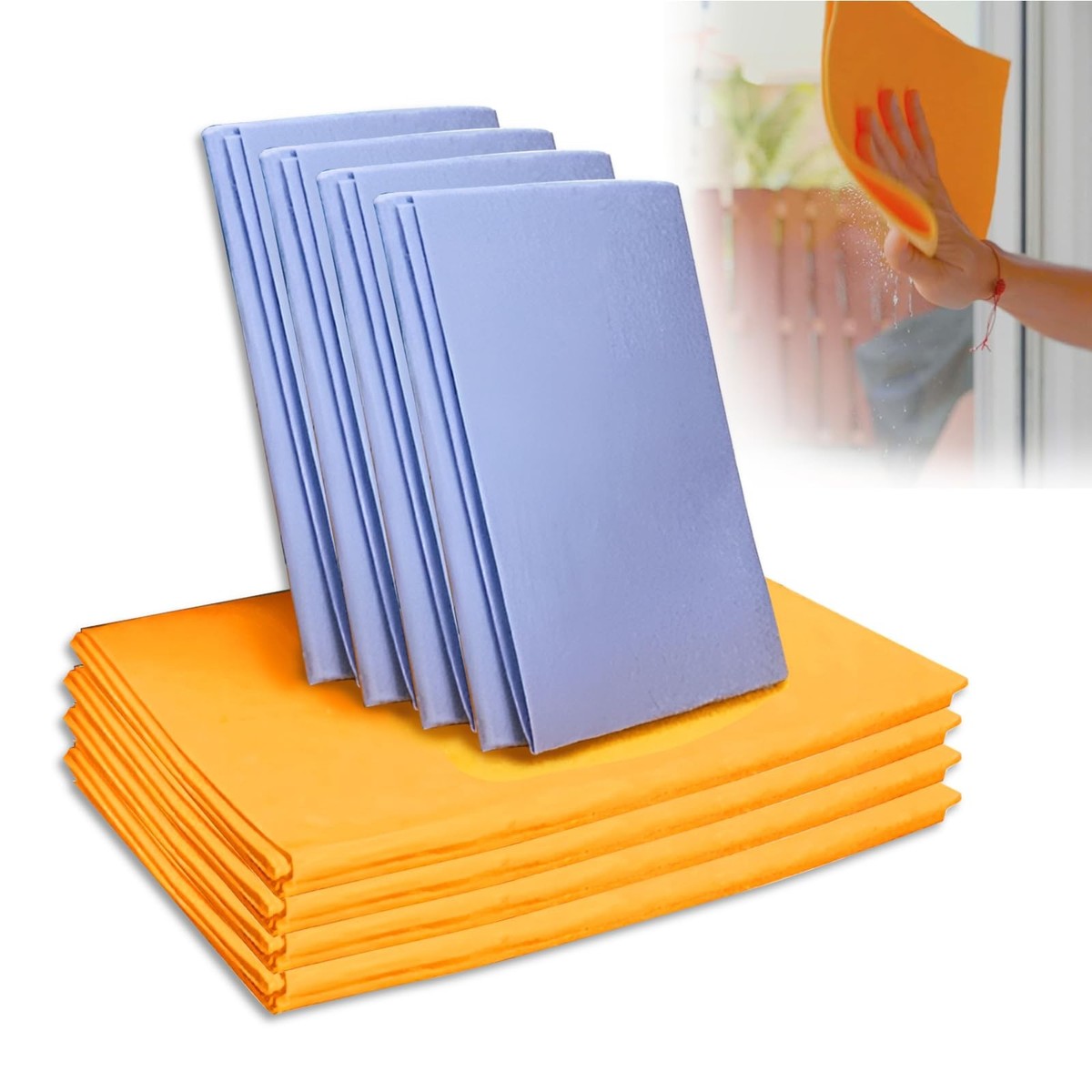
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vegan leather material
In an era where ethical consumption is paramount, navigating the global market for vegan leather material presents both opportunities and challenges for international B2B buyers. As businesses increasingly seek sustainable alternatives to traditional leather, understanding the diverse types of vegan leather, such as those derived from polyurethane, cactus, or mushroom sources, becomes essential. This guide aims to equip you with comprehensive insights into the various applications of vegan leather across industries, from fashion to automotive upholstery.
In addition to exploring the environmental impacts and sustainability claims associated with these materials, we will delve into critical aspects of supplier vetting, pricing structures, and market trends. By arming yourself with this knowledge, you will be better positioned to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your company’s values and operational needs.
