Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather for footwear
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality leather for footwear presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The complexity of the leather market—characterized by a multitude of types, grades, and tanning processes—demands a keen understanding of not only the product but also the suppliers behind it. This guide is designed to equip buyers with the insights needed to navigate the diverse world of leather, from identifying various leather types to understanding their specific applications in footwear manufacturing.
By exploring the nuances of leather quality, including the distinctions between full grain, top grain, and corrected grain, as well as the implications of different tanning methods, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of what to look for when selecting materials. Additionally, we will delve into the critical aspect of supplier vetting to ensure that you partner with reputable manufacturers who adhere to ethical and quality standards.
With this guide, you will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business needs and market demands. From cost considerations to sustainability practices, our aim is to provide you with actionable insights that will enhance your sourcing strategy and ultimately contribute to the success of your footwear business.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 Leather For Footwear Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather for footwear
- Understanding leather for footwear Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of leather for footwear
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather for footwear’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather for footwear
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather for footwear
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather for footwear’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather for footwear Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather for footwear With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather for footwear
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather for footwear Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather for footwear
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather for footwear
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding leather for footwear Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Grain Leather | Retains natural grain and pores, offering superior durability and breathability. | High-end dress shoes, boots | Pros: Exceptional quality, ages beautifully. Cons: Higher cost, may require special care. |
| Top Grain Leather | Sanded and treated for a smoother finish, slightly less durable than full grain. | Casual shoes, high-end sneakers | Pros: More affordable than full grain, versatile. Cons: Less breathability, can wear faster. |
| Suede | Soft, napped finish created from the inner layer of the hide, offering a unique texture. | Casual footwear, fashion shoes | Pros: Stylish appearance, lightweight. Cons: Less water-resistant, can stain easily. |
| Exotic Leathers | Includes materials like crocodile and ostrich, known for unique patterns and textures. | Luxury footwear, high-fashion items | Pros: Unique aesthetics, high market demand. Cons: Expensive, requires careful sourcing due to regulations. |
| Vegetable Tanned Leather | Tanned using natural substances, yielding a thicker hide with a distinctive patina. | Accessories, specialty shoes | Pros: Eco-friendly, develops character over time. Cons: Can be stiff initially, longer tanning process. |
What Are the Characteristics of Full Grain Leather for Footwear?
Full grain leather is the highest quality leather available, characterized by its natural grain and pores that remain intact. This type of leather is exceptionally durable and breathable, making it ideal for high-end dress shoes and boots. B2B buyers should consider sourcing from reputable tanneries known for their quality control, as full grain leather can command a higher price. The aging process enhances its appeal, making it a preferred choice for luxury footwear brands looking to convey craftsmanship and quality.
How Does Top Grain Leather Compare to Other Types?
Top grain leather is created by sanding down the top layer of full grain leather, resulting in a smoother finish. While it offers a balance between quality and affordability, it is slightly less durable than full grain leather. This type is suitable for casual shoes and high-end sneakers, appealing to buyers who prioritize aesthetics and comfort. When purchasing, buyers should ensure they are aware of the leather’s treatment process, as this can affect its longevity and performance.
Why Choose Suede for Casual Footwear?
Suede is recognized for its soft, velvety texture, derived from the inner layer of animal hides. It is predominantly used in casual footwear and fashion shoes due to its stylish appearance and lightweight nature. However, B2B buyers should be cautious about its care requirements, as suede is less water-resistant and can be prone to staining. When sourcing suede, it’s essential to consider the quality of the hide and the tanning processes used, which can significantly impact the final product’s durability.
What Are the Benefits of Exotic Leathers in Footwear?
Exotic leathers such as crocodile, ostrich, and python are celebrated for their unique patterns and textures, making them a sought-after material in luxury footwear. These leathers can elevate a brand’s image and appeal to high-end markets. However, B2B buyers must navigate the complexities of sourcing, including compliance with international regulations and ensuring authenticity. The rarity and craftsmanship associated with exotic leathers often result in higher price points, necessitating careful market positioning.
What Makes Vegetable Tanned Leather Unique for Footwear?
Vegetable tanned leather is processed using natural tannins from plants, resulting in a thicker hide that develops a rich patina over time. This eco-friendly option is popular for accessories and specialty shoes, appealing to environmentally conscious brands. B2B buyers should be aware that while vegetable tanned leather can be stiffer initially, it offers excellent durability and character as it ages. Understanding the sourcing and tanning process is crucial for ensuring product quality and sustainability.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
Key Industrial Applications of leather for footwear
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of leather for footwear | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion Retail | High-end dress shoes | Enhances brand image and appeals to luxury consumers | Sourcing from reputable tanneries, ensuring quality standards, and understanding leather grades (full grain vs. corrected grain). |
| Sports and Athletic | Performance footwear for athletes | Increases durability and comfort, improving athletic performance | Need for lightweight yet strong leather, moisture-wicking properties, and compliance with industry standards. |
| Safety and Workwear | Safety boots and footwear | Provides protection and compliance with safety regulations | Leather must meet specific safety standards (e.g., steel toe, slip-resistant), and sourcing should consider local regulations. |
| Outdoor and Adventure | Hiking and trekking shoes | Offers durability and weather resistance for extreme conditions | Focus on waterproofing treatments, breathability, and sourcing from regions with a reputation for high-quality outdoor leathers. |
| Custom Leather Goods | Bespoke footwear for individuals | Personalization enhances customer loyalty and satisfaction | Sourcing unique leathers (exotic or specialty) and ensuring craftsmanship aligns with customer expectations. |
How is Leather for Footwear Used in the Fashion Retail Sector?
