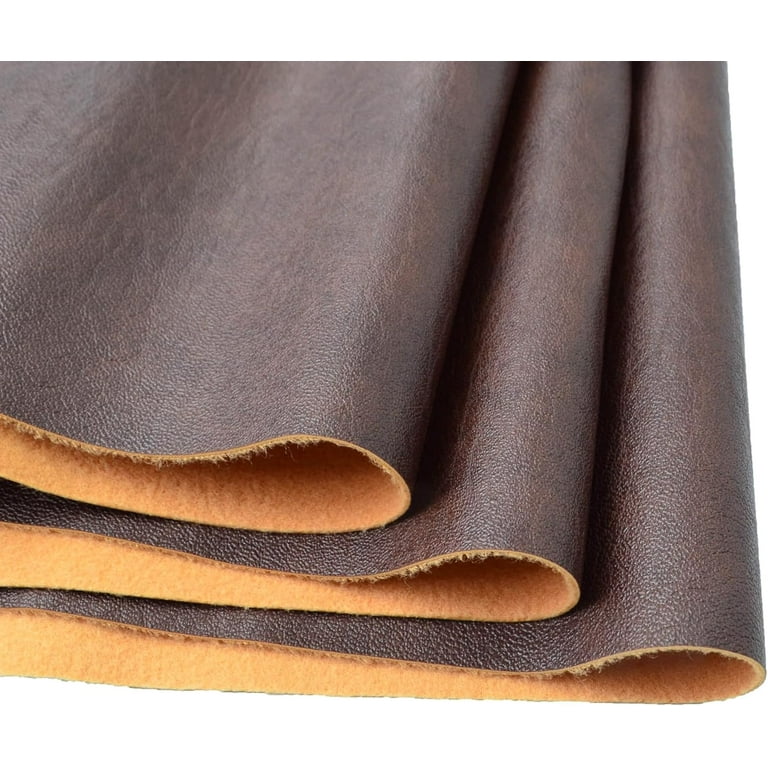
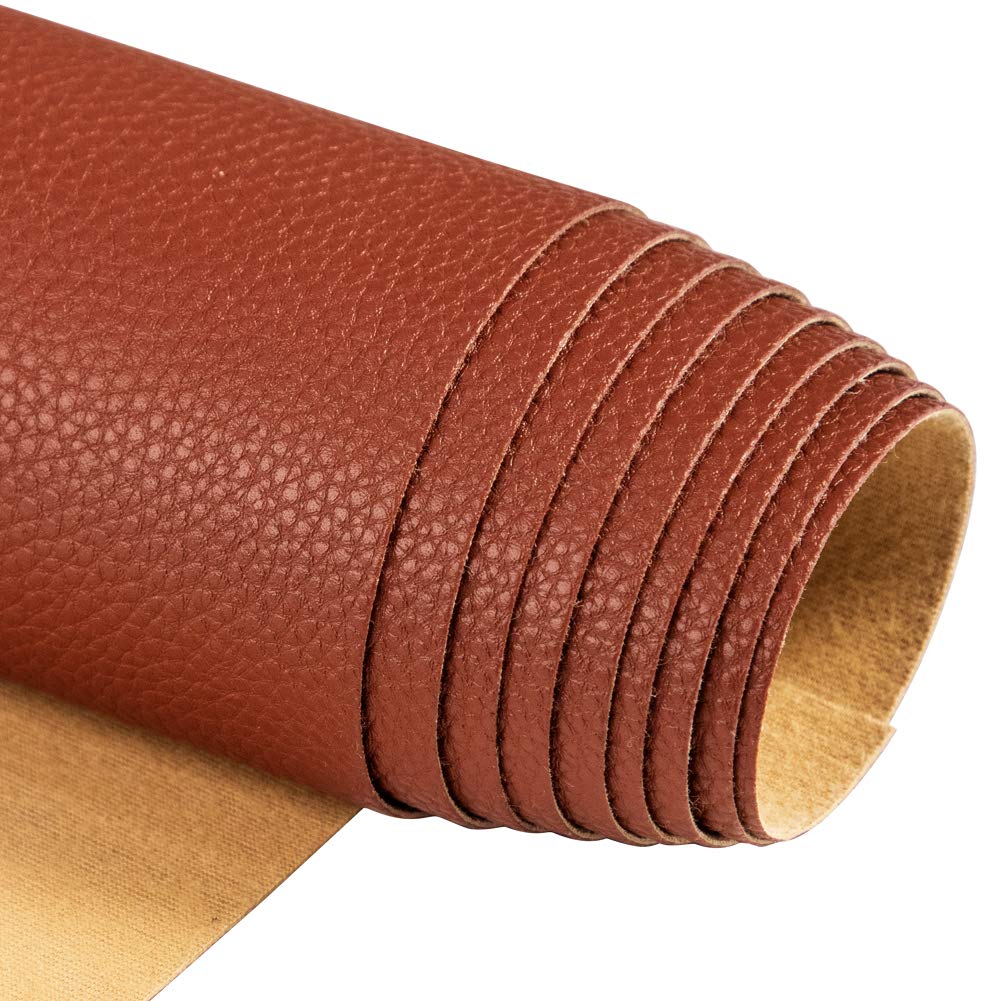
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for swaid material
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality swaid material presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The demand for luxurious and versatile suede-like materials has soared, driven by their applications in fashion, upholstery, and automotive industries. However, navigating the complexities of global supply chains, fluctuating costs, and varying quality standards can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international B2B buyers by providing in-depth insights into the world of swaid material. We will explore the different types of swaid, their various applications, and the essential considerations for supplier vetting. Additionally, we will delve into cost analysis, helping buyers make informed decisions that align with their budgetary constraints and quality expectations.
