Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for recycled leather vs bonded leather
As the demand for sustainable materials rises, international B2B buyers are increasingly tasked with sourcing options like recycled leather and bonded leather. Each presents unique advantages and challenges, making it essential for businesses to understand these materials deeply. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of recycled leather versus bonded leather, offering valuable insights into their types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
In a global market marked by rapid changes and evolving consumer preferences, being informed is crucial for making strategic purchasing decisions. For buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam—this guide serves as an indispensable resource. It equips stakeholders with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing sustainable materials effectively.
By exploring the environmental benefits, durability, and versatility of these leather alternatives, buyers can align their procurement strategies with sustainability goals while ensuring product quality. Furthermore, understanding the market landscape, including the recycling capabilities and cost implications, will empower businesses to make decisions that not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Recycled Leather Vs Bonded Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Understanding recycled leather vs bonded leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of recycled leather vs bonded leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘recycled leather vs bonded leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘recycled leather vs bonded leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for recycled leather vs bonded leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing recycled leather vs bonded leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the recycled leather vs bonded leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for recycled leather vs bonded leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding recycled leather vs bonded leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Leather | Made from post-consumer or post-industrial leather waste; retains some natural properties. | Fashion, upholstery, automotive interiors | Pros: Eco-friendly, unique textures. Cons: Variable quality and durability. |
| Bonded Leather | Composed of leather scraps bonded together with adhesives; often has a synthetic finish. | Furniture, accessories, low-cost fashion | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile design options. Cons: Less durable than genuine leather. |
| PU Leather | Synthetic leather with a polyurethane coating; often marketed as vegan. | Fashion, upholstery, automotive interiors | Pros: Water-resistant, easy to clean. Cons: Non-biodegradable, limited recyclability. |
| Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Tanned using natural materials; biodegradable and more environmentally friendly. | High-end fashion, artisanal goods | Pros: Eco-friendly, unique aging process. Cons: More expensive, less water-resistant. |
| Chrome-Tanned Leather | Tanned using chromium salts; common but less sustainable. | Mass-produced goods, footwear, bags | Pros: Durable, widely available. Cons: Environmental concerns, potential toxicity. |
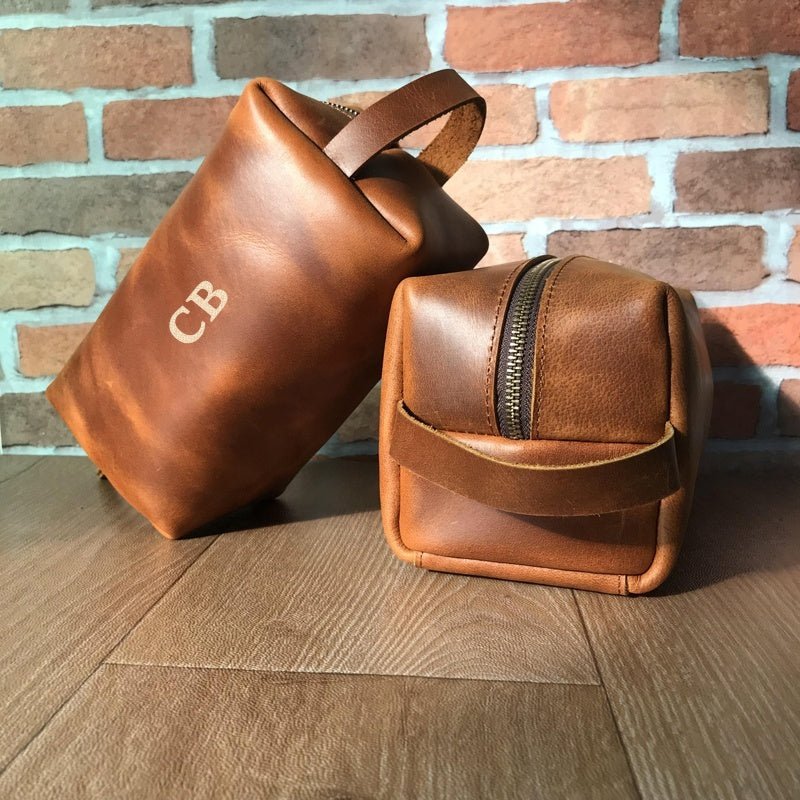
What are the Characteristics of Recycled Leather for B2B Buyers?
Recycled leather is produced from waste generated during the manufacturing process or from discarded leather goods. It retains some natural properties of leather, making it suitable for high-quality applications such as fashion and automotive interiors. B2B buyers should consider sourcing recycled leather for sustainable product lines, as it appeals to eco-conscious consumers. However, variability in quality can pose challenges, necessitating rigorous supplier assessments to ensure consistency and performance.

Illustrative image related to recycled leather vs bonded leather
How Does Bonded Leather Differ in Suitability for Business Applications?
Bonded leather is created from leather scraps that are bonded with adhesives, resulting in a product that mimics genuine leather but is typically less durable. It is often used in cost-sensitive applications, such as furniture and accessories, where aesthetic appeal is prioritized over longevity. Buyers should weigh the cost benefits against potential durability issues, especially in high-traffic environments. Understanding the target market’s expectations can guide decisions on whether bonded leather aligns with brand values.
What are the Key Features and Applications of PU Leather in B2B Markets?
