Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to make a leather scabbard
In today’s competitive landscape, navigating the global market for crafting leather scabbards presents unique challenges for B2B buyers. Whether you’re sourcing materials or seeking skilled artisans, understanding the nuances of production can significantly impact your bottom line. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of making leather scabbards, covering various types, applications, and essential techniques that ensure quality and durability.
From exploring the best leather types to selecting the right wood cores, this resource equips international buyers—particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Brazil and Germany—with actionable insights. You will learn how to effectively vet suppliers, assess cost considerations, and leverage local craftsmanship to meet specific market demands.
By providing detailed instructions and expert tips, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance product offerings and streamline your supply chain. With an emphasis on quality and craftsmanship, you can position your business to cater to the growing demand for custom leather goods, ensuring that your scabbards not only meet but exceed customer expectations.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 How To Make A Leather Scabbard Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to make a leather scabbard
- Understanding how to make a leather scabbard Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of how to make a leather scabbard
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to make a leather scabbard’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to make a leather scabbard
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to make a leather scabbard
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to make a leather scabbard’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to make a leather scabbard Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to make a leather scabbard With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to make a leather scabbard
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to make a leather scabbard Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to make a leather scabbard
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to make a leather scabbard
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding how to make a leather scabbard Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood-Core Scabbard | Features a carved wood core, often made from poplar or oak | Custom sword manufacturers | Pros: Durable, traditional craftsmanship. Cons: Time-consuming to produce, requires skilled labor. |
| Slat Method Scabbard | Utilizes thin wood slats, bent to fit the blade | Artisanal leather goods | Pros: Lightweight, flexible design. Cons: May lack robustness compared to solid wood options. |
| Basic Slot Scabbard | Simple construction with a 1/4″ slot for blade insertion | Mass production for retail | Pros: Cost-effective, easier to manufacture. Cons: May not provide as snug a fit, less aesthetic appeal. |
| Custom-Fit Scabbard | Tailored to specific sword dimensions and designs | High-end sword retailers | Pros: Perfect fit, enhances the weapon’s presentation. Cons: Higher production costs, longer lead times. |
| Historical Replica | Mimics traditional scabbard styles from specific eras | Museums, reenactment groups | Pros: Unique aesthetic, appeals to collectors. Cons: May not be functional for modern use, requires specific craftsmanship. |
What Are the Characteristics of Wood-Core Scabbards?
Wood-core scabbards are a traditional choice featuring a carved wood core, typically made from poplar or oak. The wood is shaped to snugly fit the blade, providing both protection and aesthetic appeal. B2B buyers in the custom sword manufacturing sector often prefer this type for its durability and historical authenticity. However, the process is labor-intensive and requires skilled artisans, which can lead to higher production costs and longer timelines.
How Do Slat Method Scabbards Differ in Design?
The slat method involves using thin wood slats that are bent to accommodate the blade’s shape. This technique allows for a lightweight yet flexible design, making it popular among artisanal leather goods producers. B2B buyers may find this method appealing for its unique craftsmanship and reduced weight, although it may not offer the same level of durability as solid wood-core alternatives. It is essential to consider the balance between flexibility and robustness when choosing this option.
What Makes Basic Slot Scabbards a Practical Choice?
Basic slot scabbards are characterized by their straightforward design, featuring a simple 1/4″ slot for blade insertion. This type is highly suitable for mass production and is often used in retail settings. B2B buyers benefit from the cost-effectiveness and faster manufacturing times associated with this design. However, the trade-off may include a less secure fit and reduced visual appeal compared to more complex designs, making it less ideal for high-end applications.
Why Opt for Custom-Fit Scabbards?
Custom-fit scabbards are designed specifically for individual sword dimensions and styles, ensuring a perfect fit. This type is favored by high-end sword retailers and collectors who prioritize aesthetics and functionality. While these scabbards enhance the overall presentation of the weapon, they come with increased production costs and longer lead times. B2B buyers should weigh these factors against their target market’s needs when considering this option.
What Are the Benefits of Historical Replica Scabbards?
Historical replica scabbards are crafted to mimic the styles and techniques of specific eras, making them ideal for museums and reenactment groups. These scabbards offer a unique aesthetic that appeals to collectors and history enthusiasts. However, their functionality may be limited for modern use, and the craftsmanship required can be specialized and costly. B2B buyers should consider the target audience’s appreciation for historical accuracy versus practical functionality when selecting this type.
Key Industrial Applications of how to make a leather scabbard
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to make a leather scabbard | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Military & Defense | Custom scabbards for ceremonial and practical use | Enhances the aesthetic appeal and functionality of weapons | Sourcing durable, high-quality leather; compliance with military specifications |
| Craftsmanship & Artisanship | Production of bespoke leather scabbards for collectors | Increases product value and customer satisfaction through customization | Access to skilled artisans; sourcing unique leather types and tools |
| Historical Reenactment | Creating historically accurate scabbards | Attracts niche markets and enhances authenticity for reenactment events | Research on historical designs; sourcing period-appropriate materials |
| Retail & E-commerce | Selling ready-made or customizable leather scabbards | Expands product offerings and caters to diverse customer needs | Reliable supply chain for consistent quality; online marketing strategies |
| Outdoor & Sporting Goods | Scabbards for hunting or sporting knives | Provides protection and ease of transport for outdoor enthusiasts | Sourcing lightweight, weather-resistant materials; understanding target demographics |
How is ‘how to make a leather scabbard’ used in Military & Defense Applications?
In the military sector, leather scabbards are crafted for both ceremonial and operational purposes. These scabbards not only serve to protect blades but also enhance the visual appeal of weapons during parades and official ceremonies. Buyers in this sector require scabbards that meet stringent quality standards, ensuring durability and functionality in various environments. Moreover, compliance with military specifications is crucial, necessitating a reliable supply of high-quality leather and skilled craftsmanship.
What Role Does ‘how to make a leather scabbard’ Play in Craftsmanship & Artisanship?
Artisans and craftsmen utilize the techniques of making leather scabbards to produce bespoke items that appeal to collectors and enthusiasts. Customization is a significant selling point, allowing artisans to cater to specific client requests, thereby increasing the perceived value of their products. Buyers in this market often seek unique leather types and specialized tools, making it essential to establish connections with suppliers who can provide rare materials and high-quality equipment.
Why is ‘how to make a leather scabbard’ Important for Historical Reenactment?
