Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather technology
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality leather technology solutions presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The complexity of navigating various suppliers, understanding the intricacies of leather production, and ensuring compliance with environmental standards can be daunting. This guide is designed to illuminate the essential aspects of the leather technology market, offering a comprehensive overview of types, applications, and innovative solutions tailored to your business needs.
From the preparation stages of tanning to the finishing processes that enhance product durability and aesthetics, this guide covers every facet of leather technology. It also delves into supplier vetting procedures, cost considerations, and sustainability practices that are becoming increasingly vital in the global market.
By empowering you with actionable insights and data-driven strategies, this resource enables informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational goals. Whether you are based in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—regions known for their diverse leather markets—this guide will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing leather products and technologies. With a focus on quality, environmental responsibility, and innovation, we aim to support your business in leveraging the full potential of leather technology for enhanced competitive advantage.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Leather Technology Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather technology
- Understanding leather technology Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of leather technology
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather technology’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather technology
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather technology
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather technology’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather technology Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather technology With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather technology
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather technology Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather technology
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather technology
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding leather technology Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetable Tanned | Uses natural tannins from plant sources, eco-friendly. | Footwear, belts, bags, and upholstery. | Pros: Environmentally sustainable, unique aging. Cons: Longer processing time, less water-resistant. |
| Chrome Tanned | Utilizes chromium salts for faster tanning and durability. | Automotive interiors, fashion accessories. | Pros: Quick production, high durability. Cons: Environmental concerns, less natural feel. |
| Synthetic Leather | Made from plastic-based materials, mimicking real leather. | Fashion, furniture, and automotive. | Pros: Cost-effective, animal-friendly. Cons: Less breathable, may lack authenticity. |
| Exotic Leather | Sourced from non-traditional animals, unique textures. | High-end fashion, luxury goods. | Pros: Unique aesthetic appeal, high value. Cons: Ethical concerns, higher cost. |
| Suede | Napped finish created from the underside of the hide. | Apparel, accessories, and upholstery. | Pros: Soft texture, stylish appearance. Cons: Less durable, requires special care. |
What Are the Characteristics of Vegetable Tanned Leather?
Vegetable-tanned leather is distinguished by its use of natural tannins derived from plant materials, making it an eco-friendly option. This type is often favored for products where aesthetics and environmental impact are prioritized, such as footwear, belts, and bags. B2B buyers should consider the longer processing times associated with vegetable tanning, which can affect production schedules. The leather develops a unique patina over time, enhancing its character and appeal.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
How Does Chrome Tanned Leather Differ from Other Types?
Chrome-tanned leather is processed using chromium salts, which allows for a faster tanning process and results in a highly durable product. This type is commonly used in automotive interiors and fashion accessories, where durability and resistance to wear are essential. For B2B buyers, the rapid production cycle is a significant advantage. However, concerns about the environmental impact of chromium processing should be carefully evaluated, especially in markets with stringent regulations.
What Are the Benefits of Synthetic Leather for B2B Buyers?
Synthetic leather, crafted from plastic-based materials, offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional leather. It is widely used in fashion, furniture, and automotive applications, appealing to manufacturers looking for budget-friendly solutions. While synthetic leather is animal-friendly and easier to maintain, buyers should note that it may lack the breathability and authenticity of real leather. Understanding the target market’s preferences can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
What Makes Exotic Leather a Unique Choice for Luxury Markets?
Exotic leather, sourced from non-traditional animals such as crocodiles or ostriches, offers distinctive textures and patterns that appeal to high-end fashion and luxury goods markets. The unique aesthetic and high value of exotic leather make it a sought-after material for upscale products. However, ethical concerns and high costs associated with sourcing and processing these materials can pose challenges for B2B buyers. Ensuring compliance with international regulations regarding exotic leathers is crucial for businesses in this sector.
Why is Suede Preferred in Fashion and Upholstery?
Suede is characterized by its soft, napped finish, which provides a stylish appearance and luxurious feel. It is commonly used in apparel, accessories, and upholstery, where tactile qualities are valued. B2B buyers should consider the care requirements for suede, as it is less durable and more susceptible to stains compared to other leather types. Understanding the specific needs of the target market can guide purchasing decisions regarding suede products.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Key Industrial Applications of leather technology
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of leather technology | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Footwear | Production of high-quality leather shoes | Enhances product durability and aesthetic appeal, leading to higher customer satisfaction and repeat sales. | Sourcing sustainable leather, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, and quality assurance. |
| Automotive | Upholstery for vehicle interiors | Provides luxury feel and durability, boosting brand image and customer loyalty. | Availability of specialized automotive-grade leather, adherence to safety standards, and customization options. |
| Fashion and Accessories | Creation of premium handbags and belts | Differentiates products in a competitive market, appealing to luxury consumers. | Need for innovative designs, sourcing from ethical suppliers, and maintaining consistent quality. |
| Furniture | Upholstery for residential and commercial use | Increases product lifespan and comfort, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing replacement costs. | Consideration of leather grades, sourcing from environmentally responsible tanneries, and customization capabilities. |
| Sporting Goods | Manufacturing of leather sports equipment | Improves performance and durability of products, appealing to professional and amateur athletes alike. | Importance of sourcing high-performance leather, ensuring compliance with sports industry standards, and durability testing. |
How is Leather Technology Applied in the Footwear Industry?
