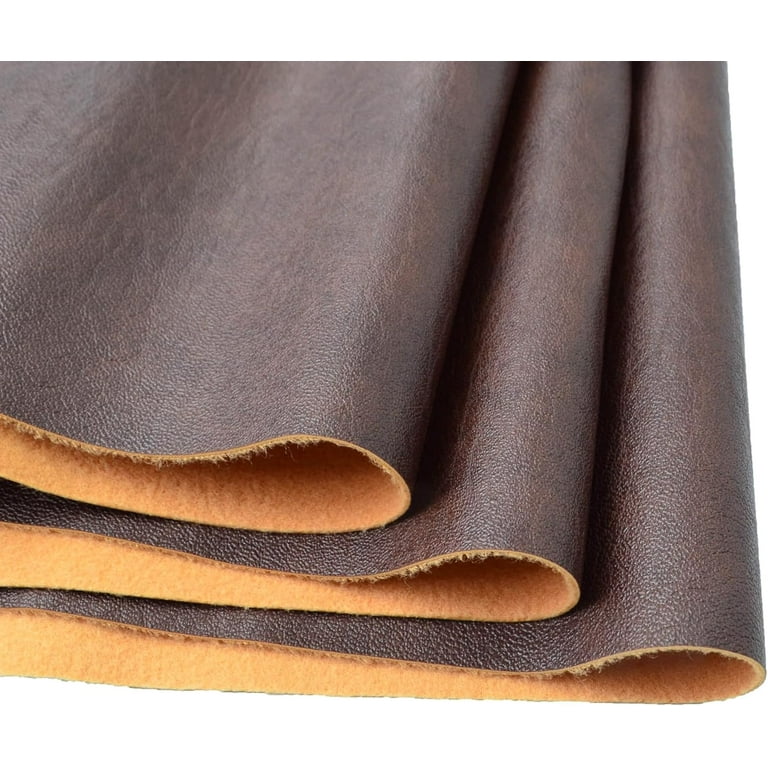
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for the leather factory
In the dynamic landscape of global commerce, B2B buyers face the critical challenge of sourcing high-quality leather products that meet diverse market needs. Whether you are looking to procure premium leather for fashion, automotive, or industrial applications, understanding the intricacies of the leather factory market is paramount. This guide offers an in-depth exploration of the leather manufacturing sector, addressing essential aspects such as types of leather, applications across various industries, effective supplier vetting strategies, and cost considerations.
By providing actionable insights and industry best practices, this guide equips international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam—with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions. The leather market is not only influenced by traditional craftsmanship but also by evolving trends and economic factors, including competition from overseas manufacturers.
Navigating this complex environment requires a comprehensive understanding of supplier capabilities, product specifications, and market dynamics. This resource aims to demystify these elements, empowering you to establish successful partnerships and secure the best value for your leather sourcing needs. With this guide, you will be well-positioned to leverage the opportunities within the global leather industry and enhance your business’s competitive edge.
Table Of Contents
- Top 7 The Leather Factory Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for the leather factory
- Understanding the leather factory Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of the leather factory
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘the leather factory’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for the leather factory
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for the leather factory
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘the leather factory’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for the leather factory Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing the leather factory With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for the leather factory
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the the leather factory Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of the leather factory
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for the leather factory
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding the leather factory Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Grain Leather Factory | Specializes in high-quality, unaltered leather hides that retain natural grain and markings. | Luxury goods, high-end fashion, furniture. | Pros: Exceptional durability and aesthetics. Cons: Higher cost; limited supply. |
| Tannery-Based Factory | Focuses on the tanning process, converting raw hides into leather through various methods (chrome, vegetable). | Leather production for apparel, accessories, upholstery. | Pros: Diverse leather types; scalable production. Cons: Environmental concerns with tanning processes. |
| Cut-and-Sew Factory | Primarily engaged in cutting leather and sewing it into finished products, often using pre-tanned hides. | Garments, bags, automotive interiors. | Pros: Faster turnaround; lower production costs. Cons: May compromise on material quality. |
| Specialty Leather Factory | Produces specific types of leather (e.g., suede, nubuck) or specialized products (e.g., embossed leather). | Niche markets like artisan crafts, luxury goods. | Pros: Unique offerings; strong market differentiation. Cons: Limited production volume; potentially higher prices. |
| Upcycled Leather Factory | Utilizes waste leather or recycled materials to create new products, promoting sustainability. | Eco-friendly brands, fashion, home décor. | Pros: Sustainable practices; cost-effective. Cons: Variable quality; may require more marketing to educate consumers. |
What Are the Characteristics of Full-Grain Leather Factories?
Full-grain leather factories are known for their commitment to producing the highest quality leather. They utilize unaltered hides that showcase the natural grain and imperfections, making each piece unique. These factories cater primarily to luxury markets, including high-end fashion and bespoke furniture. B2B buyers should consider the durability and aesthetic appeal of full-grain leather, as well as the associated higher costs and potential supply limitations.
How Do Tannery-Based Factories Operate?
Tannery-based factories are essential in the leather supply chain, focusing on transforming raw hides into finished leather through tanning processes like chrome or vegetable tanning. These facilities can produce a wide variety of leather types, making them versatile suppliers for various applications such as apparel and upholstery. Buyers should evaluate the environmental impact of the tanning processes, as well as the quality and consistency of the leather produced.
What Is the Role of Cut-and-Sew Factories in Leather Production?
Cut-and-sew factories specialize in the assembly of leather products, taking pre-tanned hides and turning them into finished goods such as garments and bags. These factories typically offer quicker turnaround times and lower production costs, making them attractive for brands seeking efficiency. However, B2B buyers should be aware that the focus on speed may sometimes compromise the quality of the materials used.
What Makes Specialty Leather Factories Unique?
Specialty leather factories focus on producing specific types of leather or unique products, such as suede or embossed leather. They serve niche markets, including artisan crafts and luxury items, offering distinctive products that set brands apart in a crowded marketplace. Buyers should consider the uniqueness and craftsmanship involved, though they may face challenges related to production volume and pricing.
How Do Upcycled Leather Factories Contribute to Sustainability?
Upcycled leather factories are increasingly popular among eco-conscious brands, utilizing waste leather or recycled materials to create new products. This approach not only promotes sustainability but can also be cost-effective. B2B buyers should assess the quality of the upcycled materials and the factory’s commitment to sustainable practices, as these factors can influence brand perception and marketability.