The historical reenactment community values authenticity, and leather scabbards play a crucial role in this. Crafting historically accurate scabbards not only meets the needs of reenactors but also attracts niche markets that prioritize historical fidelity. Buyers in this sector must conduct thorough research on historical designs and ensure they source period-appropriate materials, which may involve working with specialized suppliers who understand the nuances of historical accuracy.
How Does ‘how to make a leather scabbard’ Benefit Retail & E-commerce?
In the retail sector, businesses can expand their product offerings by including ready-made or customizable leather scabbards. This diversification caters to a broader customer base, allowing retailers to meet varying preferences and needs. For success, businesses must establish a reliable supply chain that ensures consistent quality and develop effective online marketing strategies to reach their target audience effectively.
What is the Application of ‘how to make a leather scabbard’ in Outdoor & Sporting Goods?
In the outdoor and sporting goods industry, leather scabbards are essential for protecting hunting knives and other tools. They provide ease of transport and ensure the safety of both the user and the equipment. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing lightweight, weather-resistant materials that can withstand outdoor conditions while also appealing to outdoor enthusiasts who value functionality and aesthetics in their gear. Understanding the target demographics is crucial for tailoring products to meet specific needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to make a leather scabbard’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Sourcing Quality Leather for Scabbards
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, struggle to find high-quality leather that meets their specifications for scabbard production. The leather market can be inconsistent, and buyers may encounter issues with leather that lacks durability, uniformity, or proper treatment. This inconsistency can lead to increased production costs and customer dissatisfaction if the final product does not meet the expected quality standards.
The Solution: To address this sourcing challenge, B2B buyers should establish relationships with reputable leather suppliers known for their quality control processes. It’s essential to request samples from potential suppliers to assess the leather’s thickness, finish, and overall quality before committing to larger orders. Additionally, buyers can consider sourcing vegetable-tanned leather, which not only offers a traditional aesthetic but also provides durability and resistance to wear. Engaging with suppliers that have certifications for sustainable practices can also align with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, thereby enhancing marketability.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Accurate Measurements for Scabbard Construction
The Problem: In the process of making leather scabbards, precise measurements are critical. Buyers often face challenges in accurately measuring sword blades, which can lead to ill-fitting scabbards. This issue can be particularly pronounced for manufacturers who handle a variety of sword types and sizes, resulting in wasted materials and increased labor costs when adjustments or remakes are necessary.
The Solution: To mitigate measurement errors, B2B buyers should implement a standardized measurement protocol for all sword types. This includes creating a detailed template that outlines the necessary measurements for different blade styles, including length, width, and thickness. Investing in high-quality calipers and measuring tools can enhance accuracy. Additionally, incorporating a trial-and-error phase using inexpensive materials can help refine the fitting process before committing to leather. Establishing a feedback loop with skilled craftsmen can also ensure that best practices in measurement are followed, reducing the risk of costly errors.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Challenges in Leather Sewing Techniques
The Problem: Many manufacturers encounter difficulties when it comes to sewing leather scabbards. Inadequate sewing techniques can result in weak seams, leading to product failure and customer complaints. This issue is particularly relevant for B2B buyers who may not have extensive experience in leatherworking or who are training new staff in these techniques.
The Solution: To enhance sewing skills, B2B buyers should invest in training programs that focus specifically on leather sewing techniques. Utilizing resources such as online tutorials, workshops, or partnering with experienced leather craftsmen can provide valuable insights. Additionally, using the right tools—such as heavy-duty waxed thread and specialized needles—can significantly improve the quality of the seams. Implementing a quality control process where finished scabbards are tested for strength and durability before delivery can also ensure that only high-quality products reach customers. Encouraging a culture of craftsmanship and attention to detail within the production team can foster improved techniques and overall product quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to make a leather scabbard
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Leather Scabbard Production?
When selecting materials for leather scabbard production, several options are commonly considered, each with distinct properties and implications for performance and usability. The most prevalent materials include vegetable-tanned leather, chrome-tanned leather, synthetic leather, and wood for the core. Understanding these materials from a B2B perspective is crucial for international buyers looking to meet specific market needs.
How Does Vegetable-Tanned Leather Perform in Scabbard Construction?
Vegetable-tanned leather is a traditional choice for crafting leather scabbards. It is tanned using natural tannins found in plant materials, resulting in a durable and environmentally friendly product. Key properties include excellent breathability, resistance to moisture, and a natural aesthetic that ages beautifully over time.
Pros: This type of leather is highly durable and can withstand significant wear and tear, making it suitable for protective applications. Additionally, it can be dyed and finished in various ways, allowing for customization.
Cons: However, vegetable-tanned leather can be more expensive than other types and may require more complex manufacturing processes, such as careful stitching and finishing.
Impact on Application: It is particularly well-suited for applications where aesthetics and durability are paramount, such as high-end sword scabbards.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe (Germany) may prefer this material due to its eco-friendly attributes, while those in Africa and South America might consider the availability and cost of sourcing.
What Advantages Does Chrome-Tanned Leather Offer for Scabbards?
Chrome-tanned leather is another popular option, known for its soft texture and flexibility. This leather is treated with chromium salts, which allows for faster tanning processes and results in a more pliable product.
Pros: The primary advantage of chrome-tanned leather is its resistance to water and staining, making it easier to maintain. It also tends to be less expensive than vegetable-tanned leather.
Cons: However, it may not have the same level of durability or aesthetic appeal as vegetable-tanned leather and can be less environmentally friendly due to the chemicals used in the tanning process.
Impact on Application: This leather is ideal for scabbards that require frequent handling and exposure to moisture, such as those used in humid climates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and South America may find chrome-tanned leather more accessible and cost-effective, but they should be aware of compliance with environmental regulations regarding chemical use.
How Do Synthetic Leathers Compare in Scabbard Manufacturing?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), is a man-made alternative to traditional leather. It mimics the look and feel of real leather while offering unique properties.
Pros: Synthetic leather is typically more affordable, lightweight, and resistant to water and stains. Its manufacturing process can be less complex, allowing for mass production.
Cons: On the downside, synthetic leather may not provide the same level of durability or breathability as genuine leather, potentially leading to a shorter lifespan for the scabbard.
