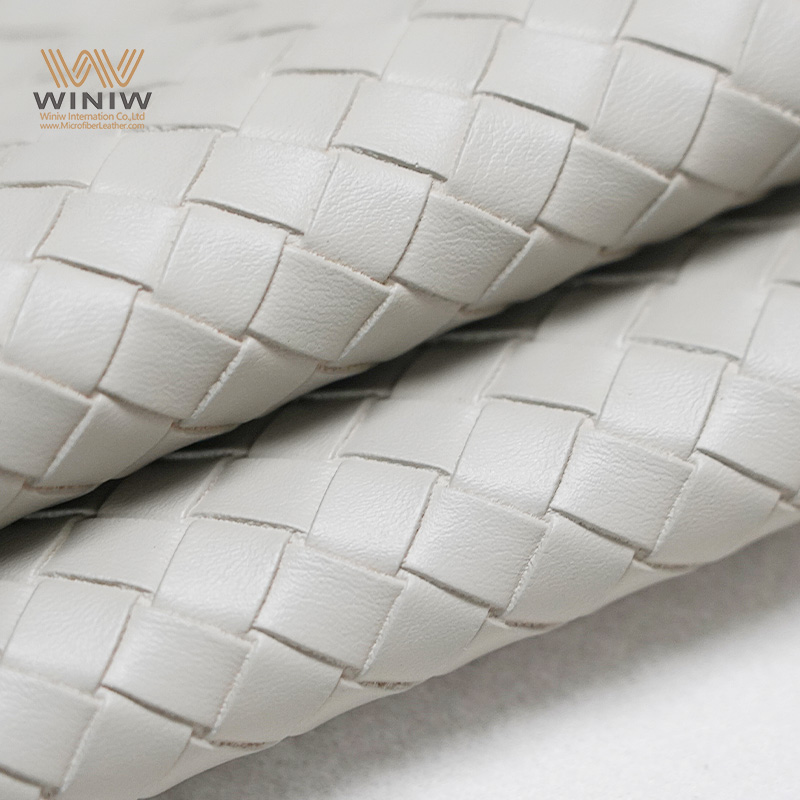
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather manufacturer
The global market for faux leather manufacturers presents a unique opportunity for B2B buyers seeking high-quality, sustainable alternatives to traditional leather. However, navigating this diverse landscape can be challenging, especially when sourcing materials that meet specific performance and aesthetic requirements while remaining cost-effective. This guide is designed to simplify that process, offering insights into various types of faux leather, their applications across multiple industries, and best practices for supplier vetting.
From polyurethane to innovative plant-based leathers, buyers will discover a range of materials tailored for upholstery, fashion, and automotive industries. Additionally, we delve into critical factors such as production costs, sustainability practices, and compliance with international quality standards, ensuring that your purchasing decisions are informed and strategic.
This comprehensive resource empowers international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Germany, to make educated choices. By understanding the nuances of faux leather manufacturing and the suppliers behind them, you can confidently select materials that not only meet your business needs but also align with consumer demands for ethical and eco-friendly options. Whether you are expanding your product line or seeking reliable partners, this guide will be an invaluable tool in your sourcing journey.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Faux Leather Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather manufacturer
- Understanding faux leather manufacturer Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of faux leather manufacturer
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather manufacturer
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather manufacturer
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather manufacturer’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather manufacturer Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather manufacturer With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather manufacturer
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather manufacturer Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather manufacturer
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather manufacturer
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding faux leather manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane Faux Leather | Soft, pliable, and available in various textures | Upholstery, fashion accessories, automotive | Pros: Durable, easy to clean. Cons: Can be less breathable than natural leather. |
| Plant-Based Faux Leather | Made from sustainable materials like pineapple, cactus | Eco-friendly products, fashion, furniture | Pros: Environmentally friendly, unique aesthetics. Cons: May be less durable than synthetic options. |
| PVC Faux Leather | Cost-effective, versatile, and widely available | Upholstery, bags, and apparel | Pros: Affordable, water-resistant. Cons: Less eco-friendly, potential for chemical off-gassing. |
| Microsuede | Soft texture, mimics suede, easy to maintain | Home furnishings, automotive interiors | Pros: Luxurious feel, stain-resistant. Cons: Can wear out faster than other materials. |
| Silicone Faux Leather | High-performance, solvent-free manufacturing process | High-end upholstery, medical applications | Pros: Durable, resistant to heat and moisture. Cons: Higher cost compared to other types. |
What are the Characteristics of Polyurethane Faux Leather?
