution: To address these concerns, suppliers can provide comprehensive care guides tailored specifically for suede leather products. This should include detailed instructions on cleaning methods, protective treatments, and maintenance routines. For instance, recommending the use of a suede protector spray can help prevent stains and water damage. Additionally, offering training sessions or workshops for retailers on proper suede care can empower them to educate their customers effectively. Buyers should also consider sourcing suede that has been treated for enhanced durability, thus alleviating concerns about everyday wear and tear.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
Scenario 3: Navigating Market Trends and Customer Preferences in Suede Leather
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently face the challenge of keeping up with evolving market trends and customer preferences when it comes to suede leather. As fashion and design industries are heavily influenced by seasonal trends, buyers need to be agile in their sourcing strategies. Misjudging trends can lead to overstocking unpopular items or missing out on high-demand products, which can significantly impact profitability.
The Solution: To stay ahead of market trends, buyers should implement a robust market analysis strategy. This includes monitoring fashion shows, industry reports, and social media trends that highlight emerging styles and consumer preferences. Collaborating with trend forecasting agencies can also provide valuable insights into what colors, textures, and styles are gaining popularity. Additionally, engaging in direct communication with end consumers through surveys or feedback channels can help buyers understand their specific preferences. By aligning their sourcing strategies with these insights, B2B buyers can more effectively position their products in the market, reducing the risk of excess inventory and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is suede leather
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Suede Leather Production?
When considering suede leather for various applications, it is essential to analyze the common materials used in its production. Each material has distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact product performance and suitability for specific markets.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
What Are the Key Properties of Lambskin Suede?
Lambskin suede is renowned for its softness and luxurious feel, making it a popular choice for high-end fashion items such as jackets, shoes, and accessories. The key properties of lambskin suede include a fine nap texture and lightweight nature. It generally performs well in moderate temperatures but is less durable under extreme wear conditions.
Pros: The primary advantage of lambskin suede is its exceptional softness and comfort, which enhances the overall user experience. It is also relatively easy to dye, allowing for a wide range of colors and styles.
Cons: However, lambskin suede is less durable compared to other types, making it more susceptible to wear and tear. Its higher cost can also be a barrier for mass-market applications.
How Does Cowhide Suede Compare in Terms of Performance?
Cowhide suede is thicker and more robust than lambskin, making it suitable for applications requiring greater durability, such as upholstery and workwear. Its properties include a coarse texture and a higher resistance to wear and tear, making it ideal for heavy-duty use.
Pros: The key advantage of cowhide suede is its durability, which allows it to withstand harsher conditions and extend the lifespan of products. It is also more cost-effective than lambskin, making it a favorable option for bulk purchases.
Cons: The downside is that cowhide suede can be less comfortable and flexible than lambskin, which may limit its use in fashion-forward applications. Additionally, its thicker nature can complicate manufacturing processes, requiring more specialized equipment.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
What Is the Role of Pigskin Suede in the Market?
Pigskin suede is another material used in suede production, characterized by its unique texture and durability. It is often utilized in applications such as gloves and footwear, where both comfort and strength are essential.
Pros: Pigskin suede offers a good balance between durability and comfort, making it versatile for various applications. It is also relatively resistant to moisture, which can be advantageous in specific environments.
Cons: However, pigskin suede can be less aesthetically appealing compared to lambskin or cowhide, limiting its use in luxury markets. Its processing can also be more complex, impacting production timelines.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
What Considerations Should International B2B Buyers Keep in Mind?
When sourcing suede leather materials, international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider compliance with local regulations and standards. Common standards such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS may apply, depending on the end-use application. Additionally, cultural preferences can influence material choice; for example, softer lambskin may be favored in luxury markets, while more durable cowhide may be preferred in industrial applications.
Summary Table of Suede Leather Materials
| Materiał | Typical Use Case for what is suede leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lambskin Suede | High-end fashion items (jackets, shoes) | Exceptional softness and comfort | Less durable, higher cost | High |
| Cowhide Suede | Upholstery, workwear | High durability and cost-effectiveness | Less comfortable, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Pigskin Suede | Gloves, footwear | Good balance of durability and comfort | Aesthetically less appealing | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the various materials used in suede leather production, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is suede leather
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Suede Leather?