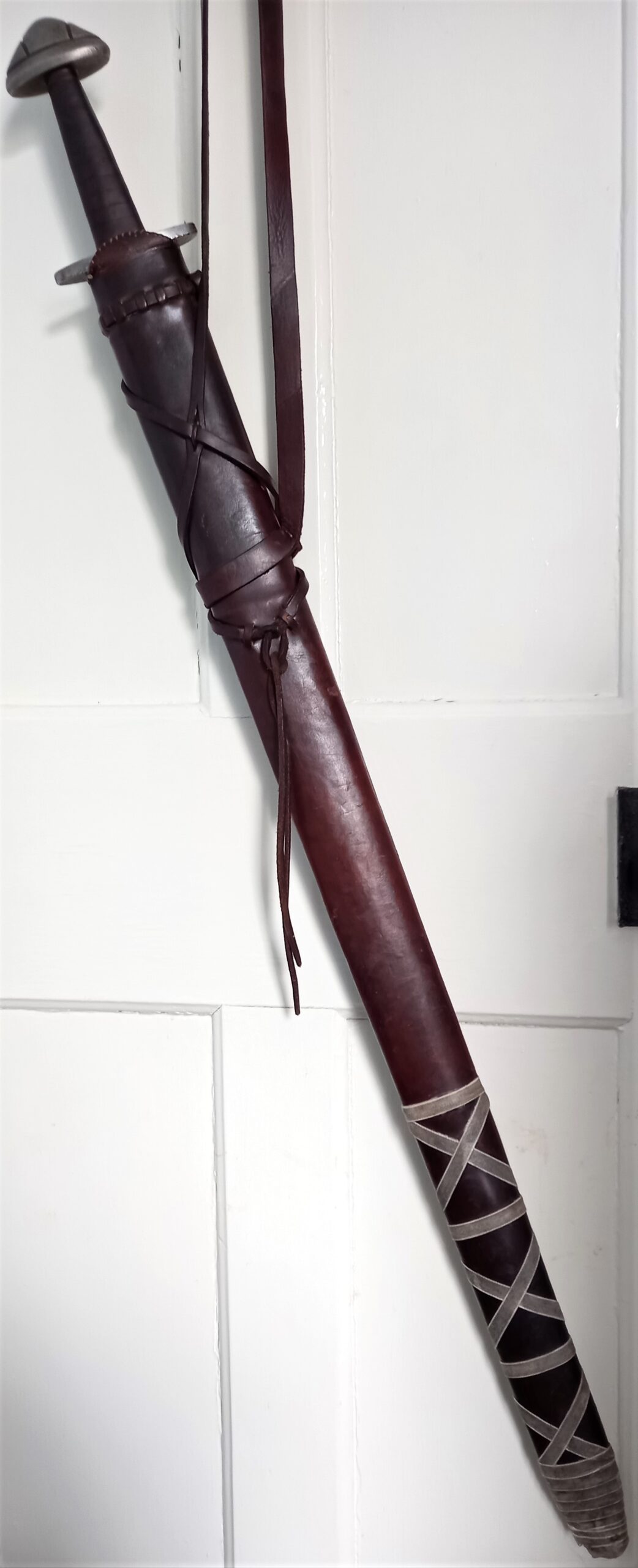

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
Impact on Application: It is suitable for budget-friendly applications where aesthetics are less critical, such as promotional items or lower-end products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa may appreciate the cost-effectiveness of synthetic leather, but they should ensure that the material meets local quality standards.
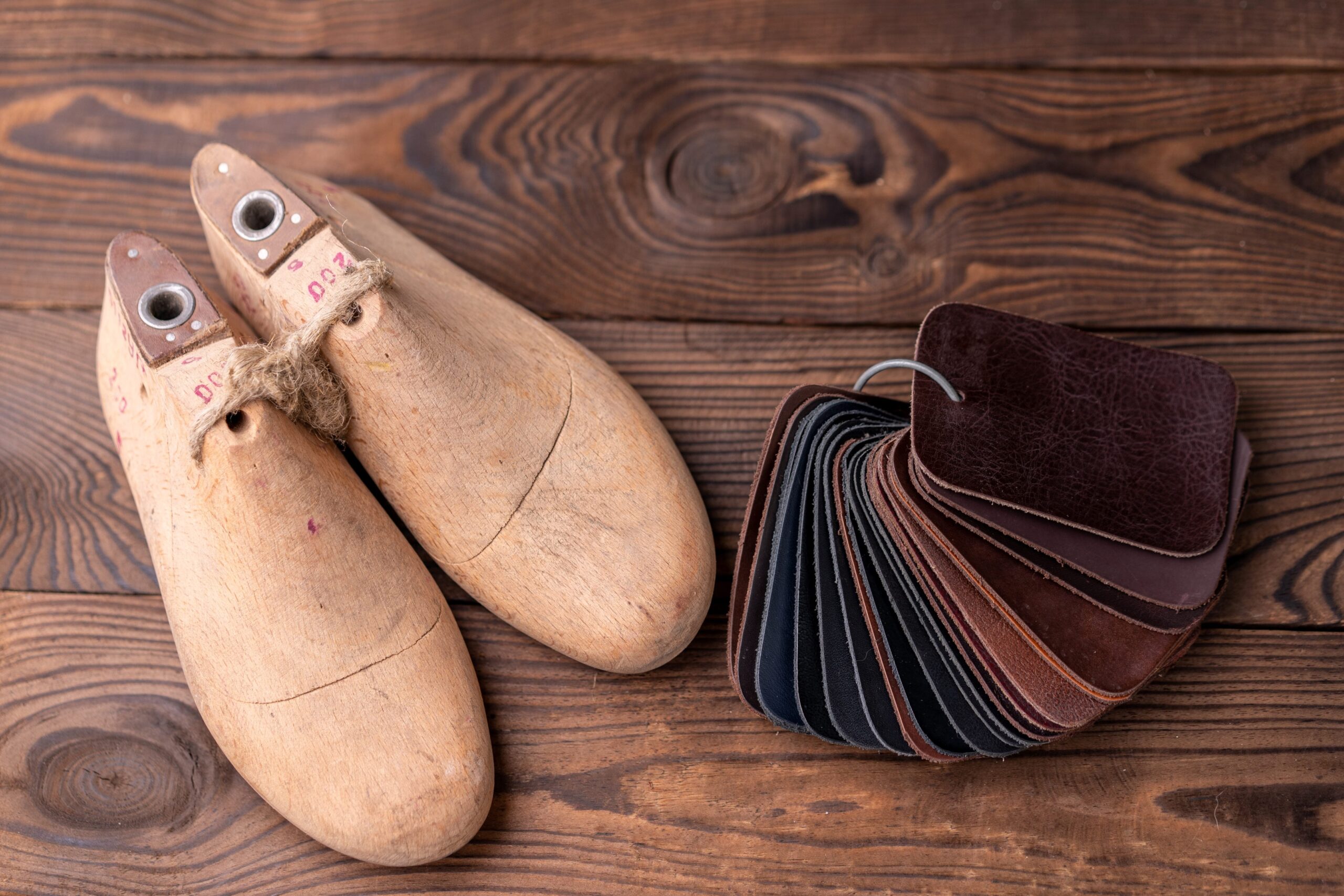
What Role Does Wood Play in Scabbard Construction?
