Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for seude leather
In the ever-evolving landscape of leather goods, sourcing high-quality suede leather presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers. With its luxurious texture and versatility, suede has carved out a niche in various applications, from fashion accessories to upholstery. However, navigating the global market requires a keen understanding of the different types of suede, the nuances of supplier vetting, and the cost implications associated with procurement.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of suede leather, offering insights into its various types, ideal applications, and best practices for sourcing. We will explore the qualities that distinguish Italian suede from other varieties, examine the critical factors in supplier selection, and provide actionable tips for negotiating costs effectively. By equipping buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—especially in regions like Saudi Arabia and Germany—with this knowledge, we aim to empower informed purchasing decisions that meet both quality standards and budget constraints.
As the demand for suede leather continues to grow, understanding these dynamics will not only enhance the buying process but also foster long-term relationships with suppliers. With this guide in hand, you will be well-prepared to make strategic decisions that elevate your business offerings and cater to the sophisticated tastes of your clientele.
Table Of Contents
- Top 8 Seude Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for seude leather
- Understanding seude leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of seude leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘seude leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for seude leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for seude leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘seude leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for seude leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing seude leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for seude leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the seude leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of seude leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for seude leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding seude leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Italian Suede | Luxuriously soft, finely finished with vibrant colors | High-end fashion, luxury goods | Pros: Premium quality, aesthetic appeal. Cons: Higher cost, requires careful maintenance. |
| Nubuck | Sanded outer layer, durable with a slight sheen | Footwear, upholstery, bags | Pros: Durable, water-resistant. Cons: Less soft than traditional suede, limited color options. |
| Pigmented Suede | Treated with pigments for enhanced color and durability | Casual apparel, accessories | Pros: Colorfast, easier to clean. Cons: May lack the natural feel of untreated suede. |
| Split Suede | Made from the fibrous layer of the hide, often less expensive | Budget-friendly goods, entry-level products | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Less durable, may show wear faster. |
| Exotic Suede | Sourced from unique animals (e.g., goats, lambs) | Luxury items, specialty markets | Pros: Unique textures, high-end appeal. Cons: Limited supply, higher price point. |
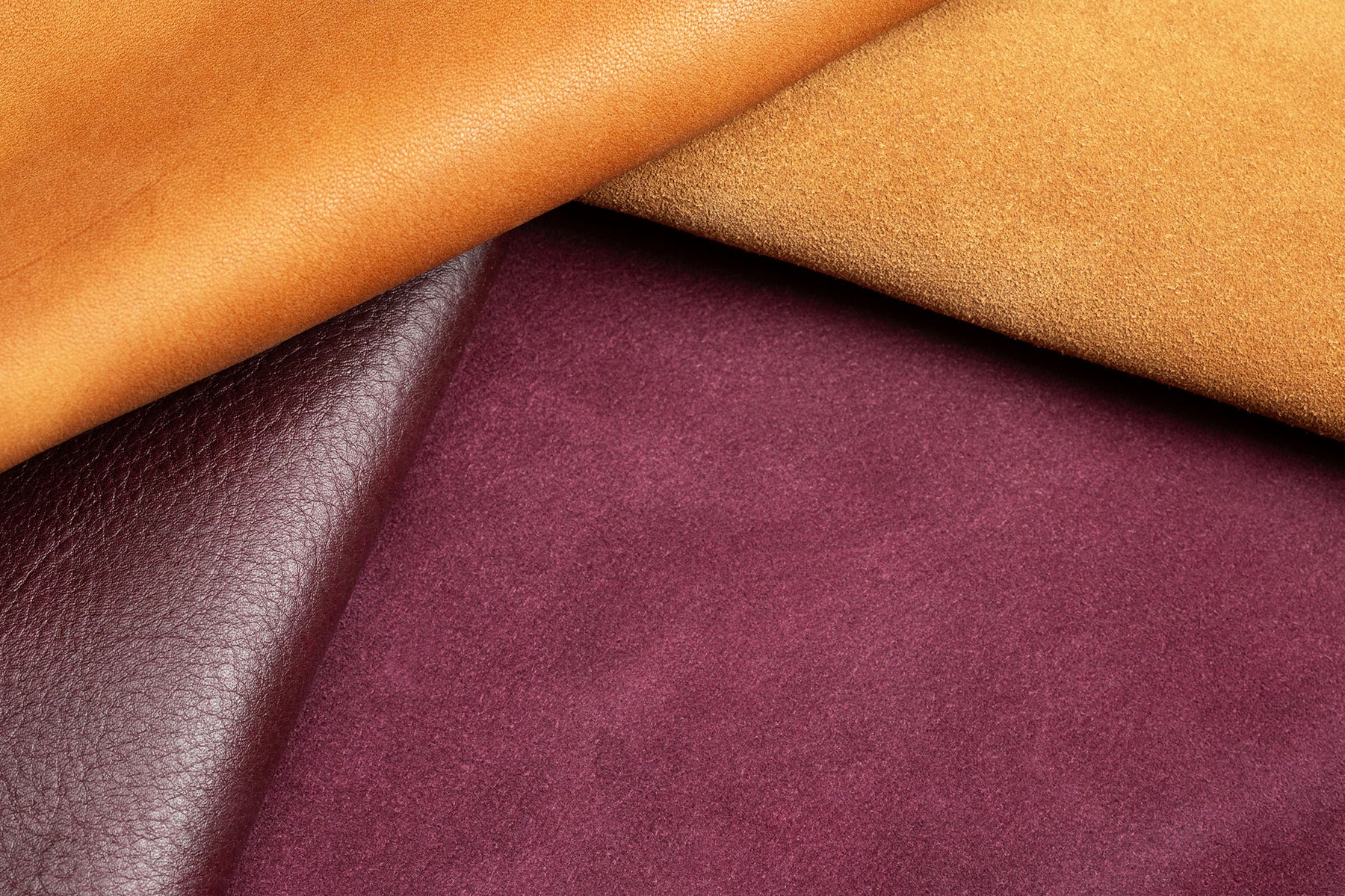
What Are the Key Characteristics of Italian Suede?
Italian suede is renowned for its luxurious softness and vibrant color options. It is meticulously tanned using premium aniline dyes, resulting in a rich texture that appeals to high-end fashion brands and luxury goods manufacturers. When considering B2B purchases, buyers should assess the quality of the tanning process and the consistency of color across batches. Italian suede is ideal for upscale handbags, shoes, and jackets, but its higher price point necessitates careful consideration of target market positioning.
How Does Nubuck Differ from Traditional Suede?
Nubuck is created from the outer layer of the hide and is sanded to create a soft, velvety surface with a slight sheen. This durability makes it a popular choice for footwear and upholstery, where resistance to wear is essential. B2B buyers should note that while nubuck offers a stylish appearance, it may not have the same softness as traditional suede. Its water-resistant properties make it suitable for various applications, but careful maintenance is still required to preserve its appearance.