Suede leather production involves a series of meticulous stages that transform raw animal hides into the final product. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers who seek to ensure quality and consistency in their suede leather sourcing.
Material Preparation: What Steps Are Involved?
The first stage in suede manufacturing is the careful selection and preparation of animal hides. Typically sourced from lamb, goats, pigs, or calves, these hides must be cleaned and treated to remove any impurities. The hides are soaked in water and treated with chemicals to prevent decay. This process, known as liming, ensures that the collagen fibers remain intact.
Once treated, the hides are split to separate the top grain from the flesh side. The flesh side is what will become suede, characterized by its soft texture. This splitting process is critical as it determines the thickness and overall quality of the suede.
Forming: How Is Suede Shaped into Final Products?
After preparation, the suede undergoes a forming process where it is cut and shaped into various products. This may include jackets, shoes, bags, and upholstery materials. Skilled artisans often use cutting machines that ensure precision, maintaining the integrity of the suede’s nap, which is essential for achieving the desired aesthetic and tactile quality.
In addition to cutting, some manufacturers may apply techniques like embossing or laser engraving to enhance the visual appeal of the suede. These techniques allow for customization and differentiation in the marketplace, which can be a selling point for B2B buyers looking for unique offerings.
Assembly: What Are the Key Considerations?
During the assembly stage, the formed suede pieces are stitched together to create the final product. This process requires skilled craftsmanship to ensure that seams are strong and aesthetically pleasing. The choice of thread and stitching technique can significantly impact the durability and appearance of the finished item.
Quality control at this stage is crucial. Ensuring that stitching is consistent and that there are no visible flaws can affect the product’s marketability. For B2B buyers, understanding the assembly methods used by suppliers can provide insights into the potential longevity and performance of the suede products.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
Finishing: What Techniques Enhance Suede Quality?
The finishing process involves treating the suede to improve its texture and appearance. Techniques such as buffing, dyeing, and applying protective coatings are common. Buffing enhances the nap, giving the suede its characteristic softness, while dyeing allows for a range of color options.
Protective coatings can also be applied to increase water resistance and durability, addressing common concerns regarding suede maintenance. B2B buyers should inquire about the finishing processes to understand how these treatments might affect the product’s performance in various environments.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of suede leather manufacturing. Buyers should be aware of both international and industry-specific standards that suppliers must adhere to in order to ensure product quality and safety.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Suede Leather?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management standards globally. It focuses on meeting customer expectations and delivering customer satisfaction. Suppliers that comply with ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to maintaining high-quality standards throughout their manufacturing processes.
Additionally, B2B buyers should consider other certifications that may be relevant, such as the OEKO-TEX Standard 100, which ensures that textiles are free from harmful substances. This is particularly important for buyers in industries like fashion and upholstery, where consumer safety is paramount.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in suede leather production typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage checks the quality of raw materials upon arrival. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers conduct thorough inspections to ensure that only high-quality hides are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor processes and ensure compliance with quality standards. Buyers can request reports detailing these inspections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a final inspection ensures that they meet specified quality criteria. This includes checking for defects, color consistency, and overall craftsmanship.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they receive high-quality suede leather products. Here are actionable steps to consider:
What Steps Can Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
Conducting audits is one of the most effective ways to verify supplier quality. Buyers should consider performing on-site inspections or hiring third-party inspection services to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This can provide insights into their adherence to industry standards and their overall operational efficiency.
What Documentation Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should request documentation that outlines the supplier’s quality control processes, including:
-
Quality Assurance Reports: These documents provide insights into the testing methods used and the outcomes of inspections.
-
Certificates of Compliance: Suppliers should provide certifications that demonstrate adherence to international standards, such as ISO 9001 or OEKO-TEX.
-
Testing Reports: Buyers can request reports from common testing methods, such as tensile strength tests, colorfastness tests, and water resistance evaluations.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers operating in diverse markets, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have varying standards and expectations for suede leather quality. For example, buyers from Europe may prioritize eco-friendly production practices, while those in the Middle East might focus on durability due to climatic conditions. Understanding these regional preferences can guide buyers in selecting suppliers that align with their specific market demands.
What Challenges Might Buyers Face in Ensuring Quality?
