Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fabric vs leather
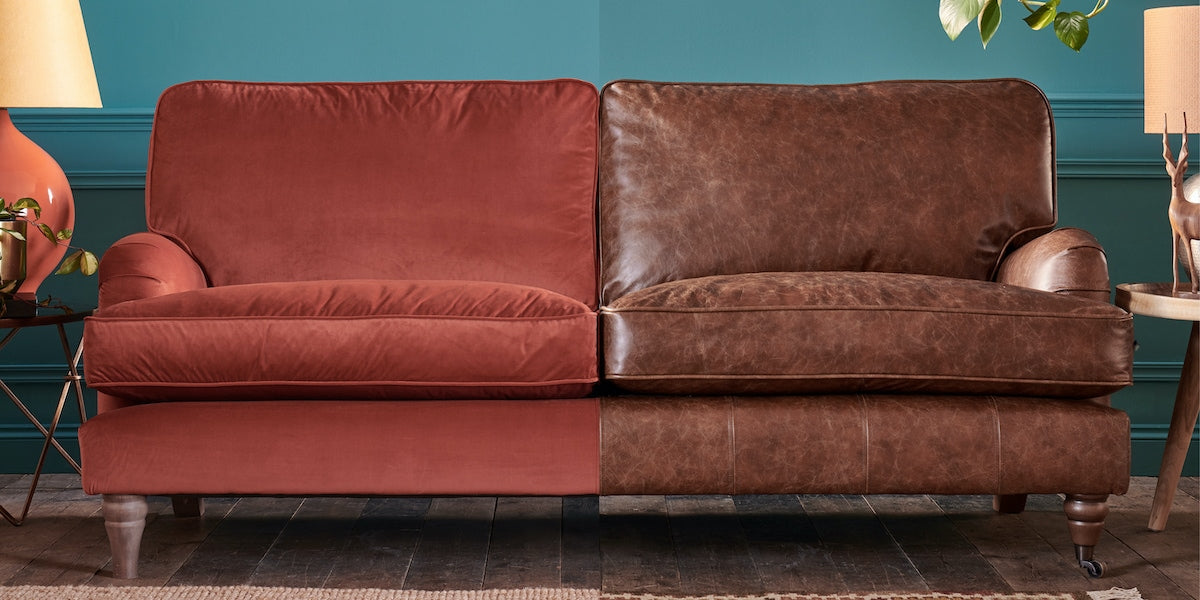
In the competitive landscape of sourcing materials for furniture and upholstery, the choice between fabric and leather can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you are sourcing durable seating solutions for corporate offices or selecting stylish materials for high-end residential projects, understanding the nuances of fabric vs leather is essential. This guide delves deep into the benefits and drawbacks of each material, providing insights into types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations that are crucial for decision-making.
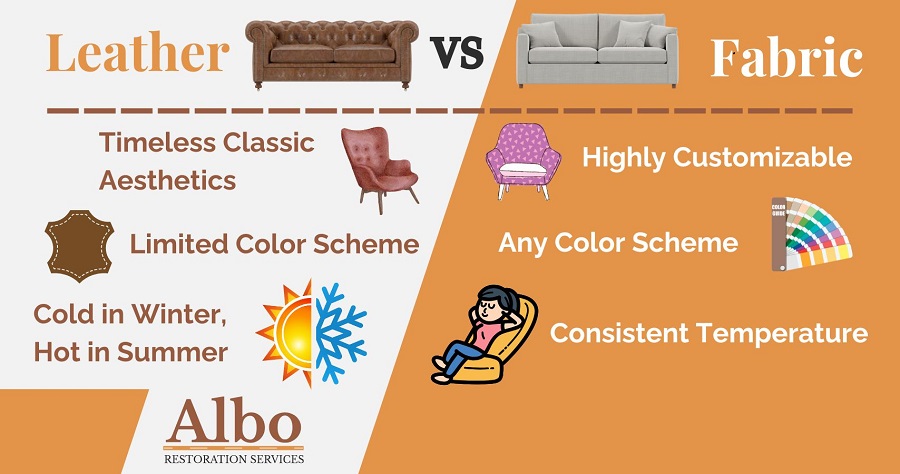
Fabric and leather each offer unique advantages that can align with specific business needs. From the aesthetic appeal and comfort of fabric to the durability and elegance of leather, the right choice can influence customer satisfaction and brand reputation. As buyers from diverse regions—such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—navigate varying market demands and consumer preferences, this comprehensive resource equips them with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions.
