Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is faux leather real leather
In the competitive landscape of global sourcing, understanding the nuances between faux leather and real leather is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. As international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Brazil and Nigeria, navigate their options, the question of whether faux leather is truly a viable alternative to real leather becomes paramount. This guide delves into the critical aspects of both materials, offering insights into their types, applications, and environmental impacts.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, you will explore the various characteristics that distinguish faux leather from genuine leather, including durability, maintenance, and aesthetic appeal. We will also provide guidance on vetting suppliers, assessing product quality, and understanding cost implications, ensuring that your sourcing strategy aligns with both budgetary constraints and quality expectations. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can confidently select the right materials for your business needs, whether you are in the fashion industry, furniture manufacturing, or automotive sectors.
Ultimately, this guide serves as your essential tool for navigating the complexities of faux leather versus real leather, empowering you to make choices that resonate with your brand’s values while meeting the demands of your market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 Is Faux Leather Real Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for is faux leather real leather
- Understanding is faux leather real leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of is faux leather real leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is faux leather real leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for is faux leather real leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is faux leather real leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is faux leather real leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is faux leather real leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is faux leather real leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is faux leather real leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is faux leather real leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is faux leather real leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is faux leather real leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding is faux leather real leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC Faux Leather | Made from polyvinyl chloride; typically less durable; smooth finish | Fashion accessories, upholstery | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to clean. Cons: Less durable, can wear out quickly. |
| PU Faux Leather | Composed of polyurethane; more flexible and breathable than PVC | Apparel, bags, footwear | Pros: More durable than PVC, resembles real leather. Cons: Can still wear out over time. |
| Skóra wegańska | Made from various synthetic materials; marketed as eco-friendly | Eco-conscious brands, fashion | Pros: No animal products, diverse textures. Cons: Environmental impact varies by production methods. |
| Skóra z mikrofibry | Ultra-fine synthetic fibers; mimics the texture of real leather | High-end fashion, automotive interiors | Pros: High durability, water-resistant. Cons: Higher cost than other faux options. |
| Biodegradable Leather | Made from natural materials like cork or fruit waste; eco-friendly | Sustainable brands, luxury goods | Pros: Environmentally friendly, unique appearance. Cons: Limited availability, potentially higher price point. |
What Are the Characteristics of PVC Faux Leather for B2B Buyers?
PVC faux leather is characterized by its smooth finish and affordability, making it a popular choice for various applications, including fashion accessories and upholstery. However, its durability is often questioned, as it may crack or wear out faster than other materials. B2B buyers should consider the trade-off between cost and longevity, especially in high-traffic environments where longevity is a concern.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
How Does PU Faux Leather Compare in Terms of Suitability?
PU faux leather is known for its flexibility and breathability, making it suitable for apparel, bags, and footwear. It closely resembles real leather in texture, which can enhance product appeal. B2B buyers should evaluate their target market’s preferences for quality and durability, as PU offers a more robust alternative to PVC while still being more affordable than genuine leather.
What Makes Vegan Leather a Unique Option for Eco-Conscious Brands?
Vegan leather is made from synthetic materials and is marketed as a cruelty-free alternative to real leather. This type of faux leather appeals to eco-conscious brands looking to align their products with sustainable practices. However, the environmental impact can vary based on the production methods used, making it essential for B2B buyers to research suppliers thoroughly to ensure their values align with their product offerings.
Why Choose Microfiber Leather for High-End Applications?
Microfiber leather is crafted from ultra-fine synthetic fibers, providing a luxurious texture that mimics real leather. It is highly durable and water-resistant, making it ideal for high-end fashion and automotive interiors. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment, as microfiber leather can be pricier than other faux options, but its longevity can justify the cost in premium markets.
What Are the Benefits of Biodegradable Leather for Sustainable Brands?
Biodegradable leather, derived from natural materials like cork or fruit waste, stands out as an environmentally friendly option. It appeals to brands focused on sustainability and can offer a unique aesthetic. However, availability may be limited, and prices may be higher than conventional faux leather. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of eco-friendliness against potential sourcing challenges and cost implications.