In the fashion retail sector, leather is predominantly used for crafting high-end dress shoes. These products not only elevate a brand’s status but also attract discerning consumers looking for luxury and quality. The challenge for international buyers lies in sourcing from reputable tanneries that provide full-grain leather, known for its durability and natural beauty. Buyers must be aware of the differences between leather grades, as marketing jargon can often mislead them regarding quality.
What Are the Applications of Leather in Sports and Athletic Footwear?
Leather is increasingly popular in the production of performance footwear, particularly for athletes. Its unique properties enhance both comfort and durability, vital for improving athletic performance. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that the leather used is lightweight and possesses moisture-wicking capabilities to maintain foot health during rigorous activities. Compliance with industry standards for performance footwear is also crucial, making it essential for buyers to understand the specific requirements of their target markets.
How is Leather Utilized in Safety and Workwear Footwear?
In the safety and workwear sector, leather is essential for creating protective footwear such as safety boots. These products must comply with safety regulations, providing features like steel toes and slip-resistant soles. International buyers should focus on sourcing leather that meets these stringent standards while also considering factors such as comfort and durability. Understanding local regulations and safety requirements in various markets, such as those in Africa and the Middle East, is critical for successful sourcing.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
What Role Does Leather Play in Outdoor and Adventure Footwear?
Outdoor and adventure footwear often utilizes leather due to its natural durability and weather resistance. Hiking and trekking shoes made from high-quality leather can withstand extreme conditions, making them ideal for outdoor enthusiasts. Buyers should prioritize leather that has undergone waterproofing treatments and offers breathability to ensure comfort during long treks. Sourcing from regions known for their expertise in outdoor leather production can also enhance product quality.
How is Leather Sourced for Custom Leather Goods?
The custom leather goods market thrives on personalization, with bespoke footwear becoming increasingly popular among consumers. Leather for this application must be unique, often sourced from exotic or specialty tanneries. Buyers need to ensure that the craftsmanship aligns with customer expectations, emphasizing quality and attention to detail. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements of the target demographic, including preferences for leather types and finishes, is crucial for success in this competitive sector.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather for footwear’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Leather for Footwear Production
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing high-quality leather that meets both aesthetic and functional requirements for footwear. With a plethora of suppliers claiming to offer “genuine leather,” it can be overwhelming to differentiate between various grades, such as full grain, top grain, and corrected grain leathers. This confusion can lead to purchasing decisions that result in subpar products, affecting the overall quality and reputation of their footwear brand.
The Solution:
To mitigate the risk of sourcing inferior leather, B2B buyers should establish clear criteria for assessing leather quality. First, work closely with suppliers who provide detailed documentation regarding the leather’s origin, tanning process, and quality grade. Prioritize partnerships with reputable tanneries known for their transparency and quality, such as those based in Italy or France. It’s also beneficial to request samples for physical evaluation before committing to larger orders. By investing time in evaluating samples—checking for grain consistency, softness, and durability—buyers can ensure they select leather that aligns with their brand’s standards.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
Scenario 2: Understanding the Tanning Process and Its Impact on Leather Quality
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers are unaware of how different tanning processes can significantly affect the properties of leather. For instance, vegetable-tanned leather is often more environmentally friendly and develops a unique patina over time, while chrome-tanned leather offers immediate softness but may not age as gracefully. This lack of knowledge can lead to mismatches between the leather’s characteristics and the intended use in footwear, resulting in customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution:
To navigate this complexity, buyers should prioritize education on tanning processes and their implications for leather performance. Engaging in workshops or webinars with industry experts can provide invaluable insights. Additionally, when selecting leather, consider the end-use of the footwear—whether it’s for casual, formal, or rugged applications—and choose the tanning method that best complements that use. For instance, for high-end dress shoes, opt for vegetable-tanned leather to ensure longevity and character. Documenting these preferences and sharing them with suppliers will facilitate better sourcing decisions aligned with product goals.