Key Industrial Applications of the leather factory
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of the leather factory | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion and Apparel | Production of high-quality leather garments | Enhances brand reputation through premium offerings | Quality of leather, sustainability certifications |
| Automotive | Manufacturing leather interiors for vehicles | Improves customer experience and luxury appeal | Durability, safety standards, and color matching |
| Furniture | Creation of leather upholstery for furniture | Adds aesthetic value and comfort to products | Leather grades, treatment processes, and design options |
| Sporting Goods | Development of leather equipment and accessories | Increases product performance and longevity | Material strength, weight considerations, and sourcing timelines |
| Accessories and Goods | Crafting leather bags, wallets, and belts | Diversifies product range and meets market demand | Customization options, lead times, and price points |
How is the Leather Factory Used in Fashion and Apparel?
In the fashion industry, leather factories are pivotal in producing high-quality leather garments, including jackets, coats, and accessories. These products often serve as luxury items, enhancing brand reputation and attracting discerning customers. Buyers from regions such as Europe and the Middle East particularly seek premium leather that meets stringent quality and sustainability standards. This includes verifying the sourcing of leather and ensuring that it aligns with eco-friendly practices, which are increasingly demanded by consumers.
What Role Does the Leather Factory Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Leather factories are essential in the automotive sector, where they supply premium leather for vehicle interiors. The use of high-quality leather in seats, dashboards, and trims not only elevates the aesthetic appeal of vehicles but also enhances customer comfort and satisfaction. International buyers must consider factors such as durability, safety standards, and color matching to ensure that the leather complements the overall design of the vehicle while meeting regulatory requirements.
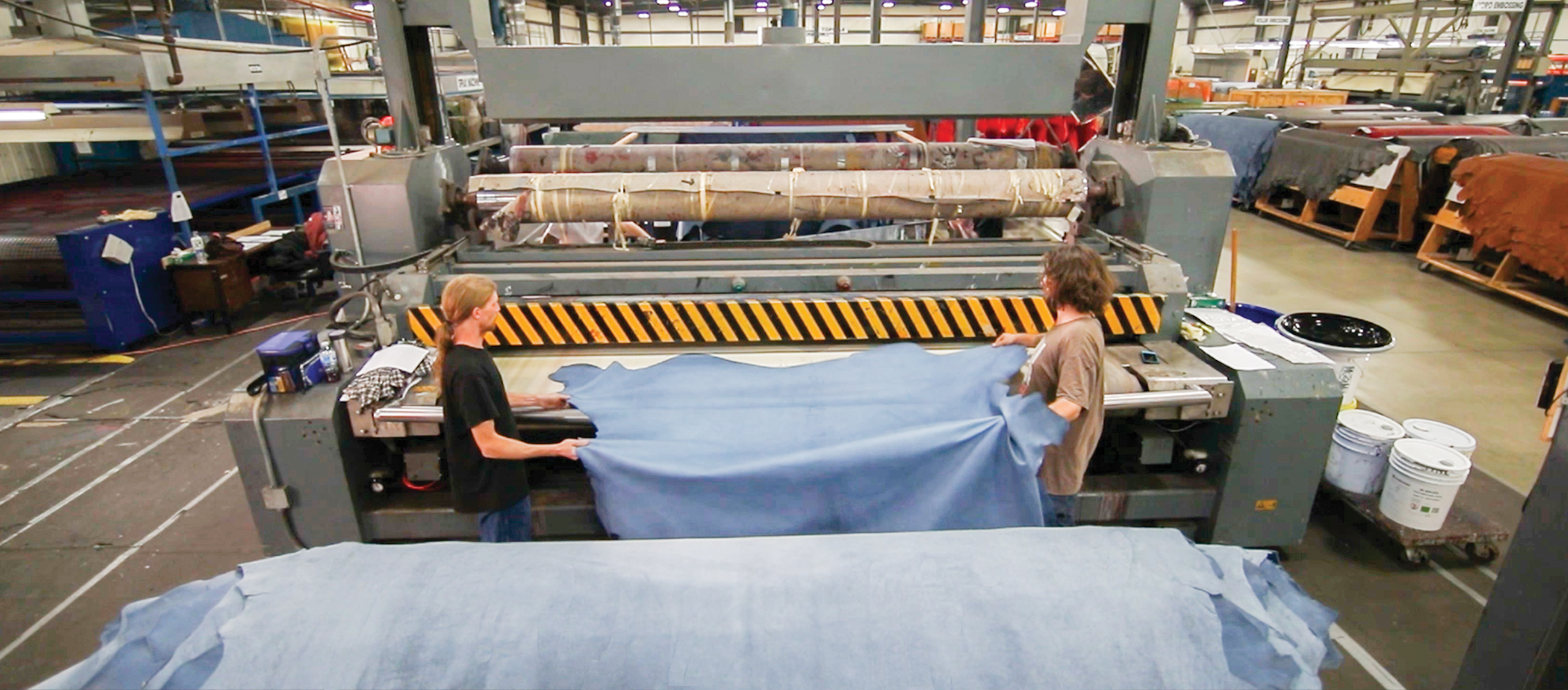

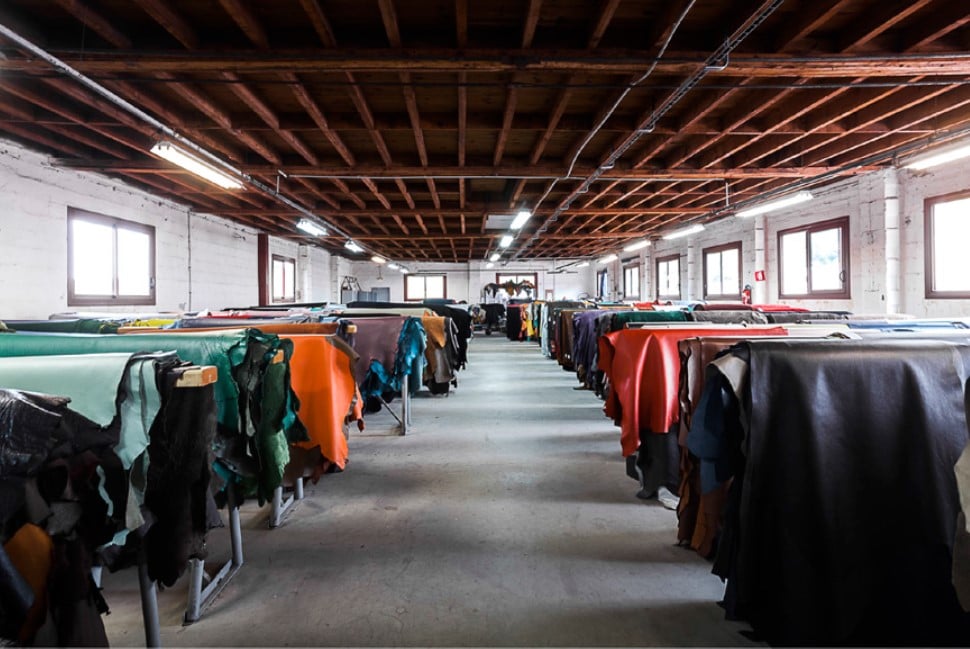
Illustrative image related to the leather factory
How Does the Leather Factory Contribute to Furniture Design?