Particularly for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries such as Saudi Arabia and Germany—this guide offers tailored strategies to navigate the complexities of sourcing vegan leather. With a focus on quality, compliance, and ethical sourcing, you can enhance your product offerings while contributing to a more sustainable future. Embrace the potential of vegan leather and transform your supply chain with confidence.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 Vegan Leather Material Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vegan leather material
- Understanding vegan leather material Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of vegan leather material
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vegan leather material’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vegan leather material
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vegan leather material
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vegan leather material’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vegan leather material Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vegan leather material With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vegan leather material
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vegan leather material Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vegan leather material
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vegan leather material
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
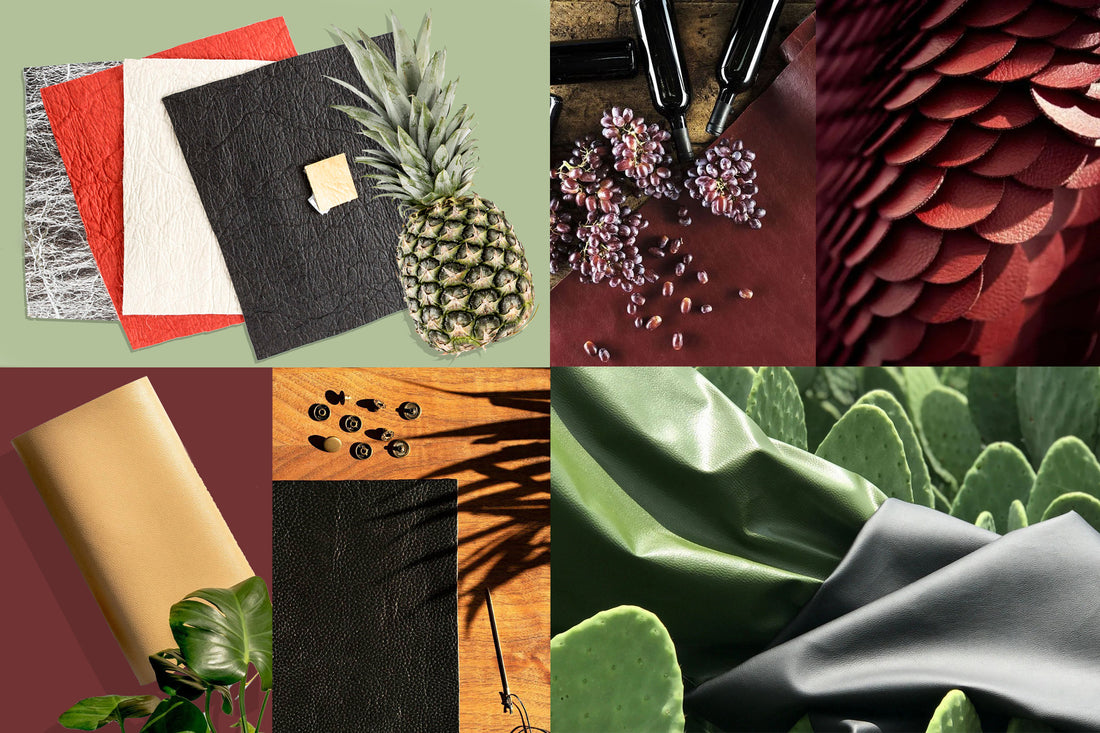
Understanding vegan leather material Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Flexible, breathable, and more eco-friendly than PVC | Fashion, upholstery, automotive interiors | Pros: Good flexibility, water-resistant. Cons: Shorter lifespan than leather. |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Cost-effective, widely available, but less eco-friendly | Fashion accessories, low-cost goods | Pros: Inexpensive and durable. Cons: Environmental concerns in production. |
| Bio-based Vegan Leather | Made from natural materials like pineapple leaves or mushrooms | High-end fashion, luxury goods | Pros: Sustainable sourcing, unique aesthetics. Cons: Higher production costs. |
| Microfiber Leather | Made from synthetic fibers, mimics genuine leather texture | Upholstery, bags, and shoes | Pros: Durable and easy to clean. Cons: May lack breathability. |
| Apple Leather | Derived from apple waste, eco-friendly alternative | Fashion, accessories, and footwear | Pros: Sustainable and biodegradable. Cons: Limited availability and higher costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Polyurethane (PU) Vegan Leather?
Polyurethane (PU) vegan leather is renowned for its flexibility and breathability, making it a popular choice in the fashion and automotive industries. PU leather is more eco-friendly compared to traditional PVC, although it is still a synthetic material. B2B buyers should consider the balance between quality and cost, as PU offers a good compromise between durability and aesthetic appeal. Its water-resistant properties also make it suitable for various applications, but its lifespan typically ranges from 2 to 5 years, which may necessitate more frequent replacements.
How Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Vegan Leather Compare?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is one of the oldest forms of vegan leather, favored for its low cost and widespread availability. However, it faces significant criticism due to the harmful environmental impact of its production process. B2B buyers should weigh the affordability of PVC against its eco-unfriendliness, especially as consumer demand shifts towards sustainable practices. While PVC can be durable and resistant to wear, its long-term environmental implications may deter businesses looking to align with ethical consumer values.
Why Choose Bio-based Vegan Leather for Premium Products?
Bio-based vegan leather, made from materials such as pineapple leaves or mushrooms, represents a significant advancement in sustainable fashion. This type of vegan leather appeals to luxury brands and high-end markets due to its unique aesthetics and sustainable sourcing. B2B buyers should consider the potential for higher production costs and limited availability, but the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly products can justify the investment. This material not only supports sustainability but also enhances brand reputation.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
What Are the Benefits of Microfiber Leather?
Microfiber leather is crafted from synthetic fibers and is designed to mimic the texture of genuine leather. Its durability and ease of cleaning make it an attractive option for upholstery and accessories. B2B buyers should note that while microfiber leather is robust, it may lack breathability, which could be a consideration for certain applications. Its versatility and resistance to wear make it a popular choice in industries where longevity is crucial.
How Is Apple Leather Revolutionizing the Vegan Leather Market?
Apple leather, derived from apple waste, is an innovative and eco-friendly alternative gaining traction in the fashion industry. This material is not only sustainable and biodegradable but also offers a unique texture that appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. B2B buyers should be aware of the potential for higher costs and limited sourcing options, but the material’s sustainable credentials can enhance brand image and attract a growing market segment focused on ethical consumption.
Key Industrial Applications of vegan leather material
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vegan leather material | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Footwear and Accessories | Aligns with sustainable consumer trends | Quality, durability, and eco-certifications |
| Automotive | Interior Upholstery | Enhances brand image with eco-friendliness | Compliance with safety standards, durability |
| Furniture & Upholstery | Sofas and Chairs | Offers a modern aesthetic with easy maintenance | Material sourcing, stain resistance, and style |
| Sports Equipment | Protective Gear (e.g., gloves, pads) | Lightweight, flexible, and durable | Performance specifications, safety regulations |
| Electronics | Cases and Covers for Devices | Customizable and lightweight protection | Material thickness, flexibility, and aesthetics |
How is Vegan Leather Material Used in the Fashion & Apparel Industry?
In the fashion industry, vegan leather is predominantly utilized for footwear and accessories, appealing to brands seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional leather. Its versatility allows designers to create a variety of styles while addressing consumer demand for ethical fashion. International B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that offer durability and eco-certifications to ensure they meet market expectations in regions like Europe and South America, where sustainability is increasingly valued.
What Role Does Vegan Leather Play in the Automotive Sector?
Vegan leather is becoming a popular choice for automotive interior upholstery, providing a luxurious look without the ethical implications of animal leather. By incorporating vegan leather, automotive brands can enhance their eco-friendly image, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should focus on sourcing materials that comply with safety standards and exhibit high durability to withstand the wear and tear of automotive use.
How is Vegan Leather Transforming Furniture & Upholstery?
In the furniture sector, vegan leather is used for sofas and chairs, offering a contemporary aesthetic with low maintenance requirements. This material allows manufacturers to cater to the growing demand for stylish yet sustainable products. B2B buyers, especially in European markets, should consider sourcing options that emphasize stain resistance and a variety of styles to meet diverse consumer preferences.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
Why is Vegan Leather Important in Sports Equipment Manufacturing?