By exploring critical factors like maintenance requirements, lifespan, and cost-effectiveness, this guide empowers businesses to select the most suitable materials for their projects. With actionable insights and expert recommendations, you can confidently address the challenges of sourcing the perfect upholstery solutions that meet both budgetary constraints and aesthetic aspirations.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Fabric Vs Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fabric vs leather
- Understanding fabric vs leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of fabric vs leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fabric vs leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for fabric vs leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fabric vs leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fabric vs leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fabric vs leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fabric vs leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fabric vs leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fabric vs leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fabric vs leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fabric vs leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding fabric vs leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton Fabric | Soft, breathable, and available in various patterns | Upholstery, curtains, and soft goods | Pros: Affordable, wide range of colors; Cons: Less durable, prone to staining. |
| Polyester Fabric | Durable, stain-resistant, and easy to clean | Commercial furniture, automotive seats | Pros: High durability, low maintenance; Cons: Can feel less luxurious than natural fibers. |
| Echtes Leder | Luxurious feel, high durability, and natural aging | High-end furniture, automotive interiors | Pros: Long-lasting, timeless appeal; Cons: Expensive, susceptible to scratches. |
| Kunstleder | Cost-effective alternative to genuine leather | Budget furniture, fashion accessories | Pros: Affordable, versatile styles; Cons: Less durable, can wear out quickly. |
| Mikrofaser | Soft, stain-resistant, and easy to maintain | Residential and commercial upholstery | Pros: Comfortable, resistant to spills; Cons: Can attract dust and may not be as breathable. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Cotton Fabric in B2B Purchases?
Cotton fabric is widely recognized for its softness and breathability, making it a popular choice for upholstery, curtains, and other soft goods. Its versatility allows it to be dyed in a multitude of colors and patterns, appealing to various aesthetic preferences. However, B2B buyers should consider its durability; while cotton is affordable and comfortable, it may not withstand heavy wear and tear, especially in high-traffic areas. Regular maintenance and stain protection treatments can enhance its longevity, making it a suitable option for less demanding applications.
How Does Polyester Fabric Compare for Commercial Uses?
Polyester fabric stands out for its durability and stain-resistant properties, making it ideal for commercial furniture and automotive seats. This synthetic option is not only easy to clean but also maintains its shape well, even with frequent use. B2B buyers in sectors that require robust materials, such as hospitality and transportation, will find polyester advantageous. However, while it offers excellent performance, polyester may lack the luxurious feel of natural fibers, which could be a consideration for high-end markets.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
What Makes Genuine Leather a Preferred Choice for Luxury Applications?
Genuine leather is synonymous with luxury and durability, making it a preferred choice for high-end furniture and automotive interiors. Its unique ability to age beautifully adds to its appeal, providing a timeless quality that many buyers seek. B2B purchasers should recognize that while genuine leather is an investment, its longevity and aesthetic value often justify the higher price point. However, potential buyers must also consider its susceptibility to scratches and the need for regular conditioning to maintain its appearance.
Why Choose Faux Leather for Budget-Friendly Options?
Faux leather, or synthetic leather, serves as a cost-effective alternative to genuine leather, making it popular in budget furniture and fashion accessories. This material offers versatility in styles and colors, appealing to a broad market. B2B buyers should note, however, that while faux leather is affordable and easy to maintain, it may not provide the same durability or luxurious feel as genuine leather. Understanding the target market’s preferences will be crucial when considering faux leather for specific applications.
What Are the Benefits of Microfiber in Residential and Commercial Upholstery?
Microfiber is a synthetic fabric known for its softness and resistance to stains, making it an excellent choice for both residential and commercial upholstery. Its fine fibers allow it to repel spills, making maintenance straightforward and reducing the likelihood of permanent stains. B2B buyers should consider microfiber for environments where comfort and practicality are paramount, such as in family-oriented spaces or busy offices. However, it can attract dust and may not be as breathable as other materials, which could be a drawback in certain applications.
Key Industrial Applications of fabric vs leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fabric vs leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automobilindustrie | Upholstery for seats and interiors | Enhanced comfort and aesthetic appeal; fabric offers warmth while leather provides a premium feel. | Durability, ease of cleaning, and compliance with safety regulations. |
| Furniture Manufacturing | Sofas and chairs | Customization options in color and texture for diverse market needs; fabric is often more cost-effective. | Quality of materials, design flexibility, and production scalability. |
| Fashion & Apparel | Clothing and accessories | Versatile design possibilities; fabric allows for a broader range of styles while leather offers luxury. | Trends, material sourcing, and ethical considerations in leather production. |
| Hospitality | Upholstery for hotels and restaurants | Enhances guest comfort and aesthetic; fabric can be more stain-resistant, while leather adds elegance. | Maintenance requirements, durability under high traffic, and style options. |
| Home Decor | Curtains, cushions, and upholstery | Fabric provides endless design possibilities, while leather offers a classic, timeless appeal. | Availability of designs, fabric treatment for stains, and ecological impact of sourcing. |
How is Fabric Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, fabric is widely used for vehicle upholstery, providing comfort and aesthetic appeal. Fabric seats tend to be warmer in cooler climates and are often treated for stain resistance, making them practical for everyday use. International buyers need to consider the durability of the fabric, compliance with safety regulations, and ease of cleaning, especially in regions with high humidity or dust levels, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East.
What Role Does Leather Play in Furniture Manufacturing?
Leather is a staple in furniture manufacturing, particularly for high-end sofas and chairs. Its durability and luxurious appearance appeal to consumers looking for premium products. However, fabric is often preferred for its cost-effectiveness and variety in design. B2B buyers should assess the quality of leather and fabric options, considering factors like production scalability and the potential for customization to meet diverse market demands across South America and Europe.
