Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for artificial leather
As international B2B buyers increasingly seek sustainable and cost-effective materials, the challenge of sourcing high-quality artificial leather has come to the forefront. With its growing popularity as a versatile alternative to genuine leather, artificial leather—also known as faux leather or synthetic leather—offers a unique combination of durability, aesthetic appeal, and affordability. This comprehensive guide will navigate you through the diverse landscape of artificial leather, exploring various types such as polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), their myriad applications across industries, and key factors for vetting suppliers.
Throughout this guide, you will gain insights into the critical aspects of purchasing artificial leather, including cost considerations, environmental impact, and maintenance requirements. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you will make informed decisions that not only meet your project’s specific needs but also align with ethical and sustainable practices.
Whether you are sourcing materials for furniture upholstery, automotive interiors, or innovative fashion products, this guide serves as an essential resource for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Brazil and Vietnam. With a focus on actionable insights and strategic sourcing, we aim to empower you to confidently navigate the global market for artificial leather, ensuring that your purchasing decisions drive both profitability and sustainability.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 Artificial Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for artificial leather
- Understanding artificial leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of artificial leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘artificial leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for artificial leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for artificial leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘artificial leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for artificial leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing artificial leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for artificial leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the artificial leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of artificial leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for artificial leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding artificial leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| PU Leather | Soft, supple feel; embossed grain for leather-like texture; made with polyurethane. | Upholstery for residential and commercial furniture, automotive interiors. | Pros: Affordable, easy to clean, durable. Cons: Less breathable than genuine leather. |
| PVC Leather | Made from polyvinyl chloride; typically more rigid; available in a wide range of colors. | Marine upholstery, commercial transport seating, fashion accessories. | Pros: Water-resistant, low maintenance. Cons: Can be less durable than PU leather. |
| Vegan Leather | Made from sustainable materials like cork or apple peels; eco-friendly alternative. | Fashion items, eco-conscious brands, high-end upholstery. | Pros: Environmentally friendly, unique textures. Cons: May have higher production costs. |
| Microfiber Leather | Ultra-fine synthetic fibers; mimics the softness and texture of real leather. | Luxury upholstery, automotive interiors, fashion accessories. | Pros: Soft, breathable, and durable. Cons: Can be more expensive than other synthetic options. |
| Naugahyde | A specific brand of vinyl upholstery; known for its durability and wide application. | Commercial furniture, healthcare facilities, automotive. | Pros: Highly durable, stain-resistant. Cons: Limited color options compared to other types. |
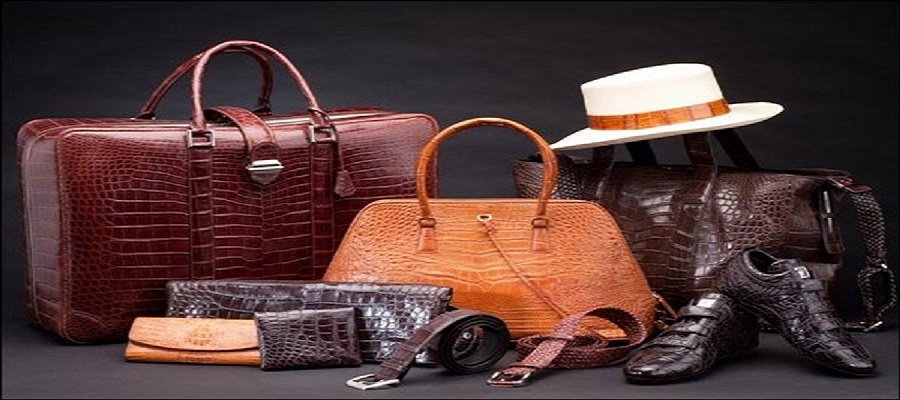
What Are the Characteristics of PU Leather?
PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is recognized for its softness and flexibility, closely resembling genuine leather. It is produced by coating a fabric backing with a flexible polymer, making it an ideal choice for various upholstery applications, particularly in residential and commercial furniture. B2B buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of PU leather, as it can be significantly less expensive than genuine leather while offering ease of maintenance and durability. However, its lower breathability may be a consideration for certain applications.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
How Does PVC Leather Differ from Other Types?
PVC leather, made from polyvinyl chloride, is characterized by its rigidity and wide array of color options. It is particularly suited for applications in marine environments and commercial transport seating due to its water-resistant properties. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of low maintenance and affordability against potential durability concerns, as PVC may not withstand wear as well as other materials. Its aesthetic versatility makes it a popular choice for fashion accessories as well.
Why Choose Vegan Leather for Sustainable Practices?
Vegan leather is crafted from sustainable materials such as cork or apple peels, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional leather. It appeals to brands aiming to position themselves as environmentally conscious. B2B buyers should consider the unique textures and innovative designs that vegan leather can offer, although it may come with higher production costs. Its growing popularity in fashion and high-end upholstery indicates a shifting market toward sustainable options.
What Makes Microfiber Leather a Premium Choice?
Microfiber leather is made from ultra-fine synthetic fibers, providing a luxurious feel and appearance similar to real leather. It is often used in luxury upholstery and automotive interiors. B2B buyers should note its excellent breathability and durability, making it suitable for high-end applications. While it may be more expensive than other synthetic options, the quality and performance can justify the investment, especially in markets where premium materials are in demand.
How Does Naugahyde Stand Out in the Market?
Naugahyde is a well-known brand of vinyl upholstery that is recognized for its durability and application versatility. Commonly used in commercial settings such as healthcare facilities and automotive interiors, it offers significant resistance to stains and wear. B2B buyers should consider Naugahyde for projects requiring high-performance materials, though they may find a limited range of colors compared to other synthetic leathers. Its established reputation makes it a reliable choice for bulk purchasing.
