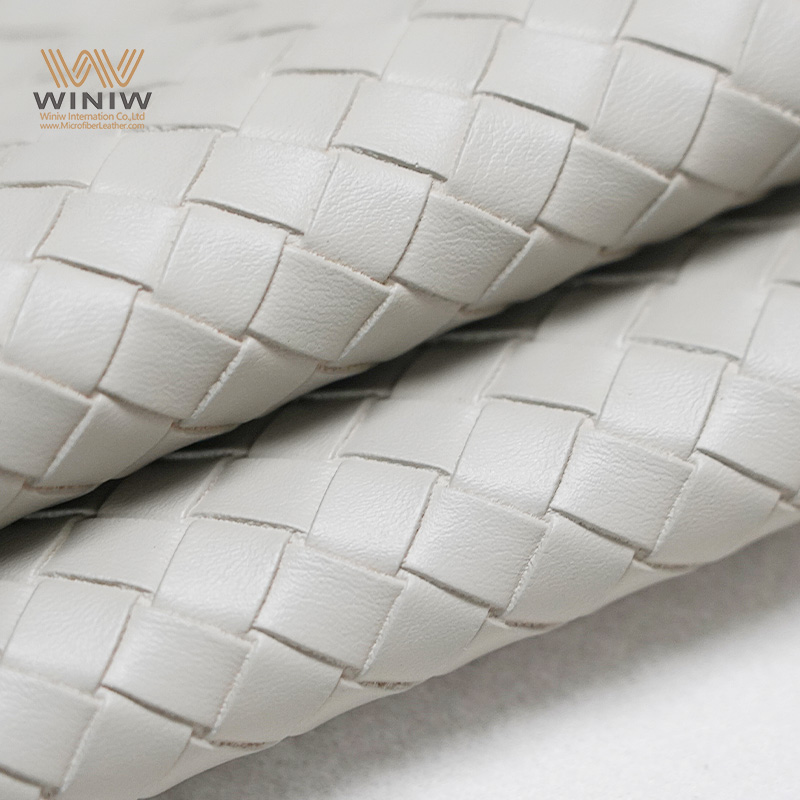
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather thick
In an increasingly interconnected global marketplace, sourcing quality leather thick can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. Whether you’re looking to procure durable leather for manufacturing products in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the complexities of leather thickness is crucial. Variations in quality, type, and sourcing practices can lead to costly mistakes that affect product integrity and business reputation. This guide is designed to equip international buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate these challenges effectively.
Our comprehensive exploration covers the various types of leather thick, their applications in different industries, and the nuances of supplier vetting. We delve into the critical aspects of cost analysis, ensuring you understand the factors that influence pricing and how to negotiate better deals. Additionally, we provide insights on identifying reputable suppliers and understanding the quality indicators of leather thickness, which can greatly impact your purchasing decisions.
By empowering B2B buyers with this essential information, we aim to facilitate informed purchasing decisions that not only meet specific project needs but also enhance overall business efficiency. Whether you are in Vietnam, Germany, or elsewhere, this guide serves as a valuable resource to enhance your sourcing strategy and ensure the successful procurement of leather thick that meets your quality standards.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Leather Thick Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather thick
- Understanding leather thick Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of leather thick
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather thick’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather thick
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather thick
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather thick’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather thick Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather thick With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather thick
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather thick Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather thick
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather thick
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding leather thick Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetable Tanned | Eco-friendly, retains natural grain, firm feel | Handbags, belts, wallets | Pros: Durable, ages beautifully. Cons: Can be more expensive, longer production time. |
| Chrome Tanned | Soft, supple, and uniform thickness | Apparel, upholstery, automotive | Pros: Quick tanning process, wide color range. Cons: Less environmentally friendly, may not age as well. |
| Wildleder | Napped finish, soft texture | Footwear, garments, accessories | Pros: Luxurious feel, good for fashion items. Cons: Less durable, can stain easily. |
| Nubuck | Sanded top grain, velvety surface | Luxury footwear, bags | Pros: Durable, water-resistant treatment available. Cons: Requires special care, can be expensive. |
| Full Grain | Retains original texture, highest quality | High-end furniture, luxury goods | Pros: Strong, develops a unique patina. Cons: Costly, heavier than other types. |
What Are the Characteristics of Vegetable Tanned Leather?
Vegetable tanned leather is known for its eco-friendly tanning process, utilizing natural tannins from plant sources. This type of leather retains the hide’s natural grain and is firm, making it suitable for products that require durability, such as handbags, belts, and wallets. B2B buyers should consider its longevity and aesthetic appeal, as it ages beautifully over time. However, it often comes at a higher price point and may require longer lead times for production.
Why Choose Chrome Tanned Leather for Your Products?
Chrome tanned leather is recognized for its softness and uniform thickness, making it ideal for applications in apparel, upholstery, and automotive interiors. The quick tanning process allows for a wide range of colors and finishes, appealing to manufacturers looking for versatility in design. While it is cost-effective and readily available, buyers should note that chrome tanning is less environmentally friendly and may not develop the same character over time as vegetable tanned leather.
What Makes Suede a Popular Choice for Fashion Items?
Suede features a napped finish that gives it a soft texture, making it a luxurious option for fashion items such as footwear, garments, and accessories. Its aesthetic appeal is a significant selling point for B2B buyers in the fashion industry. However, suede is less durable than other leather types and is prone to staining, which may necessitate special care and maintenance.
How Does Nubuck Compare to Other Leather Types?
