Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fabric similar to leather
In an era where sustainability and ethical sourcing are at the forefront of consumer demands, navigating the global market for fabric similar to leather presents unique challenges for B2B buyers. Whether you’re sourcing high-quality upholstery materials for furniture or durable fabrics for fashion applications, understanding the diverse landscape of leather alternatives is crucial. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of materials available, from synthetic options like polyurethane and PVC to innovative plant-based alternatives such as mushroom and pineapple leather.
By delving into the applications, performance characteristics, and cost considerations of these alternatives, international B2B buyers—particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Saudi Arabia and Brazil—will be equipped to make informed purchasing decisions. The guide also emphasizes the importance of supplier vetting, offering practical insights on how to assess quality, sustainability, and compliance with international standards.
In a market characterized by rapid innovation and shifting consumer preferences, this resource empowers businesses to not only meet their material needs but also align with the growing demand for sustainable and ethically produced fabrics. Equip your procurement strategy with the knowledge to select the right fabric similar to leather, ensuring both quality and responsibility in your sourcing process.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Fabric Similar To Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fabric similar to leather
- Understanding fabric similar to leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of fabric similar to leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fabric similar to leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for fabric similar to leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fabric similar to leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fabric similar to leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fabric similar to leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fabric similar to leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fabric similar to leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fabric similar to leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fabric similar to leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fabric similar to leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
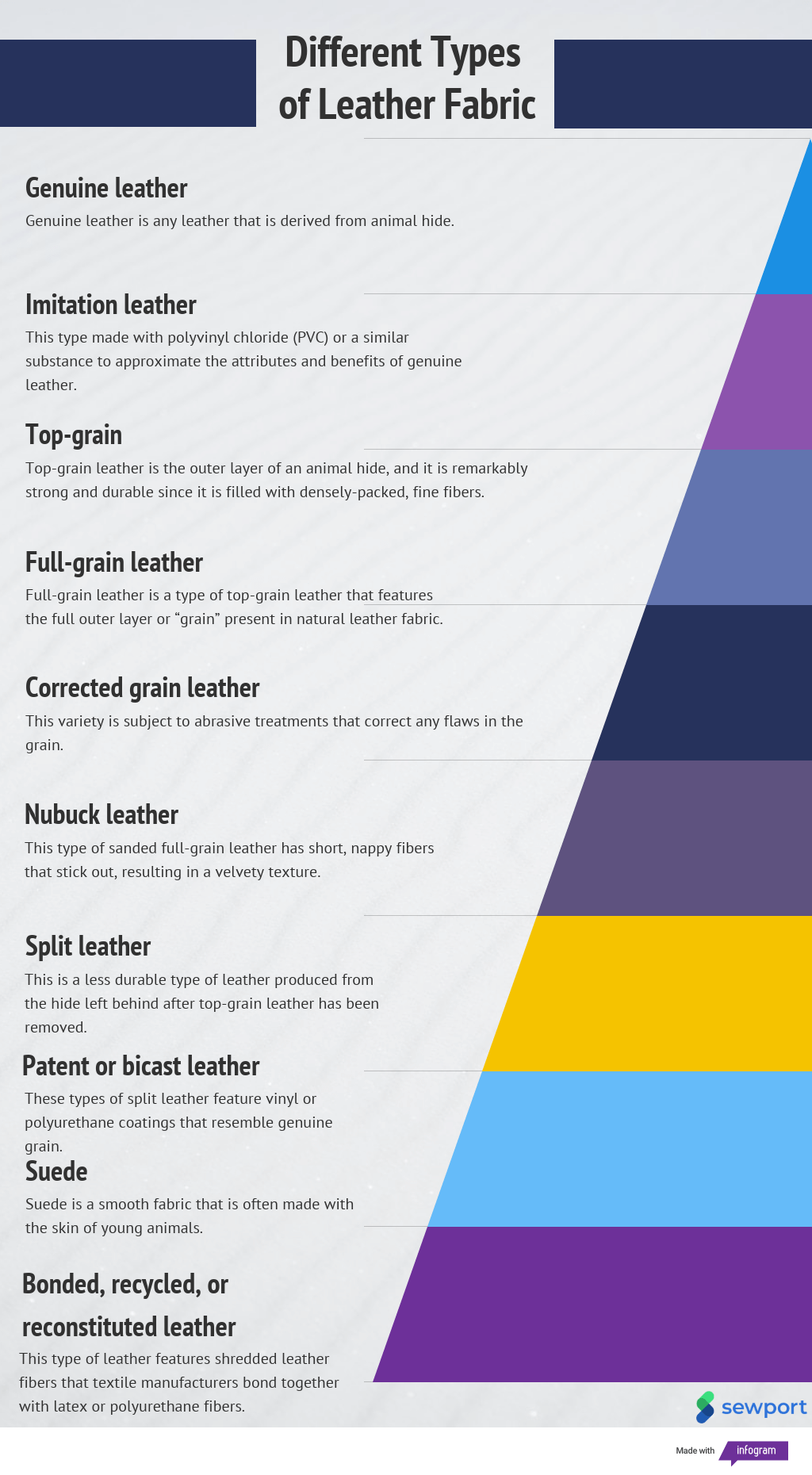
Understanding fabric similar to leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faux Leather (PVC/PU) | Made from synthetic materials, often coated with a plastic layer | Fashion, upholstery, automotive | Pros: Cost-effective, water-resistant. Cons: Less durable, environmental concerns. |
| Microsuede | Fine polyester fibers mimicking suede, highly stain-resistant | Apparel, furniture, accessories | Pros: Soft feel, breathable. Cons: Microplastic pollution, flammable. |
| Waxed Canvas | Natural fabric treated for water resistance, durable | Outdoor gear, bags, apparel | Pros: Aesthetically pleasing, biodegradable options. Cons: Requires maintenance, less durable. |
| Cactus Leather | Sustainable plant-based alternative, flexible and durable | Fashion, accessories, upholstery | Pros: Eco-friendly, unique texture. Cons: Limited availability, higher cost. |
| Apple Leather | Made from apple waste, biodegradable, offers a leather-like feel | Fashion, accessories, upholstery | Pros: Sustainable sourcing, unique branding. Cons: Durability may be variable. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Faux Leather (PVC/PU)?