Polyurethane (PU) faux leather is a synthetic alternative that is soft and pliable, making it a preferred choice for various applications, including upholstery and fashion accessories. Its versatility allows manufacturers to create a wide range of textures and finishes, catering to diverse aesthetic demands. When purchasing PU leather, buyers should consider its durability and ease of cleaning, as well as its potential lack of breathability compared to natural leather.
How Does Plant-Based Faux Leather Stand Out?
Plant-based faux leather, derived from sustainable sources such as pineapple, cactus, and grapes, offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials. This type of faux leather is gaining traction in industries focused on sustainability, including fashion and furniture. B2B buyers should assess the unique aesthetics and environmental benefits of plant-based leathers, while also considering their relative durability and performance in comparison to synthetic options.
Why Choose PVC Faux Leather for Cost-Effectiveness?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) faux leather is known for its affordability and versatility, making it a popular choice for upholstery, bags, and apparel. Its water-resistant properties make it suitable for a variety of environments, including outdoor applications. Buyers should weigh the cost advantages against the environmental impact and potential health concerns associated with PVC, particularly regarding chemical off-gassing.
What are the Benefits of Microsuede Faux Leather?
Microsuede is a synthetic fabric that closely resembles the texture of suede, providing a luxurious feel at a lower cost. Its stain-resistant qualities make it ideal for home furnishings and automotive interiors. B2B buyers interested in microsuede should consider its maintenance ease and aesthetic appeal, while also being mindful that it may wear out faster than more robust materials.
How Does Silicone Faux Leather Compare in Performance?
Silicone faux leather is a high-performance material that utilizes a solvent-free manufacturing process, making it a sustainable option for high-end upholstery and medical applications. Its resistance to heat and moisture contributes to its durability, though it typically comes at a higher price point. Buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits of silicone leather against its initial investment, particularly for applications requiring enhanced durability and sustainability.
Key Industrial Applications of faux leather manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of faux leather manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Interior upholstery for vehicles | Enhances aesthetics and durability while reducing weight | Compliance with safety regulations; UV resistance; availability of various textures and colors |
| Furniture | Upholstery for sofas and chairs | Cost-effective alternative to genuine leather with easy maintenance | Durability standards; fire resistance; variety of styles and patterns |
| Fashion and Apparel | Clothing and accessories | Offers a stylish, cruelty-free option for fashion brands | Eco-friendliness; customization options; supplier reliability |
| Home Decor | Wall coverings and decorative items | Provides a luxurious look without the high cost of real leather | Adhesive compatibility; ease of installation; design versatility |
| Hospitality and Contract | Upholstery for hotels and restaurants | Durable and easy-to-clean materials enhance customer experience | Compliance with industry-specific standards; stain resistance; availability in bulk |
How is Faux Leather Used in the Automotive Industry?
Faux leather manufacturers supply materials for vehicle interiors, including seats, door panels, and dashboards. This synthetic alternative not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of vehicles but also contributes to weight reduction, which can improve fuel efficiency. International buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and the Middle East, should prioritize sourcing materials that comply with safety and environmental regulations, ensuring UV resistance and durability to withstand varying climates.
What are the Benefits of Faux Leather in Furniture Upholstery?
In the furniture sector, faux leather is widely used for upholstery on sofas, chairs, and other furnishings. This material offers a cost-effective solution that mimics the luxurious feel of genuine leather while being easier to clean and maintain. Buyers from South America and Africa should look for suppliers that meet durability standards and provide a variety of styles and patterns to cater to diverse market preferences.
How is Faux Leather Revolutionizing Fashion and Apparel?
Faux leather plays a pivotal role in the fashion industry, offering designers a cruelty-free option for clothing and accessories. Its versatility allows for various textures and colors, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. B2B buyers in Europe, especially those focusing on sustainable fashion, should ensure that their suppliers can provide eco-friendly options and reliable customization capabilities to meet evolving market demands.
In What Ways is Faux Leather Utilized in Home Decor?
Faux leather is increasingly popular in home decor, used for wall coverings, decorative items, and even furniture accents. This material provides a luxurious appearance without the high costs associated with real leather. Buyers in the Middle East should consider sourcing materials that are compatible with various adhesives and easy to install, offering design versatility for diverse interior styles.
Why is Faux Leather Important for the Hospitality Sector?
In the hospitality industry, faux leather is commonly used for upholstery in hotels and restaurants, where durability and ease of cleaning are paramount. This material enhances the customer experience by providing a high-end look while being practical for high-traffic environments. Buyers from Africa and South America should focus on suppliers that comply with industry-specific standards, ensuring stain resistance and availability for bulk orders to accommodate large-scale projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing High-Quality Faux Leather That Meets International Standards
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with finding faux leather manufacturers that meet their specific quality and regulatory standards, especially when operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Many suppliers offer products that may not comply with stringent safety regulations or environmental standards, which can lead to costly compliance issues, product recalls, and damage to brand reputation.
