Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to make a leather holster
In the competitive landscape of leather craftsmanship, understanding how to make a leather holster presents both opportunities and challenges for B2B buyers globally. Sourcing high-quality materials, ensuring compatibility with various firearm models, and meeting diverse consumer preferences are just a few hurdles that businesses face. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of leather holster production, covering essential aspects such as types of holsters, their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets such as Vietnam and Saudi Arabia, will find actionable insights tailored to their unique needs. By exploring best practices in leather selection, design techniques, and assembly methods, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that align with market demands and regulatory standards.
Furthermore, it highlights the importance of establishing reliable supplier relationships to ensure consistent quality and timely delivery. As the demand for custom leather goods continues to rise, understanding these key elements will not only enhance product offerings but also foster sustainable growth in the leather industry. Whether you are a seasoned manufacturer or an emerging player, this guide serves as a valuable resource to navigate the complexities of the leather holster market effectively.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 How To Make A Leather Holster Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to make a leather holster
- Understanding how to make a leather holster Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to make a leather holster
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to make a leather holster’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to make a leather holster
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to make a leather holster
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to make a leather holster’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to make a leather holster Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to make a leather holster With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to make a leather holster
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to make a leather holster Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to make a leather holster
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to make a leather holster
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how to make a leather holster Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fitted Leather Holster | Custom-molded to fit specific firearm models | Law enforcement, personal defense | Pros: High retention, tailored fit. Cons: Time-consuming to produce. |
| OWB Holster | Outside the waistband design, often with adjustable cant | Tactical gear suppliers | Pros: Quick draw, versatile. Cons: Less concealment compared to IWB. |
| IWB Holster | Inside the waistband design for concealed carry | Retailers of concealed carry gear | Pros: Enhanced concealment, comfort. Cons: Limited accessibility. |
| Crossdraw Holster | Designed for drawing from the opposite side of the body | Specialty firearm retailers | Pros: Ideal for seated positions. Cons: May be less secure during movement. |
| Shoulder Holster | Suspended from the shoulder for easy access | Law enforcement, security firms | Pros: Distributes weight, discreet. Cons: Bulkier, can be uncomfortable for extended wear. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Fitted Leather Holsters?
Fitted leather holsters are meticulously designed to match specific firearm models, ensuring a snug fit and optimal retention. This type is favored in law enforcement and personal defense markets where firearm security is paramount. Buyers should consider the customization capabilities and the time required for production, as these holsters often involve extensive craftsmanship.
How Do OWB Holsters Differ from Other Types?
Outside the waistband (OWB) holsters feature a design that allows for easy access and a quick draw. They are commonly used in tactical applications and are adjustable for cant, making them versatile for various carrying positions. For B2B buyers, the trade-off between accessibility and concealment is crucial, as these holsters are less discreet than their IWB counterparts.
What Makes IWB Holsters Popular for Concealed Carry?
Inside the waistband (IWB) holsters are designed for concealed carry, providing a discreet option for firearm transport. They are particularly popular among retailers specializing in concealed carry gear. Buyers should evaluate comfort and accessibility, as IWB holsters can limit quick access to firearms, making them suitable for environments where discretion is essential.
What are the Advantages of Crossdraw Holsters?
Crossdraw holsters are crafted for drawing from the opposite side of the body, making them ideal for individuals who spend extended periods seated, such as in vehicles. Specialty firearm retailers often stock these holsters due to their unique functionality. However, B2B buyers must consider the potential for reduced security during movement, as the design may not retain the firearm as securely as other styles.
How Do Shoulder Holsters Function in Tactical Scenarios?
Shoulder holsters are suspended from the shoulder and allow for easy access to firearms while distributing weight evenly across the torso. They are commonly utilized by law enforcement and security firms, offering discreet carry options. Buyers should weigh the benefits of comfort and concealment against the bulkiness that can make them less suitable for everyday wear.
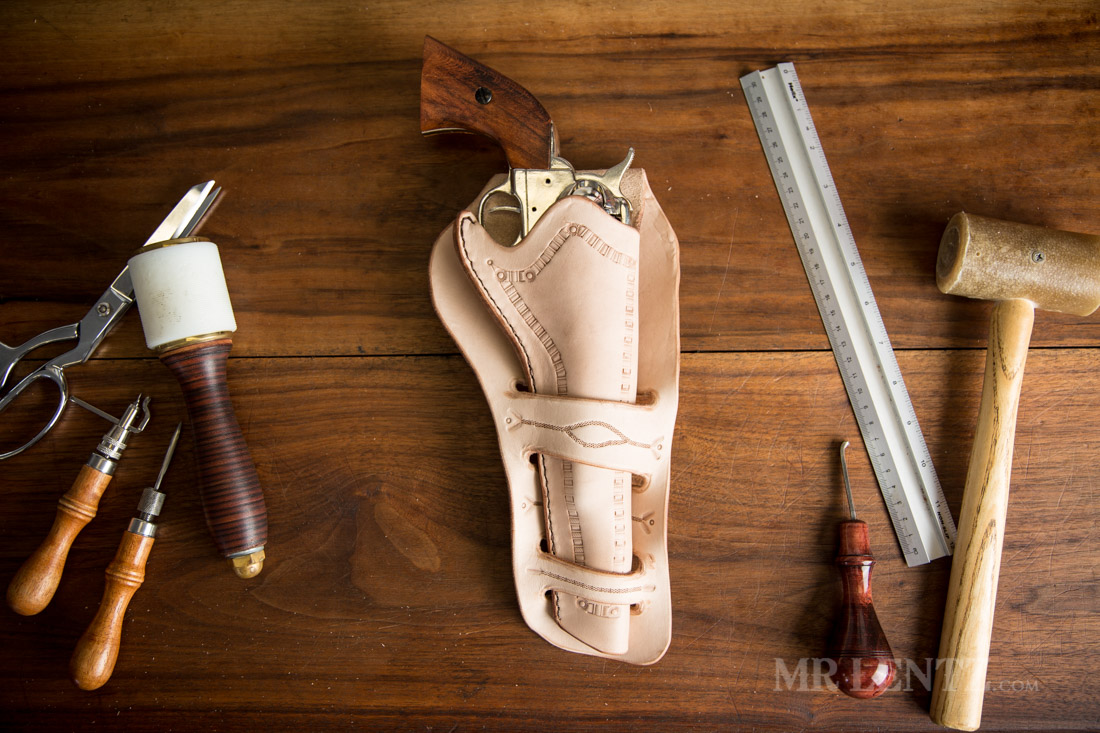

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Key Industrial Applications of how to make a leather holster
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to make a leather holster | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Law Enforcement | Custom holsters for firearms used by police officers | Enhanced safety and accessibility for officers in the field | Need for durable, secure materials; compliance with local regulations |
| Military | Tactical holsters for soldiers’ sidearms | Improved functionality and quick access during operations | Requirement for lightweight, high-strength leather; resistance to environmental conditions |
| Outdoor Recreation | Holsters for hunting and outdoor sports equipment | Increased convenience and safety for hunters and sports enthusiasts | Sourcing weather-resistant leather; ensuring fit for various firearm models |
| Fashion and Lifestyle | Custom leather holsters as fashion accessories | Unique branding opportunity and differentiation in the market | Focus on aesthetic appeal; sourcing high-quality, full-grain leather |
| E-commerce and Retail | Selling DIY leather holster kits | Expanding product offerings and attracting DIY enthusiasts | Ensuring comprehensive instructional materials; quality leather sourcing for kits |
How Can Law Enforcement Benefit from Custom Leather Holsters?