Faux leather, primarily composed of PVC or polyurethane, is one of the most widely used leather alternatives. It mimics the look and feel of genuine leather while being significantly more cost-effective. Commonly employed in fashion, upholstery, and automotive industries, faux leather is appreciated for its water-resistant properties. However, buyers should consider its durability, as it can crack or flake over time, and its environmental impact due to plastic content.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
How Does Microsuede Compare to Traditional Leather?
Microsuede is crafted from fine polyester fibers designed to replicate the softness of suede. This material is highly stain-resistant and breathable, making it popular in apparel, furniture, and accessories. For B2B buyers, microsuede offers a luxurious feel at a lower cost. However, its production raises concerns about microplastic pollution, and it is also flammable, which may affect its suitability for certain applications.
Why Choose Waxed Canvas for Outdoor Applications?
Waxed canvas is a robust natural fabric treated with wax to enhance its water resistance, making it ideal for outdoor gear, bags, and apparel. This material combines aesthetic appeal with functionality, allowing for a unique look while being biodegradable. B2B buyers should note that while waxed canvas is durable, it does require regular maintenance to preserve its integrity, and its performance may not match that of synthetic alternatives.
What Are the Advantages of Cactus Leather?
Cactus leather is an innovative, sustainable alternative derived from the prickly pear cactus. Its flexibility and durability make it suitable for fashion, accessories, and upholstery. For environmentally conscious buyers, cactus leather represents a unique selling point and appeals to the growing demand for sustainable materials. However, availability can be limited, and prices may be higher compared to traditional synthetic options.
How Does Apple Leather Stand Out in the Market?
Apple leather, produced from apple waste, offers a biodegradable alternative with a leather-like texture. It is gaining traction in the fashion and accessory industries, particularly among brands focused on sustainability. B2B buyers may find apple leather advantageous for its unique branding potential and eco-friendly appeal. However, the durability of apple leather can vary, which necessitates thorough testing before large-scale applications.
Key Industrial Applications of fabric similar to leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fabric similar to leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Upholstery and interiors | Enhances aesthetic appeal, durability, and ease of maintenance | Ensure compliance with regional automotive standards and regulations |
| Fashion & Apparel | Clothing and accessories | Appeals to eco-conscious consumers, versatile design options | Sourcing sustainable materials that meet fashion trends and quality standards |
| Furniture & Home Decor | Upholstered furniture and decorative items | Offers luxury feel at lower costs, easy to clean and maintain | Evaluate durability, stain resistance, and environmental impact of materials |
| Footwear | Shoe linings and exteriors | Provides comfort, breathability, and style | Consider material flexibility and weight for different shoe types |
| Industrial & Commercial | Workwear and protective gear | Combines comfort with durability for demanding environments | Focus on abrasion resistance and compliance with safety regulations |
How is fabric similar to leather used in the automotive industry?
In the automotive sector, fabric similar to leather is extensively utilized for upholstery and interiors, offering an appealing aesthetic while ensuring durability and ease of maintenance. This alternative material provides a cost-effective solution that meets the design requirements of modern vehicles. International buyers should consider sourcing options that comply with regional automotive standards to ensure quality and longevity of the upholstery, especially in markets like Saudi Arabia and Brazil, where climate can impact material performance.
What are the benefits of using fabric similar to leather in fashion and apparel?