Why is Fabric Important in Fashion and Apparel?
In the fashion industry, fabric is essential for creating a wide range of clothing and accessories, allowing for creativity in design and comfort. While leather offers a classic look, fabric provides versatility in styles, patterns, and textures. Buyers must stay updated on fashion trends and consider ethical sourcing practices, especially regarding leather, to align with consumer preferences in European and South American markets.
How Does Fabric vs Leather Impact the Hospitality Sector?
The hospitality industry utilizes both fabric and leather for upholstery in hotels and restaurants. Fabric can be treated to resist stains, making it ideal for high-traffic areas, while leather adds an element of luxury. Buyers need to focus on maintenance requirements and durability, ensuring the materials can withstand frequent use and align with the establishment’s aesthetic. This is particularly important in regions like the Middle East, where high-end hospitality is a key market.
What are the Benefits of Fabric in Home Decor?
Fabric plays a crucial role in home decor, with applications ranging from curtains to cushions and upholstery. It allows for a vast array of design options, making it easier for businesses to cater to diverse consumer preferences. Leather, while offering a timeless appeal, may not provide the same level of customization. Buyers should consider the ecological impact of sourcing materials and the treatment processes for fabric to ensure longevity and sustainability in their product offerings.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fabric vs leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Striking the Right Balance Between Cost and Quality
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the trade-off between cost and quality when selecting between fabric and leather for office furniture. Budget constraints are common, especially for businesses in emerging markets in Africa and South America, where the initial purchase price can be a significant factor. Buyers may find themselves torn between opting for a lower-cost fabric option that may not hold up over time versus investing in more expensive leather, which, while durable, can strain their budgets.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis that includes not just the initial purchase price but also long-term maintenance and durability costs. For fabric, consider sourcing high-performance textiles that are stain-resistant and durable, which may carry a higher upfront cost but save on replacement expenses in the long run. When considering leather, opt for grades that offer a balance between quality and price, such as corrected grain leather, which can provide a sleek appearance at a lower cost. Additionally, negotiating bulk purchase agreements with suppliers can help reduce overall costs, allowing businesses to invest in higher-quality materials without exceeding budget limits.
Scenario 2: Addressing Maintenance and Longevity Concerns
The Problem: Maintenance and longevity are significant pain points for B2B buyers, particularly in sectors like hospitality and healthcare where furniture must withstand heavy use. Fabric can be prone to staining and wear, while leather, although durable, can be susceptible to scratches and requires regular conditioning. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the maintenance requirements and unsure about which material would be more suitable for their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
The Solution: To effectively address maintenance concerns, buyers should seek out suppliers who provide comprehensive maintenance guides and recommendations tailored to the specific materials. For fabric, look for options treated with stain-resistant finishes that can simplify cleaning. Incorporating furniture with removable and washable covers can also extend the life of fabric upholstery. For leather, establish a regular conditioning schedule using high-quality leather care products to maintain its appearance and durability. Engaging with suppliers who offer warranties or maintenance programs can also provide peace of mind, ensuring that any issues can be promptly addressed without incurring additional costs.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Aesthetic Versatility and Brand Alignment
The Problem: Aesthetic considerations play a crucial role in furniture selection for B2B buyers, especially in sectors like retail and corporate offices where the furniture reflects the brand image. Buyers may find it challenging to achieve the desired look and feel with either fabric or leather due to limitations in color, pattern, and texture options. The need for a cohesive design that aligns with branding while also considering the functional aspects of the furniture can complicate the decision-making process.
The Solution: To resolve this aesthetic dilemma, buyers should leverage the extensive variety of fabric options available in the market. Unlike leather, which often has limited color and texture variations, fabric can offer a vast range of patterns, colors, and textures that can enhance brand identity. When sourcing, consider custom upholstery services that allow for bespoke designs tailored to the brand’s visual identity. For leather, explore options like colored or textured leathers that can provide a unique look while still delivering the durability associated with leather. Additionally, employing a design consultant can help ensure that the selected materials not only meet aesthetic goals but also align with the overall functionality and durability requirements of the space.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fabric vs leather
What Are the Key Properties of Common Fabric and Leather Materials?
When selecting between fabric and leather for various applications, it’s essential to understand the specific properties of each material. This analysis focuses on four common materials: cotton, polyester, genuine leather, and synthetic leather, examining their performance characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Cotton Fabric: A Natural Choice
Key Properties: Cotton is a natural fiber known for its breathability and softness. It has good tensile strength but can be less durable under heavy use. Cotton typically has a temperature rating that allows for comfort in both warm and cool environments.
Pros & Cons: Cotton is comfortable and hypoallergenic, making it suitable for various applications, including upholstery and clothing. However, it is prone to wrinkling and staining, requiring regular maintenance. Additionally, cotton can be more expensive than some synthetic alternatives, impacting overall manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Cotton is compatible with dyes and finishes, allowing for a wide range of colors and patterns. However, its susceptibility to moisture can limit its use in humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local climate conditions when choosing cotton. Compliance with local textile standards (e.g., ASTM) is also crucial.