International buyers may face challenges such as language barriers, differences in quality expectations, and logistical issues. Establishing clear communication channels and maintaining ongoing relationships with suppliers can help mitigate these challenges. Additionally, leveraging technology for real-time tracking and communication can enhance transparency throughout the supply chain.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for suede leather is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production, relevant quality standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their sourcing strategies and ultimately lead to successful business outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is suede leather’
In the competitive landscape of sourcing materials, understanding the nuances of suede leather is crucial for B2B buyers. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help you effectively procure suede leather, ensuring you meet your business needs while maximizing quality and value.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by establishing clear technical specifications for the suede leather you require. This includes factors such as thickness, texture, and finish. Understanding these parameters will guide your sourcing decisions and ensure that the leather meets the intended application, whether for fashion items, upholstery, or accessories.
- Grubość: Specify the desired thickness based on the end product’s requirements.
- Texture: Determine if you need a soft, smooth feel or a more rugged appearance.
Step 2: Research Different Types of Suede
Familiarize yourself with the various types of suede available in the market. Suede can be made from different animal hides, each offering unique qualities and appearances. Knowing the differences can influence your sourcing strategy based on factors like durability and cost.
- Sheepskin Suede: Soft and lightweight, ideal for high-end fashion.
- Cowhide Suede: More robust and rougher, suitable for durable applications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before finalizing a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, product samples, and references from other businesses in your industry. This step is essential to ensure that the supplier can meet your quality standards and delivery timelines.
- References: Ask for testimonials from clients who have purchased similar products.
- Samples: Evaluate the quality of suede through physical samples to confirm it meets your specifications.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and adhere to industry standards. Certifications related to environmental sustainability, animal welfare, and product quality can be indicators of a reputable supplier. This verification helps mitigate risks associated with sourcing materials.
- Environmental Compliance: Check for certifications like ISO 14001.
- Quality Standards: Look for adherence to leather quality standards such as ISO 17100.
Step 5: Assess Pricing Structures and Terms
Discuss pricing structures upfront to ensure transparency and avoid future misunderstandings. Consider factors such as minimum order quantities, payment terms, and shipping costs. Understanding these elements will help you budget effectively and manage cash flow.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing tiers based on order volume.
- Payment Terms: Clarify payment methods and timelines to avoid delays.
Step 6: Negotiate Contracts and Agreements
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, negotiate terms and conditions that protect your interests. Ensure that contracts clearly outline specifications, delivery schedules, and penalties for non-compliance. This step is vital for establishing a solid working relationship and ensuring accountability.
- Delivery Timelines: Specify delivery dates and any penalties for delays.
- Quality Assurance: Include clauses that allow for quality checks upon delivery.
Step 7: Plan for Quality Control
Implement a quality control plan to monitor the suede leather’s quality upon receipt. This should involve inspecting the leather for any defects or inconsistencies that may affect your final product. Establishing a robust quality control process helps maintain high standards and ensures customer satisfaction.
- Inspection Protocols: Develop a checklist for inspecting suede quality.
- Feedback Loop: Create a process for addressing any quality issues with the supplier promptly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing suede leather, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is suede leather Sourcing
When sourcing suede leather, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing factors is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will equip you with actionable insights to navigate the complexities of suede leather procurement effectively.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Suede Leather Sourcing?
The cost structure of suede leather is influenced by several components:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the quality of the animal hide. Suede is typically derived from lambskin, goat, or cowhide, with lambskin being the most expensive due to its softness and delicacy. Prices can vary significantly based on the type of hide and its sourcing origin.
-
Labor: Labor costs are associated with both the tanning and manufacturing processes. Skilled artisans are often required for high-quality suede production, which can increase labor costs. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing but may compromise on quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, but investments in advanced technology might be necessary for high-quality production.
-
Tooling: The costs for molds, dies, and other production tools can be significant, especially for custom designs. Custom tooling can increase initial costs but may lead to better product differentiation in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the suede leather meets specific quality standards involves additional QC costs. This is particularly important for B2B buyers who require certification for quality and compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the distance, shipping method, and Incoterms. Import duties and tariffs can also affect the final price, particularly for buyers in regions with strict trade regulations.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on the competitive landscape and their positioning in the market.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Suede Leather Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of suede leather:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically benefit from lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom suede products often come with higher costs due to the additional resources and time required for bespoke production. Clearly defining specifications can help manage costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Higher-quality hides or those with specific certifications (like eco-friendly tanning processes) will command premium prices.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and financial stability of suppliers are crucial. Established suppliers may charge more but can offer better quality assurance and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms is vital. Different Incoterms can affect the total cost of ownership, including responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following tips to optimize your sourcing strategy:
-
Negotiate: Always negotiate pricing, especially on larger orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the purchase price but also logistics, potential tariffs, and quality assurance costs. A lower initial price may lead to higher long-term costs if quality issues arise.
