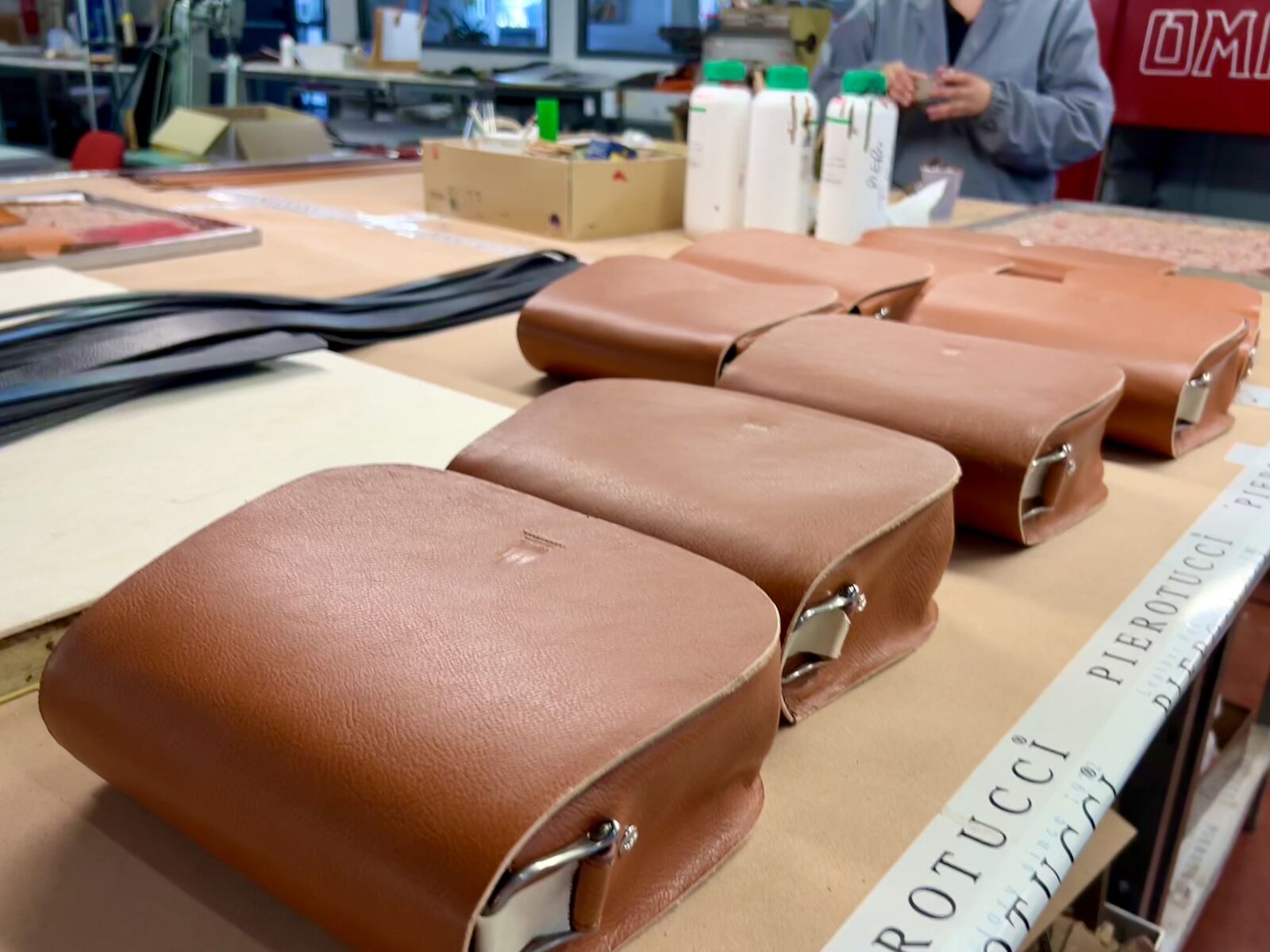
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather technology
Navigating the complexities of sourcing innovative leather technology can be daunting for international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The challenge lies not only in identifying high-quality suppliers but also in understanding the latest advancements that enhance sustainability and efficiency in production. This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for businesses seeking to explore the multifaceted world of leather technology. From the various types of leather treatments and applications to strategies for effective supplier vetting and cost considerations, we cover every aspect that influences informed purchasing decisions.
As the leather industry evolves, driven by demands for sustainability and innovation, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay ahead of trends and technologies. This guide empowers decision-makers by providing actionable insights into sourcing eco-friendly materials, adopting advanced manufacturing processes, and evaluating the credentials of potential suppliers. By addressing these critical areas, international buyers can confidently navigate the global market for leather technology, ensuring their investments align with both quality and environmental responsibility. With our expertise, you will be equipped to make strategic decisions that enhance your product offerings and meet the growing consumer demand for sustainable leather goods.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Leather Technology Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather technology
- Understanding leather technology Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of leather technology
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather technology’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather technology
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather technology
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather technology’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather technology Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather technology With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather technology
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather technology Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather technology
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather technology
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding leather technology Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetable Tanning | Utilizes natural plant extracts, chrome-free process | Footwear, bags, furniture | Pros: Eco-friendly, biodegradable. Cons: Longer processing time, may require more care. |
| Chrome Tanning | Fast tanning process using chromium salts | Fashion, automotive, accessories | Pros: Quick production, vibrant colors. Cons: Environmental concerns, potential toxicity. |
| Synthetic Leather | Man-made materials, often PVC or polyurethane | Fashion, upholstery, automotive interiors | Pros: Cost-effective, diverse textures. Cons: Less breathable, environmental impact from production. |
| Bio-Fabricated Leather | Made from organic materials like mycelium or fruit waste | Eco-conscious fashion, luxury goods | Pros: Sustainable, cruelty-free. Cons: Limited availability, higher cost. |
| Recycled Leather | Made from repurposed leather scraps | Accessories, fashion, upcycled products | Pros: Reduces waste, unique textures. Cons: Quality variability, may not suit all applications. |
What are the characteristics of Vegetable Tanning Leather Technology?
Vegetable tanning is a traditional method that employs natural plant extracts, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious businesses. This process is typically slower than chrome tanning, which may extend production times but results in a more durable and biodegradable product. Suitable for high-end products such as footwear, bags, and furniture, vegetable-tanned leather is known for its rich patina over time. When purchasing, buyers should consider the leather’s care requirements and its potential for aging, which can enhance product value.
How does Chrome Tanning differ from other leather technologies?