By addressing key concerns and offering actionable solutions, this guide aims to streamline the purchasing process for businesses looking to enhance their product offerings with high-quality swaid materials. Whether you are a buyer in Nigeria seeking reliable suppliers or a manufacturer in Brazil looking to expand your product line, this resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the global market effectively.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Swaid Material Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for swaid material
- Understanding swaid material Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of swaid material
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘swaid material’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for swaid material
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for swaid material
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘swaid material’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for swaid material Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing swaid material With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for swaid material
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the swaid material Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of swaid material
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for swaid material
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding swaid material Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Italian Suede | Silky soft texture, aniline-dyed, single-sided | High-end fashion items, luxury accessories | Pros: Premium quality, rich color options. Cons: Expensive, less durable in wet conditions. |
| Synthetic Suede | Man-made fibers, more durable, machine washable | Apparel, upholstery, automotive interiors | Pros: Cost-effective, easier maintenance. Cons: Lacks the luxurious feel of real suede. |
| Nubuck | Sanded top grain leather, soft and velvety finish | Footwear, jackets, furniture upholstery | Pros: Durable, water-resistant treatments available. Cons: Can stain easily, requires care. |
| Microfiber Suede | Ultra-fine synthetic fibers, soft and lightweight | Fashion accessories, home textiles | Pros: Lightweight, good breathability. Cons: May not have the same prestige as genuine suede. |
| Deerskin Suede | Soft, supple texture, naturally water-resistant | High-end gloves, apparel, specialty items | Pros: Unique softness, good for delicate applications. Cons: Higher cost, limited availability. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Italian Suede?
Italian suede is renowned for its luxurious feel and exquisite finish, often produced from lambskin or calfskin. This type of suede is typically aniline-dyed, allowing for vibrant color penetration. Its single-sided buffing creates a soft, velvety texture that is highly sought after in luxury fashion markets. B2B buyers should consider its applications in high-end garments and accessories, as well as the need for specialized care due to its sensitivity to moisture and stains, making it less suitable for everyday wear.
How Does Synthetic Suede Compare to Natural Options?
Synthetic suede, crafted from man-made fibers, offers an alternative that is both cost-effective and durable. It is often machine washable, making it an appealing option for businesses looking for low-maintenance materials. Common applications include apparel and automotive interiors. However, while synthetic suede mimics the look and feel of genuine suede, it may lack the luxurious appeal that high-end brands desire. Buyers should weigh these factors when considering synthetic options for their product lines.
Why Choose Nubuck for Durability?
Nubuck is a type of leather that has been sanded or buffed to create a soft, velvety surface. Unlike traditional suede, which is made from the underside of animal hides, nubuck uses the outer layer, making it more durable. It is commonly used in footwear and outerwear, as well as upholstery applications. While nubuck is less prone to wear and tear, it can still stain easily and requires careful maintenance. B2B buyers should consider the balance between durability and the necessary upkeep when selecting nubuck for their products.
What Are the Benefits of Microfiber Suede?
Microfiber suede is made from ultra-fine synthetic fibers, offering a lightweight and breathable alternative to traditional suede. This material is often used in fashion accessories and home textiles, making it versatile for various applications. Its ease of cleaning and maintenance is a significant advantage for B2B buyers, particularly in industries where frequent washing is necessary. However, it may not carry the same luxury connotation as genuine suede, which is a consideration for brands targeting upscale markets.
What Makes Deerskin Suede Unique?
Deerskin suede is characterized by its exceptional softness and natural water resistance, making it ideal for high-end gloves and specialty apparel. The unique texture of deerskin adds a level of comfort that is hard to replicate with synthetic materials. However, due to its limited availability and higher production costs, it may not be suitable for all B2B applications. Buyers should assess the market demand for deerskin products and the potential for premium pricing when incorporating this material into their offerings.