Key Industrial Applications of artificial leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of artificial leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Upholstery for car interiors | Cost-effective, durable, and easy to maintain | Compliance with automotive standards, availability in desired colors |
| Furniture Manufacturing | Residential and commercial upholstery | Aesthetic appeal with lower costs compared to genuine leather | Quality certifications, stain and abrasion resistance |
| Fashion and Apparel | Jackets, handbags, and accessories | Versatile design options and ethical appeal | Sourcing sustainable materials, color variety, and durability |
| Marine and Outdoor Equipment | Upholstery for boats and outdoor furniture | Weather resistance and easy maintenance | UV resistance, water-proofing, and adherence to safety standards |
| Health Care | Upholstery for medical furniture and equipment | Hygiene, ease of cleaning, and durability | Compliance with health regulations, antimicrobial properties |
How is Artificial Leather Used in Automotive Upholstery?
In the automotive sector, artificial leather is widely utilized for upholstery in car interiors. It offers an attractive alternative to genuine leather, providing similar aesthetics at a fraction of the cost—up to 75% less. This material is not only durable but also resistant to stains and easy to clean, making it ideal for vehicles exposed to everyday wear and tear. International buyers should prioritize suppliers that comply with automotive safety standards and offer a wide range of color and texture options to meet diverse consumer preferences.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
What Role Does Artificial Leather Play in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing industry, artificial leather is increasingly favored for both residential and commercial upholstery. Its ability to mimic the luxurious look of genuine leather while being more affordable appeals to a broad market. The material’s resistance to stains and ease of maintenance are crucial benefits for businesses catering to high-traffic environments like hotels and restaurants. Buyers should consider sourcing materials that meet quality certifications and offer a variety of styles and colors to enhance their product offerings.
Why is Artificial Leather Important in Fashion and Apparel?
Artificial leather has carved a niche in the fashion and apparel industry, particularly for items like jackets, handbags, and accessories. Its versatility allows designers to explore a myriad of colors and styles, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers who prefer cruelty-free options. For international B2B buyers, sourcing from manufacturers that emphasize sustainable practices and provide high-quality finishes is essential for maintaining brand reputation and meeting consumer expectations.
How is Artificial Leather Applied in Marine and Outdoor Equipment?
In the marine sector, artificial leather is used for upholstery in boats and outdoor furniture due to its weather-resistant properties. It withstands exposure to the elements, ensuring longevity and aesthetic appeal in outdoor settings. Buyers should focus on sourcing materials that offer UV resistance and waterproofing features, as these properties are vital for maintaining the integrity of marine and outdoor applications over time.
What Are the Benefits of Artificial Leather in Health Care Settings?
Artificial leather is increasingly adopted in health care for upholstery on medical furniture and equipment. Its easy-to-clean nature and durability help maintain hygiene standards, which are critical in medical environments. Buyers in this sector should prioritize materials that comply with health regulations and possess antimicrobial properties to ensure safety and cleanliness in patient care settings.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘artificial leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Assurance in Bulk Orders of Artificial Leather
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with the quality consistency of artificial leather when placing bulk orders. Variations in texture, color, and durability can lead to significant discrepancies in product offerings, ultimately affecting customer satisfaction and brand reputation. This issue is particularly pronounced when sourcing from different manufacturers or when attempting to meet specific industry standards, such as those required in the automotive or furniture sectors. A buyer might receive a shipment where the faux leather does not meet the expected specifications, leading to costly returns and production delays.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should implement a rigorous quality assurance process. Start by establishing clear specifications and quality standards that must be met by suppliers. Request samples from potential vendors before placing large orders to evaluate texture, durability, and color fidelity. It’s also advisable to visit manufacturing facilities when possible, or to request third-party inspections before shipment. Utilizing a standardized testing protocol, such as abrasion resistance and colorfastness tests, can further ensure the material meets required standards. Additionally, building long-term relationships with a trusted supplier can provide consistency in quality, making it easier to maintain product standards over time.
Scenario 2: Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Sourcing
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are increasingly pressured to consider the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. Traditional artificial leather, particularly those made from PVC, can be associated with environmental degradation and toxicity. Buyers face the dilemma of balancing cost and quality against the need for sustainable materials, especially as consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious and demanding eco-friendly products. This pressure can lead to hesitation in sourcing artificial leather, particularly in regions where sustainable practices are becoming regulatory requirements.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should actively seek suppliers that offer eco-friendly alternatives, such as PU leather made from vegetable oils or recycled materials. Engaging in dialogue with suppliers about their manufacturing processes and the environmental certifications they hold (like OEKO-TEX or GOTS) can help ensure that the materials sourced are sustainable. Moreover, consider implementing a sustainability policy that prioritizes eco-friendly materials, which can also serve as a unique selling point for your business. Participating in sustainability forums and trade shows can provide valuable insights into new innovations in synthetic leather that meet both environmental and quality standards.
Scenario 3: The Challenge of Customization and Design Flexibility
The Problem: In the competitive B2B landscape, customization options are essential for meeting diverse client needs. However, many artificial leather products come with limited design options, which can restrict a buyer’s ability to differentiate their offerings. For instance, a furniture manufacturer may find it challenging to procure artificial leather in specific colors, textures, or patterns that align with their brand identity or client specifications. This limitation can stifle creativity and innovation, hindering business growth and market competitiveness.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should partner with manufacturers known for their customization capabilities. Before placing orders, inquire about the range of colors, patterns, and finishes available. Many suppliers now offer digital design tools that allow buyers to visualize and select custom options before production. Furthermore, consider establishing a collaborative relationship with a supplier who can work with your design team to create bespoke solutions tailored to your specific needs. Investing in custom development, even for small batches, can provide a competitive edge and enhance brand differentiation in the marketplace. By staying ahead of trends and consumer preferences, you can ensure that your offerings resonate with the target audience.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for artificial leather
What Are the Key Materials Used in Artificial Leather?
