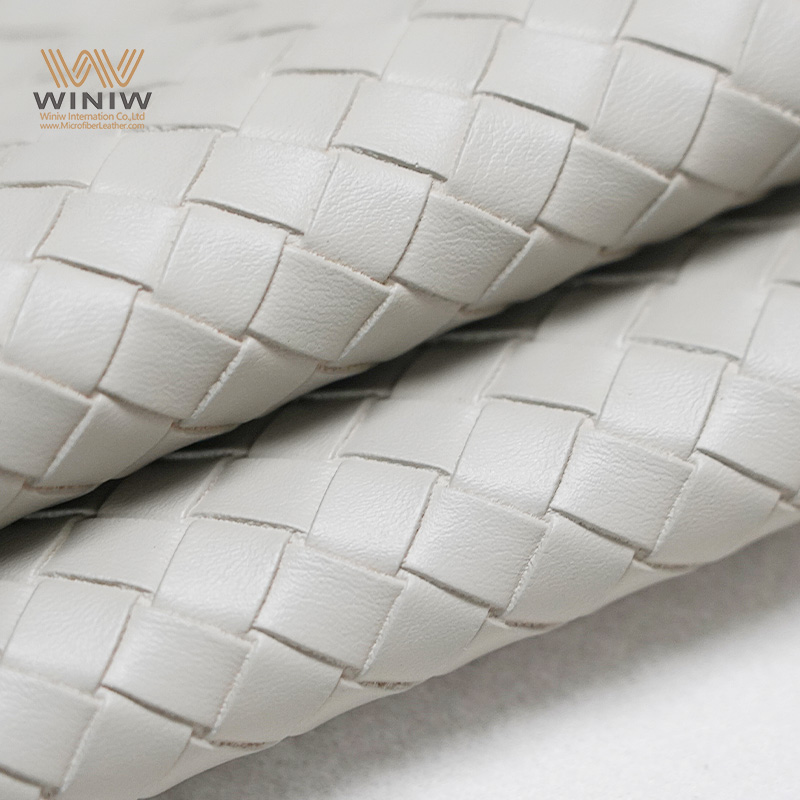
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather fabric
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality faux leather fabric can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses seek to balance aesthetic appeal with ethical and environmental considerations, the demand for versatile, cost-effective alternatives to genuine leather continues to rise. This guide is designed to illuminate the complexities of the global faux leather market, providing insights into various fabric types, their applications across industries, and strategies for vetting reliable suppliers.
By exploring the intricacies of faux leather—including its diverse textures and finishes, such as pebble, crocodile, and shimmer—buyers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to make informed purchasing decisions. Furthermore, the guide will delve into crucial aspects like cost analysis, market trends, and sustainability practices, empowering businesses to align their sourcing strategies with their brand values.
Whether you’re looking to enhance your product line or meet specific consumer demands, this resource aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the faux leather landscape confidently. With actionable insights tailored to the unique needs of B2B buyers across multiple regions, you will be well-prepared to capitalize on the opportunities presented by this growing market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Faux Leather Fabric Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather fabric
- Understanding faux leather fabric Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of faux leather fabric
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather fabric’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather fabric
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather fabric
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather fabric’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather fabric Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather fabric With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather fabric
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather fabric Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather fabric
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather fabric
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding faux leather fabric Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Soft, flexible, and breathable; mimics real leather closely | Apparel, upholstery, automotive interiors | Pros: Eco-friendlier than PVC, good durability. Cons: Can be more expensive than PVC. |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Highly durable, water-resistant, and available in various finishes | Upholstery, bags, footwear | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Less breathable, environmental concerns. |
| Vegan Leather | Made from plant-based materials or synthetic alternatives | Eco-friendly fashion, accessories | Pros: Sustainable, appealing to conscious consumers. Cons: May vary in quality and durability. |
| Microfiber | Ultra-soft texture, lightweight, and easy to clean | High-end fashion, automotive interiors | Pros: Luxurious feel, stain-resistant. Cons: Can be more expensive, limited color options. |
| Faux Suede | Soft, matte finish, mimics the look of suede | Apparel, upholstery, accessories | Pros: Soft texture, good for fashion. Cons: Less durable than other faux leathers. |
What Are the Characteristics of Polyurethane (PU) Faux Leather?
Polyurethane (PU) faux leather is recognized for its soft, flexible texture that closely resembles genuine leather. It is more breathable than its PVC counterpart, making it suitable for clothing and upholstery applications. When sourcing PU faux leather, buyers should consider the quality of the material, as higher-end products offer better durability and resistance to wear. Additionally, its eco-friendliness compared to PVC can be a strong selling point in markets focused on sustainability.
Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
How Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Faux Leather Compare?
PVC faux leather is a widely used synthetic alternative, known for its durability and water resistance. It comes in various finishes and colors, making it a versatile choice for upholstery and accessories. However, buyers must consider the environmental impact of PVC production, as it is less breathable than PU. While PVC is often more cost-effective, its lower quality may not appeal to high-end markets. Buyers should evaluate whether the price point aligns with their target demographic and product positioning.