Nubuck is a type of leather that has been sanded to create a velvety surface, providing a luxurious feel that is often sought after in luxury footwear and bags. This leather is durable and can be treated for water resistance, making it suitable for various applications. However, it requires special care to maintain its appearance, and buyers should be prepared for a higher price point compared to standard leather options.
What Are the Advantages of Full Grain Leather?
Full grain leather is the highest quality leather available, retaining the hide’s original texture and natural imperfections. It is exceptionally strong and develops a unique patina over time, making it a favored choice for high-end furniture and luxury goods. While full grain leather offers unmatched durability and aesthetic appeal, it is also one of the most expensive options on the market and tends to be heavier than other leather types, which may influence shipping costs and manufacturing processes.
Key Industrial Applications of leather thick
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of leather thick | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automobilindustrie | Upholstery for luxury vehicles | Enhances vehicle aesthetics and durability | Sourcing from certified tanneries; ensuring color and texture consistency |
| Fashion & Accessories | High-end handbags and belts | Provides a premium feel and long-lasting products | Focus on ethical sourcing; consider thickness for specific designs |
| Industrial Equipment | Protective gear and workwear | Offers durability and protection in hazardous environments | Compliance with safety standards; sourcing for specific thickness and temper |
| Furniture & Interior Design | Upholstery for sofas and chairs | Adds luxury and comfort; enhances brand image | Ensure compatibility with design specifications; sourcing for specific textures |
| Equestrian Equipment | Saddles and bridles | Ensures comfort and durability for both horse and rider | Consider weight and flexibility; sourcing from specialized leather suppliers |
How is Leather Thick Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, thick leather is primarily utilized for upholstery in luxury vehicles. This application enhances the aesthetic appeal and durability of the interior, providing a premium feel that appeals to high-end consumers. Buyers should focus on sourcing leather from certified tanneries to ensure quality and consistency in color and texture. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements for different car models is crucial, as variations in thickness can affect the installation process and overall look.
What Role Does Leather Thick Play in Fashion & Accessories?
Thick leather is a staple in the fashion industry, particularly for high-end handbags, belts, and other accessories. The use of thick leather not only elevates the product’s perceived value but also contributes to its longevity, appealing to discerning consumers. For B2B buyers, it is essential to focus on ethical sourcing practices and consider the thickness required for specific designs to ensure product integrity and customer satisfaction.
How is Leather Thick Essential for Industrial Equipment?
In the industrial sector, thick leather is commonly used in protective gear and workwear, offering durability and protection in hazardous environments. This application is vital for industries such as construction and manufacturing, where safety is paramount. Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant safety standards and consider sourcing leather with specific thickness and temper to meet the rigorous demands of these applications.
Why is Leather Thick Important for Furniture & Interior Design?
Thick leather is extensively used in the furniture industry for upholstery in sofas and chairs. This material not only adds a luxurious touch but also enhances comfort and durability, ultimately improving brand image. B2B buyers in this sector must ensure that the leather sourced aligns with design specifications and customer expectations, focusing on the right textures and finishes for various furniture styles.
How is Leather Thick Utilized in Equestrian Equipment?
In the equestrian industry, thick leather is crucial for manufacturing saddles and bridles. This application ensures both comfort and durability for horses and riders, making it a key consideration for equestrian businesses. Buyers should pay attention to the weight and flexibility of the leather, sourcing from specialized suppliers who can provide the necessary quality and performance characteristics for equestrian applications.