The Solution: To effectively source high-quality faux leather, buyers should prioritize manufacturers who provide transparent documentation regarding compliance with international standards such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) and ISO certifications. Engage with suppliers who can furnish samples and test results before placing bulk orders. Additionally, consider manufacturers that use advanced technologies, like hydro-based polymers, which are less harmful to the environment. Conducting on-site visits or virtual audits can further ensure that the production processes align with sustainability practices and quality benchmarks.
Scenario 2: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions and Lead Times
The Problem: International buyers often face challenges related to supply chain disruptions, which can significantly extend lead times for faux leather products. Factors such as geopolitical tensions, shipping delays, and raw material shortages can jeopardize project timelines and result in financial losses. Companies may find themselves unable to fulfill customer orders on time, leading to dissatisfaction and potential loss of business.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, B2B buyers should develop relationships with multiple faux leather suppliers across different regions. This diversification strategy not only provides alternative sourcing options but also helps in negotiating better lead times. Implementing a just-in-time inventory system can reduce the need for large stockpiles, allowing for more flexibility. Additionally, leveraging technology such as supply chain management software can enhance visibility into inventory levels and shipment statuses, enabling proactive adjustments when disruptions arise.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Longevity and Performance of Faux Leather Products
The Problem: Buyers often express concerns about the durability and maintenance of faux leather products. They may encounter issues with fading, cracking, or peeling over time, especially in high-usage applications like upholstery and automotive interiors. These problems can lead to increased replacement costs and negatively impact customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To ensure the longevity and performance of faux leather, it is crucial to select materials that are specifically designed for durability. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturing process and the types of coatings used on the faux leather. Products like Sta-Kleen silicone or advanced polyurethane blends offer superior resistance to wear and tear. Furthermore, implementing a proper care and maintenance routine—such as using appropriate cleaning agents and avoiding excessive exposure to sunlight—can significantly extend the life of the material. Training staff on maintenance best practices can also enhance the overall customer experience and reduce replacement frequency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather manufacturer
What Are the Key Materials Used in Faux Leather Manufacturing?
Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is produced using various materials, each with distinct properties and applications. Understanding these materials is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse international markets. Below, we analyze four common materials used in faux leather production: Polyurethane (PU), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Plant-Based Leathers, and Microsuede.
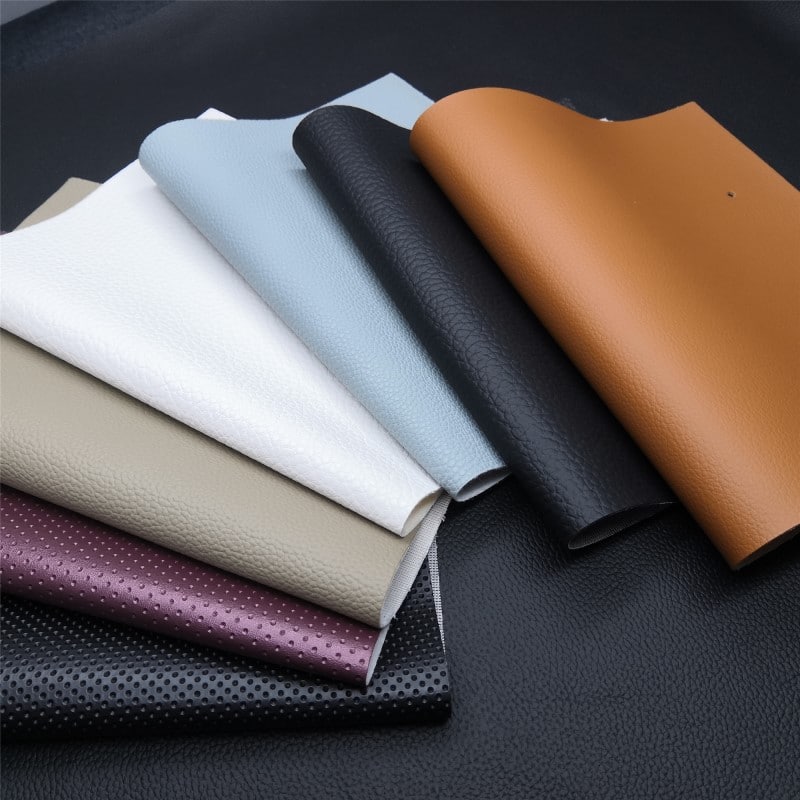

Illustrative image related to faux leather manufacturer
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Perform in Faux Leather Applications?