Why Choose Vegan Leather for Sustainable Applications?
Vegan leather, made from plant-based materials or innovative synthetic alternatives, caters to the growing demand for sustainable and ethical products. This type of faux leather appeals to eco-conscious consumers and brands aiming to reduce their environmental footprint. When purchasing vegan leather, B2B buyers should assess the sourcing and production methods to ensure the material aligns with their sustainability goals. While vegan leather can be more expensive, its marketability can justify the investment.
What Makes Microfiber a Luxurious Option?
Microfiber faux leather offers an ultra-soft texture that is both lightweight and easy to maintain, making it an appealing choice for high-end fashion and automotive interiors. Its stain-resistant properties enhance its usability in various applications. Buyers should be aware that while microfiber can provide a luxurious feel, it may also come at a higher price point. Limited color options might restrict design flexibility, so it’s essential to evaluate the target market’s preferences before making bulk purchases.
When Should You Consider Faux Suede?
Faux suede is characterized by its soft, matte finish and is often used in apparel and home décor. While it provides a fashionable look, its durability is generally lower compared to other faux leather types. Buyers should weigh the aesthetic appeal against the potential need for more frequent replacement in high-use areas. Faux suede can be a great option for fashion items, but B2B buyers should ensure it meets their quality standards to avoid customer dissatisfaction.
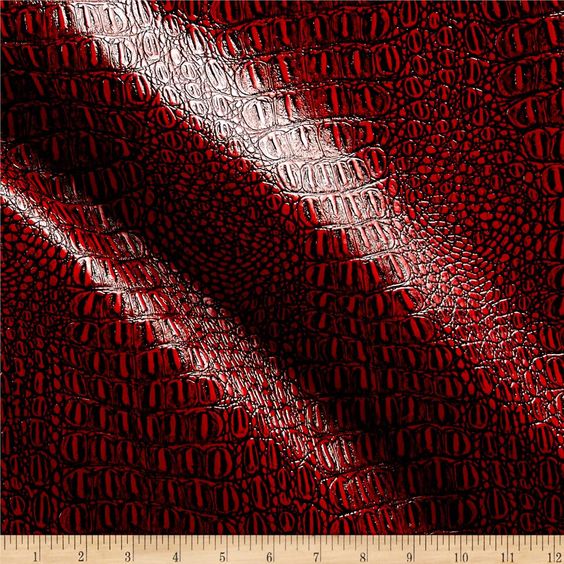

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
Key Industrial Applications of faux leather fabric
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of faux leather fabric | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Jackets, skirts, and pants | Offers a stylish, cost-effective alternative to genuine leather; easy to maintain. | Ensure compliance with international quality standards; consider fabric texture and finish options. |
| Automotive | Upholstery and interior trim for vehicles | Enhances aesthetic appeal and durability while reducing costs; easy to clean and maintain. | Look for UV resistance and fire-retardant properties; verify supplier’s sustainability practices. |
| Furniture & Upholstery | Sofas, chairs, and decorative items | Provides a luxurious look at a lower price point; durable and easy to clean. | Assess the fabric’s abrasion resistance and colorfastness; consider sourcing from eco-friendly manufacturers. |
| Sports & Leisure | Equipment covers and activewear | Lightweight, durable, and water-resistant; suitable for high-performance applications. | Evaluate the fabric’s breathability and moisture-wicking properties; ensure compliance with safety standards. |
| Accessories & Goods | Handbags, wallets, and belts | Versatile design options; allows for creative branding opportunities while being cost-effective. | Check for customization options and minimum order quantities; ensure that the fabric meets ethical sourcing standards. |
How is Faux Leather Fabric Used in the Fashion & Apparel Industry?
Faux leather fabric is widely utilized in the fashion and apparel industry for crafting stylish jackets, skirts, and pants. Its ability to mimic the luxurious appearance of genuine leather while being more affordable makes it a preferred choice for designers and manufacturers. This material not only offers aesthetic appeal but also simplifies maintenance, as it is typically easier to clean. International buyers should prioritize sourcing options that meet global quality standards and consider various textures and finishes to cater to diverse consumer preferences.
What Role Does Faux Leather Play in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, faux leather fabric is commonly used for upholstery and interior trim. It enhances the aesthetic appeal of vehicles while providing durability at a lower cost compared to genuine leather. Additionally, faux leather is easier to clean, making it a practical choice for automotive applications. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing fabrics that exhibit UV resistance and fire-retardant properties, ensuring safety and longevity for vehicle interiors.
How is Faux Leather Fabric Beneficial for Furniture & Upholstery?
Faux leather fabric is an excellent choice for furniture and upholstery, including sofas, chairs, and decorative items. It offers a luxurious appearance without the high price tag associated with real leather, making it attractive for both manufacturers and consumers. Moreover, its durability and ease of cleaning make it suitable for homes with children or pets. When sourcing faux leather for furniture, buyers should assess the fabric’s abrasion resistance and colorfastness, while also considering eco-friendly options to meet growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
In What Ways is Faux Leather Used in Sports & Leisure Equipment?
