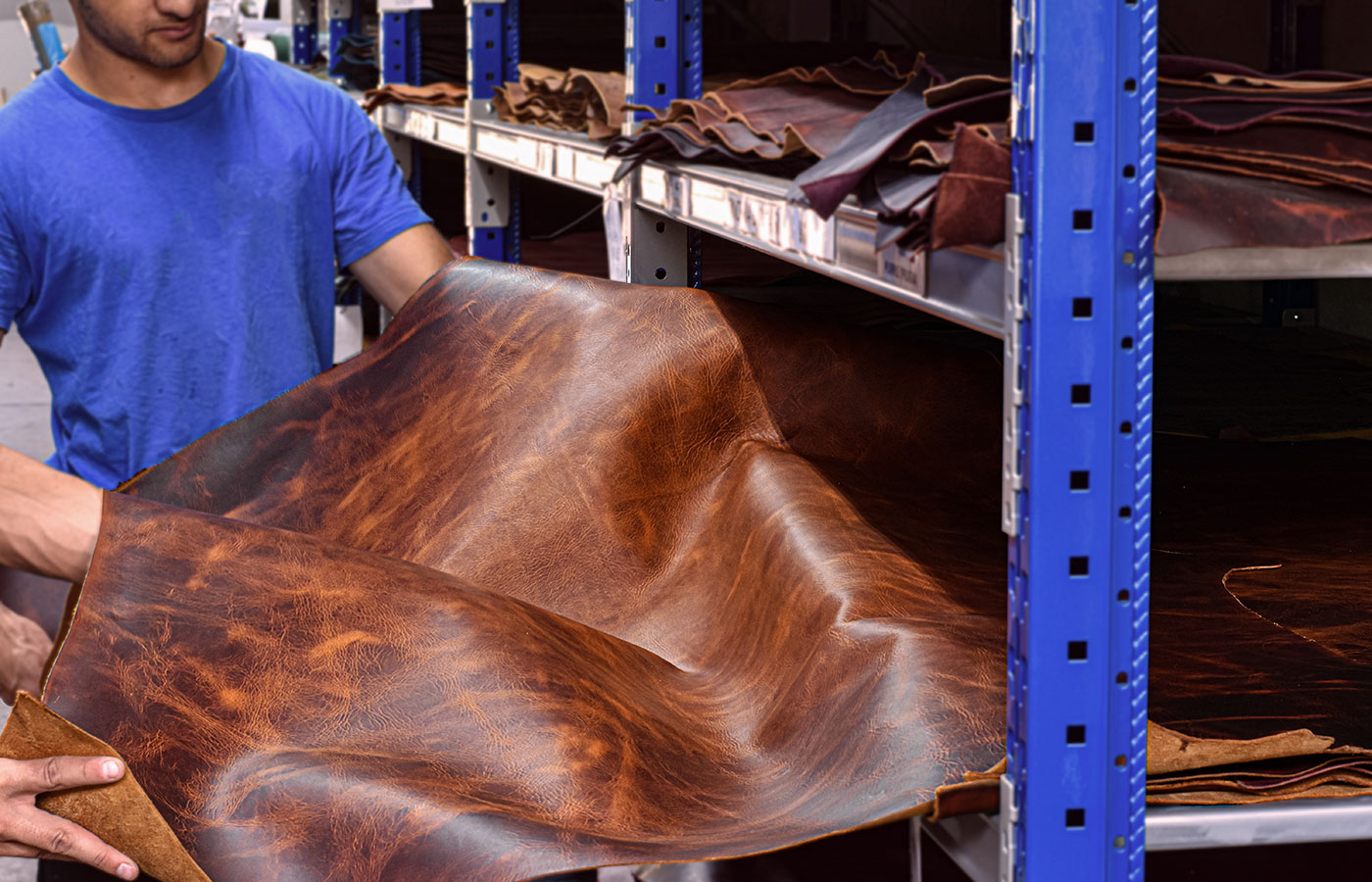
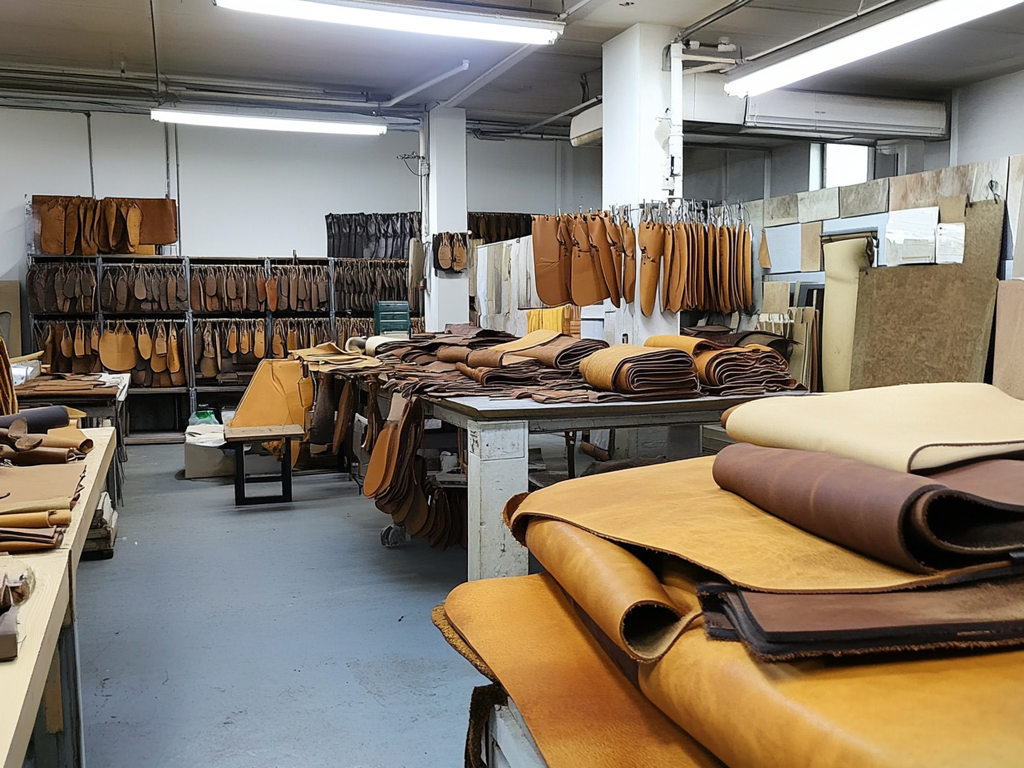
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for synthetic artificial leather
Navigating the complexities of sourcing synthetic artificial leather presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets like Nigeria and Vietnam. As demand for sustainable and ethically produced materials grows, understanding the nuances of synthetic leather—its types, applications, and sourcing options—becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide serves as an essential resource, offering insights into the various forms of synthetic leather, such as polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), along with their respective benefits and limitations.