In law enforcement, custom leather holsters are essential for ensuring the safety and accessibility of firearms for police officers. These holsters are designed to fit specific firearm models, providing a secure fit that allows for quick access during critical situations. International buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East must consider local regulations regarding firearm storage and carry, ensuring that their holster designs comply with these laws. Sourcing durable leather that can withstand wear and tear in various environments is critical for maintaining officer safety.
What Role Do Tactical Holsters Play in Military Operations?
In military applications, tactical holsters are vital for soldiers who require quick access to their sidearms during operations. These holsters need to be lightweight yet robust enough to endure harsh conditions. Buyers from Europe and South America should look for high-strength leather that offers both flexibility and durability. Additionally, considerations around camouflage designs and compatibility with military gear can enhance operational effectiveness, making it essential to source materials that meet these specific requirements.
How Do Outdoor Recreation Markets Utilize Leather Holsters?
For outdoor recreation, particularly in hunting and shooting sports, leather holsters provide a practical solution for safely carrying firearms. The demand for holsters that can withstand the elements is significant, particularly in regions like South America where outdoor activities are prevalent. Buyers should prioritize sourcing weather-resistant leather and consider the specific needs of various firearm models. This ensures that the holster not only serves its functional purpose but also enhances the user experience in outdoor settings.
What Opportunities Exist in Fashion and Lifestyle Markets with Leather Holsters?
In the fashion and lifestyle sectors, leather holsters are increasingly being marketed as stylish accessories. Customization options allow for unique branding opportunities, appealing to a demographic that values both aesthetics and functionality. Buyers in this space, particularly in Europe, should focus on sourcing high-quality, full-grain leather that enhances the product’s visual appeal while maintaining durability. Additionally, understanding market trends in fashion can guide the design process to ensure products align with consumer preferences.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
How Can E-commerce and Retail Businesses Leverage DIY Leather Holster Kits?
E-commerce platforms can capitalize on the growing DIY trend by offering leather holster kits that enable customers to create their own holsters. This not only diversifies product offerings but also attracts a niche market of DIY enthusiasts. For successful sourcing, businesses should ensure that kits include comprehensive instructional materials and high-quality leather suitable for crafting. Buyers from various regions must also consider the logistics of shipping leather products, ensuring compliance with international trade regulations related to leather goods.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to make a leather holster’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing High-Quality Leather for Holsters
The Problem: One of the foremost challenges B2B buyers face when making leather holsters is sourcing high-quality leather. With a variety of leather types available—vegetable-tanned, chrome-tanned, and synthetic options—it can be overwhelming to determine which type will provide the durability and functionality required for holster-making. Poor-quality leather can lead to issues such as stretching, warping, or even rusting firearms, which can compromise safety and performance.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing 7-8 oz vegetable-tanned full-grain leather, as it provides the necessary strength and durability for holster applications. When selecting suppliers, it’s essential to establish relationships with reputable leather suppliers known for their quality. Buyers should request samples to assess the leather’s texture, weight, and flexibility before making a bulk purchase. Additionally, engaging in discussions with suppliers about the leather’s origin and processing can yield insights into its long-term performance characteristics. Implementing a strict quality control process upon receiving shipments will help ensure that only the best materials are used in production, minimizing defects and enhancing product reliability.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Proper Fit for Firearms in Custom Holsters
The Problem: Creating a holster that fits a specific firearm perfectly is another significant pain point. A poorly fitting holster can lead to unsafe handling, discomfort for the user, and a higher rate of product returns. Many buyers struggle with the intricacies of measuring and designing holsters that accommodate different firearm shapes and sizes, which can vary significantly across manufacturers.
The Solution: To achieve optimal fit, buyers should invest time in the pattern-making process before cutting leather. Utilizing detailed templates that account for the firearm’s dimensions is critical. For those unsure about creating their own patterns, purchasing pre-made templates specific to popular models (like Glock) can save time and ensure accuracy. Buyers can also employ techniques such as vacuum forming, where leather is molded around the firearm to ensure a snug fit. Additionally, incorporating adjustable features in holster design can cater to varying user preferences while maintaining safety and usability. Engaging skilled artisans or leather craftsmen with experience in holster-making can further enhance the fitting process.
Scenario 3: Mastering the Assembly and Finishing Techniques
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties during the assembly and finishing stages of holster-making. Without proper techniques, the final product may lack durability or aesthetic appeal. Common issues include misalignment of parts, improper stitching, and inadequate finishing, which can lead to product failures and dissatisfied customers.
The Solution: To address these challenges, buyers should invest in training or workshops focused on leather crafting techniques, particularly in assembly and finishing. Comprehensive guides and video tutorials can provide visual demonstrations of best practices, ensuring a better understanding of techniques like gluing, stitching, and edge finishing. Utilizing high-quality adhesives, such as Barge Cement, along with the right tools for stitching and edge finishing can elevate the overall quality of the holster. Implementing a step-by-step quality assurance checklist during the assembly process will help identify potential issues before the product reaches the customer, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and reducing returns. Regular feedback loops from customers can also provide valuable insights into areas of improvement for future holster designs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to make a leather holster
What Are the Key Materials for Making a Leather Holster?
When selecting materials for leather holster production, it is essential to consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of various types of leather. This analysis focuses on four common materials: vegetable-tanned leather, chrome-tanned leather, suede leather, and synthetic leather. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly influence the performance and suitability of the final product.
How Does Vegetable-Tanned Leather Perform in Holster Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Vegetable-tanned leather is known for its durability and strength. It has excellent resistance to wear and tear, making it suitable for holster applications where longevity is crucial. This type of leather is also breathable, which helps to prevent moisture buildup around the firearm.
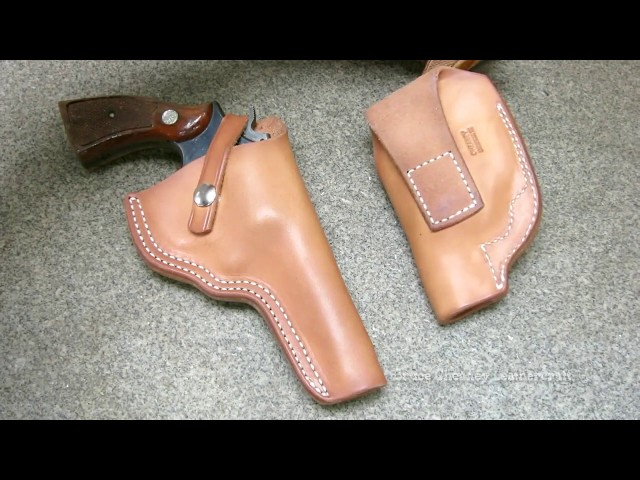

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of vegetable-tanned leather is its environmental friendliness and ability to develop a rich patina over time. However, it can be more expensive than other types of leather and may require more complex manufacturing processes, such as longer tanning times.