In the sports and leisure sector, faux leather fabric is utilized for equipment covers and activewear due to its lightweight, durable, and water-resistant characteristics. This makes it ideal for high-performance applications where functionality is crucial. Buyers should evaluate the fabric’s breathability and moisture-wicking properties to ensure comfort during use, while also ensuring compliance with safety standards specific to sports equipment.

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
How Can Faux Leather Fabric Enhance Accessories & Goods?
Faux leather is a versatile material for creating handbags, wallets, and belts, allowing for a wide range of design possibilities. It offers businesses a cost-effective solution that does not compromise on style, enabling creative branding opportunities. When sourcing faux leather for accessories, buyers should inquire about customization options and minimum order quantities, while also ensuring that the fabric aligns with ethical sourcing standards to meet consumer expectations for sustainability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather fabric’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misalignment Between Faux Leather Quality and Customer Expectations
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when sourcing faux leather that meets both quality standards and customer expectations. Inconsistent fabric quality across suppliers can lead to issues such as premature wear and tear, color fading, or an undesirable finish that doesn’t align with the intended product design. This misalignment can result in customer dissatisfaction and increased return rates, ultimately impacting the buyer’s reputation and bottom line.
The Solution: To effectively mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should establish clear quality benchmarks and specifications before sourcing faux leather. Engaging in thorough market research to identify reputable suppliers known for consistency in quality is crucial. Additionally, consider requesting samples from potential vendors to evaluate the texture, durability, and overall appearance of the fabric in relation to your product’s requirements. By establishing strong relationships with suppliers and communicating your quality expectations clearly, you can ensure a better alignment between the faux leather sourced and the expectations of your end customers.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Finding Environmentally Friendly Faux Leather Options
The Problem: With growing consumer awareness about sustainability, many B2B buyers are under pressure to source environmentally friendly materials. However, the synthetic nature of most faux leather fabrics, traditionally made from PVC and other petroleum-based products, poses a challenge. Buyers may struggle to find options that not only meet ethical standards but also maintain the aesthetic and functional properties of traditional faux leather.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should proactively seek out suppliers who specialize in sustainable or bio-based faux leather options. These alternatives, such as those made from polyurethane (PU) or innovative plant-based materials, can provide the desired look and feel without the environmental drawbacks. Conducting due diligence on suppliers’ manufacturing processes and certifications can reveal their commitment to sustainability. Additionally, developing partnerships with environmentally-focused manufacturers can allow for more customized solutions that meet both aesthetic and ethical standards, enabling your products to stand out in a competitive market.

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
Scenario 3: Challenges in Fabric Care and Maintenance
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues related to the care and maintenance of faux leather products, which can be less intuitive compared to genuine leather. Misunderstanding the cleaning and care requirements can lead to fabric damage, such as cracking or peeling, ultimately resulting in increased costs for replacements or repairs. This knowledge gap can also lead to negative customer experiences and reduced brand loyalty.
The Solution: Providing comprehensive care guidelines for faux leather products is essential. B2B buyers should educate themselves about the specific cleaning and maintenance requirements of the faux leather they are sourcing. This includes understanding the correct cleaning agents, recommended washing temperatures, and proper storage conditions to prevent damage. Additionally, creating and distributing care instruction labels for the end-users can enhance customer satisfaction and longevity of the products. By taking these proactive steps, you can minimize issues related to fabric care and maintain the quality and appearance of your faux leather offerings over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather fabric
What Are the Key Properties of Common Faux Leather Materials?
Faux leather, a popular alternative to genuine leather, is primarily made from synthetic materials that mimic the appearance and feel of real leather. Understanding the various materials used in faux leather production is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing for industries such as fashion, upholstery, and automotive. Here, we analyze four common materials used in faux leather, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)?
PVC is one of the most widely used materials for faux leather. It is known for its durability and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for various applications, including upholstery and fashion accessories.
- Key Properties: PVC faux leather can withstand moderate temperature variations and has a good resistance to abrasion. However, it has a low breathability factor, which may lead to discomfort in warmer climates.
- Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and widely available, but it can be less environmentally friendly due to its production process. While it offers good durability, it may not be as soft or luxurious in feel compared to other materials.
- Impact on Application: PVC is compatible with a wide range of media, including printing and dyeing, making it versatile for branding and customization.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with strict environmental regulations, such as parts of Europe, should ensure compliance with standards like REACH and RoHS. Additionally, understanding local preferences for material softness and finish is crucial.
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Compare to PVC?
Polyurethane is another common material used in faux leather production, known for its softer texture and more luxurious feel.

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
- Key Properties: PU faux leather has better breathability and flexibility compared to PVC, making it suitable for clothing and accessories that require a comfortable fit.
- Pros & Cons: While PU offers a more premium feel and is generally more environmentally friendly, it tends to be more expensive than PVC. Its durability is also slightly lower, which may affect its longevity in high-wear applications.
- Impact on Application: PU is ideal for high-end fashion items and upholstery where aesthetics are critical, but it may not be the best choice for heavy-duty applications.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying quality of PU materials available in different markets. Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM and ISO, is essential for ensuring product quality.