In addition, we delve into the diverse applications of synthetic leather across industries, from fashion and upholstery to automotive and accessories. Buyers will find valuable strategies for vetting suppliers, evaluating product quality, and understanding cost dynamics, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge to navigate the global market, this guide empowers stakeholders from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to confidently source synthetic leather that meets their business needs while aligning with ethical and sustainability standards. Whether you are a manufacturer, retailer, or designer, our insights will help you leverage the advantages of synthetic leather in your product offerings and supply chain strategies.
Table Of Contents
- Top 8 Synthetic Artificial Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for synthetic artificial leather
- Understanding synthetic artificial leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of synthetic artificial leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘synthetic artificial leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for synthetic artificial leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for synthetic artificial leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘synthetic artificial leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for synthetic artificial leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing synthetic artificial leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for synthetic artificial leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the synthetic artificial leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of synthetic artificial leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for synthetic artificial leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding synthetic artificial leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Soft touch, high durability, breathable | Upholstery, fashion accessories, automotive | Pros: Flexible, eco-friendlier than PVC. Cons: Higher cost than PVC. |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Cost-effective, water-resistant, less breathable | Furniture, bags, shoes, protective gear | Pros: Affordable, versatile. Cons: Less environmentally friendly, can feel less authentic. |
| Vegan Leather | Made from plant-based materials, biodegradable options | Fashion, upholstery, eco-conscious brands | Pros: Ethical choice, biodegradable options. Cons: Limited availability, can be pricier. |
| Microfiber | Ultra-soft, high stain resistance, durable | Upholstery, clothing, accessories | Pros: Easy to clean, mimics real leather. Cons: Can be less breathable. |
| Leatherette | General term for synthetic leather, often a blend | General upholstery, fashion items | Pros: Wide availability, customizable. Cons: Quality can vary significantly. |
What are the Characteristics of Polyurethane (PU) Synthetic Leather?
Polyurethane (PU) synthetic leather is known for its soft touch and high durability, making it an ideal choice for various applications. It is more breathable than PVC and often used in upholstery, fashion accessories, and automotive interiors. B2B buyers should consider the higher cost of PU compared to PVC, but its eco-friendlier properties and premium feel can justify the investment, especially for brands targeting a quality-conscious market.
How Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Compare in Synthetic Leather?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used types of synthetic leather due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility. It is often employed in furniture, bags, shoes, and protective gear. While PVC offers affordability and a range of colors, buyers should be aware of its lower environmental impact and potential discomfort due to reduced breathability. Companies focusing on budget-friendly options may find PVC suitable, but should also consider the growing demand for more sustainable alternatives.
Why Choose Vegan Leather for Ethical B2B Sourcing?
Vegan leather is gaining traction as an ethical alternative to traditional synthetic leathers, often made from plant-based materials. This type of leather can be biodegradable, appealing to eco-conscious brands. Its primary applications include fashion and upholstery. Buyers should note that while vegan leather aligns with sustainability goals, its availability may be limited, and costs can be higher than synthetic counterparts. Brands looking to enhance their corporate social responsibility should explore vegan options.
What Advantages Does Microfiber Offer in Synthetic Leather?
Microfiber synthetic leather is recognized for its ultra-soft texture and high stain resistance, making it a popular choice for upholstery, clothing, and accessories. Its easy-to-clean nature mimics the appearance of real leather, appealing to consumers seeking practical yet stylish options. B2B buyers should be aware, however, that microfiber can lack breathability, which may not be suitable for all applications. Brands focusing on durability and ease of maintenance may find microfiber an excellent fit.
How Can Leatherette Serve Diverse B2B Needs?
Leatherette serves as a general term for synthetic leather, often encompassing various blends and formulations. Its wide availability and customization options make it suitable for general upholstery and fashion items. However, the quality of leatherette can vary significantly, so B2B buyers should conduct thorough evaluations of suppliers to ensure product consistency. This type of synthetic leather offers flexibility in design and application, making it a valuable resource for businesses catering to diverse market needs.
Key Industrial Applications of synthetic artificial leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Synthetic Artificial Leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Upholstery for car interiors | Enhanced durability and ease of maintenance | Quality of materials, resistance to wear, and color options |
| Furniture | Upholstery for sofas and chairs | Cost-effective alternative to genuine leather | Fire retardancy, environmental certifications, and design flexibility |
| Fashion & Apparel | Jackets, handbags, and footwear | Trend adaptability and ethical sourcing options | Material composition, breathability, and ease of cleaning |
| Sports Equipment | Protective gear and sports bags | Lightweight and resistant to abrasions | Compliance with safety standards and durability under stress |
| Home Decor | Wall coverings and decorative accents | Versatile aesthetics and easy installation | Customization options and moisture resistance |
How is Synthetic Artificial Leather Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, synthetic artificial leather is primarily used for upholstery in car interiors, including seats, door panels, and dashboards. Its durability and resistance to stains make it an attractive option for manufacturers and suppliers, especially in regions with diverse climates. International buyers should consider the material’s wear resistance, ease of cleaning, and color options to meet consumer preferences. Additionally, the ability to customize textures and finishes can cater to luxury markets, enhancing brand appeal.