Wood is often used as a core material in leather scabbard construction, providing structural integrity and shape. Common choices include poplar and oak, each with unique properties.
Pros: Wood cores offer excellent strength and can be shaped to fit various blade profiles. They also help maintain the scabbard’s shape over time.
Cons: However, wood can be susceptible to moisture and warping, which may compromise the scabbard’s effectiveness if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: A well-constructed wood core enhances the overall durability and functionality of the scabbard, making it suitable for high-quality applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of specific wood types in their region and the associated environmental regulations that may impact sourcing.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Leather Scabbards
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to make a leather scabbard | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetable-Tanned Leather | High-end sword scabbards | Durable and aesthetically pleasing | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Chrome-Tanned Leather | Everyday use scabbards | Water-resistant and easy to maintain | Less durable, environmentally unfriendly | Medium |
| Synthetic Leather | Budget-friendly scabbards | Affordable and lightweight | Shorter lifespan, less breathable | Low |
| Wood (Poplar/Oak) | Core for leather scabbards | Provides structural integrity | Susceptible to moisture and warping | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material options for leather scabbard production, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market expectations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to make a leather scabbard
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Leather Scabbard?
The process of manufacturing a leather scabbard involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring the final product meets quality standards and customer expectations.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
How is Material Prepared for Leather Scabbard Production?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality vegetable-tanned leather is typically preferred for its durability and aesthetic appeal. The leather must be sourced from reputable suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. Key considerations include the thickness of the leather, which usually ranges from 2 to 3 ounces, and its texture, which should be consistent without blemishes.
In addition to leather, the wood core, usually made from poplar or similar hardwood, is prepared. The wood must be cut to size and shaped to create a snug fit for the sword blade. This involves chiseling and sanding the wood to achieve the desired dimensions. It’s essential to avoid using sandpaper on the interior of the core to prevent any residue from scratching the blade.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Process of a Scabbard?
The forming process involves crafting the leather around the wood core. This is often accomplished using techniques such as wet molding, where the leather is soaked to make it pliable before wrapping it around the core. This method allows for a precise fit and helps eliminate wrinkles in the leather, ensuring a clean and professional appearance.
For the wooden core, different forming methods can be employed. The “carving method” involves chiseling the wood into shape, while the “slat method” uses thin strips of wood that are bent and glued together. Both techniques require careful measurement and craftsmanship to ensure that the final product fits the sword securely.
How is Assembly of the Leather Scabbard Conducted?
Once the leather is molded and the core is shaped, the next step is assembly. The leather is sewn around the wooden core, typically using a two-needle technique. This method provides strength and durability, essential for a product designed to protect a blade. The choice of thread is critical; heavy-duty waxed thread or artificial sinew is recommended for its strength.
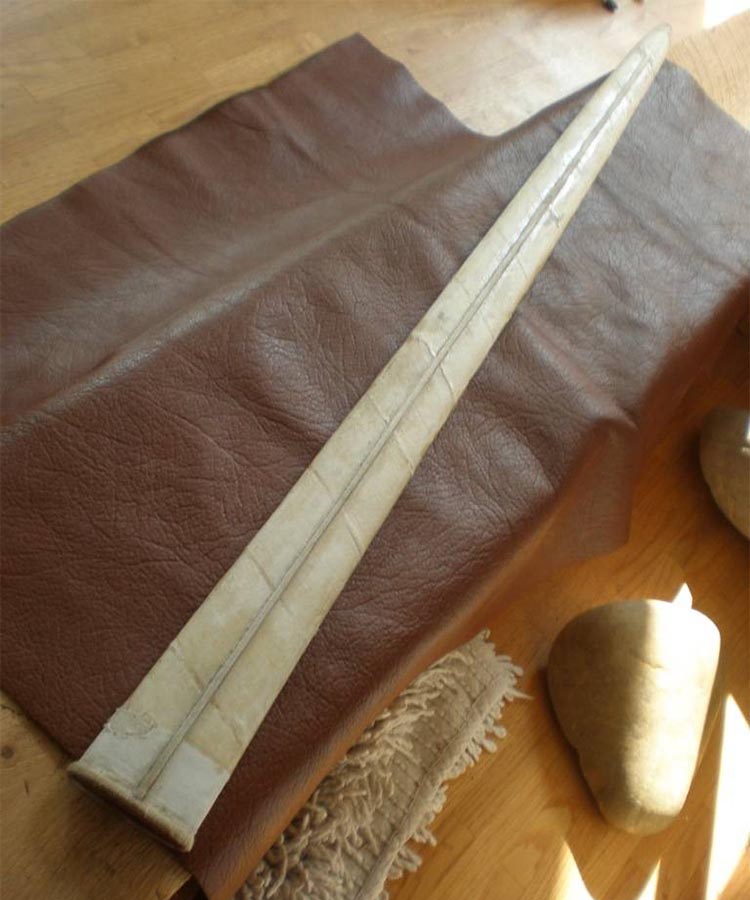

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
During assembly, it is crucial to maintain even spacing between stitches and ensure that the leather fits snugly without any gaps. Quality control checkpoints should be established at this stage to verify that the assembly meets specified tolerances.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Applied to Leather Scabbards?
The finishing stage involves several processes aimed at enhancing the scabbard’s appearance and longevity. This may include dyeing the leather to achieve the desired color, applying a sealant to protect against moisture, and polishing the leather to enhance its luster.