Polyester Fabric: The Versatile Synthetic
Key Properties: Polyester is a synthetic fabric known for its strength, durability, and resistance to shrinking and stretching. It performs well under pressure and has good moisture-wicking properties, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of polyester is its durability and ease of care. It resists stains and fading, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. However, it may not be as breathable as natural fibers, which can affect comfort in warmer climates.
Impact on Application: Polyester is often used in commercial upholstery and outdoor furniture due to its weather resistance. Its compatibility with various finishes enhances its versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO) for safety and environmental impact. Polyester’s affordability makes it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers.
Genuine Leather: The Premium Option
Key Properties: Genuine leather is a durable material that ages well, developing a unique patina over time. It has excellent tensile strength and can withstand significant pressure, making it ideal for high-end furniture and accessories.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of leather is its luxurious appearance and durability. It is easy to clean and hypoallergenic. However, genuine leather is often more expensive and can be susceptible to scratches and temperature fluctuations.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
Impact on Application: Leather is commonly used in luxury furniture, automotive interiors, and fashion accessories. Its compatibility with various design styles enhances its appeal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like the Middle East should consider local preferences for leather types (e.g., full-grain vs. top-grain). Compliance with animal welfare standards and sourcing regulations is also essential.
Synthetic Leather: The Affordable Alternative
Key Properties: Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane or PVC, mimics the look and feel of genuine leather. It is lightweight and resistant to moisture and stains.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of synthetic leather is its cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance. However, it may not offer the same durability or breathability as genuine leather, potentially leading to a shorter lifespan.
Impact on Application: Synthetic leather is widely used in budget-friendly furniture, automotive interiors, and fashion items. Its versatility allows for a range of colors and textures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the environmental impact of synthetic materials and ensure compliance with local regulations regarding chemical use.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for fabric vs leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Upholstery, clothing | Breathable and hypoallergenic | Prone to wrinkling and staining | Medium |
| Polyester | Commercial upholstery, outdoor furniture | Durable and easy to care for | Less breathable than natural fibers | Low |
| Echtes Leder | Luxury furniture, automotive interiors | Luxurious appearance and durability | Higher cost and temperature sensitivity | Hoch |
| Synthetic Leather | Budget furniture, automotive interiors | Cost-effective and easy maintenance | Less durable than genuine leather | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of fabric and leather materials, offering valuable insights for B2B buyers navigating their options in diverse international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fabric vs leather
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Fabric and Leather?
The manufacturing processes for fabric and leather differ significantly, reflecting the unique properties and requirements of each material. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and compliance in their supply chains.
Material Preparation: How Are Fabric and Leather Sourced and Processed?
Fabric Manufacturing:
The first stage in fabric manufacturing involves sourcing raw materials, which can include cotton, polyester, linen, or blends. These fibers undergo several preparatory steps, such as spinning into yarn and dyeing. The yarn is then woven or knitted into fabric using techniques like plain weaving, twill, or satin. Advanced technology, such as digital printing, may also be employed for customized designs.
Leather Manufacturing:
In contrast, leather production begins with the selection of animal hides, typically from cattle, goats, or sheep. The hides are then treated through a process called tanning, which preserves the material and enhances its durability. Tanning can be done using vegetable or chrome methods, each imparting different characteristics to the leather. After tanning, the leather is dyed and finished to achieve the desired texture and appearance.
What Are the Main Forming Techniques Used in Fabric and Leather Production?
Fabric Forming Techniques:
In fabric production, various forming techniques are utilized depending on the end product. For upholstery fabrics, methods like weaving and knitting are predominant. For technical fabrics used in industries like automotive or aerospace, non-woven techniques may be employed.
Leather Forming Techniques:
Leather is generally shaped through cutting and sewing processes. Techniques such as die-cutting allow for precise shapes, while hand-stitching or machine stitching ensures durability and aesthetics. Additionally, leather can be embossed or printed to add texture and design elements.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Fabric and Leather Manufacturing?
Assembly for Fabric Products:
Once the fabric is prepared, the next stage is assembly, which involves stitching the fabric pieces together to create the final product. Quality control during this phase is critical; workers must ensure that seams are strong and that the fabric is not distorted. Automated sewing machines can enhance efficiency, but skilled labor is still essential for quality assurance.
Assembly for Leather Products:
For leather goods, assembly is similarly intricate. Each piece of leather must be aligned precisely, and stitching must be performed with care to prevent tearing or fraying. The assembly process may also include adding features like zippers, buttons, or other hardware, which requires meticulous attention to detail.
What Are the Finishing Techniques Applied to Fabric and Leather?
Finishing Techniques for Fabric:
Finishing treatments for fabric can include processes like flame retardant application, water repellency, or softening treatments. These processes enhance the durability and usability of the fabric for various applications, from upholstery to clothing. The finishing stage is also where final inspections for quality and defects take place.