Vegan leather is increasingly used in sports equipment, such as protective gear and gloves, due to its lightweight and flexible properties. This material not only provides durability but also meets the specific performance needs of athletes. Buyers in regions like South America should ensure that sourced vegan leather complies with safety regulations and performance specifications to maintain product integrity and athlete safety.
How is Vegan Leather Beneficial for Electronics?
In the electronics industry, vegan leather is utilized for cases and covers, providing customizable and lightweight protection for devices. This application meets the demand for stylish yet functional accessories, appealing to tech-savvy consumers. International B2B buyers should consider the material’s thickness, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal to ensure compatibility with various electronic products, particularly in competitive markets across Europe and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vegan leather material’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Vegan Leather for Sustainable Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find high-quality vegan leather that meets both ethical standards and customer expectations. With a plethora of options available, including PVC and PU, it can be challenging to discern which materials are truly sustainable and ethically sourced. Buyers may fear that choosing cheaper synthetic options could damage their brand reputation, especially if their target market values sustainability. Additionally, inconsistent quality across suppliers can lead to production delays or product failures, creating a significant risk for businesses reliant on vegan leather for their offerings.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable suppliers who specialize in sustainable materials. Conduct thorough research to identify companies that provide certifications for their vegan leather, such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX certification, which indicate responsible sourcing and production processes. Establishing direct communication with suppliers can also help clarify the materials used and the sustainability practices in place. Consider forming partnerships with suppliers who utilize innovative materials like mycelium or plant-based alternatives, which not only enhance product offerings but also align with consumer preferences for eco-friendly solutions. This proactive approach ensures that buyers can confidently meet market demands while reinforcing their commitment to sustainability.
Scenario 2: Addressing Durability Concerns with Vegan Leather
The Problem: One of the most common pain points for B2B buyers is the perception that vegan leather lacks the durability and longevity associated with traditional animal leather. Buyers may worry that products made from vegan leather will not withstand the rigors of everyday use, leading to higher return rates, dissatisfied customers, and ultimately, a negative impact on their brand image. This concern is particularly acute in industries such as fashion and automotive, where product durability is paramount.
The Solution: To mitigate concerns regarding durability, buyers should focus on specifying higher-grade vegan leather options, such as those made from polyurethane (PU) or innovative plant-based materials, which have shown to offer enhanced resilience. Educate your team about the different types of vegan leather and their respective properties, emphasizing those that are treated for durability, stain resistance, and water resistance. Additionally, consider conducting performance tests to validate the durability of the selected materials before full-scale production. By providing warranties or guarantees on products made from high-quality vegan leather, buyers can instill confidence in their customers, reinforcing the message that vegan leather can be both stylish and durable.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost Expectations for Vegan Leather Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often face budget constraints when sourcing vegan leather, especially when attempting to balance quality with cost. Vegan leather can vary widely in price, and cheaper options may compromise on quality, while premium options could exceed budget limits. This situation creates a dilemma, particularly for businesses looking to offer competitive pricing without sacrificing the integrity of their products.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs, buyers should adopt a strategic sourcing approach that includes bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers. This not only reduces the per-unit cost but also provides leverage to negotiate better terms. Additionally, consider exploring emerging alternatives such as bio-based vegan leathers made from agricultural waste, which may offer competitive pricing while appealing to eco-conscious consumers. Collaborating with suppliers on product development can also lead to innovative solutions that meet budgetary constraints without sacrificing quality. Implementing a tiered product strategy, where different product lines feature varying levels of vegan leather quality and pricing, can help cater to different market segments and maximize profitability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vegan leather material
What Are the Key Materials Used in Vegan Leather Production?
When selecting vegan leather for various applications, understanding the different materials available is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials used in vegan leather production: Polyurethane (PU), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Natural Fibers (like Piñatex), and Mushroom Leather. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact product performance and suitability.
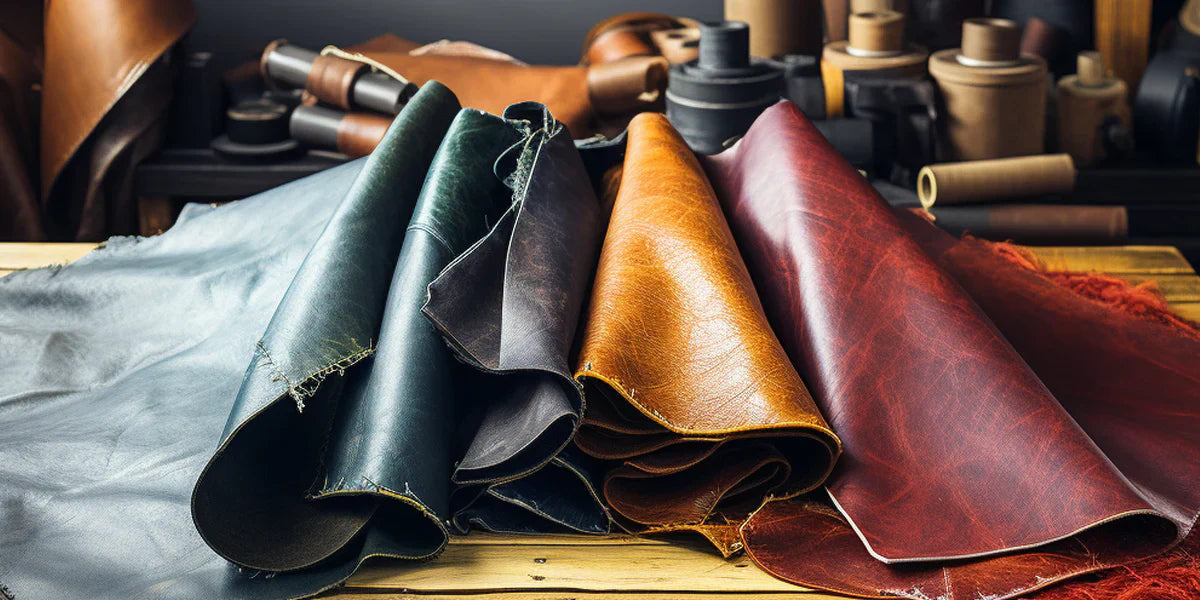
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Compare as a Vegan Leather Material?