PU leather is a synthetic alternative to traditional leather, coated with polyurethane. It is popular in fashion and automotive sectors due to its water-resistant properties and ease of maintenance. For B2B buyers, PU leather offers a vegan-friendly option that can attract a broader customer base. However, its non-biodegradable nature raises environmental concerns, making it essential for companies to balance market demand with sustainability commitments.
Why Consider Vegetable-Tanned Leather for High-End Products?
Vegetable-tanned leather is processed using natural materials, making it biodegradable and environmentally friendly. This type of leather is favored in high-end fashion and artisanal goods, where unique aesthetics and craftsmanship are valued. B2B buyers should consider the premium pricing associated with vegetable-tanned leather, as it can enhance brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. The distinctive aging process also adds character, making products more desirable.
What Should Buyers Know About Chrome-Tanned Leather?
Chrome-tanned leather is processed using chromium salts, making it durable and widely available, which is why it is commonly used in mass-produced goods like footwear and bags. B2B buyers need to be aware of the environmental implications associated with chrome tanning, including potential toxicity. While it offers practical benefits, such as resistance to wear and tear, companies should evaluate the impact on their sustainability goals and consumer perceptions before committing to chrome-tanned leather sources.
Key Industrial Applications of recycled leather vs bonded leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Recycled Leather vs Bonded Leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Interior upholstery and trim materials | Enhanced sustainability profile and reduced waste impact | Quality certification of recycled content; compliance with automotive standards |
| Fashion and Apparel | Clothing, accessories, and footwear | Strong market appeal due to eco-conscious consumer trends | Source from certified recyclers; ensure durability and aesthetics |
| Furniture Manufacturing | Upholstery for sofas, chairs, and decorative items | Cost-effective alternative with a unique, premium appearance | Assess material longevity; consider fire safety standards |
| Home Decor | Decorative items and wall coverings | Differentiation in product offerings and alignment with sustainability goals | Verify the origin of materials; check for design versatility |
| Luxury Goods | High-end bags, wallets, and belts | Appeal to affluent consumers seeking sustainable luxury products | Ensure traceability of materials; focus on craftsmanship and brand reputation |
How is Recycled Leather Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, recycled leather is increasingly utilized for interior upholstery and trim materials. This application not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of vehicles but also significantly reduces waste by repurposing leather scraps from manufacturing processes. For international buyers, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, sourcing recycled leather that meets stringent automotive standards is crucial. Compliance with safety regulations and quality certifications can ensure that the materials used do not compromise vehicle integrity.
What Role Does Recycled Leather Play in Fashion and Apparel?
Recycled leather is a popular choice in the fashion and apparel sector for clothing, accessories, and footwear. It offers a sustainable alternative that resonates with eco-conscious consumers, thereby enhancing brand image and marketability. Buyers from Africa and South America should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who can guarantee the recycled content’s quality and durability. Additionally, understanding the aesthetic appeal of the recycled leather can help in making informed purchasing decisions that align with current fashion trends.
How is Bonded Leather Applied in Furniture Manufacturing?
In furniture manufacturing, bonded leather is often used for upholstery on sofas, chairs, and decorative items. This material provides a cost-effective alternative to genuine leather while offering a stylish finish. Businesses seeking bonded leather must consider its longevity and maintenance requirements, especially in regions with varied climates like Europe and the Middle East. Ensuring that the bonded leather meets industry standards for durability and safety can enhance product appeal and customer satisfaction.
What are the Benefits of Recycled Leather in Home Decor?
Recycled leather is utilized in home decor for items such as decorative accents and wall coverings. This application allows manufacturers to offer unique, eco-friendly products that cater to growing consumer demand for sustainable options. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets, verifying the origin and quality of recycled leather is essential to ensure product integrity and market competitiveness. The versatility of recycled leather in design can also open up new opportunities for innovative product lines.
Why Choose Recycled Leather for Luxury Goods?
In the luxury goods sector, recycled leather is increasingly sought after for high-end bags, wallets, and belts. This trend is driven by affluent consumers who prioritize sustainability without compromising on quality. For B2B buyers, especially in regions like Saudi Arabia and Europe, sourcing recycled leather that maintains the craftsmanship and aesthetic appeal of luxury items is paramount. Ensuring traceability and ethical sourcing can enhance brand reputation and align with consumer values in the luxury market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘recycled leather vs bonded leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding Material Composition and Quality
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to differentiate between recycled leather and bonded leather due to the lack of clear labeling and understanding of material properties. This confusion can lead to sourcing decisions that may compromise product quality and sustainability goals. For instance, a buyer aiming to enhance their brand’s eco-friendly image may inadvertently purchase bonded leather, which is often made from lower-quality materials and contains synthetic components, rather than recycled leather that aligns with their values.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should establish a rigorous sourcing process that includes detailed inquiries about material composition. Request certifications and documentation from suppliers that clarify whether the leather is truly recycled or bonded. Additionally, conducting material testing can provide insights into durability and environmental impact. Collaborating with reputable suppliers who specialize in recycled leather can ensure that products meet sustainability standards while maintaining high quality. Consider creating a checklist for supplier assessments that includes questions about the sourcing, processing methods, and certifications related to recycled leather to ensure alignment with your brand values.
Scenario 2: Navigating the Environmental Claims
The Problem: With the increasing emphasis on sustainability, buyers are often faced with exaggerated claims about the environmental benefits of recycled and bonded leather. Misleading marketing can lead to confusion, making it difficult for buyers to determine which option is genuinely more sustainable. For example, a buyer may choose bonded leather, believing it to be a sustainable alternative, only to discover later that its production process is environmentally detrimental.