What Are the Advantages of Using Bio-Based Faux Leather?
Bio-based faux leather, often made from plant-derived materials, is gaining traction as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional synthetic options.
- Key Properties: This material typically offers similar durability to PU and PVC but with enhanced biodegradability. Its thermal properties vary based on the specific plant materials used.
- Pros & Cons: The primary advantage is its reduced environmental impact; however, bio-based faux leather can be more expensive and less widely available than conventional options.
- Impact on Application: Its eco-friendly nature makes it suitable for brands focusing on sustainability, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider local market readiness for bio-based materials, including consumer acceptance and potential certifications needed for marketing.
How Does Recycled Faux Leather Fit into the Market?
Recycled faux leather, made from post-consumer waste, is an innovative solution that addresses both sustainability and performance.
- Key Properties: This material can exhibit similar durability and aesthetic qualities as traditional faux leather, depending on the recycling process.
- Pros & Cons: The main advantage is its reduced environmental footprint; however, quality can be inconsistent, and it may require specific manufacturing processes that can complicate production.
- Impact on Application: Recycled faux leather is suitable for brands looking to enhance their sustainability credentials while still delivering quality products.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that recycled materials meet local regulations and standards, particularly in markets like Europe, where sustainability is a key purchasing factor.
Summary Table of Faux Leather Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for faux leather fabric | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Upholstery, Fashion Accessories | Cost-effective and durable | Low breathability and environmental concerns | Low |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Clothing, High-end Fashion Items | Soft texture and luxurious feel | Higher cost and lower durability | Med |
| Bio-Based Faux Leather | Sustainable Fashion, Eco-friendly Products | Reduced environmental impact | Higher cost and limited availability | High |
| Recycled Faux Leather | Sustainable Brands, Eco-conscious Products | Lower environmental footprint | Inconsistent quality and complex production | Med |
This strategic analysis of faux leather materials provides B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions based on their specific market needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather fabric
What Are the Main Stages of Faux Leather Fabric Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of faux leather fabric involves several key stages that ensure the production of a high-quality, durable material suitable for various applications. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Faux Leather Production?
Material preparation begins with selecting the appropriate base textile, which is typically made from polyester or cotton. This base is then coated with either polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), both of which are synthetic materials known for their durability and flexibility.
The preparation process may also include treatments to enhance the base textile’s properties, such as water resistance or flame retardancy. This is crucial, as the quality of the base material directly influences the final product’s performance and aesthetics. Additionally, suppliers often conduct tests on the materials to ensure they meet specific standards before moving to the next phase.
What Techniques Are Used to Form Faux Leather?
Once the material is prepared, the forming stage involves applying the plastic coating to the base textile. This is typically achieved through techniques such as:
- Calendering: This method involves passing the textile through rollers that apply heat and pressure to bond the plastic to the fabric. It ensures an even coating and a smooth finish.
- Coating: This technique includes spraying or pouring the plastic over the base material. It allows for various textures and finishes, which can mimic real leather’s appearance.
- Lamination: In this process, a layer of foam or other materials may be added between the base fabric and the plastic coating to provide additional cushioning and a more authentic leather feel.
These techniques can be adjusted based on the desired characteristics of the final product, such as thickness, flexibility, and texture.
How Is Faux Leather Fabric Assembled and Finished?
After forming, the assembly stage involves cutting the coated material into specified shapes and sizes for various applications, such as upholstery, garments, or accessories. This step may also include sewing or bonding different pieces together, depending on the product design.
Finishing processes are critical for enhancing the faux leather’s aesthetic appeal and performance. Common finishing techniques include:
- Printing: This can add patterns or colors, allowing for customization that meets market demands.
- Embossing: This technique creates textures that mimic natural leather grains, providing a more luxurious feel.
- Top Coating: A protective layer is often applied to enhance durability and resistance to stains or scratches.
These finishing touches not only improve the visual quality of the faux leather but also increase its longevity and usability.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Faux Leather Fabric?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the faux leather manufacturing process to ensure that the products meet international standards and customer expectations. Several key standards and certifications are relevant:

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
- ISO 9001: This international standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable to manufacturers of faux leather. It emphasizes consistent quality, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Particularly important for products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates that the product complies with EU safety and environmental requirements.
- API Standards: While primarily relevant for the oil and gas sector, certain API standards can apply to faux leather used in specialized industrial applications.
Adhering to these standards not only enhances product quality but also builds trust with B2B buyers, particularly in regions with stringent regulatory environments.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Faux Leather Production?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints established to ensure the product’s integrity at various stages. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials before they are used in production. Suppliers should verify that all materials meet the specified standards and are free from defects.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the adherence to quality standards. This includes checking the thickness of the plastic coating and ensuring that there are no inconsistencies in texture or color.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the products are shipped, a final inspection is performed to assess the overall quality, including durability tests and aesthetic evaluations. This step is crucial for identifying any defects that may have occurred during production.
These QC checkpoints are essential for maintaining high standards and ensuring that the final products meet the expectations of B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical to ensuring product reliability. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control practices. Buyers should request access to their quality management documentation and audit reports.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide comprehensive quality reports detailing testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These inspectors can verify that the products meet specified standards and are free from defects before shipment.