What Advantages Does Pigmented Suede Offer?
Pigmented suede is treated with pigments, enhancing its color and durability. This type is commonly used in casual apparel and accessories due to its colorfastness and ease of cleaning. For B2B buyers, this can be a significant advantage, as products made from pigmented suede tend to maintain their appearance longer in high-traffic environments. However, buyers should be aware that pigmented suede may not provide the same natural feel as untreated options, which could affect consumer perception.
Why Choose Split Suede for Budget-Friendly Solutions?
Split suede is derived from the fibrous layer of the hide, making it a cost-effective alternative to traditional suede. It is versatile and widely used in budget-friendly goods, including entry-level products. For B2B buyers, split suede presents an opportunity to offer affordable options without compromising too much on quality. However, it is essential to consider its durability, as split suede may show wear faster than higher-grade alternatives, which could impact customer satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
What Makes Exotic Suede Unique in the Market?
Exotic suede, sourced from unique animals like goats and lambs, provides distinctive textures and aesthetics that appeal to luxury markets. This type is often used in high-end items, making it a coveted material for specialty markets. B2B buyers should evaluate the availability and sourcing of exotic suede, as its limited supply can lead to higher price points. The unique characteristics of exotic suede can elevate product offerings, but buyers must balance exclusivity with market demand.
Key Industrial Applications of seude leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Suede Leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Suede jackets and bags | Enhances product appeal with luxury and softness | Sourcing from reputable tanneries for quality; color and texture consistency are critical. |
| Footwear | Casual and stylish shoes | Provides comfort and a unique aesthetic | Assess durability and maintenance requirements; sourcing from regions known for craftsmanship is advantageous. |
| Upholstery & Furniture | Sofas and cushions | Adds a touch of luxury and comfort to interior design | Ensure color fastness and stain resistance; consider local climate impacts on material longevity. |
| Automotive | Interior detailing and upholstery | Elevates brand image and customer experience | Evaluate fire resistance and cleaning ease; compliance with regional automotive standards is crucial. |
| Leather Goods | Wallets and accessories | Offers a premium feel and differentiates products | Focus on sourcing sustainable and ethically produced suede; consistency in thickness and finish is essential. |
How is Suede Leather Used in the Fashion & Apparel Industry?
In the fashion and apparel industry, suede leather is predominantly used for creating jackets and bags. Its soft texture and luxurious feel make it an attractive choice for high-end fashion brands. Suede not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of products but also provides comfort, making it suitable for casual wear. For international buyers, especially those from Europe and the Middle East, sourcing quality suede from renowned tanneries ensures consistency and durability, which are essential for maintaining brand reputation.
What are the Applications of Suede Leather in Footwear?
Suede is widely utilized in the footwear sector for crafting stylish and comfortable shoes, including boots and sneakers. The material’s unique texture offers a fashionable alternative to traditional leather, appealing to consumers looking for both style and comfort. Buyers must consider the durability of suede, as well as its maintenance requirements, when sourcing. Partnering with suppliers known for their craftsmanship, particularly in regions with a strong footwear manufacturing history, can yield superior products.
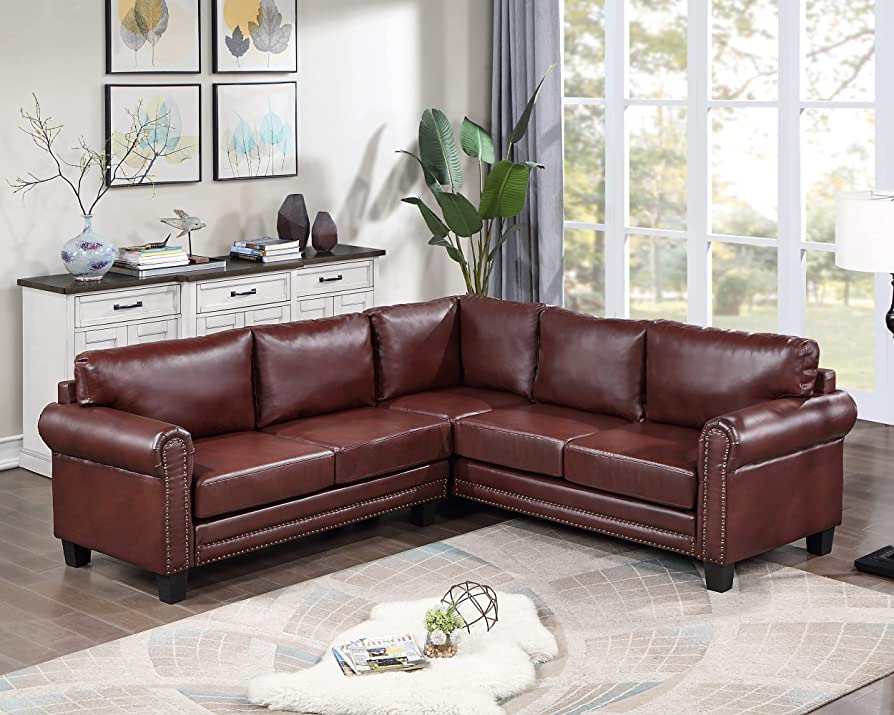
In What Ways is Suede Leather Applied in Upholstery & Furniture?
In the upholstery and furniture sector, suede leather is often used for sofas and cushions, adding a luxurious touch to living spaces. Its soft, plush surface enhances comfort, making it a popular choice for high-end interior design projects. Buyers should ensure that the suede is treated for color fastness and stain resistance, especially in climates where wear and tear can be more pronounced. Sourcing from suppliers who specialize in upholstery-grade suede can provide the necessary durability and aesthetic appeal.
How is Suede Leather Beneficial in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry employs suede leather for interior detailing and upholstery, enhancing the luxury feel of vehicles. This material not only elevates the overall brand image but also improves the customer experience through its soft touch. Buyers need to evaluate the fire resistance properties of suede and its ease of cleaning, as these factors are critical for compliance with automotive safety standards. Sourcing suede that meets these standards from reputable suppliers is vital for ensuring both quality and safety.
What Role Does Suede Leather Play in Leather Goods?