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, buyers should prioritize transparency by seeking suppliers who provide comprehensive sustainability reports and life cycle analyses of their products. Engaging in dialogues with manufacturers about their environmental impact, including energy consumption and waste generation during production, is essential. Buyers can also look for third-party certifications that validate sustainability claims, such as Global Recycled Standard (GRS) or OEKO-TEX. By establishing a criterion for evaluating sustainability claims, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their corporate responsibility objectives.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Sourcing and Supply Chain Challenges
The Problem: Sourcing recycled leather can be particularly challenging due to limited availability and variability in quality, especially in regions where recycling infrastructures are still developing. Buyers may face delays or inconsistencies in supply, which can hinder production timelines and affect their ability to meet customer demands. This is especially pertinent for businesses looking to introduce sustainable lines of products quickly.
The Solution: To mitigate sourcing challenges, buyers should diversify their supplier base and build relationships with multiple manufacturers of recycled leather. Engaging with suppliers from different geographical regions, such as Europe or North America, where recycling processes are more established, can enhance reliability. Additionally, buyers can consider forming partnerships with local recycling initiatives to secure a steady supply of materials. Establishing long-term contracts or collaborative agreements can also provide stability in sourcing. Finally, integrating flexible inventory management systems can help accommodate fluctuations in supply, ensuring that production schedules remain intact even when sourcing challenges arise.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for recycled leather vs bonded leather
What Are the Key Properties of Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather?
Recycled Leather: Properties and Applications
Recycled leather is produced from post-consumer and post-industrial leather waste, which is mechanically processed into fibers and then reconstituted with adhesives. This material retains some of the original leather’s properties, such as durability and aesthetic appeal, while offering a more sustainable option. The temperature resistance of recycled leather can vary but generally withstands moderate heat, making it suitable for various applications, including upholstery and fashion accessories.
Pros of recycled leather include its eco-friendly credentials, as it helps reduce waste in the leather industry. It is often perceived as a premium product due to its authentic leather look and feel. However, the cons include potential variability in quality, as the material composition can differ based on the source of the recycled leather. The manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for sorting and processing different types of leather.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, the availability of recycled leather can be limited, and compliance with local environmental regulations is crucial. Buyers should also consider the standards for durability and safety, such as ASTM or DIN, that may apply to their specific applications.
Bonded Leather: Properties and Applications
Bonded leather, on the other hand, is made by combining leather scraps with a polyurethane or latex binder, resulting in a material that resembles leather but is fundamentally different in composition. Its temperature and pressure ratings are generally lower than those of recycled leather, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
The key advantages of bonded leather include its cost-effectiveness and versatility, as it can be produced in various textures and finishes. However, the disadvantages are significant; bonded leather is typically less durable and may not age as gracefully as genuine leather or recycled leather. It is also more susceptible to wear and tear, which can lead to a shorter lifecycle for products made from this material.
For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, understanding the environmental impact of bonded leather production is essential, as there is a growing demand for sustainable materials. Compliance with EU regulations regarding waste and chemical usage is particularly relevant.
Summary Table of Material Comparisons
| Material | Typical Use Case for recycled leather vs bonded leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Leather | Upholstery, fashion accessories, automotive interiors | Eco-friendly and sustainable | Variable quality and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Bonded Leather | Furniture, bookbinding, budget-friendly fashion items | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower durability and shorter lifecycle | Low |
This comparative analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of recycled leather and bonded leather. Understanding these factors can help in making informed decisions that align with sustainability goals and application requirements.
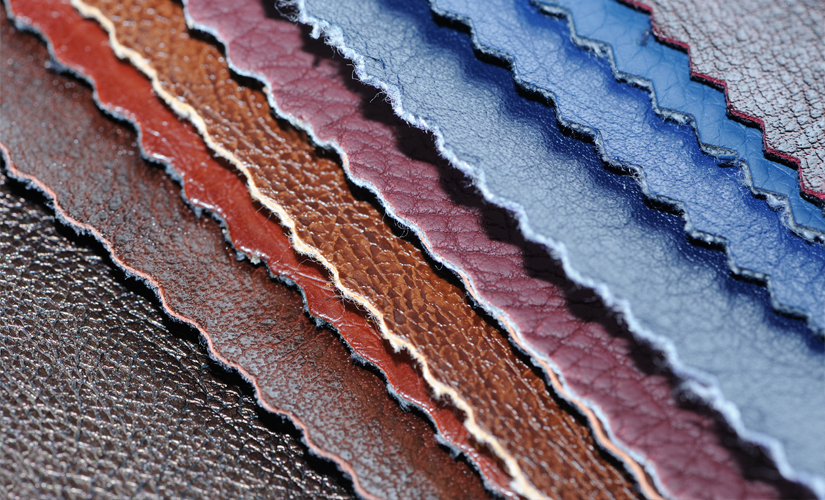

Illustrative image related to recycled leather vs bonded leather
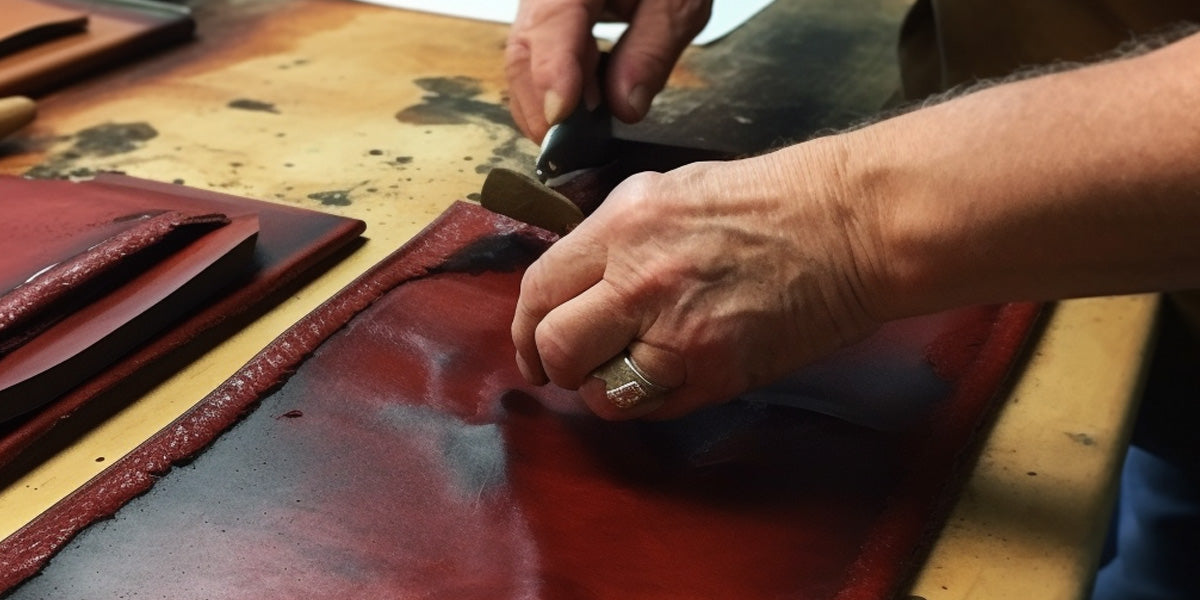