Finishing touches, such as adding decorative elements or functional hardware (e.g., buckles or straps), also occur during this stage. Quality assurance should be rigorous at this point to ensure that the final product is aesthetically pleasing and free of defects.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for Leather Scabbards?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for leather scabbards. Adhering to international standards, such as ISO 9001, ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE for European markets or API for specific applications may be relevant.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established in Leather Scabbard Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints should be integrated into every stage of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet the required specifications. For leather, checks should include thickness, texture, and color consistency.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This checkpoint occurs during the forming and assembly stages. Manufacturers should conduct random inspections to verify that dimensions, stitching quality, and fit are within acceptable limits.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the scabbards are packaged for shipment, a thorough inspection should be conducted. This includes checking for defects, ensuring the finish is applied correctly, and confirming that all assembly elements function as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers looking to source leather scabbards should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help buyers assess their adherence to quality standards. This includes reviewing their manufacturing processes, quality control checkpoints, and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation detailing their quality assurance processes, including results from internal inspections and any third-party certifications.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring independent inspectors to assess the quality of the products can provide an unbiased evaluation. This is particularly important for international transactions, where buyers may not have direct oversight.
-
Understand QC Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have specific requirements or standards. For example, buyers from Europe may place a higher emphasis on CE marking, while those in the Middle East might focus on local compliance certifications. It is crucial for buyers to be aware of these differences to ensure compliance and avoid potential issues.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality in Leather Scabbards?
Testing methods for leather scabbards can include:
-
Durability Testing: Assessing the strength of the leather and stitching to ensure it can withstand regular use.
-
Moisture Resistance Testing: Checking the effectiveness of sealants and finishes in protecting the leather from moisture damage.
-
Fit Testing: Ensuring that the scabbard securely holds the sword without being too loose or too tight.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing leather scabbards, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specifications and market demands.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to make a leather scabbard’
To effectively procure the necessary components and expertise for creating a leather scabbard, follow this detailed sourcing checklist. This guide will help you streamline your supplier selection and ensure you acquire high-quality materials and craftsmanship.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the leather scabbard, including dimensions, materials, and design features. This step is crucial as it ensures that you and potential suppliers are on the same page regarding what is needed.
– Materials: Specify the type of leather (e.g., vegetable-tanned, chrome-tanned) and wood (e.g., poplar, oak) you prefer.
– Design: Note any specific features such as the type of stitching or additional elements like chapes or risers.
Step 2: Identify Reliable Suppliers
Research and compile a list of suppliers known for their expertise in leatherworking and scabbard production. Selecting a reputable supplier can significantly impact the quality of your final product.
– Industry Reputation: Look for suppliers with positive reviews and a strong presence in the leather goods market.
– Experience: Prefer suppliers with a proven track record in producing leather scabbards or similar items.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region to assess their reliability.
– Quality Assurance: Inquire about their quality control processes to ensure that they maintain high standards throughout production.
– Past Work: Review examples of their previous projects, especially those similar in scope and design to your requirements.
Step 4: Request Samples
Obtain samples of both leather and wood materials to evaluate their quality firsthand. This step is essential for assessing texture, durability, and overall craftsmanship.
– Material Quality: Check for consistency in thickness and finish in leather samples, as well as the sturdiness of wood cores.
– Craftsmanship: Review the stitching and assembly quality in any sample scabbards to gauge the supplier’s skill level.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Terms
Compare pricing structures and payment terms among different suppliers to ensure you get a competitive deal without sacrificing quality.
– Cost Transparency: Ask for a detailed breakdown of costs, including materials, labor, and shipping.
– Payment Terms: Understand the payment schedule, including deposits and final payments, to avoid any financial surprises.
Step 6: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that suppliers adhere to industry standards and regulations, especially if you are sourcing from international markets. This verification helps mitigate risks associated with compliance issues.
– Sustainability Practices: Check if the supplier follows sustainable practices, particularly in sourcing leather and wood.
– Certifications: Look for certifications related to quality management (e.g., ISO) or environmental standards (e.g., LEED).
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication
Maintain open lines of communication throughout the sourcing process. Clear communication fosters a better working relationship and minimizes misunderstandings.
– Regular Updates: Set expectations for updates on production timelines and any potential challenges.
– Feedback Mechanism: Implement a system for providing feedback on samples and production stages to ensure alignment with your vision.
By following this checklist, you can effectively source the materials and expertise needed to create high-quality leather scabbards tailored to your specifications.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to make a leather scabbard Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing for manufacturing leather scabbards is critical for international B2B buyers. This analysis aims to break down the various cost components and price influencers while offering actionable insights for effective procurement.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Making a Leather Scabbard?
-
Materials: The primary materials include high-quality vegetable-tanned leather, wood (often poplar for the core), and threading materials. Leather prices can vary significantly based on thickness, quality, and sourcing location. For instance, vegetable-tanned leather can range from $5 to $15 per square foot, while wood costs are typically lower, around $2 to $5 per board foot.
-
Labor: Labor costs will depend on the complexity of the scabbard design and the skill level required for craftsmanship. Skilled artisans may charge between $20 to $50 per hour, while less experienced labor may cost less. The labor intensity of the project, including cutting, sewing, and finishing, will affect total labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs for utilities, rent, and administrative expenses associated with the production facility. Overhead can be estimated as a percentage of direct labor and material costs, typically ranging from 10% to 30%.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for equipment such as cutting machines, sewing machines, and molds can be significant, particularly for custom designs. These costs can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the equipment quality and the complexity of the scabbard design.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing a quality assurance process is essential to ensure product consistency and durability. QC expenses can add another 5% to 10% to the overall production costs, especially if international quality certifications are required.
-
Logistics: Transportation and import/export fees can impact total costs, particularly for international buyers. Shipping rates vary based on distance, mode of transport, and weight, and can be an additional 5% to 15% of the total cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin of 20% to 50% on top of their total costs, depending on market conditions, brand positioning, and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Leather Scabbard Costs?
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders can significantly reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Manufacturers often offer discounts for larger orders, making it crucial for buyers to negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific requirements (e.g., unique sizes, colors, or embellishments) can increase costs due to the need for specialized materials or additional labor. Clear communication of specifications can help mitigate unexpected costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials or certifications (such as eco-friendly or fair-trade standards) often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but their reliability can justify the higher cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is essential for managing logistics costs and responsibilities. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect total landed costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
- Conduct Market Research: Understanding market rates and supplier benchmarks can empower buyers during negotiations.
- Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront cost but the long-term value, including durability, maintenance, and potential resale value.
- Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, terms, and service.
- Be Open to Alternatives: If a supplier cannot meet your price, consider negotiating for alternative materials or modifications that can reduce costs without compromising quality.