Polyurethane (PU) is one of the most popular materials for faux leather due to its versatility and performance characteristics. PU faux leather is known for its soft texture, flexibility, and durability. It can withstand moderate temperature variations and has good abrasion resistance, making it suitable for upholstery and fashion applications.
Pros: PU is lightweight, easy to clean, and available in a wide range of textures and colors. It also offers a more environmentally friendly option compared to PVC, as it can be produced without harmful chemicals.
Cons: However, PU may not be as durable as PVC in extreme conditions, particularly in high-pressure environments. The manufacturing process can be more complex, potentially increasing costs.
Impact on Application: PU is compatible with various media, including upholstery for furniture and automotive interiors, making it a versatile choice for manufacturers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where regulations on material safety and environmental impact are stringent.

Illustrative image related to faux leather manufacturer
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is another widely used material in faux leather production, known for its durability and water resistance. PVC can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor applications and high-wear environments.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and offers excellent durability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from upholstery to automotive interiors.
Cons: However, PVC is less breathable than PU, which can lead to discomfort in certain applications. The environmental impact of PVC production is also a concern, as it can release harmful chemicals during manufacturing.
Impact on Application: PVC’s durability makes it suitable for applications requiring high resistance to wear and tear, such as commercial upholstery and marine environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying regulations regarding PVC use in different regions, particularly in Europe, where there is a push for sustainable materials.
How Do Plant-Based Leathers Compare in Faux Leather Manufacturing?
Plant-based leathers, such as Piñatex and Desserto, are emerging as innovative alternatives to traditional faux leather materials. These materials are derived from agricultural by-products, making them sustainable options.
Pros: They offer unique aesthetics and are biodegradable, appealing to eco-conscious consumers. Their production processes often have a lower environmental impact compared to synthetic options.
Cons: However, plant-based leathers may not yet match the durability or versatility of PU and PVC, which could limit their application in high-wear environments.

Illustrative image related to faux leather manufacturer
Impact on Application: These materials are particularly suited for fashion and accessory applications, where aesthetics and sustainability are prioritized.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the sourcing and production standards of plant-based leathers, ensuring they meet local regulations and consumer expectations in their respective markets.
What Role Does Microsuede Play in Faux Leather Applications?
Microsuede is a synthetic fabric that mimics the look and feel of suede leather. It is often used in upholstery and fashion due to its soft texture and luxurious appearance.
Pros: Microsuede is easy to clean, resistant to stains, and offers a high-end look at a lower cost compared to genuine suede.

Illustrative image related to faux leather manufacturer
Cons: While it is durable, microsuede may not be as robust as PU or PVC in high-stress applications, limiting its use in certain industrial settings.
Impact on Application: It is ideal for soft furnishings, clothing, and accessories, providing a luxurious feel without the ethical concerns associated with animal leather.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that microsuede products comply with relevant textile standards in their regions, particularly concerning chemical safety and environmental impact.
Summary of Material Selection for Faux Leather Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for faux leather manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Upholstery, fashion accessories | Soft texture, eco-friendliness | Less durable in extreme conditions | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Commercial upholstery, marine applications | High durability, cost-effective | Less breathable, environmental concerns | Low |
| Plant-Based Leathers | Fashion, accessories | Sustainable, biodegradable | Limited durability in high-wear applications | Medium to High |
| Microsuede | Upholstery, clothing | Luxurious feel, easy to clean | Not as robust as PU or PVC | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in faux leather manufacturing, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather manufacturer
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Faux Leather?
The manufacturing process of faux leather involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both aesthetic and functional requirements. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The first step involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, often polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). These materials are then compounded with additives to enhance properties such as flexibility, durability, and weather resistance. The preparation stage also includes dyeing the base materials to achieve the desired color and texture, which is crucial for meeting market demands.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials are processed into sheets or rolls. Techniques such as calendering, where the material is passed through rollers, are commonly used to achieve a uniform thickness. This process can also incorporate texture patterns that mimic natural leather, giving faux leather its distinctive look.
-
Assembly: Once the sheets are formed, they are cut into specified dimensions for various applications, whether upholstery, fashion, or accessories. During this phase, manufacturers may also laminate additional layers for enhanced durability or aesthetic appeal.
-
Finishing: The final stage of production involves applying coatings and treatments to improve the faux leather’s surface properties, such as scratch resistance and water repellency. This can include the application of protective films or chemical treatments that enhance both the look and longevity of the material.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Faux Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the faux leather manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Here’s a breakdown of the quality assurance measures typically implemented:
-
Adherence to International Standards: Many faux leather manufacturers comply with ISO 9001, a quality management standard that emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for safety standards and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications for material quality are essential for suppliers targeting international markets.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Effective quality control is structured around several key checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, samples are taken at various stages to check for adherence to quality specifications.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the finished products undergo rigorous testing for durability, colorfastness, and other performance metrics to ensure they meet customer requirements. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of faux leather. These may include:
– Tensile Strength Testing: To measure the material’s resistance to breaking under tension.