Finishing Techniques for Leather:
Leather finishing involves several steps, including buffing, polishing, and applying protective coatings. These treatments not only improve the appearance but also enhance the leather’s resistance to wear and environmental factors. Proper finishing is crucial, as it can significantly affect the lifespan of leather products.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers need to be aware of various international standards that govern manufacturing quality. Key standards include:

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system and is applicable to all manufacturing sectors, ensuring that products consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: Particularly relevant for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates that the product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For companies involved in the oil and gas sector, API standards ensure that products meet the necessary safety and quality requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential to maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified quality criteria before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, IPQC monitors various parameters to ensure compliance with quality standards. This may involve random sampling and testing of products at different stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, FQC ensures that the final product meets all specifications and quality requirements before it is shipped to customers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to quality control standards, B2B buyers can employ several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help assess their QC processes, including defect rates and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an impartial assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices and product quality.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital. Factors such as local regulations, cultural differences in manufacturing practices, and logistical challenges can impact product quality.
-
Cultural Considerations: Buyers should consider the cultural context of manufacturing practices in different regions, as these can affect quality standards and expectations.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Being aware of both local and international regulations is crucial for ensuring product compliance and avoiding legal issues.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain: Understanding the logistics of transporting materials and finished products can also affect quality, particularly in terms of how products are handled and stored.
By understanding these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance for fabric and leather, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their sourcing aligns with their quality expectations and business needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fabric vs leather’
Einführung
Navigating the procurement process for fabric or leather products can be challenging, especially for B2B buyers targeting diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This checklist provides a step-by-step guide to help you make informed decisions that align with your business needs, ensuring the best return on investment and satisfaction for your customers.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
Step 1: Identify Your Target Market Needs
Understanding your target market is essential for making the right choice between fabric and leather. Consider factors such as climate, cultural preferences, and customer demographics. For instance, leather might appeal more in upscale markets, while durable, stain-resistant fabrics may be preferred in family-oriented regions.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the products you intend to source. This includes durability, maintenance requirements, color options, and any specific certifications that may be necessary for your market. A well-defined specification will streamline the sourcing process and help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, it’s crucial to vet your suppliers thoroughly. Request comprehensive company profiles, case studies, and references from other businesses in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers who demonstrate a robust understanding of the fabric or leather market and have a proven track record of quality.
- Check for certifications: Ensure that the suppliers meet industry standards and sustainability practices, which can be a deciding factor for many buyers today.
- Assess their manufacturing capabilities: Understand their production capacity and technology to ensure they can meet your demands.
Step 4: Compare Material Qualities
Conduct a side-by-side comparison of the fabric and leather options available. Consider attributes such as comfort, durability, and maintenance. For example, while leather is generally easier to clean and hypoallergenic, fabric can offer more design versatility and warmth.
- Request samples: Always ask for samples to evaluate the feel and quality firsthand before making a bulk purchase.
- Inquire about warranties: A good warranty can indicate a supplier’s confidence in their product quality.
Step 5: Analyze Cost Implications
Cost is a critical factor in your sourcing decision. While leather may have a higher upfront cost, consider the total lifecycle cost, including maintenance and durability. Fabric may be less expensive initially but could require more frequent replacements.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
- Budget for hidden costs: Don’t forget to account for shipping, import duties, and potential tariffs, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
- Negotiate payment terms: Favorable payment terms can help manage cash flow and reduce financial risk.
Step 6: Assess Sustainability Practices
Sustainability is increasingly important in global sourcing. Evaluate suppliers based on their environmental practices and the sustainability of their materials. This not only aligns with global trends but can also enhance your brand reputation.
- Look for eco-certifications: Certifications like OEKO-TEX or FSC can indicate responsible sourcing and manufacturing practices.
- Discuss waste management: Understanding how suppliers handle waste and by-products can give insight into their overall sustainability commitment.
Step 7: Make an Informed Decision
After gathering all necessary information, compile your findings to make a well-informed decision. Consider not just the immediate costs but also the long-term implications of your choice. Engage with stakeholders within your organization to ensure alignment with overall business strategy and customer expectations.
By following this practical sourcing guide, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of choosing between fabric and leather, ensuring a strategic approach that meets both business and customer needs.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fabric vs leather Sourcing
When evaluating the cost and pricing dynamics between fabric and leather sourcing, several critical components and influencers come into play. Understanding these aspects can help international B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Fabric vs Leather Sourcing?
-
Materials: The primary cost differentiator between fabric and leather is the material itself. Leather, especially high-quality varieties, tends to be significantly more expensive than most fabrics. Fabric options can range widely in price, from budget synthetics to premium natural fibers. Buyers should consider the lifecycle and durability of materials when assessing costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the complexity of manufacturing and the skill level required. Leather typically requires more skilled labor for cutting, stitching, and finishing processes, which can increase overall production costs. In contrast, fabric can be easier to work with, potentially reducing labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead includes costs associated with facilities, equipment, and utilities. Leather production often entails higher overhead due to specialized machinery needed for processing hides. Fabric production may have lower overhead but can vary depending on the type of fabric being manufactured.
-
Tooling: The tooling costs for leather often involve higher initial investments in specialized tools. Fabric production may require less specialized tooling, which can lead to lower upfront costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Leather products typically require stringent quality control processes to ensure that the final product meets high standards, especially in terms of texture and appearance. Fabric, while also requiring QC, may have less stringent requirements depending on the application.