Impact on Application: Its compatibility with dyes and finishes allows for high customization, which is beneficial for brands looking to offer unique designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local environmental regulations regarding tanning processes. Additionally, understanding the preferences for leather types in different markets can guide purchasing decisions.
What Are the Characteristics of Chrome-Tanned Leather?
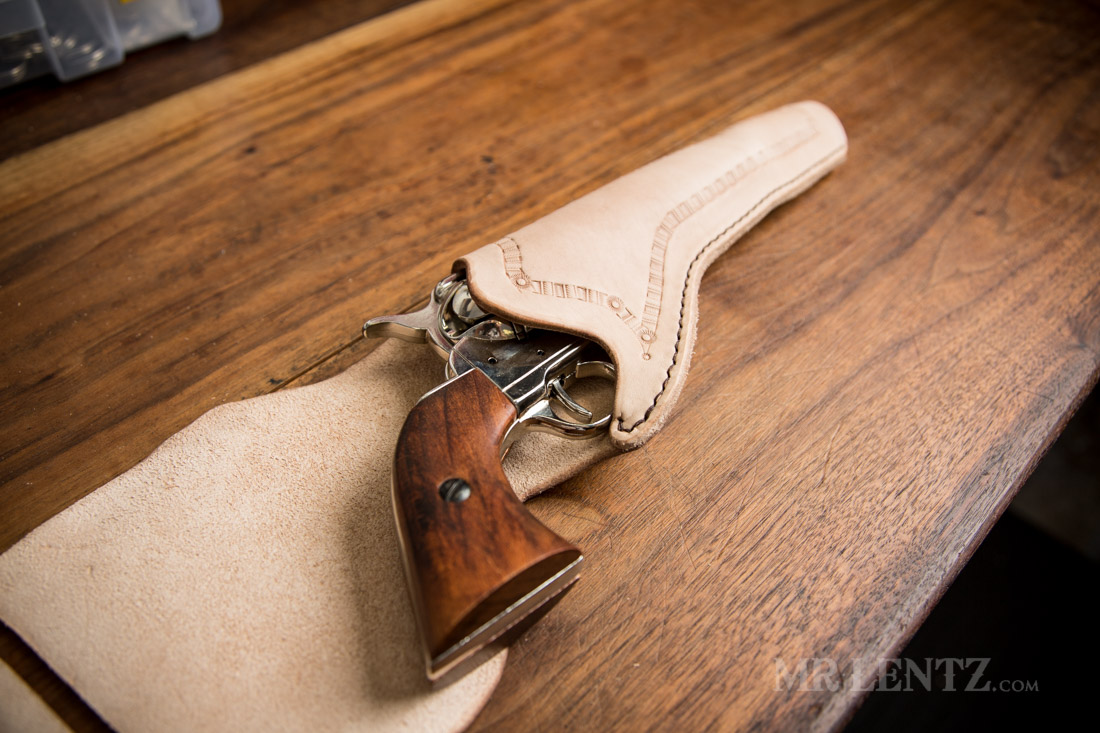
Key Properties: Chrome-tanned leather is known for its softness and flexibility. It offers good resistance to water and is less prone to drying out compared to vegetable-tanned leather.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of chrome-tanned leather is its affordability and ease of production, making it a popular choice for mass production. However, it is less durable than vegetable-tanned leather and can lead to rusting of firearms due to the chemicals used in the tanning process.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Impact on Application: While it can be suitable for light-duty holsters, it may not withstand heavy use, making it less ideal for tactical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the potential environmental impact of chrome tanning and seek suppliers who comply with international standards like REACH or local regulations in their respective countries.
How Does Suede Leather Compare for Holster Use?
Key Properties: Suede leather is characterized by its soft texture and high absorbency. It provides a unique aesthetic appeal and comfort when worn against the body.
Pros & Cons: The softness of suede can enhance comfort for the wearer, but it is generally less durable and more susceptible to staining and wear compared to other leather types. This limits its use in holsters designed for rugged environments.
Impact on Application: Suede is more suitable for fashion-oriented holsters rather than those intended for heavy-duty use.
Considerations for International Buyers: Suede may not be readily available in all regions, and buyers should ensure they source from reputable suppliers who can guarantee quality and consistency.
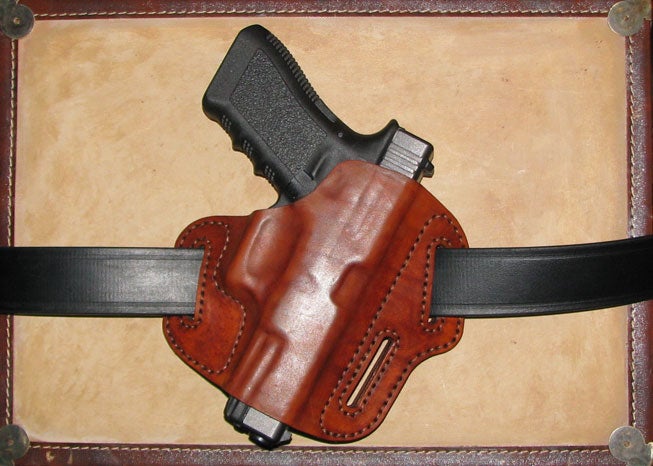
What Are the Advantages of Synthetic Leather in Holster Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers a waterproof and highly durable option. It is resistant to fading and cracking, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of synthetic leather is its cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance. However, it may lack the aesthetic appeal and breathability of genuine leather, which can be a drawback for some consumers.