Conclusion
While indicative prices can provide a rough framework, actual costs will vary based on numerous factors. B2B buyers must engage in thorough research and proactive negotiation to secure the best deals for leather scabbards. Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to make a leather scabbard With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives for Crafting a Scabbard
When considering how to create a scabbard for swords or other bladed tools, the traditional method of making a leather scabbard is one of several viable options. Each method comes with its unique set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential for B2B buyers to evaluate alternatives based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and suitability for specific use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How To Make A Leather Scabbard | Alternative 1: Plastic Scabbard | Alternative 2: Metal Scabbard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability; good aesthetics | Moderate durability; lightweight | Very high durability; heavy |
| Cost | Moderate to high (depending on leather quality) | Low to moderate | High due to material and fabrication costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skill in leatherworking | Easy; can be mass-produced | Moderate; requires specialized fabrication |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning | Low maintenance | Low maintenance but can corrode |
| Best Use Case | Traditional settings, custom pieces | Everyday use, budget constraints | Military, ceremonial, or high-end applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
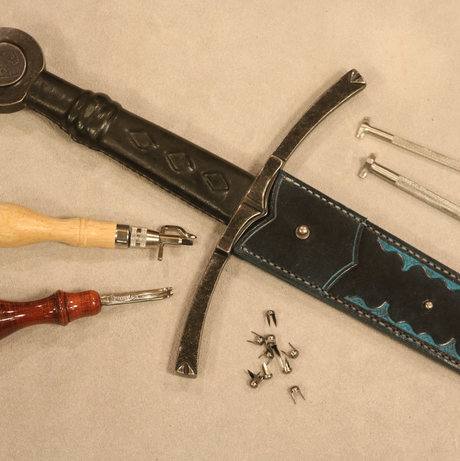
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Plastic Scabbards?
Plastic scabbards offer an affordable alternative for those looking for lightweight and easily produced options. They are often molded, which allows for quick production and a lower cost per unit. However, while plastic can provide adequate protection for the blade, it typically lacks the aesthetic appeal and durability of leather. Additionally, plastic may not offer the same level of grip or feel as leather, making it less desirable for collectors or those in traditional martial arts settings. They are best suited for budget-conscious buyers needing functional solutions for everyday use.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
How Do Metal Scabbards Compare to Leather Scabbards?
Metal scabbards provide exceptional durability and protection for blades, often seen in military or ceremonial contexts. They can withstand harsh environments and are less susceptible to wear and tear compared to leather. However, the weight of metal can be a significant drawback, making them less practical for everyday carry. Metal scabbards also require specialized fabrication, which can drive up costs and complicate the production process. They are most beneficial for users who prioritize durability and protection over weight and aesthetics.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Scabbard Solution?
Selecting the right scabbard solution requires careful consideration of specific needs and use cases. Buyers should assess the intended application—whether for daily use, ceremonial purposes, or as collectible items—along with budget constraints. Leather scabbards are ideal for those seeking a balance between aesthetics and functionality, while plastic options cater to cost-sensitive customers. Metal scabbards stand out for their durability and protective qualities, making them suitable for high-stakes environments. Ultimately, understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and brand values.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to make a leather scabbard
What Are the Essential Technical Properties for Making a Leather Scabbard?
When manufacturing leather scabbards, understanding the technical properties is crucial for ensuring quality and functionality. Here are some key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality and type of leather used, typically vegetable-tanned leather, which is favored for its durability and ability to age well.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade leather enhances the scabbard’s longevity and aesthetics, making it more appealing to buyers. It’s essential for manufacturers to source leather that meets specific quality standards to maintain consistency in their product offerings. -
Thickness Tolerance
– Definition: The acceptable variation in the thickness of the leather, usually measured in ounces (1 ounce = 1/64 inch). Common thickness for scabbards ranges from 2 to 3 ounces.
– B2B Importance: Consistent thickness ensures a snug fit around the blade and contributes to the scabbard’s overall strength. Variations outside the specified tolerance can lead to issues such as warping or insufficient protection for the blade. -
Water Resistance
– Definition: The ability of the leather and any applied finishes to resist moisture absorption.
– B2B Importance: Water resistance is critical for outdoor applications where exposure to elements is common. Buyers in regions with high humidity or rainfall should prioritize scabbards that incorporate water-resistant treatments to extend product life. -
Stitching Strength
– Definition: The tensile strength of the thread used for sewing the leather, with options like heavy-duty waxed thread or artificial sinew.
– B2B Importance: Strong stitching prevents the seams from failing under stress, ensuring the scabbard remains intact during use. Manufacturers must ensure that stitching techniques and materials are consistent with industry standards to avoid product returns. -
Finish Type
– Definition: The protective coating applied to the leather, which can include dyes, sealants, or waxes.
– B2B Importance: The finish impacts both the appearance and durability of the scabbard. A high-quality finish not only enhances visual appeal but also adds protection against wear and environmental factors, which is a significant selling point for buyers.