In furniture manufacturing, leather factories provide materials for upholstery that significantly enhance the aesthetic and tactile qualities of furniture pieces. Leather upholstery adds a touch of elegance and comfort, making it a preferred choice for high-end furniture brands. Buyers looking to source leather for this application should focus on leather grades, treatment processes, and available design options to ensure that the final product meets both functional and aesthetic demands.
What is the Importance of Leather in Sporting Goods?
The sporting goods industry relies on leather factories to produce equipment and accessories that require high durability and performance, such as gloves, balls, and protective gear. The quality of leather affects the product’s longevity and usability, making it crucial for buyers to assess material strength and weight considerations. Additionally, timely sourcing and delivery schedules are vital to align with production cycles and market demands.
How Can Leather Factories Support Accessory and Goods Production?
Leather factories are instrumental in the creation of various accessories, including bags, wallets, and belts, allowing businesses to diversify their product offerings. These items often require customization options to meet specific consumer preferences. Buyers should evaluate lead times and price points to ensure competitive positioning in the market while also considering the unique attributes of leather that can enhance product appeal.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘the leather factory’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Leather Materials at Competitive Prices
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of sourcing high-quality leather materials that meet their specific standards while remaining cost-effective. With the influx of cheaper alternatives from international competitors, especially from countries like China, buyers are often torn between quality and price. This dilemma can lead to subpar products that fail to meet customer expectations, resulting in lost sales and damaged reputations.
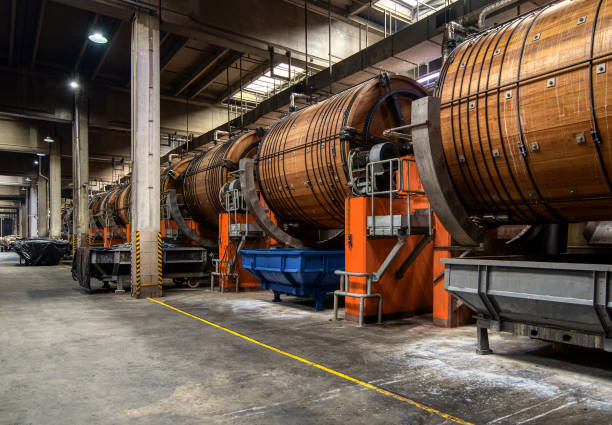

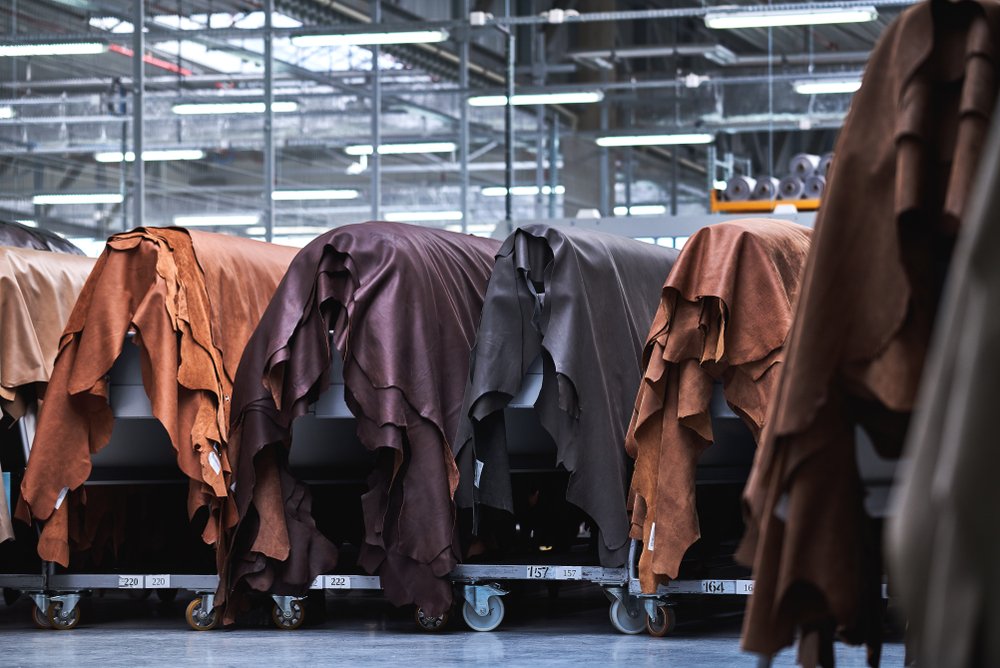
Illustrative image related to the leather factory
The Solution: To effectively source quality leather at competitive prices, buyers should establish strong relationships with reputable leather factories that prioritize quality control. Conducting thorough research to identify factories with a history of high standards and positive reviews is crucial. Additionally, buyers can negotiate bulk purchase agreements to secure lower prices without compromising on quality. It’s also advisable to request samples before committing to larger orders, allowing buyers to assess the leather’s texture, durability, and overall quality firsthand. Engaging in transparent communication about expectations regarding leather grades and finishes will further ensure that the sourced materials align with the buyer’s product requirements.
Scenario 2: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Supply chain disruptions can be a significant pain point for B2B buyers in the leather industry, particularly when unexpected events—such as political instability, natural disasters, or logistical challenges—occur. These disruptions can lead to delays in receiving essential materials, resulting in production halts and the inability to meet customer demands.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, buyers should diversify their supplier base by sourcing leather from multiple factories across different regions. This strategy reduces dependency on a single source and provides alternatives in case of disruptions. Implementing a just-in-time inventory system can also help manage stock levels efficiently and avoid over-commitment to one supplier. Moreover, maintaining open lines of communication with suppliers can provide early warnings about potential disruptions, allowing buyers to adjust their production schedules proactively. Collaborating with logistics experts to explore alternative shipping routes can further enhance resilience in the supply chain.
Scenario 3: Navigating Compliance and Ethical Sourcing Concerns
The Problem: With increasing consumer awareness regarding sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers are often pressured to ensure that their leather products are sourced responsibly. This concern becomes a pain point when buyers are unsure of the ethical practices of their suppliers, which can lead to reputational risks and loss of consumer trust.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing from leather factories that are certified for ethical practices and environmental sustainability. Requesting documentation and certifications that demonstrate compliance with labor laws and environmental standards is essential. Additionally, conducting site visits or audits can provide firsthand insight into the factory’s operations and ethical practices. Establishing partnerships with suppliers who transparently share their sourcing processes can also enhance credibility. Furthermore, incorporating sustainability into the brand messaging can resonate with conscious consumers, creating a competitive advantage in the market. Engaging in discussions about the factory’s efforts to minimize waste and promote sustainable practices can help buyers align their values with their sourcing decisions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for the leather factory
When selecting materials for leather production, B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence product performance, manufacturing complexity, and cost. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in leather factories, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Cowhide Leather in Leather Manufacturing?