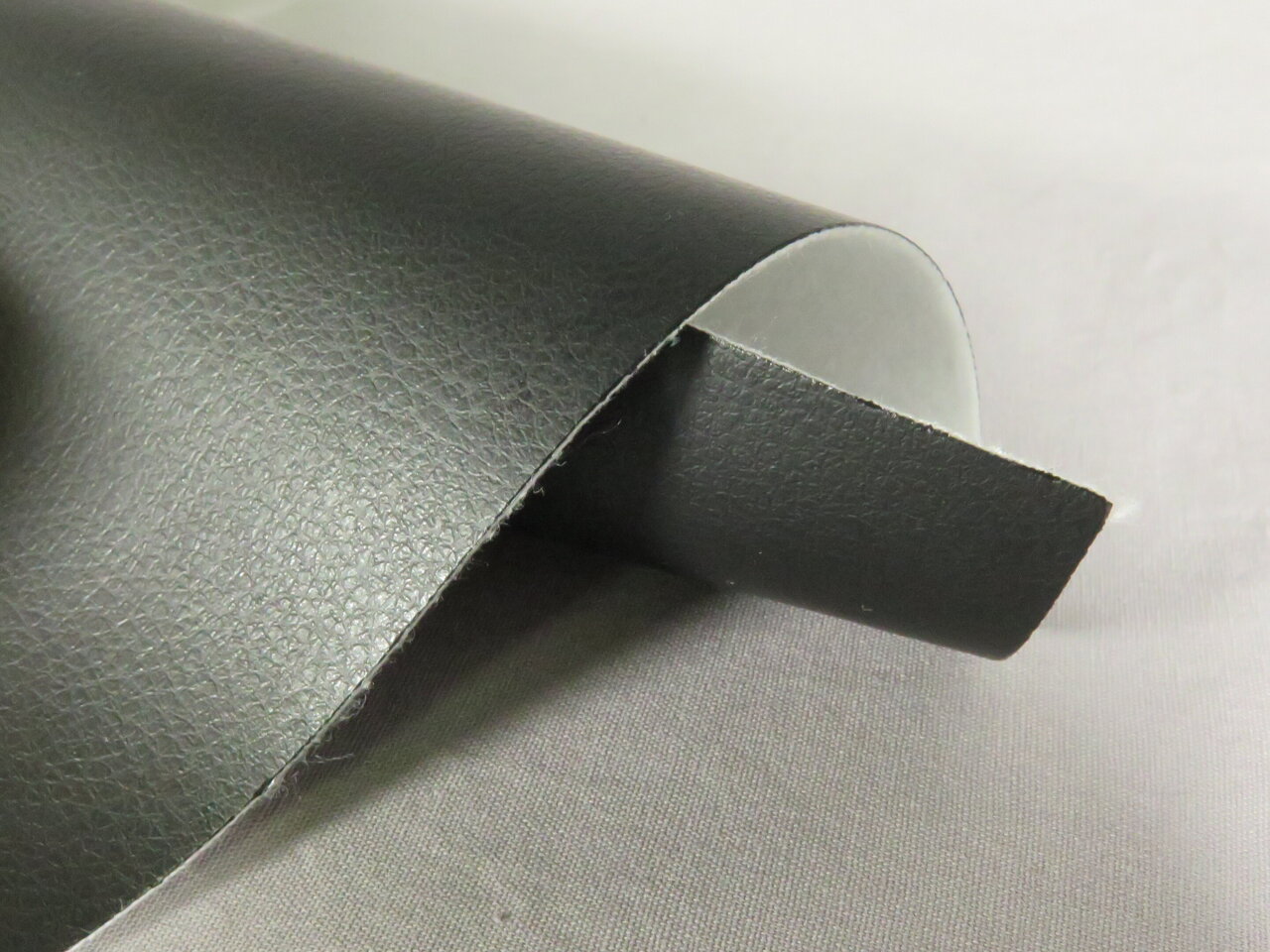
Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
What are the Benefits of Synthetic Artificial Leather in Furniture?
Synthetic leather is widely used in furniture upholstery, providing a cost-effective alternative to genuine leather while maintaining aesthetic appeal. It is particularly beneficial for businesses targeting family-oriented consumers, as its stain-resistant properties make it ideal for homes with children and pets. Buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that meet fire safety standards and offer a range of colors and textures to match various design styles. Environmental certifications can also be a deciding factor for eco-conscious markets.
How Does Synthetic Artificial Leather Enhance Fashion & Apparel?
In the fashion and apparel industry, synthetic artificial leather is favored for its versatility in producing jackets, handbags, and footwear. It allows designers to create trendy items without the ethical concerns associated with animal leather. For B2B buyers, sourcing synthetic leather requires attention to material composition, breathability, and ease of maintenance to ensure customer satisfaction. Additionally, the ability to offer unique colors and patterns can help brands stand out in competitive markets.
Why is Synthetic Artificial Leather Important in Sports Equipment?
Synthetic artificial leather is increasingly used in sports equipment, such as protective gear and sports bags, due to its lightweight nature and high abrasion resistance. These properties are crucial for ensuring athlete safety and performance. Buyers in this sector should ensure that the materials comply with relevant safety standards and are durable enough to withstand rigorous use. The adaptability of synthetic leather allows for various designs, appealing to both professional and amateur sports markets.
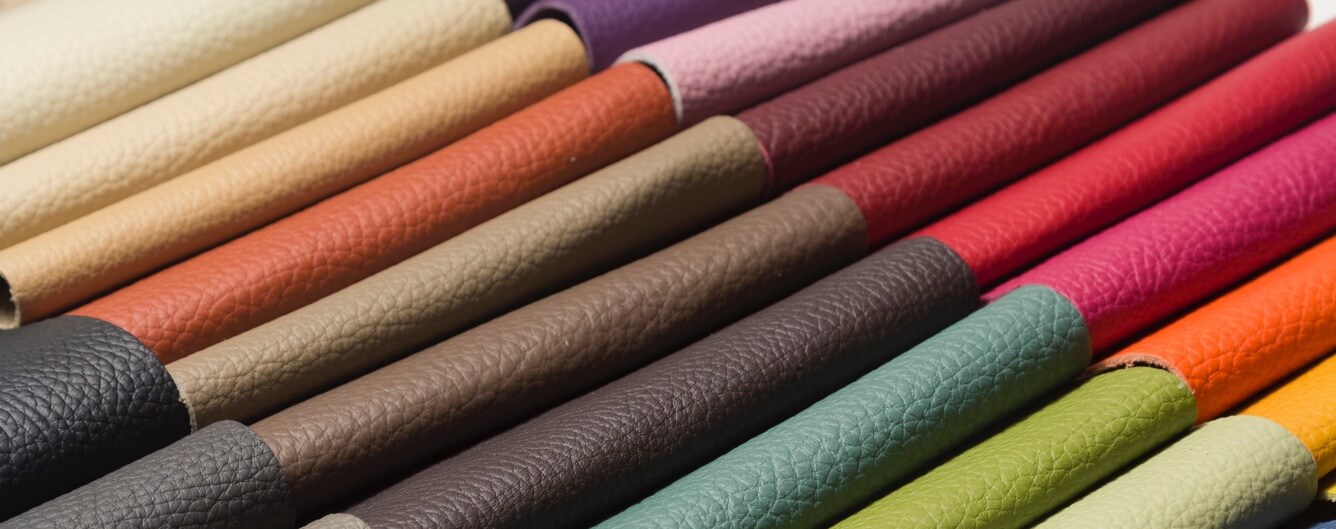

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
How is Synthetic Artificial Leather Utilized in Home Decor?