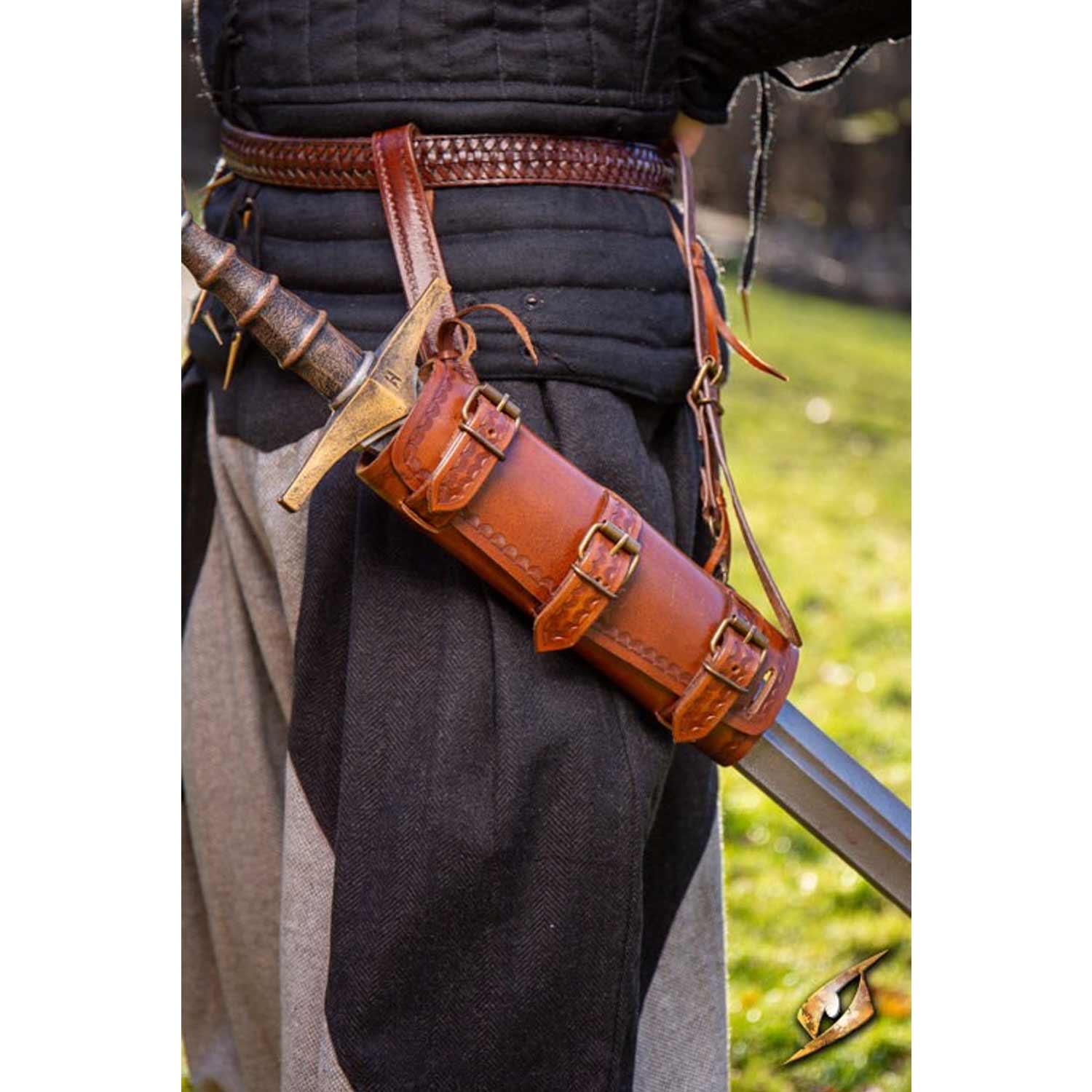
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Leather Scabbard Industry?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication between manufacturers and buyers. Here are some important terms:

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or products that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: For buyers, partnering with an OEM can streamline the production process by leveraging specialized manufacturing capabilities, ensuring high-quality components in their leather scabbards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. It helps in planning purchases, especially for businesses looking to minimize upfront costs while ensuring they meet production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document that solicits bids from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and specifications from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed decision-making and cost-effectiveness in sourcing materials for leather scabbards. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions, including shipping and delivery.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers and sellers clarify shipping responsibilities, cost allocation, and risk management, ensuring smooth international transactions and avoiding misunderstandings. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is essential for buyers to plan their production schedules effectively. It allows businesses to synchronize their inventory and sales processes, ensuring they meet customer demands without delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing leather scabbards, ultimately enhancing their product offerings and market competitiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to make a leather scabbard Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Leather Scabbard Market?
The leather scabbard market is shaped by various global drivers, including the resurgence of traditional craftsmanship, increasing demand for custom and artisanal products, and a growing appreciation for historical weaponry among collectors and reenactors. The rise of e-commerce platforms facilitates international trade, allowing buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to access high-quality leather goods. This expansion is further supported by advancements in B2B technology, such as inventory management systems and digital payment solutions, which streamline the sourcing process for international buyers.
Emerging trends such as the incorporation of advanced materials and techniques are becoming significant in the production of leather scabbards. Buyers are increasingly looking for scabbards that not only serve their functional purpose but also exhibit aesthetic appeal and durability. Additionally, trends towards customization and personalization are gaining traction, with consumers seeking bespoke products that reflect their individual preferences. As a result, suppliers who can offer flexible manufacturing solutions and quick turnaround times will be at a competitive advantage.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Leather Scabbards?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the leather scabbard sector, driven by increasing consumer awareness regarding environmental impacts and ethical sourcing practices. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, which include using vegetable-tanned leather and sourcing materials from responsible suppliers. This shift is not only beneficial for the environment but also enhances brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with labor standards and environmental regulations, which can be validated through certifications such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification. By opting for suppliers with ‘green’ credentials, businesses can mitigate risks associated with unethical practices and appeal to a growing segment of environmentally-conscious consumers. Additionally, adopting sustainable practices can lead to cost savings in the long run, as they often result in more efficient production processes and reduced waste.
What Is the Historical Context of Leather Scabbard Production?
The evolution of leather scabbard production dates back centuries, with roots in various cultures that utilized leather for protective and aesthetic purposes. Historically, scabbards were not merely functional; they were often adorned with intricate designs that reflected the craftsmanship of the era. Traditional methods of scabbard production involved creating wood cores, which were then covered with leather, a technique that remains relevant today.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
As the market has evolved, so too have the materials and techniques used in scabbard production. Modern manufacturers are now blending traditional craftsmanship with contemporary innovations, resulting in products that cater to both historical purists and modern consumers. Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers as it informs their sourcing decisions and helps them identify suppliers who honor the art of traditional leatherwork while also embracing modern production methods.
How Can B2B Buyers Navigate Market Dynamics Effectively?
For international B2B buyers looking to navigate the leather scabbard market, understanding the interplay between craftsmanship, sustainability, and market trends is crucial. By staying informed about the latest developments and aligning sourcing strategies with ethical practices, buyers can ensure they meet customer demands while also supporting responsible manufacturing. Establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers who share similar values can further enhance competitiveness in this niche market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to make a leather scabbard
1. How do I choose the right leather for making a scabbard?
Selecting the appropriate leather is crucial for durability and aesthetics. Vegetable-tanned leather, typically 2-3 ounces thick, is recommended for its firmness and ability to mold to shapes. It’s essential to consider the type of sword the scabbard will hold; heavier blades may require thicker leather for added support. Additionally, inspect leather for defects like scars or inconsistencies that could affect the final product. When sourcing, ensure your supplier can provide consistent quality and availability to meet your production needs.