-
Stay Informed About Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional market trends and pricing dynamics. Prices can fluctuate based on supply chain disruptions, currency exchange rates, and seasonal demand.
-
Establish Strong Relationships with Suppliers: Building rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms, improved communication, and more favorable pricing in future transactions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for suede leather can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. Buyers should seek multiple quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing aligned with their quality and specification needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is suede leather With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Suede Leather: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of leather products, suede leather stands out for its unique texture and aesthetic appeal. However, various alternatives exist that may cater to different business needs, preferences, and budgets. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of suede compared to these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is Suede Leather | Alternative 1 Name: Nubuck Leather | Alternative 2 Name: Synthetic Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Soft, luxurious feel; less durable than full-grain leather | Durable with a similar texture to suede; more resistant to stains | Highly durable; resistant to moisture and wear; can mimic various textures |
| Cost | Generally moderate to high, depending on animal type and quality | Moderate; can be more expensive than suede due to processing | Typically lower; offers cost-effective solutions for bulk purchases |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to work with for fashion items; requires specific care | Similar ease of use; may require specialized tools for finishing | Very easy to work with; widely available in various forms and styles |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning and special care to avoid stains | Requires similar care but is more resistant to wear | Low maintenance; usually easy to clean and maintain |
| Best Use Case | Fashion items, jackets, and casual footwear | High-quality fashion items and accessories where durability is key | Cost-effective solutions for mass production, upholstery, and casual wear |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Nubuck Leather?
Nubuck leather, made from the outer layer of the hide, is often compared to suede due to its similar texture. However, it is more durable and resistant to stains, making it a suitable alternative for high-end products that need to withstand wear over time. The downside is that nubuck can be more expensive than suede, and it also requires care to maintain its appearance. Businesses seeking to balance luxury with durability may find nubuck to be an ideal choice.
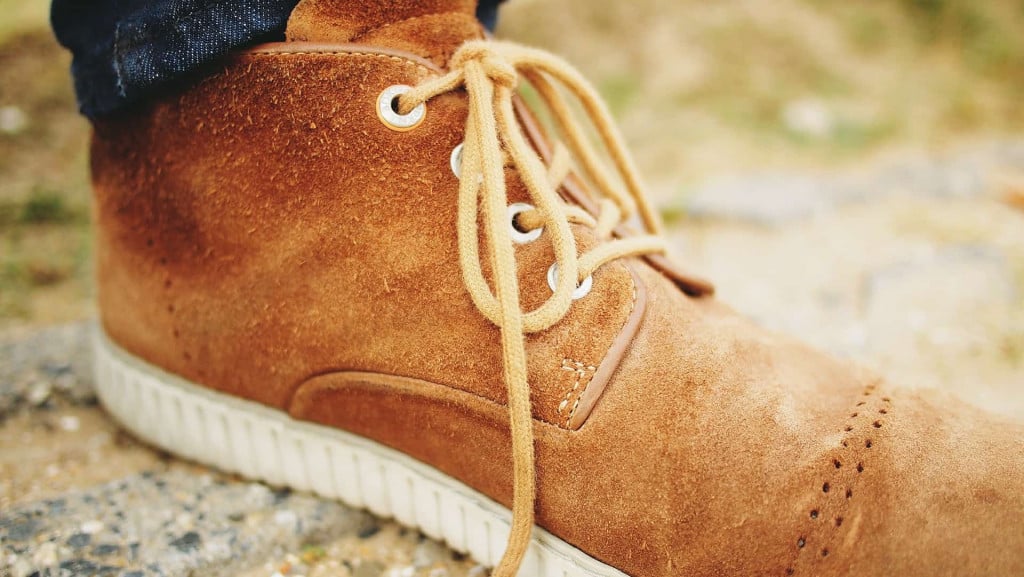

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
How Does Synthetic Leather Compare to Suede Leather?