Scenario 3: Addressing Environmental and Ethical Concerns in Leather Sourcing
The Problem:
With increasing scrutiny on sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers are under pressure to ensure that their leather suppliers adhere to environmental regulations and ethical labor practices. The leather industry is often criticized for its environmental footprint, particularly regarding waste management and chemical usage in tanning processes. Buyers may struggle to find suppliers who meet these ethical standards without compromising on quality.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should implement a rigorous supplier evaluation process that includes sustainability and ethical considerations. Begin by creating a checklist of certifications and standards that suppliers should meet, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certifications for labor practices. Establishing long-term partnerships with tanneries that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices—like using eco-friendly tanning methods or recycling water—can enhance the brand’s image and meet consumer demand for responsible sourcing. Additionally, consider incorporating leather alternatives made from sustainable materials as part of your product line, diversifying your offerings while aligning with ethical consumer trends.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
By addressing these common pain points with actionable solutions, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing leather for footwear more effectively, ultimately leading to improved product quality and brand reputation.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather for footwear
What Are the Key Properties of Common Leather Materials for Footwear?
When selecting leather for footwear, B2B buyers must consider various materials, each with unique properties and applications. Here, we analyze four common types of leather: Full Grain Leather, Suede, Calfskin, and Exotic Leather. Each material has distinct characteristics that influence its performance and suitability for different footwear applications.
How Does Full Grain Leather Perform in Footwear Applications?
Full Grain Leather is the highest quality leather available, retaining the natural grain and pores of the hide. This type of leather is known for its exceptional durability and breathability, making it ideal for high-end dress shoes and boots. Its temperature resistance allows it to perform well in various climates, while its ability to develop a beautiful patina over time enhances its aesthetic appeal.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
Pros: Full Grain Leather is highly durable, ages well, and provides excellent breathability. It is suitable for formal and casual footwear.
Cons: The cost of Full Grain Leather is relatively high, and its manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for skilled craftsmanship.
Impact on Application: Full Grain Leather is compatible with various shoe designs and styles, making it a versatile choice for international markets. Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM for quality assurance.
What Advantages Does Suede Offer for Footwear?
Suede, characterized by its soft, velvety texture, is made from the inner layer of the hide. It is often used in casual footwear due to its unique aesthetic and comfort. Suede is lightweight and flexible, providing a comfortable fit for everyday wear.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
Pros: Suede offers a stylish appearance, is lightweight, and provides a comfortable fit. It is also relatively water-resistant when treated properly.
Cons: While durable, suede is more susceptible to stains and damage from water compared to other leathers. Maintenance can be more demanding, requiring specific cleaning products.
Impact on Application: Suede is popular in fashion-forward markets, particularly in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should consider local climate conditions that may affect suede’s performance, ensuring they choose treated options for moisture resistance.
Why Is Calfskin a Preferred Choice for Footwear?
Calfskin is derived from young cattle and is known for its smooth texture and durability. It is widely used for both formal and casual footwear due to its versatility and aesthetic appeal. Calfskin can withstand moderate wear and tear, making it suitable for everyday use.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
Pros: Calfskin is durable, ages beautifully, and is available in various finishes. Its smooth surface is ideal for high-quality dress shoes.
Cons: The cost of calfskin can vary significantly, with premium options being quite expensive. Additionally, it may require more care to maintain its appearance.
Impact on Application: Calfskin is favored in markets that prioritize luxury and quality, such as Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should verify the source and tanning process to ensure compliance with ethical standards.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
What Are the Considerations for Using Exotic Leather in Footwear?
Exotic leathers, such as crocodile or ostrich, are prized for their unique textures and rarity. These materials are often used in high-end footwear, appealing to luxury markets. Exotic leathers are durable and can offer a distinctive look, making them suitable for statement pieces.
Pros: Exotic leathers provide a unique aesthetic, high durability, and exclusivity. They can command premium prices in luxury markets.
Cons: The cost of exotic leather is significantly higher than traditional leathers, and sourcing can be complex due to regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure compliance with CITES regulations to avoid legal issues.
Impact on Application: Exotic leathers are particularly appealing in affluent markets across Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should be aware of the ethical implications and ensure proper documentation for sourcing.
Summary Table of Leather Materials for Footwear
| Material | Typical Use Case for leather for footwear | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Grain Leather | High-end dress shoes and boots | Exceptional durability and breathability | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Suede | Casual footwear | Stylish appearance and comfort | Susceptible to stains and water damage | Medium |
| Calfskin | Formal and casual shoes | Versatile and aesthetically appealing | Varies in cost; requires maintenance | Medium to High |
| Exotic Leather | Luxury footwear | Unique aesthetic and exclusivity | Very high cost and regulatory complexity | High |
This guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the strategic selection of leather materials for footwear, considering performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather for footwear
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Leather for Footwear?
Manufacturing leather for footwear involves several critical stages, each requiring specialized techniques to ensure quality and durability. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Leather Production?
The first step in the leather manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves sourcing high-quality hides. The hides are typically obtained from cattle, but exotic leathers from goats, pigs, or even reptiles may also be used. Once sourced, the hides undergo a series of treatments, including:

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
- Curing: This process prevents decomposition and prepares the hides for tanning. It can involve salting or drying.
- Soaking: The hides are soaked to remove salt and impurities, making them pliable for further processing.
- Fleshing: This involves removing excess flesh and fat from the hide to ensure a uniform thickness.
After preparation, the hides are ready for the tanning process, which is crucial for determining the leather’s properties.