-
Logistics: Transporting leather can be costlier due to its weight and the need for careful handling to prevent damage. Conversely, fabric is generally lighter and easier to ship, which can lead to lower logistics costs.
-
Margin: The profit margin on leather products is generally higher due to their premium positioning in the market. Fabric can also yield good margins, especially for high-end designs, but often has to compete on price.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Fabric and Leather Sourcing?
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Buyers looking for bulk purchases can negotiate better pricing. High-volume orders often lead to discounts, particularly for fabric, which has a broader range of suppliers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom orders, whether in fabric or leather, can lead to increased costs. Unique designs or specific requirements often require additional tooling or labor, influencing overall pricing.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The presence of certifications (like OEKO-TEX for fabric) can affect costs. Buyers should be aware that higher-quality materials will generally command higher prices, but they may also offer better durability and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their quality assurance and timely delivery, while less reputable suppliers may offer lower prices but at higher risk.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly influence total costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Help with Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Buyers should actively negotiate terms, especially for large orders. Leverage volume to secure better pricing and terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating options, consider not just the purchase price but the TCO, including maintenance, durability, and potential resale value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be mindful of regional economic factors, currency fluctuations, and trade tariffs that can affect pricing. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage during negotiations.
In conclusion, careful consideration of the cost structure and price influencers in fabric vs leather sourcing is essential for B2B buyers. By analyzing these elements and employing strategic negotiation tactics, buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies and achieve better value in their purchases.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fabric vs leather With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Fabric and Leather
When considering upholstery materials for furniture, the choice between fabric and leather is often at the forefront of decision-making. However, it’s essential to explore viable alternatives that may better suit specific business needs. These alternatives can provide unique benefits and cater to diverse market demands, especially for international buyers looking to balance aesthetics, functionality, and cost.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Fabric Vs Leather | Alternative 1: Faux Leather | Alternative 2: Microfiber |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Softer and more comfortable; less durable | Mimics leather appearance; less durable than real leather | Highly durable; stain-resistant and easy to clean |
| Cost | Generally more affordable than leather | Usually cheaper than both fabric and leather | Similar to fabric, often slightly higher |
| Ease of Implementation | Widely available, easy to source | Readily available, simple to manufacture | Accessible; often requires special care in production |
| Wartung | Requires regular cleaning, prone to staining | Easy to clean; resistant to spills | Very easy to maintain; stain-resistant |
| Best Use Case | Family homes, casual environments | Modern and trendy settings; budget-conscious buyers | High-traffic areas, commercial use, or pet-friendly spaces |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Faux Leather?
Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather or vegan leather, offers a stylish alternative to traditional leather. One of its main advantages is its affordability, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious businesses. Faux leather is also easier to clean and maintain, providing a practical choice for environments where spills and stains are common. However, it may not offer the same level of durability as genuine leather or high-quality fabrics and can wear out more quickly under heavy use.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
How Does Microfiber Compare as an Upholstery Option?
Microfiber is a synthetic material known for its durability and ease of maintenance. It is exceptionally resistant to stains and spills, making it ideal for high-traffic areas such as offices and family spaces. Microfiber upholstery can provide a soft, luxurious feel similar to fabric, while also being more resilient than many traditional fabrics. However, it may not have the same aesthetic appeal as leather or high-end fabrics, which could impact its suitability in upscale settings.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Upholstery Solution?
For B2B buyers navigating the upholstery market, the decision between fabric, leather, and their alternatives hinges on specific operational needs and target demographics. Understanding the performance, cost implications, maintenance requirements, and best use cases of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions. Factors such as environmental conditions, customer preferences, and budget constraints should guide the selection process. By evaluating these criteria, businesses can choose the upholstery solution that aligns best with their branding and functional requirements, ensuring satisfaction for both themselves and their clientele.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fabric vs leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Fabric and Leather?
Understanding the technical properties of fabric and leather is crucial for B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions. Here are essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Definition: Material grade refers to the quality and classification of the fabric or leather based on its composition, durability, and finish. Higher grades typically indicate better performance and longevity.
B2B Importance: Buyers need to evaluate the material grade to ensure that the chosen fabric or leather meets the specific requirements of their applications, such as wear resistance in high-traffic areas or aesthetic appeal in luxury items.
2. Durability Rating
Definition: This rating assesses how well a material withstands wear and tear over time. For fabrics, it often involves tests like Martindale abrasion, while leather durability can be gauged through its tensile strength and crack resistance.
B2B Importance: A higher durability rating is essential for products that experience regular use, as it affects the product lifecycle and overall cost-effectiveness, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
3. Care Requirements
Definition: Care requirements outline the maintenance necessary to keep the fabric or leather in optimal condition. This may include cleaning methods, frequency of care, and protective treatments.
B2B Importance: Understanding care requirements helps businesses anticipate ongoing maintenance costs and customer satisfaction levels, especially for end-users who may have specific lifestyle needs (e.g., families with pets).
4. Tolerance Levels
Definition: Tolerance levels indicate acceptable variations in the dimensions and characteristics of the materials. This could involve color consistency, texture uniformity, and thickness.