Key Industrial Applications of swaid material
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of swaid material | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Suede jackets and footwear | Enhances product luxury appeal and comfort | Ensure high-quality tanning processes and color options. |
| Automotive | Seat covers and interior linings | Provides a premium look and feel, enhancing customer experience | Look for durability and stain resistance in sourcing. |
| Home Décor | Upholstery for furniture | Adds a touch of elegance and warmth to interiors | Verify compatibility with cleaning and maintenance standards. |
| Accessories | Designer handbags and belts | Increases perceived value and brand prestige | Source from reputable suppliers for quality assurance. |
| Sports Equipment | Specialized gloves | Offers superior grip and comfort for athletes | Prioritize sourcing that meets performance and durability standards. |
How is swaid material utilized in the fashion and apparel industry?
In the fashion sector, swaid material is primarily used for crafting jackets and footwear, where its soft texture and luxurious feel enhance the overall aesthetic. Suede products are often marketed as high-end items, appealing to consumers seeking comfort and style. B2B buyers in this industry should focus on sourcing suede from reputable suppliers that ensure consistent quality, proper tanning methods, and a variety of dye colors to meet fashion trends.
What role does swaid material play in the automotive sector?
Within the automotive industry, swaid material is utilized for seat covers and interior linings, providing a sophisticated appearance that elevates the vehicle’s interior design. Suede’s soft texture contributes to passenger comfort, while its visual appeal can enhance the overall brand image of the vehicle. Buyers must consider the material’s durability and stain resistance, ensuring that it can withstand the rigors of daily use while maintaining its luxurious look.
How is swaid material incorporated into home décor?
In home décor, swaid material serves as upholstery for furniture, imparting an elegant and cozy ambiance to living spaces. Its unique texture and variety of colors allow designers to create visually striking pieces that attract consumers looking for upscale home furnishings. Buyers in this sector should ensure that the suede meets cleaning and maintenance standards, as the material can be prone to staining and requires careful handling.
What are the applications of swaid material in fashion accessories?
Swaid material is highly sought after in the accessories sector, especially for designer handbags and belts, due to its luxurious feel and visual appeal. These products often command higher price points, thus enhancing brand prestige and attracting discerning consumers. For B2B buyers, it’s crucial to source suede from suppliers known for quality assurance to maintain the integrity and value of the finished products.
How is swaid material used in sports equipment?
In the sports equipment industry, swaid material is commonly used for specialized gloves, where its soft texture offers superior grip and comfort for athletes. This application is particularly relevant in sports where dexterity and tactile feedback are essential. Buyers should prioritize sourcing suede that meets specific performance and durability standards, ensuring that the gloves can withstand rigorous use while providing athletes with the comfort they need.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘swaid material’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Quality Suede Material
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find high-quality suede material that meets their specifications. With a multitude of suppliers and varying quality standards, it can be overwhelming to ensure that the suede is not only aesthetically pleasing but also durable enough for its intended use. Buyers may receive samples that do not accurately represent the final product, leading to inconsistencies in production and potential reputational damage if the final products do not meet customer expectations.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, B2B buyers should establish clear specifications and quality standards before engaging with suppliers. This includes defining the desired characteristics of the suede, such as thickness, softness, and color. It is advisable to request detailed product descriptions and certifications that verify the material’s quality. Building relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in suede and have established quality control processes can ensure a more reliable supply chain. Additionally, consider conducting site visits to suppliers’ facilities to evaluate their production methods and quality assurance protocols. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of receiving subpar materials.
Scenario 2: Maintenance and Care Concerns with Suede Products
The Problem: Suede is known for its luxurious feel but also requires specific care and maintenance to keep it looking good. B2B buyers often face challenges in educating their customers about how to properly care for suede products, leading to potential customer dissatisfaction and increased returns. Many buyers lack the resources to provide detailed care instructions, which can result in damaged products and loss of sales.
The Solution: To address maintenance concerns, B2B buyers should invest in creating comprehensive care guides for suede products. These guides should include information on cleaning methods, recommended products, and tips for protecting suede from stains and water damage. Offering value-added services such as warranty programs or professional cleaning services can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Additionally, consider partnering with cleaning product manufacturers to provide suitable care solutions tailored for suede, which can be bundled with the product at the point of sale. Educating customers on proper care will not only prolong the life of the products but also enhance their overall experience with the brand.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Product Versatility and Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often find that suede is not as versatile as other materials, limiting its application in various products. For instance, while suede is ideal for certain fashion items, its susceptibility to moisture makes it unsuitable for outdoor or heavy-duty applications. This can lead to challenges in product development and inventory management, as buyers may struggle to find suitable uses for suede in their product lines.
The Solution: To maximize the utility of suede, B2B buyers should consider diversifying their product offerings by incorporating synthetic suede alternatives that mimic the look and feel of genuine suede but offer greater durability and stain resistance. Additionally, conducting market research to identify niche applications for suede can help buyers tap into specialized markets where suede is still favored. Collaborating with designers and product developers can also lead to innovative uses of suede, such as combining it with other materials to enhance durability while retaining the luxurious appearance. By exploring these avenues, buyers can expand their product range and better meet market demand.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for swaid material
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Swaid Material?