Impact on Application: Synthetic leather can be an excellent choice for tactical holsters where durability and weather resistance are more critical than traditional leather aesthetics.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that synthetic materials comply with local regulations regarding chemical use and environmental impact, especially in regions with strict standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Leather Holster Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to make a leather holster | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Custom, high-end holsters requiring durability and aesthetics | Environmentally friendly, develops patina | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | Hoch |
| Chrome-Tanned Leather | Mass-produced holsters for casual use | Cost-effective, flexible | Less durable, rust potential | Medium |
| Suede Leather | Fashion-oriented holsters for light use | Soft, comfortable texture | Less durable, prone to staining | Medium |
| Synthetic Leather | Tactical holsters needing weather resistance | Cost-effective, easy maintenance | Lacks traditional leather aesthetics | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive overview of the various leather types suitable for holster manufacturing, enabling informed decisions based on performance, cost, and market preferences.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to make a leather holster
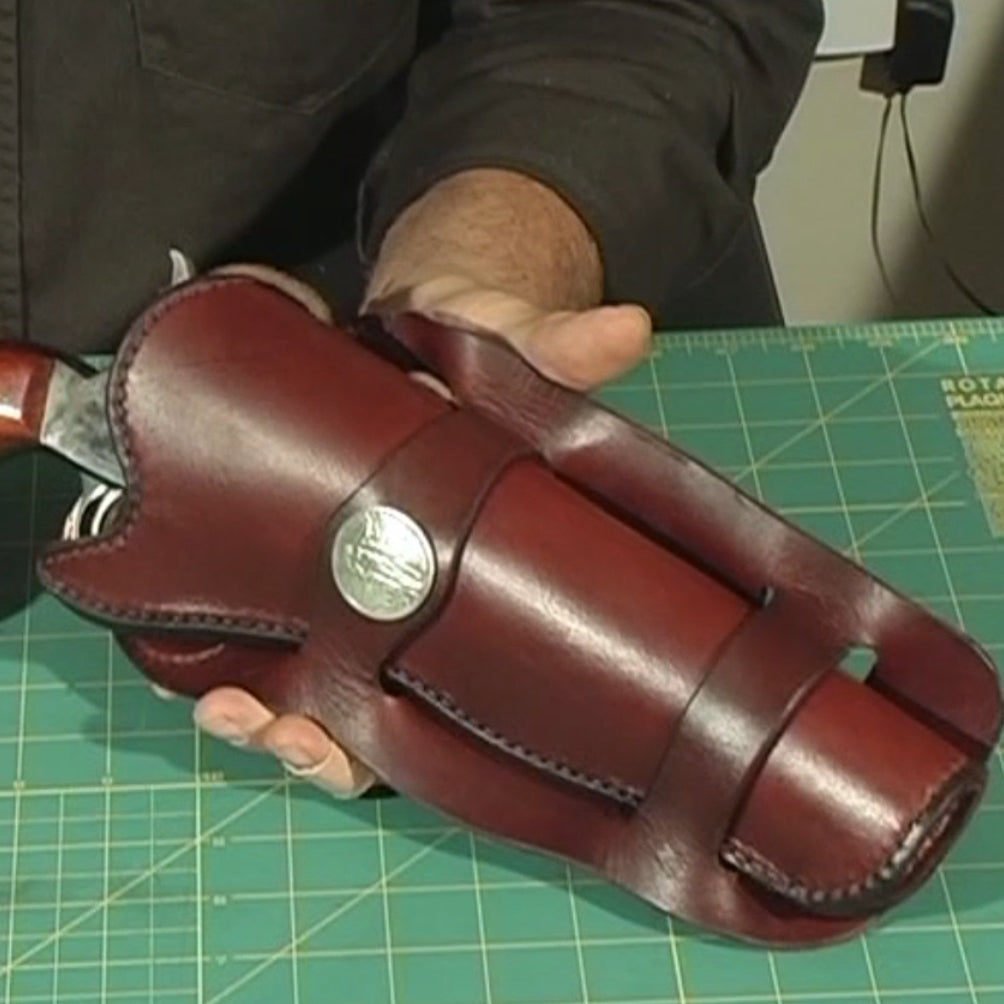
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Leather Holsters?
The manufacturing process of leather holsters involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage requires specific techniques to ensure the final product meets quality and functional standards.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
How Is Material Prepared for Leather Holsters?
The choice of leather is paramount in holster production. High-quality, vegetable-tanned full-grain leather, ideally 7-8 oz in thickness, is preferred for its durability and resistance to wear. During material preparation, leather is sourced from reputable suppliers to ensure consistency in quality.
The leather is cut into appropriate shapes based on templates designed for specific firearm models. It’s essential to avoid using chrome-tanned leather, as it can corrode firearms. This stage also includes pre-conditioning the leather, which may involve soaking it in water or alcohol to enhance malleability for the forming stage.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Process?
The forming stage is crucial for creating a holster that securely fits the firearm. The leather pieces are soaked and then wrapped around a model of the firearm, often using vacuum bags to create a tight fit. This method allows the leather to take on the precise shape of the gun, ensuring a snug and secure hold.
Key techniques include:
– Vacuum Forming: Utilizing vacuum bags to remove air and compress the leather around the firearm mold.
– Detailing: Using tools such as deer antlers to accentuate edges and contours after the leather has dried.
– Drying: Allowing the leather to dry in its formed shape is critical for maintaining the fit.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
How Is the Assembly of Leather Holsters Conducted?
Once the leather is formed, the assembly stage begins. This involves adhering the two leather pieces together, ensuring they align perfectly. High-quality adhesives, such as Barge Cement, are commonly used, and clamps may be employed to maintain pressure while the glue sets.
During assembly, the layout of belt loops and attachment points is carefully considered to ensure proper angle and ease of wear. Once aligned, the leather is cut to shape, and stitching lines are marked using a leather stitching groover. Common stitching techniques include saddle stitching, where two needles are used to create a durable seam.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance the Quality of Leather Holsters?
The finishing stage is essential for both aesthetic and protective qualities. After assembly, edges are beveled and sanded to remove roughness, providing a polished look. Treatments, such as Neatsfoot oil, are applied to condition the leather, enhancing its durability and appearance.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Additional finishing processes may involve dyeing, sealing, or applying water-resistant coatings to improve the holster’s longevity and performance in various environments.
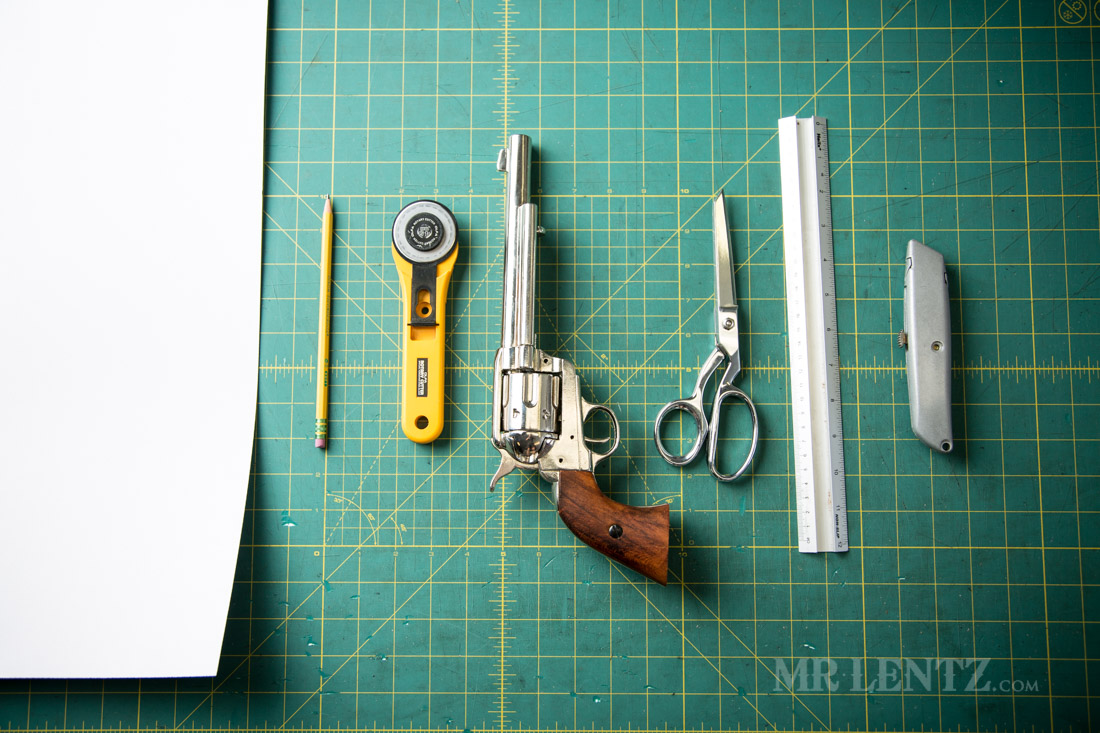
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Leather Holster Production?