Within the fashion and apparel industry, fabrics similar to leather are increasingly popular for clothing and accessories, catering to the growing demand for sustainable and vegan options. These materials allow brands to appeal to eco-conscious consumers while maintaining versatility in design. For international buyers, it is crucial to source materials that not only align with current fashion trends but also meet rigorous quality standards, as markets in Europe and South America often prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing.
How does fabric similar to leather enhance furniture and home decor?
In furniture and home decor, fabric similar to leather is frequently used for upholstered pieces and decorative items, providing a luxurious feel without the high costs associated with genuine leather. These materials are also easier to clean and maintain, making them attractive to both manufacturers and consumers. Buyers should evaluate the durability and stain resistance of these fabrics, particularly in regions with varying climates, ensuring that the products can withstand wear and tear in diverse environments.
Why is fabric similar to leather important for footwear?
In the footwear industry, fabrics similar to leather are employed for both linings and exteriors, offering comfort, breathability, and stylish options for various shoe designs. The flexibility and lightweight nature of these materials can enhance overall shoe performance. International buyers must consider the specific requirements of different shoe types, ensuring that the sourced materials can withstand daily use while providing the necessary comfort and aesthetic appeal expected by consumers.
What role does fabric similar to leather play in industrial and commercial applications?
Fabric similar to leather is increasingly used in workwear and protective gear, combining comfort with durability to meet the demands of various industrial environments. This type of material can offer abrasion resistance and ease of maintenance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing materials that comply with safety regulations, particularly in regions where industrial standards are strictly enforced, ensuring both worker safety and product longevity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fabric similar to leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Concerns in Vegan Leather Options
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find high-quality alternatives to traditional leather. With the rise of various vegan leather products, distinguishing between genuinely durable options and inferior materials can be challenging. Many buyers report that they have received samples that looked promising but failed to hold up under normal usage conditions. This inconsistency not only affects product reputation but can also lead to increased returns and customer dissatisfaction.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should establish rigorous quality assessment protocols for sourcing vegan leather alternatives. This includes requesting detailed specifications and performance data from suppliers, such as abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and water resistance. Buyers should also consider conducting third-party testing on samples before making bulk orders. Furthermore, building relationships with reputable manufacturers known for their commitment to quality can ensure access to reliable materials. Attending industry trade shows and workshops can provide insights into new innovations in vegan leather and facilitate direct discussions with manufacturers about their production processes.
Scenario 2: Environmental Impact and Sustainability Certifications
The Problem: As sustainability becomes a priority for consumers, B2B buyers face pressure to ensure that the materials they source align with eco-friendly practices. Many fabrics marketed as “eco-friendly” often lack transparency regarding their environmental impact, leaving buyers uncertain about their actual sustainability credentials. This can lead to potential backlash from environmentally conscious customers and stakeholders.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that come with verifiable sustainability certifications, such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX® certification. Engaging with suppliers who provide clear documentation on the lifecycle of their materials, including sourcing, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life considerations, is crucial. Additionally, buyers can request a sustainability audit from suppliers to evaluate their practices. By leveraging platforms that specialize in sustainable materials and connecting with manufacturers committed to environmentally responsible practices, buyers can ensure that their sourcing decisions reflect genuine sustainability efforts.
Scenario 3: Addressing Cost vs. Performance Dilemmas
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the dilemma of balancing cost and performance when selecting fabrics similar to leather. While cheaper options may seem appealing, they often compromise on quality, leading to increased costs down the line due to replacements or repairs. Conversely, investing in high-quality materials can strain budgets, particularly for businesses operating in price-sensitive markets.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should adopt a total cost of ownership (TCO) approach when evaluating fabric options. This means considering not only the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with durability, maintenance, and potential replacements. Conducting a lifecycle analysis of different fabric options can help buyers make informed decisions. Additionally, exploring bulk purchasing agreements or long-term contracts with suppliers can provide cost savings. Collaborating with design teams to innovate and create products that maximize the performance of higher-quality materials can also justify the investment by enhancing the overall value proposition to end customers.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fabric similar to leather
What Are the Key Properties of Common Leather-Like Fabrics?
When selecting materials similar to leather, it’s essential to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for various applications. Here, we analyze four prevalent alternatives: Polyurethane (PU), PVC, Microsuede, and Cork Leather. Each material presents unique characteristics that can significantly impact the end product’s performance, durability, and market acceptance.
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Compare as a Leather Alternative?
Polyurethane is a synthetic material known for its flexibility and durability. It can mimic the texture and appearance of genuine leather while being lighter and more pliable. PU has good temperature resistance, typically performing well in moderate conditions, but it may not withstand extreme temperatures or prolonged exposure to UV light without degrading.
Pros: PU is relatively inexpensive, easy to clean, and available in various colors and textures. It is water-resistant, making it suitable for products exposed to moisture.
Cons: Over time, PU can crack or wear down, particularly in high-stress applications. Its production involves petrochemicals, raising environmental concerns.