What Techniques Are Used in Tanning Leather?
Tanning is a vital step that transforms raw hides into durable leather. The two primary tanning methods are:
- Chrome Tanning: This is the most common method, utilizing chromium salts to produce soft, flexible leather. Chrome-tanned leather is resistant to water and has a shorter processing time.
- Vegetable Tanning: Using natural tannins from plant sources, this method is more environmentally friendly and results in stiffer leather that develops a rich patina over time.
Each method produces leather with distinct characteristics, impacting the end product’s suitability for various footwear styles.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
How Are Leather Components Formed and Assembled?
Once tanned, the leather is cut and formed into various shoe components. This includes:
- Cutting: Patterns for different shoe parts, such as uppers, linings, and soles, are cut from the leather. Precision is crucial, as any defects can affect the final product.
- Stitching: Components are stitched together using high-strength threads. This can be done by hand or machine, depending on the desired quality and style.
- Lasting: The shoe is shaped around a mold, known as a last, to create the final form. This step is essential for ensuring proper fit and comfort.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance Leather Quality?
Finishing is the final stage in leather production, enhancing the appearance and functionality of the material. Key techniques include:
- Dyeing: Leather can be dyed using various methods, including aniline or semi-aniline processes, to achieve desired colors and shades.
- Coating: Protective coatings may be applied to improve water resistance and durability. This is particularly important for footwear exposed to harsh conditions.
- Polishing and Buffing: These processes add shine and enhance the leather’s aesthetic appeal.
Each finishing technique adds value, impacting the product’s marketability and longevity.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the leather manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. Key QA practices include:
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable to manufacturers across various industries, including leather production.
- CE Marking: In the European market, this certification indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
Understanding these certifications can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality leather products.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Leather Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are critical for maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages helps identify defects early and allows for corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products ensures they meet quality standards before shipment.
Implementing these checkpoints helps manufacturers maintain consistent quality and reduces the likelihood of defects reaching the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify their suppliers’ quality control practices. Here are some actionable strategies:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Buyers should look for certifications that validate compliance with international standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to share quality reports detailing testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken in response to defects.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. This is particularly important for international transactions where transparency is crucial.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate specific nuances in quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and business cultures can help buyers establish effective communication with suppliers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulations governing leather production and trade. Buyers must be aware of these regulations to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Efficient logistics are vital for ensuring timely delivery and maintaining quality during transportation. Buyers should consider the entire supply chain, from production to delivery.
By understanding these nuances, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and build strong partnerships with reliable leather suppliers.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for leather used in footwear are intricate and require careful consideration. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes not only helps in sourcing high-quality products but also ensures compliance with international standards. By engaging in thorough audits, requesting quality documentation, and remaining aware of regional regulations, buyers can establish successful partnerships that yield superior leather goods for footwear.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather for footwear’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of leather for footwear can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. This checklist serves as a practical guide to help you identify and source high-quality leather that meets your specific requirements. By following these steps, you can ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your business needs and quality standards.
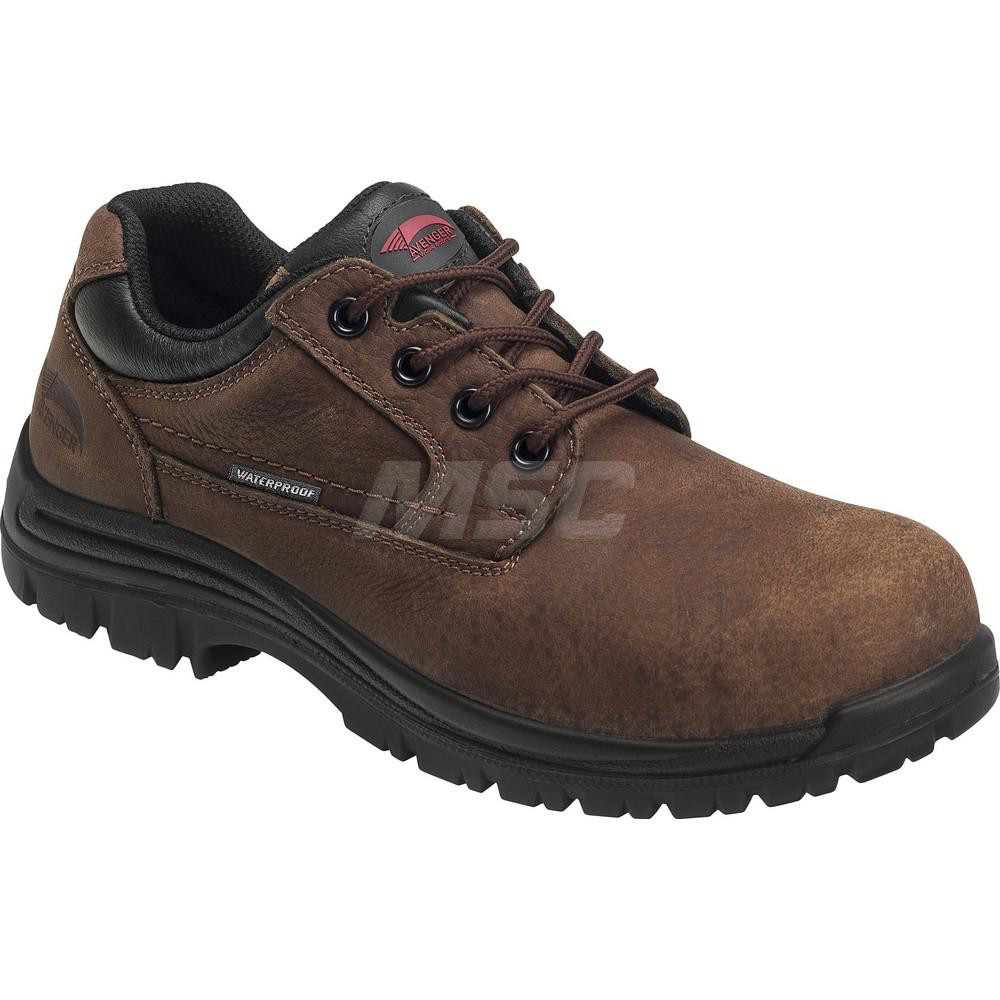

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications for the leather you need, including type, grade, and treatment. This step is crucial as it establishes your baseline requirements and helps prevent miscommunication with suppliers.