– Abrasion Resistance Testing: To evaluate how well the faux leather can withstand wear and tear.
– Water Repellency Testing: To ensure the material can resist moisture, which is crucial for upholstery applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of faux leather manufacturers is vital for ensuring product reliability. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. Buyers should look for transparency in the supplier’s operations, including their adherence to international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed reports on their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These documents can serve as proof of compliance with standards and quality metrics.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can further validate the quality claims made by suppliers. These independent inspectors can perform assessments throughout the manufacturing process, providing unbiased reports on quality compliance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate several nuances in quality control when sourcing faux leather. Understanding regional standards and practices is essential:

Illustrative image related to faux leather manufacturer
-
Regional Compliance Standards: Different regions may have specific compliance requirements. For example, buyers in Europe might prioritize CE compliance, while those in the Middle East may focus on local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Buyers should also be aware of cultural differences that may affect quality expectations. For instance, certain markets may prioritize eco-friendly materials more than others, necessitating a thorough understanding of the supplier’s sustainability practices.
-
Communication and Documentation: Clear communication regarding quality expectations and specifications is critical. Buyers should ensure that all agreements are documented, detailing quality standards, testing methods, and delivery expectations to avoid misunderstandings.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for faux leather are comprehensive and multifaceted. B2B buyers must familiarize themselves with these processes to make informed sourcing decisions. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, implementing effective quality control measures, and recognizing the nuances of international standards, buyers can ensure they partner with reputable suppliers that deliver high-quality faux leather products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather manufacturer’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to source faux leather manufacturers. By following these steps, you can ensure that you partner with a reliable supplier who meets your specific requirements and quality standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to potential suppliers, clarify your requirements regarding material type, texture, thickness, and application. Faux leather comes in various forms, such as polyurethane and plant-based alternatives like Piñatex or Desserto. Clearly defined specifications will help you communicate effectively with manufacturers and ensure they can meet your needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify manufacturers specializing in faux leather. Look for suppliers with a strong online presence, positive reviews, and a portfolio showcasing their products. Utilize B2B platforms and trade shows to discover reputable companies, and take note of those that align with your target market in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your choices, verify the certifications of potential suppliers. Certifications such as ISO, GRS (Global Recycled Standard), or OEKO-TEX indicate a commitment to quality and sustainability. Ensure that the supplier adheres to environmental regulations and ethical manufacturing practices, as these factors are increasingly important to B2B buyers.
Step 4: Request Sample Products
Always ask for samples before placing a bulk order. This will allow you to assess the quality, texture, and durability of the faux leather firsthand. Pay attention to aspects such as flexibility, colorfastness, and ease of maintenance to ensure that the product meets your standards and expectations.
Step 5: Inquire About Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)
Different suppliers have varying policies regarding minimum order quantities. Understanding these requirements is crucial for budgeting and inventory planning. If you are a smaller business or are testing a new product line, look for suppliers that offer flexible MOQs to accommodate your needs.
Step 6: Discuss Pricing and Payment Terms
Initiate discussions on pricing structures and payment terms early in the sourcing process. Ensure you receive a detailed quote that includes all potential costs, such as shipping and customs duties. Clear communication about payment methods, timelines, and possible discounts for bulk orders can help you secure a favorable deal.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Once you have selected a supplier, establish clear communication channels for ongoing support. This includes understanding how to reach them for inquiries, order tracking, and addressing any issues that may arise. A responsive supplier will enhance your partnership and ensure a smoother procurement process.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process and make informed decisions when selecting a faux leather manufacturer that aligns with your business goals and values.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Faux Leather?
When analyzing the cost structure of faux leather manufacturing, several critical components must be considered.
-
Materials: The type of faux leather being sourced significantly impacts costs. For example, polyurethane-based products generally have different pricing compared to plant-based alternatives like Piñatex or Desserto cactus leather. The quality of raw materials can vary widely, affecting both durability and price.
-
Labor: Labor costs depend on the geographical location of the manufacturing facility. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can affect quality and lead times. Conversely, regions with higher labor costs often provide superior craftsmanship, which can justify a higher price point.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses associated with production. Efficient manufacturers often have streamlined processes that can lower these overhead costs, ultimately affecting the price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for customized products. Manufacturers often amortize these costs over larger production runs, making it essential for buyers to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs).