Artificial leather, commonly known as faux leather, is produced from various synthetic materials, each with unique properties and applications. Understanding these materials is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Below, we analyze four common materials used in artificial leather production: Polyurethane (PU), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Microfiber, and Bio-based Leather.
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Leather Perform in Various Applications?
Polyurethane leather, often referred to as PU leather, is a popular choice due to its soft texture and leather-like appearance. It is created by coating a fabric backing with a flexible polymer, resulting in a durable and aesthetically pleasing product. PU leather is water-resistant and easy to clean, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including furniture upholstery and automotive interiors.
Pros: PU leather is cost-effective, typically up to 75% cheaper than genuine leather. It is also highly flexible in terms of color and design, allowing for innovative product offerings.
Cons: While PU leather is durable, it may not withstand extreme temperatures as well as some other materials. Over time, it can be prone to wear and tear, particularly in high-use environments.
Impact on Application: PU leather is compatible with various media, including upholstery and fashion accessories. Its water resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications as well.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding chemical use in production. Standards such as ASTM and DIN may apply, particularly for automotive and furniture applications.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Leather?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) leather is another widely used synthetic material. It is produced by layering a plastic coating over a fabric base, resulting in a material that is both durable and cost-effective.
Pros: PVC leather is highly resistant to stains and moisture, making it easy to clean and maintain. Its durability makes it suitable for high-traffic areas.
Cons: PVC leather can be less breathable than other options, leading to discomfort in certain applications like clothing. Additionally, it may not offer the same luxurious feel as PU leather.
Impact on Application: PVC leather is commonly used in commercial settings, such as restaurants and healthcare facilities, where durability and ease of maintenance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations is essential, as PVC production can release harmful chemicals. Buyers should also consider local preferences for material feel and aesthetics, particularly in markets like Europe where sustainability is a growing concern.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
How Does Microfiber Leather Compare to Other Artificial Leather Materials?
Microfiber leather is made from ultra-fine synthetic fibers that mimic the texture and appearance of real leather. This material is known for its softness and flexibility.
Pros: Microfiber leather is highly durable, resistant to stains, and easy to clean. It also offers a luxurious feel, making it suitable for high-end applications.
Cons: It can be more expensive than PU and PVC leather, which may deter some budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, its production process can be more complex.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
Impact on Application: Microfiber leather is ideal for products that require a high-end appearance, such as luxury handbags and premium upholstery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the sourcing and manufacturing processes to ensure compliance with ethical standards, especially in regions like Europe where consumer demand for sustainable products is increasing.
What Is Bio-based Leather and Its Relevance in the Market?
Bio-based leather is an emerging alternative made from sustainable materials such as plant fibers or recycled plastics. This material addresses both environmental concerns and the demand for cruelty-free products.
Pros: Bio-based leather is biodegradable and often produced with a lower environmental impact. It appeals to eco-conscious consumers and can differentiate products in a competitive market.
Cons: The technology for producing bio-based leather is still developing, which can lead to higher costs and limited availability in some regions.
Impact on Application: This material is suitable for a variety of applications, including fashion and automotive, particularly in markets that prioritize sustainability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for certifications that guarantee the sustainability of bio-based leather products. Understanding local market trends regarding eco-friendly materials is also essential for successful product positioning.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
Summary Table of Artificial Leather Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for artificial leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Furniture upholstery, automotive interiors | Soft texture and water resistance | Prone to wear over time | Low |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Commercial upholstery, healthcare facilities | Highly resistant to stains and moisture | Less breathable than other materials | Low |
| Microfiber | Luxury handbags, premium upholstery | Luxurious feel and high durability | Higher cost and complex production | Med |
| Bio-based Leather | Fashion items, automotive applications | Eco-friendly and biodegradable | Limited availability and higher costs | High |
This comprehensive analysis provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to select the most suitable artificial leather material for their specific applications. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each type will aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with market demands and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for artificial leather
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Artificial Leather?
The manufacturing process for artificial leather involves several key stages, each essential for creating a high-quality product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers ensure they are sourcing from reliable suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The primary materials for artificial leather are synthetic polymers, primarily polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The first step in the manufacturing process involves sourcing high-quality raw materials. This includes mixing these polymers with additives to enhance properties like flexibility, durability, and resistance to water and stains.
During this stage, suppliers often conduct preliminary quality checks on the raw materials to ensure they meet industry standards. This may involve verifying the chemical composition and conducting tests for toxic substances, especially for buyers concerned with environmental and health regulations.
2. Forming: How Is the Artificial Leather Created?
Once the materials are prepared, the next phase is forming. This typically involves applying a polymer coating to a fabric backing, which can be made from various materials, including cotton, polyester, or a blend. The coating process is crucial as it determines the final texture and appearance of the artificial leather.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
Techniques such as calendaring, where the polymer is pressed between rollers, are commonly used to achieve the desired thickness and finish. Some manufacturers also employ embossing techniques to create a grain pattern that mimics genuine leather. This stage is vital for ensuring that the final product meets aesthetic and functional requirements.
3. Assembly: What Processes Are Involved?
The assembly stage involves cutting the formed artificial leather into specific shapes and sizes for various applications, such as upholstery, clothing, and accessories. This step often includes stitching or bonding components together.
Quality control measures during assembly may include checking for defects in seams, color consistency, and overall craftsmanship. Suppliers should have a robust system for tracking production batches to identify any issues that arise during this phase.
4. Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared?
Finishing is the final stage of the manufacturing process. It includes applying protective coatings to enhance durability, stain resistance, and ease of cleaning. Common finishes may include topcoats that provide additional UV protection or antimicrobial properties.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
At this stage, manufacturers also conduct final quality checks to ensure that the artificial leather meets both aesthetic and functional specifications. This may involve visual inspections and physical tests for durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Artificial Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a crucial aspect of artificial leather production, particularly for B2B buyers who require consistent, high-quality materials. Understanding the relevant international standards and quality control checkpoints can help buyers make informed decisions.