In the footwear sector, leather technology plays a crucial role in producing high-quality shoes that combine durability with style. Advanced tanning methods stabilize the leather, ensuring it withstands wear and tear while maintaining flexibility. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing sustainable leather that meets environmental regulations is vital. Ensuring consistent quality and ethical sourcing practices can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Are the Benefits of Leather Technology in Automotive Upholstery?
Leather technology is integral to automotive upholstery, providing a luxurious feel that enhances the overall driving experience. The tanning process used creates a durable material that resists wear and provides comfort, thereby improving customer satisfaction. B2B buyers from the Middle East and Europe must consider sourcing automotive-grade leather that complies with safety standards and offers customization options to meet diverse consumer preferences.
How Does Leather Technology Enhance Fashion and Accessories?
In the fashion industry, leather technology is pivotal for creating premium handbags, belts, and other accessories. The unique properties of leather allow for innovative designs that appeal to luxury consumers, differentiating products in a crowded marketplace. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from ethical suppliers to ensure quality and sustainability, as consumers increasingly demand transparency in the production process.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
What Role Does Leather Technology Play in Furniture Manufacturing?
Leather technology is essential in the furniture sector, particularly for upholstery in residential and commercial settings. High-quality leather enhances the aesthetic appeal and durability of furniture, leading to increased customer satisfaction and reduced replacement costs. For B2B buyers, it is crucial to consider the grade of leather, the sourcing practices of tanneries, and the customization capabilities available to meet specific design needs.
How is Leather Technology Utilized in Sporting Goods?
Leather technology is employed in the production of various sporting goods, such as balls, gloves, and protective gear. The material’s inherent strength and flexibility enhance the performance and longevity of these products, making them appealing to both professional athletes and enthusiasts. International buyers should focus on sourcing high-performance leather that meets industry standards and undergoes rigorous durability testing to ensure product reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather technology’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance in Leather Production
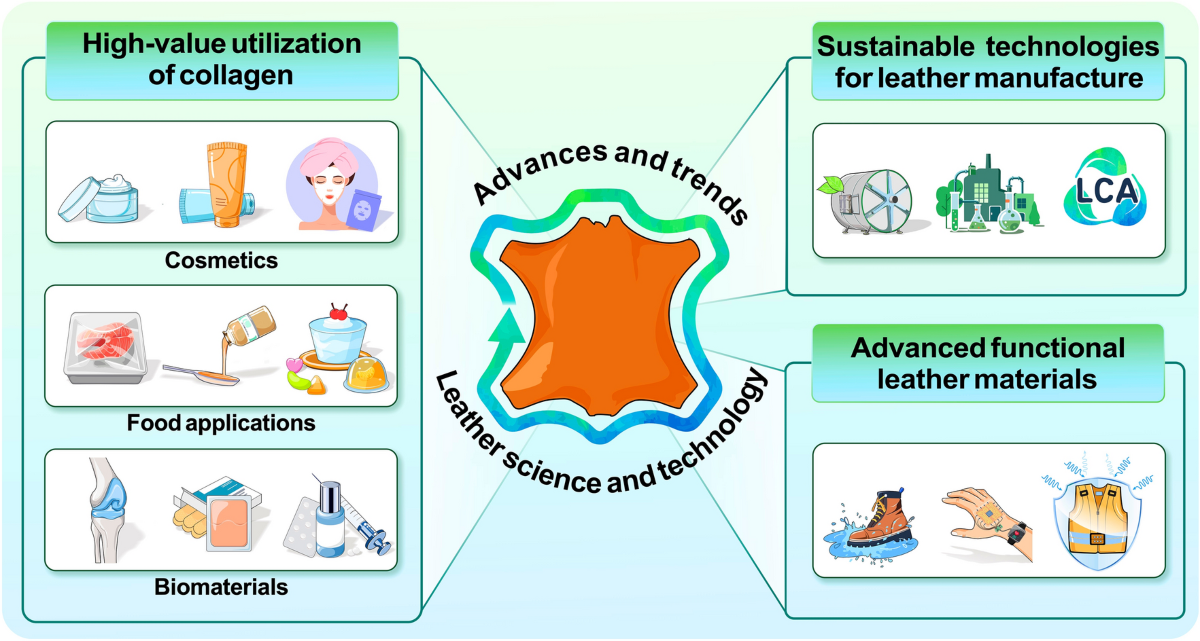
The Problem: For B2B buyers in the leather industry, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations can be daunting. Countries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe have stringent laws governing chemical use, waste management, and emissions related to leather production. Buyers may struggle to keep up with varying regulations, risking fines and damaging their reputations. This complexity can lead to the use of outdated or non-compliant technologies, which not only incur legal consequences but also hinder operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
The Solution: To navigate regulatory compliance effectively, B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who offer environmentally friendly leather technologies and chemicals. This means sourcing from companies that provide transparent Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and maintain certifications for their products. Additionally, buyers should invest in training programs for their staff on the latest compliance standards and sustainable practices. Leveraging technology, such as compliance management software, can help track regulatory changes in different regions, allowing businesses to adapt swiftly. By staying informed and proactive, companies can not only meet compliance but also enhance their brand image as environmentally responsible players in the leather market.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Quality Variability in Leather Goods
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers in the leather technology sector is the inconsistency in leather quality. Variability can stem from differences in raw materials, manufacturing processes, and finishing techniques. This inconsistency can lead to customer dissatisfaction, increased return rates, and potential loss of business, particularly when serving high-end markets where quality is paramount.