Impact on Application: PU is widely used in fashion, upholstery, and automotive industries. However, buyers must ensure that the end products meet local environmental regulations.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of PVC?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is another synthetic alternative that is tough and versatile. It is often used in applications requiring durability and resistance to chemicals and moisture. PVC can withstand higher temperatures than PU, but it can become brittle in extreme cold.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and offers excellent water resistance, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and automotive interiors.
Cons: Its rigidity can limit its applications, and like PU, it is derived from petroleum, raising sustainability issues. PVC is also less breathable than other materials, which can impact comfort in clothing applications.
Impact on Application: PVC is commonly used in upholstery and automotive sectors, but compliance with environmental standards, particularly in Europe, is crucial for market acceptance.
How Does Microsuede Perform as a Leather Alternative?
Microsuede, made from polyester fibers, mimics the soft texture of suede while offering enhanced durability. It is breathable and stain-resistant, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including apparel and home furnishings.
Pros: Microsuede is easy to maintain, lightweight, and has a low water footprint during production. It provides comfort and aesthetic appeal similar to leather.
Cons: While microsuede is durable, it is susceptible to microplastic pollution and can release toxic fumes when incinerated. Its flammability is also a concern.
Impact on Application: Given its comfort and aesthetic qualities, microsuede is popular in fashion and upholstery. However, international buyers should consider local regulations regarding plastic materials.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
What Are the Unique Properties of Cork Leather?
Cork leather, derived from the bark of cork oak trees, is a sustainable alternative that is biodegradable and recyclable. It is lightweight, flexible, and offers a unique texture that can appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Pros: Cork leather is naturally water-resistant and has a low environmental impact, as it can be harvested without harming the tree.
Cons: Its durability may not match that of synthetic alternatives, and it often requires a backing material for added strength. Chemical treatments are necessary to enhance its longevity.
Impact on Application: Cork leather is gaining traction in eco-friendly fashion and accessories. Buyers should ensure compliance with sustainability certifications, which can vary by region.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for fabric similar to leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Fashion, upholstery, automotive | Flexible and durable | Can crack over time | Medium |
| PVC | Upholstery, automotive interiors | Cost-effective and water-resistant | Less breathable, environmental concerns | Low |
| Microsuede | Apparel, home furnishings | Soft texture, easy maintenance | Microplastic pollution, flammability | Medium |
| Cork Leather | Eco-friendly fashion, accessories | Sustainable and biodegradable | Durability concerns, requires backing | Medium |
Selecting the right material similar to leather involves a careful evaluation of these properties, pros and cons, and compliance with international standards, especially for B2B buyers in diverse markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fabric similar to leather
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Fabric Similar to Leather?
The manufacturing process for fabrics that mimic leather involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets quality and performance standards. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing materials.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing raw materials, which can include synthetic polymers like PVC and PU, natural fibers such as cotton or hemp, or innovative alternatives like mushroom or pineapple leather. Each material requires specific preparation methods. For instance, natural fibers must be cleaned, treated, and sometimes dyed to enhance durability and aesthetics. In contrast, synthetic materials undergo polymerization processes where chemical reactions produce the desired polymer base.
Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their material sourcing practices and sustainability standards. Transparency in sourcing can indicate the quality of the final product and its environmental impact.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Fabric Similar to Leather?
Once raw materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This stage involves various techniques, including extrusion, coating, and lamination. For instance, in the case of PVC and PU, the polymer is often extruded into sheets or coated onto a fabric base to create a flexible, leather-like texture.
Lamination may involve bonding multiple layers together to enhance durability and performance. For innovative materials like cork or mushroom leather, forming may require pressing or molding to achieve the desired texture and structure.
B2B buyers should inquire about the forming techniques used by suppliers, as these can significantly influence the product’s quality and usability.
Assembly: How Are Different Layers and Components Joined Together?
The assembly stage incorporates various components of the fabric. For synthetic leather alternatives, this may involve stitching or bonding layers of the fabric, including a backing that provides structural integrity. In contrast, natural fabrics may require additional treatments to ensure that they hold up under stress and usage.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
Quality in assembly is critical; poorly constructed products may lead to issues such as peeling, cracking, or premature wear. Buyers should consider suppliers’ capabilities in assembly techniques and the robustness of their finished products.
Finishing: What Finishing Techniques Enhance the Final Product?
Finishing processes are essential for achieving the desired aesthetic and functional qualities in fabric similar to leather. Techniques may include applying coatings for water resistance, embossing for texture, or dyeing for color. These finishing touches not only improve the product’s appearance but also enhance its durability and usability.
Buyers should request information on finishing techniques from potential suppliers, as these can vary widely and affect both the product’s performance and its marketability.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
What Are the Quality Assurance Measures for Fabric Similar to Leather?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product meets specific industry standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding these QA measures is crucial for maintaining supply chain integrity.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with relevant international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles applicable across industries. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for safety and environmental compliance or API standards for materials used in certain applications should also be considered.