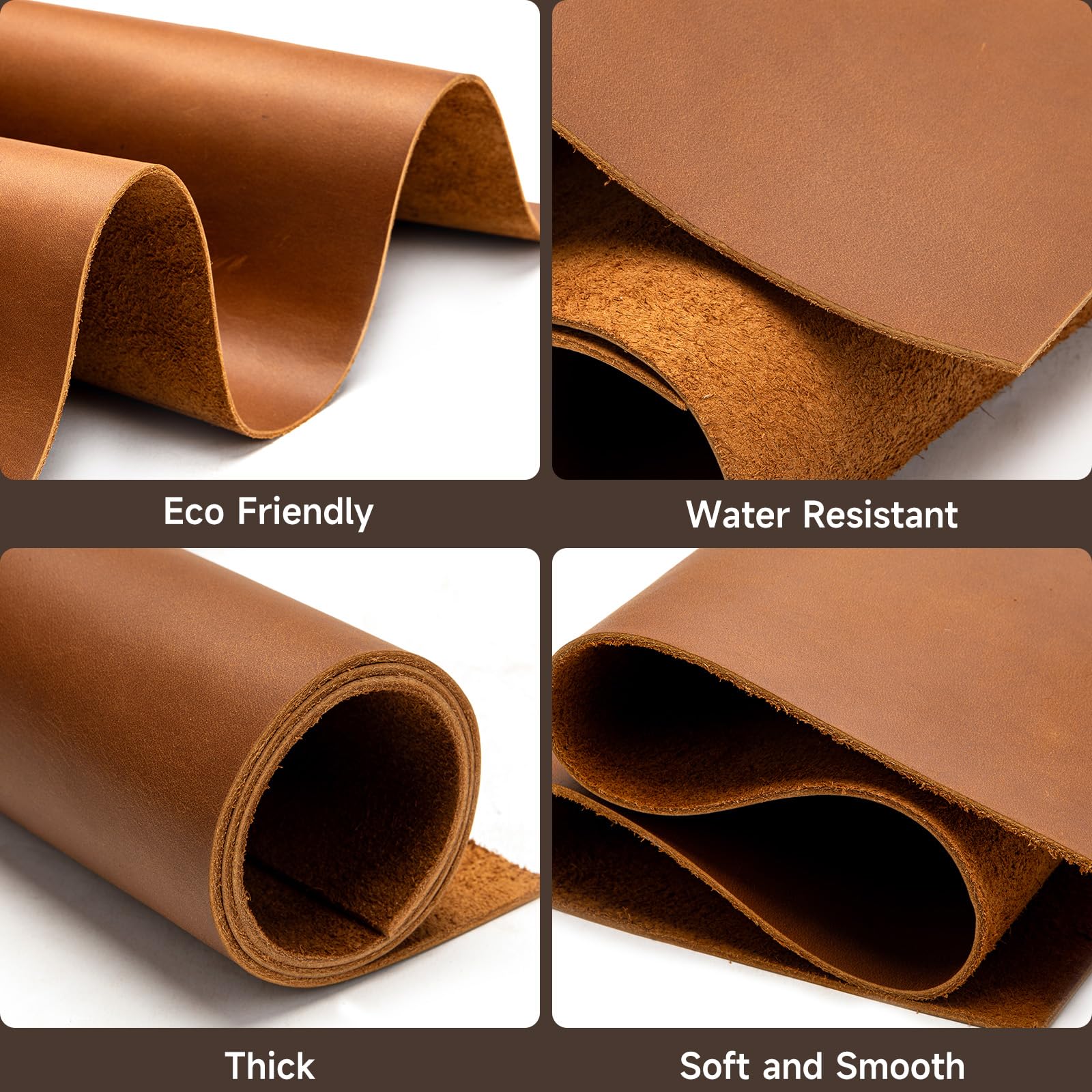

Illustrative image related to leather thick
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather thick’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Thickness for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to choose the appropriate thickness of leather for their specific applications, such as crafting high-end handbags or durable upholstery. The confusion arises from the varying requirements of different products and the fact that leather thickness is often measured in ounces, which can be misleading. A buyer may opt for a leather that appears thick enough but turns out to be too soft or too stiff for their intended use, leading to product failure and wasted resources.
The Solution: To effectively select the right leather thickness, buyers should first understand the specific requirements of their end products. They can start by creating a detailed specifications document that outlines the desired attributes such as durability, flexibility, and appearance. It’s essential to refer to comprehensive leather thickness charts available from reputable suppliers, which detail the recommended uses for various thicknesses. Furthermore, buyers should request samples of different thicknesses and temper types to evaluate how each performs in real-world applications. This hands-on approach not only clarifies which thickness best meets their needs but also enhances their understanding of the material’s properties.
Scenario 2: Incompatibility with Machinery for Thick Leather Sewing
The Problem: A common challenge for B2B buyers, especially those in manufacturing or production, is ensuring that their sewing machines can handle thicker leather. Many standard sewing machines are not equipped to sew through heavy materials, leading to operational delays and increased costs. Buyers may find themselves unable to complete orders on time due to machinery limitations, or worse, they may damage their equipment while trying to work with unsuitable leather.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their current machinery against the requirements for sewing thick leather. This includes consulting the user manual for maximum thickness specifications and considering investing in heavy-duty sewing machines designed specifically for leatherwork. For those who are not ready to upgrade their equipment, a practical alternative is to utilize hand-stitching techniques or specialized leather needles that can accommodate thicker materials. Additionally, buyers should engage with suppliers who offer detailed guidance on compatible machinery or services for leather preparation, such as skiving, which can reduce thickness in critical areas without compromising the integrity of the leather.
Scenario 3: Variability in Leather Quality and Thickness
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of inconsistent quality and thickness in leather products, as natural hides can vary significantly. This inconsistency can lead to unexpected complications in production, such as mismatched pieces or defects that affect the aesthetic and functional qualities of the final product. When sourcing leather from different suppliers, buyers may inadvertently receive materials that do not meet their quality standards, causing delays and impacting customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should establish strong relationships with reputable suppliers who can guarantee consistent quality through stringent quality control measures. Implementing a robust vendor evaluation process can help ensure that suppliers adhere to specific standards regarding leather thickness and quality. Additionally, buyers should consider requesting documentation such as certification of material properties or batch testing results to verify consistency. It’s also beneficial to invest in a leather testing kit, which allows for on-site quality checks before incorporating the leather into production. By taking these proactive steps, buyers can significantly reduce variability and enhance the reliability of their leather sourcing process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather thick
What Are the Key Properties of Different Types of Thick Leather?
When selecting thick leather for various applications, it’s essential to understand the distinct properties of the materials available. Here, we analyze four common types of thick leather: Full Grain, Top Grain, Suede, and Nubuck. Each type has unique characteristics that influence their performance in specific applications.