In home decor, synthetic artificial leather is used for wall coverings and decorative accents, offering a stylish yet practical solution. Its ease of installation and maintenance makes it a popular choice for interior designers and homeowners alike. For international buyers, sourcing options should include customization capabilities and moisture resistance to suit different environments. The aesthetic versatility of synthetic leather allows it to complement various interior styles, making it an attractive option for diverse markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘synthetic artificial leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Assessing Quality and Durability of Synthetic Leather
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with determining the quality and durability of synthetic leather products before making a purchase. This challenge is especially pronounced when sourcing from international suppliers, where variations in manufacturing standards and material compositions can lead to significant discrepancies. Buyers may receive samples that look promising, only to find that the final products do not meet their quality expectations, leading to increased return rates, wasted resources, and potential damage to their reputation in the market.
The Solution: To effectively assess the quality of synthetic leather, buyers should implement a rigorous supplier evaluation process. This includes requesting detailed product specifications and certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards, such as ISO or ASTM. Additionally, conducting on-site visits to manufacturing facilities can provide insights into production processes and quality control measures. When evaluating samples, buyers should focus on characteristics such as thickness, texture, and flexibility, while also checking for certifications related to durability and abrasion resistance. Engaging with suppliers who offer a transparent supply chain and detailed product testing results can further mitigate the risks associated with quality discrepancies.
Scenario 2: Environmental Concerns Over Synthetic Leather Products
The Problem: As global awareness of environmental issues rises, B2B buyers are increasingly confronted with concerns regarding the sustainability of synthetic leather. Traditional faux leather is often made from PVC or PU, which raises concerns about biodegradability and the release of harmful chemicals during production. Buyers who prioritize sustainability may find it challenging to source synthetic leather options that align with their corporate social responsibility goals, leading to potential backlash from consumers and stakeholders.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
The Solution: To address environmental concerns, buyers should explore suppliers who specialize in innovative, eco-friendly synthetic leather alternatives. These may include materials made from recycled plastics or plant-based sources, which offer a more sustainable option without sacrificing quality. When sourcing, buyers should inquire about the entire lifecycle of the product, including its production methods, chemical composition, and end-of-life disposal options. Collaborating with suppliers who are committed to sustainable practices can enhance a company’s brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, buyers can consider establishing partnerships with manufacturers that invest in sustainable technologies or certifications to further validate their commitment to environmental stewardship.
Scenario 3: Limited Customization Options for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find that the synthetic leather options available in the market do not meet their specific design or functional requirements. Industries such as automotive, furniture, and fashion often require unique colors, textures, and performance characteristics, but suppliers may offer limited customization options. This lack of flexibility can hinder product development and limit the ability to create differentiated offerings in a competitive market.
The Solution: To overcome limitations in customization, buyers should actively seek out manufacturers that specialize in bespoke synthetic leather solutions. It is beneficial to establish clear communication about the desired specifications, including color matching, texture variations, and any specific performance attributes required for the intended application. Engaging in collaborative product development with suppliers can lead to tailored solutions that meet specific needs. Furthermore, buyers can leverage technology such as digital printing and advanced dyeing techniques, which allow for greater flexibility in design without significantly increasing production costs. Building long-term relationships with manufacturers that prioritize innovation and customization can ultimately lead to a more successful product line and enhanced market competitiveness.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for synthetic artificial leather
What Are the Key Materials Used in Synthetic Artificial Leather?
When selecting synthetic artificial leather for various applications, understanding the properties and implications of the materials used is crucial for B2B buyers. This guide examines four common materials: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Polyurethane (PU), Vegetable-Based Leather, and Microfiber. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
How Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Perform in Synthetic Leather Applications?
PVC is one of the most widely used materials in synthetic leather production. It is known for its durability and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for various applications, including upholstery and fashion accessories. PVC-based synthetic leather typically has a low breathability rating, which can lead to discomfort in certain applications, such as clothing.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and readily available, making it an attractive option for manufacturers. Its resistance to stains and easy maintenance are significant advantages for end-users.
Cons: However, PVC is less flexible than other materials, which can limit its applications. Additionally, concerns about environmental impact and biodegradability have led to increased scrutiny of PVC products.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, compliance with local environmental regulations is essential. Many countries are moving towards stricter regulations regarding the use of PVC, making it crucial for buyers to stay informed about compliance standards.
What Advantages Does Polyurethane (PU) Offer for Synthetic Leather?
Polyurethane (PU) is another popular choice for synthetic leather, known for its soft texture and high flexibility. PU synthetic leather mimics the feel of genuine leather more closely than PVC, making it a preferred choice for high-end fashion and upholstery applications.
Pros: PU is highly versatile and can be produced in a wide range of colors and textures. Its breathability is superior to that of PVC, enhancing comfort in clothing and upholstery.
Cons: The manufacturing process for PU is more complex and costly than for PVC, which can increase the final product price. Additionally, PU may not be as durable as PVC in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or heavy wear.
For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it is essential to consider compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN when sourcing PU materials. The growing demand for sustainable products also makes it necessary to evaluate the environmental impact of PU production.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
How Does Vegetable-Based Leather Compare to Traditional Synthetic Options?