Synthetic leather, or faux leather, offers an affordable and versatile alternative to suede. It mimics the look and feel of real leather while being highly resistant to moisture and wear, making it suitable for various applications, from upholstery to fashion. The primary advantage lies in its cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance. However, synthetic leather may lack the authentic texture and breathability of natural suede, which could be a consideration for brands emphasizing luxury and craftsmanship.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When selecting between suede leather and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including product application, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Suede offers a unique aesthetic and soft texture, ideal for fashion-oriented items. In contrast, nubuck provides durability with a similar look, while synthetic leather serves as a cost-effective solution for high-volume production. By carefully evaluating these options, businesses can align their material choices with their brand values and customer expectations, ensuring a successful outcome in their product offerings.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is suede leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Suede Leather?
When it comes to sourcing suede leather for various applications, understanding its technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality classification of suede leather, which can vary significantly based on the animal source and processing method. Common grades include top-grain, genuine, and split suede. Higher grades, like top-grain, offer better durability and aesthetic appeal, making them suitable for high-end products. For manufacturers and retailers, selecting the appropriate material grade directly impacts product quality and customer satisfaction.
2. Thickness
The thickness of suede leather is measured in millimeters and can range from 0.6 mm to 2.0 mm. Thicker suede tends to be more durable and suitable for products that require longevity, such as footwear and jackets. Understanding thickness is vital for companies to ensure that the suede meets the intended use and performance criteria, especially in high-demand markets.
3. Nap Height
Nap height refers to the length of the raised fibers on the surface of suede. A higher nap can provide a softer feel and a more luxurious appearance but may also be more susceptible to wear and staining. For B2B buyers, selecting the right nap height is essential based on the intended use of the suede, as it affects both aesthetics and maintenance requirements.
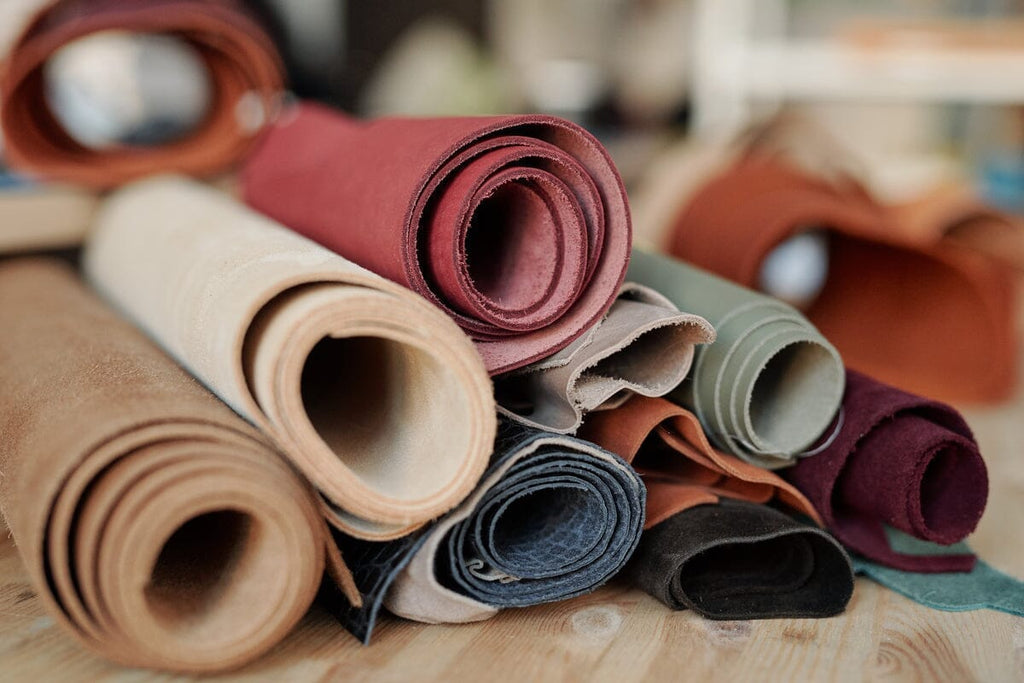

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
4. Color Fastness
Color fastness indicates how well the dye used in suede retains its color when exposed to light, washing, or abrasion. This property is particularly important for products that will undergo frequent use or exposure to the elements. Buyers should ensure that the suede meets industry standards for color fastness to maintain product integrity and customer satisfaction.