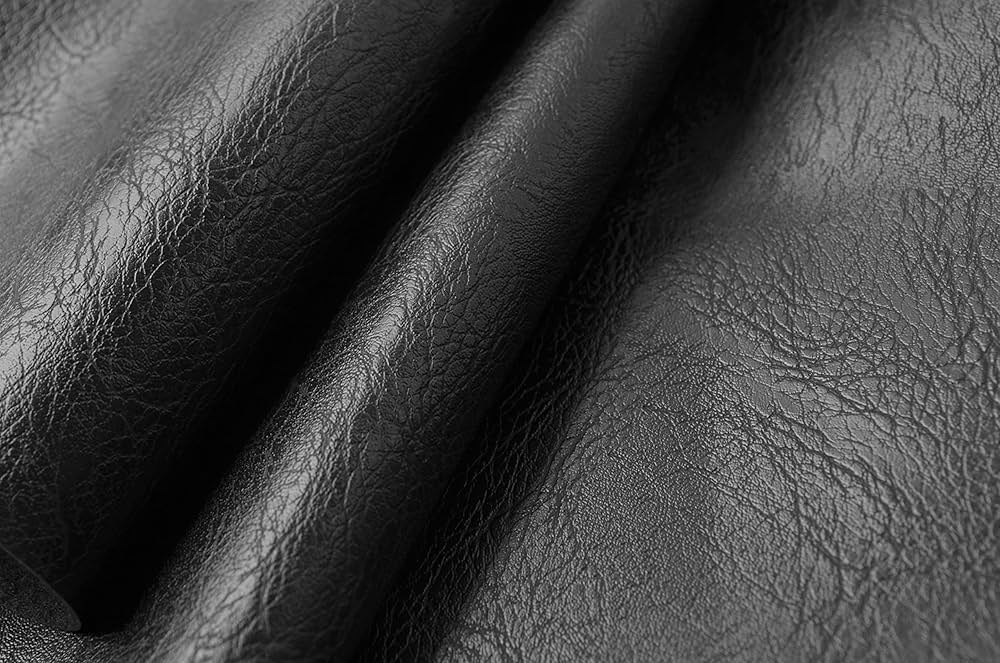
What Are the Key Properties of Full Grain Leather?
Full grain leather is made from the top layer of the hide, preserving the natural grain. This type of leather is known for its durability and breathability, making it suitable for high-end products like luxury bags and furniture.

Illustrative image related to leather thick
- Key Properties: High tensile strength, excellent breathability, and natural resistance to moisture.
- Pros: Extremely durable and develops a rich patina over time. It is also resistant to wear and tear, making it ideal for long-lasting products.
- Cons: Higher cost compared to other types of leather and may require more maintenance to preserve its appearance.
- Impact on Application: Best suited for products that require longevity and aesthetic appeal, such as high-quality handbags and upholstery.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international leather standards (e.g., ISO 16128) is crucial, especially for markets in Europe and the Middle East, where quality expectations are high.
How Does Top Grain Leather Compare to Full Grain?
Top grain leather is similar to full grain but has been sanded and treated to remove imperfections. This process gives it a more uniform appearance but may reduce some of its natural durability.
- Key Properties: Good durability, easier to clean, and a more consistent finish.
- Pros: Offers a balance between quality and cost, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including bags and wallets.
- Cons: Less breathable than full grain leather and may not develop the same character over time.
- Impact on Application: Suitable for products that require a polished look without the premium price tag of full grain leather.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the leather meets local regulations regarding chemical treatments, particularly in regions with stringent environmental laws.
What Are the Unique Features of Suede Leather?
Suede leather is made from the underside of the hide, resulting in a soft, velvety texture. It is often used in fashion items and accessories.
- Key Properties: Soft texture, lightweight, and good insulation properties.
- Pros: Provides a unique aesthetic and is often more affordable than full grain or top grain leather.
- Cons: Less durable and more susceptible to staining and water damage.
- Impact on Application: Best for fashion items and accessories where style is prioritized over durability.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Suede may not be suitable for humid climates, and buyers should consider local preferences for leather types in their markets.
How Does Nubuck Leather Perform in Various Applications?
Nubuck leather is similar to suede but is made from the outer side of the hide, giving it a finer texture and more durability.
- Key Properties: Soft and durable with a brushed finish.
- Pros: Offers a luxurious feel while maintaining good durability, making it suitable for both fashion and functional products.
- Cons: Like suede, it can be prone to staining and requires special care.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for upscale products like shoes and jackets that benefit from a soft touch.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Nubuck’s care requirements should be communicated clearly to customers, especially in regions where leather care products may not be readily available.
Summary Table of Thick Leather Types
| Material | Typical Use Case for leather thick | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Grain | Luxury bags, high-end furniture | Extremely durable; develops rich patina | Higher cost; requires maintenance | Hoch |
| Top Grain | Wallets, bags | Good balance of quality and cost | Less breathable; uniform appearance | Medium |
| Wildleder | Fashion items, accessories | Unique aesthetic; often more affordable | Less durable; prone to staining | Low |
| Nubuck | Upscale shoes, jackets | Luxurious feel; good durability | Requires special care; prone to staining | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of thick leather materials, allowing international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and market considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather thick
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Thick Leather?
The manufacturing process for thick leather involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both aesthetic and functional requirements. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess quality and suitability for their applications.
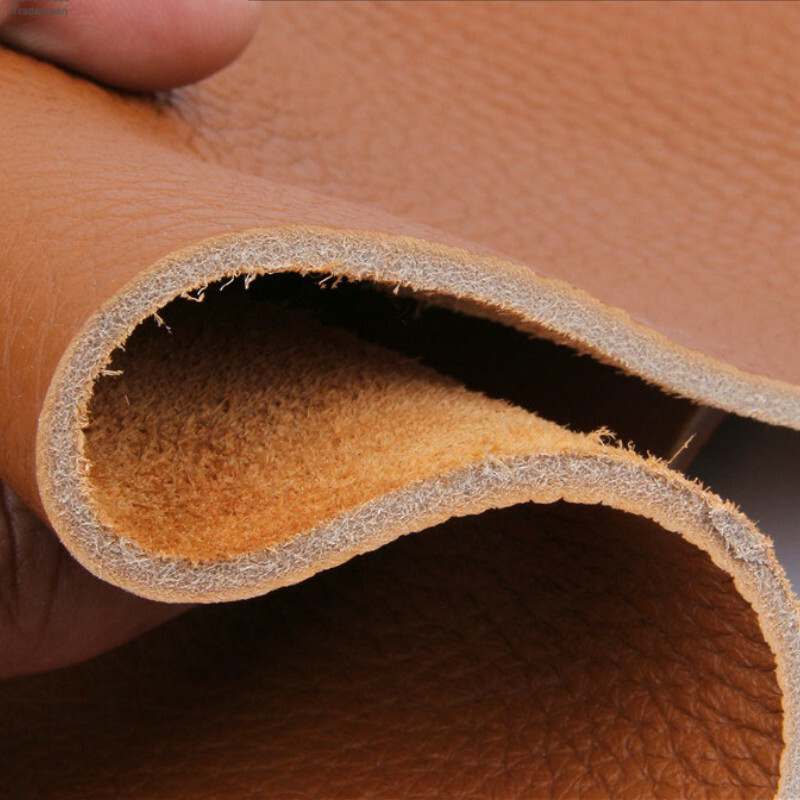

Illustrative image related to leather thick
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Leather Processed?