ISO 9001: What Does It Mean for Quality Management?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard for quality management systems (QMS). Manufacturers that comply with ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement. For B2B buyers, sourcing from ISO-certified suppliers can provide assurance that the manufacturing processes are regularly evaluated and optimized.
CE Marking: What Does It Indicate for Product Safety?
In Europe, the CE marking indicates that a product meets specific safety, health, and environmental protection standards. For artificial leather used in consumer goods, obtaining CE certification can be a significant selling point. Buyers should inquire whether their suppliers have the necessary certifications to ensure compliance with local regulations.
API Certification: Why Is It Important for Specific Industries?
The American Petroleum Institute (API) certification may be relevant for artificial leather used in industrial applications, such as automotive and marine upholstery. This certification indicates that the materials meet rigorous standards for performance and safety. B2B buyers should consider whether their suppliers hold relevant API certifications for their intended use.
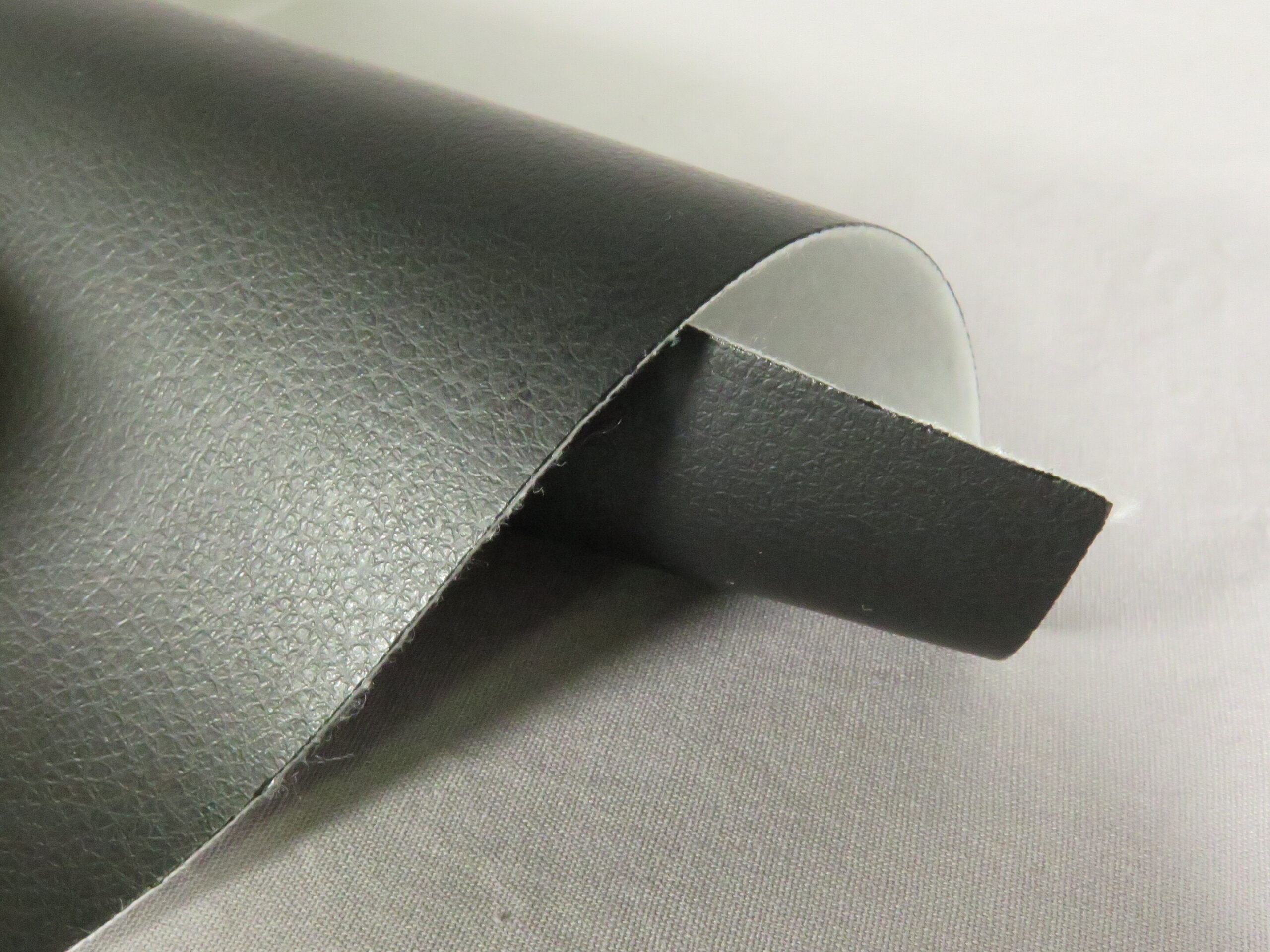
Illustrative image related to artificial leather
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Artificial Leather Manufacturing?
Quality control is integral to ensuring that artificial leather products meet industry standards. Key checkpoints include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
IQC: How Do Suppliers Ensure Raw Material Quality?
Incoming Quality Control (IQC) is the first checkpoint in the quality assurance process. Suppliers assess the quality of raw materials before they are used in production. Common practices include sampling and testing for compliance with specifications, checking for defects, and ensuring that materials are free from harmful substances.
IPQC: What Monitoring Occurs During Production?
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) involves monitoring the manufacturing process to catch defects early. This may include real-time inspections during the coating, forming, and assembly stages. By maintaining stringent IPQC measures, manufacturers can reduce the risk of producing substandard products and ensure that they meet customer specifications.
FQC: How Is the Final Product Evaluated?