Vegetable-based leather is an emerging alternative that addresses some environmental concerns associated with traditional synthetic leathers. Made from plant materials, this type of synthetic leather is biodegradable and often free from harmful chemicals.
Pros: The primary advantage of vegetable-based leather is its eco-friendliness. It appeals to consumers seeking sustainable options, making it a strong selling point in markets focused on ethical consumption.
Cons: However, vegetable-based leather is often more expensive to produce, which can limit its market reach. Its durability and resistance to water may also be inferior compared to PVC and PU.
International buyers, particularly those in environmentally conscious markets like Europe, should prioritize sourcing vegetable-based leather to align with sustainability initiatives. Compliance with organic and eco-labeling standards can enhance marketability.
What Role Does Microfiber Play in Synthetic Leather Production?
Microfiber is a synthetic material made from ultra-fine fibers, often used in high-quality synthetic leather products. It offers a unique combination of softness, durability, and breathability, making it ideal for luxury applications.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
Pros: Microfiber synthetic leather is lightweight, easy to clean, and resistant to wear and tear. It is also highly customizable, allowing for various textures and finishes.
Cons: The primary limitation of microfiber is its cost, which is typically higher than PVC and PU. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be resource-intensive, raising concerns about sustainability.
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, understanding the balance between cost and quality is crucial. Microfiber products may appeal to premium markets, but buyers must ensure they meet local demand and compliance standards.
Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
Summary Table of Material Comparisons
| Material | Typical Use Case for synthetic artificial leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Upholstery, fashion accessories | Cost-effective and moisture-resistant | Low flexibility and environmental concerns | Low |
| Polyurethane (PU) | High-end fashion, upholstery | Soft texture and high flexibility | Higher manufacturing cost and durability concerns | Medium |
| Vegetable-Based Leather | Eco-friendly products, fashion | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Higher production costs and lower durability | High |
| Microfiber | Luxury applications, high-quality upholstery | Lightweight and customizable | Higher cost and resource-intensive manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations across different regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for synthetic artificial leather
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Synthetic Artificial Leather?
The manufacturing process of synthetic artificial leather involves several key stages, each of which plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and durability of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality synthetic leather.
1. Material Preparation: How Is the Base Material Sourced and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is sourcing and preparing the base material. Typically, synthetic leather is made from a combination of cotton or polyester fabrics. These materials are selected for their porous and rough textures, which allow for better adhesion to the plastic overlay.
In some cases, manufacturers produce their own base materials, but more commonly, they procure them from specialized suppliers. This step often involves pre-treating the fabrics to enhance their surface properties, ensuring optimal bonding with the synthetic polymer later in the process.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Create the Synthetic Leather?
The forming stage involves applying a layer of plastic, usually made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), to the prepared base fabric. The choice between PU and PVC often depends on the intended application, as each offers unique characteristics.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
-
PU Production: The production of PU involves a complex chemical reaction between isocyanates and polyols. Additives are introduced to achieve the desired flexibility and texture. The resulting polymer is then processed to create a flexible material that mimics the properties of genuine leather.
-
PVC Production: PVC is produced by combining salt and petroleum derivatives. The process includes several stages of chemical transformation to create a flexible, durable polymer. Plasticizers are added to ensure that the final product is suitable for various applications.
Once the plastic is formulated, it is applied to the base material using techniques such as heat lamination or coating. This process ensures that the plastic adheres uniformly, creating a consistent appearance and feel.
3. Assembly: How Is Synthetic Leather Cut and Prepared for Use?
After the plastic has been applied, the synthetic leather is cut into the desired shapes and sizes. Manufacturers often sell synthetic leather by the yard, and it can be further processed into various products such as upholstery, garments, and accessories.
During the assembly phase, manufacturers may also add additional layers or treatments to enhance the product’s properties, such as water resistance or stain repellency. This customization allows for the creation of synthetic leather products that meet specific market demands.
4. Finishing: What Final Touches Are Applied to Enhance Quality?
The finishing stage involves applying any final treatments to enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of the synthetic leather. This can include dyeing, embossing, or applying protective coatings. These processes are crucial for achieving the desired look and feel of the final product, as well as improving its durability.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Commonly Implemented?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the synthetic leather manufacturing process. B2B buyers should be aware of the various international standards and industry-specific certifications that manufacturers should adhere to.
Relevant International Standards: What Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
-
ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European Union, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards for products derived from petroleum, ensuring that synthetic leather products meet specific quality and safety requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure that products meet the required standards. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, QC personnel monitor production to identify any deviations from quality standards. This real-time inspection helps catch issues early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, a thorough inspection of the finished product is conducted. This includes checking for defects, measuring physical properties, and ensuring compliance with specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical to ensuring product reliability. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Buyers should perform regular audits of their suppliers’ facilities. This allows them to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports outlining the results of their QC inspections. This documentation can offer insights into their manufacturing practices and product consistency.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These organizations can conduct thorough evaluations and provide certification reports.
What Are the Nuances of QC for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances that may affect quality control:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements for synthetic leather products. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations to ensure compliance.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother communication and negotiation with suppliers regarding quality expectations.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping can pose risks to product quality. Buyers should work with suppliers who have robust logistics and handling processes to mitigate potential damage during transport.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Synthetic Artificial Leather Manufacturing
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for synthetic artificial leather are critical considerations for B2B buyers. By understanding the stages of production and the importance of quality control, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing synthetic leather products. Engaging with suppliers who adhere to international standards and implementing rigorous QC checks will ensure that businesses receive high-quality, reliable products that meet their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘synthetic artificial leather’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in procuring synthetic artificial leather. By following this checklist, you can ensure that you select a reliable supplier, obtain high-quality materials, and make informed purchasing decisions tailored to your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications required for your synthetic leather products, including desired properties such as durability, texture, color, and compliance with industry standards. Establishing these parameters upfront helps streamline the sourcing process and ensures you communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers.
- Considerations:
- What applications will the synthetic leather be used for (e.g., upholstery, fashion, automotive)?
- Are there specific certifications or environmental standards that the material must meet?
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in synthetic artificial leather. Look for manufacturers with a solid reputation in the industry and a track record of meeting customer needs.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
- Tips:
- Utilize trade platforms and industry directories to compile a list of candidates.