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for recycled leather vs bonded leather
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather?
Understanding the manufacturing processes for both recycled leather and bonded leather is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Each material undergoes distinct manufacturing stages, which influence quality, durability, and environmental impact.
How Is Recycled Leather Manufactured?
-
Material Preparation
The first step in recycled leather production involves sourcing leather waste, typically derived from post-industrial scraps or post-consumer products. These leather pieces undergo sorting to remove non-leather components (e.g., linings, hardware) and are then processed. Two main techniques are employed:
– Mechanical Recycling: Leather scraps are shredded into fibers and then reconstituted using adhesives.
– Chemical Recycling: Leather is chemically broken down to extract collagen and other usable components, which can then be remolded. -
Forming
The prepared leather fibers are then mixed with bonding agents. This mixture is spread onto a backing material to form sheets of recycled leather. Depending on the desired thickness and texture, variations in the composition and application techniques can be used. -
Assembly
The formed sheets are cut and assembled into various products, such as bags, upholstery, and accessories. This stage often involves stitching, which requires attention to detail to ensure durability. -
Finishing
The final stage includes surface treatments, which can involve dyeing, coating, or embossing. These finishes not only enhance aesthetics but also improve water resistance and durability. Sustainable practices can be adopted here, such as using eco-friendly dyes.
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Bonded Leather?
-
Material Preparation
Bonded leather is produced from leather scraps or fibers mixed with synthetic materials. The preparation phase involves shredding the leather into small pieces and mixing it with polyurethane or other binders to create a composite material. -
Forming
Similar to recycled leather, the mixture is spread onto a backing material. The formation process often includes pressing the composite under heat and pressure to ensure a uniform thickness and consistency. -
Assembly
After forming, the bonded leather sheets are cut into specific shapes for various applications. This may involve automated cutting machines to ensure precision and reduce waste. -
Finishing
Bonded leather typically undergoes finishing processes that may include coating with a protective layer to enhance durability and aesthetics. The finishing stage may involve chemical treatments to improve resistance to wear and staining.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for both recycled leather and bonded leather. Adhering to international and industry-specific standards is essential to ensure product quality and safety.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
- ISO 9001: This standard sets the criteria for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality in products and services. Manufacturers adhering to ISO 9001 are likely to have robust processes in place.
- CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for industries such as automotive, where bonded leather may be used in interiors, API standards ensure that materials meet specific quality criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses raw materials, ensuring they meet specified standards before they enter production. For recycled leather, this involves checking the quality of leather waste, while for bonded leather, it includes verifying the quality of synthetic materials.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are crucial. This includes monitoring the forming and assembly stages to ensure consistency and adherence to specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products leave the factory, they undergo final inspections to assess overall quality. This includes testing for durability, aesthetic quality, and compliance with relevant standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential for maintaining high standards in their own operations.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing process, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including testing results and compliance certifications, provides transparency and assurance regarding product quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control processes and product quality.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
When sourcing recycled or bonded leather, international buyers should consider the following nuances:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding material sourcing, environmental impact, and product safety. Familiarity with these regulations is crucial to avoid compliance issues.
- Cultural Expectations: Buyers should be aware of cultural preferences for leather products, which may influence material choices and design specifications.
- Logistical Challenges: Importing materials or products may involve complex logistics, including tariffs, customs regulations, and shipping considerations. Understanding these factors can prevent delays and additional costs.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for recycled leather and bonded leather, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and sustainability goals.