– Considerations: Identify the leather type (e.g., full grain, top grain, suede) based on the intended use, such as formal shoes or casual footwear.
– Quality Standards: Set criteria for durability, finish, and texture to ensure the leather meets your performance expectations.
Step 2: Research and Identify Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers. This is essential to ensure you are engaging with reputable manufacturers who can deliver the quality you need.
– Sources: Use industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to identify suppliers specializing in footwear leather.
– Geographic Focus: Pay attention to suppliers from regions known for high-quality leather production, such as Italy, France, and the USA.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.
– Documentation: Ask for certifications that verify the quality and ethical sourcing of their leather, such as ISO or environmental compliance.
– Sample Requests: Always request samples of the leather to assess its quality firsthand.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirm that your chosen suppliers have the necessary certifications to assure quality and compliance with international standards. This step mitigates risks associated with sourcing substandard materials.
– Key Certifications: Look for certifications such as LWG (Leather Working Group) for sustainable practices and traceability.
– Sustainability Practices: Inquire about the supplier’s tanning processes and adherence to environmental regulations.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms that align with your budget and quality expectations. This step is vital to ensure long-term value and cost-effectiveness.
– Price Comparison: Compare prices among suppliers while considering the quality and type of leather offered.
– Payment Terms: Discuss payment options, lead times, and minimum order quantities to establish a mutually beneficial agreement.
Step 6: Assess Logistics and Shipping
Evaluate the logistics involved in transporting the leather from the supplier to your location. Understanding shipping options and costs is crucial for budgeting and timeline management.
– Shipping Methods: Consider air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost savings, depending on your urgency.
– Customs and Duties: Familiarize yourself with any import duties or regulations that may apply to leather products in your region.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a quality control process to ensure that the leather received meets your specifications. This step is essential for maintaining product quality and consistency in your footwear line.
– Inspection Protocols: Set up inspection checkpoints upon delivery to verify that the leather aligns with the agreed-upon specifications.
– Feedback Loop: Create a system for providing feedback to suppliers on quality issues, fostering continuous improvement in your supply chain.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process and build strong relationships with suppliers that contribute to the success of your footwear business.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather for footwear Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather for Footwear Sourcing?
When sourcing leather for footwear, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
-
Materials: The cost of raw leather varies significantly based on the type (e.g., full-grain, top-grain, or exotic leathers), quality, and source. Full-grain leather, which retains the natural grain and pores, commands a premium price compared to corrected or genuine leathers. Exotic leathers, such as crocodile or ostrich, are not only rare but also heavily regulated, leading to higher costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs differ based on the manufacturing location. Regions with higher labor costs may yield better craftsmanship, which is essential for premium footwear. Conversely, countries with lower labor costs might offer more competitive pricing, but the quality may vary.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs of running the production facility, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and other production tools can be significant. Custom designs require specialized tooling, which can escalate costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the leather meets specific quality standards incurs costs, particularly for international buyers who may require certifications. QC is vital for maintaining brand reputation and minimizing returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, weight, and shipping methods. Buyers should consider Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, impacting overall logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the expected margin can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Leather for Footwear Sourcing?
Several factors influence pricing in the leather footwear market, particularly for international B2B transactions.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Higher order volumes often lead to discounts, allowing buyers to negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as unique colors, textures, or treatments, can raise costs. Buyers should assess whether customization adds sufficient value to justify the higher price.
-
Quality and Certifications: Premium leathers with certifications (e.g., environmentally friendly tanning processes) may cost more. Buyers should balance the need for certification with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record, while new entrants might offer lower prices to attract customers.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International Buyers of Leather for Footwear?