When selecting materials for swaid applications, it is essential to consider the properties that will affect product performance. Common materials include genuine suede leather, synthetic suede, and other textile alternatives. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its suitability for specific applications.
Genuine Suede Leather
Genuine suede leather is derived from the underside of animal hides, primarily lamb, goat, or calf. Its key properties include a soft texture and a matte finish, which make it appealing for high-end fashion items. However, it has low moisture resistance and is prone to staining, which can limit its use in environments with high humidity or exposure to liquids.
Pros: Genuine suede offers a luxurious feel and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for high-end products such as jackets, shoes, and handbags. Its unique texture enhances the tactile experience for users.
Cons: The primary drawbacks are its high maintenance requirements and susceptibility to damage from water and stains. Additionally, it is relatively expensive, which may deter some buyers.
Impact on Application: Suede is best suited for indoor use or in controlled environments. Its low durability against the elements makes it less suitable for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of the import regulations regarding animal products and ensure compliance with local standards. The demand for genuine leather may vary based on cultural preferences and economic factors.
Synthetic Suede
Synthetic suede, often made from polyester or nylon, mimics the look and feel of genuine suede while offering improved durability and stain resistance. Its properties include higher moisture resistance and ease of cleaning, making it a practical alternative for various applications.
Pros: The primary advantage of synthetic suede is its lower cost and ease of maintenance. It can be machine washed and is less prone to staining, making it suitable for everyday use.
Cons: While synthetic suede replicates the aesthetic of genuine suede, it may lack the luxurious feel and breathability associated with natural materials. Additionally, its environmental impact can be a concern due to the use of synthetic fibers.
Impact on Application: Synthetic suede is versatile and can be used in a wider range of applications, including upholstery, clothing, and accessories. Its durability makes it suitable for environments where wear and tear are a concern.

Illustrative image related to swaid material
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with environmental regulations and standards for synthetic materials in their respective countries. Preferences may vary, with some markets favoring natural over synthetic materials.
Microfiber Suede
Microfiber suede is a synthetic alternative that offers a soft texture similar to genuine suede. It is made from ultra-fine polyester fibers, providing excellent durability and stain resistance. Its properties include high breathability and moisture-wicking capabilities.
Pros: Microfiber suede is highly durable and easy to clean, making it a popular choice for upholstery and fashion items. It is also lightweight and can be produced in various colors and textures.
Cons: The primary limitation is that it may not provide the same luxurious feel as genuine suede. Additionally, some buyers may prefer natural materials for sustainability reasons.
Impact on Application: Microfiber suede is ideal for applications requiring durability and ease of maintenance, such as automotive interiors and activewear.

Illustrative image related to swaid material
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of microfiber suede in their regions and any potential import duties. Compliance with textile standards such as ASTM or JIS may also be relevant.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Swaid Material
| Material | Typical Use Case for swaid material | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genuine Suede Leather | High-end fashion items, jackets, shoes | Luxurious feel and aesthetic appeal | High maintenance and low moisture resistance | High |
| Synthetic Suede | Everyday clothing, upholstery | Lower cost and easy maintenance | Lacks luxurious feel and breathability | Medium |
| Microfiber Suede | Upholstery, automotive interiors | Highly durable and easy to clean | May not provide the same luxury feel | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the various materials available for swaid applications. By considering the properties, pros and cons, and specific market considerations, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their product requirements and regional preferences.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for swaid material
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Swaid Material?
The production of swaid material, a type of suede, involves several meticulous stages that ensure quality and consistency. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers.

Illustrative image related to swaid material
Material Preparation: How Is Swaid Material Initially Prepared?
The first stage in manufacturing swaid material is the selection and preparation of the animal hides, typically sourced from lamb or goat skins. After the hides are sourced, they undergo a process called liming, where natural lime is applied to remove hair follicles. This is followed by tanning, where tannins are introduced to preserve the leather and prevent decomposition. The quality of the initial hides significantly influences the final product, so suppliers must ensure they source hides that meet specific standards.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Form Swaid Material?
Once the hides are tanned, they are thinned and split to achieve the desired napped texture characteristic of swaid. This process not only enhances the softness but also prepares the leather for further treatments. Advanced techniques, such as sanding and buffing, are employed to create an even surface, enhancing the material’s visual appeal and tactile quality. The use of specialized machinery is common in this stage to ensure uniform thickness and texture across batches.
Assembly: How Is Swaid Material Assembled into Final Products?
After the forming process, the next step involves cutting the suede into specific shapes for various applications, such as garments, accessories, and upholstery. Skilled artisans often handle this stage to ensure precision and adherence to design specifications. The assembly can include stitching or bonding processes, depending on the product type. This phase is critical, as improper assembly can lead to product failures, making supplier expertise essential.
Finishing: What Are the Final Touches Applied to Swaid Material?
The finishing stage involves applying dyes, waterproofing agents, or other treatments to enhance the appearance and durability of the swaid. Dyes can be applied using various techniques, including immersion or spray, allowing for a range of colors and finishes. A final quality check during this phase ensures that the product meets aesthetic and functional standards before it is packaged for shipping.