Illustrative image related to recycled leather vs bonded leather
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘recycled leather vs bonded leather’
This guide aims to equip B2B buyers with a practical checklist for sourcing recycled leather and bonded leather. Understanding the differences between these materials and the associated procurement process can help businesses make informed choices, align with sustainability goals, and meet customer demands.
Step 1: Understand Material Characteristics
Before making a procurement decision, it’s essential to grasp the distinct properties of recycled leather and bonded leather. Recycled leather is made from repurposed leather scraps, offering a more sustainable option with varying quality levels, while bonded leather combines leather fibers with synthetic materials, often resulting in a lower-cost product. Knowing these characteristics helps you align your sourcing strategy with your product requirements.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for your procurement strategy. Consider factors such as durability, texture, and finish that match your end products. Additionally, determine the acceptable percentage of recycled content if you’re opting for recycled leather, as this will influence supplier selection and product quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Supplier certifications can indicate the quality and sustainability of materials. Look for certifications related to environmental impact, such as Global Recycle Standard (GRS) for recycled leather or ISO certifications for bonded leather production processes. These certifications ensure compliance with international standards and reinforce your commitment to sustainability.
Step 4: Assess Environmental Impact
Given the increasing focus on sustainability, evaluate the environmental implications of both materials. Recycled leather typically has a lower carbon footprint compared to bonded leather, which often involves synthetic processes. Understanding these impacts can enhance your brand’s reputation and align with eco-friendly market trends.
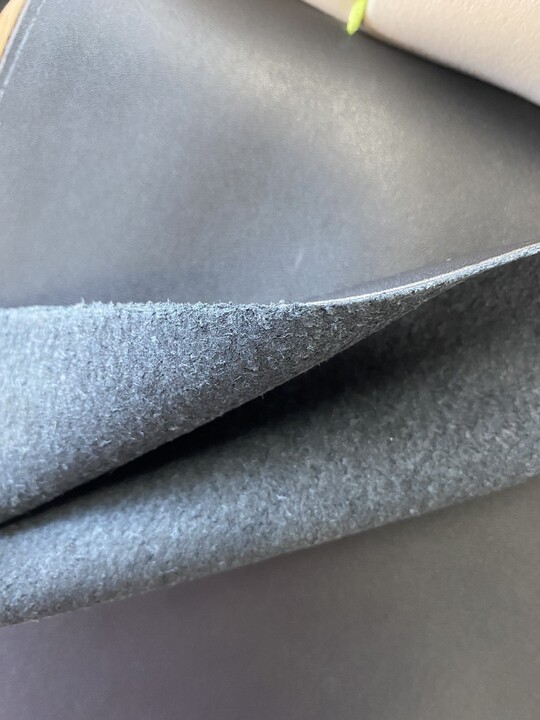

Illustrative image related to recycled leather vs bonded leather
Step 5: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Before making bulk purchases, request samples from potential suppliers. This step allows you to evaluate the texture, durability, and overall quality of the materials firsthand. It’s also an opportunity to assess how well the materials meet your specific design and functional requirements.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified potential suppliers and assessed their materials, engage in negotiations. Discuss pricing, minimum order quantities, lead times, and payment terms. Consider the long-term relationship potential with suppliers, as establishing a solid partnership can lead to better pricing and service over time.
Step 7: Implement a Quality Control Process
Establish a quality control process to ensure that the materials received meet your specifications. This could involve on-site inspections or third-party quality assurance testing. Consistent quality checks will help mitigate risks associated with material defects and ensure customer satisfaction with the final products.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing recycled leather and bonded leather effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business goals and sustainability commitments.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for recycled leather vs bonded leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Recycled Leather vs Bonded Leather?
When analyzing the cost structure of recycled leather versus bonded leather, several components come into play. For both materials, the primary cost components include raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.

Illustrative image related to recycled leather vs bonded leather
-
Materials: Recycled leather is typically derived from post-industrial or post-consumer leather waste, which can lead to lower material costs if sourced efficiently. However, the recycling process may involve additional expenses, such as cleaning and processing. In contrast, bonded leather, made from leather scraps mixed with polyurethane or other materials, often has a lower upfront cost but may involve higher long-term sustainability concerns.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the complexity of the processing methods. Recycled leather may require more skilled labor for sorting, cleaning, and processing, especially if using advanced recycling technologies. Bonded leather production can be less labor-intensive due to more straightforward manufacturing processes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with machinery, energy consumption, and maintenance. Recycled leather production facilities may face higher overhead due to the need for specialized equipment for recycling processes. Bonded leather manufacturers may have a more streamlined operation, potentially resulting in lower overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The tooling costs for both types of leather can vary based on the complexity of the designs and the customization required. Recycled leather may necessitate more versatile tooling to accommodate the unique textures and characteristics of the sourced materials.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is crucial for both materials. Recycled leather may require rigorous QC processes to ensure consistency, especially if sourced from varied waste streams. Bonded leather can have more standardized quality checks, but the presence of synthetic materials may raise concerns about durability and longevity.
-
Logistics: The logistics of sourcing and transporting recycled leather can be more complex due to the need for specialized facilities and the potential for longer supply chains. Bonded leather, often produced in larger, centralized facilities, may benefit from more efficient logistics.
-
Margin: Profit margins can fluctuate based on the perceived value of sustainability. While recycled leather may command a premium price in eco-conscious markets, bonded leather can be marketed as a cost-effective alternative, impacting the overall pricing strategy.
What Influences Pricing for Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather?