Chrome tanning is recognized for its speed and efficiency, utilizing chromium salts to achieve vibrant colors and a softer feel. This method is widely adopted in the fashion and automotive industries due to its ability to produce leather quickly while maintaining quality. However, buyers must weigh the benefits against environmental concerns, as the process can introduce toxic elements into the supply chain. It is essential for B2B buyers to ensure compliance with environmental regulations when sourcing chrome-tanned leather.
Why choose Synthetic Leather for your business needs?
Synthetic leather, often made from PVC or polyurethane, offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional leather. It is versatile and can mimic various textures and appearances, making it suitable for fashion, upholstery, and automotive interiors. However, while synthetic leather is durable and easy to clean, it may lack breathability and has a significant environmental impact during production. B2B buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between price and sustainability when considering synthetic options for their product lines.
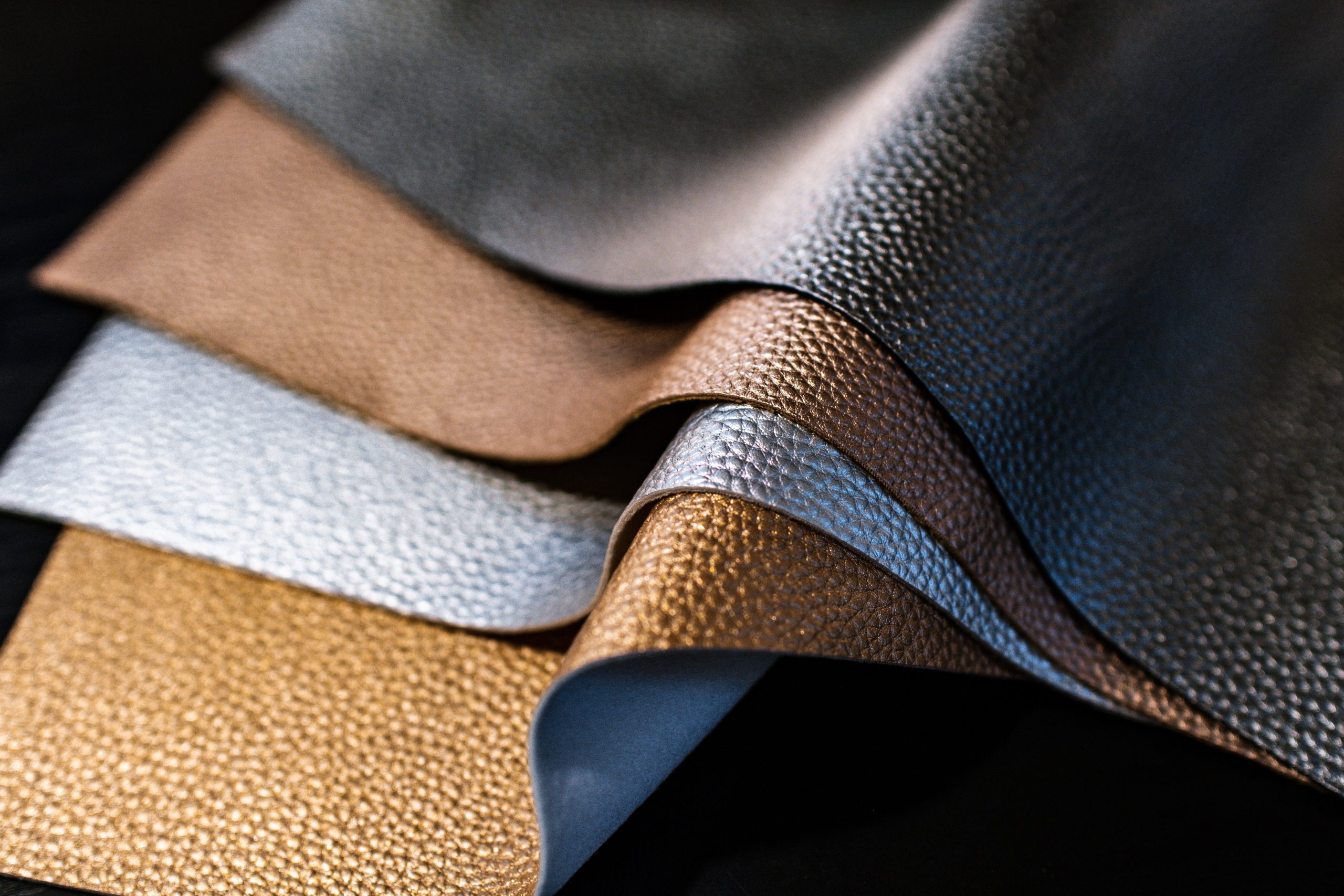

Illustrative image related to leather technology
What advantages does Bio-Fabricated Leather bring to the market?
Bio-fabricated leather represents a new frontier in sustainable materials, utilizing organic resources like mycelium or apple waste. This type of leather appeals to eco-conscious brands seeking cruelty-free alternatives. While it offers promising sustainability benefits, such as reduced environmental impact, the availability and cost can be limiting factors. B2B buyers should assess the market demand for sustainable products and consider the unique selling propositions that bio-fabricated leather can provide.
How can Recycled Leather contribute to sustainability in your supply chain?
Recycled leather, crafted from repurposed scraps, is an innovative solution that helps minimize waste in the leather industry. This type of leather can be utilized in various applications, including accessories and fashion, offering unique textures and aesthetics. While it promotes sustainability, buyers must be aware of potential quality variability and ensure that the recycled leather meets their specific requirements. Understanding the sourcing and processing methods can aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with sustainability goals.
Key Industrial Applications of leather technology
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Leather Technology | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion and Apparel | Eco-friendly tanning processes | Enhanced brand reputation and compliance with sustainability standards | Source from suppliers offering innovative, low-impact tanning methods |
| Automotive | Leather seat manufacturing with advanced durability | Increased customer satisfaction and product longevity | Ensure compliance with automotive standards and durability testing |
| Footwear | Use of biodegradable leather alternatives | Appeal to eco-conscious consumers and reduced waste | Verify certifications for sustainable materials and production methods |
| Furniture and Interiors | Custom leather upholstery solutions | Improved aesthetics and durability of furniture products | Look for suppliers with customizable options and quality assurance |
| Sports Equipment | High-performance leather for sports gear | Enhanced performance and durability in extreme conditions | Prioritize suppliers with proven track records in sports equipment |
How is Leather Technology Used in the Fashion and Apparel Industry?
In the fashion and apparel sector, leather technology focuses on eco-friendly tanning processes that minimize environmental impact. By utilizing vegetable-based tanning or other sustainable methods, manufacturers can produce high-quality leather while adhering to strict environmental regulations. This approach not only enhances brand reputation but also attracts a growing base of eco-conscious consumers. International buyers, particularly from Africa and Europe, should prioritize suppliers who provide transparency in their sourcing and production processes, ensuring compliance with sustainability standards.