Cowhide leather is one of the most widely used materials in the leather industry due to its durability and versatility. It typically has a high tensile strength, making it suitable for a variety of applications, from jackets to upholstery. Cowhide can withstand significant wear and tear, and it is resistant to moisture and heat, which enhances its longevity.
Pros: The primary advantages of cowhide include its durability, natural grain patterns, and ability to take dye well, allowing for a wide range of aesthetic options. Its cost-effectiveness makes it a popular choice for large-scale production.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Cons: However, cowhide can be heavier than other leathers, which may not be suitable for all applications. Additionally, the tanning process can be environmentally intensive, raising concerns about sustainability.
Impact on Application: Cowhide is compatible with various media, including paints and dyes, making it ideal for custom designs.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East may need to comply with strict environmental regulations regarding tanning processes, while buyers in Africa and South America may prioritize cost and local sourcing.
How Does Lambskin Leather Compare to Cowhide in Terms of Performance?
Lambskin leather is known for its softness and luxurious feel, often used in high-end fashion items and accessories. It has a lower tensile strength compared to cowhide but offers a unique texture that appeals to consumers seeking comfort and style.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Pros: The primary advantage of lambskin is its supple nature, which allows for comfortable wear and a high-quality finish. It is lightweight and easy to work with, making it suitable for intricate designs.
Cons: However, lambskin is less durable than cowhide and can be more susceptible to scratches and wear. This limits its use in products that require high durability.
Impact on Application: Lambskin is often used in fashion garments and luxury items, where aesthetic appeal is prioritized over durability.
International Considerations: Buyers in high-end markets, such as Europe, may favor lambskin for luxury products, while buyers in regions like Africa may find it less practical due to cost and durability concerns.
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Suede as a Leather Material?
Suede, made from the underside of animal hides, offers a unique texture that is soft and velvety. It is commonly used in fashion and upholstery.
Pros: Suede is lightweight and provides a distinctive aesthetic appeal. It can be dyed easily, allowing for a variety of colors and styles.
Cons: On the downside, suede is more challenging to clean and maintain compared to other leather types. It is also less water-resistant, which can limit its applications in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Suede is often used in fashion items and decorative upholstery, where its texture can enhance visual appeal.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
International Considerations: Buyers in humid climates, such as parts of South America and the Middle East, may need to consider the maintenance challenges associated with suede.
How Does Synthetic Leather Compare to Natural Leather in Terms of Cost and Sustainability?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), has gained popularity as an alternative to natural leather. It offers a variety of textures and colors and is generally more affordable.
Pros: Synthetic leather is often more cost-effective and easier to maintain than natural leather. It is also considered more environmentally friendly, as it does not require animal hides.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Cons: However, synthetic leather typically lacks the durability and breathability of natural leather, which can lead to a shorter lifespan for products made from it.
Impact on Application: Synthetic leather is widely used in fashion, upholstery, and automotive applications, where cost and ease of maintenance are prioritized.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions focused on sustainability may prefer synthetic options, especially in Europe, where eco-friendly materials are increasingly demanded.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Leather Factories
| Material | Typical Use Case for the leather factory | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cowhide Leather | Jackets, upholstery, bags | High durability and versatility | Heavier than alternatives | Medium |
| Lambskin Leather | High-end fashion items | Softness and luxurious feel | Less durable than cowhide | High |
| Suede | Fashion items, upholstery | Unique texture and aesthetic appeal | Difficult to clean and maintain | Medium |
| Synthetic Leather | Fashion, automotive, upholstery | Cost-effective and easy to maintain | Less durable and breathable | Low |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for the leather factory
What Are the Key Stages in the Leather Manufacturing Process?
The leather manufacturing process consists of several critical stages that transform raw hides into finished leather products. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers based on their expertise and capabilities.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
-
Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection of high-quality raw hides, which are often sourced from cattle, sheep, or goats. These hides undergo a thorough cleaning process to remove hair, flesh, and fat. The next step involves soaking the hides in a solution to rehydrate them, making them pliable for further processing. This stage is crucial, as the quality of the raw material directly affects the final product. -
Forming
After preparation, the hides are treated with chemicals in a process known as tanning. This step stabilizes the collagen fibers, preventing decomposition. There are various tanning methods, including vegetable tanning, chrome tanning, and synthetic tanning, each imparting different characteristics to the leather. Once tanned, the hides are further processed through techniques such as splitting (to achieve desired thickness) and shaving (for a smooth finish). -
Assembly
In this stage, the leather is cut into specific patterns and shapes as per design requirements. Skilled artisans may hand-stitch or machine-stitch the pieces together, depending on the product type. This is also where additional features, such as linings or hardware, are incorporated. The assembly process requires precision and craftsmanship, ensuring that the final product meets design specifications and quality standards. -
Finishing
The final stage involves applying finishes to enhance the leather’s appearance and durability. This may include dyeing, coating, and polishing. Different finishing techniques can provide various textures and colors, catering to market demands. Quality finishing is essential not only for aesthetics but also for protecting the leather from wear and environmental factors.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of leather manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Here are some key aspects of QA in the leather industry:
-
International Standards and Certifications
Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is crucial for leather manufacturers. ISO 9001 specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS), focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe, help buyers verify the safety and quality of leather goods. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective QA involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line. Suppliers are often required to provide certificates of authenticity and quality for their hides.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to ensure adherence to quality standards. This includes checking the tanning process, stitching quality, and adherence to design specifications.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the products are completed, a final inspection is performed to evaluate the overall quality and compliance with specifications. This step ensures that any defects are identified and addressed before shipment. -
Common Testing Methods in Leather Quality Assurance
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality of leather products. These may include:
– Physical Testing: Assessing strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance to ensure durability.
– Chemical Testing: Evaluating the presence of harmful substances such as heavy metals or allergens.