Several factors influence the pricing of recycled versus bonded leather:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, which is a crucial consideration for B2B buyers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products often come with additional costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses, particularly with recycled leather, where variations in material quality can affect final products.
-
Materials and Certifications: The source of materials and any sustainability certifications can impact pricing. Recycled leather products often come with certifications that may justify a higher price point in environmentally conscious markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capacity, and geographical location can influence costs. Suppliers in regions with established recycling infrastructures may offer more competitive pricing for recycled leather.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is essential for international buyers. These terms dictate who bears the shipping costs and risks, directly impacting the total cost.
What Should Buyers Consider for Cost-Efficiency in International Sourcing?
B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should keep several strategies in mind to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume and long-term relationships to negotiate better terms. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or favorable payment terms for committed buyers.
-
Total Cost of Ownership: Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, potential waste, and end-of-life disposal costs. This is particularly relevant for recycled leather, which may offer lower long-term environmental impact.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. Prices may fluctuate based on local demand, currency exchange rates, and trade tariffs, especially in international transactions.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices for recycled leather and bonded leather can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. For accurate and up-to-date pricing, buyers should consult with suppliers directly, as these prices are subject to change based on market conditions and operational costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing recycled leather vs bonded leather With Other Solutions
Exploring Viable Alternatives to Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather
As the demand for sustainable and innovative materials increases, businesses are exploring various alternatives to traditional leather products. This section examines recycled leather and bonded leather, comparing them with alternative solutions like vegan leather and polyurethane (PU) leather. Each option presents unique characteristics that can significantly impact a buyer’s decision based on performance, cost, and sustainability.
| Comparison Aspect | Recycled Leather Vs Bonded Leather | Vegan Leather | Polyurethane (PU) Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable; varies by manufacturing | Generally less durable; depends on materials used | Moderate durability; prone to wear |
| Cost | Mid-range; price varies by source | Can be higher due to raw materials | Generally lower cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized processes for recycling | Easier to manufacture; widely available | Simple production processes |
| Maintenance | Similar to traditional leather; requires care | Varies; often easier to clean | Low maintenance; wipes clean easily |
| Best Use Case | Fashion and upholstery; eco-conscious brands | Fashion, accessories; vegan markets | Budget-friendly products; mass production |
Understanding Vegan Leather as an Alternative
Vegan leather, made from plant-based materials or synthetic fibers, offers a cruelty-free option that appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. Its production often involves less energy than traditional leather, but the durability can vary significantly based on the materials used. While it is an attractive option for fashion and accessories targeting vegan markets, some types may not withstand heavy wear, making them less suitable for high-usage applications.
Evaluating Polyurethane (PU) Leather
Polyurethane leather is a synthetic alternative that mimics the look and feel of genuine leather while often coming at a lower price point. It is easier to produce than both recycled and bonded leather, making it a popular choice for mass-market products. However, PU leather is less durable and may wear out quicker than its counterparts, especially in high-friction applications. Additionally, its non-biodegradable nature raises environmental concerns, which could deter eco-conscious brands.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting between recycled leather, bonded leather, and their alternatives, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific needs, including cost constraints, desired product lifespan, and sustainability goals. Recycled leather presents a compelling choice for brands focused on eco-friendliness, while bonded leather may appeal to those seeking a cost-effective solution. On the other hand, vegan leather and PU leather provide additional options, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. Ultimately, understanding the performance, cost implications, and maintenance requirements of each material will enable businesses to make informed decisions that align with their operational objectives and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for recycled leather vs bonded leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather?
Understanding the technical properties of recycled leather and bonded leather is essential for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Composition
– Recycled Leather: This material is produced from scraps or post-consumer leather, often mixed with synthetic fibers or adhesives. Its composition can vary widely, affecting durability and quality.
– Bonded Leather: Made from leather scraps bonded together with polyurethane or latex, this material typically has a higher synthetic content. Buyers should assess the ratio of leather to synthetic material, as this impacts the product’s longevity and aesthetic appeal. -
Durability Rating
– The durability of leather products is crucial for long-term applications. Recycled leather tends to have a lower durability rating compared to high-quality natural leather but can outperform bonded leather in certain applications. Buyers should inquire about the expected lifespan and wear resistance of products made from these materials. -
Weight Tolerance
– Weight tolerance refers to how much stress a material can withstand without deforming. It is especially important for products like bags, furniture, or automotive interiors. Recycled leather often has a higher weight tolerance due to its fibrous structure, while bonded leather may be more susceptible to tearing. -
Finishing Options
– The finishing process can significantly impact the final appearance and usability of leather products. Recycled leather can be finished in various ways to enhance its look and feel, whereas bonded leather often has a uniform surface treatment. Understanding finishing options is crucial for aesthetic and functional requirements. -
Environmental Impact Rating
– Many companies are prioritizing sustainable practices. Recycled leather is often marketed as an eco-friendly option, as it reduces waste in the leather industry. Buyers should look for certifications or ratings that indicate the environmental impact of both materials, including energy consumption during production. -
Cost per Unit
– Cost is a significant factor in B2B transactions. Recycled leather can sometimes be more expensive due to its production processes and sourcing. In contrast, bonded leather often offers a lower price point but may compromise on quality. Buyers should analyze the cost in relation to the expected lifespan and performance of the materials.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Recycled and Bonded Leather?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts or products that are sold under another company’s brand name. In the leather industry, an OEM might produce leather goods for a fashion brand, impacting pricing and supply chain dynamics. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is vital for B2B buyers to align their purchasing strategies with supplier capabilities, especially when sourcing recycled or bonded leather. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. Including detailed specifications for recycled or bonded leather in an RFQ can help ensure accurate quotes and facilitate better negotiation outcomes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are predefined commercial terms used in international trade to clarify responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions involving imported leather products, as they dictate who bears the risk at various points in the shipping process. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. It is crucial for inventory management and production schedules. Understanding lead times for recycled and bonded leather can help buyers plan their procurement strategies more effectively. -
Sustainability Certification
– This refers to various certifications that indicate a product meets specific environmental and ethical standards. Buyers should look for certifications like Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or Leather Working Group (LWG) to ensure they are sourcing responsibly.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing recycled and bonded leather more effectively, aligning their purchasing decisions with business objectives and market trends.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the recycled leather vs bonded leather Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Impacting Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather Sourcing?