Quality control (QC) is critical in ensuring that leather holsters meet international standards and buyer expectations. Implementing a robust QC process involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing stages.
How Do International Standards Apply to Leather Holster Manufacturing?
For manufacturers targeting international markets, adherence to standards such as ISO 9001 is vital. This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that processes consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
Industry-specific certifications, like CE marking in Europe, ensure that products meet safety and environmental standards. For regions like the Middle East, compliance with local regulations can also be necessary, emphasizing the importance of understanding regional requirements.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints can be categorized into three main areas:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Ensuring that the leather meets specified quality standards is crucial.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, random inspections should be conducted to monitor the quality at various stages, including forming, assembly, and finishing. This helps identify any deviations early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the holsters are completed, a thorough inspection should be conducted to assess overall quality, fit, and finish. This is the last line of defense to ensure that only products meeting specifications are shipped.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Quality?
Common testing methods for leather holsters include:
– Durability Testing: Assessing the strength of seams and the leather’s resistance to wear.
– Fit Testing: Ensuring that the holster securely fits the intended firearm.
– Environmental Testing: Evaluating the leather’s performance under various conditions, such as moisture exposure.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers. Here are several strategies to ensure compliance with quality standards:
What Audit Practices Should Be Considered?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control practices. Buyers should assess the following:
– Certification Verification: Ensure that suppliers hold relevant certifications such as ISO 9001.
– Production Facility Visits: If feasible, visiting the manufacturing site can provide direct insight into the processes and quality measures in place.
How Can Reports and Third-Party Inspections Assist in Quality Assurance?
Requesting quality control reports from suppliers can help buyers assess compliance with specified standards. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the product quality before shipment.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
What Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
For buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of international trade, including tariffs, import regulations, and local market standards, is essential. Establishing clear communication channels and expectations regarding quality can mitigate potential risks associated with international procurement.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for leather holsters are intricate and require careful attention to detail. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to make a leather holster’
To assist B2B buyers in the leather holster manufacturing industry, this practical sourcing guide outlines the essential steps for procuring the necessary materials and expertise to create high-quality leather holsters.
Step 1: Identify Your Target Market
Understanding the specific needs and preferences of your target market is crucial for successful product development. Research the demographics, regional preferences, and legal regulations regarding holsters in your target regions—particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Tailoring your designs and materials to fit these markets can significantly enhance your product’s acceptance and sales potential.
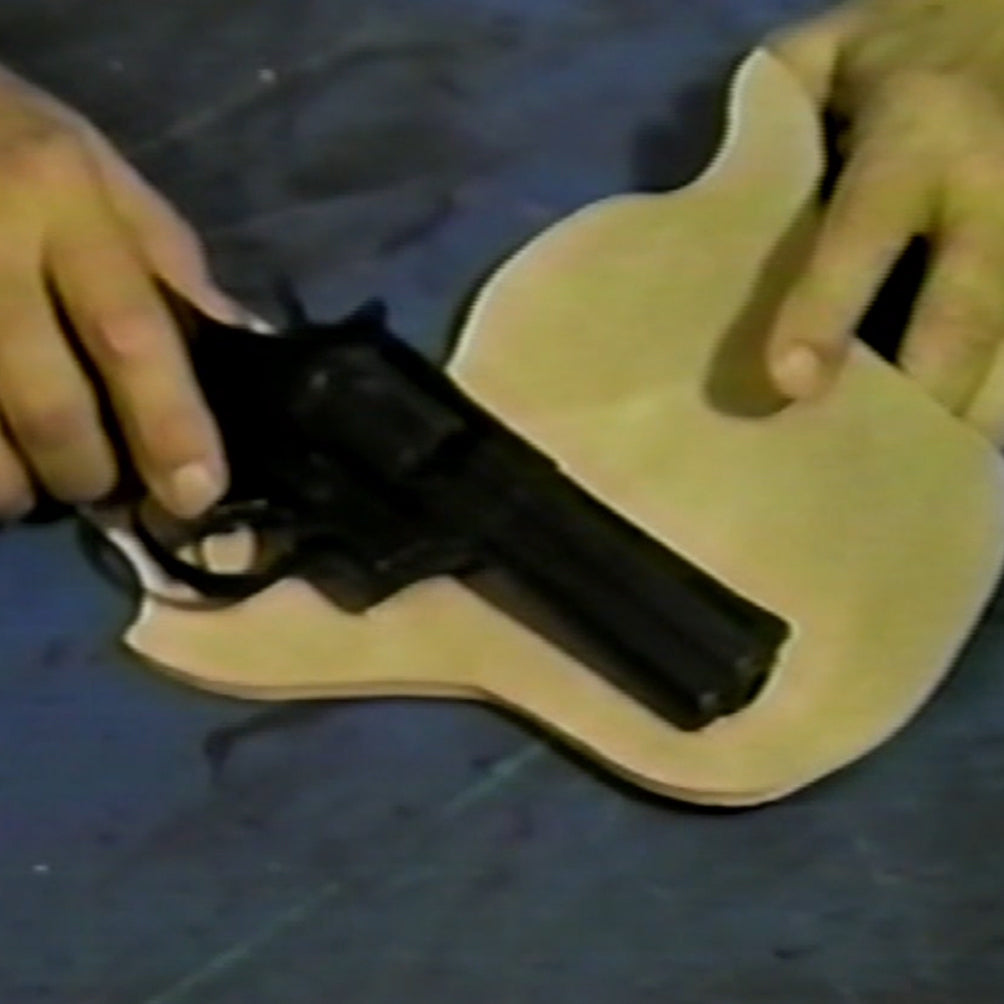

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Step 2: Source Quality Leather
Selecting the right leather is foundational to producing a durable and functional holster. Aim for 7-8 oz vegetable-tanned full-grain leather, which is both strong and aesthetically pleasing. Avoid chrome-tanned leather, as it can corrode metal parts of firearms. Ensure that suppliers can provide documentation of leather quality and origin, which is essential for compliance and customer trust.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s vital to conduct thorough evaluations. Request samples of leather and other materials to assess their quality and suitability for holster making. Check for customer reviews, case studies, and references from other businesses in the industry to gauge reliability and performance. This step helps mitigate risks associated with poor-quality materials.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that your suppliers adhere to international and regional standards for leather products. This includes environmental regulations regarding tanning processes and product safety standards. Compliance not only protects your business from legal issues but also enhances your brand’s reputation in the marketplace.
Step 5: Assess Supplier Production Capabilities
Understanding the production capabilities of your suppliers is essential for planning your inventory and meeting demand. Inquire about their production capacity, lead times, and ability to scale operations. This information is vital for developing a reliable supply chain and ensuring timely delivery of your holsters.
Step 6: Consider Customization Options
Customization can set your product apart in a competitive market. Engage with suppliers who offer custom patterns and sizes tailored to various firearm models. This flexibility can attract a broader customer base and increase market share. Discuss the potential for co-branding or exclusive designs that align with your business strategy.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implementing a robust quality control process is critical for maintaining product consistency and customer satisfaction. Define clear quality metrics and standards for leather thickness, stitching quality, and overall design. Regular audits and inspections during production can help identify issues early, reducing waste and ensuring a high-quality final product.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively source the materials and expertise needed to create high-quality leather holsters tailored to their specific market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to make a leather holster Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Making a Leather Holster?