Key Properties: Polyurethane is known for its flexibility and breathability. It can withstand moderate temperatures and is generally resistant to abrasion and water, making it suitable for various applications, including fashion and upholstery.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
Pros & Cons: PU leather is more durable than PVC, with a lifespan of 3-5 years under normal use. It is also more environmentally friendly than PVC, as it can be produced with less toxic chemicals. However, PU can still be prone to wear and discoloration over time, particularly in high-usage items. The manufacturing process can be complex, which may increase costs.
Impact on Application: PU is compatible with a wide range of media, including dyes and treatments, allowing for diverse design options. It is particularly suitable for fashion items, automotive interiors, and furniture.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial, especially in regions like Europe where environmental regulations are stringent. Buyers should also consider sourcing PU from manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices.
What Are the Characteristics of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) as Vegan Leather?
Key Properties: PVC is a cost-effective synthetic material known for its durability and resistance to moisture and stains. However, it has a lower temperature tolerance and can become brittle over time.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
Pros & Cons: PVC is inexpensive and widely available, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. However, it is less environmentally friendly due to the harmful chemicals used in its production. The lifespan of PVC products is generally shorter than those made from PU or natural fibers, typically lasting around 2-4 years.
Impact on Application: PVC is suitable for items that require water resistance, such as bags and outdoor gear. However, its rigidity may limit its use in applications requiring flexibility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the environmental concerns associated with PVC, particularly in regions with strict regulations. Compliance with local standards and consumer preferences for eco-friendly materials is increasingly important.
How Do Natural Fibers Like Piñatex Perform in Vegan Leather Applications?
Key Properties: Piñatex, made from pineapple leaf fibers, is biodegradable and offers good breathability. It has a unique texture and aesthetic appeal, making it popular in high-end fashion.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of Piñatex is its sustainability, as it utilizes agricultural waste. However, it may not be as durable as synthetic options, with a lifespan of 2-3 years depending on usage. The manufacturing process can also be more complex, impacting costs.
Impact on Application: Piñatex is ideal for fashion items, accessories, and upholstery where aesthetics are paramount. Its natural composition allows for compatibility with eco-conscious branding.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the sourcing practices of Piñatex producers and ensure compliance with international sustainability standards. Markets in Europe and North America are increasingly favoring such eco-friendly materials.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
What Are the Advantages of Mushroom Leather in Vegan Leather Production?
Key Properties: Mushroom leather, or mycelium leather, is made from fungal mycelium and is biodegradable. It has a unique texture and can be produced with varying thicknesses.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of mushroom leather is its sustainability; it is a renewable resource and can decompose naturally. However, its availability and production scalability are still developing, which may affect pricing and supply consistency.
Impact on Application: Mushroom leather is suitable for high-end fashion items and accessories, appealing to consumers looking for luxury and sustainability. Its unique properties can also lend themselves to innovative design applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: As with other natural materials, buyers should ensure that mushroom leather complies with relevant environmental standards. Awareness of the supply chain and sourcing practices is essential, especially in regions with growing eco-conscious consumer bases.
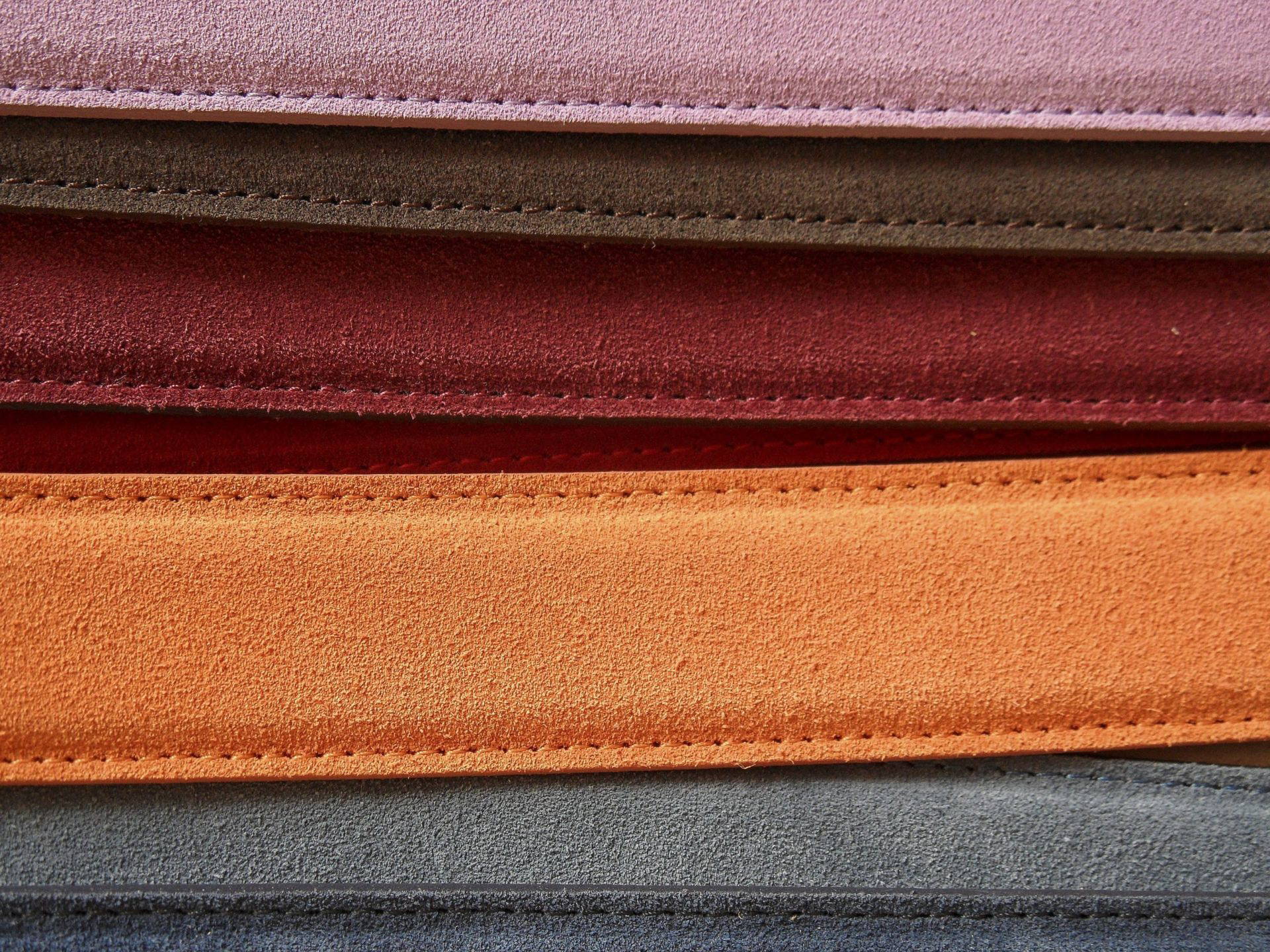

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
Summary of Vegan Leather Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for vegan leather material | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Fashion, upholstery, automotive interiors | Flexible, breathable, more durable | Prone to wear and discoloration | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Bags, outdoor gear | Cost-effective, widely available | Less environmentally friendly, shorter lifespan | Low |
| Natural Fibers (Piñatex) | Fashion items, accessories | Sustainable, biodegradable | Less durable, complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Mushroom Leather | High-end fashion items, accessories | Renewable, unique texture | Limited availability, developing market | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the various vegan leather materials available, helping them make informed decisions that align with their product requirements and sustainability goals.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vegan leather material
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Vegan Leather Material?