The journey of thick leather begins with raw hides, which are typically sourced from cattle, pigs, or other animals. The first step is curing, which can be done through salting or tanning. Tanning is crucial as it transforms raw hides into a durable material resistant to decay. Common tanning methods include vegetable tanning, which uses natural plant extracts, and chrome tanning, offering faster processing times and a wider range of colors.
After tanning, hides are split to achieve uniform thickness. This is done using a splitting machine, which ensures consistency across the hide. The hides may also undergo processes like trimming and cleaning to remove any imperfections that could affect quality.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Thick Leather?
Once the hides are prepared, the next step is forming, which involves cutting the leather into desired shapes and sizes. Precision cutting machines are often employed to ensure accuracy, especially for large orders. Techniques such as die cutting can be used for complex shapes, ensuring efficiency and reducing waste.
After cutting, the leather may be subjected to skiving, a process that thins specific areas to enhance flexibility or to create edges that can be easily folded or stitched. This is particularly important for products requiring intricate designs or where weight reduction is necessary.
Assembly: How Are Different Components Joined Together?
The assembly stage involves stitching or bonding pieces of leather together to create the final product. For thick leather, it is crucial to use heavy-duty sewing machines capable of handling the material’s density. Hand-stitching is also common for premium products, providing durability and a bespoke feel.
Quality stitching techniques include double stitching for added strength and the use of waxed threads that resist fraying. Rivets, snaps, and other hardware may also be incorporated, depending on the product design. This stage is critical as it determines the structural integrity and longevity of the finished item.
Finishing: What Are the Final Steps in Leather Production?
Finishing is the last step in the manufacturing process, where the leather undergoes treatments to enhance its appearance and durability. Techniques such as dyeing, polishing, and applying protective coatings are common. These processes not only improve aesthetics but also increase resistance to water, stains, and abrasion.
Quality assurance during this stage is vital. Products are often subjected to tests that evaluate color fastness, surface smoothness, and overall finish quality. A well-finished leather product will display a rich texture and uniform color, essential for B2B buyers focused on brand presentation.

Illustrative image related to leather thick
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Thick Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of the thick leather manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. Understanding the QA protocols can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Thick Leather?
International quality standards, such as ISO 9001, provide a framework for quality management systems across industries, including leather manufacturing. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a supplier adheres to quality management principles, including customer focus, process approach, and continual improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for safety and compliance in the European market and API standards for oil and gas applications can further assure buyers of product reliability and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Leather Production?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:

Illustrative image related to leather thick
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assessing raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes at various stages, including material preparation, forming, and assembly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting a comprehensive assessment of the finished products, checking for defects, dimensions, and overall quality.
These checkpoints help identify and rectify issues early, minimizing waste and ensuring that only high-quality leather products reach the market.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Thick Leather?
Testing methods for thick leather typically include:
- Physical Testing: Assessing tensile strength, tear resistance, and abrasion resistance.
- Chemical Testing: Evaluating the leather’s resistance to water, oils, and other substances.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for defects such as color inconsistencies, blemishes, or improper stitching.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific tests conducted and the results to ensure the leather meets their standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s QC processes is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are actionable steps to consider:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to evaluate the manufacturing processes, equipment, and quality control measures in place. This provides insight into the supplier’s adherence to standards and practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask for documentation detailing QC processes, results from recent tests, and any certifications the supplier holds. This transparency can build trust and confidence.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies to assess the quality of the leather before shipment. This is particularly important for large orders or when dealing with new suppliers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances in quality control. For instance:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations can help in negotiations and assessments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the supplier complies with local regulations regarding leather production and export, as this can affect product quality and marketability.
- Logistical Considerations: Be mindful of how transportation and storage can impact leather quality. Proper handling is essential to maintain the integrity of thick leather during shipping.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing thick leather, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather thick’
To effectively procure ‘leather thick’ for your business needs, it’s essential to follow a structured approach that ensures you select the right materials from reliable suppliers. This checklist serves as a practical guide for B2B buyers, helping you navigate the complexities of sourcing thick leather.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific requirements for the leather you intend to purchase. Consider factors such as thickness (measured in ounces), temper (soft, semi-soft, semi-stiff, stiff), and type (e.g., vegetable-tanned, chrome-tanned).
– Thickness Considerations: Understand how thickness affects the leather’s suitability for your project. For instance, heavier leather (6-10 oz) may be ideal for durable products like belts or boots, while lighter options (3-5 oz) might suit bags or upholstery.