What International Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of sourcing swaid material, and understanding relevant international standards helps B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Swaid Material?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management standards worldwide. It focuses on ensuring consistency and quality in manufacturing processes, making it essential for suppliers of swaid material. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe, may apply, depending on the end-use of the material. Buyers should verify that their suppliers adhere to these standards to ensure product reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Swaid Material Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is vital at every stage of the manufacturing process. Implementing systematic QC checkpoints helps maintain product integrity and performance.
What Are the Different Quality Control Checkpoints?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify their quality and compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to ensure processes are followed correctly. This includes checking the thickness of the leather, texture consistency, and dye application.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs before the product is shipped. This step confirms that the finished goods meet all quality standards and are free from defects.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Swaid Material Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers should be familiar with common testing methods employed to ensure the quality of swaid material. These methods include:
- Physical Testing: Evaluates the material’s durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear.
- Chemical Testing: Assesses the tanning agents and dyes used to ensure they are safe and meet regulatory standards.
- Environmental Testing: Determines how well the material withstands various environmental conditions, which is crucial for products exposed to moisture or heat.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Ensuring that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures is essential for B2B buyers. Here are effective strategies for verification:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Verify Supplier QC?
-
Conduct Audits: Regularly auditing suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers should develop a checklist based on industry standards to guide these audits.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and compliance certificates.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. This step is particularly important for buyers in regions like Africa or South America, where local oversight may be limited.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing swaid material internationally, B2B buyers must navigate various certification and quality nuances.
How Do Regional Regulations Affect Quality Control for Swaid Material?
Different regions have specific regulations and standards that suppliers must comply with. For instance, the European Union has stringent requirements for materials entering its market, necessitating CE marking. Buyers from Africa and South America may face fewer regulations, but they should still ensure suppliers meet international quality standards to avoid issues with product returns or market access.

Illustrative image related to swaid material
Conclusion: Why Quality Assurance Matters in Sourcing Swaid Material
In the competitive landscape of international B2B sourcing, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for swaid material is paramount. By being knowledgeable about these stages, relevant standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specifications and market demands.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘swaid material’
This practical guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to source suede material effectively. It outlines critical steps to ensure that your procurement process is efficient, reliable, and aligned with your business requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly articulating the specific requirements for the suede material you need. Consider factors such as thickness, color, and texture, as these will impact the final application of the material in your products. Be precise about whether you require genuine leather or synthetic alternatives, as this will influence pricing and supplier capabilities.
Step 2: Research Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a solid reputation in the suede material market. Look for companies that have been in business for several years and have positive reviews from other B2B buyers. Utilize industry-specific platforms, trade shows, and online directories to gather a list of potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to vet them thoroughly. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This will help you understand their reliability and product quality. Additionally, inquire about their production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your demands.
Step 4: Verify Quality Standards
Confirm that the suppliers adhere to international quality standards for suede production. This includes checking for certifications that indicate sustainable and ethical sourcing practices. Quality assurance processes should also be in place, such as regular inspections and testing of the suede for durability and finish.
Step 5: Request Samples
Always request samples before placing a bulk order. This allows you to assess the texture, color, and overall quality of the suede material firsthand. Use this opportunity to evaluate how the suede performs in your specific applications, ensuring it meets your standards before making a larger investment.
Step 6: Understand Pricing Structures
Discuss pricing in detail with potential suppliers to understand their cost structures. Be aware of the factors that influence pricing, including material quality, order quantities, and shipping costs. This knowledge will enable you to negotiate effectively and choose a supplier that offers the best value for your budget.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication
Effective communication with your supplier is vital for a successful sourcing experience. Ensure that you have a clear channel for discussing timelines, order modifications, and any issues that may arise during the procurement process. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can lead to better service and cooperation in the long run.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for suede material, ensuring they select the right suppliers and materials that align with their business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for swaid material Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Swaid Material Sourcing?
When sourcing swaid material, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and procurement strategies. The primary cost components include:

Illustrative image related to swaid material
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant factor, especially since suede can be derived from various animal skins or synthetic alternatives. The choice of material directly impacts the price, with premium sources like Italian suede commanding higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this may come at the expense of quality. Skilled labor is essential for tanning and finishing processes, which can add to costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, rent, and other operational expenses incurred during production. Efficient production facilities can help minimize overhead, thereby reducing the final cost of the material.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized production runs can be a significant upfront cost. However, once established, this can lead to cost savings in larger volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of swaid material is essential, particularly for high-end applications. Investment in QC processes can increase upfront costs but can prevent costly returns or reputational damage later.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on distance and mode of transport. International buyers must consider these costs in their total procurement budget.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover risks and operational costs. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Swaid Material Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of swaid materials, which can significantly impact the total cost for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often attract discounts. Suppliers may have a tiered pricing structure, where prices decrease as order sizes increase.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom colors, sizes, or finishes can lead to higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The use of high-quality materials and compliance with international certifications (e.g., eco-friendly processes) can raise prices but may be necessary for certain markets.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their quality assurance and consistency.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) can affect overall costs. Understanding these terms is vital for managing risks and expenses associated with international trade.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Prices for Swaid Materials?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost-management strategies are vital:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider all costs associated with the material, including shipping, handling, and potential waste or defects. A higher upfront price may result in lower overall costs if quality is superior.