Effective negotiation is essential for maximizing value in leather sourcing. Here are some actionable tips:
-
Research Market Rates: Understand the current market prices for various types of leather. This knowledge empowers buyers to negotiate more effectively.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Suppliers are more likely to offer discounts to reliable partners.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the leather, including maintenance, durability, and potential returns due to quality issues. A lower initial price may not always equate to better value.
-
Leverage Incoterms: Familiarize yourself with Incoterms to negotiate shipping and logistics responsibilities effectively. This understanding can help avoid unexpected costs.
-
Be Transparent About Your Needs: Clearly communicate your requirements and expectations. Transparency helps suppliers propose solutions that align with your goals, potentially leading to cost savings.
Conclusion: Why Are Indicative Prices Important for Buyers?
It’s essential to note that prices in the leather footwear market can vary widely based on numerous factors. Buyers should seek indicative prices as a starting point, but remain flexible and open to negotiation. Understanding the complexities of cost structures and price influencers will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions in their sourcing endeavors.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather for footwear With Other Solutions
When considering materials for footwear, leather stands out as a traditional and premium choice. However, with evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements, several alternatives have emerged. This section will analyze the viability of leather for footwear against other solutions, focusing on synthetic materials, canvas, and rubber.
| Comparison Aspect | Leather For Footwear | Synthetic Materials | Canvas | Rubber |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, breathable, and molds to foot shape. Excellent for formal and casual styles. | Offers flexibility and water resistance, but may not breathe as well as leather. | Lightweight and breathable but lacks durability and water resistance. | Highly durable, waterproof, and easy to clean, ideal for specific applications. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to quality sourcing and processing. | Usually lower; cost-effective for mass production. | Affordable, making it accessible for various markets. | Moderate; can be cost-effective depending on the application. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled craftsmanship; sourcing high-quality leather can be challenging. | Easily mass-produced and available in various designs. | Simple to manufacture and print designs, widely available. | Can be molded into various forms; however, specialized production may be needed for specific footwear. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning and care to maintain appearance and longevity. | Low maintenance; easy to clean and care for. | Easy to clean but may fade or wear quickly. | Very low maintenance; resistant to dirt and moisture. |
| Best Use Case | High-end fashion, formal wear, and outdoor shoes requiring durability. | Everyday casual shoes, athletic footwear, and fashion trends. | Summer footwear, casual shoes, and promotional items. | Work boots, rain boots, and athletic footwear for wet conditions. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Synthetic Materials for Footwear?
Synthetic materials, such as polyurethane or PVC, offer a compelling alternative to leather. These materials are typically lighter, more affordable, and resistant to water and stains. However, they may lack the breathability and comfort of leather, potentially leading to foot odor and discomfort in prolonged wear. Additionally, while they can mimic the appearance of leather, the tactile experience and aging characteristics differ significantly.
How Does Canvas Compare to Leather in Footwear Production?
Canvas is another alternative that appeals to budget-conscious consumers. It is lightweight, breathable, and can be easily printed with vibrant designs, making it popular for casual shoes. However, canvas lacks the durability and water resistance of leather, making it less suitable for formal occasions or outdoor activities. While it is cost-effective, the longevity of canvas footwear is often lower, resulting in more frequent replacements.
What Benefits Does Rubber Provide as a Footwear Material?
Rubber is primarily known for its durability and waterproof properties, making it ideal for specific footwear applications such as rain boots and athletic shoes. It is easy to clean and maintain, which appeals to consumers looking for low-maintenance options. However, rubber can be heavy and less breathable than leather, leading to discomfort in warmer conditions. Its aesthetic appeal is also limited compared to the luxurious look of leather.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
How Can B2B Buyers Decide Between Leather and Its Alternatives?
When choosing between leather and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including target market, intended use, and budget constraints. If the focus is on high-end fashion or durability, leather remains the superior choice. However, for mass-produced casual footwear or specific functional applications like rain boots, synthetic materials, canvas, or rubber may offer a better balance of cost and performance. Understanding the unique selling propositions of each material will enable buyers to align their product offerings with consumer preferences and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather for footwear
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Leather for Footwear?
When sourcing leather for footwear, understanding the technical properties is crucial for ensuring quality, durability, and performance. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the classification of leather based on its quality and characteristics. Common grades include full-grain, top-grain, corrected grain, and genuine leather.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade leathers, such as full-grain, maintain the natural grain and pores, providing superior durability and breathability. Buyers should prioritize higher grades for premium footwear to ensure longevity and customer satisfaction. -
Thickness
– Definition: Leather thickness is measured in millimeters or ounces and affects the leather’s durability and flexibility.
– B2B Importance: Thicker leather typically offers more durability, making it suitable for heavy-use footwear like boots. Conversely, thinner leather may be preferred for dress shoes, where flexibility and comfort are essential. -
Tanning Process
– Definition: The tanning process preserves the leather and determines its properties, such as softness, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Common methods include chrome tanning and vegetable tanning.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the tanning process helps buyers assess the leather’s sustainability and suitability for their products. Vegetable-tanned leather, for example, is often favored for eco-friendly footwear lines. -
Water Resistance
– Definition: This property indicates how well the leather can repel water and resist moisture damage.