– Environmental Testing: Ensuring that the tanning process adheres to environmental regulations, particularly in regions with strict environmental laws.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality assurance practices of leather suppliers is essential. Here are actionable strategies:
-
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Audits can be performed by the buyer’s quality assurance team or through third-party inspection agencies. This helps ensure that suppliers maintain consistent quality standards and comply with international regulations. -
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports
Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality assurance reports that outline their QA processes, testing results, and compliance with international standards. These reports provide transparency and build trust between buyers and suppliers. -
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can help verify the quality of leather products before shipment. These agencies conduct independent assessments, ensuring that the products meet specified quality standards and reducing the risk of receiving subpar goods.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various nuances in quality control that can impact their purchasing decisions:
-
Understanding Regional Regulations
Different regions have specific regulations regarding leather products, including safety, environmental impact, and labeling requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues. -
Cultural Considerations in Quality Perception
Quality perceptions can vary by culture. For instance, certain markets may prioritize durability over aesthetics or vice versa. Understanding these cultural nuances can help buyers select products that align with market expectations. -
Building Long-Term Relationships with Suppliers
Establishing long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers fosters better communication and understanding regarding quality expectations. This collaborative approach can lead to improved product quality and more favorable terms for both parties.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in leather production is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality leather products that meet their specific needs and market demands.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘the leather factory’
The following guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in effectively sourcing leather products from factories. By following this checklist, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions, minimizing risk and enhancing the quality of their procurement process.
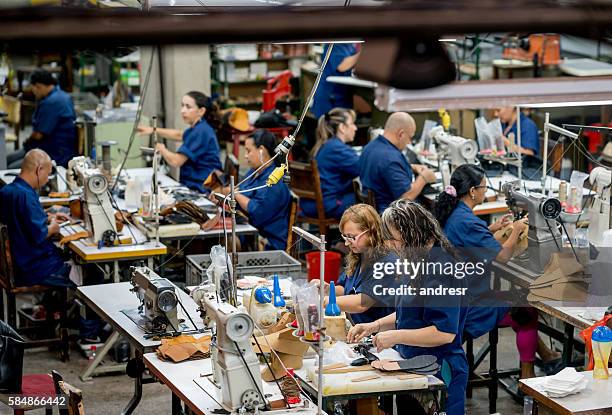

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Step 1: Identify Your Product Requirements
Clearly define the type of leather goods you need, including specifications such as size, color, and finish. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for your sourcing strategy. Understanding your product requirements helps you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensures you receive samples that meet your expectations.
- Product categories: Jackets, bags, upholstery, etc.
- Material specifications: Full-grain, top-grain, or corrected-grain leather.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential leather factories that specialize in your required products. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry networks to compile a list of candidates. A well-researched list increases the chances of finding reliable suppliers who can meet your quality and delivery standards.
- Use platforms: Alibaba, Global Sources, and industry-specific trade shows.
- Check reviews and ratings: Look for feedback from previous clients to gauge supplier reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO, REACH, or other industry standards. Certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to quality management and environmental safety practices, which is vital for maintaining product quality and compliance with international regulations.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
- Request documentation: Ask for copies of their certifications.
- Check for compliance: Ensure they meet the specific regulations applicable to your market.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Quality Checks
Before finalizing a supplier, request samples of their products to assess quality firsthand. This step is essential to ensure that the leather meets your specifications and standards. Examine the samples for craftsmanship, durability, and finish.
- Assess quality: Look for defects, consistency in color, and texture.
- Test durability: Conduct tests for wear and tear to ensure the product’s longevity.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate terms such as pricing, payment methods, and delivery timelines. Clear terms help to establish a mutual understanding and avoid potential disputes later. Ensure that both parties agree on quality standards and consequences for non-compliance.
- Discuss payment terms: Consider options like letters of credit or escrow services for security.
- Establish clear timelines: Set realistic deadlines for production and delivery.
Step 6: Finalize the Contract
Draft a comprehensive contract that outlines all agreed-upon terms, including product specifications, pricing, delivery schedules, and quality assurance protocols. A well-structured contract protects both parties and serves as a reference point in case of disputes.
- Include penalties: Specify penalties for late deliveries or substandard products.
- Review legalities: Ensure that the contract complies with international trade laws and regulations.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Maintain open lines of communication with your supplier throughout the production process. Regular updates and feedback can help address issues proactively and foster a strong partnership. Establishing communication protocols ensures transparency and enhances the collaboration experience.
- Use technology: Leverage tools like video calls and project management software for regular updates.
- Set points of contact: Designate specific individuals for communication to streamline interactions.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing leather products more effectively, ensuring high-quality outcomes that meet their business needs.
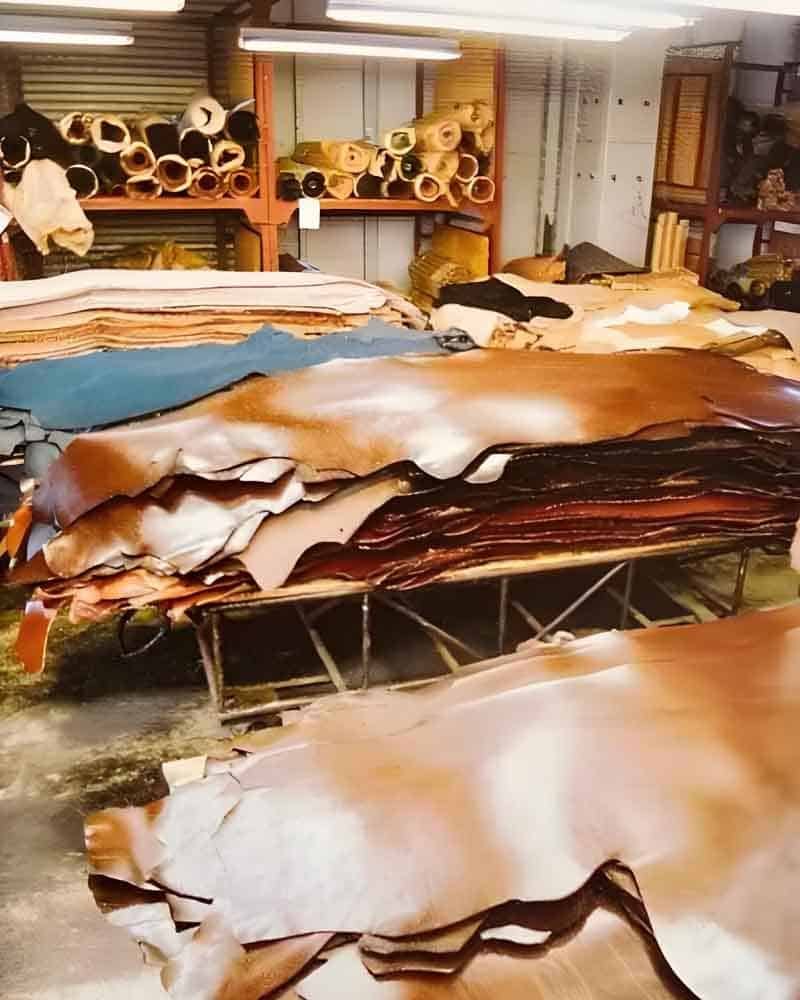

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for the leather factory Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Factory Sourcing?