-
Build Relationships: Establish long-term relationships with suppliers. Trust can lead to better pricing and priority service, especially in fluctuating markets.
-
Be Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of market conditions, including supply chain disruptions or changes in material availability, can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Don’t settle for the first offer. Collect quotes from various suppliers to understand the market range and negotiate better terms.
-
Consider the Payment Terms: Flexible payment options can influence pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for upfront payments or longer payment terms, depending on the buyer’s creditworthiness.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for swaid materials can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and regional factors. The figures mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing swaid material With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Swaid Material
In the realm of materials used for various applications, particularly in the fashion and automotive industries, swaid material stands out for its softness and aesthetic appeal. However, as buyers assess their options, it is crucial to consider viable alternatives that may offer different benefits. This section will compare swaid material against two notable alternatives: synthetic suede and traditional leather. Each option has unique characteristics that cater to specific needs, especially for international buyers from diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Swaid Material | Synthetic Suede | Traditional Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Soft, luxurious feel; less durable; prone to staining | Durable, stain-resistant; mimics suede feel | Highly durable; resistant to wear and weather |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower | Higher initial cost, but lasts longer |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling; not machine washable | Easy to cut and sew; machine washable | Requires skilled labor for cutting and stitching |
| Maintenance | High; needs professional cleaning | Low; regular washing suffices | Moderate; requires conditioning and occasional cleaning |
| Best Use Case | High-end fashion items; indoor use | Everyday apparel and accessories | Durable goods like bags, shoes, and furniture |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Synthetic Suede
Synthetic suede, often made from polyester or microfiber, offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional swaid material. Its primary advantages include durability and ease of maintenance, as it can be machine washed without losing its texture or appearance. This makes it an appealing choice for manufacturers producing items that require frequent cleaning or exposure to the elements. However, while synthetic suede mimics the look and feel of real suede, it may lack the luxurious touch and authenticity that some consumers seek, which can affect its market appeal in high-end fashion.
Traditional Leather
Traditional leather is a time-tested material known for its robustness and longevity. Its durability makes it suitable for various applications, including footwear, bags, and upholstery. Traditional leather also offers a premium aesthetic that is often associated with luxury products. However, it comes with a higher price point and requires regular maintenance to prevent drying and cracking. Additionally, sourcing traditional leather can raise ethical concerns regarding animal welfare, which may deter some buyers. Nonetheless, for businesses focused on quality and longevity, traditional leather remains a compelling option.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate material for your business needs, consider the specific application and target market. Swaid material offers a unique luxury appeal, ideal for high-end fashion items, but it requires careful maintenance. In contrast, synthetic suede presents a budget-friendly and low-maintenance option, making it suitable for everyday use. Traditional leather, while more expensive, provides unmatched durability and a classic aesthetic that appeals to consumers seeking premium products. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each alternative allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their brand’s values and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for swaid material
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Swaid Material?
Understanding the essential technical properties of swaid material is crucial for B2B buyers, as these specifications influence product quality and suitability for various applications. Here are some key properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality of the leather used in swaid production. Higher grades typically indicate better softness, durability, and aesthetic appeal. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate grade is vital as it affects the final product’s marketability and price point. Premium grades are often preferred for high-end applications such as luxury fashion items, while lower grades may suffice for more utilitarian uses.
2. Thickness Tolerance
Thickness tolerance measures the allowable variation in the leather’s thickness. For swaid, this can impact the comfort and fit of garments or accessories. A tighter tolerance ensures consistency in production, leading to higher quality products. Buyers should pay attention to this specification, as variations can result in mismatched products, impacting customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
3. Finish Type
The finish type of swaid material can significantly alter its appearance and performance. Common finishes include aniline, semi-aniline, and pigmented. Each finish has different properties regarding color retention, softness, and resistance to stains. Understanding finish types allows buyers to select materials that best meet their end-use requirements, ensuring the longevity and aesthetic appeal of the final product.
4. Breathability
Breathability refers to the material’s ability to allow air and moisture to pass through. For clothing and accessories, higher breathability is often preferred as it enhances comfort, particularly in warmer climates. B2B buyers should consider the breathability of swaid when targeting specific markets, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where climate plays a significant role in consumer preferences.