Final Quality Control (FQC) is the last checkpoint before products are shipped to clients. This phase typically includes comprehensive testing for durability, flexibility, and aesthetic qualities. B2B buyers should request FQC reports to verify that the products meet their specific requirements.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers uphold high-quality standards throughout the manufacturing process. Here are some actionable insights:
Conducting Supplier Audits: What Should Buyers Look For?
Performing supplier audits is an effective way to assess quality control processes. Buyers should look for documentation of quality management systems, evidence of compliance with international standards, and records of past quality issues and resolutions. Audits can also help identify areas for improvement in the supplier’s processes.
Requesting Quality Reports: What Information Should Be Included?
Buyers should request quality reports from their suppliers, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results. These reports provide insight into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and can help buyers make informed decisions.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections: How Can They Ensure Objectivity?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an extra layer of assurance for buyers. These agencies can perform independent assessments of the manufacturing process and final products, ensuring that they meet specified standards and requirements.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may face unique challenges in ensuring quality control. Here are key considerations:
Understanding Regional Regulations: What Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations regarding product safety and environmental impact. This understanding can help in selecting suppliers that comply with both international standards and local laws, reducing the risk of regulatory issues.
Language and Cultural Barriers: How Can They Be Overcome?
Language differences and cultural nuances can complicate communication with suppliers. Establishing clear channels of communication and possibly hiring local representatives can help bridge these gaps, ensuring that quality expectations are clearly conveyed and understood.
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: What Are the Best Practices?
Logistics can impact the quality of artificial leather products. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that products are transported under optimal conditions, minimizing risks related to damage or degradation during transit.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards for artificial leather, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘artificial leather’
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving market for artificial leather, B2B buyers must adopt a systematic approach to sourcing. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help international buyers navigate the complexities of procuring artificial leather, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers for their needs. By following these steps, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and sustainability goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the requirements for your artificial leather. Identifying the specific characteristics—such as thickness, texture, color, and intended application—is crucial. This step ensures that you procure materials suitable for your projects, whether for upholstery, automotive interiors, or fashion accessories.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
- Consider performance attributes: Look for water resistance, durability, and ease of cleaning, as these factors will impact the longevity and maintenance of your products.
- Specify compliance needs: If your products must meet certain industry standards or regulations, clearly define these in your specifications.
Step 2: Research Material Types
Understand the different types of artificial leather available. Familiarize yourself with various materials like PU leather, PVC leather, and newer vegetable-based alternatives. Each type has unique properties that may better suit specific applications.
- Evaluate sustainability: Consider the environmental impact of your material choices. Eco-friendly options can enhance your brand’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Assess durability and maintenance: Different materials offer varied levels of abrasion resistance and ease of cleaning, which can affect long-term performance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Assess their experience, reputation, and product offerings to ensure they align with your needs. Request company profiles, case studies, and references to gauge their reliability and service quality.
- Check for certifications: Ensure suppliers have relevant certifications such as ISO or environmental standards, which can provide assurance of product quality and ethical practices.
- Request samples: Always ask for material samples to evaluate their quality firsthand before making bulk purchases.
Step 4: Compare Pricing Structures
Analyze pricing from multiple suppliers. Understanding the cost structure will help you identify competitive pricing and assess the value offered by different suppliers.
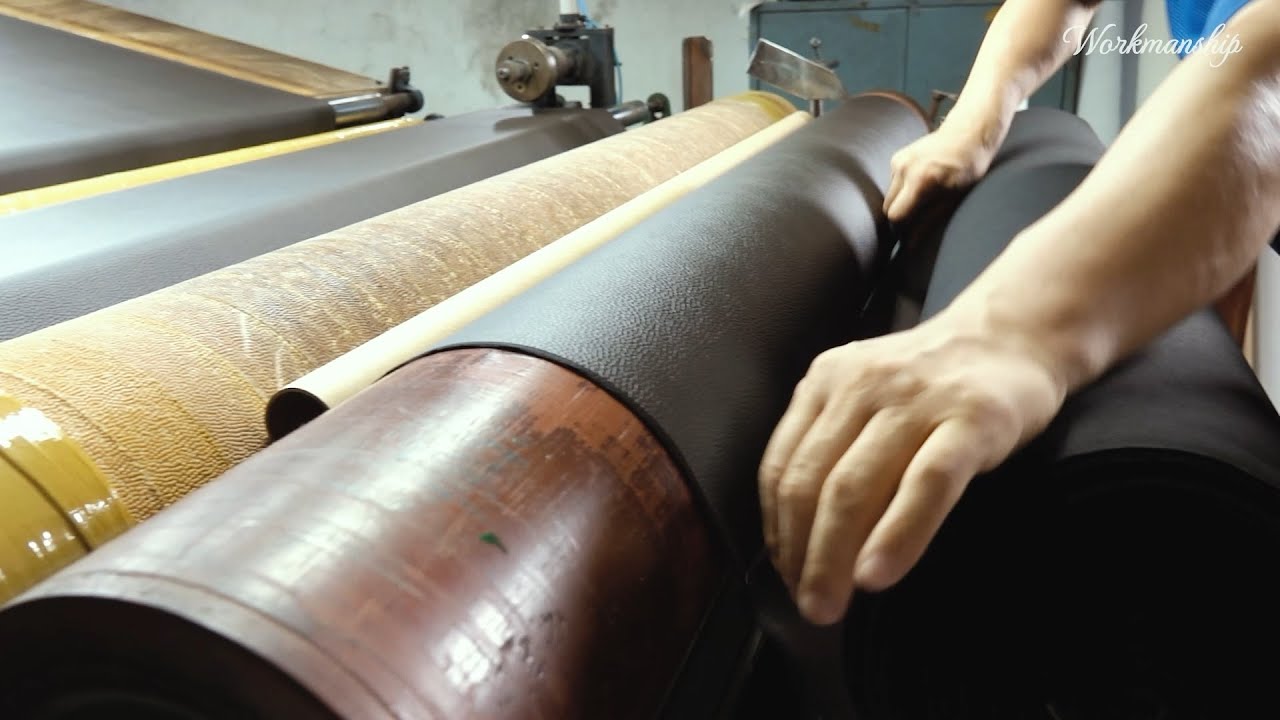

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
- Inquire about bulk discounts: Many suppliers offer reduced rates for larger orders, which can significantly impact your overall procurement costs.