The Solution: To address quality variability, buyers should establish stringent quality control protocols throughout the supply chain. This includes selecting suppliers with a proven track record of consistent quality and utilizing advanced analytical tools to assess leather properties such as tensile strength, flexibility, and moisture content. Implementing a comprehensive supplier evaluation system can help ensure that only the best materials are used. Furthermore, investing in technology that automates quality checks during the tanning and finishing processes can significantly reduce variability. Regular audits and feedback loops with suppliers can foster continuous improvement, ensuring that the leather products meet the high standards expected by customers.
Scenario 3: Reducing Environmental Impact of Leather Production
The Problem: As global awareness of environmental issues grows, B2B buyers face pressure to reduce the ecological footprint of their leather production processes. Traditional leather tanning methods often involve harmful chemicals and generate significant waste, leading to environmental degradation. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the need to transition to more sustainable practices while maintaining profitability and product quality.
The Solution: To minimize environmental impact, buyers should explore innovative leather technologies that prioritize sustainability. This includes sourcing from tanneries that utilize eco-friendly tanning methods, such as vegetable tanning or synthetic alternatives that reduce harmful emissions and waste. Additionally, implementing a circular economy approach—whereby waste is repurposed or recycled—can significantly lower a company’s ecological footprint. Buyers can also engage in partnerships with sustainability-focused organizations to enhance their practices and gain access to new technologies. Investing in research and development for biodegradable or less harmful leather alternatives will not only meet consumer demand for sustainability but also position the business as a leader in responsible leather production.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather technology
What Are the Key Materials Used in Leather Technology?
In the leather technology sector, the choice of materials significantly influences product quality, performance, and sustainability. Here, we analyze four common materials used in leather technology, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
1. Cattle Hide
Key Properties: Cattle hide is known for its durability and flexibility, making it suitable for various applications, including footwear, bags, and upholstery. It has excellent tensile strength and can withstand high temperatures during processing.
Pros & Cons: Cattle hide is highly durable, offering long-lasting products. However, it can be expensive, and the tanning process is complex and time-consuming. Additionally, variations in quality can arise based on the source of the hide.
Impact on Application: Cattle hide is compatible with a wide range of finishing processes, allowing for diverse aesthetic applications. Its natural properties also provide good water resistance when treated properly.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding animal welfare and environmental standards. Common certifications include ISO and ASTM standards, which are critical for ensuring product quality and safety.
Illustrative image related to leather technology
2. Pigskin
Key Properties: Pigskin is lighter than cattle hide and possesses good breathability and moisture-wicking properties. It is also resistant to tearing and has a unique texture that adds aesthetic appeal.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of pigskin is its cost-effectiveness compared to cattle hide, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious manufacturers. However, it may not be as durable as cattle hide, limiting its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Pigskin is often used in fashion accessories and garments due to its softness and flexibility. Its moisture-wicking properties enhance comfort in wearable products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider cultural preferences, as pigskin is less accepted in certain markets due to dietary restrictions. Compliance with local regulations regarding animal products is also essential.
3. Synthetic Leather (PU and PVC)
Key Properties: Synthetic leather, made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), mimics the appearance and texture of real leather while offering water resistance and ease of cleaning.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Pros & Cons: Synthetic leather is generally more affordable and easier to produce than natural leather. However, it lacks the breathability and aging characteristics of genuine leather, which may affect the long-term appeal of products.