- Review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge supplier reliability.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, ensure that your selected suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO standards or environmental compliance (e.g., REACH or RoHS). This verification is critical to ensuring the quality and safety of the materials you will be purchasing.
- Key Points:
- Certifications can also indicate a commitment to sustainable practices, which may be important to your brand.
- Request documentation or proof of certifications to validate claims made by the supplier.
Step 4: Request Samples for Evaluation
Ask for product samples from shortlisted suppliers to assess the quality and characteristics of their synthetic leather. This step is essential for understanding how the material performs in real-world applications.
- What to Look For:
- Evaluate the texture, flexibility, and durability of the sample.
- Consider how well it meets your initial specifications and if it aligns with your brand’s aesthetic.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have evaluated samples, request detailed quotations from suppliers, including pricing, payment terms, and any bulk order discounts. Understanding the cost structure is vital for budgeting and financial planning.
- Considerations:
- Compare pricing across different suppliers, but also weigh the quality and service offered.
- Be clear about payment terms to avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process.
Step 6: Review Logistics and Shipping Options
Examine the logistical capabilities of your chosen suppliers, including lead times, shipping methods, and delivery reliability. Effective logistics are crucial for ensuring that your materials arrive on time and in good condition.
- Important Factors:
- Inquire about the supplier’s experience in exporting to your region, especially if you’re sourcing from overseas.
- Ensure that they can accommodate your required delivery schedule and can handle potential customs regulations.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Develop a clear communication plan that outlines how you will interact with the supplier throughout the procurement process.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
- Action Items:
- Set regular check-ins or updates to monitor order status and address any concerns.
- Designate points of contact from both sides to streamline communication and problem resolution.
By following this checklist, you can confidently navigate the sourcing process for synthetic artificial leather, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for synthetic artificial leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Synthetic Artificial Leather Production?
Understanding the cost structure of synthetic artificial leather is essential for international B2B buyers looking to source this material effectively. The primary components of the cost structure include:
-
Materials: The most significant cost factor is the raw materials used in production. Synthetic leather typically consists of a base fabric (cotton or polyester) and a plastic coating, predominantly polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The price of these materials can fluctuate based on global oil prices, as they are petroleum-based, or the availability of cotton and polyester.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the production location. Countries with lower labor costs, such as Vietnam or certain African nations, can offer competitive pricing. However, this can also impact quality, making it essential for buyers to assess the skill level and experience of the workforce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Efficient factories may have lower overhead, which can contribute to better pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom designs may require specialized tooling, which can increase initial costs. Buyers should consider whether they need unique molds or machinery for their orders and negotiate this upfront.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of synthetic leather is critical, especially for high-end applications. Investing in robust QC processes can add to costs but may save money in the long run by reducing defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs depend on the distance from the manufacturer and the chosen shipping method. International shipping can add significant costs, especially if customs duties and tariffs are involved.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a margin into their pricing to ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and the demand for synthetic leather.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence the pricing of synthetic artificial leather, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts. Buyers should evaluate their needs to determine if they can commit to higher volumes, thereby reducing per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom colors, patterns, or finishes can increase costs. Buyers should clarify specifications upfront to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials or certifications (e.g., eco-friendly options) can raise costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these features against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reputation, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of delivery can significantly affect pricing. Understanding whether the quoted price includes shipping, insurance, and duties (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for calculating the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
To optimize sourcing strategies for synthetic artificial leather, international buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures. Understanding their cost components can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider factors like maintenance, durability, and potential waste. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers, especially from Africa, South America, and the Middle East, should be aware of regional pricing differences and the implications of currency fluctuations.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to assess quality. This can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the product meets expectations.
Final Considerations
While the synthetic artificial leather market offers numerous opportunities, buyers must navigate a complex landscape of costs and pricing influences. The information provided here serves as a guide for making informed sourcing decisions, but it is important to consult with suppliers and industry experts for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information. Always approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your needs and the market dynamics at play.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing synthetic artificial leather With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Synthetic Artificial Leather
As businesses seek sustainable and innovative materials, synthetic artificial leather has become a popular choice due to its versatility and ethical production. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications or align more closely with corporate sustainability goals. This analysis compares synthetic artificial leather with two notable alternatives: natural leather and plant-based leather, highlighting key performance metrics, cost considerations, and use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Synthetic Artificial Leather | Natural Leather | Plant-Based Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Water-resistant, less durable than real leather; may feel plasticky | Highly durable, breathable, and develops a rich patina over time | Varies by type; can be durable but often less so than real leather |
| Cost | Generally lower cost; varies by quality and brand | Higher cost due to animal husbandry and processing | Mid-range cost; often competitive with high-quality synthetic options |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to source and manufacture; widely available | Requires careful sourcing and processing | Emerging market; sourcing may be limited depending on region |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean, but less resilient to wear | Requires conditioning and special care to maintain appearance | Maintenance depends on the specific material used; generally requires care |
| Best Use Case | Upholstery, fashion accessories, and items requiring waterproofing | High-end fashion, luxury goods, and durable products | Eco-conscious products, fashion items, and upholstery seeking sustainable alternatives |
What are the Pros and Cons of Natural Leather Compared to Synthetic Artificial Leather?
Natural leather offers superior durability and breathability compared to synthetic options. It develops a unique character over time, which can be appealing for luxury goods and high-end applications. However, its higher cost and the ethical concerns surrounding animal welfare can deter environmentally conscious buyers. Maintenance is another consideration, as natural leather requires regular conditioning to retain its appearance and longevity.
How Does Plant-Based Leather Stand Against Synthetic Artificial Leather?
Plant-based leather, made from materials like pineapple leaves or mushroom mycelium, presents a compelling alternative for eco-conscious brands. It is biodegradable and often produced with fewer harmful chemicals than traditional synthetic leather. However, the market for plant-based options is still developing, which may limit availability and consistency in quality. While it can be more sustainable, buyers should consider performance aspects, as some plant-based leathers may not match the durability of synthetic or natural leather.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Leather Alternative?