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the faux leather meets specific standards incurs additional costs. Companies with stringent QC processes may charge more, but this can lead to better long-term performance and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on distance, shipping method, and Incoterms. International buyers must factor in customs duties and tariffs, which can substantially increase the total cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a margin that reflects their operational risks and market conditions. Understanding how this margin is structured can provide insights into pricing flexibility.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Faux Leather Sourcing?
Several factors influence the final pricing of faux leather, making it vital for buyers to understand these nuances.

Illustrative image related to faux leather manufacturer
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Manufacturers often provide tiered pricing based on order volume. Larger orders can reduce per-unit costs, incentivizing bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products generally incur higher costs due to additional processing and tooling requirements. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials often come with certifications that ensure compliance with international standards. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certified materials against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record, while newer manufacturers might offer lower prices to gain market entry.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly influence logistics costs and responsibilities. Buyers should select terms that minimize their total cost while aligning with their risk tolerance.
What Are Essential Tips for Buyers When Sourcing Faux Leather?
-
Negotiation Tactics: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing and terms. Establishing a long-term relationship can lead to better deals and flexibility in future orders.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, not just the upfront price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and potential for returns or replacements.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be mindful of currency fluctuations and import regulations that can affect pricing. Building relationships with local distributors may mitigate some risks.
-
Quality Assurance: Before finalizing orders, request samples to verify quality. This step can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the product meets expectations.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Understanding market dynamics can help buyers make timely decisions. Keeping an eye on trends in sustainability and material innovation can lead to sourcing opportunities that align with market demands.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and other factors. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence and obtain quotes tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather manufacturer With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Faux Leather Manufacturing
In today’s competitive market, businesses are increasingly seeking sustainable and cost-effective materials for their products. Faux leather, known for its versatility and affordability, is a popular choice among manufacturers. However, several alternative solutions are emerging, each with its unique benefits and challenges. This analysis explores these alternatives, providing B2B buyers with insights to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Faux Leather Manufacturer | Alternative 1: Plant-Based Leather | Alternative 2: Natural Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, water-resistant | Varies by material; often durable | Highly durable, high-quality |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Moderate to high | High |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to source and fabricate | Requires specialized knowledge | Requires skilled artisans |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Moderate; depends on specific material | High; requires conditioning |
| Best Use Case | Upholstery, fashion, accessories | Eco-friendly products, fashion | Luxury goods, high-end upholstery |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Plant-Based Leather
Plant-based leather options, such as Piñatex (made from pineapple fibers), Desserto (from cactus), and Vegea (from grape waste), are gaining traction as eco-friendly alternatives. These materials not only offer a unique aesthetic but also promote sustainability by utilizing agricultural waste. However, their performance can vary significantly based on the material and manufacturing process. While some plant-based leathers are durable, they may not always match the longevity and wear resistance of traditional faux leather. Cost can also be a factor, as these innovative materials tend to be priced higher than conventional options, making them a consideration for brands focusing on sustainability.
2. Natural Leather
Natural leather is renowned for its premium quality and durability, making it a favored choice for luxury goods and high-end upholstery. It provides a classic look and feel that faux leather cannot replicate. However, the higher cost associated with natural leather can be a barrier for many manufacturers, especially those targeting budget-conscious consumers. Additionally, sourcing natural leather often involves complex supply chains and ethical considerations regarding animal welfare. Maintenance is another challenge, as natural leather requires regular conditioning and care to maintain its appearance over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When evaluating options for faux leather manufacturing, B2B buyers must weigh the specific needs of their business against the characteristics of each alternative. Factors such as target market, budget constraints, and desired product lifespan should guide the decision-making process. For instance, businesses focused on sustainability may lean towards plant-based leathers, while those prioritizing luxury may opt for natural leather despite the higher costs. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of each material’s pros and cons will enable buyers to select the most suitable solution for their manufacturing needs.

Illustrative image related to faux leather manufacturer
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather manufacturer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Faux Leather?
Understanding the essential technical properties of faux leather is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable materials for various applications. Here are some of the most critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality of the faux leather, typically determined by its composition and manufacturing process. Common grades include polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). A higher material grade often results in better durability, texture, and overall performance. For manufacturers, specifying the right material grade ensures that the end product meets customer expectations and regulatory standards.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance in faux leather manufacturing indicates the permissible variation in thickness, texture, and color. This specification is vital for maintaining consistency across production batches. A narrow tolerance range can enhance the product’s aesthetic appeal and functionality, making it essential for businesses that prioritize quality and uniformity in their offerings.
3. Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance measures how well the material withstands wear and tear from friction. This property is particularly important for products subjected to frequent use, such as upholstery and footwear. Higher abrasion resistance translates to longer-lasting products, reducing returns and increasing customer satisfaction.