Compliance with these standards not only demonstrates a supplier’s commitment to quality but also enhances the credibility of the product in international markets.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify their quality and conformity to specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify and rectify issues before they escalate.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product ensures it meets all quality standards before shipment.
Implementing these QC checkpoints can help mitigate risks and ensure that only high-quality products reach the market.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Product Quality?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality of fabric similar to leather. Common tests include:
- Durability Testing: Evaluating the material’s resistance to wear and tear.
- Water Resistance Testing: Assessing the fabric’s ability to repel water and prevent damage.
- Flammability Testing: Ensuring compliance with safety regulations regarding fire resistance.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Evaluating how well the fabric withstands exposure to various chemicals.
B2B buyers should request information on the specific testing methods used by suppliers to ensure that products meet their needs.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Ensuring that suppliers adhere to robust quality control practices is essential for B2B buyers. Here are several strategies for verification:

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Buyers can perform on-site audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. These audits provide valuable insights into the supplier’s capabilities and commitment to quality.
How Can Buyers Request Quality Control Reports?
Buyers should request detailed quality control reports from suppliers. These reports should outline testing results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues. A thorough review of these documents can help buyers gauge the reliability of the supplier.
Should Buyers Consider Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These services often include product testing, factory audits, and compliance checks, offering an additional layer of assurance for B2B buyers.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have specific quality standards and regulations that suppliers must comply with. Buyers should be aware of these regional nuances, as they can affect product availability, cost, and compliance.
What Should Buyers Know About Cultural and Communication Differences?
Cultural differences may influence how quality control practices are implemented and communicated. B2B buyers should foster open lines of communication with suppliers to ensure mutual understanding of quality expectations and standards.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for fabric similar to leather, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions, ensuring that they procure high-quality products that meet their specific needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fabric similar to leather’
This guide provides a structured approach for B2B buyers looking to source fabrics similar to leather, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business needs and sustainability goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by outlining the specific characteristics you require from the fabric. Consider factors such as durability, water resistance, breathability, and aesthetic appeal. Clearly defining these parameters will help streamline your search and ensure that the materials you consider meet your application requirements.
- Durability: Assess the fabric’s resistance to wear and tear.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Determine whether you need a specific texture or color that aligns with your brand.
Step 2: Research Available Alternatives
Explore the various types of leather-like fabrics available in the market, such as synthetic options (PVC, PU), natural alternatives (cork, waxed cotton), and innovative materials (mushroom, pineapple leather). Understanding these alternatives will help you identify which materials best fit your sustainability and performance criteria.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
- Synthetic Options: Note that while these may be cost-effective, they often have environmental implications.
- Natural Alternatives: These options can offer unique aesthetics but may require specific care and handling.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify the certifications of potential suppliers to ensure compliance with international standards for quality, safety, and sustainability. Certifications like OEKO-TEX, GOTS, and others can provide assurance that the materials are responsibly sourced and produced.
- Quality Assurance: Look for suppliers with a track record of delivering high-quality materials.
- Sustainability Practices: Ensure that the supplier adheres to sustainable practices that align with your company’s values.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the fabrics you’re considering. Testing these samples for performance, durability, and aesthetics will provide valuable insights into how well they meet your specifications.
- Performance Testing: Check for water resistance, flexibility, and ease of cleaning.
- Aesthetic Evaluation: Assess the look and feel of the fabric in real-world applications.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, initiate negotiations on pricing, minimum order quantities, and payment terms. Understanding the total cost of ownership—including shipping, duties, and any potential tariffs—is crucial for budgeting.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders or long-term contracts.
- Payment Flexibility: Ensure the terms are favorable and align with your cash flow requirements.
Step 6: Establish a Clear Communication Channel
Set up a reliable communication channel with your chosen supplier to facilitate ongoing discussions regarding order updates, quality assurance, and potential issues. Effective communication helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures a smoother procurement process.
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to discuss order status and any changes in specifications.
- Feedback Mechanism: Establish a process for providing feedback on product quality and supplier performance.
Step 7: Plan for End-of-Life Management
Consider the end-of-life implications of the materials you source. Evaluate how the fabrics can be disposed of or recycled at the end of their lifecycle. This step is critical for ensuring that your sourcing aligns with sustainability goals.
- Recyclability: Investigate whether the materials can be recycled or repurposed.
- Waste Management: Develop a plan for managing waste effectively to minimize environmental impact.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing fabrics similar to leather, ultimately enhancing product quality and aligning with sustainability objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fabric similar to leather Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of fabrics similar to leather is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will cover the key components of cost, the influencers of pricing, and provide actionable tips for buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategy.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Fabric Similar to Leather?