What Role Does Leather Technology Play in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, leather technology is crucial for manufacturing high-quality leather seats that offer both comfort and durability. Advanced processes enhance the leather’s resistance to wear and tear, making it suitable for various climatic conditions. This results in increased customer satisfaction and a longer product lifespan. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with automotive industry standards and conduct rigorous durability testing to meet consumer expectations, particularly in regions with diverse weather conditions like the Middle East and South America.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
How is Leather Technology Transforming Footwear Production?
Leather technology in footwear production often involves the use of biodegradable leather alternatives, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. By integrating sustainable materials like Mylo™ or Appleskin™, brands can reduce waste and enhance their market appeal. Buyers should verify the certifications of these sustainable materials and the production methods used to ensure they align with their brand values and customer expectations. This is particularly important in regions like Europe, where consumer demand for sustainable products is rapidly growing.
What Are the Applications of Leather Technology in Furniture and Interiors?
In the furniture and interiors sector, leather technology is leveraged for custom upholstery solutions that enhance both aesthetics and durability. This application allows manufacturers to create unique designs while ensuring the longevity of the products. Buyers should seek suppliers that offer customizable options and have robust quality assurance processes in place. This is particularly relevant for international buyers in Africa and the Middle East, where unique design preferences can drive demand for tailored solutions.
How Does Leather Technology Enhance Sports Equipment?
Leather technology plays a pivotal role in producing high-performance sports gear, utilizing advanced materials that withstand extreme conditions. This application ensures that products are not only durable but also enhance athletic performance. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in sports equipment and an understanding of the specific demands of various sports. This is crucial for international buyers, especially from regions where sports culture is rapidly evolving, such as South America and Europe.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather technology’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Environmental Compliance in Leather Production
The Problem: As global awareness regarding sustainability rises, many B2B buyers in the leather industry face pressure to comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Buyers often find themselves overwhelmed by the complexity of these requirements, which can vary significantly across regions such as Africa, South America, and Europe. Additionally, there is a growing demand from consumers for eco-friendly products, making it crucial for companies to not only meet legal standards but also consumer expectations. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines, damaged reputations, and lost business opportunities.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
The Solution: To effectively navigate environmental compliance, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who utilize sustainable practices and eco-friendly leather technologies. This includes seeking out tanneries that implement waterless tanning methods or employ natural tannins, such as vegetable-based options. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, including factory audits and supplier assessments, to ensure that their partners are compliant with local and international regulations. Additionally, investing in technology that monitors and manages waste and emissions can significantly enhance compliance efforts. Regular training and updates for staff on environmental regulations will also help maintain adherence and foster a culture of sustainability within the organization.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Quality Control Challenges in Leather Products
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience quality control issues when sourcing leather materials, leading to inconsistent product quality that can impact brand reputation and customer satisfaction. Factors such as variations in raw material quality, processing methods, and supply chain inconsistencies contribute to these challenges. For instance, buyers may encounter leather that is either too stiff or too porous, affecting the final product’s durability and appearance. This inconsistency can result in increased returns, customer complaints, and lost sales opportunities.
The Solution: Establishing a robust quality assurance process is vital for overcoming these challenges. B2B buyers should collaborate closely with their leather suppliers to define clear quality standards and specifications before placing orders. Implementing a system of regular inspections and testing—both on raw materials and finished products—can help identify issues early in the production process. Additionally, leveraging advanced technologies such as AI and automated monitoring systems can enhance quality control measures by providing real-time data on production processes. Investing in training for quality assurance personnel on the latest quality standards and best practices will also ensure that the end products consistently meet buyer expectations.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions in Leather Sourcing
The Problem: Global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by recent geopolitical events and pandemics, pose significant challenges for B2B buyers in the leather industry. Buyers often face delays in raw material shipments, resulting in production halts and missed deadlines. This unpredictability not only strains relationships with customers but can also lead to increased costs as companies scramble for alternative sources. The complexity of the leather supply chain, involving multiple stakeholders and geographic locations, further complicates the issue.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain disruptions, B2B buyers should diversify their supplier base by sourcing leather from multiple regions and suppliers. This approach minimizes reliance on any single source and enhances resilience against localized disruptions. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also foster better communication and collaboration, allowing for quicker adjustments during unforeseen circumstances. Additionally, implementing supply chain management software can provide real-time insights into inventory levels, shipment tracking, and potential bottlenecks. Buyers should also consider building strategic partnerships with logistics providers to enhance flexibility and responsiveness in their supply chain operations, ensuring that they can maintain continuity even in challenging times.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather technology
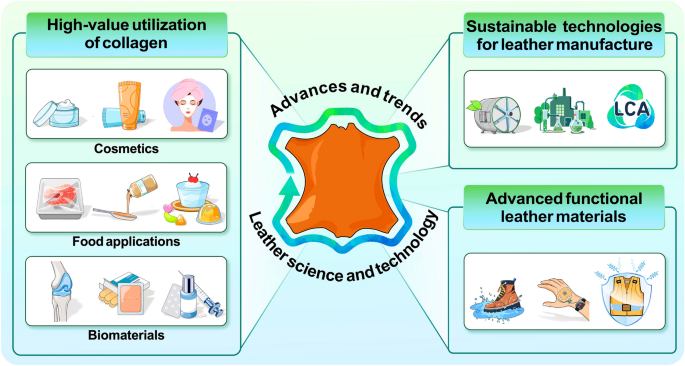
What Are the Key Materials Used in Leather Technology?
In the leather technology sector, the selection of materials is crucial for ensuring product performance, sustainability, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in leather technology, focusing on their properties, pros and cons, and implications for international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
How Does Genuine Leather Perform in Leather Technology Applications?
Genuine leather, derived from animal hides, is a traditional material known for its durability and aesthetic appeal. Key properties include high tensile strength, breathability, and natural moisture-wicking abilities.
Pros: Genuine leather is exceptionally durable, ages well, and can be treated to enhance water resistance. It is also biodegradable, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: However, it can be expensive and may require complex manufacturing processes, including tanning and finishing, which can increase lead times. Additionally, genuine leather’s sourcing can raise ethical concerns among consumers.
Impact on Application: Genuine leather is suitable for high-end products such as luxury handbags and automotive interiors, where durability and aesthetics are paramount.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Considerations for B2B Buyers: International buyers should be aware of compliance with animal welfare regulations and certifications like the Leather Working Group (LWG). In regions like Europe, sustainability certifications are increasingly important.
What Are the Advantages of Synthetic Leather in the Leather Industry?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers a versatile alternative to genuine leather. Key properties include water resistance and ease of cleaning.