B2B Importance: Tolerance levels are crucial for ensuring that materials meet manufacturing specifications, thus preventing production issues and ensuring product quality, particularly in large-scale operations.
5. Colorfastness
Definition: Colorfastness measures how well a fabric or leather maintains its color when exposed to light, washing, or abrasion.
B2B Importance: For products that will be used in varying environments, such as outdoor furniture or apparel, high colorfastness is vital to ensure longevity and aesthetic appeal, which can significantly influence customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Fabric and Leather Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
1. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
Definition: MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
Importance: Understanding MOQ helps buyers negotiate better purchasing terms and manage inventory levels effectively, ensuring they do not overcommit resources.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
2. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Definition: OEM denotes a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
Importance: In the context of fabric and leather, knowing about OEM relationships can help businesses identify potential partners for custom products or specific fabrications.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
Definition: An RFQ is a document that solicits price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services.
Importance: Utilizing RFQs allows buyers to compare multiple suppliers’ pricing and terms, ensuring they secure the best deal for their fabric or leather needs.
Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Definition: Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
Importance: Understanding Incoterms is critical for B2B buyers involved in cross-border trade, as they define who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and liability, helping to avoid disputes.
5. Upholstery Grade
Definition: This term classifies the suitability of fabrics and leathers for specific applications based on their durability and comfort.
Importance: Buyers should consider upholstery grade when selecting materials for furniture or automotive applications, as it directly impacts the product’s lifespan and comfort level.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, optimizing their procurement processes and enhancing product offerings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fabric vs leather Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Fabric vs. Leather Sector?
The global fabric vs. leather market is undergoing significant transformation driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and the increasing importance of sustainability. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international B2B buyers are witnessing a shift towards multifunctional and versatile designs, with fabric options gaining traction due to their affordability and diverse aesthetic appeal. Emerging technologies like digital printing and innovative textile treatments are enhancing the functionality and design of fabric products, making them more appealing to consumers seeking unique and personalized solutions.
Moreover, leather remains a sought-after material for its durability and luxury status, particularly in high-end markets. However, the rise of eco-conscious consumers is prompting manufacturers to explore sustainable leather alternatives, such as plant-based leathers and recycled materials. This trend is particularly evident in Europe, where regulatory measures are pushing for more sustainable practices. In the Middle East and Africa, the demand for durable materials that can withstand environmental challenges is driving interest in both high-quality fabrics and leather, with buyers increasingly prioritizing long-term value over initial costs.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Trends in the Fabric vs. Leather Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor for B2B buyers when sourcing materials in the fabric vs. leather sector. The environmental impact of production processes is under scrutiny, and businesses are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain practices. Ethical sourcing is no longer optional; it is essential for companies aiming to meet consumer expectations and regulatory standards. This is particularly true in regions like Europe, where consumers are more likely to support brands that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather
In the realm of fabrics, buyers are increasingly opting for materials certified by organizations such as OEKO-TEX or Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), which ensure that textiles are produced without harmful chemicals and in environmentally friendly conditions. For leather, sourcing from tanneries that adhere to ethical practices and environmental regulations is crucial. Certifications like the Leather Working Group (LWG) provide assurance that leather products are sourced responsibly, considering both environmental impact and animal welfare. As international buyers become more discerning, the emphasis on sustainability will continue to shape sourcing strategies across the fabric and leather sectors.
What Is the Historical Context of the Fabric vs. Leather Market for B2B Buyers?
The fabric vs. leather market has a rich history that has shaped its current dynamics. Traditionally, leather was viewed as a premium material, associated with luxury and durability, while fabric was often seen as a more accessible option. This perception began to change in the late 20th century as advancements in textile technology introduced a wider array of high-performance fabrics that offered durability, comfort, and aesthetic versatility.
In the early 2000s, the rise of fast fashion and mass production significantly impacted both sectors, leading to an increase in synthetic materials and a focus on cost-effective production methods. However, this shift also brought attention to the environmental ramifications of such practices, paving the way for the current trend toward sustainability and ethical sourcing. Today, B2B buyers must navigate a landscape that values both the historical prestige of leather and the innovative potential of modern fabrics, making informed sourcing decisions that align with evolving consumer values and market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fabric vs leather
-
How do I choose between fabric and leather for my business needs?
Choosing between fabric and leather depends on several factors, including your target market, budget, and the intended use of the product. Fabric is often more affordable and offers a wider range of colors and patterns, making it suitable for casual or family-oriented products. Leather, on the other hand, conveys a sense of luxury and durability, appealing to high-end consumers. Consider the demographics of your customers and the long-term maintenance requirements of each material when making your decision. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing fabric or leather?
When sourcing fabric or leather, prioritize quality, durability, and supplier reliability. Assess the material’s specifications, such as weight, texture, and resistance to wear and tear. Additionally, evaluate the supplier’s reputation, production capabilities, and adherence to international quality standards. It’s also essential to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs), customization options, and lead times to ensure that the supplier can meet your business needs efficiently. -
What are the advantages of sourcing locally versus internationally for fabric or leather?