In the leather goods sector, suede is often used for crafting wallets and various accessories, providing a premium feel that distinguishes products in a competitive market. The unique texture of suede appeals to consumers seeking luxury items, making it an essential material for high-quality leather goods. Buyers should prioritize sourcing sustainable and ethically produced suede to align with growing consumer demand for responsible manufacturing practices. Consistency in thickness and finish is crucial for maintaining product quality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘seude leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the Sourcing of Quality Suede Leather
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when sourcing high-quality suede leather that meets their specific requirements. This can include issues like inconsistent quality across suppliers, variations in dye lots, or even the risk of counterfeit materials being marketed as genuine suede. For businesses in industries such as fashion, upholstery, or leather goods, the integrity of the material is paramount. If a buyer receives substandard suede, it not only affects their product quality but can also damage their brand reputation and lead to financial losses.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, buyers should prioritize establishing long-term relationships with reputable suppliers known for their quality and transparency. Conducting thorough due diligence is essential; this includes visiting tanneries if possible, requesting samples, and reviewing certifications that guarantee the authenticity of the suede. Buyers should also consider specifying their needs in detail, such as color consistency, thickness, and texture. Using a standardized quality assessment checklist during the procurement process can help ensure that the received materials match the agreed specifications. Additionally, implementing a robust quality control system upon receipt can identify potential issues early, allowing for swift resolutions.
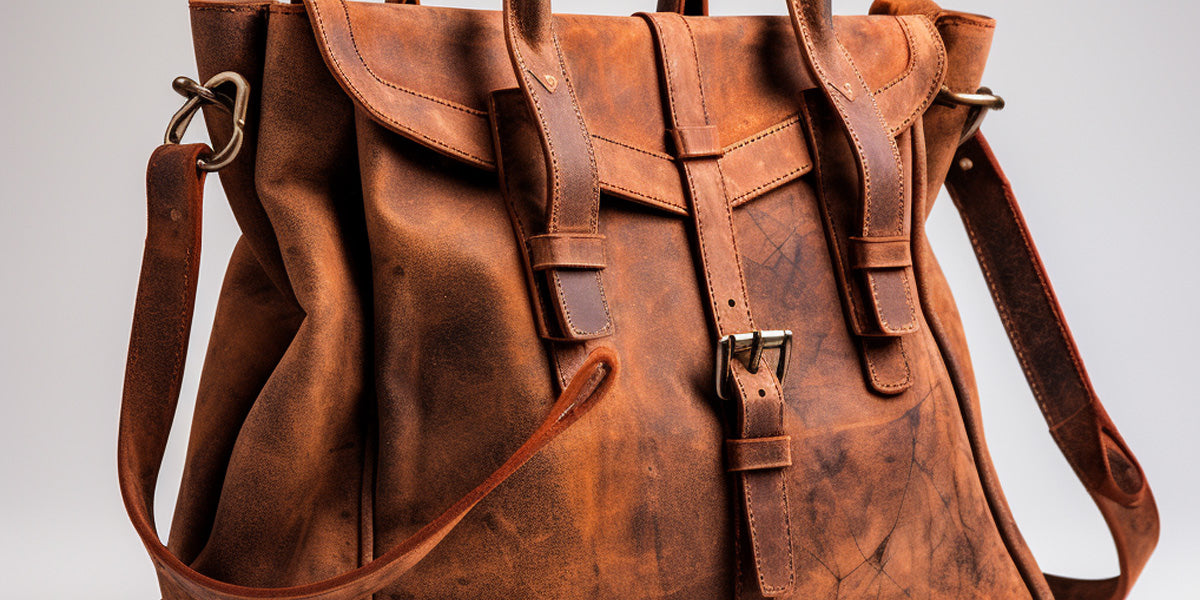
Scenario 2: Understanding the Care and Maintenance of Suede Leather Products
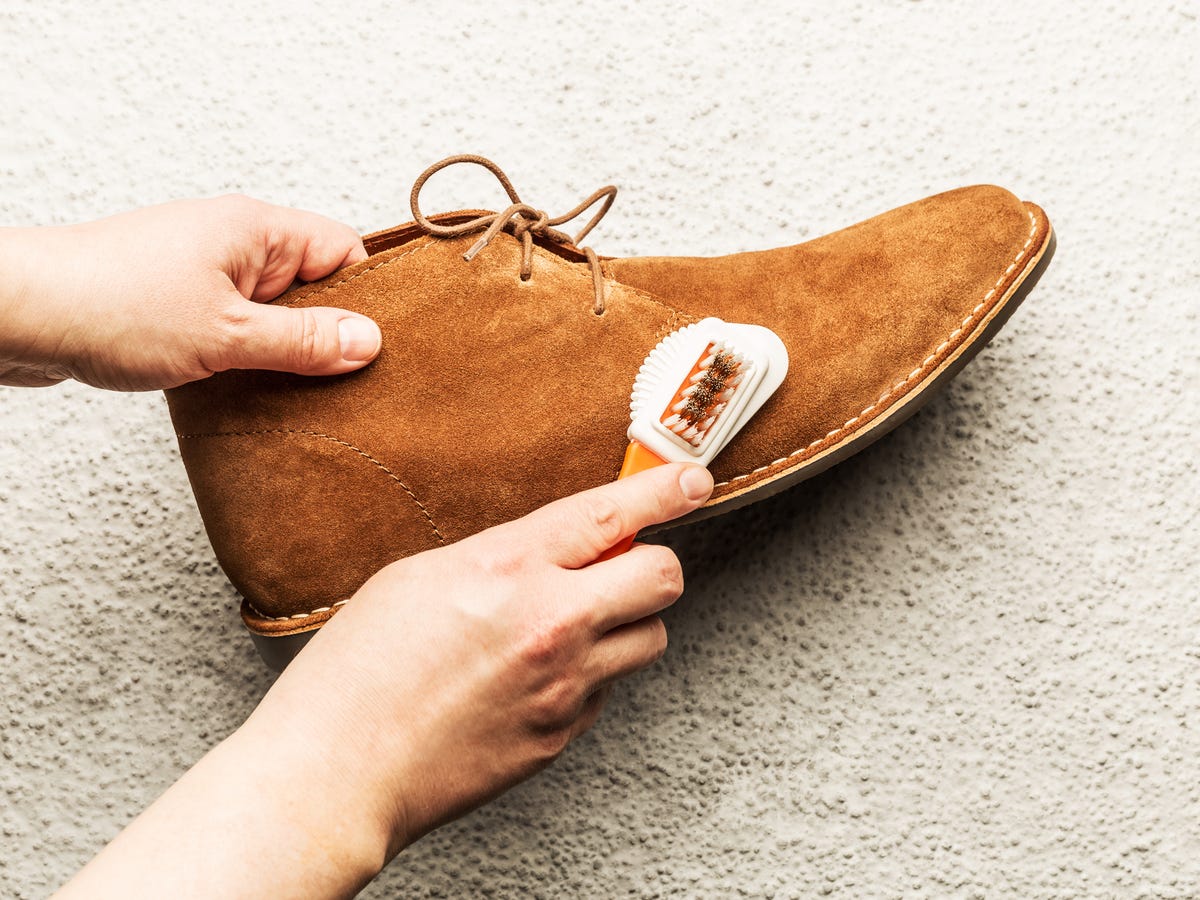
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are unaware of the specific care requirements for suede leather, leading to premature wear and damage of their products. Unlike traditional leather, suede is more susceptible to staining, water damage, and wear due to its unique structure and texture. This lack of knowledge can result in increased returns, dissatisfied customers, and a higher cost of ownership for businesses dealing in suede products, whether they be clothing, footwear, or upholstery.