The manufacturing process of vegan leather involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets quality standards and customer expectations. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers select reliable suppliers and assess the quality of the vegan leather they intend to purchase.
Material Preparation: What Are the Raw Materials Used?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Vegan leather can be made from various substrates, including synthetic materials like polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), as well as natural fibers derived from plants such as pineapple leaves, apple peels, and mushrooms.
During this stage, the raw materials undergo cleansing and treatment to remove impurities. For synthetic materials, this may involve chemical processes to enhance their leather-like properties. In contrast, natural materials are often treated with eco-friendly agents to preserve their integrity while ensuring that they can mimic the look and feel of genuine leather.
How Is Vegan Leather Formed?
The forming stage is crucial for shaping the prepared materials into sheets or other desired forms. This is typically achieved through techniques such as extrusion, calendering, or lamination, depending on the type of vegan leather being produced.
-
Extrusion: For synthetic vegan leather, the raw materials are melted and extruded through a die to create sheets. This method allows for uniform thickness and texture.
-
Calendering: This technique involves passing the material through rollers to create a thin, flexible sheet. It is particularly useful for achieving a specific texture that mimics natural leather.
-
Lamination: In cases where multiple materials are used, lamination is employed to bond layers together, enhancing durability and aesthetics.
What Assembly Techniques Are Used in Vegan Leather Production?
Once the sheets are formed, the next stage is assembly. This involves cutting the sheets into specific patterns and stitching them together to create final products like bags, shoes, and upholstery.
Innovative sewing techniques are often employed to ensure durability and aesthetic appeal. Additionally, heat sealing and bonding methods may be used to join edges or create waterproof seams, which are particularly important in products like footwear and outerwear.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Vegan Leather?
The finishing stage is where the final aesthetic qualities of the vegan leather are achieved. This may include dyeing, embossing, and applying protective coatings.
- Dyeing: Vegan leather can be dyed in various colors, allowing manufacturers to offer a wide range of options to customers.
- Embossing: This technique is used to create textures that resemble natural leather grains, enhancing the visual appeal.
- Protective Coatings: To improve durability and resistance to wear and tear, a protective layer may be applied. This is particularly important for products that will be exposed to varying environmental conditions.
What International Standards and Quality Control Practices Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality control (QC) is critical in the manufacturing process of vegan leather to ensure that products meet both safety and performance standards. For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant international standards and QC checkpoints is essential.
Which International Standards Should Suppliers Adhere To?
Suppliers of vegan leather should comply with various international standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: If the vegan leather is intended for specialized applications, such as automotive or medical uses, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in vegan leather manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, periodic checks are conducted to ensure that processes are followed correctly and that products meet quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, a thorough inspection is performed to verify that the finished products meet all specifications and quality requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. This can be done through on-site inspections or third-party auditing firms.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers assess the performance history of suppliers and identify any recurring issues.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer unbiased evaluations of the supplier’s QC processes and product quality. This is particularly beneficial for international buyers who may not have the means to conduct on-site audits.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may face unique challenges when sourcing vegan leather.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding regional expectations regarding quality and ethical standards is crucial. Buyers should ensure that suppliers align with these expectations.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding materials, environmental impact, and safety. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations in the markets they serve.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain: Quality can also be affected by logistics, including transportation and storage. Buyers should work with suppliers who have robust supply chain management practices to maintain product integrity.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Vegan Leather Manufacturing
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for vegan leather are complex but essential for delivering high-quality products. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough quality control measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and secure reliable partnerships in the growing vegan leather market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vegan leather material’
The following guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in the effective sourcing of vegan leather materials. With increasing demand for sustainable and ethical products, understanding the nuances of vegan leather will empower businesses to make informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Identifying the specific qualities and characteristics you require from vegan leather is crucial. Consider aspects such as thickness, texture, durability, and water resistance. Establishing clear specifications will help in filtering suppliers and ensuring that the material meets your product needs.
Step 2: Research Material Composition
Vegan leather can be made from various materials, including polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and natural fibers like pineapple leaves or cactus. Understanding the environmental impact and performance characteristics of these materials will guide you in selecting the most suitable option for your brand’s ethos and product requirements.
- Key Considerations:
- Assess the biodegradability and sustainability of the materials.
- Investigate the production process to ensure it aligns with your company’s values.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, thorough evaluation is essential. Request detailed company profiles, product samples, and references from other businesses in your industry. This step mitigates risks associated with quality assurance and reliability.
- What to Look For:
- Supplier certifications related to sustainability and ethical practices.
- Reviews and testimonials from previous clients.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications that validate their claims about sustainability and ethical production. Certifications can include ISO standards, Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), or certifications from recognized environmental organizations.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
- Importance:
- Certifications provide credibility and assurance regarding the quality and environmental impact of the vegan leather.