Pros: Synthetic leather is generally more affordable than genuine leather and can be produced in various colors and textures. It is also free from animal products, appealing to vegan consumers.
Cons: However, synthetic leather may lack the breathability and durability of genuine leather. Its production can involve petrochemical processes, raising environmental concerns.
Impact on Application: Synthetic leather is widely used in fashion, upholstery, and automotive applications where cost and design flexibility are significant factors.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: International buyers should consider the environmental impact of synthetic materials and ensure compliance with relevant regulations, such as REACH in Europe.
How Do Eco-Friendly Alternatives Like Mylo™ and Appleskin™ Compare?
Innovative materials like Mylo™ (made from mycelium) and Appleskin™ (derived from apple waste) are gaining traction as sustainable alternatives to traditional leather. Key properties include biodegradability and reduced environmental impact.
Pros: These materials are eco-friendly and can significantly lower the carbon footprint associated with leather production. They also appeal to a growing market of environmentally conscious consumers.
Cons: The production processes for these materials can be complex and may result in higher costs. Additionally, they may not yet match the durability and performance characteristics of traditional leather.
Impact on Application: Eco-friendly alternatives are particularly suitable for fashion and accessories aimed at a sustainability-focused demographic.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the certifications and sustainability claims of these materials. Compliance with local regulations regarding bio-based materials is also essential, especially in markets like Europe.
What Role Does Recycled Leather Play in Sustainable Leather Technology?
Recycled leather, made from repurposed leather scraps, offers a sustainable solution that minimizes waste. Key properties include durability and a unique aesthetic due to the variety of textures and colors.
Pros: Recycled leather reduces the need for virgin hides, making it a more sustainable option. It also retains many of the desirable properties of genuine leather, such as breathability.
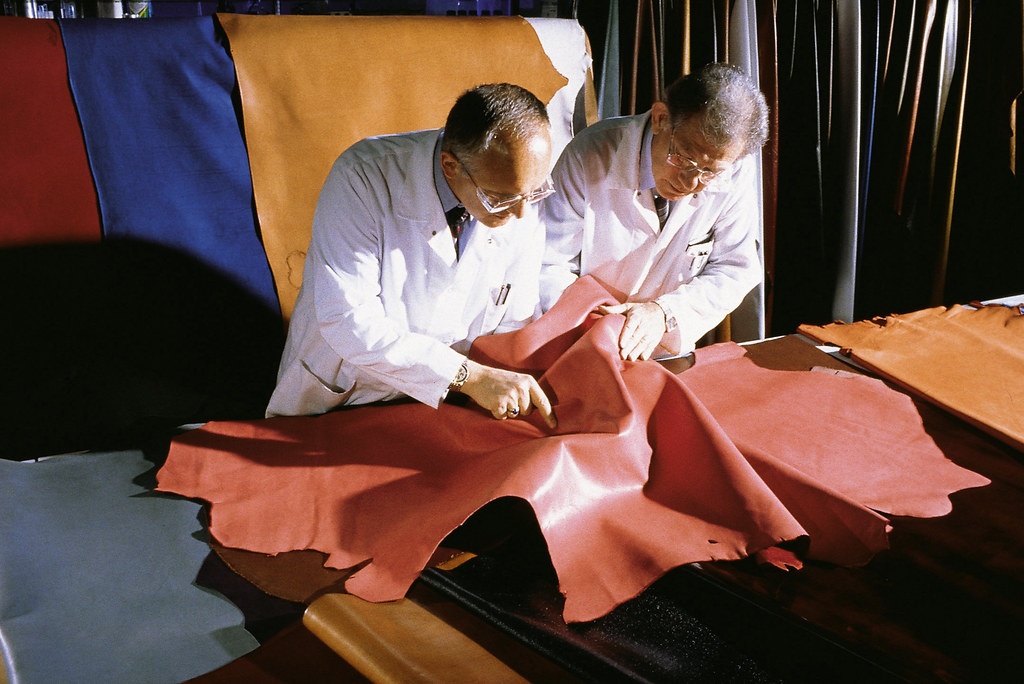

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Cons: The availability of high-quality recycled leather can be inconsistent, and the manufacturing process may be complex, affecting scalability.
Impact on Application: Recycled leather is ideal for products where sustainability is a selling point, such as eco-friendly fashion lines and accessories.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Buyers should verify the sourcing and processing methods of recycled leather to ensure compliance with sustainability standards, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Illustrative image related to leather technology
Summary of Materials in Leather Technology
| Material | Typical Use Case for leather technology | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genuine Leather | Luxury handbags, automotive interiors | High durability and aesthetic appeal | Expensive and complex manufacturing | High |
| Synthetic Leather | Fashion, upholstery, automotive | Cost-effective and design flexibility | Less durable and potential environmental issues | Medium |
| Mylo™/Appleskin™ | Eco-friendly fashion and accessories | Sustainable and biodegradable | Higher costs and variable durability | High |
| Recycled Leather | Eco-friendly fashion lines | Reduces waste and retains leather properties | Inconsistent availability | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options in leather technology, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, sustainability, and compliance considerations.
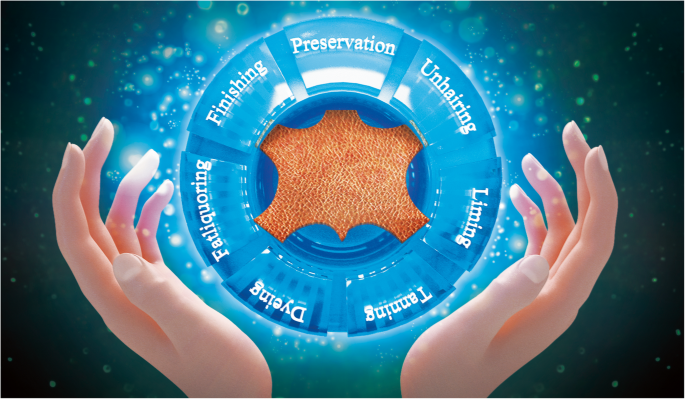
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather technology
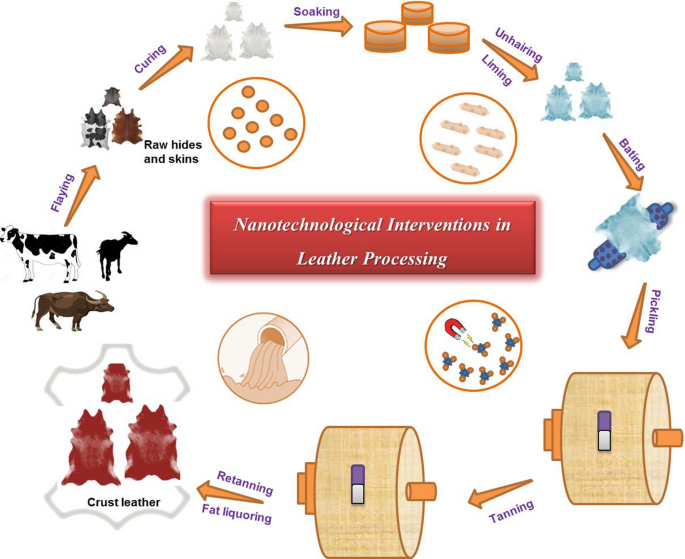
What Are the Main Stages of Leather Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing of leather involves several critical stages that transform raw hides into finished products. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers to ensure the quality and reliability of the leather they procure.