When sourcing leather holsters, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and pricing strategies. The primary components include:
-
Materials: High-quality leather is paramount. For holsters, vegetable-tanned full-grain leather, typically 7-8 oz in thickness, is recommended. Prices for this material can range from $5 to $10 per square foot, depending on the supplier and the leather’s origin. Additional materials such as adhesives, threads, and hardware (like Chicago screws) should also be factored in, potentially adding an extra $2 to $5 per holster.
-
Labor: Labor costs will vary based on location and skill level. In regions like Europe and North America, skilled labor costs can range from $20 to $50 per hour. In contrast, countries in Africa and South America may offer lower labor rates, ranging from $5 to $15 per hour. The complexity of the holster design will dictate the total labor hours required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and indirect labor. A rough estimate for overhead can be about 15-25% of total production costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for molds and cutting tools can be significant but are often amortized over large production runs. Expect to invest $500 to $2,000 for quality tools, depending on the complexity of the holster designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that every holster meets quality standards is crucial. QC processes can add approximately 5-10% to the total production cost, depending on the level of scrutiny and testing required.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary widely based on the origin and destination. International shipping can add $1 to $3 per unit, depending on the shipping method and Incoterms. For bulk orders, consider using sea freight to reduce costs.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin of 20-50% on top of total costs, influenced by market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Leather Holster Sourcing?
Several factors can significantly influence pricing for B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically yield better pricing due to economies of scale. Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary, so negotiating favorable terms is essential.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or unique specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Sourcing from suppliers that provide certified materials (e.g., eco-friendly leather) may incur higher costs but can add value in the market.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often provide better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs and risks. This can affect total landed costs significantly.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Leather Holster Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Build strong relationships with suppliers to negotiate better prices, especially for repeat orders. Leverage your purchasing power as a B2B buyer.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate total cost of ownership, which includes not only the initial purchase price but also shipping, duties, and potential returns or defects.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions have varying pricing structures and expectations. For instance, buyers in the Middle East may prioritize quick delivery, while those in South America may focus more on cost.
-
Quality Over Price: While lower prices may be appealing, investing in higher-quality materials and craftsmanship can reduce long-term costs associated with returns and customer dissatisfaction.
Disclaimer
Prices and costs mentioned are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to ensure the best sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to make a leather holster With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Methods for Leather Holster Creation
In the world of leather holster production, various methods and technologies exist that cater to the needs of different manufacturers and artisans. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their production processes, costs, and product quality. This analysis compares the traditional method of making a leather holster with two viable alternatives: synthetic holster production and injection molding techniques.
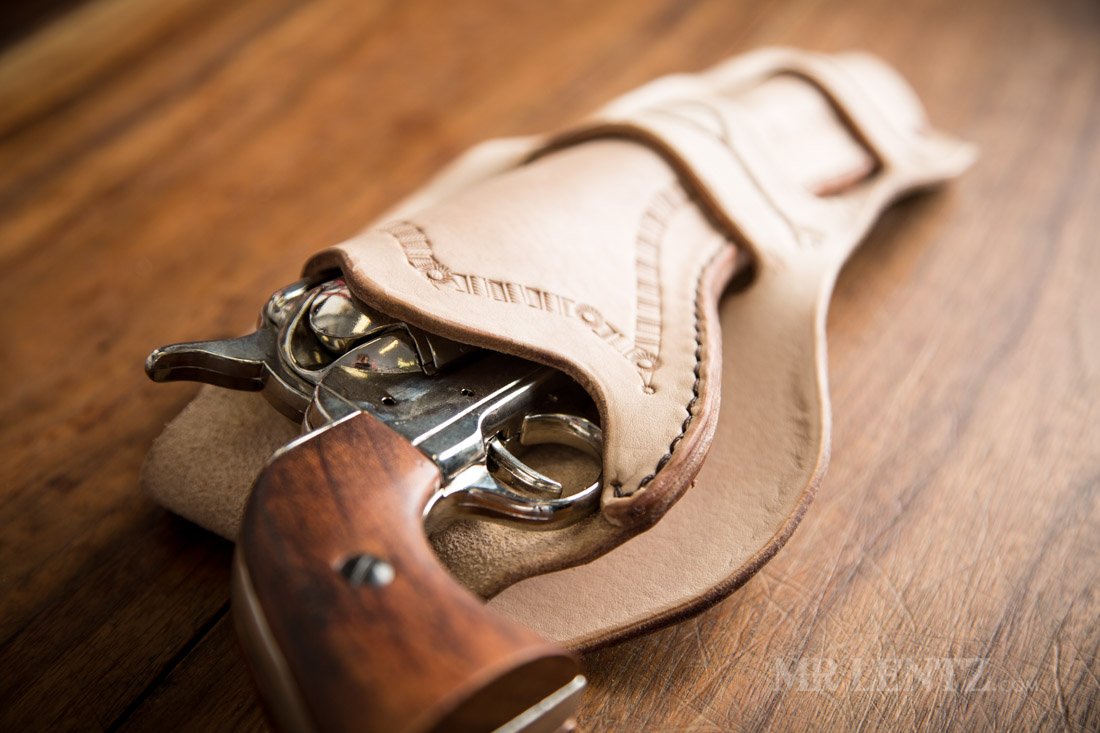

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How to Make a Leather Holster | Synthetic Holster Production | Injection Molding Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability and custom fit | Moderate durability, less custom fit | High durability, consistent quality |
| Cost | Moderate to high (materials & labor) | Lower initial cost, but potential for higher long-term costs | High initial setup cost, but low production costs per unit |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and time | Easier, less skilled labor needed | Requires specialized equipment and design skills |
| Wartung | Requires regular care (oiling, conditioning) | Minimal maintenance required | Low maintenance, but disposal issues |
| Best Use Case | Custom, high-end markets | Mass production for budget-conscious consumers | High-volume production with uniform specifications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Synthetic Holster Production
Synthetic holsters are made from materials such as nylon or Kydex, which offer several advantages over traditional leather. They are often lighter and more resistant to the elements, which makes them suitable for outdoor and tactical applications. However, while synthetic options can be produced at a lower initial cost, they may not provide the same level of durability or aesthetic appeal as leather. Additionally, they typically lack the custom fit and comfort that leather holsters offer, making them less desirable for high-end or bespoke markets.
2. Injection Molding Techniques
Injection molding involves creating holsters from thermoplastic materials that are molded to fit specific firearm models. This method allows for high-volume production and consistent quality, making it ideal for manufacturers looking to scale operations. Although the initial setup cost for injection molding can be significant due to the need for specialized molds and machinery, the cost per unit decreases as production scales. However, injection-molded holsters may not offer the same level of customization and luxury feel as leather options, which could limit their appeal in markets that prioritize craftsmanship and personal touch.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Holster Production Method
For B2B buyers, selecting the right method for holster production involves evaluating multiple factors including performance, cost, and target market. If the goal is to produce high-quality, custom-fit holsters for niche markets, traditional leather crafting remains a strong choice despite its higher labor costs and maintenance requirements. On the other hand, if the priority is to achieve lower costs and faster production times for mass-market products, synthetic materials or injection molding may be more suitable. Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific needs of the business, the expectations of the target audience, and the desired balance between quality and cost-efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to make a leather holster
What Are the Key Technical Properties Essential for Making a Leather Holster?