When sourcing from a leather factory, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. Key components include:
-
Materials: The type of leather (e.g., cowhide, lambskin) significantly impacts costs. Premium materials often command higher prices due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. Fluctuations in raw material prices can affect overall sourcing costs, necessitating close monitoring of market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on location and skill level required for craftsmanship. Factories in regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but quality may be a trade-off. It’s essential to evaluate the factory’s labor practices and worker conditions as they can influence product quality and sustainability.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Factories with advanced machinery may have higher overhead but can produce higher-quality products more efficiently.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom designs or specialized products can be substantial. Buyers should factor these into their total cost, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure product consistency and compliance with international standards. This can add to the cost but is crucial for maintaining brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary based on distance, volume, and chosen Incoterms (terms of trade). Understanding these factors can help buyers better estimate total shipping expenses.
-
Margin: Factories typically include a markup to cover costs and generate profit. Buyers should be aware of standard margins in the leather industry to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Leather Factory Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing structure of leather products:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders often yield lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their purchasing capabilities to leverage volume discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products can lead to higher costs due to additional tooling and design work. Clearly defining requirements can help manage expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials or those with certifications (e.g., environmentally friendly or ethically sourced) may come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certification against potential cost increases.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but can offer better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for determining who bears the cost and risk at various points in the shipping process. This knowledge helps in accurately calculating total landed costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Leather Sourcing?
To navigate the complexities of leather factory sourcing, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Building relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Open discussions about costs, volumes, and long-term partnerships can yield favorable outcomes.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase prices, consider the total cost over the product’s lifecycle, including maintenance, durability, and potential waste. This holistic view can guide better purchasing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local economic conditions, labor costs, and material availability. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct market research to understand these dynamics.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly monitoring leather market trends, including pricing fluctuations and emerging suppliers, can help buyers make informed decisions and negotiate effectively.
Conclusion
Sourcing from a leather factory involves a multifaceted cost structure influenced by various factors. By understanding these components, price influencers, and strategic buying tips, international B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing efficiency and achieve better pricing outcomes. Always remember that indicative prices can vary significantly based on market conditions and individual supplier negotiations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing the leather factory With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions for Leather Production
In the competitive landscape of leather production, B2B buyers are often faced with multiple options. This analysis compares ‘the leather factory’ model against two alternative solutions: Tandy Leather and synthetic leather manufacturing. By evaluating performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals.
| Comparison Aspect | The Leather Factory | Tandy Leather | Synthetic Leather Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality, handcrafted leather with unique designs | Diverse range of leathercraft supplies for customization | Consistent quality, but often lacks the unique texture of genuine leather |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on customization | Generally lower, with bulk purchase options available | Typically lower than genuine leather, but varies with quality |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor for production | Easy to source materials and tools for DIY projects | Streamlined manufacturing process, often automated |
| Maintenance | Requires care and proper storage to maintain quality | Low maintenance for tools; leather care products available | Minimal maintenance; durable and often water-resistant |
| Best Use Case | Custom, high-end leather goods | Hobbyists and small businesses focused on leathercraft | Mass production of affordable leather goods for various industries |
Evaluating Tandy Leather as an Alternative
Tandy Leather offers a comprehensive selection of leathercraft supplies, including tools, dyes, and hardware. This option is particularly appealing for small businesses and individual artisans who wish to create custom leather products. The primary advantage of Tandy is its affordability and accessibility; however, the quality may vary based on the materials chosen. Additionally, the learning curve for leathercraft techniques can be steep, requiring time and investment in skill development.
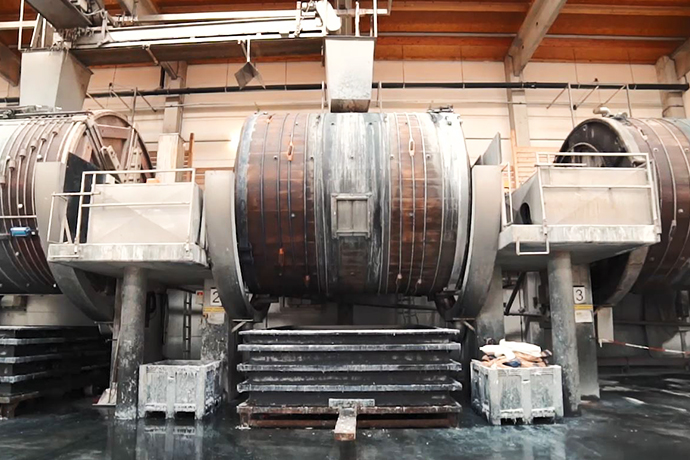

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Considering Synthetic Leather Manufacturing
Synthetic leather, or vegan leather, has gained popularity as a cost-effective alternative to traditional leather. Its manufacturing process allows for high-volume production, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to scale quickly. Synthetic leather is often more durable and easier to maintain than genuine leather, which can be a significant advantage for mass-market products. However, it may lack the unique aesthetic and tactile qualities of real leather, which could be a drawback for luxury brands aiming to convey authenticity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When selecting the appropriate leather solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific needs, including budget, desired product quality, and production capacity. For companies focused on luxury and customization, traditional leather factories may be the best fit, while those looking for cost-effective, scalable solutions might find synthetic leather more suitable. Tandy Leather serves as a valuable resource for artisans and smaller businesses seeking flexibility and a hands-on approach. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each option will empower buyers to make decisions that align with their strategic objectives and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for the leather factory
What Are the Key Technical Properties Relevant to Leather Manufacturing?
Understanding the technical properties of leather is vital for B2B buyers in the leather industry. Here are some critical specifications that influence the quality, durability, and suitability of leather products for various applications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality classification of leather based on its physical characteristics, such as grain quality, color, and imperfections. Common grades include full-grain, top-grain, and split leather. For buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the final product meets quality expectations and is fit for its intended purpose, whether for fashion, upholstery, or industrial applications.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels define the permissible variation in the dimensions and characteristics of leather products. This includes thickness, weight, and color consistency. For B2B buyers, understanding these tolerances is crucial as they directly affect the manufacturability and aesthetic appeal of leather goods. A tighter tolerance often indicates higher quality and can justify premium pricing.