- They can enhance your brand’s reputation by showcasing commitment to ethical sourcing.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Obtaining samples from potential suppliers is a vital step in the sourcing process. Testing these samples for quality, texture, and durability will help you determine if they meet your specifications and expectations.
- Testing Focus Areas:
- Evaluate the feel and aesthetic appeal of the material.
- Conduct durability tests to assess wear and tear over time.
Step 6: Assess Cost and Pricing Structure
Understanding the pricing structure of vegan leather materials is essential for budget planning. Compare quotes from different suppliers, but also consider the long-term value and quality of the material.
- Cost Considerations:
- Inquire about bulk pricing options and minimum order quantities.
- Factor in potential hidden costs such as shipping, tariffs, and delivery timelines.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, enter negotiations regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Clear communication at this stage will help establish a strong business relationship and minimize misunderstandings in the future.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
- Negotiation Tips:
- Be transparent about your expectations and requirements.
- Discuss potential discounts for long-term partnerships or larger orders.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively source high-quality vegan leather materials that align with their business goals and sustainability commitments.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vegan leather material Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Vegan Leather Material Sourcing?
When sourcing vegan leather, it is crucial to understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the price. Common options like polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are less expensive, while innovative alternatives such as pineapple leather or mushroom-based products can command a premium price.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and depend on the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for high-quality vegan leather production, impacting the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, leading to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and machinery for producing specific designs can be substantial. Custom tooling for unique specifications or designs will increase upfront costs but may be justified by higher margins on exclusive products.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures is essential to maintain product standards. These costs can add to the price but are necessary to ensure customer satisfaction and minimize returns.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, play a significant role, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and fuel prices will influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the average margin in your specific market can assist in negotiating fair pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Vegan Leather Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of vegan leather, particularly for B2B buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often come with discounts, while small orders may incur higher per-unit costs. Understanding supplier MOQs can help buyers negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific performance characteristics can lead to increased costs. Clearly defining requirements upfront can streamline the process and reduce unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Premium materials with eco-certifications or ethical production standards can be more expensive. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and geographical location of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their brand value, while emerging suppliers may offer competitive rates.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly impact total costs. Understanding responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs duties is essential for accurate cost estimation.
What Are the Best Tips for B2B Buyers in Vegan Leather Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency and value in sourcing vegan leather, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage bulk purchasing and long-term relationships to negotiate better prices. Establishing rapport with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance costs, durability, and potential waste over the product’s lifecycle to make informed decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Currency fluctuations and tariffs can significantly affect costs. Buyers should stay informed about international trade agreements and market conditions.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay updated on the latest developments in vegan leather technologies and consumer preferences. This knowledge can help identify cost-effective sourcing opportunities and innovative materials.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost and pricing landscape of vegan leather material sourcing requires a comprehensive understanding of various components and influencing factors. By strategically evaluating these aspects, international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can optimize their sourcing strategies and achieve better value. Keep in mind that the prices discussed are indicative and may vary based on numerous factors specific to each transaction.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vegan leather material With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Vegan Leather Material
As the demand for sustainable and ethical materials grows, businesses are increasingly exploring alternatives to traditional vegan leather. This section compares vegan leather with other viable solutions, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions. The alternatives considered include traditional animal leather and innovative biodegradable materials derived from natural sources.
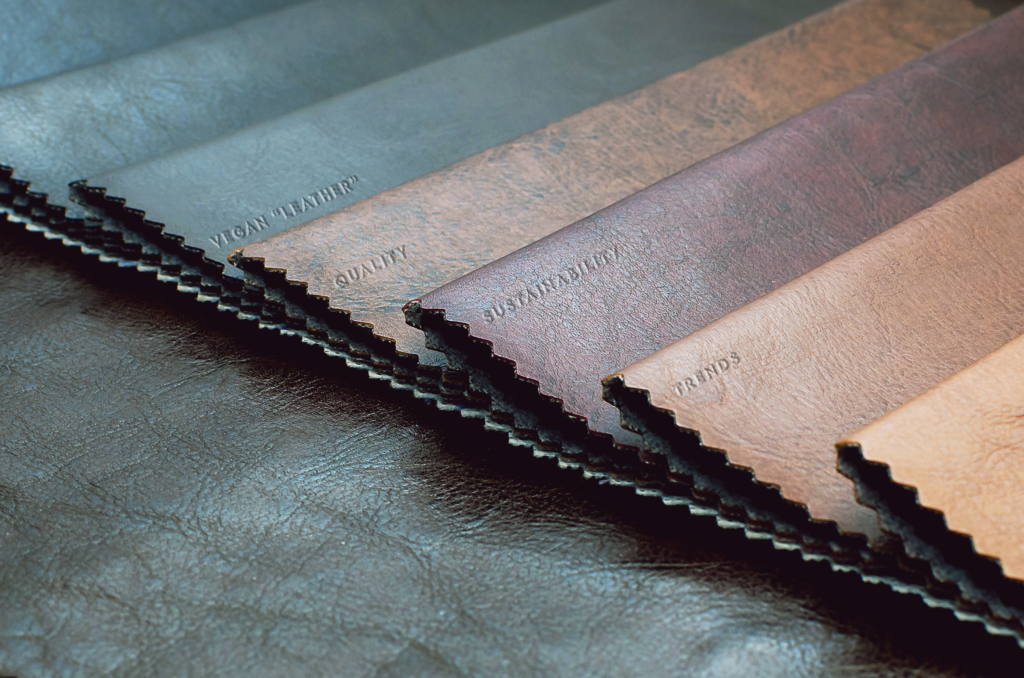

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Vegan Leather Material | Traditional Animal Leather | Biodegradable Natural Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate durability (2-5 years) | High durability (up to a lifetime) | Varies (generally good but less than animal leather) |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher initial investment | Mid-range, depending on sourcing |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to manufacture and source | Complex due to tanning processes | Varies; some require special techniques |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, less upkeep | Requires conditioning and care | Generally low maintenance, but care varies |
| Best Use Case | Fashion, upholstery, accessories | High-end fashion, luxury goods | Eco-conscious brands, sustainable products |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Animal Leather?
Traditional animal leather is renowned for its durability and timeless appeal. It can last a lifetime with proper care, making it a long-term investment. However, its production involves significant ethical and environmental concerns, including animal welfare issues and a high carbon footprint due to the intensive farming practices associated with livestock. Additionally, the tanning process often employs toxic chemicals, raising health and environmental risks, especially in developing regions.