1. Material Preparation: How Are Raw Hides Processed?
The first step in leather manufacturing is the preparation of raw hides. This process begins with the sourcing of animal hides, typically from cattle raised for food, which helps maintain a sustainable cycle. Once obtained, the hides undergo a rigorous cleaning process to remove hair, flesh, and any impurities. This is often achieved through liming, where the hides are soaked in a lime solution.
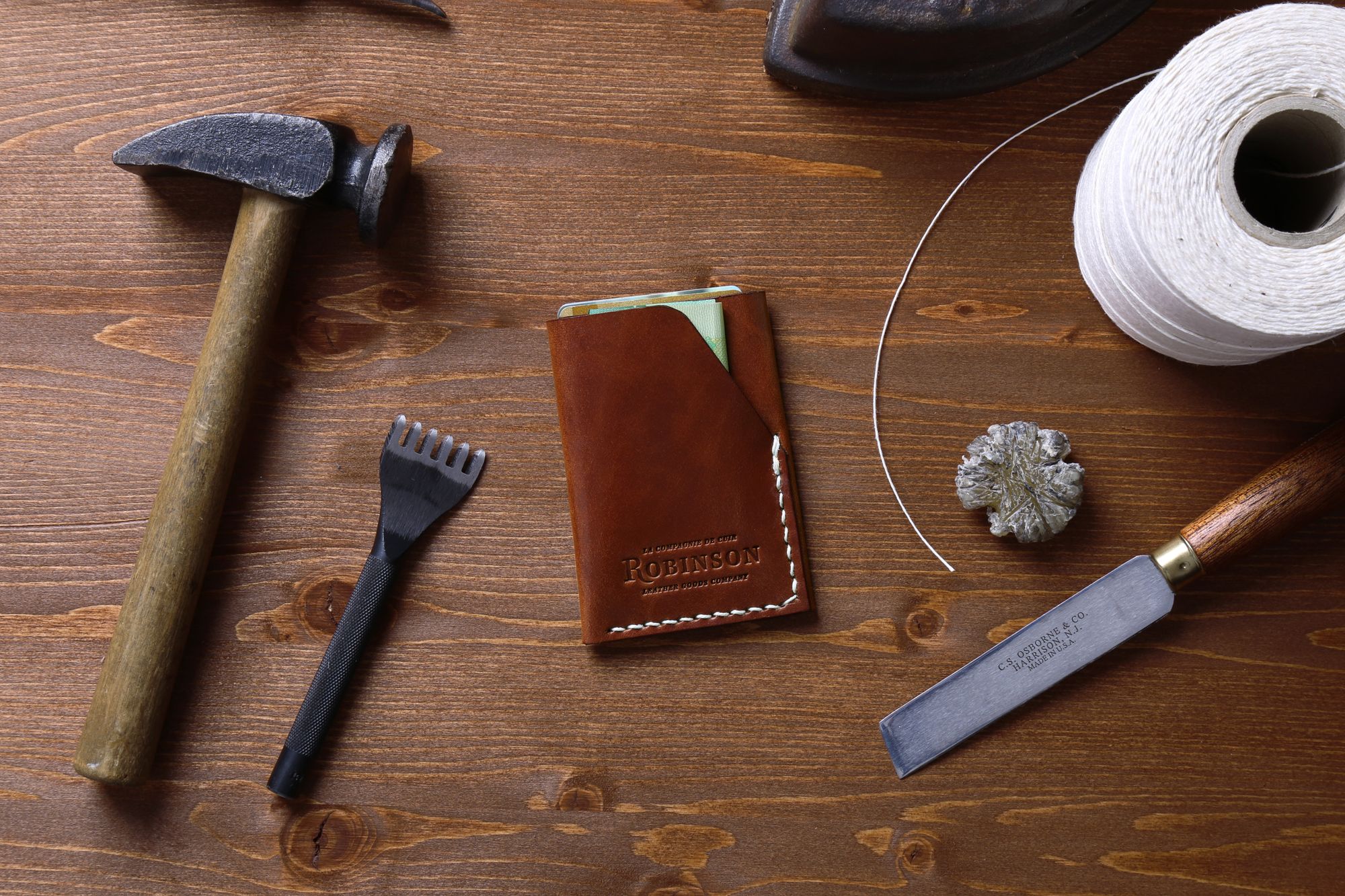

Illustrative image related to leather technology
After cleaning, the hides are delimed and pickled to prepare them for tanning. This stage is crucial, as it affects the leather’s quality and durability. Buyers should verify that their suppliers use eco-friendly and efficient methods in this stage, such as waterless tanning or enzyme-based processes, which significantly reduce chemical use.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Leather?
Forming involves shaping the leather into the desired product. This can be achieved through various techniques, including cutting, stamping, and molding. Advanced technologies like laser cutting and 3D printing are becoming increasingly popular in the leather industry, allowing for precise designs and customized products.
In this phase, attention to detail is paramount. The quality of cutting and shaping directly influences the final product’s aesthetics and functionality. Buyers should inquire about the equipment and techniques used by suppliers to ensure they meet international standards and customer specifications.
3. Assembly: How Is Leather Constructed into Finished Products?
Once the leather is shaped, it moves into the assembly stage. Here, various components are stitched together to create the final product, whether it be bags, shoes, or other leather goods. This process may involve additional treatments, such as applying adhesives or using rivets for added strength.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Quality control during assembly is vital. Each stitch must be precise, and the assembly should follow strict guidelines to ensure durability and performance. B2B buyers should look for suppliers who employ skilled artisans and utilize automated systems to maintain consistency and quality across batches.
4. Finishing: What Are the Final Touches Applied to Leather Products?
The finishing stage adds the final touches to leather products, enhancing their appearance and performance. This may include dyeing, polishing, and applying protective coatings. Finishing techniques can significantly impact the leather’s texture, colorfastness, and resistance to wear and moisture.