The cost structure for sourcing fabric alternatives to leather comprises several critical components:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver, material selection influences the overall pricing significantly. For instance, synthetic materials like PVC and PU are typically cheaper than natural alternatives like cork or plant-based leathers, which may have higher sourcing costs due to limited availability and processing requirements.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. Manufacturing locations in Asia may offer lower labor costs compared to Europe or North America, but this can be offset by quality considerations and compliance with labor standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs, impacting the final pricing of the fabric.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom designs can be substantial, especially for unique fabric patterns or textures. Buyers should consider whether the tooling costs can be amortized over larger order volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Maintaining quality standards incurs costs, particularly for materials that require rigorous testing and certification (e.g., eco-friendly certifications). This aspect is crucial for buyers in regions with stringent quality requirements.
-
Logistics: Freight costs can vary widely based on the shipping method, distance, and Incoterms. International buyers must factor in potential tariffs, customs duties, and delivery timelines when calculating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the typical margins in the fabric industry can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Fabric Similar to Leather?
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders usually qualify for volume discounts. Understanding the MOQ requirements of suppliers can lead to better pricing arrangements.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized fabrics or specific performance characteristics (e.g., waterproofing, UV resistance) can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the additional features are necessary for their application.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with sustainability certifications typically command higher prices. Buyers should assess the long-term value these materials offer against their immediate costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capacity can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better service but at a premium.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly affect logistics costs. Terms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) may lead to higher prices due to included shipping costs, while EXW (Ex Works) might offer lower upfront pricing but require buyers to manage logistics.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Optimize Costs When Sourcing Fabric?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume purchases and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers may be more willing to offer discounts for committed business.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential waste disposal of the fabric. A higher upfront cost may result in lower TCO if the material lasts longer.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Trade: Understand currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing, especially in markets like Africa and South America. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local market conditions and demand trends that may influence pricing.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Evaluate multiple suppliers to understand market pricing and identify competitive offers. Look for suppliers that provide transparent pricing models.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: The fabric market is evolving rapidly, particularly with the rise of sustainable and innovative materials. Staying informed can help buyers make strategic sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and other external factors. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence to ascertain the most accurate pricing for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fabric similar to leather With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives: Comparing Fabric Similar to Leather with Other Solutions
The demand for sustainable materials has led to a surge in interest for fabrics that mimic leather. As B2B buyers evaluate their options, understanding how these alternatives stack up against traditional fabric similar to leather becomes essential. This section provides a comparative analysis of ‘fabric similar to leather’ against two viable alternatives: polyurethane (PU) leather and waxed cotton canvas.
| Comparison Aspect | Fabric Similar To Leather | Polyurethane (PU) Leather | Waxed Cotton Canvas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, flexible, water-resistant; resembles leather closely | Durable, flexible, but less breathable than genuine leather | Less durable than leather; water-resistant when treated |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on the material source | Generally lower cost; varies by quality | Typically lower cost; very affordable option |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific manufacturing processes; may need skilled labor | Easy to implement in manufacturing; widely available | Simple production process; easy to source materials |
| Maintenance | Requires regular care to maintain appearance | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Requires regular reapplication of wax for durability |
| Best Use Case | Fashion, upholstery, automotive applications | Fashion accessories, upholstery, footwear | Outdoor gear, bags, and casual apparel |
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Leather Compare?
Polyurethane leather has gained significant traction as a synthetic alternative to traditional leather. One of its main advantages is cost; PU leather is generally more affordable than fabric similar to leather, making it accessible for budget-conscious projects. Its production is straightforward, allowing for rapid manufacturing and consistent quality. However, while PU leather mimics the appearance of genuine leather, it may lack breathability and long-term durability. Additionally, concerns about its environmental impact arise due to its petroleum-based origins, making it less appealing for eco-conscious buyers.
What Are the Advantages of Waxed Cotton Canvas?
Waxed cotton canvas stands out as a more natural alternative, offering a unique aesthetic and functional benefits. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to work with, making it suitable for a variety of applications, from bags to outdoor gear. The wax treatment provides water resistance, enhancing its utility in outdoor settings. However, it is essential to note that waxed cotton is less durable than both fabric similar to leather and PU leather, necessitating regular maintenance to prolong its life. While it is an eco-friendlier option, its performance may not meet the expectations of high-end fashion applications.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When selecting the right material, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and environmental impact. Fabric similar to leather offers a premium feel and durability, making it ideal for luxury items. In contrast, PU leather presents a cost-effective and easy-to-manufacture option, albeit with potential environmental trade-offs. Waxed cotton canvas, while the most affordable and sustainable, may not match the performance standards required for high-end products. By thoroughly evaluating these alternatives, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their brand values and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fabric similar to leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Fabric Similar to Leather?