How Do Biodegradable Natural Materials Compare?
Biodegradable natural materials, such as those derived from mushroom mycelium or agricultural by-products like pineapple leaves, are emerging as innovative alternatives. These materials can decompose naturally, reducing waste and environmental impact. They often require less energy to produce compared to both traditional leather and synthetic alternatives. However, their durability may not match that of animal leather, and their performance can vary significantly based on the specific material used. Businesses focusing on sustainability may find these materials align well with their brand values.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Material for Your Needs
When selecting the right material, B2B buyers should consider their target market, brand values, and product application. Vegan leather offers a versatile, cost-effective solution for various applications, particularly in fashion and accessories. However, if durability and longevity are paramount, traditional animal leather might be preferable despite its ethical implications. On the other hand, biodegradable natural materials present an innovative, sustainable option for brands committed to reducing their environmental impact, though they may require careful sourcing and testing. Ultimately, aligning material choice with business goals and consumer expectations is crucial for success in today’s eco-conscious market.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vegan leather material
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Vegan Leather Material?
When considering vegan leather for B2B applications, understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications to be aware of:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of vegan leather, typically classified into categories such as PU (polyurethane) and PVC (polyvinyl chloride). PU is often regarded as the superior option due to its flexibility and breathability, making it suitable for high-end fashion products. Understanding material grade helps buyers assess durability, appearance, and suitability for specific applications, such as upholstery or fashion.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the acceptable variations in thickness and density of the vegan leather. This specification is essential for manufacturers who require precise measurements for cutting and assembling products. Variations outside these tolerances can lead to production inefficiencies, increased waste, and potential quality issues in the final product.
3. Water Resistance
Water resistance is a critical property that determines how well vegan leather can withstand moisture without degrading. This property is especially important for products used in outdoor settings or those exposed to spills. Buyers must ensure that the vegan leather meets specific water resistance standards to maintain the longevity and functionality of their products.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
4. UV Stability
UV stability refers to the ability of vegan leather to resist degradation when exposed to sunlight. This characteristic is vital for outdoor applications, such as automotive interiors or outdoor furniture. Buyers should inquire about UV stability ratings to ensure that the vegan leather will maintain its color and integrity over time.
5. Biodegradability
Biodegradability indicates how well a material can decompose in natural environments. While many synthetic vegan leathers have limited biodegradability, newer options made from natural fibers, such as pineapple leaves or mushroom-based materials, offer improved environmental benefits. Understanding biodegradability is essential for companies aiming to enhance their sustainability credentials.
6. Flame Resistance
Flame resistance is the material’s ability to withstand ignition and prevent the spread of flames. This property is particularly important in industries like automotive and upholstery, where safety standards are stringent. Buyers should verify compliance with relevant fire safety regulations to mitigate risks associated with flammability.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Vegan Leather Industry?
Navigating the vegan leather market involves understanding industry-specific terminology. Here are some key terms that are frequently encountered:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or products that are used in another company’s final product. In the vegan leather industry, OEMs may supply materials to brands that incorporate them into finished goods. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure quality and consistency in their supply chain.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This process is essential for comparing costs and ensuring competitive pricing. Buyers should be clear about their specifications in the RFQ to receive accurate and comparable quotes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is crucial when sourcing vegan leather from international suppliers.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the context of vegan leather, understanding lead times can help buyers plan their production schedules and manage customer expectations effectively.
6. Certification
Certification in the vegan leather industry often refers to third-party validation of sustainability claims or material quality. Certifications can enhance credibility and marketability, making it essential for buyers to verify and prioritize suppliers with recognized certifications.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right vegan leather products for their specific needs while navigating the complexities of the market.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vegan leather material Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Vegan Leather Material Sector?
The vegan leather market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable and ethical alternatives to traditional leather. By 2025, the global vegan leather market is projected to reach $89.6 billion, reflecting a robust shift in purchasing behaviors across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key drivers include heightened awareness of animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and the rise of eco-conscious brands. The proliferation of high-profile brands adopting vegan leather—ranging from luxury fashion houses to mainstream retailers—signals a broader acceptance and desire for these materials.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing include the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain to enhance supply chain transparency and efficiency. Businesses are increasingly focusing on sourcing practices that prioritize traceability, ensuring that materials are responsibly obtained. Additionally, the rise of innovative materials derived from organic sources, such as mushrooms, apples, and cacti, presents new opportunities for manufacturers and suppliers. These developments not only cater to evolving consumer preferences but also align with global sustainability goals.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affecting the Vegan Leather Material Sector?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the vegan leather conversation. While vegan leather is often perceived as a more environmentally friendly option than animal leather, the production processes for synthetic materials like polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) still raise ecological concerns. The use of fossil fuels and the generation of microplastics during the lifecycle of these materials contribute to environmental degradation. Therefore, international buyers must prioritize suppliers that offer sustainably sourced vegan leather alternatives.
Ethical sourcing is equally crucial in this sector. B2B buyers should seek partnerships with manufacturers who adhere to recognized sustainability certifications, such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX® certifications. These certifications ensure that vegan leather products meet rigorous environmental and social standards. By investing in ethical supply chains, businesses can enhance their brand reputation, appeal to eco-conscious consumers, and mitigate risks associated with environmental regulations.
How Has the Vegan Leather Material Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of vegan leather can be traced back to its origins in the early 20th century, when synthetic alternatives were first introduced. Initially, materials like PVC dominated the market due to their affordability and accessibility. However, growing environmental and health concerns regarding PVC and other synthetic materials have led to the emergence of more sustainable options, such as PU and plant-based leathers.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
In recent years, technological advancements have propelled the development of innovative vegan leather alternatives derived from natural sources, which have gained traction among manufacturers and consumers alike. This shift not only reflects changing consumer preferences but also signifies a broader movement toward sustainability within the fashion and materials industries. As the market continues to mature, B2B buyers must stay informed about these advancements to make well-informed sourcing decisions that align with their sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vegan leather material
-
How do I ensure the quality of vegan leather materials before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of vegan leather, consider requesting samples from potential suppliers. Evaluate the texture, durability, and flexibility of the material to determine if it meets your standards. Additionally, inquire about the manufacturing processes and certifications, such as ISO or OEKO-TEX, which indicate adherence to quality and environmental standards. Establishing clear communication regarding your quality expectations and any specific industry requirements can also help mitigate risks associated with subpar materials. -
What are the key factors to consider when selecting a vegan leather supplier?