Buyers should seek suppliers who offer a variety of finishing options and can provide samples for quality assessment. It’s essential to understand the types of finishes used and their long-term effects on product durability and maintenance.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Leather Technology?
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of leather manufacturing that ensures products meet specific standards and regulations. For B2B buyers, understanding QA processes is essential to ensure the reliability and quality of the leather sourced.
What International Standards Should Leather Manufacturers Follow?
The leather industry adheres to various international standards, with ISO 9001 being a cornerstone for quality management systems. This standard ensures that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, certifications such as CE marking and API standards are relevant in specific markets.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with recognized certifications, as these indicate a commitment to quality and adherence to best practices.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Leather Production?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to maintaining product quality throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes to identify and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive assessments of finished products before they are shipped.
Buyers should establish clear communication with suppliers regarding their QC processes and request access to inspection reports and quality metrics.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Leather Quality Control?
Testing methods for leather products can include physical, chemical, and environmental assessments. Common tests include:
- Tensile Strength Tests: To assess durability and resistance to tearing.
- Water Resistance Tests: Evaluating how well the leather withstands moisture.
- Colorfastness Tests: Ensuring that dyes do not bleed or fade under various conditions.
Buyers should inquire about the specific testing methods employed by suppliers and the results of these tests to ensure product quality.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verification of supplier quality control practices is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in international markets. Here are several strategies to ensure quality:
1. Conducting Supplier Audits: What Should Buyers Look For?
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing practices and quality control measures. Buyers should look for compliance with international standards, the presence of robust QA systems, and evidence of continuous improvement initiatives.
2. Requesting Quality Reports: What Information Should Be Included?
Suppliers should be able to provide detailed quality reports that outline inspection results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken in response to quality issues. These documents should be readily accessible and transparent.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
3. Utilizing Third-Party Inspections: How Can They Enhance Trust?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of supplier quality control practices. These services can conduct audits and testing, offering additional assurance regarding the reliability of the supplier’s products.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate additional complexities in quality control, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Differences in regulations, standards, and cultural practices can impact quality assurance.
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers should familiarize themselves with the regulatory landscape in the supplier’s country, ensuring that products comply with local laws and international trade agreements.
-
Cultural Sensitivity in Quality Expectations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and craftsmanship. Buyers should communicate their standards clearly and work collaboratively with suppliers to align on expectations.
-
Logistical Considerations: Quality can also be affected by the logistics of transporting leather products across borders. Buyers should consider the impact of shipping conditions on product integrity and plan accordingly.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance in leather technology is vital for B2B buyers seeking high-quality leather products. By focusing on these areas, buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships with suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather technology’
In the complex world of leather technology, sourcing the right materials and suppliers is crucial for ensuring quality, sustainability, and compliance with industry standards. This checklist serves as a practical guide for B2B buyers looking to procure leather technology solutions effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the leather products you intend to source. This includes understanding the type of leather, tanning processes, and any specific chemical treatments needed. By having precise specifications, you can communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers and ensure that their offerings align with your quality standards.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Step 2: Research Sustainable Practices
Investigate suppliers that prioritize sustainability in their production processes. Look for companies that utilize eco-friendly tanning methods, such as vegetable or enzyme-based tanning, which reduce environmental impact. Additionally, consider suppliers who source hides from regenerative farms, as this supports biodiversity and sustainable agricultural practices.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, vet suppliers thoroughly to ensure they meet your standards. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Assess their production capacity, technological capabilities, and experience in the leather sector to gauge their reliability and expertise.
Step 4: Check Certifications and Compliance
Verify that your potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or other industry-specific standards. These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to international quality and environmental practices, which is crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring product quality.
Step 5: Assess Quality Control Measures
Inquire about the quality control processes implemented by suppliers. A robust quality management system should include regular testing of raw materials and finished products to ensure they meet your specifications. Look for suppliers who can provide documentation of their quality assurance processes, such as Material Data Safety Sheets (MSDS).
Step 6: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples before finalizing a procurement decision. Testing these samples allows you to assess the leather’s quality, durability, and performance in real-world applications. This step is essential to verify that the supplier can deliver products that meet your technical and aesthetic requirements.
Illustrative image related to leather technology
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Ensure that the contract includes clear terms for product returns, warranties, and service support. This will help to establish a mutually beneficial relationship and protect your investment.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing leather technology, ensuring that they select suppliers who align with their business needs and sustainability goals. This strategic approach not only enhances product quality but also fosters long-term partnerships in the leather industry.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather technology Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Technology Sourcing?
In the leather technology sector, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of leather significantly influence the cost. Premium hides, organic tanning agents, and innovative bio-based materials like Mylo™ and Appleskin™ often come at a higher price point but can offer long-term sustainability benefits.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in leather production, especially for traditional crafting techniques and quality assurance. Labor costs can vary significantly by region, with countries like Vietnam and Brazil often offering competitive rates compared to Europe and North America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Companies investing in eco-friendly processes or advanced machinery may experience higher overhead initially, but these costs can be mitigated through efficiency gains over time.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling for customized designs or specialized production techniques can add to the initial cost. However, investing in the right tools can enhance efficiency and quality in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product consistency and adherence to international standards. Although this may increase upfront costs, it reduces the risk of defects and returns, ultimately benefiting the buyer.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the geographical location of the supplier and the buyer. International shipping, customs duties, and local tariffs must be factored into the overall cost structure.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This can vary widely based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Leather Technology Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing in leather technology sourcing:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) often dictate pricing structures. Higher volume orders typically result in lower per-unit costs, making it crucial for buyers to assess their purchasing needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized orders or unique specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Eco-friendly or innovative materials may have premium costs but can appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet specific certifications (e.g., ISO, eco-labels) often command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate the importance of these certifications in their market.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service quality can also influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer peace of mind regarding quality and delivery timelines.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly affect total costs. Buyers must understand these terms to accurately assess their total landed costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Leather Technology Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing, especially when ordering in bulk. Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to negotiate better deals.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, logistics, and potential waste. A slightly higher upfront investment may lead to lower long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, international tariffs, and trade agreements that can impact pricing. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to more favorable terms over time.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand local pricing trends and supplier capabilities. This knowledge will empower you to make informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices in the leather technology sector can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should seek updated quotes and consider potential price changes when planning their sourcing strategies.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather technology With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Leather Technology: What Are the Options?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of material technology, the leather industry faces increasing scrutiny regarding sustainability and performance. As the demand for eco-friendly and innovative solutions grows, it is essential for B2B buyers to explore alternatives to traditional leather technology. This analysis compares leather technology with two notable alternatives: bio-fabricated materials and recycled leather. Each solution offers distinct advantages and challenges, making it crucial for buyers to understand their implications.