When selecting the right leather alternative, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific needs, including durability, cost, and environmental impact. For applications where performance and longevity are paramount, natural leather may be the best option despite its higher price. Conversely, if cost and low maintenance are critical, synthetic artificial leather remains a strong contender. For businesses focused on sustainability and innovation, exploring plant-based leather could align better with their corporate values while appealing to a growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. Ultimately, the decision should reflect both practical requirements and brand ethos to ensure a coherent and responsible product offering.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for synthetic artificial leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Synthetic Artificial Leather?
When sourcing synthetic artificial leather, understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the most critical specifications:
-
Material Composition
– Synthetic artificial leather is primarily made from two types of plastics: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and Polyurethane (PU). Each has distinct characteristics affecting durability, flexibility, and cost. PVC is generally more affordable but less breathable, while PU offers better comfort and a more leather-like appearance. Buyers should consider their end-use applications when selecting the material. -
Thickness
– The thickness of synthetic leather is measured in millimeters (mm) and impacts its durability and application. Thicker materials are typically more durable and suitable for heavy-use items like upholstery and automotive interiors, while thinner options may be used for fashion accessories. Understanding the required thickness helps buyers ensure the product meets their specific performance needs. -
Abrasion Resistance
– This property measures how well synthetic leather can withstand wear and tear. It is often tested using the Martindale test, which evaluates how many rubs the material can endure before showing signs of damage. High abrasion resistance is essential for products that will experience frequent contact, such as furniture or clothing. Buyers should prioritize this specification based on the expected use of the material. -
Water Resistance
– Synthetic leather typically offers varying degrees of water resistance, which is crucial for applications in environments exposed to moisture. While most synthetic leathers are water-resistant, the level of water repellency can differ based on the manufacturing process and coatings used. Buyers should assess their specific needs, particularly in regions with humid climates or for products like outdoor furniture. -
Colorfastness
– Colorfastness refers to how well the color of synthetic leather maintains its vibrancy when exposed to light, washing, or friction. This property is especially important for products that will be subjected to sunlight or frequent cleaning. Ensuring high colorfastness is essential for maintaining the aesthetic appeal of synthetic leather in consumer goods. -
Breathability
– Although synthetic leather generally has lower breathability compared to genuine leather, some products are designed to enhance airflow. Breathability is crucial for garments and upholstery, as it affects comfort. Buyers should consider this property, especially when selecting materials for clothing or items intended for prolonged contact with skin.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Synthetic Artificial Leather Sourcing?
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation in the procurement process. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to a company that produces parts or products that are then marketed by another company. In the context of synthetic leather, buyers may engage with OEMs to create custom products tailored to specific design requirements or branding. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, as it affects inventory levels and overall costs. Manufacturers often set MOQs to ensure cost efficiency in production, which may vary based on material type and complexity. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products. This process allows buyers to compare pricing, terms, and conditions from multiple suppliers. A well-structured RFQ can lead to better deals and more favorable terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for international buyers to navigate shipping, insurance, and liability issues effectively. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. It is a critical factor for supply chain management, affecting inventory levels and production schedules. Buyers should inquire about lead times to ensure timely delivery and meet market demand. -
Bespoke
– Bespoke refers to custom-made products tailored to specific requirements. In the synthetic leather industry, bespoke options allow buyers to create unique designs or specifications that cater to their target market, enhancing brand differentiation.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminology can empower B2B buyers to make more informed decisions when sourcing synthetic artificial leather, ultimately leading to better outcomes for their businesses.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the synthetic artificial leather Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Synthetic Artificial Leather?
The synthetic artificial leather market is witnessing significant growth, driven by various global factors. Increasing demand for sustainable and cruelty-free alternatives to genuine leather, combined with advancements in manufacturing technologies, is shaping the landscape. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The rise of e-commerce and digital platforms is facilitating direct sourcing from manufacturers, enabling buyers to access a wider range of products with competitive pricing. Additionally, the growing influence of social media is pushing brands to explore innovative designs and colors, catering to diverse consumer preferences.
Emerging trends in the sector include the introduction of eco-friendly materials, such as plant-based synthetic leathers, which appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. The market is also seeing an increase in customization options, allowing businesses to differentiate their offerings. Buyers are encouraged to leverage data analytics for trend forecasting and inventory management, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Furthermore, regional trade agreements and tariffs are impacting sourcing strategies, necessitating a keen understanding of geopolitical dynamics.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in Synthetic Artificial Leather?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor for B2B buyers in the synthetic artificial leather market. The environmental impact of conventional synthetic leather production, primarily involving petroleum-based materials, has raised concerns about pollution and waste. As a result, there is a growing emphasis on ethical sourcing practices that prioritize environmental stewardship. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide transparency regarding their supply chains and production processes.
Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and OEKO-TEX® are gaining traction, offering assurance that materials are produced sustainably and without harmful chemicals. These certifications not only enhance product appeal but also align with the values of environmentally conscious consumers, making them a crucial consideration for B2B buyers aiming to build a responsible brand image. Adopting sustainable practices can also mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance and enhance overall brand reputation in the marketplace.
What Is the Evolution of Synthetic Artificial Leather Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of synthetic artificial leather has been marked by significant milestones that are relevant to B2B buyers today. Initially developed in the early 20th century, the first notable synthetic leather, Naugahyde, emerged as a wartime alternative to genuine leather. Over the decades, the production processes have evolved, with advancements in materials such as polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) becoming prevalent.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
The 1970s saw a backlash against synthetic materials due to environmental concerns, prompting manufacturers to explore alternatives that address these issues. Recent innovations have led to the development of biodegradable and plant-based synthetic leathers, appealing to a market that increasingly values sustainability. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can inform sourcing decisions, as it highlights the importance of choosing suppliers who are not only technologically advanced but also committed to ethical and sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of synthetic artificial leather
-
How do I ensure the quality of synthetic artificial leather from suppliers?
To ensure quality, it’s crucial to establish a clear quality assurance (QA) process before initiating orders. Request samples to evaluate texture, durability, and color fidelity. Additionally, ask about the supplier’s production standards and certifications, such as ISO or other relevant industry-specific standards. Conduct factory visits or third-party inspections if possible, especially for high-volume orders, to assess the manufacturing process and equipment used. Finally, consider implementing a trial order to monitor the quality over time before committing to larger purchases. -
What are the key factors in choosing a supplier for synthetic artificial leather?