- Consider total cost of ownership: Factor in shipping, duties, and potential wastage to calculate the true cost of the material.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms. Secure agreements on pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms that suit your business needs.
- Clarify return policies: Ensure you understand the supplier’s policies regarding returns or exchanges, particularly in cases of defective materials.
- Discuss lead times: Confirm lead times for production and delivery to align with your project timelines.
Step 6: Finalize Your Order
Complete the procurement process with a clear order confirmation. Double-check all specifications, quantities, and pricing before finalizing the order to avoid any misunderstandings.
- Document everything: Maintain clear records of all communications and agreements to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Establish a follow-up plan: Set a schedule to check in with the supplier during production and after delivery to address any issues promptly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source artificial leather that meets their specific needs while fostering strong supplier relationships.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for artificial leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Artificial Leather Sourcing?
When sourcing artificial leather, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The base material, often polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), accounts for a significant portion of the total cost. Prices can vary based on the quality and source of the raw materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs depend on the region of production. Countries with lower labor costs, such as Vietnam or certain African nations, may provide more competitive pricing, but it’s essential to assess the quality of workmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and other operational expenses. Efficient production processes can minimize these costs, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: For custom designs or specific textures, tooling costs can be significant. Buyers should consider these expenses when requiring bespoke products.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the product meets specified standards can add to the cost. However, investing in thorough QC can prevent costly returns and dissatisfaction later.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on the supplier’s location, chosen shipping method, and distance. Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, can also influence these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will factor in their profit margin, which can vary based on competition and market demand. Understanding the typical margins in your target region can help in negotiations.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Artificial Leather Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of artificial leather, particularly in international B2B transactions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically benefit from bulk pricing, reducing the per-unit cost. Negotiating MOQs can lead to more favorable pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs and specific performance characteristics (e.g., water resistance, color matching) can increase costs. It is vital to weigh the benefits of customization against the additional expense.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as eco-friendly or hypoallergenic standards) can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these attributes based on their end-use.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance, reliability, and after-sales support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect overall costs and risk exposure during shipping.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Artificial Leather Procurement?
To enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing artificial leather, consider these actionable tips:
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating not just on price, but also on payment terms, delivery schedules, and after-sales support. Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better deals over time.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and potential returns when calculating the TCO. Higher-quality artificial leather may have a higher upfront cost but lower long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can affect pricing. Additionally, understanding local market conditions in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe is essential for making competitive offers.
-
Conduct Market Research: Regularly assess market prices and trends to ensure you are getting a fair deal. Engaging with industry associations or trade shows can provide insights into pricing standards and emerging suppliers.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for artificial leather can fluctuate based on market conditions, raw material availability, and regional economic factors. The information provided here is indicative and should be verified with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing artificial leather With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Artificial Leather
As the demand for sustainable and ethical materials grows, B2B buyers are increasingly exploring alternatives to artificial leather. While artificial leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers several advantages such as cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance, there are other viable options available. This section will compare artificial leather with two notable alternatives: genuine leather and vegetable-tanned leather, highlighting their distinct features to help buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Artificial Leather | Genuine Leather | Vegetable-Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable and easy to clean; less breathable than leather | Highly durable; ages well; breathable | Durable; environmentally friendly; develops a unique patina |
| Cost | 75% less than genuine leather | Higher initial cost due to sourcing and processing | Moderate; generally more expensive than artificial leather but cheaper than high-end genuine leather |
| Ease of Implementation | Readily available; can be purchased by the yard | Requires skilled craftsmanship for production | Longer production time; requires skilled artisans |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean; resistant to stains and mildew | Requires regular conditioning and care | Requires specific maintenance to preserve natural qualities |
| Best Use Case | Upholstery, automotive, and fashion items | High-end fashion, furniture, and accessories | Eco-conscious consumers seeking durable and unique products |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Genuine Leather
Genuine leather is prized for its durability, breathability, and natural aesthetics. It is often viewed as a luxury material, making it ideal for high-end fashion items and premium furniture. However, the cost of genuine leather can be significantly higher due to sourcing and processing requirements. Additionally, it necessitates regular maintenance, such as conditioning and protection against moisture, which can be a drawback for some businesses. Despite these challenges, genuine leather’s longevity and the prestige associated with it make it a sought-after choice for many B2B buyers.
Vegetable-Tanned Leather
Vegetable-tanned leather offers an eco-friendly alternative to both artificial and genuine leather. It is produced using natural tannins derived from plant sources, making it biodegradable and less harmful to the environment. This leather develops a unique patina over time, enhancing its character and appeal. However, the production process can be longer and more labor-intensive, often requiring skilled artisans to achieve the desired quality. While it typically falls between the cost of artificial and high-end genuine leather, its sustainability and unique properties attract eco-conscious businesses looking to differentiate their products.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right material for your B2B needs, consider factors such as performance, cost, maintenance requirements, and environmental impact. Artificial leather may be suitable for projects requiring cost-effective and low-maintenance solutions, while genuine leather appeals to buyers seeking luxury and durability. Vegetable-tanned leather serves as an excellent choice for those prioritizing sustainability without compromising on quality. By evaluating these alternatives against your specific use cases and brand values, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for artificial leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Artificial Leather?