Key Industrial Applications of is faux leather real leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of is faux leather real leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Handbags, jackets, and footwear production | Cost-effective alternatives with trendy appeal | Quality of materials, durability, and ethical sourcing practices |
| Automotive | Upholstery for car interiors | Enhanced aesthetic appeal and comfort for consumers | Compliance with safety standards and material performance |
| Furniture | Upholstered furniture and decor items | Versatile design options and lower maintenance costs | Availability of colors, textures, and environmental impact |
| Home Décor | Decorative items, cushions, and wall coverings | Customization potential and modern aesthetics | Sourcing sustainable materials and production methods |
| Sports Equipment | Protective gear, bags, and accessories | Lightweight and durable options for athletes | Performance standards and regulatory compliance |
How is Faux Leather Used in Fashion & Apparel?
In the fashion industry, faux leather is widely used for producing handbags, jackets, and footwear. This material offers a cost-effective alternative that appeals to eco-conscious consumers seeking cruelty-free products. International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, should consider the quality of faux leather, as it must meet durability and aesthetic standards to compete with genuine leather. Additionally, ethical sourcing is crucial to enhance brand reputation and consumer trust.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
What Role Does Faux Leather Play in Automotive Upholstery?
Faux leather is increasingly utilized in automotive upholstery, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and comfort of car interiors. It allows manufacturers to offer a luxurious feel at a lower cost while also addressing the growing consumer demand for vegan-friendly options. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe must ensure that the materials comply with safety standards and perform well under various conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and wear resistance, to maintain customer satisfaction.
How is Faux Leather Applied in Furniture Design?
In the furniture sector, faux leather is commonly used for upholstered items like sofas and chairs, providing a stylish and modern look. Its lower maintenance requirements compared to real leather make it an attractive choice for both manufacturers and consumers. B2B buyers in Europe and Africa should focus on sourcing faux leather that offers a variety of colors and textures to meet diverse consumer preferences while also considering the environmental impact of the materials used.
What are the Benefits of Using Faux Leather in Home Décor?
Faux leather is an excellent choice for home décor applications, including decorative items, cushions, and wall coverings. Its customization potential allows designers to create unique and appealing products that align with current trends. International buyers from regions like South America and the Middle East should prioritize sustainable sourcing practices to meet increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products while also keeping an eye on production costs.
How is Faux Leather Utilized in Sports Equipment?
In the sports equipment industry, faux leather is commonly used for protective gear, bags, and accessories, providing lightweight and durable options that cater to athletes’ needs. This material allows manufacturers to create products that are both functional and visually appealing. Buyers, especially from Africa and Europe, should focus on performance standards and regulatory compliance to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the equipment while also considering the longevity of the materials used.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘is faux leather real leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Material Authenticity
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in fashion and upholstery industries, face challenges in discerning between faux leather and real leather. This confusion can lead to purchasing decisions that do not align with their brand values or customer expectations. For example, a buyer sourcing materials for a luxury handbag line may inadvertently order faux leather under the assumption it was genuine, resulting in potential brand dilution and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it is crucial for buyers to establish clear specifications in their procurement process. This includes requesting samples and detailed product descriptions from suppliers. Buyers should look for certifications or labels that indicate the authenticity of the leather. Additionally, conducting supplier audits can ensure that materials sourced meet the desired quality standards. Implementing a thorough vetting process can help buyers confidently differentiate between faux and real leather, aligning their purchases with brand positioning and customer expectations.
Scenario 2: Misunderstanding Durability and Longevity
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the misconception regarding the durability of faux leather compared to real leather. Buyers often assume that faux leather is a cost-effective alternative that will perform similarly over time. However, many discover that faux leather products tend to wear out more quickly, leading to increased replacement costs and potential damage to their brand’s reputation if products fail prematurely.
The Solution: Buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of the total cost of ownership (TCO) when sourcing materials. This involves not only considering the initial purchase price but also the expected lifespan of the product. Engaging with manufacturers who can provide insights into the longevity of their materials is essential. Additionally, requesting performance tests or customer reviews can provide evidence of durability. By selecting high-quality faux leather with proven longevity or opting for real leather when durability is paramount, buyers can make more informed decisions that support their long-term business objectives.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
Scenario 3: Environmental and Ethical Considerations
The Problem: As sustainability becomes a priority for many businesses, B2B buyers often grapple with the environmental implications of their material choices. While faux leather is marketed as a vegan alternative, its production processes can be harmful to the environment, leading to ethical dilemmas for brands that value sustainability. Buyers may find themselves in a position where they need to balance customer demand for cruelty-free products with the desire to minimize environmental impact.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing materials from suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes looking for faux leather products made from recycled materials or those that utilize eco-friendly production methods. Additionally, buyers can engage in transparent conversations with suppliers about their sourcing practices and the environmental impact of their materials. Investing in education on the lifecycle of both real and faux leather can empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their company’s sustainability goals. By choosing suppliers committed to ethical practices, buyers can enhance their brand’s reputation while meeting consumer demand for responsible products.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for is faux leather real leather
What Are the Common Materials Used in Faux Leather?