5. Water Resistance
While suede is known for its softness, it is also more absorbent than traditional leather. Some manufacturers treat suede to enhance its water resistance, making it suitable for specific applications like outdoor apparel. Understanding the level of water resistance is essential for B2B buyers to ensure that the suede will perform adequately in its intended environment.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Suede Leather Industry?
Navigating the world of suede leather involves familiarizing oneself with key industry terms that facilitate effective communication and transactions. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should know:

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or products that are used in another company’s end product. In the suede leather industry, an OEM may supply finished suede goods to a brand that markets them under its own label. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for companies looking to expand their product lines or enter new markets.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps companies assess whether a supplier aligns with their purchasing strategy and production needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products, such as suede leather. This process is essential for B2B buyers to obtain competitive pricing and understand the market value of the materials they intend to purchase.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping, insurance, and risk management when sourcing suede leather from global suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the suede leather industry, lead times can vary based on factors such as production capacity and shipping logistics. Awareness of lead times is essential for buyers to effectively plan their inventory and meet market demands.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their sourcing strategy for suede leather.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is suede leather Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Suede Leather Sector?
The suede leather market is currently experiencing significant growth driven by diverse global factors. Increasing demand for luxury goods, particularly in the fashion and automotive industries, is a primary driver. Regions such as Europe and the Middle East have seen a resurgence in high-end suede products, including footwear, jackets, and upholstery, catering to a growing consumer preference for soft textures and premium quality. Meanwhile, emerging markets in Africa and South America are witnessing a rise in local craftsmanship, fostering a unique blend of traditional and contemporary suede products that appeal to both local and international buyers.
Technological advancements in production processes are also reshaping the suede leather landscape. Innovations in tanning methods, such as eco-friendly and water-saving techniques, are becoming more prevalent, allowing manufacturers to meet rising sustainability expectations. Furthermore, digital platforms for sourcing and procurement are making it easier for B2B buyers to connect with suppliers globally, enhancing transparency and efficiency in the supply chain. This shift towards digitalization is particularly beneficial for buyers in regions like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia, where traditional sourcing practices are evolving.
How Is Sustainability Impacting the Sourcing of Suede Leather?
The environmental impact of leather production, including suede, has become a crucial concern for B2B buyers. The leather industry is often scrutinized for its resource-intensive processes and carbon footprint. Consequently, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who adopt environmentally friendly methods, such as vegetable tanning and the use of recycled materials, to minimize their ecological impact.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining importance, as consumers demand transparency regarding the origins of their products. Certifications such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) and Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) are becoming benchmarks for responsible sourcing, indicating that products meet rigorous environmental and social standards. B2B buyers from regions like Africa and Europe are particularly keen on these certifications, as they enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Incorporating these sustainable practices not only helps mitigate environmental issues but also opens up new market opportunities for suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing.
What Is the Historical Context of Suede Leather in the Global Market?
The history of suede leather dates back to ancient civilizations, where animal hides were utilized for clothing and protection. The term “suede” originates from the French phrase “gants de Suede,” meaning “gloves from Sweden,” reflecting its association with luxury and fine craftsmanship. Throughout the 20th century, suede became synonymous with high fashion, particularly in the realm of footwear and apparel.
As global markets evolved, so did the methods of production and the types of animal hides used, with lambskin and cowhide emerging as the most popular choices. The evolution of suede has been marked by its adaptability to changing fashion trends and consumer preferences, which has solidified its status in both luxury and everyday markets. Today, the historical significance of suede continues to influence modern design and manufacturing practices, making it a vital component of the global leather industry.
In conclusion, the suede leather sector is navigating a dynamic landscape influenced by technological advancements, sustainability, and a rich history that appeals to international B2B buyers. Understanding these market dynamics is essential for making informed sourcing decisions that align with contemporary consumer values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is suede leather
-
How do I identify quality suede leather when sourcing?
To identify quality suede leather, examine the texture, thickness, and overall appearance. High-quality suede should have a soft, plush feel with a consistent nap and a uniform color. Look for suede made from younger animals, as it tends to be softer and more durable. Additionally, consider the source; reputable suppliers often provide details about the animal hide used, the tanning process, and any certifications. Request samples to assess the quality firsthand before making a bulk purchase. -
What is the best type of suede leather for fashion items?