The Solution: It is crucial for buyers to invest in educating their teams about the care and maintenance of suede leather. Providing comprehensive training sessions on proper cleaning techniques, such as using specialized suede brushes and cleaners, can significantly extend the life of the products. Creating user-friendly care guides for end consumers also helps maintain product integrity. In addition, offering a range of protective sprays that repel water and stains can be an attractive value-add for customers. Furthermore, buyers should explore partnerships with leather care product manufacturers to provide exclusive maintenance kits that can be bundled with suede leather products, enhancing customer satisfaction and retention.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
Scenario 3: Managing Seasonal Demand Fluctuations in Suede Leather
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the seasonal demand fluctuations typical in the fashion and upholstery industries. For instance, suede products may see a surge in popularity during certain seasons, leading to challenges in inventory management. Overestimating demand can lead to excess stock and increased holding costs, while underestimating it can result in lost sales opportunities and strained supplier relationships due to rushed orders.
The Solution: To effectively manage these fluctuations, buyers should leverage data analytics to forecast demand accurately. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and consumer behavior, companies can develop a more reliable demand forecast. Additionally, implementing a just-in-time inventory strategy can help minimize excess stock while ensuring that the necessary materials are on hand when demand spikes. Engaging in collaborative planning with suppliers can also enhance responsiveness; this includes sharing forecasts and lead times to ensure suppliers can accommodate sudden increases in orders without compromising quality. Finally, diversifying the supplier base can provide additional flexibility, allowing buyers to pivot quickly in response to changing market conditions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for seude leather
What Are the Key Materials Used in Suede Leather Production?
When selecting suede leather for various applications, understanding the materials involved is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the production of suede leather, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
1. Cowhide
Key Properties: Cowhide is known for its substantial thickness and durability, offering a temperature resistance that makes it suitable for various climates. It can withstand significant wear and tear, making it ideal for products that require longevity.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of cowhide is its durability and resistance to abrasion, which is beneficial for high-use items like bags and jackets. However, it can be heavier and more expensive than other options, which may impact manufacturing costs and end-product pricing.
Impact on Application: Cowhide’s robust nature makes it suitable for items requiring structural integrity, such as bags and upholstery. Its compatibility with various dyes allows for a wide range of color options.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, particularly in markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia, where quality assurance is critical. Buyers should also consider the sourcing of cowhide, as ethical sourcing is increasingly important in regions like Europe.
2. Lambskin
Key Properties: Lambskin is renowned for its softness and lightweight characteristics. It offers a luxurious feel and has good temperature regulation properties, making it comfortable for wear.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
Pros & Cons: The softness of lambskin is a significant advantage for fashion items, providing a premium touch. However, it is less durable than cowhide and may not withstand heavy use, which limits its application in more rugged products.
Impact on Application: Ideal for high-end fashion items like jackets and handbags, lambskin lends itself well to products where aesthetics are paramount. However, its lower durability means it may not be suitable for items exposed to harsh conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Africa and South America, where climate can vary significantly, understanding the care and maintenance of lambskin is crucial. Buyers should also be aware of potential import regulations regarding animal products.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
3. Goat Leather
Key Properties: Goat leather is known for its unique grain and flexibility. It provides a good balance of softness and durability, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility of goat leather allows for intricate designs and is often more affordable than lambskin. However, it may not have the same luxurious feel as lambskin or cowhide, which could affect marketability in high-end segments.
Impact on Application: Goat leather is versatile and can be used in both casual and formal products, making it suitable for a wide range of items from bags to upholstery. Its unique grain can enhance aesthetic appeal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Goat leather is popular in many regions, including the Middle East, where traditional craftsmanship is valued. Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards and preferences for leather quality.
4. Pigskin
Key Properties: Pigskin is characterized by its toughness and resistance to moisture. It offers good breathability and is often less expensive than other leathers.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of pigskin is its affordability and durability, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects. However, it may lack the aesthetic appeal of other leathers, which could limit its use in luxury products.
Impact on Application: Pigskin is often used in items that require resilience, such as workwear and casual bags. Its moisture resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Europe, where sustainability is a growing concern, buyers should inquire about the sourcing and processing of pigskin. Compliance with EU regulations regarding animal welfare is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Suede Leather
| Material | Typical Use Case for suede leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cowhide | Bags, upholstery | High durability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Lambskin | High-end fashion items | Luxurious feel | Less durable | High |
| Goat Leather | Versatile applications | Good balance of softness and durability | Less luxurious feel | Medium |
| Pigskin | Workwear, casual bags | Affordable and moisture-resistant | Lacks aesthetic appeal | Low |
This guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials used in suede leather production, enabling informed decisions that align with market demands and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for seude leather
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Suede Leather?
The manufacturing process of suede leather involves several essential stages, each contributing to the final product’s quality, texture, and performance. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions about sourcing suede leather.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
-
Material Preparation
The first step in suede leather manufacturing is sourcing high-quality hides, typically from cow, goat, or lamb. The hides are selected based on their thickness and grain quality. Once received, the hides undergo a thorough cleaning process to remove any impurities, including dirt, hair, and fat. This is crucial as any remaining contaminants can adversely affect the tanning process. -
Tanning
Tanning transforms raw hides into durable leather. For suede, the process often involves either chrome or vegetable tanning. Chrome tanning is quicker and provides a more consistent color, while vegetable tanning is more environmentally friendly and results in a softer feel. After tanning, the hides are rinsed and dried to eliminate excess moisture. -
Buffing and Finishing
After tanning, the hides are buffed to create the characteristic nap of suede. This involves a fine sanding technique that removes the outer layer of the hide, exposing the softer, inner flesh side. The buffing process is essential to achieve the velvety texture that distinguishes suede from other leather types. Following buffing, aniline dyes may be applied to enhance color penetration, ensuring a rich, uniform appearance. -
Cutting and Forming
Once finished, the suede hides are cut into desired shapes and sizes for various applications, such as bags, jackets, or upholstery. Precision cutting is critical to minimize waste and ensure consistency in product dimensions. Advanced cutting techniques, including laser cutting, may be employed for intricate designs. -
Assembly
The assembly process involves stitching or bonding the cut suede pieces together. High-quality thread and adhesives are utilized to ensure durability and longevity in the final product. The assembly stage is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the finished item. -
Final Finishing
The last stage of manufacturing includes quality checks, additional finishing treatments, and packaging. This may involve applying protective coatings to enhance water resistance or stain repellency. Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during shipping.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Suede Leather Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in suede leather manufacturing to ensure the final product meets both industry standards and customer expectations. Effective QA processes include adherence to international standards, systematic checkpoints, and testing methods.