5. Water Resistance
Water resistance is a critical property for determining the durability of swaid material, especially in outerwear and footwear applications. While traditional swaid is not waterproof, some manufacturers apply treatments to enhance water resistance. Buyers should inquire about these treatments to ensure that the materials can withstand the environmental conditions typical of their target markets.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Swaid Material?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are some common terms relevant to swaid material:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or products that are used in another company’s final product. In the swaid industry, this often refers to manufacturers who create custom designs for brands. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure quality and compatibility in their product lines.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For swaid materials, MOQs can vary widely based on the supplier and the material grade. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to effectively manage inventory and production costs, especially when launching new products.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the context of swaid materials, an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and clarify specifications, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to mitigate risks associated with shipping and delivery. For example, terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) specify who is responsible for shipping costs and insurance, impacting overall pricing and logistics.

Illustrative image related to swaid material
5. Tanning Process
The tanning process refers to the treatment of animal hides to convert them into leather. Different tanning methods (vegetable, chrome, etc.) can affect the characteristics of swaid material, such as softness and durability. Buyers should be informed about tanning processes to select materials that align with their product quality and ethical sourcing requirements.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing swaid material, ensuring they choose the right products for their target markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the swaid material Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Swaid Material Sector?
The global swaid material market is experiencing a notable shift driven by various factors, including evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and sustainability concerns. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe engage with this market, understanding these dynamics becomes crucial. The increasing demand for luxury items, particularly in fashion and interior design, is propelling the need for high-quality swaid materials. Buyers are particularly drawn to Italian and other premium sources due to their craftsmanship and quality assurance.
Emerging technologies in sourcing are reshaping how businesses procure swaid materials. Digital platforms are facilitating transparent supply chains, allowing buyers to verify the origin and quality of the materials they purchase. Moreover, artificial intelligence and machine learning are being utilized to predict trends in consumer demand, enabling suppliers to adjust their offerings accordingly. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in fast-growing markets, where rapid shifts in consumer preferences necessitate agility in sourcing.
Furthermore, international trade agreements and tariffs are influencing sourcing strategies. Buyers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and logistics to ensure timely and cost-effective procurement. For instance, buyers in Nigeria and Brazil may find it advantageous to source from local suppliers to mitigate import duties while ensuring compliance with regional standards.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing Trends in the Swaid Material Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the sourcing of swaid materials. The environmental impact of leather production, including water usage and chemical runoff, has prompted buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. Ethical sourcing is not just a trend but a necessity for businesses aiming to maintain their brand reputation and meet consumer expectations.
Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who offer sustainable certifications, such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or certifications from the Leather Working Group (LWG). These certifications ensure that the materials are produced under environmentally responsible conditions and that animal welfare standards are upheld. By prioritizing suppliers with these certifications, businesses can enhance their marketability and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.

Illustrative image related to swaid material
The rise of synthetic alternatives to traditional swaid materials also reflects this shift towards sustainability. While synthetic options can reduce reliance on animal hides, they still require careful consideration regarding their environmental impact. Buyers are encouraged to assess the lifecycle of these materials, including their recyclability and the resources required for their production.
What Is the Historical Context of Swaid Material and Its Evolution in B2B Markets?
The history of swaid material dates back centuries, with its roots in Sweden, where artisans began developing soft leather from the inner skin of animals. Initially, the use of suede was limited primarily to glove-making, but as its appeal grew, so did its applications. The 19th century saw the expansion of suede into various fashion items, including jackets, shoes, and handbags, marking its transition into a luxury material.
Today, the swaid material sector has evolved into a significant player in the global textile market, with China emerging as a dominant producer. The contemporary market reflects a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern manufacturing techniques, catering to an increasingly diverse range of applications. As international B2B buyers seek high-quality materials, understanding the historical significance and evolution of swaid can provide valuable insights into its current market dynamics and future potential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of swaid material
-
How do I choose the right supplier for suede material?
Selecting the right supplier for suede material involves thorough research and vetting. Start by assessing the supplier’s reputation through reviews and testimonials from other B2B buyers. Verify their production capabilities, quality certifications, and compliance with international standards. It’s also beneficial to request samples to evaluate the quality of the suede firsthand. Finally, establish clear communication channels to discuss your specific needs, including customization options and lead times. -
What factors should I consider when negotiating payment terms with a suede supplier?
When negotiating payment terms, consider the supplier’s payment flexibility, such as deposits, payment upon delivery, or net payment terms. Evaluate the impact of payment terms on your cash flow and budget. Additionally, inquire about currency exchange rates if dealing with international suppliers, as fluctuations can affect costs. Establishing a clear agreement in writing can prevent misunderstandings later and build trust between both parties. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for suede materials?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for suede materials can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of suede. Generally, MOQs can range from a few yards to several hundred yards, depending on production capabilities and inventory. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your business needs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses. -
How can I ensure the quality of suede material before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of suede material, request samples from suppliers to inspect texture, thickness, and color consistency. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes and certifications. Understanding their tanning and finishing techniques is crucial, as these affect the suede’s durability and appearance. Establishing a quality control checklist can help you assess the materials upon arrival, ensuring they meet your standards. -
What customization options are available for suede materials?