Impact on Application: This material is widely used in automotive interiors, furniture, and fashion items. Its versatility allows for various colors and textures, appealing to a broad market.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of environmental concerns associated with synthetic materials, particularly PVC. Compliance with regulations such as REACH in Europe is crucial for market entry.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
4. Exotic Leathers (e.g., Crocodile, Snake)
Key Properties: Exotic leathers are known for their unique aesthetics and texture, providing a high-end appeal. They are typically more durable than standard leathers, with excellent resistance to wear.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of exotic leathers is their luxury status, making them highly desirable in premium markets. However, they come with a high price tag and are subject to strict regulations regarding sourcing and trade.
Impact on Application: Exotic leathers are often used in high-end fashion, luxury accessories, and bespoke products. Their unique patterns and textures enhance product differentiation.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must navigate complex regulations surrounding the trade of exotic leathers, including CITES compliance. Understanding market demand and ethical sourcing is essential for maintaining brand reputation.
Summary Table of Material Selection in Leather Technology
| Materiał | Typical Use Case for leather technology | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle Hide | Footwear, bags, upholstery | High durability | Expensive and complex processing | High |
| Pigskin | Fashion accessories, garments | Cost-effective | Less durable than cattle hide | Medium |
| Synthetic Leather | Automotive interiors, furniture | Affordable and easy to clean | Lacks breathability | Low |
| Exotic Leathers | High-end fashion, luxury accessories | Unique aesthetics and luxury appeal | High cost and strict regulations | High |
This guide serves as a strategic resource for B2B buyers in the leather technology sector, providing insights into material selection that align with market demands and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather technology
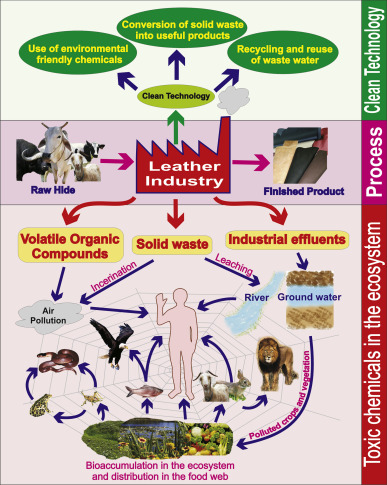
What Are the Main Stages of Leather Manufacturing?
The leather manufacturing process is a sophisticated blend of art and science, comprised of several critical stages. Each stage contributes significantly to the quality and durability of the final product. The primary stages include:
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves several subprocesses to prepare the raw hides for tanning. The hides undergo soaking to remove salt and dirt, followed by hair removal through liming. Deliming, bating, and bleaching may also occur, which prepare the hide by removing impurities and enhancing its quality. Pickling is another preparatory step that helps to stabilize the hide before it enters the tanning phase.
-
Tanning: Tanning is arguably the most crucial step in leather production, as it transforms raw hides into a stable and durable material. Various methods exist, including chrome tanning and vegetable tanning. In chrome tanning, hides are immersed in a solution containing chromium salts, while vegetable tanning uses natural tannins derived from plant sources. The choice of tanning method affects the leather’s properties, such as flexibility, color, and resistance to water and decay.
-
Crusting: Following tanning, the crusting process further enhances the leather’s quality. This stage includes thinning, lubricating, and coloring the leather. Chemicals used during this phase must be effectively fixed to ensure longevity. The crusting process concludes with drying and softening the leather, making it pliable and ready for finishing.
-
Finishing: Finishing operations apply a protective layer and aesthetic enhancements to the leather. Techniques such as oiling, polishing, and embossing are common, allowing manufacturers to create unique textures and appearances. This stage can significantly influence the leather’s marketability, as it enhances both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
What Key Techniques Are Used in Leather Production?
Throughout these stages, various techniques are employed to ensure high-quality leather production. Notable methods include:
-
Drum Tanning: This technique involves placing hides in a rotating drum filled with tanning liquor, allowing for even penetration of tanning agents. This method is efficient and produces consistent results.
-
Spray Finishing: In this finishing technique, a spray application of finishing agents provides an even coat over the leather surface, ensuring uniformity and enhancing the leather’s durability.
-
Dyeing Techniques: Various dyeing methods, such as immersion and surface dyeing, are utilized to impart color to leather. Each technique offers different aesthetic outcomes and affects the leather’s final appearance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance in leather manufacturing is critical for maintaining product standards and meeting customer expectations. Several international and industry-specific standards guide these processes:
-
International Standards: ISO 9001 is the most recognized quality management standard globally, outlining requirements for effective quality management systems. Compliance with this standard ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are relevant in specific contexts, ensuring that products meet safety and performance standards applicable to their respective markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Leather Production?