In the realm of faux leather, several materials are commonly utilized, each with distinct properties and implications for B2B buyers. Understanding these materials can guide international buyers in making informed decisions that align with their product requirements and market expectations.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
What Are the Key Properties of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) in Faux Leather?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used materials in faux leather production. It offers significant versatility and is often favored for its cost-effectiveness. PVC can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications, including upholstery and fashion accessories. However, it is less durable than some alternatives, particularly in high-wear scenarios.
Pros: PVC is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, allowing for mass production. It is also water-resistant, making it suitable for environments where moisture exposure is a concern.
Cons: The main drawback of PVC is its lower durability compared to real leather. Over time, it can crack and degrade, particularly when exposed to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight. Additionally, the production process can involve harmful chemicals, raising environmental concerns.
Impact on Application: PVC faux leather is compatible with a variety of media, but its longevity can be an issue in high-traffic areas. Buyers should consider the expected wear and tear when selecting PVC for their products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with regulations such as REACH in Europe or similar standards in other regions is crucial. Buyers from Africa and South America may also want to consider local preferences for eco-friendly materials.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Compare as a Faux Leather Material?
Polyurethane (PU) is another popular material for faux leather, known for its more realistic appearance and feel compared to PVC. PU can handle higher temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for a wider range of applications, including fashion, automotive, and furniture.
Pros: PU faux leather is more durable than PVC, offering greater resistance to wear and tear. It also has a softer texture and is often perceived as more luxurious, which can enhance the product’s appeal.
Cons: The manufacturing process for PU can be more complex and costly than PVC, which may affect the final product’s pricing. Additionally, while PU is more environmentally friendly than PVC, it still raises concerns regarding biodegradability.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
Impact on Application: PU is highly compatible with various media and is often used in high-end products where aesthetics and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the differences in manufacturing standards and regulations across regions, particularly in Europe where stricter environmental regulations may apply.
What Role Does Recycled Materials Play in Faux Leather Production?
The use of recycled materials in faux leather production is an emerging trend that appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. These materials can include recycled plastics or textiles, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional faux leather.
Pros: Utilizing recycled materials can significantly reduce environmental impact and appeal to a growing market segment that prioritizes sustainability. It can also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
Cons: The quality and durability of recycled faux leather can vary widely depending on the source material. This inconsistency may pose challenges in meeting customer expectations.
Impact on Application: Recycled faux leather can be suitable for a range of products, but buyers must ensure that the quality meets their specific application needs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with sustainability certifications and standards is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe may find that recycled materials align well with local consumer preferences and regulatory frameworks.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
Summary Table of Faux Leather Materials
| Materiał | Typical Use Case for is faux leather real leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Upholstery, fashion accessories | Cost-effective and water-resistant | Less durable, can degrade over time | Low |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Fashion, automotive, furniture | More durable and luxurious feel | Higher manufacturing cost, environmental concerns | Medium |
| Recycled Materials | Sustainable fashion, eco-friendly products | Reduces environmental impact, appeals to eco-conscious consumers | Quality can vary, potential durability issues | Medium to High |
This analysis provides valuable insights into the materials used in faux leather production, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for is faux leather real leather
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Faux Leather?
Faux leather, often marketed as “vegan leather,” undergoes a detailed manufacturing process that involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The primary raw materials for faux leather are polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyurethane (PU). PVC is a versatile plastic that provides durability, while PU is known for its softer texture and more leather-like feel. The preparation phase includes:

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
- Sourcing: Suppliers must ensure that the raw materials comply with international regulations regarding safety and environmental impact.
- Compounding: The chosen materials are mixed with additives to enhance properties such as flexibility, durability, and color.
B2B buyers should verify the sourcing of these materials, ensuring they come from reputable suppliers with transparency in their production processes.
How Is Faux Leather Formed?
The forming stage is where the faux leather begins to take shape. This involves several techniques:
- Coating: A common method where a substrate (often fabric) is coated with a layer of PVC or PU. This can be done using processes like calendaring or spraying.
- Extrusion: This technique involves melting the plastic and forcing it through a mold to create sheets of faux leather.