The global leather market is undergoing significant transformation, driven by sustainability concerns and shifting consumer preferences. In 2023, the leather industry produced approximately 8 million tons of waste, highlighting a substantial opportunity for recycled leather to capture market share. B2B buyers, particularly from emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly prioritizing sustainable sourcing. The rise of eco-consciousness has led to a surge in demand for recycled leather, which is seen as a viable alternative to traditional leather and bonded leather.
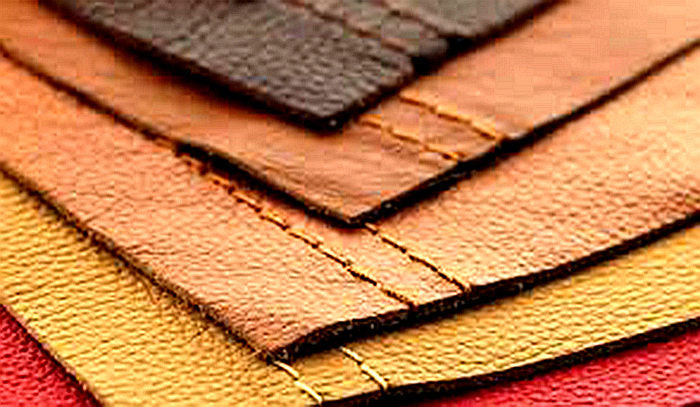

Illustrative image related to recycled leather vs bonded leather
Emerging technologies are reshaping the recycling landscape, with mechanical and chemical recycling methods gaining traction. Mechanical recycling, which involves shredding and reconstituting leather fibers, is currently the most prevalent method. Meanwhile, chemical recycling is emerging as a promising alternative, offering higher quality outputs despite its higher energy requirements. B2B buyers should keep an eye on innovations in recycling technologies that enhance product quality and reduce environmental impact.
Another key trend is the increasing integration of recycled leather into mainstream fashion and furniture industries. Major brands are adopting recycled leather to meet sustainability targets, creating new market opportunities. Buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam should assess suppliers’ capabilities in integrating recycled materials, as this could influence procurement decisions and product offerings.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence B2B Decisions in the Leather Sector?
Sustainability is no longer a mere buzzword; it has become a critical factor in B2B procurement strategies. The environmental impact of leather production is substantial, with traditional methods often involving toxic chemicals that pose significant ecological risks. In contrast, recycled leather presents a more sustainable option by repurposing existing materials and reducing landfill waste. B2B buyers must evaluate the sustainability credentials of suppliers, focusing on their recycling practices and the overall lifecycle of their products.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are increasingly seeking partners who adhere to responsible supply chain practices. Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) can serve as benchmarks for sustainable sourcing. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that are transparent about their sourcing methods and can demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations. This not only helps mitigate risks but also aligns with the values of socially conscious consumers.
Furthermore, the demand for green certifications is growing among buyers in diverse markets. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who can provide documentation of their sustainability practices, as this can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to eco-aware consumers. As the market evolves, the emphasis on sustainable and ethical sourcing will likely intensify, shaping the future of the recycled leather and bonded leather sectors.

Illustrative image related to recycled leather vs bonded leather
What Is the Historical Context of Recycled Leather and Bonded Leather in the Market?
The journey of recycled leather and bonded leather began as a response to the environmental challenges posed by the traditional leather industry. Historically, leather production was resource-intensive, often leading to significant waste and pollution. The introduction of recycled leather in the late 20th century marked a turning point, as manufacturers began to explore ways to repurpose leather scraps and reduce waste.
Bonded leather emerged as a cost-effective alternative, created by combining leather fibers with adhesives and backing materials. While it offered a more affordable option for consumers, it lacked the durability and authenticity of genuine leather. Over the years, the demand for recycled leather has grown, driven by advancements in recycling technologies and increasing consumer awareness regarding sustainability. This evolution reflects broader trends in the global market, where sustainable and ethically produced materials are becoming pivotal in the decision-making processes of B2B buyers.
As the industry continues to adapt to these changing dynamics, understanding the historical context of recycled and bonded leather can help B2B buyers make informed sourcing decisions that align with market trends and consumer expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of recycled leather vs bonded leather
-
How do I determine the quality of recycled leather when sourcing?
To assess the quality of recycled leather, evaluate its composition and manufacturing process. Request samples from suppliers to examine texture, durability, and appearance. Look for certifications that indicate sustainable practices and quality standards. Engaging in discussions about the source of the leather and the recycling methods used can provide insights into its overall quality. Additionally, consider customer reviews and case studies from other businesses to gauge the supplier’s reliability. -
What are the environmental benefits of using recycled leather over bonded leather?