Customization options for suede materials may include color, texture, and size variations. Many suppliers offer dyeing services to match specific color requirements and can provide different finishes, such as embossed or printed designs. Discuss your project specifications with the supplier to explore available customization possibilities. Keep in mind that custom orders may impact lead times and pricing, so plan accordingly. -
How do I handle logistics when sourcing suede materials internationally?
Managing logistics for international suede material sourcing involves coordinating shipping, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and understand the necessary documentation for customs. Consider using freight forwarders for efficiency and expertise in navigating logistics challenges. Ensure you have a clear agreement on shipping terms, including Incoterms, to avoid unexpected costs and delays. -
What are the common uses of suede material in various industries?
Suede material is widely used across several industries, including fashion, automotive, and home décor. In fashion, it’s popular for shoes, jackets, and handbags due to its luxurious feel. In the automotive sector, suede is often used for upholstery and interior detailing, providing a premium look. Additionally, home décor items like cushions and throws leverage suede’s aesthetic appeal. Understanding these applications can help you target the right market for your products. -
What are the best practices for maintaining suede products?
Maintaining suede products requires careful handling to preserve their appearance and longevity. Avoid exposure to moisture, as suede is not water-resistant and can stain easily. Regularly brush the surface with a suede brush to remove dirt and restore the nap. For deeper cleaning, professional cleaning services are recommended. Educating your customers about proper care can enhance their experience and satisfaction with suede products.
Top 5 Swaid Material Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Leather Hide Store – Premium Suede Leather
Domain: leatherhidestore.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Suede leather offered in a variety of colors and sizes. Tanned with premium aniline dyes that penetrate the entire leather. Each piece is finished through a fine sanding process for an even surface and velvety touch. Suede is single-sided, with only the top side fully buffed and polished. Ideal for applications like shoes, handbags, luggage, and furniture. Care instructions include using a suede p…
2. The Fabric Outlet – Suede Fabric by the Yard
Domain: thefabricoutlet.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Suede Fabric by the Yard at The Fabric Outlet. This faux leather suede fabric is smooth, durable, and easy to care for, ideal for both rustic and contemporary furniture. Available in various styles and shades. Sold by the yard with prices starting from $29.99 to $39.99 per yard. Specific products include Doro Suede, Vista, GEO – Herringbone Suede, and Blitz. Shipping available within the United St…
3. Sewport – Suede Fabric
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“fabric_name”: “Suede Fabric”, “also_known_as”: [“Fuzzy leather”, “napped leather”, “Ultrasuede”], “fabric_composition”: “The underside of animal skins or a similar synthetic material”, “fabric_properties”: {“breathability”: “Low”, “moisture_wicking”: “Low”, “heat_retention”: “High”, “stretchability”: “Low”, “prone_to_pilling”: “Low”}, “origin”: {“first_produced”: “Sweden”, “biggest_exporting_cou…
4. MasterClass – Suede vs. Nubuck
Domain: masterclass.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Suede is a type of leather made from the underside of animal skin, primarily lamb, goat, or calf. It has a soft, napped finish and is known for its luxurious feel. Nubuck, on the other hand, is made from the outer side of the hide and is sanded to create a velvety texture. Both suede and nubuck are more delicate than traditional leather and require special care to maintain their appearance.
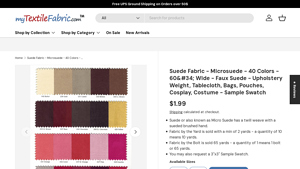
5. My Textile Fabric – Microsuede Swatches
Domain: mytextilefabric.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Suede Fabric – Microsuede – 40 Colors – 60″ Wide – Faux Suede – Upholstery Weight, Tablecloth, Bags, Pouches, Cosplay, Costume – Sample Swatch. Price: $1.99 per sample swatch. Fabric type: Microsuede, 100% polyester, dry clean only. Fabric weight: Approximately 225 grams per square meter. Available sizes: Sold by the yard (minimum 2 yards) and by the bolt (65 yards). Sample swatch size: 3″x3″. Col…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for swaid material
In summary, strategic sourcing of suede material presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The demand for high-quality suede products, ranging from fashion accessories to upholstery, is on the rise. Buyers must prioritize sourcing from reputable suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and offer premium materials that meet the evolving standards of consumers.
By leveraging strong supplier relationships and understanding market trends, businesses can navigate the complexities of suede procurement effectively. The potential for growth in various sectors, including fashion and automotive, underscores the importance of making informed sourcing decisions.
As we look ahead, it is crucial for buyers to stay abreast of innovations in both genuine and synthetic suede alternatives, which can offer competitive advantages. Embracing a strategic approach to sourcing will not only enhance product offerings but also strengthen market position. We encourage B2B buyers to explore partnerships with trusted suppliers and invest in quality materials that resonate with today’s discerning consumers. Your commitment to excellence in sourcing can pave the way for future success in the suede market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.