-
Check for Certifications: Buyers should look for relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 or CE marking. These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to established quality management practices and complies with international standards.
-
Gather Customer Feedback: Engaging with other businesses that have sourced from the same supplier can provide valuable insights into their quality control and overall reliability.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers often face unique challenges when it comes to quality control and certification. Differences in regulations, quality expectations, and cultural practices can impact the sourcing process. Here are some considerations:
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that the products comply with local regulations in their respective markets, which may differ significantly from those in the supplier’s country.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding cultural nuances can facilitate better communication and foster stronger relationships with suppliers, enhancing the overall quality assurance process.
- Logistical Challenges: Shipping and customs regulations can impact product delivery and quality. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that all logistical aspects are managed efficiently.
By navigating these complexities and implementing robust verification processes, international B2B buyers can ensure they source high-quality faux leather fabrics that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather fabric’
To assist B2B buyers in successfully procuring faux leather fabric, this guide offers a structured checklist. By following these steps, you will ensure that your sourcing process is thorough, efficient, and aligned with your business needs.

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the desired characteristics of the faux leather you need. This includes specifications such as thickness, texture, color, and durability. Establishing these parameters early on helps in communicating effectively with suppliers and ensures that you receive products that meet your quality standards.
- Consider factors like intended use (e.g., upholstery, fashion, accessories) to narrow down your options.
- Specify any environmental or ethical considerations if sourcing vegan or eco-friendly materials.
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Investigate potential suppliers to verify their legitimacy and capabilities. Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards, such as ISO certifications or eco-labels. This step is essential to ensure that you are partnering with reputable manufacturers.
- Request documentation that outlines their production processes and quality control measures.
- Check online reviews and industry forums for feedback from previous clients.
Step 3: Evaluate Product Samples
Request samples of the faux leather fabric before making bulk purchases. This allows you to assess the quality, texture, and overall feel of the material firsthand. Ensuring that the samples meet your specifications is crucial for maintaining your brand’s quality.
- Examine the sample for durability, color fastness, and ease of maintenance.
- Consider how the fabric performs under different conditions, such as exposure to sunlight or moisture.
Step 4: Compare Pricing and Terms
Analyze pricing structures and payment terms from different suppliers. While cost is a significant factor, it’s important to balance it with quality and service. Ensure that the pricing aligns with your budget while also considering the total cost of ownership.
- Look for hidden costs such as shipping fees, customs duties, and minimum order quantities.
- Negotiate payment terms that work for your cash flow, such as deposits or installment payments.
Step 5: Verify Production Capabilities
Assess the supplier’s production capacity to meet your demands. Confirm that they can handle your required volume and delivery timelines without compromising quality. Understanding their production capabilities will help you avoid delays in your supply chain.
- Inquire about their lead times and flexibility in handling rush orders or changes in order quantities.
- Investigate their production technology and workforce expertise to gauge reliability.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Set up effective communication protocols with your chosen supplier. Clear communication is vital for addressing any issues that may arise during the sourcing process. Establishing regular check-ins can foster a strong working relationship.
- Specify the primary points of contact and preferred methods of communication (e.g., email, phone).
- Discuss how you will handle updates on production status and any necessary adjustments.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Draft and sign a detailed contract outlining all agreed-upon terms. This should include pricing, delivery schedules, quality standards, and return policies. A well-structured contract protects both parties and minimizes the risk of misunderstandings.
- Ensure that the contract includes clauses for quality assurance and liability in case of defects.
- Consider incorporating a dispute resolution process to handle any potential conflicts amicably.
By following this step-by-step sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of procuring faux leather fabric effectively, ensuring quality, compliance, and value throughout the process.

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather fabric Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Faux Leather Fabric Sourcing?
When sourcing faux leather fabric, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The base materials for faux leather typically involve PVC or PU, both of which have fluctuating market prices influenced by petroleum costs. Vegetable-based alternatives are also emerging but may carry a premium due to their sustainable nature.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly by region. Countries with lower labor costs, such as those in Southeast Asia, may offer competitive pricing compared to European manufacturers. However, consider the skill level and experience required for specialized faux leather production, which can affect overall labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, so it’s advisable to assess the operational efficiency of potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific faux leather textures or finishes can be a significant upfront investment. While it may increase initial costs, tooling can enhance product differentiation and justify higher price points.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of faux leather is vital, especially for high-end applications. QC processes will add to the cost, but they are essential for maintaining product standards and avoiding costly returns or reputational damage.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, mode of transport, and current fuel prices. International buyers should be particularly aware of these costs, as they can significantly impact the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition, market demand, and the perceived value of the faux leather offered.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Pricing?
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) are critical factors in determining pricing. Generally, larger orders will attract lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Conversely, small orders may incur higher costs per unit as fixed costs are spread over fewer items.
Customization, such as specific textures or colors, can also influence pricing. Suppliers may charge a premium for custom orders due to the additional resources required for design and tooling. It’s advisable for buyers to clearly communicate their needs upfront to avoid unexpected costs.