When selecting a vegan leather supplier, assess their reputation in the market, production capabilities, and compliance with international standards. Investigate their sourcing practices for raw materials to ensure sustainability and ethical production. Additionally, review their customer service and responsiveness, as these qualities will be crucial for ongoing collaboration. Requesting references from other clients can provide insights into their reliability and product quality. -
What customization options are available for vegan leather products?
Many suppliers offer customization options for vegan leather, including color, texture, and finish. You can often request specific patterns or prints to align with your brand identity. Discuss your needs with the supplier to explore available options, including embossing or debossing features. Be sure to clarify any minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom designs, as these can vary significantly between manufacturers. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for vegan leather?
Minimum order quantities for vegan leather can vary widely based on the supplier and the type of material requested. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand square meters. It’s important to communicate your project needs early in the negotiation process to find a supplier willing to accommodate your order size. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses, so it’s worth exploring these options. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing vegan leather internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of vegan leather typically include options like advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, often ranging from 30% to 50% of the total order value. Discussing payment terms early in negotiations helps establish clear expectations and can prevent future misunderstandings. Be sure to also consider currency fluctuations and international transaction fees that may affect overall costs. -
How can I manage logistics when importing vegan leather?
Managing logistics for importing vegan leather requires careful planning. Collaborate with your supplier to understand shipping methods, estimated delivery times, and potential customs regulations. It’s advisable to work with a freight forwarder experienced in handling materials like vegan leather to navigate international shipping complexities. Additionally, ensure you are familiar with import duties and taxes in your country to avoid unexpected costs upon arrival. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement when sourcing vegan leather?
Implementing quality assurance measures involves setting clear specifications for the vegan leather you require and conducting thorough inspections upon receipt. Consider third-party quality inspections, especially for large orders, to verify that the materials meet your standards. Establishing a return policy with your supplier for defective products can also safeguard your investment. Regular communication and feedback with the supplier can further enhance quality control. -
Are there specific certifications to look for in vegan leather materials?
When sourcing vegan leather, look for certifications that indicate sustainable and ethical practices. Key certifications include OEKO-TEX, which ensures that materials are free from harmful substances, and Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), which applies to organic materials. Certifications like Fair Trade or those related to carbon neutrality can also be beneficial, particularly for buyers focused on sustainability. These certifications can enhance your brand’s reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Top 6 Vegan Leather Material Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carl Friedrik – Vegan Leather Essentials
Domain: carlfriedrik.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Vegan leather is made from synthetic materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyurethane (PU), as well as natural fibers from sources such as cactus plants, agave leaves, and pineapple leaves. It is characterized by being waterproof, thin, stain-resistant, and flexible, but generally has a shorter lifespan of 2-5 years compared to real leather, which can last a lifetime. Vegan leather is used…
2. Reddit – Vegan Leather Alternatives
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: High quality vegan leathers mentioned include Apple leather and cactus leather. Kraft-Tex is suggested as a durable, leather-like material made from wood and cork. Waxed canvas is recommended as an alternative that lasts long and develops a patina. Upholstery shops may have vinyls that withstand extreme temperatures and wear.
3. Alternative Leathers – Desserto® Cactus Leather
Domain: alternativeleathers.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Desserto® Cactus Leather”,”price”:”From $18.00″,”description”:”Unique and environmentally friendly material used by iconic brands such as Fossil, Adidas, and Mercedes. Developed in Mexico.”},{“name”:”Piñatex® Original Pineapple Leather”,”price”:”From $24.00″,”description”:”Sustainable alternative developed in the 1990s, used by trusted brands worldwide.”},{“name”:”Vegea® Grap…
4. WebMD – Vegan Leather Overview
Domain: webmd.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Vegan leather is a material made from plant-based or sustainable sources, serving as an eco-friendly alternative to animal leather. It is artificial, synthetic, or ‘faux’ leather made from agricultural waste products and sustainable biomaterials. Common materials used to manufacture vegan leather include: polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride, cork, cactus, kombucha cellulose (SCOBY), mushroom mycelium…
5. Immaculate Vegan – Sustainable Leather Alternatives
Domain: immaculatevegan.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Vegan leather is made from various materials including apple leather, cactus leather, grape leather, corn leather, piñatex (pineapple leather), cork leather, and MIRUM. These materials are often considered sustainable alternatives to traditional leather, with some being biodegradable. The article discusses the sustainability of these materials and their growing popularity in the fashion industry.
6. District Leathers – Vegan Saffiano Textured Cactus Leather
Domain: districtleathers.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Vegan & Recycled Leather collection includes 13 products. Key items include: 1. Vegan Saffiano Textured Cactus Leather in Olive, Black, Navy – 55″ Wide, Sale price from $79.99. 2. Hemp Vegan Leather – Sale price from $79.99. 3. Vegan Rock Magna Cactus Pebble Grain Leather – 55″ Wide, Sale price $74.99. 4. Vegan Burgundy Gaia Cactus Smooth Grain Leather – 55″ Wide, Sale price from $79.99. 5. Vegan …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vegan leather material
As the vegan leather market continues to evolve, strategic sourcing becomes critical for international B2B buyers looking to capitalize on this growing trend. The shift towards sustainable materials is not just a consumer preference; it’s becoming a market necessity. By leveraging diverse sourcing options—from traditional PU and PVC to innovative natural alternatives like cactus and mushroom-based leathers—buyers can meet both ethical standards and consumer demands for sustainability.
Key takeaways include the importance of understanding the characteristics and lifecycle impacts of various vegan leather materials. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their production processes and sustainability practices. Additionally, fostering partnerships with manufacturers who invest in eco-friendly technologies will not only enhance product offerings but also align with global sustainability goals.
Looking ahead, the vegan leather market is projected to reach $89.6 billion by 2025. This presents a unique opportunity for B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to position themselves as leaders in sustainable fashion. Embrace the future of materials by integrating vegan leather into your supply chain and responding proactively to the growing demand for ethical products. Let’s innovate together for a more sustainable tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to vegan leather material
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.