Step 2: Research Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of thick leather. Look for manufacturers and distributors with a solid reputation in the industry, particularly those who cater to your target regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
– Supplier Background: Review their history, product range, and customer testimonials. This will help you gauge their reliability and the quality of their leather products.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Qualitätssicherung: Inquire about their quality control processes and whether they provide certifications or guarantees for their leather products. This is vital for ensuring you receive materials that meet your specifications.
Step 4: Request Samples
Always request samples of the leather you are considering. This allows you to assess the quality, texture, and suitability of the leather for your intended application.
– Testing the Product: Evaluate the samples for thickness, temper, and overall quality. Consider how it feels in hand and whether it meets your project’s aesthetic and functional requirements.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Regulations
Ensure that your chosen supplier complies with local and international regulations regarding leather sourcing and processing. This is particularly important for environmental and ethical considerations.
– Sustainability Practices: Inquire about their tanning processes and whether they adhere to sustainable practices. This not only impacts your brand’s reputation but may also affect your marketability.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in discussions regarding pricing, minimum order quantities, and payment terms. Understanding these aspects is crucial to maintaining profitability in your business operations.
– Long-Term Relationships: Consider establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers who offer favorable terms, as this can lead to better pricing and priority service in the future.

Illustrative image related to leather thick
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Finally, outline the logistics for transporting the leather from the supplier to your facility. Discuss shipping options, timelines, and any potential customs issues that may arise.
– Timely Delivery: Ensure that the supplier can meet your delivery timelines, as delays can significantly impact your production schedules.
By following these steps, you can streamline the process of sourcing thick leather, ensuring that you acquire high-quality materials that meet your business needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather thick Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Thick Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of leather thick sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary components of cost include:
-
Materials: The price of raw leather is influenced by quality, thickness, and type (e.g., vegetable-tanned vs. chrome-tanned). As leather is a natural product, prices can fluctuate based on availability and market demand.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for processing leather, which includes tanning, cutting, and finishing. Labor costs vary significantly by region, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these overheads, ultimately affecting pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for specialized machinery or tools required for processing thick leather can be significant. Over time, these costs are amortized over production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that leather meets quality standards requires testing and inspection, which adds to the overall cost. Buyers should inquire about QC processes to ensure that they meet their specifications.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the origin of the leather and the destination. Factors like shipping mode (air vs. sea) and distance greatly influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and risks. Understanding the margins in your supplier’s pricing can help in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Leather Thick Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of leather thick:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized leather products can incur additional costs due to the need for specialized treatments or finishes. It’s vital to clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality leather or leather with specific certifications (e.g., eco-friendly) usually commands a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against cost.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality but at a higher cost. Conduct thorough due diligence to identify the best partners.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can impact the total landed cost. Buyers should be aware of their responsibilities under different Incoterms to avoid unforeseen expenses.
What Tips Can Buyers Use for Cost-Efficiency in Leather Thick Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing leather thick, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in negotiations not just on price, but also on payment terms, lead times, and delivery schedules. Building a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better terms in future transactions.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider all costs associated with leather sourcing, including shipping, tariffs, and potential waste in production. A lower upfront cost might result in higher long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: International buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and compliance with local regulations, which can affect pricing.
-
Sample Before Purchase: Request samples of leather to assess quality and suitability before placing large orders. This can help prevent costly mistakes.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for leather thick can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they receive competitive pricing tailored to their specific requirements. Always verify the final prices before committing to a purchase.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather thick With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Leather Solutions
When considering leather thick as a primary material for various applications, it is essential to explore alternative solutions that may offer comparable performance or unique advantages. In the B2B landscape, international buyers must weigh these options based on specific project requirements, budget constraints, and desired outcomes. This analysis will compare leather thick with synthetic leather and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), both of which serve similar purposes in products ranging from apparel to upholstery.

Illustrative image related to leather thick
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Leather Thick | Synthetic Leather | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, high-quality feel | Varies widely; can mimic leather | Very durable, weather-resistant |
| Cost | Generally higher | Lower initial cost | Cost-effective for bulk use |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor for crafting | Easier to mold and cut | Simple to work with and lightweight |
| Wartung | Requires regular conditioning | Low maintenance | Easy to clean, resistant to stains |
| Best Use Case | Premium products, luxury items | Fashion items, budget footwear | Industrial applications, outdoor furniture |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Synthetic Leather
Synthetic leather, often made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyurethane (PU), is a popular alternative to leather thick. It offers a variety of textures and colors, mimicking the look of genuine leather at a lower price point. The primary advantage of synthetic leather is its ease of maintenance; it does not require conditioning and can be wiped clean easily. However, its performance can vary significantly depending on the manufacturing quality. While it may not provide the same durability or luxurious feel as leather thick, it is an excellent choice for budget-conscious projects or fashion items where appearance is paramount.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
High-density polyethylene is a versatile thermoplastic known for its strength and durability. It is particularly resistant to moisture, chemicals, and UV light, making it suitable for outdoor applications, such as furniture and marine products. HDPE is lightweight and easy to work with, allowing for quick production and assembly processes. However, it lacks the aesthetic appeal and tactile quality of leather thick, which may be a crucial consideration for high-end products. While HDPE is cost-effective for large-scale projects, it may not be the best choice for items where a premium look and feel are essential.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution
Selecting the right material for your project requires a thorough understanding of your specific needs and constraints. Leather thick excels in durability and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for luxury items and applications where quality is paramount. In contrast, synthetic leather offers a budget-friendly alternative with low maintenance needs, suitable for fast fashion and everyday products. HDPE stands out for industrial uses, providing exceptional durability and weather resistance. By assessing the performance, cost, and intended use case of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project goals and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather thick
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Leather Thickness?