To maintain quality throughout the manufacturing process, several checkpoints are established:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint occurs at the beginning of the production cycle, where raw materials (hides, chemicals) are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC ensures that each stage of production adheres to quality standards. This may involve monitoring chemical concentrations during tanning or checking for defects during crusting.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the leather is finished, a thorough inspection is performed to assess the final product against quality benchmarks. This includes testing for durability, colorfastness, and overall aesthetic quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers maintain robust quality control practices. Here are several ways to verify supplier QC:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management practices. Buyers should assess whether suppliers adhere to international standards and maintain proper documentation.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality reports from suppliers can offer transparency regarding their QC processes and outcomes. These reports should detail testing results and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices. This is especially important for international transactions, where buyers may not have direct oversight.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
When dealing with international suppliers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers must be aware of specific QC nuances:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and practices. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and quality expectations to ensure compliance.
-
Sustainability Practices: Increasingly, buyers are prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate sustainable practices. Understanding how suppliers manage waste and utilize eco-friendly materials is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
-
Traceability and Transparency: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide traceability of their materials and processes. This transparency builds trust and ensures that products meet the desired quality and ethical standards.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in leather technology is crucial for B2B buyers. By engaging with suppliers who prioritize quality and sustainability, buyers can ensure that they receive high-quality leather products that meet their specific needs. The combination of robust manufacturing processes, adherence to international standards, and effective quality control measures will significantly enhance the value chain in the leather industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather technology’
Wprowadzenie
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring leather technology solutions, ensuring that your organization can benefit from high-quality materials and innovative processes. As the leather industry continues to evolve, understanding the key steps in sourcing technology can enhance product quality, improve sustainability, and optimize operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements for leather technology. This includes understanding the types of leather products you intend to manufacture, the specific chemical properties required, and any compliance standards that must be met.
– Identify Applications: Consider whether you need leather for footwear, automotive, or fashion accessories, as each application has unique requirements.
– Determine Quality Standards: Specify the durability, flexibility, and aesthetic qualities needed to meet your end-use expectations.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in leather technology. Look for companies with a proven track record in the industry and positive client reviews.
– Use Online Platforms: Explore B2B marketplaces, industry directories, and trade shows to find reputable suppliers.
– Assess Industry Experience: Choose suppliers with extensive experience in your specific type of leather technology or application.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers possess relevant certifications that demonstrate their commitment to quality and sustainability. This step is crucial for ensuring compliance with international standards.
– Quality Management Systems: Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate robust quality management practices.
– Environmental Standards: Certifications like ISO 14001 can assure you that the supplier adheres to environmental management practices.
Step 4: Request Samples and Technical Data
Before making a purchase decision, request samples and technical data sheets from potential suppliers. This allows you to assess the quality and performance of their products firsthand.
– Evaluate Samples: Test the leather for flexibility, color consistency, and durability against your specifications.
– Review Technical Data: Analyze the chemical compositions and processing methods to ensure they align with your production requirements.
Step 5: Conduct Supplier Audits
If feasible, conduct on-site audits of shortlisted suppliers to assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes. This step provides deeper insights into their operations.
– Inspect Facilities: Evaluate cleanliness, organization, and adherence to safety standards.
– Meet with Key Personnel: Engage with technical staff to discuss their expertise and innovation capabilities.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize terms of purchase, pricing, and delivery schedules. This step is essential for securing favorable conditions for your business.
– Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond the initial price; factor in shipping, potential tariffs, and long-term supply agreements.
– Establish Clear Terms: Ensure that terms regarding quality assurance, return policies, and delivery timelines are well-documented.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Step 7: Monitor Supplier Performance Post-Purchase
After procurement, continuously monitor supplier performance to ensure they meet the agreed-upon standards. Establish a feedback loop for ongoing communication regarding quality and service.
– Set Performance Metrics: Define KPIs such as delivery times, defect rates, and responsiveness to issues.
– Regular Reviews: Schedule regular performance reviews to address any concerns and strengthen your partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing leather technology, ensuring they partner with suppliers who can meet their needs and contribute to their business success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather technology Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Technology Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure in leather technology sourcing is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their investments. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, particularly animal hides, plays a significant role in the overall pricing. The quality of the hides (e.g., cattle vs. exotic skins) can greatly influence costs. Buyers should also consider the sourcing region, as local availability can affect pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly depending on the region of production. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to assess the skill level and expertise of the workforce, especially for specialized tasks like tanning and finishing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes and advanced technologies can help reduce overhead, which is a key area for potential savings.
-
Tooling: The investment in tooling for custom designs can be substantial. Buyers should be aware that tooling costs can be amortized over larger production runs, making it essential to negotiate Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the leather meets specified standards. While this adds to the cost, it is a necessary investment to minimize defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs can fluctuate based on the distance from the supplier and the chosen shipping methods. Understanding the total logistics expenses is vital, especially for international buyers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and the relationship with the buyer.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Leather Technology Costs?