4. UV Stability
UV stability refers to the material’s ability to resist degradation from ultraviolet light exposure. This property is essential for outdoor applications, where prolonged sunlight can lead to fading and weakening of the faux leather. Ensuring UV stability not only prolongs the lifespan of the product but also enhances its aesthetic value.

Illustrative image related to faux leather manufacturer
5. Fire Retardancy
Fire retardancy indicates how well the faux leather can resist ignition and slow down the spread of flames. This is a critical property for products used in commercial settings, such as furniture and automotive interiors. Complying with fire safety regulations is not only a legal requirement in many regions but also a selling point for safety-conscious buyers.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Faux Leather Manufacturing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly streamline communication between manufacturers and buyers. Here are some common trade terms relevant to faux leather:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or products that are sold under another company’s brand name. In the faux leather industry, OEM partnerships can lead to custom materials tailored to specific client needs, fostering innovation and competitive advantage.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory levels effectively and ensure cost-efficiency in procurement. Suppliers may set MOQs to justify production costs and minimize waste.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that potential buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. This process helps streamline purchasing decisions by allowing buyers to compare offers from multiple manufacturers, ensuring they get the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining responsibilities and liabilities in international shipping. Understanding these terms can help buyers navigate logistics and ensure compliance with trade regulations, ultimately reducing risks associated with cross-border transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to the delivery of the finished product. In the faux leather industry, understanding lead times is essential for effective supply chain management and meeting project deadlines, particularly for businesses that rely on just-in-time inventory systems.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and ensure they receive high-quality faux leather products tailored to their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather manufacturer Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Faux Leather Manufacturing Sector?
The faux leather manufacturing sector is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by a combination of environmental awareness, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. Global demand for sustainable and cruelty-free alternatives to traditional leather is a primary driver, particularly in regions like Europe, Africa, and South America, where eco-consciousness is rising. Countries such as Germany and Vietnam are at the forefront of adopting innovative materials, including plant-based and recycled options, which are increasingly favored by both consumers and businesses.
Emerging technologies in the manufacturing process, including digital printing and advanced textile engineering, are reshaping the landscape. These innovations allow for greater customization and efficiency, catering to the specific needs of B2B buyers. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms has transformed sourcing dynamics, enabling international buyers to access a wider array of products and suppliers than ever before. This shift not only enhances competition but also drives down costs, making faux leather a more attractive option for diverse applications, from upholstery to fashion.
How Can B2B Buyers Prioritize Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Faux Leather Manufacturing?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are critical considerations for B2B buyers in the faux leather sector. The environmental impact of traditional leather production is significant, involving deforestation, water consumption, and chemical pollution. In contrast, many faux leather manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices, such as utilizing plant-based materials like pineapple, cactus, and grape leather, which reduce reliance on animal products and mitigate ecological damage.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly important, as consumers and businesses alike demand transparency and responsibility from manufacturers. Certifications such as Global Recycled Standard (GRS) and OEKO-TEX® can serve as benchmarks for sustainability, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and produced with minimal environmental impact. By prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to these standards, B2B buyers can not only enhance their brand image but also contribute to a more sustainable industry.
How Has the Faux Leather Manufacturing Sector Evolved Over Time?
The faux leather industry has evolved significantly since its inception, transitioning from basic synthetic materials to sophisticated alternatives that closely mimic the look and feel of genuine leather. Initially developed in the mid-20th century, the focus was primarily on cost-effectiveness. However, recent decades have seen a marked shift towards sustainability and innovation, with manufacturers now prioritizing eco-friendly materials and ethical production processes.
Today, the sector is characterized by a diverse range of offerings, including high-performance microsuede and advanced polyurethane fabrics, which cater to a variety of applications. This evolution reflects broader societal changes, as consumers increasingly seek products that align with their values, pushing manufacturers to adapt and innovate continuously. As the market matures, the emphasis on sustainability and ethical practices will likely shape its future trajectory, presenting both challenges and opportunities for B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather manufacturer
-
How do I choose the right faux leather manufacturer for my business?
When selecting a faux leather manufacturer, consider factors such as the quality of materials, production capacity, and compliance with international standards. Evaluate their product range, including textures and finishes, to ensure they align with your design needs. Additionally, check for certifications related to sustainability and safety, as these can impact your brand’s reputation. Engage in discussions about their manufacturing processes and lead times to gauge their reliability. Lastly, seek references or reviews from other businesses to validate their performance and service quality. -
What types of faux leather are available for different applications?