- Foaming: In some cases, the faux leather is created by foaming the material, which adds a soft texture.
Understanding these techniques helps B2B buyers assess the quality and durability of the faux leather products they intend to procure.
What Are the Assembly and Finishing Processes for Faux Leather?
Once the material has been formed, it moves to the assembly stage, where different components are stitched or glued together to create finished products such as handbags, upholstery, or clothing.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of faux leather. These include:
- Embossing: Creating patterns or textures on the surface to mimic the look of real leather.
- Dyeing: Applying color to the faux leather, which can be done through various methods such as immersion or spray.
- Coating: Adding a protective layer that enhances durability and water resistance.
B2B buyers should inquire about the finishing techniques used by suppliers, as they can significantly affect the product’s longevity and appearance.
What Quality Control Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance is vital in the faux leather manufacturing process. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide guidelines for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers maintain high standards throughout production.
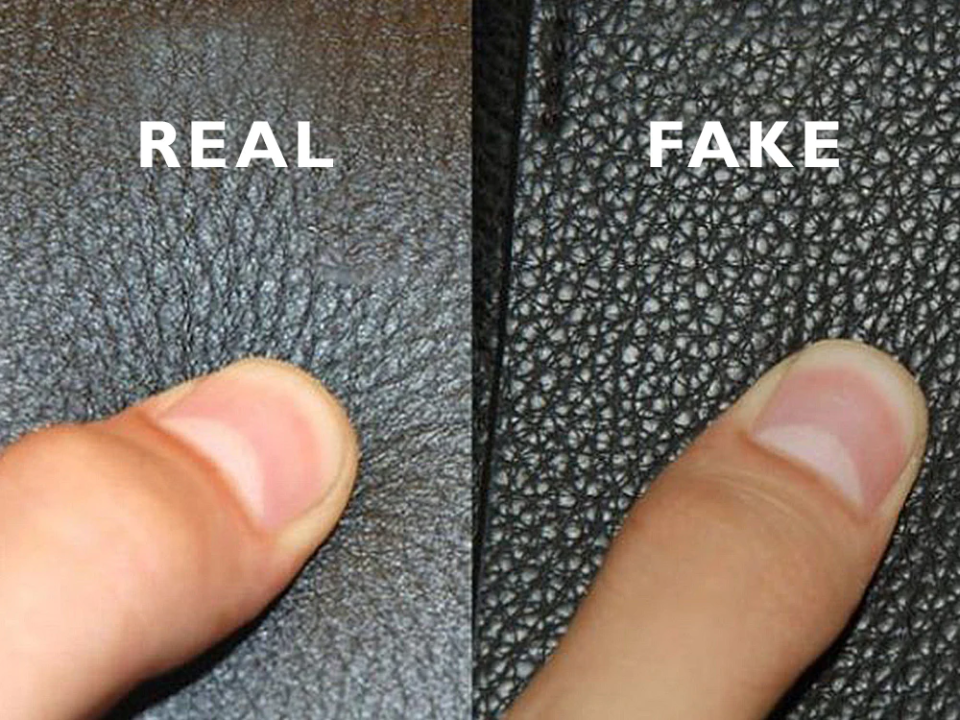
Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are critical in ensuring the final product meets specifications. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished products to ensure they meet the required standards.
B2B buyers should request detailed QC reports from suppliers, outlining their processes and any certifications they hold.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to quality standards, B2B buyers can take several actionable steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
- Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide reports on their quality control processes, including any relevant certifications (e.g., CE marking, API standards).
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring independent inspectors to evaluate production facilities can provide an unbiased view of a supplier’s quality assurance practices.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and standards is essential.
- Regional Compliance: Different markets have varying regulations regarding materials and manufacturing processes. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these to ensure compliance.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding local customs and business practices can enhance communication with suppliers, facilitating smoother transactions and quality assurance.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Faux Leather Sourcing
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for faux leather are critical for B2B buyers. By understanding the stages of production, quality control standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing faux leather products. Engaging with suppliers who demonstrate transparency and adherence to international standards will ultimately lead to higher quality outcomes and better business relationships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘is faux leather real leather’
Wprowadzenie
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in evaluating whether faux leather products are genuine leather or synthetic alternatives. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, especially when considering quality, durability, and environmental impact. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of leather sourcing effectively.
Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
Step 1: Understand Material Composition
Begin by clarifying the materials used in the products you are considering. Real leather is derived from animal hides, while faux leather is primarily made from synthetic materials like PVC or polyurethane. Knowing the composition is essential for quality assessment and to meet your brand’s sustainability goals.
- Look for product specifications that detail the material sources.
- Request safety data sheets to understand any chemical treatments involved in faux leather production.
Step 2: Define Your Quality Standards
Establish clear quality benchmarks for the leather products you wish to procure. Real leather often has unique characteristics such as natural imperfections, while faux leather features a more uniform appearance.
- Consider tactile qualities: Real leather will feel warmer and more textured compared to the cooler, smoother feel of faux leather.
- Assess durability needs: Determine if the product’s longevity aligns with your business requirements, as real leather typically lasts longer.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and ethical standards. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
- Verify their production processes: Inquire about how they source and treat their leather, particularly for eco-friendly practices.
- Check for industry certifications that indicate adherence to quality and environmental standards.
Step 4: Request Samples for Assessment
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of both faux and real leather products. This hands-on evaluation will help you better understand the differences in quality, texture, and durability.
- Conduct side-by-side comparisons to spot distinctions in appearance and feel.
- Evaluate the samples under different conditions to gauge how they respond to wear and tear.
Step 5: Assess Environmental Impact
Consider the environmental implications of your choices. While faux leather may seem more sustainable, the production processes often involve harmful chemicals.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
- Research sustainable sourcing: Inquire if the real leather is sourced from sustainable ranches and tanned using eco-friendly methods.
- Evaluate the lifecycle of the product: Real leather can be more sustainable in the long term if it lasts significantly longer than faux alternatives.
Step 6: Verify Compliance with International Standards
Ensure that the products comply with international standards, especially if you are sourcing from different regions. This will help mitigate risks associated with trade regulations and quality assurance.
- Check for compliance documentation: Request certifications that demonstrate adherence to quality and safety standards.
- Stay informed about regional regulations that may affect the import and sale of leather goods.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms of Purchase
Finally, negotiate the terms of your purchase with your chosen supplier. Clear agreements regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and quality assurance will ensure a smooth procurement process.
- Discuss return policies: Understand the terms for returns or exchanges in case the products do not meet your standards.
- Establish payment terms that are favorable and secure for both parties.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing leather products, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business values and market demands.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for is faux leather real leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Faux Leather vs. Real Leather?
When sourcing materials for faux leather and real leather products, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: Faux leather is typically made from synthetic materials like PVC or polyurethane, which can be less expensive than real leather derived from animal hides. However, the quality of faux leather can vary significantly, affecting its pricing. High-quality faux leather mimicking the appearance of real leather may come at a higher cost.
-
Labor: The labor cost associated with the production of both materials can vary based on the region. Labor costs in countries like Brazil or Nigeria may differ from those in Europe. Skilled labor is often needed for real leather production, particularly in tanning and finishing processes, which can drive up costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to machinery, maintenance, and utilities. Faux leather production may have lower overhead due to less complex manufacturing processes compared to real leather, which requires more intricate craftsmanship.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant for both materials, especially if custom designs are required. Custom molds for faux leather may be cheaper, but the initial investment in high-quality leather tooling can yield better long-term returns.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of both materials involves different QC processes. Real leather requires more rigorous testing to ensure durability and finish, potentially increasing costs. In contrast, faux leather may have standard QC processes that are less intensive.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the sourcing location. Importing real leather from countries with stringent regulations may incur higher logistics costs, while faux leather, often produced locally, may have lower shipping fees.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically set different margins for faux versus real leather based on perceived value and market demand. Understanding these margins can aid in negotiation strategies.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Faux Leather and Real Leather?
Several factors can influence pricing in the faux leather versus real leather market:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often yield better pricing. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can be crucial for cost-efficient sourcing. For instance, suppliers may offer significant discounts for bulk purchases, especially in regions like Africa or South America where demand is growing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific quality certifications can raise prices. Buyers should be clear about their requirements, as tailored products may come with a premium.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials will naturally cost more. Certifications for sustainability or ethical sourcing can also increase the price of real leather but may appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can greatly affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance and reliability, which can lead to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms can impact the overall cost. Incoterms dictate who pays for shipping, insurance, and customs, affecting the final price significantly.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Buyers Employ for Cost Efficiency?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to better pricing:
- Leverage Volume Discounts: Highlighting potential for large orders can motivate suppliers to offer better terms.