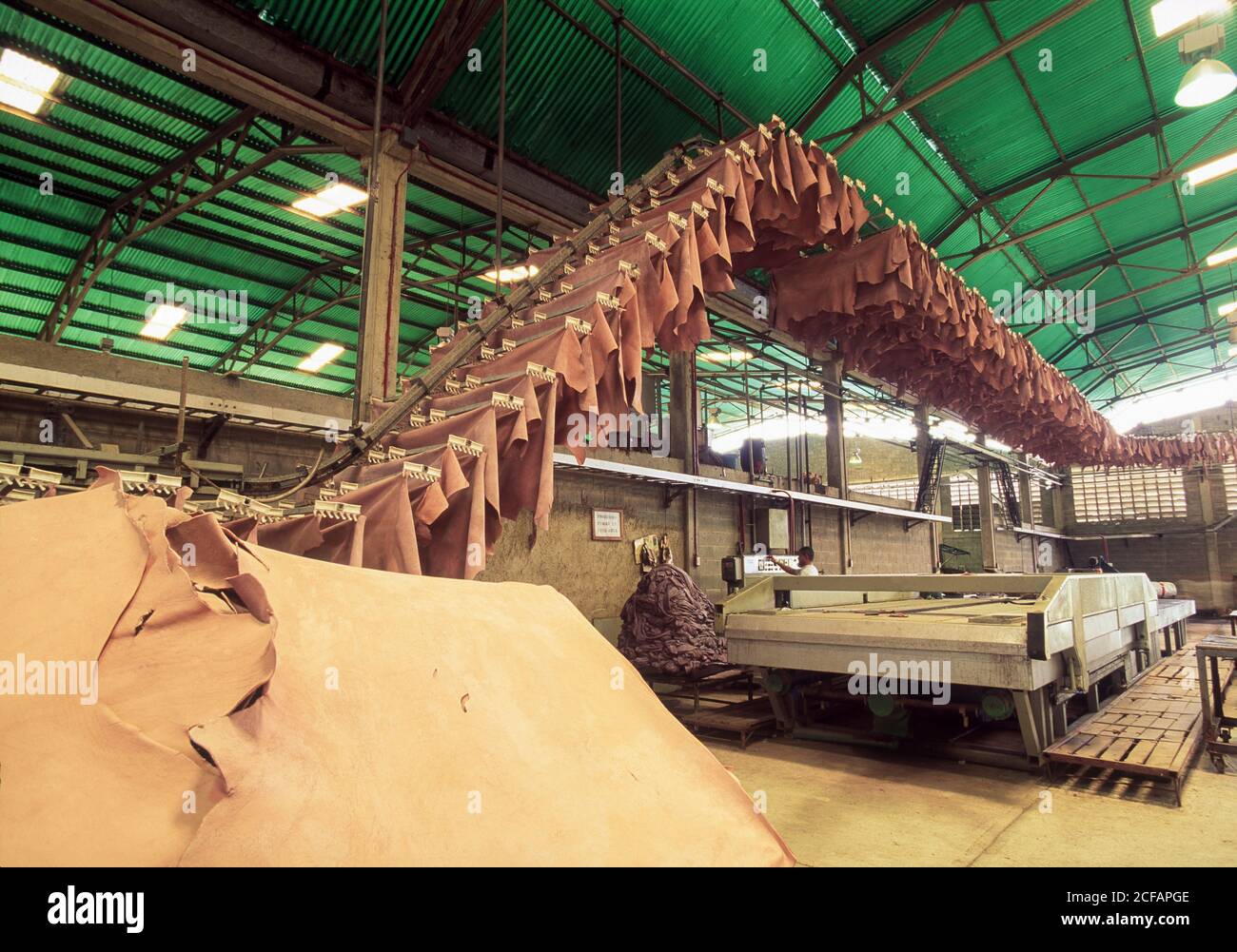

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
3. Leather Weight
Leather weight is measured in ounces per square foot (oz/ft²) or grams per square meter (g/m²). This property affects the leather’s durability, flexibility, and suitability for different applications. For instance, lighter leather may be preferred for clothing, while heavier leather is typically used for accessories and upholstery. Buyers need to specify weight requirements to ensure the final product meets functional and aesthetic criteria.
4. Finish Type
The finish type of leather impacts its appearance, feel, and durability. Common finishes include aniline, semi-aniline, and pigmented. Each type offers different levels of protection and visual appeal. B2B buyers must understand these finishes to select leather that aligns with their brand’s quality standards and customer expectations.
5. Grain Pattern
The grain pattern refers to the natural texture of the leather surface, which can be smooth, pebbled, or embossed. This property significantly influences the visual appeal and tactile experience of the final product. Buyers should consider the desired grain pattern when sourcing leather, as it affects both aesthetics and marketability.
6. Environmental Impact
Increasingly, the environmental impact of leather production is a critical consideration. This includes factors such as tanning methods (e.g., chrome vs. vegetable tanning), waste management, and sourcing of raw materials. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate sustainable practices, as this can influence brand reputation and compliance with international regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Leather Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the leather market. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should understand:

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the leather industry, this often pertains to brands that outsource the production of leather goods to specialized manufacturers. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable partners for custom products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategies and avoid excess inventory.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. It typically includes details about quantity, specifications, and delivery timelines. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ is a strategic way to gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, especially when importing leather products from different countries.
5. Tanning Process
The tanning process involves treating animal hides to preserve them and make them suitable for use. Different tanning methods, such as chrome and vegetable tanning, yield distinct characteristics in the leather. Buyers should understand the implications of different tanning processes on the leather’s quality, durability, and environmental impact.
6. Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between the initiation of an order and its completion. In the leather industry, lead times can vary significantly based on production processes and material availability. B2B buyers need to be aware of lead times to manage their supply chains effectively and meet market demands.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, negotiate better terms, and enhance their overall purchasing strategy in the leather industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the the leather factory Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Leather Factory Sector?
The leather factory sector is currently experiencing transformative shifts driven by a combination of technological advancements, consumer preferences, and global economic factors. International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate these dynamics to make informed sourcing decisions.
One significant driver is the increasing demand for high-quality, durable leather products. As consumers become more discerning, there’s a growing preference for premium materials over mass-produced alternatives. Additionally, advancements in B2B technology, such as digital supply chain management and AI-driven inventory systems, are enhancing operational efficiencies and enabling manufacturers to respond swiftly to market changes. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms allows buyers to access a broader range of suppliers globally, facilitating competitive pricing and diverse product offerings.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Emerging trends include the adoption of customization in leather products, driven by consumer desire for personalized goods. This trend is particularly evident in regions like Europe, where craftsmanship and bespoke offerings are highly valued. The Middle East and Africa are seeing a surge in the local production of leather goods, supported by favorable trade agreements and regional investments in manufacturing capabilities. Buyers should also consider geopolitical factors, such as trade tariffs and regulations, which can significantly impact sourcing strategies.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Leather Industry?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of the leather factory sector, influencing sourcing decisions among international B2B buyers. The environmental impact of leather production, particularly concerning water usage and chemical runoff, has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to eco-friendly practices, which can include the use of vegetable-tanned leather, water-efficient processes, and responsible waste management systems.