Faux leather comes in various types, including polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and plant-based alternatives like Piñatex and Desserto. PU is known for its softness and durability, making it ideal for upholstery and fashion accessories. PVC is more rigid and often used for outdoor applications due to its water resistance. Plant-based leathers offer sustainable options and appeal to eco-conscious brands. Assess the specific properties of each type to determine which best suits your product requirements, whether for furniture, fashion, or automotive uses. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for faux leather products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly between manufacturers, often depending on the type of faux leather and the complexity of the design. Some manufacturers may have a low MOQ for standard products, while customized items might require larger orders. It’s crucial to discuss MOQs upfront during negotiations to ensure they align with your business needs. If you are a smaller buyer, look for manufacturers willing to accommodate lower MOQs or those that offer sample orders for initial testing. -
What payment terms should I expect when dealing with faux leather manufacturers?
Payment terms can differ widely among manufacturers, but common practices include a deposit of 30-50% upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some manufacturers may offer net payment terms based on your creditworthiness. It is essential to clarify these terms before finalizing orders to avoid any misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods or escrow services to protect your investment, especially when dealing with international suppliers. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my faux leather orders?
To maintain high-quality standards, establish clear specifications and expectations before production begins. Request samples of the faux leather to evaluate texture, durability, and color fidelity. Many manufacturers offer QA protocols, including in-process inspections and final product testing. Consider implementing third-party inspections to verify compliance with your quality standards, especially for large orders. Document all agreements regarding quality expectations to ensure accountability throughout the manufacturing process. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing faux leather?
When importing faux leather, consider shipping methods, costs, and customs regulations in your destination country. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments but may take longer. Ensure that the manufacturer can provide the necessary documentation for customs clearance, such as certificates of origin and compliance. Familiarize yourself with local import duties and taxes to avoid unexpected costs. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in international trade can streamline the process and mitigate risks. -
How do I handle customization requests for faux leather products?
Customization requests for faux leather products should be clearly communicated to the manufacturer. Specify the desired colors, textures, and any unique patterns or finishes you require. Many manufacturers offer design services, so collaborating with their design team can facilitate the process. Be mindful of lead times for custom orders, as they may differ from standard products. It is also advisable to request prototypes or samples of the customized materials before full production to ensure they meet your expectations. -
What are the sustainability practices to consider when sourcing faux leather?
Sustainability is increasingly important in the faux leather industry. Look for manufacturers that utilize eco-friendly materials, such as plant-based leathers, and those that adhere to environmentally responsible production methods. Certifications like Global Recycled Standard (GRS) or OEKO-TEX can indicate a commitment to sustainable practices. Engage with suppliers about their waste management, energy use, and chemical handling processes. Supporting manufacturers that prioritize sustainability can enhance your brand’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Top 3 Faux Leather Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Joseph Noble – Great Fake Leather
Domain: josephnoble.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Great Fake Leather”, “Product Code”: “2400”, “Material Composition”: “100% polyurethane”, “Backing Material”: “Polyester/Cotton”, “Width”: “54 Inches”, “Weight”: “14 oz per linear yard”, “Double Rubs Rating”: “100,000 double rubs Wyzenbeek”, “Suggested Use”: “Upholstery”, “Cleaning Code”: “W/S, Bleach (10:1)”, “Disinfection Method”: “10:1 bleach dilution”, “Environmental Notes”: …
2. Adams Plastics – Imitation Leather
Domain: adamsplastics.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Imitation leather, also known as faux leather, pleather, synthetic leather, or vegan leather, is manufactured from polyurethane, PVC, or vegetable oils. Benefits include affordability, cruelty-free production, low maintenance, durability, variety in finishes and colors, uniformity, and ease of manufacturing. Two main types are Polyurethane (PU) Leather and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Leather. Applica…
3. Nevotex – Artificial & Synthetic Leather Solutions
Domain: nevotex.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Artificial & synthetic leather for public environment, furniture: chairs & sofas
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather manufacturer
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of faux leather presents an array of opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing high-quality materials that balance aesthetics, durability, and sustainability, businesses can significantly enhance their product offerings while catering to the growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives. The diverse range of textures and finishes available—from engineered polyurethane to innovative plant-based options—allows manufacturers to meet varying consumer preferences and market needs.
As the faux leather industry continues to evolve, it is crucial for buyers to forge partnerships with reliable manufacturers that emphasize sustainable practices and technological advancements. This approach not only bolsters brand reputation but also aligns with the increasing global emphasis on responsible sourcing.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to actively seek out suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to innovation and environmental stewardship. By doing so, they can position themselves advantageously in a competitive market, paving the way for future growth and success. Embrace the potential of faux leather and let it elevate your product line to meet the demands of a discerning consumer base.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to faux leather manufacturer
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.