- Request Sample Products: Before committing to large purchases, request samples to assess quality versus price.
- Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in durability and maintenance costs when comparing faux and real leather. While real leather may have a higher upfront cost, its longevity can offer better value over time.
- Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can result in better pricing and terms as trust develops.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies is vital for B2B buyers sourcing faux leather and real leather. By considering these factors, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals, ensuring they secure the best value for their investments. Keep in mind that prices can vary widely based on market conditions, so it’s advisable to conduct regular market research and stay informed about trends.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing is faux leather real leather With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Faux Leather and Real Leather
In the competitive landscape of material sourcing, B2B buyers must evaluate not only the products they choose but also the alternatives available in the market. The debate between faux leather and real leather has been prominent, but there are several other viable materials that can serve similar functions. This section compares faux leather against two notable alternatives: sustainable textile options and recycled leather.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Is Faux Leather Real Leather | Sustainable Textiles | Recycled Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate durability; less long-lasting than real leather | Varies by fabric; some outperform faux leather | Comparable to real leather; durability depends on quality |
| Cost | Generally lower than real leather | Varies widely based on the material and sourcing | Typically less expensive than real leather but can vary |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to manufacture and use | May require specialized suppliers | Requires sourcing from specific recycling processes |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Depends on the textile; can require special care | Similar to real leather; requires conditioning |
| Best Use Case | Fashion accessories, upholstery | Eco-friendly products, casual wear | High-quality goods, luxury items |
Pros and Cons of Alternatives
Sustainable Textiles
Sustainable textiles, such as organic cotton or hemp, provide an eco-friendly option that appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. These materials often have a lower environmental impact during production and can offer unique textures and aesthetics. However, performance may vary significantly based on the specific fabric chosen, and some sustainable options may not provide the durability required for high-wear applications like upholstery or bags.
Recycled Leather
Recycled leather, made from repurposed leather scraps, offers a unique alternative that combines the qualities of real leather with sustainability. It retains the look and feel of genuine leather while reducing waste, making it a compelling choice for luxury items. The primary downside is that the quality can vary depending on the sourcing and processing of the recycled material, which may affect durability and appearance. For buyers seeking high-quality leather-like products with a sustainable angle, recycled leather is an attractive option.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between faux leather, real leather, and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including performance, cost, and maintenance. Understanding the intended use case is essential; for instance, fashion accessories may thrive with faux leather, while high-end goods may demand the authenticity of real or recycled leather. Sustainable textiles offer eco-conscious alternatives that align with growing market demands for environmentally responsible products. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on balancing quality, cost, and sustainability to meet your business objectives.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for is faux leather real leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Faux Leather Compared to Real Leather?
Understanding the technical properties of faux leather and real leather is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating material quality, durability, and overall value. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Composition
– Faux Leather: Typically made from synthetic materials such as polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). These materials are engineered to mimic the appearance and feel of real leather but lack its natural characteristics.
– Real Leather: Derived from animal hides, primarily cattle. The type of leather can vary, including full-grain, top-grain, or genuine leather, each with unique qualities and uses. Understanding the source material is vital for assessing product quality and sustainability. -
Durability and Longevity
– Faux Leather: Generally has a shorter lifespan, often lasting only a few years before showing signs of wear and tear. It does not develop the same character or patina as real leather.
– Real Leather: Known for its longevity, real leather can last decades with proper care. Its ability to age beautifully adds to its value, making it a preferred choice for high-quality products. -
Environmental Impact
– Faux Leather: The production process involves chemicals that may have adverse environmental effects. While marketed as animal-friendly, the ecological footprint can be significant due to the non-biodegradable materials used.
– Real Leather: When sourced from sustainable practices, it can be less harmful to the environment. Leather is biodegradable and often utilizes hides from animals raised for food, minimizing waste. -
Maintenance Requirements
– Faux Leather: Easier to maintain, requiring only basic cleaning with soap and water. However, it may not withstand high temperatures or direct sunlight as well as real leather.
– Real Leather: Requires specific care, including conditioning and cleaning with appropriate products to maintain its appearance and prevent drying out. Proper maintenance can enhance its durability.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Faux Leather Industry?