Artificial leather, or faux leather, is characterized by several critical technical properties that significantly influence its application in various industries. Understanding these specifications is essential for B2B buyers to make informed decisions.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
1. Material Composition
Artificial leather is typically made from either Polyurethane (PU) or Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC). PU leather is known for its softness and flexibility, closely mimicking genuine leather, making it suitable for high-end applications. PVC leather, while more affordable, is generally less breathable and has a more plastic-like feel. B2B buyers should consider the composition based on the intended use, as PU is often preferred for upholstery, while PVC may be suitable for more utilitarian purposes.
2. Durability and Abrasion Resistance
Durability is a crucial property of artificial leather. It is designed to withstand wear and tear, making it an ideal choice for upholstery in high-traffic environments, such as commercial furniture and automotive interiors. Abrasion resistance is typically measured in Martindale rubs, with a higher number indicating greater durability. Understanding these metrics helps buyers select the right product for their specific application, ensuring longevity and reduced replacement costs.
3. Water and Stain Resistance
One of the standout features of artificial leather is its resistance to water and stains. Most synthetic leathers are treated to repel moisture, making them easier to clean and maintain compared to genuine leather. This property is particularly important in sectors like hospitality and healthcare, where hygiene is paramount. B2B buyers should look for products with high water and stain resistance ratings to ensure ease of maintenance.
4. Color Fastness and UV Resistance
Color fastness refers to the ability of the material to retain its color when exposed to light, washing, or rubbing. UV resistance is particularly critical for outdoor applications, as prolonged exposure to sunlight can cause fading. Evaluating these properties helps buyers ensure that the artificial leather will maintain its aesthetic appeal over time, which is essential for branding and customer satisfaction.
5. Breathability and Comfort
While artificial leather is generally less breathable than genuine leather, advancements in technology have led to the development of more breathable options. Breathability affects the comfort level of the material, especially in clothing and upholstery. B2B buyers should assess the comfort properties based on the end-use, particularly for products that will be in direct contact with skin.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Artificial Leather Industry?
In the artificial leather industry, several trade terms are commonly used that can impact purchasing decisions and negotiations. Familiarity with these terms is vital for effective communication and transaction management.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or products that are used in another company’s end product. For artificial leather, OEM suppliers often provide materials for automotive or furniture manufacturers. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source quality materials that meet specific industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers, as it influences inventory levels and purchasing strategies. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses manage cash flow and reduce excess inventory.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that a buyer sends to potential suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. In the artificial leather industry, submitting an RFQ can help businesses compare prices and negotiate better deals, ensuring that they get the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations, especially when sourcing artificial leather from global suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. In the artificial leather industry, understanding lead times is essential for inventory planning and meeting project deadlines. Buyers should factor in lead times when negotiating contracts to ensure timely delivery of materials.

Illustrative image related to artificial leather
By understanding these essential properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing artificial leather, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and market competitiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the artificial leather Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Shaping the Artificial Leather Market?
The artificial leather market is experiencing significant growth, driven by rising demand for sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to genuine leather across various industries. Factors such as the increasing awareness of animal rights, coupled with a growing trend towards eco-friendly products, are prompting manufacturers to innovate and expand their offerings in synthetic materials. In regions like Africa and South America, the demand for affordable upholstery materials is rising, particularly in the furniture and automotive sectors. Additionally, the Middle East and Europe are witnessing a shift towards high-quality faux leather that meets stringent design and durability standards.
Emerging technologies, such as advancements in polymer chemistry and manufacturing techniques, are enhancing the quality and aesthetic appeal of artificial leather. For B2B buyers, this translates to a broader selection of products that can be tailored to specific applications, from automotive interiors to high-end fashion. Sourcing trends are increasingly favoring suppliers who can provide not only a diverse range of colors and textures but also innovative features like water resistance and stain resistance. Furthermore, the rise of online platforms facilitates direct purchasing from manufacturers, reducing costs and increasing market accessibility for international buyers.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Artificial Leather?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration in the sourcing of artificial leather. The environmental impact of traditional leather production, which involves significant water use and chemical processing, is leading many companies to explore synthetic alternatives. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and production practices. This includes transparency in the supply chain, responsible use of materials, and adherence to environmental regulations.
In response to these demands, manufacturers are developing eco-friendly artificial leather options, such as those made from plant-based materials or recycled plastics. Certifications like Global Recycled Standard (GRS) and OEKO-TEX® are gaining importance, as they assure buyers of the sustainability and safety of the products. For companies looking to bolster their corporate social responsibility profile, sourcing artificial leather that meets these green standards is not just a trend but a strategic imperative. By partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a growing consumer base that values ethical products.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Evolution of Artificial Leather?
Artificial leather has its roots in the early 20th century, with the first significant development being the creation of Presstoff, a German invention used during wartime. Since then, the industry has evolved dramatically, spurred by innovations in materials science and changes in consumer preferences. Initially, synthetic leathers were viewed primarily as budget-friendly alternatives to genuine leather. However, technological advancements have significantly improved their quality, making them increasingly competitive in terms of durability and aesthetics.
The introduction of polyurethane (PU) leather in the latter half of the 20th century marked a turning point, as it offered a more supple and leather-like feel compared to earlier materials like PVC. Today, artificial leather is not only a practical choice but also a fashionable one, as brands across various sectors embrace its versatility. This evolution reflects a broader shift in consumer attitudes towards sustainability and ethical sourcing, positioning artificial leather as a viable option for both manufacturers and consumers alike. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into current market dynamics and future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of artificial leather
-
How do I select the right type of artificial leather for my business needs?
Choosing the appropriate artificial leather involves assessing the specific requirements of your project, such as durability, texture, and application. For upholstery, consider PU leather for its soft feel and stain resistance, while PVC may be suitable for more budget-conscious options. Analyze factors like environmental conditions—outdoor use may require water-resistant properties. Consult with suppliers about available grades and finishes that meet your desired specifications. Always request samples to evaluate texture and quality before making bulk purchases. -
What is the best artificial leather for automotive upholstery?