The best type of suede leather for fashion items generally comes from lambskin or sheepskin. These types are known for their softness, lightweight nature, and luxurious feel, making them ideal for clothing, shoes, and accessories. Cowhide suede, while more robust, may not provide the same level of comfort and elegance in fashion applications. When selecting suede for fashion, consider the end use and desired aesthetic to ensure you choose the appropriate type. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting suede leather suppliers?
When vetting suede leather suppliers, consider their reputation, certifications, and production capabilities. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in quality and reliability. Check for certifications such as ISO or eco-friendly practices, which can indicate a commitment to sustainability. Additionally, inquire about their sourcing practices, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and lead times. Request references from other clients to gain insight into their experience and service quality. -
What are the typical payment terms for international suede leather purchases?
Typical payment terms for international suede leather purchases can vary widely, but common practices include a deposit (usually 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or after shipment. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment through escrow services for added security. It’s essential to clarify payment terms and conditions before finalizing orders, as well as any implications for currency exchange rates and transaction fees. -
How can I customize suede leather products for my brand?
Customization of suede leather products can involve selecting specific colors, textures, and finishes to align with your brand identity. Many suppliers offer options for embossing, printing, or adding unique hardware. Discuss your requirements with the supplier early in the negotiation process to ensure they can accommodate your needs. Be prepared to provide design specifications and possibly pay a premium for custom orders, along with longer lead times for production. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing suede leather?
When importing suede leather, consider shipping methods, customs duties, and import regulations specific to your region. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments but takes longer. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as certificates of origin and quality assurance. Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding the import of animal products to avoid potential delays or penalties. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for suede leather products?
To ensure quality assurance for suede leather products, establish clear quality standards with your supplier before production begins. This can include specifications on thickness, texture, and color consistency. Request samples for approval and consider implementing a third-party inspection service to evaluate the goods before shipment. Regular communication with the supplier throughout the production process can also help address any issues early on. -
What is the environmental impact of suede leather production?
The environmental impact of suede leather production can be significant, primarily due to the tanning process and the sourcing of animal hides. Eco-friendly suppliers may use vegetable tanning methods and sustainable sourcing practices to minimize their footprint. When sourcing suede leather, inquire about the supplier’s environmental policies and practices. Certifications such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) can also indicate a commitment to sustainable practices, which can enhance your brand’s reputation in a socially-conscious market.
Top 3 What Is Suede Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Buffalo Jackson – Suede vs Leather
Domain: buffalojackson.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Suede vs Leather: Key Differences and Qualities
1. Texture:
– Suede: Soft, textured surface with a noticeable nap (fuzzy texture).
– Leather: Smooth texture from the outer side of the hide.
2. Appearance:
– Suede: Matte finish, no shine.
– Leather: Smooth, polished surface with a sheen or glossy appearance.
3. Hand Feel:
– Suede: Soft and fuzzy hand feel due to the nap.
– L…
2. Steel Horse Leather – Suede Essentials
Domain: steelhorseleather.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Suede is a type of leather made from the underside of animal skin, featuring a soft surface and a napped finish. It is primarily made from sheepskin but can also be made from goatskin, cowskin, deer skin, pigskin, and other animal skins. Suede is smoother, thinner, and less sturdy than full-grain leather.