In the B2B landscape, familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers find reputable suppliers for faux leather goods. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for businesses looking to stock faux leather items. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– A formal document sent to suppliers asking for price quotes on specific products. RFQs help businesses compare costs and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing shipping, risk, and costs associated with faux leather imports and exports. -
PU vs. PVC
– These acronyms refer to the primary materials used in faux leather. PU (polyurethane) is generally considered more environmentally friendly and higher quality than PVC (polyvinyl chloride), which is cheaper but often less durable. Familiarity with these terms can help buyers assess product quality more effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding faux leather and real leather products, ensuring they select materials that align with their business needs and sustainability goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the is faux leather real leather Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Faux Leather Sector?
The faux leather market is experiencing robust growth globally, driven by several factors including shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, and sustainability concerns. International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly drawn to faux leather due to its versatility and affordability. As the demand for animal-friendly products rises, faux leather has gained traction, often marketed as “vegan leather.” This shift is not merely a trend but reflects a broader societal movement towards ethical consumption.
Emerging technologies in manufacturing are enhancing the quality and durability of faux leather, making it a viable alternative to real leather. Innovations such as digital printing and eco-friendly materials are being adopted, allowing manufacturers to produce high-quality faux leather that mimics the aesthetic and tactile characteristics of genuine leather. B2B buyers should stay attuned to these technological advancements, as they can impact sourcing decisions and product offerings.
Moreover, the rise of e-commerce platforms has transformed how B2B transactions occur in this sector. Buyers can now access a wider range of suppliers globally, compare prices, and assess product quality through detailed online catalogs. This accessibility is vital for buyers in emerging markets like Nigeria and Brazil, where local supply chains may not yet support diverse product offerings.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Faux Leather Market?
The environmental impact of materials used in the faux leather industry is a significant concern for international B2B buyers. Traditional faux leather is often made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyurethane, both of which have environmental drawbacks during production and disposal. However, the industry is evolving, with a growing number of manufacturers seeking sustainable alternatives. Buyers should look for certifications like Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX, which indicate environmentally friendly practices.
Ethical sourcing is becoming paramount as consumers increasingly demand transparency in supply chains. B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation by partnering with suppliers who adhere to ethical practices, such as fair labor conditions and responsible sourcing of materials. This not only aligns with consumer values but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions caused by unethical practices.
Incorporating sustainable materials, such as recycled plastics or plant-based alternatives, can help businesses reduce their carbon footprint while appealing to eco-conscious consumers. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international buyers can differentiate their offerings in a competitive market.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
What Is the Historical Context of Faux Leather Development?
The faux leather industry has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially created as a lower-cost alternative to real leather, the early versions lacked the durability and aesthetic appeal of genuine leather. However, advancements in polymer technology and manufacturing processes have transformed faux leather into a desirable product in its own right.
The 21st century marked a turning point with the rise of the “vegan leather” movement, positioning faux leather as a fashionable and ethical choice. This shift has not only broadened the consumer base but also sparked innovation in design and production methods. Today, faux leather is a staple in various industries, from fashion to automotive, reflecting a growing recognition of its potential as a sustainable and ethical alternative to traditional leather.
International B2B buyers should recognize this historical context as they navigate current market dynamics, helping them make informed sourcing decisions that align with consumer preferences and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of is faux leather real leather
-
How do I determine if a supplier’s faux leather is of high quality?
To assess the quality of faux leather from suppliers, request samples to evaluate the texture, durability, and overall feel. High-quality faux leather should have a realistic texture, a pleasant smell (free from strong chemical odors), and should mimic the characteristics of genuine leather, such as flexibility and softness. Additionally, inquire about the materials used in production, specifically if they are made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and check for certifications that indicate compliance with international quality standards. -
What is the best way to negotiate payment terms with faux leather suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms with suppliers, consider factors such as order size, shipping costs, and the supplier’s payment policies. Aim for terms that align with your cash flow needs, such as 30% upfront and 70% upon delivery. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can also facilitate more favorable terms. Ensure clarity on payment methods accepted (e.g., letters of credit, bank transfers) and any potential discounts for early payments or bulk orders. -
What customization options should I expect from faux leather suppliers?
Most faux leather suppliers offer various customization options, including colors, textures, and finishes. Depending on your needs, inquire about the possibility of branding, such as embossing or printing your logo on the products. Additionally, ask about the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized products, as these can vary widely among suppliers. Customization can enhance your brand’s identity, so ensure that the supplier can meet your specific design requirements. -
How do I vet suppliers of faux leather for international trade?