Several factors influence the final price of leather products:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that allow for cost savings while meeting their demand.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique designs or specifications may incur additional costs. Customization requires careful negotiation to ensure that the buyer’s needs are met without incurring excessive charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (e.g., eco-friendly practices) may raise costs but can lead to higher market value. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between cost and quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and technological capabilities can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms determines the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial to avoid unexpected costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Leather Technology Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:

Illustrative image related to leather technology
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage in open discussions about pricing, especially regarding bulk purchases and long-term contracts. Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential resale value. This holistic view can inform better purchasing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing structures based on local market conditions, tariffs, and trade agreements. Familiarity with these nuances can aid in more effective negotiations.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of trends in leather technology and market demands can provide leverage during negotiations and sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is essential to recognize that prices for leather technology sourcing can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier relationships, and specific project requirements. Therefore, the prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be validated through direct supplier engagement and market research.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather technology With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Leather Technology
In the ever-evolving landscape of materials and manufacturing processes, businesses often seek alternatives to traditional leather technology. As global markets increasingly emphasize sustainability and innovative solutions, B2B buyers need to evaluate various options that fulfill similar functional requirements as leather, while also considering environmental impact, cost-effectiveness, and performance. This analysis compares leather technology with two viable alternatives: synthetic leather and natural fibers, providing insights for informed decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Leather Technology | Synthetic Leather | Natural Fibers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability and flexibility | Good durability, but less breathable | Varies; often less durable |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to sourcing | Generally lower upfront costs | Variable; can be low, but depends on type |
| Ease of Implementation | Established processes, requires expertise | Easier to mass-produce | Often requires specialized processing |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Varies; may require special care |
| Best Use Case | Fashion, automotive, luxury goods | Affordable fashion, accessories | Eco-friendly products, home textiles |
Analyzing Synthetic Leather: What Are Its Strengths and Weaknesses?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional leather. Its production is typically less resource-intensive, leading to lower initial costs. Additionally, synthetic leather can be manufactured in various colors and textures, making it versatile for fashion and upholstery. However, it often lacks the breathability and longevity of genuine leather, which may affect its performance in high-wear applications. While synthetic leather requires less maintenance, its environmental impact, particularly when produced from non-biodegradable materials, raises concerns for eco-conscious businesses.
Evaluating Natural Fibers: Are They a Suitable Replacement?
Natural fibers, such as cotton, hemp, and jute, present an eco-friendly alternative to leather technology. These materials are biodegradable and can often be sourced sustainably, aligning with the growing demand for environmentally responsible products. Natural fibers also offer breathability and comfort, making them suitable for clothing and home textiles. However, the performance of natural fibers can vary significantly based on the type and treatment, and they generally do not match the durability of leather or synthetic alternatives. Maintenance requirements can also be more intensive, as natural fibers may require special cleaning methods to preserve their integrity.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Make the Right Choice for Their Needs?
When selecting between leather technology and its alternatives, B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements, including product application, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. Leather technology remains a strong contender for high-end applications due to its durability and aesthetic appeal. However, synthetic leather may serve as a more cost-effective solution for budget-sensitive projects, while natural fibers can cater to environmentally conscious consumers. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will empower businesses to make informed choices that align with their strategic objectives and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather technology
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Leather Technology?
Understanding the technical properties of leather is crucial for B2B buyers seeking quality materials for manufacturing. Here are some essential specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality classification of leather based on its origin and processing. Grades can range from full-grain (the highest quality) to corrected-grain (lower quality). This specification is vital for buyers as it directly influences the durability, aesthetics, and cost of the final product. Knowing the material grade helps in selecting the right leather for specific applications, ensuring that it meets both functional and aesthetic requirements.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible variation in dimensions and properties of leather products, such as thickness and weight. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.5mm in thickness can significantly affect the leather’s performance in manufacturing. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels ensures that the leather meets manufacturing standards and that the final product maintains consistency and quality.
3. Hydrothermal Stability
This property measures the leather’s ability to withstand changes in moisture and temperature without degrading. Hydrothermal stability is crucial for products exposed to varying environmental conditions, such as automotive interiors. Buyers should consider this property when sourcing leather for applications requiring durability and resilience, as it impacts the lifespan of the final product.
4. Colorfastness
Colorfastness refers to the leather’s ability to retain its color when exposed to light, water, or friction. This property is particularly important for fashion and upholstery applications where aesthetic appeal is paramount. B2B buyers should prioritize leather with high colorfastness ratings to ensure that their products remain visually appealing over time.