When it comes to crafting a leather holster, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for ensuring quality, durability, and functionality. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The choice of leather is paramount. For holsters, a material grade of 7-8 oz vegetable-tanned full-grain leather is recommended. This type of leather offers high durability, resistance to wear, and less stretch, which is essential for maintaining the holster’s shape and ensuring a snug fit for firearms. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing leather that meets this specification to enhance the longevity of their products. -
Tolerance and Thickness
Leather thickness is typically measured in ounces, with each ounce representing approximately 1/64 of an inch. A tolerance of ±0.5 oz is acceptable for holster production. This specification is important because variations in thickness can affect the holster’s fit and functionality. Consistency in thickness ensures that the holster maintains its shape and provides adequate protection for the firearm. -
Stitching Specifications
The stitching used in leather holsters should be robust, typically involving a thread size of 0.8 mm to 1.0 mm for added strength. The stitching method, whether saddle stitch or machine stitch, must also be specified. Proper stitching not only contributes to the aesthetic but also affects the durability and load-bearing capacity of the holster. B2B buyers should specify these details in their production contracts to ensure a reliable product. -
Edge Finishing
The edges of the holster should be beveled and finished to prevent fraying and enhance the overall appearance. A chamfer angle of 45 degrees is often used for a clean finish. This finishing process not only improves aesthetics but also reduces wear and tear, which is essential for maintaining the product’s quality over time. Buyers should inquire about edge finishing techniques when evaluating suppliers. -
Moisture Resistance
Leather holsters should ideally be treated for moisture resistance, especially in regions with high humidity or exposure to elements. This treatment prolongs the lifespan of the leather and prevents mold and mildew growth. B2B buyers should consider suppliers who offer moisture-resistant options to ensure their products can withstand various environmental conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Leather Holster Manufacturing Industry?
Understanding industry-specific jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the leather holster industry, an OEM might provide leather or hardware components that other brands incorporate into their finished products. This term is vital for buyers looking to source specific components for their holster designs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. In leather holster production, MOQs can vary significantly based on the complexity of the design and the materials used. Understanding MOQs is crucial for buyers to manage inventory and production costs effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific goods or services. In leather holster manufacturing, an RFQ would detail the specifications, quantities, and timelines for delivery. This term is essential for initiating the procurement process and ensuring competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing materials internationally, as they clarify costs, risks, and logistics responsibilities. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In the leather holster industry, lead times can vary based on factors such as material availability and production schedules. Buyers must understand lead times to effectively manage their supply chain and customer expectations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance product quality and streamline procurement processes in the leather holster market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to make a leather holster Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in Leather Holster Manufacturing?
The leather holster market is currently experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for personalized and custom-made firearm accessories. Factors such as rising disposable incomes, heightened interest in outdoor activities, and a growing culture of self-defense have contributed to this surge. Additionally, technological advancements in design and manufacturing processes are enabling producers to create more tailored and functional products. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should note that market dynamics are shifting towards an emphasis on quality craftsmanship and unique designs, which are often preferred over mass-produced alternatives.
Emerging trends include the adoption of digital tools for design and pattern-making, facilitating rapid prototyping and customization. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer innovative solutions, such as 3D printing for molds or CAD software for accurate designs. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms is simplifying global sourcing, allowing buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and products. As competition intensifies, businesses that invest in branding and customer engagement will likely gain a significant edge, particularly in regions where traditional craftsmanship is highly valued.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Leather Holster Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the leather holster sector. The environmental impact of leather production is under scrutiny, prompting manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices. This includes sourcing leather from tanneries that prioritize eco-friendly processes, such as vegetable tanning, which avoids harmful chemicals associated with chrome tanning. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards and certifications, as this not only reduces ecological footprints but also enhances brand reputation.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Moreover, ethical supply chains are essential in fostering consumer trust and loyalty. B2B buyers should inquire about the sourcing practices of their suppliers, ensuring that they adhere to fair labor practices and support local communities. The growing trend towards transparency means that businesses that can provide verifiable claims of ethical sourcing will likely gain a competitive advantage. Using ‘green’ certifications, such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification, can further validate a company’s commitment to sustainability, attracting conscientious consumers and B2B partners alike.
What Is the Historical Context of Leather Holster Manufacturing?
The practice of leather holster making has evolved significantly over the centuries, tracing back to the early days of firearm use. Initially, holsters served a purely functional purpose, designed to protect the weapon and provide easy access. As firearms became more popular, the demand for holsters grew, leading to advancements in materials and techniques.
In the early 20th century, the introduction of mass production techniques made holsters more widely available, but it wasn’t until the late 20th and early 21st centuries that customization became a key focus. Today, the leather holster industry reflects a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern technology, enabling artisans and manufacturers to create unique, high-quality products that meet the specific needs of users. This evolution underscores the importance of understanding historical trends for B2B buyers looking to make informed sourcing decisions in a competitive market.
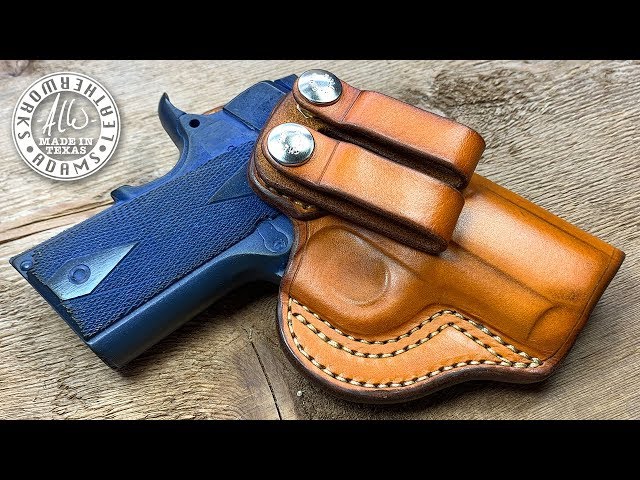

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to make a leather holster
-
How do I choose the right leather for making a holster?
Selecting the appropriate leather is crucial for durability and fit. Opt for vegetable-tanned leather in the 7-8 oz range, as it offers the right balance of strength and flexibility. Avoid chrome-tanned leathers, as they can rust firearms and lack durability. When sourcing leather, prioritize reputable suppliers who can guarantee quality. Inspect the hide to ensure you are using the back, which is smoother and less stretchy than the belly or neck areas. Always request samples to verify the leather’s characteristics before placing a bulk order. -
What tools do I need to make a leather holster?
Essential tools for crafting a leather holster include a sharp utility knife or band saw for cutting, a stitching groover, a hole punch, and stitching needles. You’ll also require adhesives like Barge Cement or PVA glue, clamps for holding pieces together, and finishing tools such as a chamfer tool and sandpaper for smoothing edges. Additionally, having a vacuum bag for forming the leather around the gun can enhance precision. Investing in quality tools will streamline the production process and improve the final product’s quality. -
How can I customize holsters for different firearm models?