Vetting suppliers for international trade involves several steps. Start by checking their business credentials, such as registration and certification documents. Request references from previous clients and investigate their reputation within the industry. Additionally, consider conducting a factory audit if feasible, to assess production capabilities and working conditions. Utilizing platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources can provide insights into supplier ratings and customer feedback, further aiding in your decision-making process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for faux leather products?
MOQs for faux leather products can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of product. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 to 1,000 units. For customized items, MOQs may be higher due to setup costs associated with manufacturing. When negotiating with suppliers, clearly communicate your needs and explore the possibility of lower MOQs, especially for initial orders or trial runs. Understanding the supplier’s production capabilities can also help in setting realistic expectations. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my faux leather orders?
To ensure quality assurance for faux leather orders, establish a clear QA process that includes detailed specifications and standards before production begins. Request samples for initial inspection and consider implementing an in-process inspection during manufacturing. Additionally, you may want to hire a third-party inspection service to conduct final checks before shipment. Communicate your QA expectations upfront to the supplier to minimize potential issues and ensure that the final product meets your quality standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing faux leather?
When importing faux leather, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and duties. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling textile imports to streamline the process. Be aware of any import regulations in your country, including tariffs on synthetic materials, and ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs. Timing is also crucial; factor in lead times for production and shipping to avoid delays in your supply chain. -
What are the environmental impacts of sourcing faux leather?
Sourcing faux leather can have environmental implications, primarily due to the materials used in production, such as PVC and polyurethane, which may release harmful chemicals during manufacturing. Opt for suppliers that employ sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials or processes. Additionally, consider the lifecycle of the product; faux leather typically has a shorter lifespan compared to real leather, leading to increased waste. Engage with suppliers who are committed to sustainability and can demonstrate efforts to minimize their environmental footprint.
Top 4 Is Faux Leather Real Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Buffalo Jackson – Real Leather Goods
Domain: buffalojackson.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Real leather is made from animal hides (buffalo or cattle) and has a natural surface with imperfections, a distinctive smell, and develops character over time. Faux leather is made from PVC or polyurethane, has a uniform texture, feels cold and synthetic, and has a plasticky smell. Real leather is more durable and improves with use, while faux leather is not designed to last.
2. Radley London – Handbags and Accessories
Domain: radleylondon.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Faux Leather vs. Genuine Leather Handbags | Radley London
– Free US shipping on orders over $100
– New: Save up to $75 off with Spend and Save
– New Arrivals: Handbags, Wallets, Accessories
– Handbag Types: Cross Body Bags, Shoulder Bags, Backpacks, Clutch Bags, Tote Bags, Satchels, Cross Body Wallets
– Wallet Types: Card Holders, Coin Purses, Sizes: Small, Medium, Large
– Materials: Leather Bags,…
3. Leather Honey – Leather Care Essentials
Domain: leatherhoney.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Leather Conditioner: from $27.99 (originally $68.95)\nLeather Cleaner: from $18.99 (originally $33.99)\nLeather Care Kit: $43.99 (originally $70.99)\nLeather Care Wipes (10 Pack): $13.99 (originally $17.99)
4. Is It Leather – Authentic Leather Identification Guide
Domain: isitleather.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Real leather is made from animal hides and may be labeled as “genuine leather” or “real leather.” It can be identified by its natural, bumpy surface, thickness of 1.0-1.4 millimeters, and unique imperfections. Tests to determine authenticity include inspecting tags for terms like “faux leather” or “vegan leather,” feeling the surface for flexibility and warmth, performing a lighter test to check f…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for is faux leather real leather
In navigating the complex landscape of leather sourcing, understanding the distinctions between faux and real leather is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Real leather, while often more expensive, offers durability, authenticity, and a unique character that can enhance product value over time. Conversely, faux leather appeals with its lower cost and vegan appeal, but it typically lacks the longevity and environmental benefits associated with sustainably sourced real leather.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets like Africa and South America, strategic sourcing of leather products should prioritize quality and sustainability. Consider the implications of sourcing decisions on your brand’s reputation and customer satisfaction. By aligning with suppliers who prioritize ethical practices and sustainable materials, you can not only meet consumer demands but also differentiate your offerings in competitive markets.
Looking ahead, the leather industry is poised for innovation, with advancements in sustainable practices and materials. Engage with your suppliers to explore options that balance quality and environmental responsibility. This proactive approach will position your business favorably in a market increasingly driven by ethical consumerism. Embrace the opportunity to source responsibly, ensuring your products resonate with today’s conscientious buyers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to is faux leather real leather
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.