5. Flexibility
Flexibility indicates how easily leather can bend and conform to shapes without cracking or losing integrity. This property is especially relevant for footwear and apparel, where comfort and fit are essential. Buyers should assess flexibility to ensure that the leather will perform well in their specific applications, offering both comfort and durability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Leather Technology?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the leather market. Here are some commonly used terms:

Illustrative image related to leather technology
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products based on the specifications provided by another company. In the leather industry, OEM partnerships are crucial for brands looking to produce leather goods without investing in manufacturing facilities. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers leverage existing expertise and resources to enhance their product offerings.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategies and negotiate better terms with suppliers, ensuring that they can meet demand without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. In leather procurement, an RFQ can streamline the sourcing process by allowing buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers. Understanding how to effectively draft and send RFQs can lead to better pricing and terms, ultimately benefiting the buyer’s bottom line.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For B2B buyers in the leather industry, familiarity with Incoterms is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring smooth transactions, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
5. Tannery Waste Management
This term encompasses the practices and regulations surrounding the disposal and treatment of waste produced during the leather tanning process. Effective waste management is not only essential for compliance with environmental regulations but also for enhancing a company’s sustainability profile. Buyers should consider suppliers’ waste management practices as part of their sourcing criteria, aligning with global sustainability trends.
Illustrative image related to leather technology
These technical properties and trade terms are foundational for B2B buyers in the leather industry, facilitating informed decision-making and fostering successful business relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather technology Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Leather Technology Sector?
The leather technology sector is experiencing a transformative phase influenced by several global drivers. The surge in demand for sustainable and ethically sourced materials is reshaping traditional leather markets. Innovations in tanning processes and the introduction of environmentally friendly chemicals have gained traction, particularly among B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and automation are also streamlining production, enhancing quality control, and reducing waste.
Moreover, the sector is witnessing a shift towards customization and personalization, driven by consumer preferences for unique products. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who seek to differentiate their offerings in competitive markets. For instance, the growing popularity of vegan and alternative leathers—such as those derived from pineapple leaves or mushrooms—presents new sourcing opportunities. As these materials gain acceptance, they open avenues for collaboration between manufacturers and innovative startups.
In regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam, where the leather industry is integral to local economies, understanding these dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers. They must stay abreast of regulatory changes and market demands to align their sourcing strategies effectively. The integration of digital platforms for sourcing and supply chain management is also becoming essential, allowing buyers to make informed decisions and build resilient supply chains.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Relationships in Leather Technology?
Sustainability is no longer a trend but a necessity in the leather technology sector. The environmental impact of leather production, particularly concerning waste and carbon emissions, has prompted international buyers to prioritize ethical sourcing practices. The leather industry has a significant role in the circular economy; by utilizing by-products from the meat industry, it minimizes landfill waste and contributes to carbon neutrality.
B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of eco-friendly tanning agents and responsible water management techniques. Certifications like the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification serve as benchmarks for ethical sourcing. These certifications not only help companies comply with regulations but also enhance their brand reputation, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Furthermore, ethical sourcing fosters trust and transparency within supply chains. B2B buyers who prioritize sustainability can strengthen their partnerships with suppliers, leading to more collaborative and innovative relationships. As the demand for sustainable leather products grows, companies that align their sourcing strategies with these principles will likely gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Leather Technology Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of leather technology has been marked by significant advancements over thousands of years. From its origins as a rudimentary method of preserving animal hides, the industry has transformed into a sophisticated sector employing cutting-edge technology. Initially, leather production was a labor-intensive process characterized by manual techniques. However, the introduction of industrialization in the 19th century revolutionized the sector, leading to mass production and the development of specialized tanning methods.
Today, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and technological innovation. Modern leather production incorporates advanced chemistry, environmental management systems, and automation to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is vital; it not only highlights the industry’s resilience but also emphasizes the ongoing opportunities for innovation and collaboration. As the sector continues to evolve, buyers who appreciate this rich history will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of sourcing in the leather technology market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather technology
-
1. How do I solve issues related to leather quality control during production?
Quality control in leather production begins with selecting high-quality raw materials and implementing rigorous testing protocols. Establish partnerships with reliable suppliers who provide transparency regarding their sourcing and processing methods. Regularly inspect samples at different production stages and utilize standardized tests to assess characteristics such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear. Additionally, consider third-party audits to validate the quality assurance processes in place, ensuring that the final product meets your standards. -
2. What is the best type of leather for high-end fashion products?
The best leather for high-end fashion products typically includes full-grain and top-grain leathers. Full-grain leather retains the natural grain and imperfections of the hide, offering durability and a unique aesthetic. Top-grain leather, while sanded to remove imperfections, maintains a luxurious feel and is more pliable. When sourcing leather for fashion, prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing, as consumers increasingly favor brands that demonstrate environmental responsibility. -
3. How can I ensure my leather supplier meets international trade compliance?
To ensure compliance with international trade regulations, verify that your leather supplier adheres to relevant local and international standards, such as REACH or ISO certifications. Request documentation proving compliance with environmental and labor laws. It’s advisable to conduct due diligence through site visits or third-party audits to assess their operations. Establishing clear contractual agreements that outline compliance expectations can also safeguard your business against potential legal issues. -
4. What customization options should I consider when sourcing leather products?
When sourcing leather products, explore customization options such as color, texture, and finish. Many suppliers offer bespoke services, allowing you to specify dimensions, designs, and branding elements, such as embossed logos. Discuss minimum order quantities (MOQs) with suppliers to understand the feasibility of custom orders. Ensure that the supplier has a robust prototype process to help visualize the final product before mass production, minimizing risks of discrepancies. -
5. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for leather products?