Customizing holsters requires creating a specific template for each firearm model. Start by measuring the firearm accurately and designing a pattern that accommodates its dimensions and contours. You can use CAD software for precision or hand-drawn templates. After cutting the leather, ensure the assembly process allows for adjustments. Partnering with experienced craftsmen or suppliers who specialize in custom designs can also facilitate tailored solutions that meet your clients’ needs effectively. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for leather holsters?
MOQs can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, for custom leather holsters, you might encounter MOQs ranging from 50 to 100 units. However, some manufacturers may accommodate smaller orders, especially for new B2B relationships. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate the best terms. Consider consolidating orders for various models to meet MOQ requirements while providing your customers with a diverse selection. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing holsters internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common options include advance payments, letters of credit, or net terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). For initial orders, suppliers may require a partial upfront payment to cover material costs. As trust builds, you may negotiate more favorable terms. Be sure to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, PayPal) and any associated fees before finalizing agreements. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my leather holster orders?
Establishing quality assurance measures is vital for maintaining product standards. Request samples before committing to larger orders, and consider conducting factory visits or audits if feasible. Define specific quality benchmarks in your purchase agreement, including leather thickness, stitching quality, and finish. Additionally, implementing a third-party inspection service can help ensure compliance with your quality expectations before shipment, minimizing risks associated with defects. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipping?
International shipping entails various logistical challenges, including customs clearance, duties, and shipping costs. Ensure you understand the regulations in both the exporting and importing countries. Working with a reliable freight forwarder can simplify the process, as they can manage paperwork and provide guidance on the best shipping methods. Additionally, consider lead times and potential delays, especially for customized orders, to keep your clients informed and satisfied. -
How can I market my leather holsters to different regions?
Marketing strategies should be tailored to the cultural and economic contexts of each region. Conduct market research to identify specific consumer preferences and trends in your target markets, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Utilize online platforms, social media, and trade shows to showcase your products. Collaborating with local distributors or influencers can also enhance visibility. Consider language and cultural nuances in your marketing materials to resonate with diverse audiences effectively.
Top 5 How To Make A Leather Holster Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Instructables – Fitted Leather Holster for Colt 1911
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Fitted Leather Holster for Colt Model 1911 .45 Caliber pistol; made from heavy weight leather (approximately 8 oz); formed using isopropyl alcohol (recommended to use water instead); assembly involves gluing two halves with Barge Cement or E6000; includes belt loops for proper angle; stitching with leather stitching groover and overstitching tool; finished with Neatsfoot oil for moisture and darke…
2. Tandy Leather – Holster Design Tutorial
Domain: tandyleather.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Tandy Leather – Holster Design Tutorial, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. MR Lentz – Leather Holster Tutorial
Domain: mrlentz.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: How to Make a Leather Holster tutorial includes the following key product details: 1. Leather Type: 7-8 oz vegetable tanned full grain leather recommended. 2. Tools and Materials Needed: Mallet, 5/16 hole punch, PVA leather glue, silicon tipped glue spreader, 6 stitch per inch marking wheel, beveler for tight curves, stitch line marking tool, scratch awl, red speedball pen, utility knife, scissors…
4. Leatherworker – Holster Manufacturing Time
Domain: leatherworker.net
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Average time to make a holster ranges from 3 to 10 days depending on the complexity and drying times. A pancake holster can take 4 to 5 hours of labor, with additional drying time of 8 hours for wet molding. Some users reported total times of 3 days including drying, while others mentioned 24 hours for molding and finishing. Prices for holsters vary, with examples given of $70 for law enforcement …
5. Reddit – 1911 Holster Making Techniques
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Holster making for a 1911 gun; techniques include tracing the gun’s silhouette on leather, leaving extra room for fit, ensuring trigger coverage, using a thick folder for pattern making, and wet molding vegetable-tanned leather.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to make a leather holster
In conclusion, the art of crafting leather holsters presents a unique opportunity for B2B buyers to harness quality materials and skilled craftsmanship. Strategic sourcing of high-grade leather, particularly vegetable-tanned varieties, is paramount to ensuring durability and functionality. By prioritizing reliable suppliers and understanding the nuances of leather types, businesses can enhance product offerings and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, the meticulous process of holster creation—from forming and assembly to finishing—emphasizes the importance of precision and attention to detail. This not only elevates the final product but also strengthens brand reputation in competitive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As global demand for quality leather goods continues to rise, now is the time to invest in robust sourcing strategies. By establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers and leveraging innovative techniques, your business can lead in the leather holster market. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your product line and meet the evolving needs of your clientele. Take the first step today towards a successful future in leather craftsmanship.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
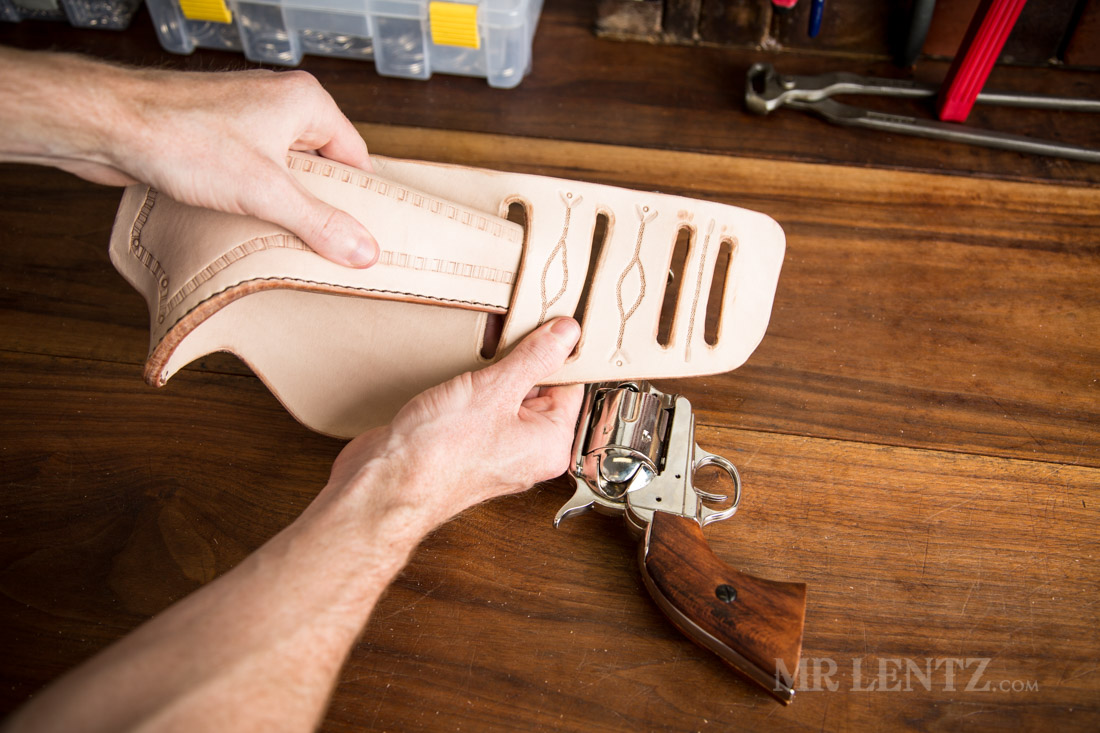

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather holster