-
Adherence to International Standards
Many manufacturers comply with ISO 9001 standards, which outline requirements for a quality management system. These standards emphasize consistent quality, customer satisfaction, and continual improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe, ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process, often categorized as Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
– IQC involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival, ensuring they meet specified quality criteria.
– IPQC monitors the production process, identifying any deviations or defects in real-time.
– FQC is the final inspection before products are shipped, verifying that they meet quality and performance standards. -
Common Testing Methods
To ensure suede leather meets durability and performance standards, manufacturers often conduct several tests, including:
– Abrasion Resistance Tests: Assessing the material’s resistance to wear and tear.
– Water Resistance Tests: Evaluating how well the suede repels moisture.
– Color Fastness Tests: Ensuring that dyes do not bleed or fade over time.
– Flexibility Tests: Determining how well the suede retains its shape and texture after repeated bending.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must be diligent in verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are actionable strategies to ensure suppliers meet high-quality standards.
-
Supplier Audits
Conducting on-site audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a supplier’s quality control measures. During an audit, buyers can evaluate the manufacturing processes, equipment, and adherence to safety and quality standards. -
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request quality assurance reports that detail the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing results and compliance with international standards. These reports provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections often include thorough assessments of production lines and final products before shipment. -
Reviewing Certifications and Compliance
Buyers should verify that suppliers possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE markings. Certifications demonstrate a commitment to maintaining high-quality standards and regulatory compliance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges and considerations when sourcing suede leather.
-
Understanding Regional Standards
Different regions may have varying quality standards and regulations. Buyers must familiarize themselves with local requirements to ensure that products meet both their expectations and legal standards. -
Cultural and Language Barriers
Communication can be a challenge when dealing with suppliers from different countries. Clear communication about quality expectations, specifications, and compliance requirements is essential. Buyers may consider hiring local intermediaries or consultants to facilitate negotiations. -
Logistics and Shipping Considerations
The shipping process can affect product quality, especially for sensitive materials like suede. Buyers should work with suppliers who have robust logistics practices to ensure that products are protected during transport. -
Building Long-term Relationships
Establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better quality assurance over time. Regular communication, feedback, and collaboration can enhance trust and improve product quality.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing suede leather, ensuring they receive high-quality materials that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘seude leather’
To assist international B2B buyers in sourcing suede leather effectively, this guide outlines essential steps that ensure informed decisions and successful procurement. Suede leather, known for its soft texture and aesthetic appeal, requires careful consideration during the sourcing process to meet quality and operational needs.
Illustrative image related to seude leather
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications for the suede leather you require. This includes the type of suede (e.g., goat, cow, or lamb), thickness, color, and finish. Understanding these parameters is critical as they directly influence the final product’s quality and performance. For instance, goat suede is typically more durable, making it suitable for high-wear applications.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in producing high-quality suede leather. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to identify reputable companies. Pay special attention to suppliers based in regions known for leather production, such as Italy and France, as they often adhere to higher quality standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers that provide transparency about their sourcing and tanning processes, as this impacts the quality and sustainability of the suede leather.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
- Check Certifications: Verify if the supplier holds relevant certifications such as ISO or environmental compliance, which can indicate adherence to industry standards.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Always request samples before placing a bulk order. This allows you to assess the quality, texture, and color consistency of the suede leather firsthand. Evaluate the samples against your specifications to ensure they meet your expectations.
- Conduct Tests: Consider performing physical tests, such as durability and colorfastness, to ensure the suede will perform well in its intended application.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate favorable terms and conditions. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery timelines, and minimum order quantities. Ensure that all agreements are documented to avoid misunderstandings later.
- Consider Long-Term Relationships: Building a long-term partnership can lead to better pricing and priority service, which is beneficial for future orders.
Step 6: Understand Shipping and Logistics Considerations
Evaluate the shipping and logistics options available for your order. Consider factors such as shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations, especially for international transactions. Engaging with a supplier who has experience in exporting can simplify the logistics process significantly.
- Plan for Duties and Taxes: Be aware of any import duties or taxes that may apply to your shipment, as these can affect your overall cost.
Step 7: Establish Quality Control Measures
Implement quality control measures to ensure that the suede leather received matches the agreed-upon specifications. This can include inspections upon arrival and periodic checks throughout the production process if you plan to order regularly.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
- Set Clear Expectations: Communicate your quality expectations with the supplier to minimize discrepancies and ensure a smooth procurement process.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing suede leather, ensuring that they secure high-quality materials that align with their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for seude leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Suede Leather Sourcing?
When sourcing suede leather, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw suede leather is influenced by the quality of hides used, which can vary based on the source (e.g., cowhide, lambskin) and tanning processes (e.g., chrome vs. vegetable tanning). High-quality suede, often sourced from Italy or France, commands a premium price.
-
Labor: Labor costs can differ significantly depending on the region of production. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can impact the quality of the final product. Skilled artisans are essential for producing high-quality suede, and their wages will reflect their expertise.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the facilities, equipment, and utilities required to produce suede leather. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs, impacting the overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for tools and machinery can be substantial. This is particularly relevant for custom orders where specific tooling is required. The amortization of these costs is typically factored into the pricing of the finished goods.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that the suede meets required specifications incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes are essential, especially for buyers in markets with strict quality standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are a critical factor in the overall cost structure. Shipping suede leather internationally can involve significant freight charges, customs duties, and insurance, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on their market position, competition, and the perceived value of their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Suede Leather Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of suede leather, making it crucial for buyers to consider them when sourcing.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often yield better pricing per unit due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customization, such as specific colors, textures, or finishes, can increase costs. Suppliers may charge a premium for bespoke solutions, especially when additional tooling is required.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The type of suede and any relevant quality certifications can influence pricing. Buyers should ensure that the materials meet their quality standards, as this can impact their brand reputation.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can also affect prices. Established suppliers may charge higher prices but can offer better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international shipping. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and customs clearance, which can affect the overall cost of sourcing suede leather.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Suede Leather?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency.
-
Negotiation: Build strong relationships with suppliers and negotiate terms that reflect your purchasing volume and loyalty. Having a clear understanding of market prices can strengthen your position.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, quality control, and potential waste. Evaluate suppliers based on their ability to minimize these costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional price differences. For example, sourcing from a supplier in Europe may involve higher initial costs but may provide better quality and longer-lasting products, ultimately reducing replacement costs.