Recycled leather significantly reduces waste by repurposing leather scraps, thus minimizing landfill contributions and conserving resources. It often requires less energy in production compared to bonded leather, which involves synthetic materials and adhesives. By choosing recycled leather, businesses can enhance their sustainability profile, meet eco-conscious consumer demand, and comply with environmental regulations, which is increasingly important in markets across Europe and beyond. -
What should I consider when comparing recycled leather and bonded leather for my product line?
When comparing recycled leather to bonded leather, evaluate factors such as durability, texture, and application suitability. Recycled leather often offers superior durability and a more authentic look, while bonded leather may be more affordable but less durable. Consider your target market’s preferences, the intended use of the product, and environmental impact. Additionally, factor in the cost implications, including potential savings on waste disposal and alignment with sustainability initiatives. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for recycled leather and bonded leather suppliers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and material types. For recycled leather, MOQs may range from 100 to 1,000 square meters, depending on the manufacturer’s capacity and material availability. Bonded leather suppliers often have lower MOQs due to the broader production base. It’s advisable to communicate your needs directly with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are a smaller business or just starting. -
How can I vet suppliers for recycled leather products?
To vet suppliers effectively, conduct thorough background checks by reviewing their history, certifications, and reputation in the market. Request references from other clients and ask about their sourcing practices and sustainability commitments. Visit their facilities if possible, or utilize virtual tours to assess their production capabilities. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes and how they handle compliance with international trade regulations. -
What payment terms are common for international transactions involving recycled leather?
Common payment terms for international transactions typically include a mix of upfront deposits (usually 30-50%) and balance payments upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit for larger orders to mitigate risks. Be sure to clarify terms with your supplier before finalizing contracts, as this can vary based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of your business relationship. Consider using escrow services for added security in transactions. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing recycled leather?
When importing recycled leather, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties that may apply in your region. Evaluate the total landed cost, including freight, insurance, and handling fees, to ensure it aligns with your budget. Partner with logistics providers experienced in handling leather products to navigate potential challenges, such as compliance with environmental standards and quality inspections at customs. Additionally, establish clear communication channels with your supplier regarding shipping timelines and documentation. -
How can I customize recycled leather products to meet my brand specifications?
Customizing recycled leather products involves discussing your design requirements with suppliers early in the sourcing process. Many manufacturers offer options for colors, textures, and finishes, allowing you to align products with your brand identity. Ensure that your specifications are clear and documented to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider requesting prototypes to evaluate how well the final product meets your expectations before committing to larger orders.
Top 5 Recycled Leather Vs Bonded Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Gionar – Recycled Leather Solutions
Domain: gionar.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Recycled leather is a sustainable alternative to traditional leather, addressing the significant waste produced by the leather industry, which generates approximately 8 million tons of waste annually, with only 20% being recycled. It differs from bonded leather, which is made from leather scraps and synthetic materials. Recycled leather is made through a process that includes collecting, sorting, …
2. Arcane Fox – Bonded Leather Essentials
Domain: arcanefox.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Bonded leather is a type of leather made from ground-up leather scraps combined with a polyurethane or latex mixture and affixed to a backing of paper or fiber. It is used in various applications including upholstery for furniture (couches, chairs, ottomans), book covers, clothing components, bags, wallets, and personal accessories. The leather content can range from 10% to 90%, affecting its func…
3. Manuel Dreesmann – Bonded Leather Insights
Domain: manuel-dreesmann.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: This company, Manuel Dreesmann – Bonded Leather Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. BAGGU – New Leather Bags
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: New leather bags from BAGGU are made from bonded leather, which is criticized for poor durability, cracking, and flaking. The material may include polyester, raising concerns about sustainability and eco-friendliness. The price for these bags is expected to be around $95, which many customers find excessive for a product made from bonded leather. There is disappointment among customers regarding t…
5. LeatherNeo – Bonded Leather Solutions
Domain: leatherneo.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Bonded leather is a cheaper alternative to real leather that maintains a similar look and feel. It is constructed from ground leather fibers glued with a polyurethane combination and connected to a paper or fiber backing. Common applications include upholstery, bookbinding, luggage, and various accessories. The composition can range from 10% to 90% leather, and it is often embossed to resemble gen…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for recycled leather vs bonded leather
In evaluating the strategic sourcing of recycled leather versus bonded leather, it is essential for international B2B buyers to consider both environmental impact and product viability. Recycled leather emerges as a sustainable alternative that not only reduces waste but also appeals to the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. Its unique properties, derived from post-industrial and post-consumer leather, offer durability and versatility across various applications, from fashion to automotive interiors.
On the other hand, bonded leather, while potentially more affordable, often lacks the quality and longevity that discerning buyers seek. Its composite nature can lead to performance issues over time, making it less attractive for long-term investments.
As global markets increasingly prioritize sustainability, sourcing recycled leather can position businesses favorably in competitive landscapes, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Companies are encouraged to align their procurement strategies with sustainable practices, thereby enhancing brand reputation and meeting regulatory demands.
Moving forward, businesses should actively explore partnerships with manufacturers specializing in recycled materials. By doing so, they can not only contribute to a circular economy but also tap into emerging markets driven by sustainability. Let’s embrace this opportunity to lead the charge towards a greener future in leather sourcing.

Illustrative image related to recycled leather vs bonded leather
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.