Sourcing locally can reduce shipping costs and lead times while providing easier communication with suppliers. It may also support local economies and ensure compliance with regional regulations. Conversely, international sourcing often offers a wider variety of materials at competitive prices. However, consider potential challenges such as import tariffs, longer shipping times, and the need for thorough supplier vetting to ensure quality and reliability. -
What are the typical payment terms in B2B fabric and leather transactions?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include payment upon order, partial payment upfront with the balance due upon delivery, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). It’s crucial to negotiate terms that safeguard your cash flow while also ensuring the supplier’s commitment to quality and timely delivery. Always confirm the payment methods accepted, such as wire transfers or letters of credit, to avoid complications. -
How can I ensure the quality of fabric or leather products from suppliers?
To ensure quality, request samples before placing bulk orders and conduct thorough inspections upon receipt. Establish clear quality assurance (QA) standards, including specifications for color, texture, and durability. Engage in regular communication with suppliers to address any concerns and consider third-party inspections if sourcing internationally. Building a strong relationship with your suppliers can also facilitate better quality control and responsiveness to issues. -
What customization options are typically available for fabric and leather products?
Customization options vary by supplier but can include color, pattern, texture, and even specific treatments for durability or stain resistance. Many suppliers offer bespoke solutions, such as custom sizes or design modifications. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to understand their capabilities and any additional costs associated with customization. This can help align your product offerings with market demands. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing fabric or leather?
Logistics play a crucial role in the success of importing fabric or leather. Consider shipping methods (air or sea), costs, and transit times. Ensure compliance with customs regulations and have a clear understanding of import duties and taxes applicable to your products. Work with reliable freight forwarders who specialize in your industry to streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. Additionally, plan for warehousing and distribution in your target market to meet customer demands promptly. -
How can I address concerns about sustainability when sourcing fabric or leather?
Sustainability is increasingly important for B2B buyers. When sourcing fabric or leather, inquire about the suppliers’ environmental practices, such as sourcing from sustainable farms or using eco-friendly dyes and treatments. Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) for fabrics or Leather Working Group (LWG) for leather can provide assurance of sustainable practices. Communicating your commitment to sustainability can also enhance your brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Top 5 Fabric Vs Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Spruce – Fabric vs. Leather Sofas: Pros and Cons
Domain: thespruce.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: The article compares the benefits and drawbacks of fabric and leather sofas. Key points include:
**Fabric Sofas:**
– **Comfort:** Softer and warmer than leather, generally more comfortable.
– **Care:** High-quality fabrics are treated for stain resistance; easier to clean than leather.
– **Color and Pattern Options:** Unlimited variety in patterns, textures, and colors.
– **Cost:** Typically…
2. Stay Home Body – Leather vs Fabric Sofas Comparison Guide
Domain: stayhomebody.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Leather vs Fabric Sofas Comparison Guide:
**Quick Comparison Sheet**
– **Comfort**:
– Fabric Sofas: Immediately soft and warm.
– Leather Sofas: Starts firm, softens over time.
– **Durability**:
– Fabric Sofas: Durable with high-quality material; stain-resistant options available.
– Leather Sofas: Very durable, lasts longer with care.
– **Maintenance**:
– Fabric Sofas:…
3. Diffen – Fabric vs Leather Comparison
Domain: diffen.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Fabric vs Leather Comparison:
– Material: Fabric is made of cloth; Leather is animal hide treated with chemicals.
– Durability: Fabric is less durable; Leather is very durable (10-15 years if maintained well) but can fade in the sun and degrade with age.
– Cost: Fabric is less expensive; Leather is a premium price luxury item.
– Colors: Fabric offers more variety; Leather has less variety, mos…
4. Facebook – Fabric Sofas
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Fabric Sofas, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. La-Z-Boy – Furniture Styles & Textures
Domain: furnitureacademy.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: La-Z-Boy offers a wide range of furniture styles, textures, and color choices, with over 900 fabrics and leathers including premium-grade and performance fabrics. Key differences between fabric and leather furniture include: 1. Comfort & Feel: Fabric offers a variety of textures and breathability, while leather adapts to body temperature and develops a natural patina over time. 2. Aesthetics and S…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fabric vs leather
In evaluating the strategic sourcing of fabric versus leather, B2B buyers must consider several critical factors to align their procurement decisions with their business objectives. Fabric offers a broader range of colors and patterns, typically at a lower cost, making it a flexible option for diverse market preferences. Its comfort and ease of maintenance appeal to families and casual settings, while its durability can vary based on fabric quality. Conversely, leather is synonymous with luxury and durability, appealing to high-end markets. Its hypoallergenic properties and elegant aesthetic can position a brand as premium, but it comes with higher costs and maintenance needs.
For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, understanding local consumer preferences is essential. Invest in market research to discern which material aligns with your target demographic’s desires. As you navigate these choices, prioritize partnerships with suppliers who offer high-quality materials and sustainable practices.
Looking ahead, the demand for both fabric and leather will continue to evolve. Engage with your suppliers to explore innovative materials and designs that cater to changing consumer trends. By strategically sourcing the right materials now, you can secure a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to fabric vs leather