When selecting a supplier, consider factors such as reputation, experience, production capacity, and compliance with international standards. Evaluate their ability to meet your specific requirements, including customization options, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and lead times. Reviews and testimonials from other businesses can provide insights into reliability and service quality. Additionally, assess their logistical capabilities and willingness to accommodate international shipping, particularly if you’re sourcing from regions like Africa or South America. -
What customization options are available for synthetic artificial leather?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including color, texture, thickness, and pattern design. Specify your requirements upfront and discuss the feasibility with potential suppliers. Some manufacturers may provide digital samples or swatches to visualize the final product. Additionally, inquire about the possibility of producing custom blends for specific applications, such as upholstery, fashion, or automotive uses. Understanding the supplier’s capabilities will help you align your project needs with their offerings. -
What are the typical payment terms for international purchases of synthetic artificial leather?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers and regions. Common terms include a deposit (usually 30-50%) before production and the balance upon completion or prior to shipping. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect both parties, such as using letters of credit or escrow services for larger transactions. Familiarize yourself with the supplier’s preferred payment methods, whether via bank transfer, PayPal, or other means, and consider currency fluctuations if dealing internationally. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for synthetic artificial leather?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs ranging from 100 to 1,000 meters, depending on the complexity of the material and customization involved. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to see if they can accommodate smaller orders, especially for initial testing or smaller projects. Some suppliers might also offer lower MOQs for standard products or stock items. -
How does international shipping work for synthetic artificial leather?
International shipping involves several steps, including selecting a reliable freight forwarder, understanding customs regulations, and determining shipping costs. Ensure that the supplier provides appropriate shipping documentation, such as bills of lading and certificates of origin. Factor in lead times for both production and shipping when planning your order. It’s also advisable to discuss incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) with your supplier to clarify responsibilities for shipping and insurance. -
What are the environmental considerations when sourcing synthetic artificial leather?
When sourcing synthetic leather, consider the environmental impact of the materials used in production. Many synthetic leathers are made from PVC or PU, which can raise concerns about biodegradability and toxic emissions during manufacturing. Look for suppliers offering eco-friendly alternatives, such as vegetable-based synthetic leather or products certified by environmental organizations. Understanding the environmental policies of your suppliers can also enhance your brand’s sustainability profile. -
What applications are best suited for synthetic artificial leather?
Synthetic artificial leather is versatile and commonly used in various applications, including upholstery for furniture and automotive interiors, fashion items like handbags and shoes, and accessories such as watch bands and phone cases. Its water-resistant properties make it ideal for environments where durability is essential, such as in homes with children or pets. Discuss your specific application needs with suppliers to find the best product suited for your intended use.
Top 8 Synthetic Artificial Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Nevotex – Artificial & Synthetic Leather
Domain: nevotex.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Artificial & synthetic leather for public environment, furniture: chairs & sofas.
2. Sewport – Faux Leather Solutions
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as pleather, vegan leather, Naugahyde, synthetic leather, artificial leather, fake leather, ersatz leather. Composition: PVC or vegetable oils. Properties: Low breathability, low moisture-wicking, low heat retention, high stretchability, low prone to pilling/bubbling. First produced in the United States, currently produced/exported mainly by China. Recommended washing: Spo…
3. Manuel Dreesmann – Eco-Friendly Leather Goods
Domain: manuel-dreesmann.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: What is PU leather – and why you should avoid! Worldwide Free Shipping Over 100€ Manuel-dreesmann offers various products including MacBook sleeves, wallets, bags (tote bags, envelope bags, neck pouches, sealife collection, woven bags, handbags), small leather goods (wallets, glasses cases, key wallets, belts, bracelets), and device sleeves (MacBook sleeves, iPad sleeves).
4. Duletai – PVC Synthetic Leather for Bags and Luggage
Domain: duletai.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: PVC synthetic leather for bags and luggage material. Type: Artificial/Synthetic leather with Polyvinyl Chloride and polyester base fabric. Characteristics: Tough, durable, resistant to stains and unwanted particles, suitable for extreme wear and weather conditions. Specifications: Technology – Calendered PVC film laminated onto knitted, non-woven backing base fabric; Material – PVC + Polyester; Th…
5. Buffalo Jackson – Faux Leather Essentials
Domain: buffalojackson.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is made from a fabric base such as polyester, which is then treated with wax, dye, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or polyurethane to create an imitation leather finish and texture. It is designed to look like real leather but has a uniform surface and feels cold and unnaturally even. Faux leather does not last as long as real leather and does not wear out …
6. Rahui – Synthetic Vegan Leather
Domain: rahui.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, Rahui – Synthetic Vegan Leather, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. LeatherCult – Synthetic Leather Apparel
Domain: leathercult.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Synthetic leather is a substitute for real leather, commonly used in jackets, vests, trousers, and other garments. It is made of a coated base material, typically nylon, rayon, or polyester, with a layer of polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) applied. Synthetic leather is more susceptible to cracking than real leather due to its laminated construction. It emerged during World War 2, with…
8. Britannica – Artificial Leather
Domain: britannica.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Artificial leather, also known as faux leather, imitation leather, or pleather, is a synthetic material designed to mimic the appearance and texture of genuine leather. Some of the earliest substitutes for leather were invented in the 19th century, with notable developments including nitrocellulose and collodion.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for synthetic artificial leather
In the rapidly evolving landscape of synthetic artificial leather, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. As demand for eco-friendly and ethically produced materials grows, leveraging suppliers who offer innovative solutions—such as vegetable-based synthetic leather—can position businesses for success. Understanding the diverse applications of synthetic leather, from upholstery to fashion, allows buyers to align their sourcing strategies with market trends and consumer preferences.
Moreover, as major producers like China continue to dominate the market, buyers must consider factors such as quality, sustainability, and compliance with international regulations to make informed purchasing decisions. Engaging in strategic partnerships with suppliers that prioritize transparency and sustainable practices will not only enhance product offerings but also improve brand reputation across diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

Illustrative image related to synthetic artificial leather
Looking ahead, the synthetic leather market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation. B2B buyers are encouraged to stay ahead of industry trends, actively seek out sustainable sourcing options, and forge relationships with forward-thinking manufacturers. By doing so, companies can ensure they remain competitive and responsive to the evolving demands of their customers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.