When sourcing fabric similar to leather, understanding specific technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Composition
The fabric’s composition directly impacts its durability, feel, and application. Common materials include polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and natural fibers like cotton or hemp. B2B buyers should assess the material composition to align with end-use requirements, such as whether the fabric will be used in automotive interiors, fashion, or upholstery.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
2. Tensile Strength
This property measures the fabric’s resistance to being pulled apart and is crucial for applications that require durability. High tensile strength indicates that the fabric can withstand significant stress without tearing, making it essential for industries like furniture manufacturing. Buyers should look for tensile strength ratings to ensure the fabric meets their specific performance criteria.
3. Water Resistance
Water resistance is an important property for fabrics intended for outdoor use or products exposed to moisture. Many synthetic alternatives offer varying degrees of water repellency, which can enhance longevity and usability. B2B buyers should inquire about water resistance ratings to ensure the fabric is suitable for their intended applications.
4. Flame Retardancy
Certain applications, especially in the automotive and aviation industries, require materials to meet specific flame retardancy standards. This property indicates how well the fabric can withstand ignition and slow the spread of flames. Buyers should verify compliance with relevant safety standards to ensure their products meet regulatory requirements.
5. Biodegradability
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, the biodegradability of materials is a significant consideration. Fabrics made from natural fibers or innovative materials like mushroom leather often have better environmental profiles. B2B buyers should assess the end-of-life options for the fabrics they select, as this can influence both brand perception and regulatory compliance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Fabric Similar to Leather?
Understanding industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms used in the trade of fabric similar to leather:
Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products or components that are sold under another company’s brand name. In the context of fabric, this could involve a supplier producing custom fabric for an automotive or furniture manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify potential partners for tailored products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory management and pricing. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can help in planning purchases and managing cash flow effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This is especially important in B2B settings where bulk purchases are common. Crafting a clear RFQ can ensure that suppliers provide accurate quotes that meet the buyer’s specifications.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers negotiate favorable terms and understand their liabilities during the shipping process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes for a supplier to fulfill an order from the moment it is placed until delivery. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is essential for supply chain management and ensuring that products are available when needed.
By familiarizing themselves with these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing fabric similar to leather, optimizing both product quality and operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fabric similar to leather Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics Driving the Fabric Similar to Leather Sector?
The global fabric similar to leather market is witnessing significant transformation, influenced by a blend of sustainability trends, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. The rise of eco-conscious consumerism is reshaping demand, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers in these markets are increasingly inclined toward alternatives that are perceived as more sustainable, such as vegan leathers made from plant-based materials, including pineapple, apple, and cactus fibers. Moreover, technological innovations are facilitating the development of synthetic and engineered materials that mimic leather’s aesthetic and functional properties while offering enhanced performance attributes.
Emerging sourcing trends indicate a shift towards digital platforms and e-commerce solutions that streamline procurement processes. For international B2B buyers, this means the ability to access a wider range of suppliers and products, often with more transparent pricing. Additionally, the integration of advanced analytics and AI in supply chain management is enabling companies to better forecast demand, optimize inventory, and reduce lead times, enhancing overall operational efficiency. The growing emphasis on circular economy principles is also noteworthy, pushing manufacturers to explore end-of-life solutions for materials and products, fostering a more sustainable lifecycle.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Fabric Similar to Leather Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount considerations for B2B buyers in the fabric similar to leather sector. The environmental impact of sourcing and manufacturing processes can be significant, particularly concerning water usage, carbon emissions, and waste generation. Buyers must prioritize suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, such as utilizing renewable resources, minimizing chemical use, and ensuring fair labor practices across their supply chains.
Green certifications, such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and OEKO-TEX, can serve as reliable indicators of a supplier’s adherence to environmental and ethical standards. Additionally, buyers should inquire about the lifecycle assessment of materials to understand their ecological footprint and recyclability. Engaging with suppliers that adopt a transparent supply chain model fosters trust and accountability, ensuring that the sourced materials align with broader corporate sustainability goals. As the demand for eco-friendly products continues to rise, aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability principles will not only enhance brand reputation but also appeal to the growing base of environmentally conscious consumers.

Illustrative image related to fabric similar to leather
What is the Historical Context of the Fabric Similar to Leather Market?
The evolution of fabric similar to leather has been shaped by both technological advancements and shifting consumer values. Initially, the market was dominated by traditional synthetic materials like PVC and PU, which offered cost-effective alternatives to genuine leather but raised concerns regarding environmental impact and sustainability. Over the last decade, however, there has been a marked shift towards innovative materials derived from natural sources, such as fruit waste and plant fibers, reflecting a growing consumer preference for sustainable and ethical options.
The introduction of new technologies, including bioengineering and material science, has facilitated the development of high-quality alternatives that closely resemble the aesthetics and durability of leather. This evolution is not only a response to consumer demand but also a proactive approach by manufacturers to address the pressing environmental challenges associated with conventional leather production. As the market continues to mature, the focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing will likely shape future innovations and sourcing strategies in the fabric similar to leather sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fabric similar to leather
-
How do I choose the right fabric similar to leather for my product line?