Minimum order quantities for leather products vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the order. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 to 1,000 units for standard items, while custom designs may require higher quantities. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify their MOQ policies and assess your production needs to find a mutually beneficial arrangement. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller brands, so it’s worth discussing your requirements. -
6. What payment terms are commonly used in B2B leather transactions?
Common payment terms in B2B leather transactions include advance payment, net 30/60/90 days, and letter of credit arrangements. Advance payments are often required for custom orders, while established relationships may allow for more favorable terms. When negotiating, consider the total order value and your cash flow needs. It’s crucial to have clear agreements in place to prevent misunderstandings regarding payment schedules and methods. -
7. How can I effectively vet potential leather suppliers?
To vet potential leather suppliers, begin by researching their reputation and history in the industry. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and testimonials to gauge their reliability and quality. Request samples of their leather products to assess quality firsthand. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing processes, sourcing of materials, and adherence to environmental standards. Establishing direct communication can also help you gauge their responsiveness and willingness to address your specific needs. -
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing leather internationally?
When sourcing leather internationally, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a logistics partner experienced in handling leather products to ensure proper handling and compliance with import/export laws. Be aware of potential tariffs and taxes that may affect your overall costs. Additionally, factor in the time required for production and delivery to align with your inventory management and sales strategies, ensuring that you maintain an adequate supply chain.
Top 5 Leather Technology Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Leather Technologies – Eco-Friendly Leather Dry-Cleaning Chemicals
Domain: leathertechnologies.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Leather Technologies, Inc. offers a range of high-quality chemicals specifically designed for leather dry-cleaning. The company emphasizes environmentally friendly products and innovative chemistry to enhance the quality of leather. They provide over 60 different chemicals for various purposes, supported by experienced technical staff and exceptional customer service.
2. Leather Industry – Sustainable Value Creation
Domain: jlse.springeropen.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: The leather industry is a sustainable sector that converts animal hides and skins into high-value products, contributing to carbon neutrality and aligning with circular economy principles. Key statistics include: 3.82 billion cattle, sheep, and goats in stock and 1.37 billion slaughtered annually (2014-2023). In 2024, China’s leather industry achieved 877.4 billion yuan in sales revenue and 47.2 b…
3. ScienceFather – Leather Technology Solutions
Domain: cad-conferences.sciencefather.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Leather Technology integrates Computer Aided Design (CAD) into leather production and goods manufacturing, enhancing precision and innovation. Key aspects include: 1. CAD-Enhanced Leather Design: Revolutionizes design with intricate patterns and textures. 2. Sustainable Leather Production: Optimizes tanning processes and reduces waste for eco-friendly practices. 3. Leather Goods Manufacturing Effi…
4. Scribd – Leather Manufacturing Process
Domain: scribd.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: The document provides information about the leather manufacturing process, which is divided into four main steps: pre-tanning, tanning, post-tanning, and finishing. The pre-tanning stage involves cleaning and preparing the raw hide through processes like soaking, unhairing, liming, deliming, and bating to remove hair and other non-collagenous materials. The tanning stage stabilizes the collagen ma…
5. GCELT – Leather Technology Education
Domain: gcelt.gov.in
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: The Government College of Engineering and Leather Technology (GCELT) is a pioneer institution in education and research in Leather Technology, originally established in 1919. It was initially named ‘Calcutta Research Tannery’ and aimed to explore indigenous resources for leather production. In 1955, it became affiliated with the University of Calcutta, offering a B. Sc. (Tech) course in Leather Te…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather technology
As the leather industry evolves, international B2B buyers are presented with unique opportunities to leverage strategic sourcing to enhance their supply chains. By prioritizing high-quality, environmentally friendly chemicals and innovative technologies, businesses can improve their leather production processes while adhering to sustainability goals. Understanding the intricate manufacturing stages—from preparatory processes to finishing techniques—allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Moreover, the growth of the leather sector is underpinned by a commitment to circular economy principles, which are becoming increasingly important in global markets. By sourcing responsibly, buyers not only contribute to reducing waste and greenhouse gas emissions but also position themselves as leaders in the quest for sustainable practices.
Looking ahead, the focus on technological advancement and high-end innovations in leather production will continue to reshape the industry landscape. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively seek partnerships with forward-thinking suppliers that prioritize quality and sustainability. Embrace this transformative journey in leather technology to secure a competitive advantage and drive growth in your market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to leather technology
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.