| Comparison Aspect | Leather Technology | Bio-Fabricated Materials | Recycled Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, high-quality finish | Varies; generally good, but less proven | Comparable to new leather, varies by source |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on quality | Often higher due to R&D costs | Generally lower than new leather |
| Ease of Implementation | Established processes, requires training | New technology; may need specialized training | Easier to implement; uses existing materials |
| Maintenance | Requires regular care and conditioning | Similar care needs as traditional leather | Varies; can be as durable as new leather |
| Best Use Case | High-end fashion, automotive, luxury goods | Sustainable fashion, vegan markets | Budget-friendly fashion, accessories |
Understanding Bio-Fabricated Materials
Bio-fabricated materials, such as Mylo™ (mushroom leather) and Appleskin™, represent a significant shift in the quest for sustainable alternatives. These materials are crafted from organic waste and offer a cruelty-free option that appeals to eco-conscious consumers. The primary advantage of bio-fabricated materials is their lower environmental impact compared to traditional leather. However, they can come with a higher price tag due to the research and development involved in their production. Additionally, while they are generally durable, the technology is still relatively new, which may lead to variability in performance and acceptance in various markets.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Evaluating Recycled Leather
Recycled leather presents an innovative approach to sustainability by repurposing scraps and offcuts from leather production. This method significantly reduces waste and utilizes existing resources, making it an attractive option for cost-sensitive buyers. The performance of recycled leather can be comparable to that of new leather, depending on the quality of the source material. However, buyers should be aware that the durability and aesthetics may vary based on the production process. Recycled leather is particularly well-suited for budget-friendly fashion lines and accessories, appealing to consumers looking for sustainable options without compromising on style.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the right material for their needs, B2B buyers should consider multiple factors, including performance requirements, cost constraints, and sustainability goals. Leather technology remains a strong choice for high-end applications where durability and aesthetics are paramount. In contrast, bio-fabricated materials may be ideal for brands targeting eco-conscious consumers who prioritize sustainability over traditional luxury. Meanwhile, recycled leather offers a practical solution for those seeking cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternatives. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s values, target market, and long-term sustainability goals, ensuring that the chosen material supports both brand integrity and consumer demand.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather technology
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Leather Technology for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the essential technical properties of leather is crucial for B2B buyers involved in the leather industry. These specifications not only influence product quality but also impact sourcing, pricing, and sustainability practices.
Illustrative image related to leather technology
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of leather based on its quality, appearance, and durability. Grades range from full-grain, which uses the top layer of the hide and retains its natural characteristics, to corrected grain, which has been sanded and treated for a uniform look. For buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is vital as it directly affects the end product’s performance and market positioning.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance in leather technology indicates the acceptable variation in dimensions and physical properties during production. This includes thickness, width, and weight of the leather. Understanding tolerance levels is essential for manufacturers to ensure compatibility with machinery and design specifications, ultimately reducing waste and improving production efficiency.
3. Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of leather—especially the tanning agents used—determines its environmental impact and suitability for various applications. For instance, vegetable tanning is more eco-friendly compared to chrome tanning. B2B buyers must be aware of these compositions as they align with sustainability goals and consumer preferences for eco-conscious products.
4. Durability
Durability refers to the ability of leather to withstand wear, tear, and environmental factors. This property is influenced by the tanning process, finishing techniques, and the quality of the raw hide. Buyers should prioritize durability to ensure that the leather products meet customer expectations for longevity, especially in high-use applications like automotive interiors or footwear.
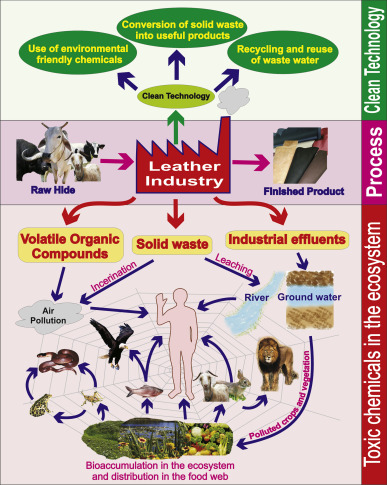
Illustrative image related to leather technology
5. Breathability
Breathability is a measure of how well leather allows moisture and air to pass through. This property is essential for applications where comfort is paramount, such as clothing and upholstery. B2B buyers should consider breathability to enhance user experience and product performance, particularly in markets with varying climate conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Leather Technology?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the leather sector. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or products that are then sold under another company’s brand name. In leather technology, this often pertains to manufacturers who supply leather components for various industries, such as automotive or fashion. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers establish reliable supply chains.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses negotiate better terms and optimize their purchasing strategies.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific quantities of products. For leather buyers, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process, allowing for comparative analysis of suppliers and ensuring competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. They specify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transport. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, as it clarifies logistics and reduces disputes.
5. Tannage
Tannage is the chemical process that transforms raw hides into leather. This term is significant for buyers focusing on sustainability, as different tanning methods (vegetable, chrome, etc.) have varying environmental impacts. Knowing the type of tannage can guide buyers in selecting products that align with their sustainability goals.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their sourcing strategies, improve product quality, and align with market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather technology Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Leather Technology?
The leather technology sector is undergoing a significant transformation driven by global demand for sustainability, innovation, and efficiency. Key market dynamics include the increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing and bio-fabrication, which allow for customization and the creation of sustainable leather alternatives. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly focused on sourcing high-quality, environmentally-friendly leather products to meet consumer preferences and regulatory requirements.
Emerging trends include the shift towards plant-based leather alternatives, such as Mylo™ and Appleskin™, which cater to the growing vegan market while minimizing the environmental footprint. Additionally, advancements in smart technologies, including AI and IoT, are optimizing production processes, improving quality control, and reducing waste. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate innovation and a commitment to sustainable practices, aligning their sourcing strategies with global trends toward circular economies.
The leather market is projected to expand significantly, reaching an estimated $700 billion by 2030. This growth is fueled by both genuine leather and synthetic alternatives, which are increasingly being integrated into high-end fashion and everyday products. For B2B buyers, understanding these trends is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with consumer demand and environmental responsibility.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Leather Technology?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are critical considerations for B2B buyers in the leather technology sector. The environmental impact of traditional leather production has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices, including waterless tanning methods and the use of biodegradable chemicals. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to stringent environmental regulations and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint.

Illustrative image related to leather technology
Ethical supply chains are also becoming a focal point, with many companies prioritizing sourcing from regenerative farms that promote biodiversity and soil health. This approach not only enhances the sustainability of leather production but also improves product traceability, allowing buyers to align their values with their sourcing decisions.