3. Billy Tannery – Suede Leather Backpacks
Domain: billytannery.co.uk
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Billy Tannery offers high-quality products made from deer suede leather, including suede leather backpacks and brown leather totes. Their suede is produced through a vegetable tanning process using mimosa bark extracts, ensuring an environmentally conscious approach. The suede is soft, durable, and has a unique velvety texture, making it suitable for various fashion and upholstery applications. Co…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is suede leather
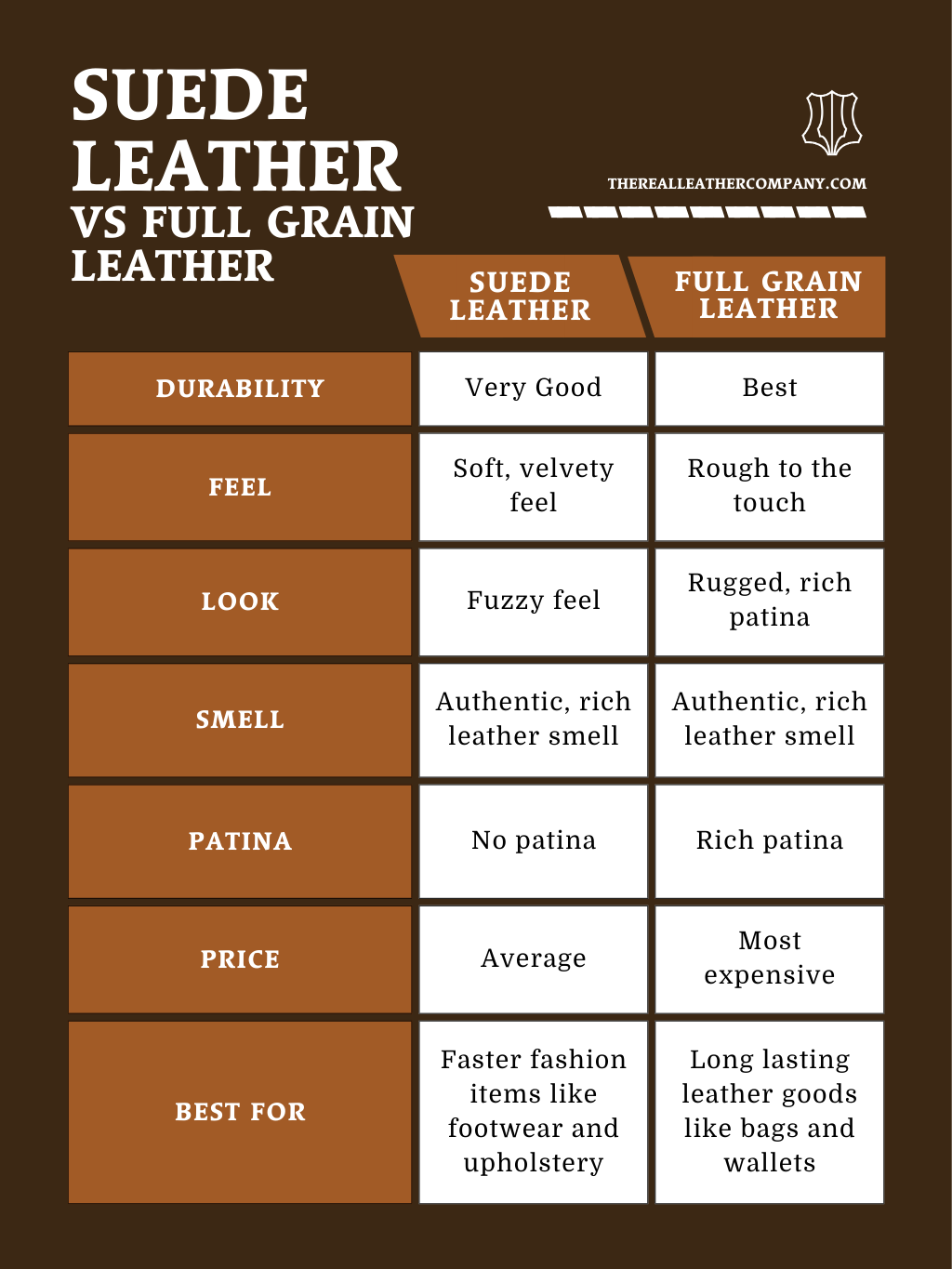
As international B2B buyers explore the opportunities presented by suede leather, understanding its unique characteristics and sourcing implications is vital. Suede, derived from the inner layer of animal hides, offers a soft texture and a luxurious feel, making it an appealing choice for various applications, from fashion accessories to upholstery. Unlike traditional leather, suede’s matte finish and casual aesthetic cater to a market that values both style and comfort.
Strategic sourcing of suede leather involves not only identifying reliable suppliers but also assessing the quality variations based on the type of animal hide used. Buyers should consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and market trends that influence consumer preferences. By leveraging insights from suppliers across regions—particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—businesses can secure competitive pricing and quality assurance.
Looking ahead, the demand for suede is expected to grow as consumers increasingly seek products that blend luxury with practicality. As you navigate your sourcing strategy, embrace partnerships that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices, ensuring your offerings resonate with a conscientious market. Engage with suppliers who share your vision, and capitalize on the rising trend of suede in the global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to what is suede leather
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.