Understanding the essential technical properties of leather thickness is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when selecting materials that meet specific project requirements. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Thickness Measurement
Leather thickness is typically measured in ounces, where one ounce equals 1/64 of an inch (approximately 0.4 mm). For instance, a leather hide labeled as “4-5 oz” means it varies between 4 and 5 ounces. This measurement is vital for determining the leather’s suitability for various applications, from footwear to upholstery. -
Material Grade
Leather is categorized into different grades based on quality and processing methods, such as full-grain, top-grain, and corrected grain. Full-grain leather, for example, is the highest quality, retaining the natural grain and imperfections, which enhances its durability and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these grades helps buyers make informed decisions regarding product longevity and performance. -
Tolerance Levels
Due to the natural variability in hides, tolerance levels specify the acceptable range of thickness. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.5 oz may be acceptable for certain applications. Knowing these tolerances is crucial for manufacturers to ensure that the leather meets precise specifications required for production processes. -
Temper
Temper refers to the leather’s pliability or stiffness, which is categorized into four types: soft, semi-soft, semi-stiff, and stiff. This characteristic affects how the leather behaves in various applications, such as whether it can hold its shape or is suitable for bending. B2B buyers should assess temper alongside thickness to ensure compatibility with their intended use. -
Finish Types
Leather finishes can vary from aniline (natural) to pigmented (dyed), affecting both appearance and performance. The choice of finish impacts durability, resistance to stains, and overall aesthetic appeal. Understanding these variations allows buyers to select leather that aligns with their brand image and functional needs. -
Grain Pattern
The grain pattern of leather affects its texture and visual appeal. Unique patterns can be desirable for high-end products, while more uniform patterns may be preferred for industrial applications. Recognizing the implications of grain patterns can aid buyers in selecting the right leather for their specific market segment.
What Are Common Trade Terminology Terms in Leather Sourcing?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the leather industry. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are branded and sold by another company. In the leather industry, this often pertains to businesses that supply components for larger brands, emphasizing the importance of quality and compliance in manufacturing. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is critical for B2B buyers to determine their purchasing strategy and manage inventory effectively, especially when entering new markets. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. This process is essential for comparing suppliers and ensuring competitive pricing, ultimately aiding in budget management. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, liability, and risk management, which is vital for smooth transactions across borders. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and ensuring timely market entry. -
Quality Assurance (QA)
QA encompasses the processes and procedures that ensure products meet specified quality standards. In leather sourcing, robust QA measures are essential for maintaining product consistency and building trust with clients.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions, streamline procurement processes, and foster long-term supplier relationships in the leather industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather thick Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends Impacting the Leather Thick Sector?
The leather thick market is experiencing notable shifts driven by global demand for high-quality, durable materials. A surge in industries such as fashion, automotive, and furniture is propelling the demand for thick leather, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Countries like Vietnam and Germany are leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques and technological innovations, such as automated cutting and digital design tools, to enhance production efficiency and reduce waste.
Additionally, the trend towards customization and personalization is reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that can offer a variety of leather thicknesses, textures, and finishes to meet specific project requirements. This demand necessitates a flexible supply chain capable of accommodating diverse customer needs, pushing manufacturers to invest in inventory management systems and just-in-time production methods.

Illustrative image related to leather thick
Moreover, the rise of e-commerce platforms is changing how businesses source leather products. International buyers are now able to access a broader range of suppliers, enabling them to compare quality and prices from different regions. The integration of technologies such as blockchain for traceability and transparency is also emerging, allowing buyers to verify the authenticity and quality of the leather they purchase.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Leather Thick Market?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor for B2B buyers in the leather thick sector. The environmental impact of leather production, particularly in terms of water usage and chemical waste, has prompted a demand for more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to ethical sourcing standards and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies that can verify their sourcing methods through certifications—such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification—are gaining a competitive edge. These certifications assure buyers that the leather is produced in an environmentally responsible manner, promoting better practices in waste management, chemical usage, and animal welfare.
Furthermore, the adoption of alternative materials, such as plant-based leathers or recycled leather, is gaining traction. B2B buyers are exploring these options not only to meet consumer demand for sustainable products but also to mitigate risks associated with traditional leather sourcing. As awareness of sustainability grows, the shift towards greener materials and practices is likely to accelerate, influencing sourcing strategies across the leather thick market.
What Is the Historical Context of the Leather Thick Market?
The leather thick sector has evolved significantly over centuries, tracing its roots back to ancient civilizations where leather was primarily used for clothing and armor. The industrial revolution marked a turning point, as mechanized tanning processes increased the availability and variety of leather products.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted from merely producing leather to enhancing quality, durability, and sustainability. The introduction of synthetic alternatives in the late 20th century posed challenges to traditional leather markets, prompting manufacturers to innovate and differentiate their products. Today, the leather thick market is characterized by a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern technology, catering to a global clientele that values both quality and sustainability. This evolution underscores the importance of understanding market dynamics and sourcing trends for B2B buyers navigating the complexities of the leather thick sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather thick
-
How do I choose the right thickness of leather for my project?
Selecting the appropriate leather thickness depends on the intended use of your product. For heavy-duty applications such as belts or bags, consider thicker leather (8 oz and above), while lighter items like wallets may require thinner leather (2-4 oz). Always review both the thickness and the temper of the leather. A thick leather may not be suitable for flexible applications, so ensure to assess the product specifications provided by suppliers. -
What is the best type of leather for durability in harsh conditions?