What Supplier Factors Should Buyers Consider?
Several supplier-related factors can influence pricing:
-
Quality Certifications: Suppliers with recognized quality certifications may charge more, but they often provide better assurance of product quality, which can reduce the risk of defects.
-
Reputation and Reliability: Established suppliers with a strong track record may offer better reliability but could come at a premium. However, the potential cost savings from avoiding delays and quality issues may justify the higher price.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed Incoterms can clarify responsibilities for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties. This knowledge is essential for calculating the total landed cost of the faux leather fabric.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
-
Research Market Prices: Familiarize yourself with current market prices and trends for faux leather to establish a baseline for negotiations.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Long-term partnerships often yield more favorable conditions.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Beyond the initial purchase price, consider all costs associated with sourcing faux leather, including logistics, storage, and potential waste. This holistic view can help identify the most cost-effective options.
-
Be Open to Alternatives: While premium faux leather options may be appealing, consider evaluating different grades or types to find a balance between quality and cost.
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate payment terms or bulk discounts. Suppliers may be willing to offer concessions to secure larger orders.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The pricing of faux leather fabric can vary widely based on factors such as market conditions, supplier location, and material specifications. The information provided here serves as a general guide and may not reflect current market prices. Always conduct thorough research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing for your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather fabric With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Faux Leather Fabric: A Comprehensive Analysis
In the quest for sustainable and cost-effective materials, faux leather fabric stands out as a popular choice. However, it’s essential for international B2B buyers to consider alternative solutions that may better suit their specific needs. This analysis provides a comparative overview of faux leather against two viable alternatives: genuine leather and vinyl.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Faux Leather Fabric | Genuine Leather | Vinyl |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, water-resistant, versatile | High durability, breathable | Highly durable, moisture-resistant |
| Cost | Lower cost per yard | Higher price point | Generally low-cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to source and cut | Requires skilled craftsmanship | Simple to work with |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, less prone to stains | Requires conditioning and care | Easy to clean, can be prone to wear |
| Best Use Case | Fashion apparel, upholstery | Luxury goods, high-end fashion | Cost-effective upholstery, accessories |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Genuine Leather?
Genuine leather is renowned for its authentic texture and durability. It is often favored in high-end fashion and luxury goods due to its natural aesthetics and breathability. However, the higher cost associated with genuine leather can be a significant barrier for many businesses, particularly in emerging markets. Additionally, the ethical concerns surrounding animal welfare and environmental impact make genuine leather less appealing for companies focused on sustainability. Despite these drawbacks, the longevity and classic appeal of genuine leather can justify its price for certain applications.
How Does Vinyl Compare to Faux Leather in Terms of Usability?
Vinyl is another synthetic alternative that competes with faux leather. It offers a high-shine finish and is typically more affordable than both faux leather and genuine leather. Vinyl is also highly durable and moisture-resistant, making it suitable for a range of applications, including upholstery and accessories. However, it may lack the breathable qualities of genuine leather and can be less comfortable in certain environments. Additionally, the production of vinyl involves PVC, which raises environmental concerns similar to those associated with traditional faux leather. Despite these issues, vinyl remains a viable option for cost-sensitive projects.
Making the Right Choice: Which Material Should B2B Buyers Choose?
When selecting the appropriate material for their needs, B2B buyers should evaluate several factors, including cost constraints, desired aesthetics, environmental considerations, and the intended use of the product. Faux leather fabric offers a balance of affordability and versatility, making it a strong contender for fashion and upholstery projects. In contrast, buyers seeking luxury or high-end applications may lean towards genuine leather, while those focused on budget-friendly solutions may find vinyl to be the most suitable option. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s values and the target market’s expectations.

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather fabric
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Faux Leather Fabric?
Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, possesses several essential technical properties that are crucial for B2B buyers in industries such as fashion, upholstery, and automotive. Understanding these properties helps in making informed procurement decisions.
What Are the Material Grades of Faux Leather?
Material grades refer to the quality and composition of the faux leather. Typically, faux leather is made from two primary materials: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and Polyurethane (PU). PVC is generally more affordable and durable, making it suitable for high-wear applications like upholstery. PU, on the other hand, offers a softer texture and is more environmentally friendly, often being used in high-end fashion items. For buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the faux leather meets the specific requirements of their end products, whether for luxury or durability.
How Does Tolerance Affect Faux Leather Quality?
Tolerance in the context of faux leather refers to the permissible limits of variation in the fabric’s dimensions and properties, such as thickness and weight. For instance, a tolerance of ±0.5 mm in thickness is common for faux leather. This specification is important for manufacturers who need to maintain consistency in their production processes, ensuring that the faux leather fits seamlessly into their designs without compromising quality.
What Is the Importance of Abrasion Resistance?
Abrasion resistance measures the material’s ability to withstand wear and tear from friction. Faux leather should ideally have a high rub count, indicating its durability over time, particularly in high-traffic areas like furniture or clothing. For B2B buyers, understanding abrasion resistance is critical for ensuring that the faux leather can endure daily use without significant deterioration, thereby enhancing the product’s lifespan and reducing replacement costs.