– B2B Importance: Water-resistant leather is crucial for footwear intended for wet conditions, enhancing the product’s functionality and appeal to customers in regions with diverse climates. -
Finish Type
– Definition: The finish refers to the surface treatment applied to leather, which can include coatings for shine, color, and protection.
– B2B Importance: Different finishes can affect the leather’s look and performance. For example, patent leather has a high-gloss finish suitable for formal occasions, while matte finishes may appeal to casual footwear markets.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Leather Footwear Industry?
In the leather footwear industry, familiarity with trade terminology is essential for smooth transactions and effective communication. Here are some key terms to know:

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or products that are used in another company’s end product.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify potential partners for custom leather products, ensuring that specifications and quality standards are met. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ refers to the smallest order quantity that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is critical for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate favorable MOQs that align with their production needs without incurring excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific quantities of goods.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs can streamline the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, thus ensuring competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, facilitating smoother international trade and logistics planning. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and meeting market demands, particularly in industries with fast-changing trends. -
Sustainability Certifications
– Definition: Certifications that verify the environmentally friendly practices in the production of leather, such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification.
– Importance: Increasingly, consumers prefer sustainably sourced products. Buyers should look for suppliers with sustainability certifications to enhance their brand’s appeal and comply with market demands for eco-friendly products.
By grasping these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right leather for their footwear needs while navigating the complexities of international trade.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather for footwear Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Leather for Footwear Sector?
The global leather for footwear market is experiencing significant evolution driven by various factors, including rising consumer demand for high-quality, durable footwear, and the growing trend towards customization. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to differentiate their product offerings, understanding the nuances of leather quality becomes paramount. Full grain and top grain leathers are increasingly favored for their durability and aesthetic appeal, while the popularity of exotic leathers is on the rise, particularly among luxury brands targeting affluent markets.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping sourcing practices. Digital platforms facilitate real-time inventory management and supply chain transparency, allowing buyers to make informed decisions. Additionally, the rise of data analytics provides insights into consumer preferences, enabling businesses to tailor their products more closely to market demands. With the global shift towards e-commerce, B2B buyers are leveraging online marketplaces and trade platforms to source leather more efficiently, thus expanding their supplier networks beyond traditional geographies.

Illustrative image related to leather for footwear
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Leather for Footwear Market?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of the leather for footwear sector, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues. The tanning process, often associated with significant environmental impact, is under scrutiny, prompting the adoption of eco-friendly practices. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who use vegetable tanning methods or other sustainable alternatives that minimize chemical usage and water consumption.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction as brands strive to ensure that their leather is sourced responsibly, avoiding illegal or unethical practices associated with exotic leathers. Certifications like the Leather Working Group (LWG) and the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to appeal to conscientious buyers. These certifications not only validate sustainable practices but also enhance brand reputation, thereby influencing purchasing decisions in competitive markets.
What Is the Historical Context of the Leather for Footwear Industry?
The leather for footwear industry has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, with evidence of leather use in ancient civilizations for footwear. Initially, leather was primarily sourced from local animals, with techniques evolving over time. The Industrial Revolution marked a significant turning point, introducing mechanized tanning processes and mass production methods that made leather more accessible.
In recent decades, globalization has transformed the industry, with sourcing shifting to countries with lower production costs. However, the focus has now shifted back towards quality and sustainability, as buyers recognize the importance of ethical practices and premium materials. This historical context is critical for B2B buyers who need to understand the legacy of leather sourcing and how it informs contemporary trends, particularly regarding consumer expectations for quality and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather for footwear
-
How do I ensure the quality of leather for footwear?
To ensure the quality of leather, start by understanding the types of leather available, such as full grain, top grain, and corrected grain. Request samples from potential suppliers to evaluate the texture, durability, and grain characteristics. Additionally, inquire about the source of the hides and the tanning process used, as these factors significantly influence quality. It is also advisable to check for certifications from reputable tanning facilities to verify the authenticity and sustainability of the leather. -
What is the best type of leather for formal footwear?
Full grain leather is widely regarded as the best choice for formal footwear due to its durability and natural appearance. It retains the hide’s original grain and pores, offering a refined look that ages beautifully over time. Calfskin leather is another excellent option, known for its smooth texture and flexibility, making it suitable for various styles of dress shoes. When sourcing, consider the specific needs of your market, as preferences may vary across regions. -
What factors should I consider when vetting leather suppliers?
When vetting leather suppliers, consider their reputation in the industry, the quality of their products, and their compliance with international regulations. Look for suppliers who provide transparent information about their sourcing and manufacturing processes. Request references from other clients and check for certifications related to ethical practices and environmental sustainability. Additionally, assess their production capacity and ability to meet your specific requirements, such as customization and minimum order quantities. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for leather?