Selecting the ideal fabric involves evaluating several factors such as end-use, durability, and aesthetics. Consider the environmental impact of the material, as sustainability is increasingly important to consumers. Research various options, like PU, PVC, and natural alternatives like cork or fruit leathers, to assess their properties. Request samples to evaluate texture, weight, and suitability for your product. Collaborate with suppliers who understand your specific requirements and can provide customized solutions tailored to your brand. -
What is the most sustainable option for fabric similar to leather?
Sustainable alternatives include materials such as cork, mushroom leather, and fruit-based textiles, which utilize agricultural by-products and are biodegradable. However, it’s crucial to evaluate the entire lifecycle of the material, including production methods and end-of-life disposal. Materials like recycled PU and PVC can also be more sustainable if sourced responsibly. Always request documentation about the sourcing and production processes from your suppliers to ensure they align with your sustainability goals. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for fabric similar to leather?
MOQs vary by supplier and the type of material ordered. Typically, synthetic fabrics like PU or PVC might have lower MOQs, often ranging from 100 to 500 meters, while more specialized or sustainable materials could require higher MOQs. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify your needs and ask if they can accommodate smaller orders for prototypes or initial runs. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can sometimes lead to more flexible terms. -
How can I vet suppliers of fabric similar to leather?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by checking their industry reputation and client references. Conduct background research on their production facilities to ensure compliance with international standards and environmental regulations. Request samples to assess the quality of their products and inquire about their sustainability practices. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing sites if possible, or engage third-party auditing firms to validate their claims. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing fabric similar to leather internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include 30% upfront and 70% upon delivery or net 30 days after receipt of goods. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk tolerance. It’s advisable to use secure payment methods, such as letters of credit or escrow services, especially for large orders. Ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid misunderstandings later. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement when sourcing fabric similar to leather?
Quality assurance begins with setting clear specifications and standards with your supplier. Establish a protocol for inspecting materials upon arrival, including checks for color consistency, durability, and overall quality. Consider third-party quality control services to conduct inspections at various stages of production. Regular communication with the supplier during the manufacturing process can also help address potential issues proactively. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the sourcing of fabric similar to leather?
Logistics and shipping can significantly affect your supply chain, particularly for international sourcing. Consider factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and potential customs delays. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in exporting fabrics and can provide reliable shipping options. Additionally, factor in storage and warehousing solutions to manage inventory effectively once the materials arrive. -
What customization options are available for fabric similar to leather?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including color, texture, and finish. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities. Custom patterns and branding can also be incorporated, but this may affect MOQs and lead times. Make sure to request samples of customized fabrics to evaluate how well they meet your expectations before placing a larger order.
Top 3 Fabric Similar To Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sallie Tomato – Faux Leather Fabrics
Domain: sallietomato.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux Leather by Sallie Tomato is a vegan alternative to leather or cork fabric, available in various textures including Weave, Pebble, Legacy, Shimmer, Crocodile, Alligator, Ostrich, and Rugged. Select Faux Leathers are offered in Lite Legacy, an ultra-thin material. The fabric is sold by quarter yard and comes in multiple colors such as Beige, Black, Blue, Brown, Green, Grey, Navy, Orange, Pink, …
2. Sewport – Faux Leather Solutions
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is a petroleum-based alternative to genuine leather. It is soft to the touch, water-resistant, and highly resistant to stains, making it easy to clean. While less durable than real leather, it is resistant to abrasions and cuts, ideal for upholstery in homes with children or pets. Faux leather can be produced in various colors, including unconventiona…
3. Kiki Textiles – Faux Leather Fabric
Domain: kikitextiles.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Faux leather (pleather) fabric by the yard available in various colors and styles. Price range: $13.99 – $14.50 per yard. Features include: ethical and animal-friendly alternative to genuine leather, realistic texture and sheen, easy to clean, resistant to wear and tear. Suitable for fashion items (jackets, handbags, clothing), upholstery (furniture), and accessories (wallets, belts, shoes). Colle…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fabric similar to leather
As the demand for sustainable and innovative alternatives to traditional leather continues to rise, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of this evolving market. The key takeaway for international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, is to prioritize materials that align with their sustainability goals while also considering performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Understanding the nuances of various fabric alternatives—ranging from synthetic options like PVC and PU to innovative plant-based materials such as pineapple and cactus leather—enables businesses to make informed decisions that enhance their product offerings. Additionally, transparency in sourcing practices will not only meet consumer demand for ethical products but also foster brand loyalty and trust.
Looking ahead, the landscape of leather alternatives is set to expand even further as technological advancements drive the development of new materials. B2B buyers are encouraged to stay ahead of trends, engage with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, and explore partnerships that facilitate the integration of these innovative fabrics into their supply chains. By doing so, they will position themselves as leaders in the market, ready to meet the evolving expectations of consumers worldwide.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.