-
Understand Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends, including fluctuations in hide prices and material availability. This knowledge can assist in timing purchases effectively.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Please note that prices for suede leather can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers are encouraged to request quotes and conduct thorough market research to obtain the most accurate pricing information tailored to their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing seude leather With Other Solutions
When considering suede leather for various applications, it’s essential to understand the alternatives available in the market. Each option presents unique attributes that can align with specific business needs, making it crucial for international B2B buyers to weigh these options carefully.
| Comparison Aspect | Suede Leather | Synthetic Leather | Nubuck Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Soft, textured, and comfortable | Durable, water-resistant | Similar to suede, but more durable |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower | Higher than suede |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling | Easy to cut and sew | Similar to suede, may need special care |
| Maintenance | Needs regular care, prone to stains | Easy to clean, low maintenance | Requires careful maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Casual wear, fashion items | Everyday use, cost-effective products | Upscale fashion, rugged items |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Synthetic Leather as an Alternative to Suede?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers a range of advantages, particularly in terms of cost and maintenance. It is generally less expensive than suede, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to minimize expenses. Additionally, synthetic leather is water-resistant and easier to clean, which can be a significant benefit in high-traffic applications. However, it lacks the luxurious feel and breathability of suede, making it less suitable for high-end fashion items or where comfort is a priority.
How Does Nubuck Leather Compare to Suede Leather?
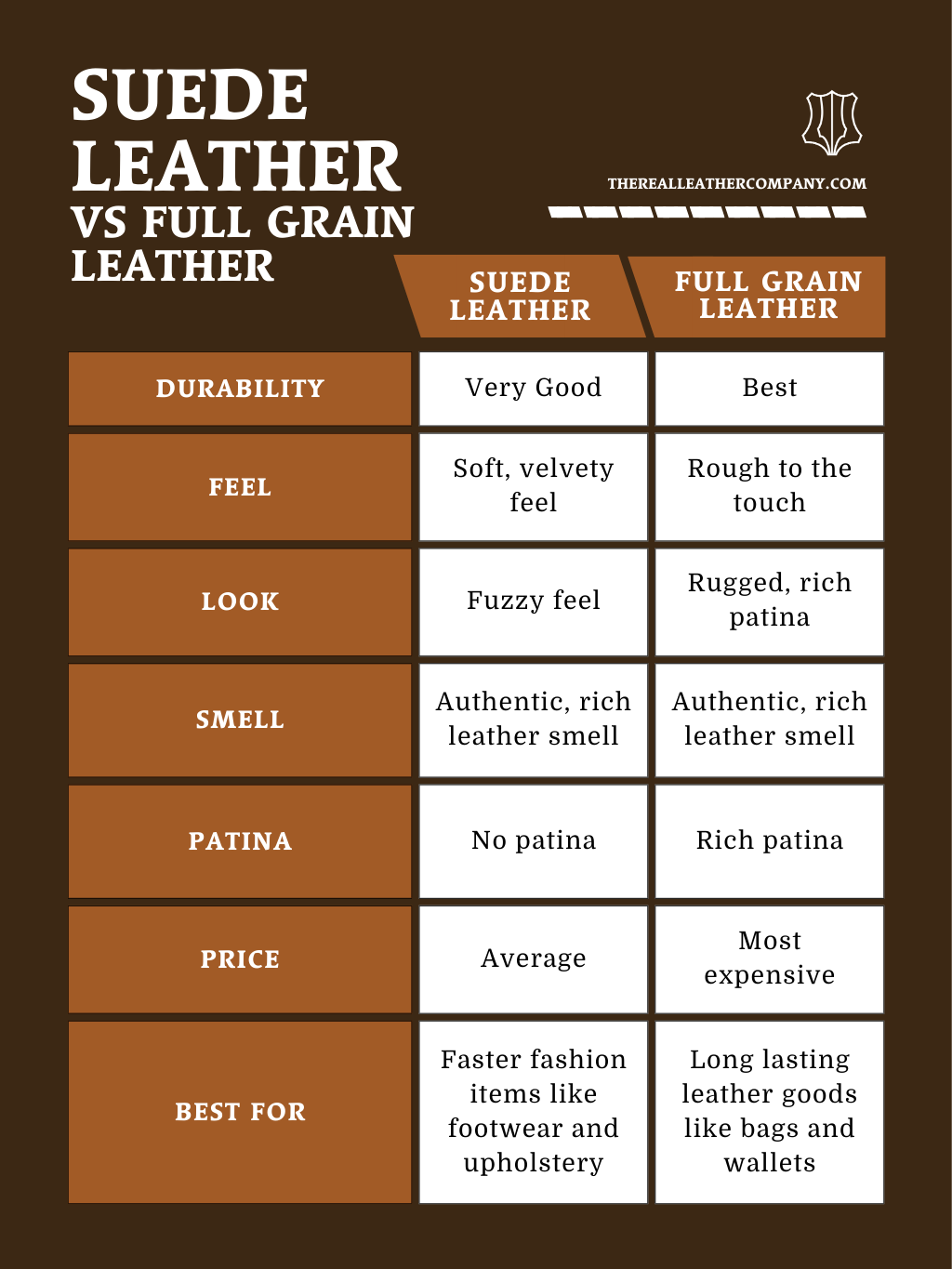
Nubuck leather, made from the outer side of the hide and sanded to create a soft texture, is often compared to suede due to its similar aesthetic. Nubuck is generally more durable and resistant to wear than suede, making it ideal for products that require longevity, such as rugged footwear or outerwear. However, nubuck tends to be more expensive due to its premium quality and the extensive processing it undergoes. It also requires careful maintenance to prevent staining and damage, which may not be ideal for all business applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Leather Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the appropriate leather solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific needs and the intended application of the material. For high-end fashion items, suede or nubuck may be preferable due to their luxurious feel and aesthetic appeal. Conversely, for products requiring durability and lower cost, synthetic leather presents a viable alternative. Additionally, considering factors such as maintenance requirements, ease of implementation, and the target market can further refine the decision-making process. Ultimately, understanding the unique characteristics of each material will empower buyers to make informed choices that align with their business goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for seude leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Suede Leather?
Suede leather, prized for its unique texture and aesthetic appeal, has several critical technical properties that B2B buyers should understand when sourcing this material.
-
Material Grade: Suede is typically classified by its source animal (e.g., cowhide, lambskin, or goatskin) and the tanning process used. Higher-grade suede, often sourced from lambskin, is softer and more luxurious, making it suitable for premium products. In contrast, lower grades may be more durable but less aesthetically pleasing. Understanding material grades helps businesses ensure they meet their quality standards and target market preferences.
-
Thickness (Tolerance): The thickness of suede can vary significantly, usually ranging from 0.8 to 1.2 mm. This specification affects not only the feel and drape of the leather but also its intended application. For instance, thicker suede is often used in upholstery, while thinner suede is preferred for clothing and accessories. Knowing the acceptable tolerance levels is crucial for manufacturers to achieve the desired end product characteristics.