For automotive upholstery, PU leather is often the best choice due to its durability, soft texture, and resistance to wear and tear. It mimics the look of genuine leather while being easier to maintain and clean. Additionally, consider materials that are specifically treated for UV resistance and moisture management to withstand varying climates. Always verify that the supplier meets the necessary automotive industry standards to ensure safety and longevity in your products. -
What are the advantages of sourcing artificial leather from international suppliers?
Sourcing artificial leather internationally can provide access to a broader range of materials and competitive pricing. Countries like China and Vietnam are major manufacturers, often offering innovative designs and sustainable options. Additionally, international suppliers may have lower production costs, allowing for more cost-effective solutions. However, it is crucial to conduct thorough due diligence on supplier credentials and quality control processes to mitigate risks associated with international trade. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when purchasing artificial leather?
MOQs for artificial leather can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of material. Typically, you might encounter MOQs ranging from 50 to 500 yards. Smaller orders may be possible but could incur higher per-unit costs. Discuss your specific needs with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your business model. Be clear about your requirements to ensure a seamless ordering process. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of artificial leather?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments before shipment, or net 30/60 terms post-delivery. Some suppliers may also accept letters of credit for larger orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that provide you with sufficient cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s confidence in your order. Always document agreed-upon terms in your purchase contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing artificial leather?
To ensure quality assurance, establish clear specifications for the materials you require, including texture, color, and durability. Request samples before placing large orders and consider implementing a third-party quality inspection service to assess materials before shipment. Maintain open communication with your supplier about quality standards and expectations. Regularly review production processes and conduct audits if necessary to ensure compliance with your quality requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing artificial leather?
When importing artificial leather, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger orders. Ensure that you comply with international trade regulations and tariffs applicable to your imports. Collaborate with logistics providers who have experience in handling such materials to streamline the shipping process and minimize delays. -
Can I customize artificial leather for my brand, and what should I know?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including unique colors, textures, and finishes to align with your brand identity. Discuss your design requirements early in the sourcing process, as customization may impact lead times and pricing. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and consider minimum order quantities that may apply to custom designs. Always request prototypes to evaluate the final product before committing to a larger order.
Top 6 Artificial Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sallie Tomato – Faux Leather
Domain: sallietomato.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux Leather by Sallie Tomato is a vegan alternative to leather or cork fabric, known for its affordability. It is soft, pliable, and available in eight textures: Weave, Pebble, Legacy, Shimmer, Crocodile, Alligator, Ostrich, and Rugged. Select Faux Leathers are offered in Lite Legacy, an ultra-thin material. The fabric is sold by the quarter yard, and currently, there are 66 products available, w…
2. Decorative Fabrics Direct – PU Leather & Faux Leather
Domain: decorativefabricsdirect.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: PU Leather & Faux Leather | Vinyl Upholstery Fabric
– Terms: Free Shipping Coupon Code: SHIPFREE for Most $199 Orders
– Shop By Use: Interior Upholstery, Outdoor Upholstery, Drapery, Curtain Lining
– Shop By Color: Black, Gray, Blue, Turquoise, Aqua, Brown, Beige, Green, Orange, Coral, Purple, Red, Pink, White, Yellow, Gold
– Shop By Pattern: Animal, Birds, Fish, Beach, Nautical, Tropical, Buffalo…
3. Sewport – Faux Leather Solutions
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is a petroleum-based alternative to genuine leather. It is soft to the touch, water-resistant, and highly resistant to stains, making it easy to clean. While less durable than real leather, it is resistant to abrasions and cuts, ideal for upholstery in homes with children or pets. Faux leather can be produced in various colors and is popular for outer…
4. Nevotex – Artificial & Synthetic Leather Solutions
Domain: nevotex.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Artificial & synthetic leather for public environment, furniture: chairs & sofas
5. Kosh – Faux Leather Types
Domain: kosh-a.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Faux leather types: 1. Polyurethane (PU) Leather – Coated with polyurethane for a sleek finish, popular for fashion items. 2. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Leather – Durable and water-resistant, used in jackets, bags, and upholstery. 3. Microfiber Leather – Soft, easy to clean, breathable, used in furniture and automotive interiors. 4. Bio-Based Leather – Made from renewable plant sources like apple, p…
6. Kiki Textiles – Faux Leather Fabric
Domain: kikitextiles.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Shop Pleather & Faux Leather Fabric by the Yard – Kiki Textiles. Collection features a range of faux leather fabrics that replicate the look and feel of genuine leather while being ethical and animal-friendly. Key features include:
– Variety of colors: Beige, Black, Brown, Burgundy, Caramel, Chocolate, Cognac, Dusty Blue, Fuchsia, Gold, Gray, Hot Pink, Ivory, Kelly Green, Lavender, Magenta, Mauve…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for artificial leather
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial leather, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal element for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains. Key advantages such as cost-effectiveness, durability, and versatility position artificial leather as a preferred choice across various industries, including automotive, fashion, and furniture. With faux leather prices being up to 75% lower than genuine leather, companies can significantly reduce procurement costs while maintaining high-quality standards.
Moreover, the increasing demand for sustainable and animal-friendly materials aligns with the growing consumer preference for eco-conscious products. By partnering with reliable suppliers who prioritize innovation in synthetic leather production, businesses can access a diverse range of options tailored to their specific needs.
Looking ahead, the market for artificial leather is set to expand, driven by advancements in material technology and a shift towards environmentally responsible practices. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are encouraged to leverage these trends by exploring partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize quality and sustainability. Embrace the opportunities that artificial leather presents, and position your business at the forefront of this dynamic industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.