Full-grain leather is widely regarded as the most durable type, as it retains the natural grain and is less susceptible to wear and tear. For applications exposed to moisture or extreme conditions, look for vegetable-tanned or chrome-tanned leathers, which offer enhanced resistance. Always inquire about the leather’s treatment and finish to ensure it meets your durability requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for thick leather?
Minimum order quantities for thick leather can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs can range from 5 to 50 hides, depending on the thickness and grade of leather. It’s advisable to confirm these details directly with suppliers, especially when considering custom orders or specific leather types. Some suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for established relationships or larger contracts. -
How can I ensure the quality of thick leather before purchasing?
To ensure quality, request samples of the leather before committing to a large order. Evaluate the samples for consistency in thickness, grain quality, and overall appearance. Additionally, consider suppliers who provide certifications or quality assurance processes, such as compliance with international leather standards. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers can also clarify their quality control measures. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing thick leather internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region. Typically, you may encounter options such as upfront payment, a percentage deposit with the balance on delivery, or payment against documents. Establishing a relationship with your supplier may lead to more favorable terms. Always ensure that the payment method offers security and protection, such as letters of credit for larger transactions. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing thick leather?
Logistics for importing thick leather involve several factors, including shipping method, customs duties, and lead times. It’s essential to choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling leather products. Be aware of the import regulations in your country, as some regions may have restrictions or tariffs on leather goods. Discussing logistics with your supplier can help streamline the process and minimize delays. -
How can I vet potential suppliers of thick leather?
To vet potential suppliers, conduct thorough research on their reputation in the industry. Check for certifications, customer reviews, and testimonials. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality standards. Additionally, visiting the supplier’s facility can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality control measures. -
Can I customize the thickness or finish of the leather I order?
Many suppliers offer customization options for leather thickness and finish. When placing an order, specify your requirements clearly, including desired thickness in ounces and any particular finishes or treatments needed. Keep in mind that customization may impact lead times and MOQs, so it’s advisable to discuss these details early in the negotiation process.
Top 5 Leather Thick Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Weaver Leather – Thickness Chart
Domain: weaverleathersupply.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Leather Thickness Chart: 1 ounce of leather equals 1/64″ in thickness. Hides may vary in thickness; those processed through a splitting machine are more consistent. The chart provides basic leather conversions and uses for each size. More ounces indicate heavier leather.
2. Leather Hide Store – Premium Upholstery Leather
Domain: leatherhidestore.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Types of leather available: Aniline, Auto Distress, Full Grain, Embossed, Italian Leather, Nappa, Nubuck, Pebble Leather, Pigmented, Pull Up, Semi Aniline. Upholstery leather is specifically mentioned for various uses. Color options include Black, Blue, Brown & Gold, Dark Brown, Green, Grey, Metallic, Orange, Pink & Purple, Red & Burgundy, Tan & Beige, Taupe, White & Cream, Yellow. Additional prod…
3. Leather Circle – Thickness Guide
Domain: leathercircle.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Leather Thickness Guide: Understanding leather thickness is crucial for durability, appearance, and functionality. Common thickness ranges include: Cowhide (1.5mm to over 5mm), Goatskin (0.8mm to 1.5mm), Lambskin (0.5mm to 1.2mm). Thickness is measured in ounces (1 oz = 1/64th inch ~0.4mm). Recommended thickness for projects: Wallets (3-4 oz), Belts (8-10 oz), Bags (5-6 oz), Book Covers (2-4 oz). …
4. Leather Box USA – Thick Buffalo Leather
Domain: leatherboxusa.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Thick buffalo leather with a matte finish; available in Rust, Dark Brown, Anthracite, and Beige colors; sizes include: Panel (12 x 6 inches, 0.5 ft2), Large Panel (18 x 12 inches, 1.5 ft2), Half Hide (approx. 49 x 23.5 inches, 8.0-8.5 ft2); robust appearance, thick and sturdy; suitable for DIY interior projects, leather staircase covering, walls, floor tiles, and sturdy bags; unique designs with n…
5. Handbagio – Leather Weight and Thickness Guide
Domain: handbagio.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Guide to Leather Weight and Thickness, written by José Max Lin, last updated August 4, 2022. Key topics include: definition of leather weight (measured in ounces per square foot), definition of leather thickness (measured in ounces), leather thickness conversion (1 oz ≈ 0.4 mm), leather thickness chart, differences between leather weights and thicknesses, choosing the right weight and thickness fo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather thick
In the realm of leather thick sourcing, understanding the nuances of leather thickness and temper is paramount. International buyers, particularly from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must prioritize strategic sourcing to ensure the selection of leather that meets their specific project requirements. Recognizing that thickness is measured in ounces, with variations in both texture and pliability, can significantly influence purchasing decisions. For instance, selecting the right temper—ranging from soft to stiff—can enhance the functionality and aesthetic appeal of the final product.
As the leather market continues to evolve, embracing innovative sourcing strategies will be essential. Engaging with reliable suppliers who offer transparency in their product specifications can streamline the procurement process, ensuring that buyers obtain high-quality materials suited for their needs. Additionally, leveraging sample swatches or rings can provide tactile insights, aiding in informed decision-making.
Looking ahead, the demand for premium leather products is projected to rise. Buyers are encouraged to stay abreast of market trends and explore partnerships with manufacturers who are committed to sustainability and quality. By doing so, they can position themselves advantageously in a competitive landscape, ensuring their offerings resonate with evolving consumer preferences.

Illustrative image related to leather thick
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.