Ethical sourcing is equally critical, as consumers demand transparency in supply chains. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in Europe and North America, where regulations on ethical labor practices are stringent. Certifications such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and the Leather Working Group (LWG) are gaining traction, providing assurance to buyers about the sustainability and ethical standards of their suppliers.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Incorporating sustainable and ethical sourcing into procurement strategies not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but can also enhance brand reputation. Buyers who prioritize these values may find a competitive edge in the marketplace, as consumers increasingly favor brands that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context of the Leather Factory Sector?
The leather factory sector has evolved significantly over the decades, shaped by technological advancements and shifting consumer demands. Traditionally, leather production was labor-intensive and localized, with artisans crafting goods by hand. The introduction of mechanization in the 19th century revolutionized the industry, allowing for mass production and greater efficiency.
In recent years, the sector has faced challenges from global competition, particularly from countries like China, where lower production costs have made it difficult for Western manufacturers to compete. However, this has also led to a resurgence in demand for quality and craftsmanship, with many buyers seeking out artisanal and bespoke leather goods as a counterpoint to mass-produced items.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
As the market continues to evolve, understanding the historical context can provide valuable insights for B2B buyers. By recognizing the industry’s trajectory, buyers can better anticipate future trends and make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their business goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of the leather factory
-
1. How do I ensure quality when sourcing leather products from a factory?
To guarantee quality when sourcing leather products, conduct thorough due diligence on the factory’s reputation and production processes. Request samples to evaluate the leather’s texture, durability, and craftsmanship. Verify certifications and standards compliance, such as ISO or Leather Working Group (LWG) certifications, to ensure adherence to industry best practices. Establish a clear quality assurance agreement detailing inspection processes and criteria. Regular communication and site visits can also help maintain quality control throughout the production process. -
2. What are the best practices for negotiating payment terms with a leather factory?
When negotiating payment terms, aim for a balance that protects both parties. Common practices include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50%) to initiate production, followed by the remainder upon delivery or before shipping. Ensure to clarify the accepted payment methods, such as bank transfers, letters of credit, or payment platforms. It’s beneficial to discuss penalties for late payments or early payment discounts. Document all terms in a formal agreement to avoid misunderstandings later. -
3. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for leather products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly based on the factory’s capacity, the type of leather products, and customization requests. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 100 units for standard products, while custom designs may require larger quantities. Discuss MOQs upfront during negotiations to understand how they align with your purchasing needs. If your order volume is low, consider asking the factory about options for smaller batches or collaborating with other buyers to meet MOQ requirements. -
4. How can I verify the legitimacy of a leather supplier?
To verify a leather supplier’s legitimacy, start by checking their business registration and licensing to confirm their operational status. Look for reviews and testimonials from previous clients to gauge reliability. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or industry-specific directories that provide ratings and feedback. Request references from past customers and conduct background checks on their financial history. Additionally, consider scheduling a factory visit or engaging a third-party inspection service to assess their operations firsthand. -
5. What customization options are typically available for leather products?
Most leather factories offer a variety of customization options, including leather type, color, size, and design features. You can also request branding elements such as embossing or printing logos. Discuss your specific requirements early in the negotiation process to ensure they can accommodate your needs. Some factories may provide design assistance or samples for approval before full production. Always confirm the lead times for custom orders, as they can be longer than standard products. -
6. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing leather products?
When importing leather products, consider the shipping methods, costs, and delivery timelines. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments but may take longer. Be aware of customs regulations and tariffs that may apply to leather imports in your country. Ensure that the factory provides all necessary documentation, such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Engaging a reliable freight forwarder can help streamline the logistics process. -
7. How do I handle quality assurance during the production of leather goods?
To manage quality assurance during production, establish a clear quality control plan that outlines inspection checkpoints and criteria. Schedule regular updates with the factory to monitor progress and address any issues promptly. Consider implementing a pre-shipment inspection by a third-party service to verify that the products meet your specifications before they are shipped. Document any quality issues and communicate with the supplier about corrective actions to ensure consistent product quality. -
8. What are the current trends in the leather industry that I should be aware of?
Current trends in the leather industry include a growing demand for sustainable and ethically sourced leather, driven by consumer awareness of environmental issues. Innovations in leather alternatives, such as vegan leather made from plant-based materials, are also on the rise. Additionally, customization and personalization are becoming increasingly popular, as consumers seek unique products. Staying informed about these trends can help you align your sourcing strategies with market demands and differentiate your offerings.
Top 7 The Leather Factory Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. eBay – E-commerce Platform
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, eBay – E-commerce Platform, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Leather Factory Shop – Handmade Leather Jackets
Domain: leatherfactoryshop.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Leather Factory Shop offers premium handmade leather jackets, including a seasonal collection made from high-quality cowhide and lambskin leather. The product range includes men’s and women’s biker jackets, bombers, hooded jackets, and moto jackets. A promotional code ‘Halloween20’ provides a 20% discount on any product. The collection emphasizes vintage motorcycling styles and is designed for war…
3. Tandy Leather – Free Shipping on Orders Over $149
Domain: tandyleather.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Tandy Leather – Free Shipping on Orders Over $149, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Facebook – Premium Quality Leather Jackets
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Premium Quality Leather Jackets, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Leather Factory Shop – Handmade Leather Jackets
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, Leather Factory Shop – Handmade Leather Jackets, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. AptDeco – Used Sofa 86
Domain: aptdeco.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: This company, AptDeco – Used Sofa 86, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Instagram – Scraping Services
Domain: instagram.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Contact us at info@scrapingdog.com for scraping Instagram. Let us know how many pages you want to scrape per month.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for the leather factory
In the evolving landscape of the leather industry, strategic sourcing stands as a critical pillar for international B2B buyers. Engaging with reliable suppliers can enhance quality, reduce costs, and foster sustainable practices that resonate with modern consumer values. By prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers who emphasize craftsmanship, ethical sourcing, and innovative techniques, businesses can differentiate themselves in competitive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
The recent challenges faced by some manufacturers, including market saturation and competitive pricing pressures from international players, underscore the importance of agility in sourcing strategies. Buyers must remain vigilant, adapting to shifts in demand and supply chain dynamics while leveraging data-driven insights to make informed decisions.
As we look ahead, the potential for growth in the leather sector is significant. By investing in strategic sourcing relationships today, businesses can position themselves for success in the future. Embrace this opportunity to connect with trusted suppliers, explore new product lines, and enhance your brand’s reputation. Together, we can drive innovation and sustainability in the leather industry, ensuring a prosperous partnership for years to come.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.