Why Is Breathability a Factor in Faux Leather?
Breathability refers to the material’s ability to allow air and moisture to pass through. Faux leather typically has lower breathability compared to genuine leather, which can impact comfort in clothing and upholstery applications. Buyers must evaluate the intended use of the fabric; for example, breathable faux leather is essential for apparel, while less breathable options may suffice for decorative upholstery.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Faux Leather Industry?
In addition to understanding technical properties, being familiar with trade terminology is vital for effective communication in the faux leather market.
What Is OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)?
OEM refers to companies that produce products that are marketed under another company’s brand. In the faux leather industry, an OEM might manufacture faux leather goods for fashion brands. This term is crucial for buyers looking to partner with manufacturers that can produce their designs while maintaining quality control.
How Does MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) Impact Purchases?
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the faux leather market, MOQs can vary widely based on the supplier and material type. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to ensure they can meet their production needs without overcommitting resources or inventory.
What Is an RFQ (Request for Quotation)?
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing for specific products. In the faux leather industry, submitting an RFQ can help businesses obtain competitive pricing and terms, enabling better budgeting and planning for production runs.
Why Are Incoterms Important in Faux Leather Trade?
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For faux leather transactions, understanding Incoterms is critical for buyers to clarify who is responsible for transportation costs, risk, and liability, ultimately affecting the total cost of procurement.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right faux leather products that meet their quality standards and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather fabric Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Faux Leather Fabric Market?
The faux leather fabric market has been significantly influenced by various global drivers and emerging trends. The increasing consumer preference for vegan and cruelty-free products is a primary catalyst, driving demand across various sectors, including fashion, automotive, and furniture. Additionally, the rising awareness of environmental issues is reshaping sourcing practices, with B2B buyers increasingly seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional leather.
Technological advancements in manufacturing processes are also noteworthy. Innovations such as the development of plant-based faux leathers and improved recycling methods are gaining traction, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and businesses alike. The market is seeing a rise in customizable options, where suppliers offer diverse textures and colors, allowing brands to differentiate their products effectively.
Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional sourcing dynamics is crucial. Countries like Germany and Vietnam are emerging as key players in the production and export of faux leather, leveraging advanced technologies and sustainable practices. Buyers in these regions should consider not only the cost but also the ethical implications and supply chain transparency when selecting suppliers.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Faux Leather Fabric?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies for faux leather fabric, driven by increasing environmental awareness and consumer demand for ethical products. Traditional faux leather production, primarily using PVC, poses significant environmental challenges, including non-biodegradability and harmful emissions during manufacturing. In response, many manufacturers are transitioning to eco-friendlier materials, such as polyurethane (PU) and even plant-based alternatives.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications like Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX. These certifications ensure that materials are produced with minimal environmental impact and adhere to ethical labor practices. Additionally, incorporating recycled materials into faux leather production is gaining popularity, providing an opportunity for buyers to enhance their sustainability credentials.
Establishing partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize ethical sourcing not only mitigates risk but also strengthens brand reputation. As consumers increasingly prefer brands that reflect their values, incorporating sustainable faux leather into product lines can provide a competitive edge in the market.
What Is the Historical Context of Faux Leather Fabric in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of faux leather fabric is rooted in the need for durable and affordable alternatives to genuine leather. The first notable synthetic leather, Naugahyde, was developed in the 1920s in the United States and quickly became popular due to its versatility and lower cost. Over the decades, technological advancements have enabled manufacturers to improve the quality and aesthetic appeal of faux leather, making it a viable option across various industries.
By the mid-20th century, faux leather had established its place in fashion and upholstery, thanks to its ability to mimic the appearance of real leather without the associated ethical concerns. However, the environmental impact of traditional synthetic leather production became a growing concern by the 1970s, leading to increased scrutiny and demand for more sustainable options.
Today, the faux leather market continues to evolve, with manufacturers exploring innovative materials and production methods that align with contemporary values of sustainability and ethical sourcing. This historical context underscores the importance of adaptability in the faux leather fabric sector, providing B2B buyers with valuable insights into future sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather fabric
-
1. How do I choose the right faux leather fabric for my project?
Selecting the appropriate faux leather fabric involves considering factors such as texture, application, and durability. Determine the end use—whether it’s for apparel, upholstery, or accessories—and select a fabric that matches the required aesthetic and functional properties. For example, if you need a soft, pliable material for fashion items, options like Pebble or Shimmer textures may be ideal. Additionally, assess the fabric’s resistance to water and stains, and ensure it meets any relevant environmental standards to align with your brand’s values. -
2. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for faux leather fabric?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers, often ranging from 50 to 500 yards, depending on the fabric type and supplier capabilities. It’s essential to communicate your project requirements early in negotiations to understand potential MOQs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for larger orders or established partnerships, while others may have stricter policies. Always confirm MOQs in advance to ensure they align with your production needs and budget. -
3. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing faux leather fabric internationally?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers, often influenced by the order size and the buyer’s creditworthiness. Common practices include a deposit (usually 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the remaining balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may accept letters of credit or offer extended payment terms for larger orders. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide a balance of security for both parties, and always ensure that the terms are clearly outlined in the contract. -
4. How can I vet suppliers for faux leather fabric?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation in the industry through reviews, testimonials, and case studies. Request samples to evaluate the quality of their faux leather products firsthand. Additionally, inquire about their production processes, certifications, and compliance with environmental standards. Establish direct communication to assess their responsiveness and reliability, and consider visiting their facilities if feasible, or utilizing third-party inspection services for quality assurance. -
5. What customization options are available for faux leather fabric?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including color matching, texture variations, and printed designs. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to determine their capabilities for bespoke orders. Some may also provide options for different finishes, such as matte or glossy, and variations in thickness. Ensure you have clear specifications and artwork ready to facilitate the customization process and expedite production timelines. -
6. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my faux leather orders?