Green certifications and materials are key indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Certifications such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and the Leather Working Group (LWG) provide assurance that the leather products meet high environmental and ethical standards. By sourcing from certified suppliers, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to the growing segment of eco-conscious consumers.
What Is the Evolution of Leather Technology and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of leather technology is marked by a transition from traditional tanning methods to innovative, sustainable practices that prioritize environmental responsibility. Historically, leather production relied heavily on chemical processes that often resulted in significant waste and pollution. However, the introduction of eco-friendly alternatives, such as vegetable tanning and enzyme-based methods, has transformed the industry.
This shift is particularly relevant for B2B buyers who are increasingly conscious of the environmental and ethical implications of their sourcing choices. The integration of advanced technologies, such as AI-driven manufacturing processes and sustainable raw material sourcing, has further enhanced the industry’s capacity to meet modern consumer demands.
As the leather market continues to evolve, buyers must stay informed about the latest innovations and trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their business goals and sustainability commitments. Understanding the historical context of leather technology can provide valuable insights into future developments and opportunities within the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather technology
-
How do I choose the right leather technology supplier for my business?
When selecting a leather technology supplier, consider their experience, product range, and environmental practices. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the industry, as well as certifications that demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Additionally, assess their customer service and technical support capabilities, which are crucial for addressing any challenges you may encounter. Engaging in direct communication to discuss your specific needs and expectations will also help ensure they can meet your requirements effectively. -
What is the best technology for sustainable leather production?
The best technologies for sustainable leather production include vegetable tanning, waterless tanning processes, and bio-based materials like Mylo™ and Appleskin™. These methods significantly reduce chemical usage and environmental impact compared to traditional chrome tanning. Additionally, innovations such as enzyme-based tanning and advanced waste management systems contribute to a more eco-friendly production process. Choosing suppliers that utilize these technologies can help your business align with growing consumer demand for sustainable products. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for leather technology products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly between suppliers and the specific products offered. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units, depending on the material and customization requirements. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly with potential suppliers and inquire about their MOQs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility, especially for first-time buyers or smaller businesses looking to test products before committing to larger orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing leather technology?
Payment terms for leather technology suppliers can vary widely, but common practices include 30% upfront payment and 70% upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms, allowing additional time for payment after the goods are received. It’s crucial to establish clear payment terms during negotiations to avoid any misunderstandings. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and that there are established procedures for handling any disputes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in my leather technology sourcing?
To ensure quality assurance in your leather technology sourcing, request detailed product specifications and quality control processes from suppliers. Conduct audits or inspections at the manufacturing facility, if possible, to evaluate their QA practices firsthand. Consider requesting samples of the products to assess their quality before placing a larger order. Additionally, establish clear communication channels for feedback and any necessary adjustments during production. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing leather technology internationally?
When sourcing leather technology internationally, consider shipping costs, customs regulations, and lead times. It’s essential to work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide insights into the best shipping methods for your products. Additionally, ensure that all necessary documentation, such as invoices and customs declarations, is in order to avoid delays at the border. Collaborating with a reliable freight forwarder can also streamline the logistics process and mitigate potential issues. -
How can I customize leather technology products to meet my specific needs?
Customization options for leather technology products depend on the supplier’s capabilities. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions, including specific formulations, colors, and finishes. When discussing your requirements, be clear about your desired specifications and any unique applications. Request samples or prototypes to evaluate the customization before finalizing your order. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate more effective collaboration on custom projects. -
What trends should I be aware of in the leather technology industry?
Key trends in the leather technology industry include a shift toward sustainable practices, advancements in biofabrication, and the integration of smart technologies. Consumers are increasingly demanding eco-friendly products, prompting suppliers to innovate in areas like plant-based leathers and waterless tanning. Additionally, technologies such as AI and automation are enhancing production efficiency and quality control. Staying informed about these trends can help your business remain competitive and responsive to market demands.
Top 5 Leather Technology Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Leather Technologies – Eco-Friendly Leather Chemicals
Domain: leathertechnologies.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Leather Technologies, Inc. offers a wide range of performance and high-quality chemicals specifically designed for leather dry-cleaning needs. They provide over 60 different chemicals for various purposes, focusing on environmentally friendly solutions. The company emphasizes innovation and state-of-the-art products, supported by experienced technical staff and exceptional customer service.
2. Lifology – Leather Technology Engineering
Domain: lifology.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Leather Technology Engineering is a new branch of engineering focused on the synthesis, production, and refining of leather, including artificial leather. It offers career opportunities in various sectors such as footwear, luggage, upholstery, and more. Key skills required include creativity, problem-solving, teamwork, and communication. Eligibility for a degree requires completion of 10+2 in the …
3. China Leather Industry – High-Value Products
Domain: jlse.springeropen.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: The leather industry converts animal hides and skins into high-value-added products, contributing to carbon neutrality and aligning with the circular economy. In 2024, China’s leather industry achieved 877.4 billion yuan in sales revenue and 47.2 billion yuan in profits, with exports of 92.9 billion US dollars. Sustainable technologies focus on green leather chemicals and eco-friendly processes, i…
4. Science Father – CAD-Enhanced Leather Technology
Domain: cad-conferences.sciencefather.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Leather technology integrates Computer Aided Design (CAD) into leather production and goods manufacturing, enhancing precision and innovation. Key aspects include: 1. CAD-Enhanced Leather Design: Revolutionizes leather design with intricate patterns and textures. 2. Sustainable Leather Production: Optimizes tanning processes and reduces waste for eco-friendly practices. 3. Leather Goods Manufactur…
5. IDTechEx – Vegan Bio-Based Leather Trends
Domain: idtechex.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, IDTechEx – Vegan Bio-Based Leather Trends, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather technology
The leather technology sector is evolving rapidly, driven by sustainability, innovation, and strategic sourcing. B2B buyers must recognize the importance of partnering with suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices, such as waterless tanning and the use of bio-based materials. This not only enhances product quality but also aligns with global trends towards responsible consumption, a key consideration for discerning markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Strategic sourcing is essential for leveraging cutting-edge technologies that improve efficiency and reduce waste. By investing in advanced materials and sustainable processes, businesses can meet the growing demand for environmentally responsible leather products while maintaining competitive pricing and high standards of craftsmanship.
Looking ahead, the future of leather technology is bright, with innovations such as augmented reality and smart textiles set to reshape consumer experiences. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage actively with suppliers who are pioneers in these advancements. By doing so, they can not only secure a reliable supply chain but also contribute to a more sustainable and innovative leather industry. Embrace these opportunities and position your business at the forefront of the leather technology revolution.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.