-
Finish Type: Suede can be finished in various ways, including buffing and sanding to enhance its softness and appearance. The finish impacts both the visual appeal and the durability of the leather. B2B buyers should specify the desired finish when placing orders to ensure the final product meets their design requirements.
-
Color Fastness: This property refers to the leather’s ability to retain its color when exposed to light, washing, or abrasion. Suede dyed with high-quality aniline dyes generally shows better color fastness. This specification is vital for products subjected to heavy use or outdoor conditions, as it ensures longevity and satisfaction for end consumers.
-
Water Resistance: While suede is not inherently water-resistant, treatments can enhance its ability to repel moisture. Understanding the level of water resistance required for specific applications—such as footwear or outdoor gear—is critical for ensuring product longevity and performance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Suede Leather Transactions?
Navigating the suede leather supply chain requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Here are several key terms relevant to B2B buyers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce components or products that are used in another company’s end products. For suede leather, OEMs may create finished goods like bags or jackets, incorporating suede sourced from various suppliers.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels and cash flow effectively. Suppliers often set MOQs to ensure production efficiency and profitability.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs when sourcing suede leather to ensure they receive competitive offers and detailed specifications from multiple suppliers.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for B2B transactions involving suede leather to avoid misunderstandings regarding shipping costs and liabilities.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the time required from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the suede leather industry, lead times can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location and production capacity. B2B buyers should always clarify lead times to ensure timely delivery aligned with their project timelines.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms enables B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, fostering successful partnerships in the suede leather industry.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the seude leather Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Suede Leather Sector?
The suede leather market is experiencing a dynamic evolution influenced by several global drivers. Increasing demand for luxury and fashion products, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, has fueled growth. International buyers are increasingly looking for high-quality suede, often sourced from renowned tanneries in Italy and France, which are recognized for their craftsmanship. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms has enabled buyers from Africa and South America to access a wider range of suede products, facilitating cross-border trade.
Emerging B2B technologies are reshaping sourcing strategies, with digital tools enhancing transparency and efficiency in the supply chain. Technologies such as blockchain are being adopted to track the provenance of suede, ensuring quality and authenticity. Furthermore, online marketplaces are allowing buyers to connect directly with manufacturers, reducing intermediaries and costs.
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in sourcing decisions, with buyers increasingly favoring suppliers that employ eco-friendly tanning processes and materials. The trend towards customization and personalization in leather goods is also gaining traction, as B2B buyers seek unique offerings that cater to specific market demands. This shift is particularly notable in the fashion and luxury sectors, where brand differentiation is paramount.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Suede Leather Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are pivotal in the suede leather sector, reflecting a growing awareness of environmental impacts among international buyers. The tanning process traditionally involves harmful chemicals, leading to significant environmental concerns. However, many suppliers are now adopting ‘green’ certifications and eco-friendly practices, such as vegetable tanning, which utilizes natural substances and minimizes harmful emissions.
Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical practices, ensuring fair labor conditions and responsible sourcing. Certifications like the Leather Working Group (LWG) and Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) are gaining traction as indicators of sustainable practices. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, a demographic that is expanding rapidly across regions.
The emphasis on sustainability extends to product design, with many businesses exploring innovative materials that mimic suede but have a lower environmental footprint. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers looking to align their product offerings with consumer values and regulatory expectations related to sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context of Suede Leather’s Development in B2B Markets?
The history of suede leather dates back to the 19th century, with its origins rooted in the desire for softer, more textured leather. Initially used for gloves and footwear, suede became associated with luxury and craftsmanship, particularly in Europe. The development of more refined tanning processes allowed for broader applications in fashion and upholstery, leading to its current status as a sought-after material.
As B2B markets evolved, the demand for suede expanded beyond traditional uses to include a variety of products such as bags, jackets, and home furnishings. This diversification has prompted international buyers to explore suede’s unique properties, which combine style with comfort. Today, suede stands as a testament to the blend of heritage and modernity, appealing to a wide range of markets globally.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of seude leather
1. How do I select the right suede leather supplier for my business?
Choosing the right supplier involves several key steps. First, conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a solid reputation in the leather industry. Look for reviews and testimonials from other businesses. Ensure the supplier complies with international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Request samples to assess the quality of their suede leather. Additionally, consider their production capacity, lead times, and ability to handle customization requests. Establishing clear communication about your needs will help ensure a successful partnership.
2. What are the most important quality indicators for suede leather?
When evaluating suede leather quality, consider factors such as softness, durability, and color consistency. High-quality suede should feel soft and supple with a uniform texture. Check for any blemishes or inconsistencies in the nap, which may indicate inferior processing. Additionally, inquire about the tanning methods used; vegetable tanning is generally preferred for its eco-friendliness and ability to retain the leather’s natural characteristics. Lastly, ask for certifications that confirm the leather meets international quality standards.
3. What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for suede leather?
Minimum order quantities for suede leather can vary significantly between suppliers, often ranging from 50 to 500 square feet, depending on the type and quality of the leather. Smaller businesses may face higher MOQs, while larger companies might negotiate lower rates. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly and discuss potential flexibility on MOQs with suppliers. Some manufacturers may allow for sample orders or smaller initial purchases to establish a working relationship.