2. What materials do I need to make a leather scabbard?
To craft a leather scabbard, you will need high-quality vegetable-tanned leather, a wood core (preferably poplar), leather adhesive, heavy-duty thread (like artificial sinew), and various hand tools such as chisels, needles, and sanders. The choice of wood is important for achieving the right fit and support for the sword. Additionally, consider embellishments like metal fittings or decorative stitching that could enhance the product’s appeal. Always source materials from reputable suppliers to ensure quality.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
3. How can I ensure the scabbard fits the sword perfectly?
Achieving a snug fit for the sword in the scabbard involves careful measurements and adjustments during the crafting process. Start by creating a wood core that closely matches the blade’s dimensions, allowing for a slight gap to accommodate the leather. Test the fit frequently throughout the shaping process, and adjust as necessary. If the fit is too loose, you can add thin leather strips inside the scabbard. Document your measurements for consistency in future orders, especially when working with different sword models.
4. What customization options should I consider for leather scabbards?
Customization can significantly enhance the appeal of leather scabbards for your clients. Options include different leather colors, textures, and finishes, as well as custom stitching patterns or embossed designs. You can also offer personalized fittings or hardware to match specific swords. Discuss these options with your supplier to understand their capabilities, including minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized products. Providing a range of customization can help you cater to diverse market preferences.
5. What are the typical lead times for producing leather scabbards?
Lead times for leather scabbard production can vary based on the complexity of the design, material availability, and the supplier’s workload. Generally, expect a timeframe of 4-8 weeks for standard orders. For customized orders, this may extend to 10-12 weeks. It’s advisable to establish clear communication with your supplier regarding timelines and potential delays. Always factor in additional time for quality assurance and shipping, especially when dealing with international logistics.
6. How do I vet suppliers for leather scabbard production?
Vetting suppliers is critical to ensure quality and reliability. Start by researching potential suppliers’ reputations through reviews and industry references. Request samples of their work to assess quality firsthand. Inquire about their production processes, material sourcing, and adherence to quality standards. Additionally, confirm their ability to meet your specific requirements regarding customization and order volume. Establishing a solid relationship with a trusted supplier can lead to long-term collaboration and consistent product quality.

Illustrative image related to how to make a leather scabbard
7. What payment terms are common in B2B transactions for leather goods?
Payment terms in B2B transactions for leather goods often vary by supplier and region. Common practices include a deposit (usually 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipping. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days) for established relationships. Always clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, letters of credit, or online payment platforms. Negotiating favorable terms can help maintain cash flow, especially for bulk orders.
8. What quality assurance measures should I implement for leather scabbards?
Implementing quality assurance (QA) measures is essential to maintain product standards. Begin by defining quality criteria, including leather thickness, stitching quality, and overall craftsmanship. Conduct regular inspections during the production process, checking for defects or inconsistencies. Additionally, consider establishing a final inspection protocol before shipping, ensuring that all products meet your specifications. Collaborating closely with your supplier on QA practices can help prevent issues and enhance customer satisfaction.
Top 6 How To Make A Leather Scabbard Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sword Site – Custom Leather Scabbards
Domain: sword-site.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: The project involves making a sword scabbard using a wood core covered with leather. Recommended wood types for the core are poplar (preferred) and oak (not ideal due to oils). The process includes creating a snug fit for the blade, which involves chiseling, sanding, and testing the fit. The scabbard can be made using a carving method or a simpler method that creates a 1/4″ slot for the blade. Add…
2. Weaver Leather Supply – Traditional Leather Scabbards & Sheaths
Domain: weaverleathersupply.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Traditional Leather Scabbard, Wet Forming Leather Sheath, Leather Axe Sheath, Leather Knife Sheath, Leather Tool Sheath, Side-Sewn Leather Sword Scabbard
3. SBG – Leather Scabbard Solutions
Domain: sbg-sword-forum.forums.net
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Solid leather scabbard for a blade of around 26 inches or longer. Concerns about rigidity for re-sheathing the blade. Previous experience with back-seamed sheaths for knives and daggers. Discussion on the difficulty of wet forming leather and the time required compared to wooden scabbards. Mention of using 5oz leather for stiffness and a piece measuring over 3.5mm (approximately 9oz). Alternative …
4. Sword Buyers Guide – Scabbard Materials Explained
Domain: sword-buyers-guide.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Materials used for making a scabbard: 1mm maple slats, lightly oiled goat fur (for lining), linen and rabbit skin glue (or PVA adhesive), thin leather sheet (to wrap around the wood core). Key features: flexible and shock-absorbing maple slats, protective goat fur lining, strong binding with hide glue, historical construction methods (gluing vs stitching), optional steel throat and chape, customiz…
5. Leatherworker.net – Sword Scabbard Leather Kit
Domain: leatherworker.net
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Leather for sword scabbard, core material: wood, outer material: leather, recommended tanning: vegetable tan, alternative tanning: oil tan (with caution), construction tips: use 4 layers of 10 oz veg tan, apply neatsfoot oil on interior layers, use contact cement for assembly, mold leather to sword shape, ensure proper drying temperature (130-145°F), include a welt around the sheath, and finish ed…
6. Instructables – Leather Craft Essentials
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Leather Punches, Leather Glue, Leather Needle Set, Snap Fasteners, Utility Knife or Scalpel, Candle Wax, Paper for Template, Optional Pulleys (cost about $4), Razor Blade, Contact Cement, Disk Sander or Orbital Sander, Black Marker for Dyeing Edges.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to make a leather scabbard
What Are the Key Takeaways for Making a Leather Scabbard?
In conclusion, the process of creating a leather scabbard involves careful planning, precise craftsmanship, and strategic sourcing of materials. By selecting quality leather, durable wood, and appropriate adhesives, manufacturers can ensure a product that not only meets aesthetic standards but also withstands the test of time. Leveraging local suppliers can reduce costs and enhance the supply chain, particularly for international buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Scabbard Production?
Strategic sourcing is vital for optimizing production efficiency and achieving cost-effectiveness. Establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers will not only improve material quality but also foster innovation in design and functionality. As you explore opportunities in this niche market, consider the benefits of collaborative partnerships that can elevate your offerings and expand your reach.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers?
As you look to the future, embrace the growing demand for custom leather goods, including scabbards, that reflect both craftsmanship and cultural significance. By staying informed about industry trends and consumer preferences, you can position your business to thrive. Take the next step—connect with suppliers, invest in quality materials, and refine your production processes to carve out a successful niche in the leather goods market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.