Minimum order quantities for leather can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of leather. Generally, MOQs can range from 50 to 500 square meters for bulk orders. For specialized or custom orders, suppliers may have higher MOQs. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers and negotiate terms that align with your business model, especially if you’re a smaller buyer or just starting. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing leather internationally?
Payment terms for international leather transactions typically include options such as upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may request a deposit of 30% to 50% before production, with the balance due before shipping. Be sure to clarify these terms upfront to avoid any misunderstandings. Additionally, consider the currency exchange rates and transaction fees that may apply, as these can impact your overall costs. -
How can I customize leather for my footwear products?
Customization options for leather can include selecting specific colors, textures, and finishes tailored to your brand’s requirements. Discuss your customization needs with the supplier, including any unique patterns or treatments you want applied. Some suppliers may offer additional services such as embossing or dyeing. Ensure that you obtain samples of customized leather before final production to guarantee that the final product meets your expectations. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I implement when sourcing leather?
Implementing robust quality assurance measures is crucial when sourcing leather. Establish clear quality standards and specifications that suppliers must adhere to, including criteria for thickness, grain quality, and color consistency. Conduct regular inspections of incoming leather shipments to verify compliance with these standards. Additionally, consider working with third-party QA agencies to perform audits and inspections, especially for larger orders or new suppliers. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for leather imports?
Logistics considerations for importing leather include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties. Choose reliable freight forwarders who specialize in leather products to ensure compliance with international shipping standards. It’s also important to factor in lead times for production and shipping when planning your inventory. Finally, ensure that you have proper documentation, such as invoices and certificates of origin, to facilitate smooth customs clearance.
Top 6 Leather For Footwear Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Shoemakers Academy – The Designer’s Guide to Shoe Leather
Domain: shoemakersacademy.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: The Designer’s Guide to Shoe Leather covers various types of shoe leather, focusing primarily on cow leather, which is the most common type used in footwear. Key details include: 1. Types of Leather: Cow, calf, pig, goat, sheep, kangaroo, alligator, ostrich, etc. 2. Tanning Process: Involves removing hair, flesh, and fat, followed by tanning to preserve fibers, which can take over 10 hours. 3. Lea…
2. HideHouse – Premium Leather Hides for Footwear
Domain: hidehouse.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Leather for shoes, boots, and sandals available in various animal hides including goat, calf, sheep, bull, water buffalo, deer, cow, pig, moose, bison. Options for footwear include 100 different hides. Various finishes available such as oiled, aniline, patent, suede, and pigmented. Sizes range from 1-10 sq ft to 45-70 sq ft. Tannage options include chrome, alum, veg, and chrome-free. Leather thick…
3. Buy Leather Online – Quality Leather for Footwear
Domain: buyleatheronline.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Leather for shoe making and footwear includes types suitable for various styles such as décolleté, boots, sneakers, and classical shoes. The leather is resistant to bending and atmospheric agents, available in rigid, semi-rigid, or soft forms. Key types include: 1. Full grain leather – retains original grain characteristics, can be opaque, shiny, printed, or embossed; 2. Corrected grain leather – …
4. RM Leather Supply – Premium Leather Goods
Domain: rmleathersupply.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: This company, RM Leather Supply – Premium Leather Goods, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Secret Cobbler – Leather Selection Guide
Domain: secretcobbler.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Choosing leather for shoes involves selecting at least 5 different types of leather. Key types include: 1. Vegetable Tanned Leather: – Traditional tanning process, free from harmful chemicals. – Ages beautifully, durable, and takes dye easily. – Can be moistened, shaped, and stamped. – Drawbacks: Soaks up water and not heat resistant. 2. Chrome Tanned Leather: – Invented in 1858, most common for s…
6. Shoegazing – Quality Leather Guide
Domain: shoegazing.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Calf leather: Soft, supple, durable; common in quality dress shoes; comes from animals under a year old; smooth full-grain recognized by fine pores. Cow and ox leather: Thicker, sturdier; used for tougher boots; often split for cheaper shoes. Horse leather: Durable; thinner front part for jackets; shell cordovan is a famous type, very durable with a shiny surface. Pigskin: Soft, supple; easy to dy…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather for footwear
The strategic sourcing of leather for footwear is critical in navigating the complexities of quality, sustainability, and market demand. By understanding the nuances of different leather types—such as full grain, top grain, and exotic leathers—international buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their product offerings. Prioritizing transparency in sourcing practices not only ensures the procurement of high-quality materials but also builds trust with consumers increasingly concerned about ethical practices.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for premium leather remains strong. Buyers should leverage relationships with reputable tanneries known for excellence, such as those in Italy, France, and the USA, to secure top-tier materials. Engaging in strategic sourcing can lead to competitive advantages, including reduced costs, improved product quality, and better alignment with consumer preferences.
Looking ahead, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay attuned to trends in sustainability and innovation within the leather industry. By embracing these changes and investing in strategic sourcing, businesses can not only meet current market demands but also position themselves as leaders in the footwear sector. Now is the time to refine your sourcing strategies and capitalize on the opportunities within this dynamic market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.