Establishing a robust quality assurance process is critical. Start by defining clear quality standards and specifications in your purchase agreement. Request pre-production samples to assess the material and workmanship. During production, consider scheduling inspections at key stages to ensure compliance with your quality requirements. Post-production, conduct a final inspection before shipment, or hire a third-party inspection service to verify the quality of the finished products. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing faux leather fabric?
When importing faux leather, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose between air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on your timeline and budget. Familiarize yourself with import tariffs and regulations specific to your country to avoid unexpected costs. Collaborating with a reliable logistics partner can help streamline the process and ensure compliance with all necessary documentation. -
8. How does sustainability factor into the sourcing of faux leather fabric?
Sustainability is increasingly important in fabric sourcing. When evaluating faux leather options, inquire about the materials used, production processes, and the supplier’s commitment to environmentally friendly practices. Look for certifications that indicate lower environmental impact, such as those related to recycled materials or non-toxic manufacturing processes. Selecting suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance your brand’s image and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Top 5 Faux Leather Fabric Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sallie Tomato – Faux Leather Collection
Domain: sallietomato.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux Leather collection by Sallie Tomato includes 66 products available in various colors and textures. Colors include Beige, Black, Blue, Brown, Green, Grey, Navy, Orange, Pink, Purple, Red, Teal, White, and Yellow. Textures available are Alligator, Basket Weave, Crocodile, Legacy, Limited Edition, Lite, Ostrich, Pebble, Rugged, and Shimmer. The fabric is sold by quarter yard and is a vegan alter…
2. Mood Fabrics – Faux Leather by the Yard
Domain: moodfabrics.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Faux Leather Fabric by the Yard | Ethical Alternative
3. Sewport – Faux Leather Fabric
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux leather fabric, also known as pleather, vegan leather, Naugahyde, synthetic leather, artificial leather, fake leather, or ersatz leather, is a petroleum-based alternative to genuine leather. It is composed of PVC or vegetable oils. Key properties include low breathability, low moisture-wicking abilities, high heat retention, and high stretchability. It is resistant to stains and easy to clean…
4. Hobby Lobby – Fabric By The Yard
Domain: hobbylobby.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {‘SKU’: ‘1533819’, ‘discounted_price’: ‘$11.19’, ‘original_price’: ‘$15.99’, ‘discount’: ‘30% Off’, ‘fabric_type’: ‘Fabric By The Yard’, ‘available_increments’: ‘1-yard increments’, ‘average_bolt_size’: ‘approximately 9 yards’, ‘width’: ’55’, ‘vertical_repeat’: ‘8.66’, ‘horizontal_repeat’: ‘8.66’, ‘color’: ‘Black’, ‘weight’: ‘Heavyweight’, ‘durability’: ‘Heavy Duty – 55,000 Double Rubs’, ‘content’…
5. Fabric Mill – Faux Leather & Vinyl Fabrics
Domain: fabricmill.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Faux leather and vinyl fabrics offer stylish, durable alternatives to genuine leather, ideal for upholstery, cushions, and accessories. Available by the yard, these materials combine practicality with a modern look. Key characteristics include:
– Durability: 50,000 to 100,000 double rubs, varies by fabric type.
– Weight: Medium to heavy.
– Opaqueness: Opaque.
– Colorfastness: High, resists fading….
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather fabric
The growing demand for faux leather fabric across various global markets highlights the importance of strategic sourcing for B2B buyers. By opting for faux leather, companies can access a versatile, cost-effective alternative that meets consumer preferences for ethical and sustainable materials. This fabric not only mimics the luxurious appeal of genuine leather but also offers durability and ease of maintenance, making it suitable for diverse applications, from fashion to upholstery.

Illustrative image related to faux leather fabric
As buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of sourcing, it is crucial to consider suppliers who prioritize quality, innovative materials, and ethical production practices. Establishing strong partnerships with manufacturers who offer a variety of textures and colors can enhance product offerings and meet evolving consumer demands.
Looking ahead, the faux leather market is poised for continued growth, driven by increasing awareness of sustainability and animal welfare. Now is the time for international buyers to engage with suppliers, leverage emerging trends, and invest in a sustainable future. By doing so, businesses can not only enhance their product lines but also contribute positively to global environmental efforts.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.