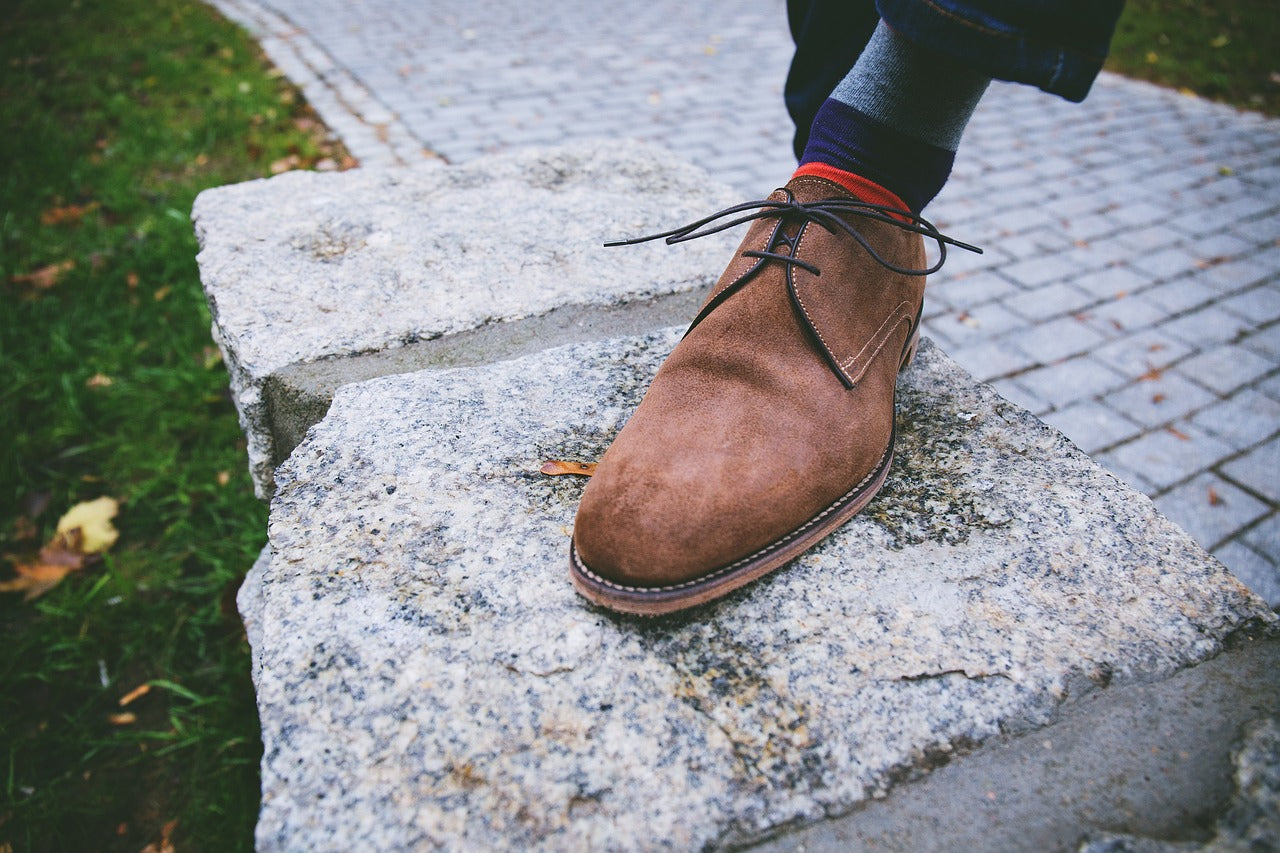

Illustrative image related to seude leather
4. How can I customize suede leather for my products?
Customization options for suede leather often include color, thickness, and finish. Many suppliers offer a range of colors and can dye the leather to match your specifications. You can also request specific textures or treatments to enhance durability or water resistance. It’s advisable to provide detailed design specifications and collaborate closely with the supplier throughout the process. Requesting samples of customized suede before finalizing the order can help ensure the final product meets your expectations.
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing suede leather internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include advance payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers require a deposit (typically 30-50%) before processing orders, especially for custom requests. It’s vital to clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow needs. Additionally, consider the implications of currency exchange rates and transaction fees when negotiating terms with international suppliers.
6. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing suede leather?
Logistics for importing suede leather involve several considerations, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on your urgency. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance, such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Be prepared for potential tariffs or duties specific to leather imports in your country. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can help streamline the logistics process.
7. How do I ensure the suede leather I receive meets my quality expectations?
To ensure that the suede leather meets your quality expectations, establish clear quality assurance protocols with your supplier. Request detailed product specifications and discuss acceptable quality standards before placing an order. Conduct inspections at various stages of production, if possible, or arrange for third-party inspections. Once the leather arrives, perform your quality checks, including examining color, texture, and any defects. Having a clear return policy in place can also help mitigate risks associated with quality discrepancies.
8. What are the environmental considerations when sourcing suede leather?
When sourcing suede leather, it’s crucial to consider the environmental impact of the tanning and production processes. Look for suppliers that use eco-friendly tanning methods, such as vegetable tanning, which minimizes harmful chemical use. Inquire about the source of the hides and whether they comply with sustainable practices. Supporting suppliers that prioritize environmental responsibility not only aligns with ethical business practices but can also enhance your brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.

Illustrative image related to seude leather
Top 8 Seude Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Leather Hide Store – Premium Suede Leather
Domain: leatherhidestore.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Suede leather offered in a variety of colors and sizes. Tanned with premium aniline dyes that penetrate through the entire leather. Each piece is finished through a fine sanding process for an even surface and velvety touch. Suede is single-sided with only the top side fully buffed and polished. Ideal for applications like shoes, handbags, luggage, and furniture. Recommended care includes using a …
2. Buffalo Jackson – Suede vs Leather
Domain: buffalojackson.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Suede vs Leather: Key Differences and Qualities
1. Texture:
– Suede: Soft, textured surface with a noticeable nap (fuzzy texture).
– Leather: Smoother texture from the outer side of the hide.
2. Appearance:
– Suede: Matte finish, no shine.
– Leather: Smooth, polished surface with a sheen or glossy appearance.
3. Hand Feel:
– Suede: Soft and fuzzy hand feel due to the nap.
…
3. RM Leather Supply – Premium Leather Goods
Domain: rmleathersupply.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: This company, RM Leather Supply – Premium Leather Goods, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Noble Shoe – Suede Leather Collection
Domain: thenobleshoe.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Suede Leather: A Durable, Easy To Wear, Stylish Leather. Misconceptions about suede include difficulty in maintenance and poor durability compared to smooth calf. High-quality suede can be easier to maintain and more durable. Key features include: 1. Stylish, Elegant & Contemporary – Suede shoes are casual yet stylish, reflecting confidence and effort in appearance. 2. Easy To Maintain & Clean – R…
5. Tandy Leather – Suede Leather Products
Domain: tandyleather.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Tandy Leather – Suede Leather Products, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Manuel Dreesmann – Fiona Tote Bag
Domain: manuel-dreesmann.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Suede Leather – A Complete Guide! Worldwide Free Shipping Over 100€ Manuel-dreesmann New Fiona bag Tote Bag With Zipper The Fiona Bag The perfect shoulder bag Tote bag with zipper Carry your belongings safely Bags Bags Tote Bags Shoulder Bags Crossbody Bags Handbags Clutches Pouches & Belt Bags Backpacks The Croissant Bag Discover our bestseller The Saka Bag Woven Craftsmanship Small Leather Goods…
7. Billy Tannery – Durable Leather Solutions
Domain: billytannery.co.uk
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: This company, Billy Tannery – Durable Leather Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. MasterClass – Suede Leather
Domain: masterclass.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Suede is a high-quality form of leather made from the underside of animal hides, characterized by a soft smooth surface. Commonly made from lambskin, it can also be produced from goats, pigs, calves, and deer. Suede is softer, thinner, and not as strong as full-grain leather. It is popular for fashion items such as shoes, accessories, and jackets. Types of suede include sheepskin suede (softest), …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for seude leather
In the realm of suede leather sourcing, strategic procurement is essential for international buyers looking to leverage this luxurious material across diverse applications. Suede, with its unique texture and aesthetic appeal, is ideal for products ranging from casual bags to sophisticated upholstery. The key takeaway for B2B buyers is to prioritize quality and supplier reliability, ensuring that the suede meets industry standards while aligning with the desired end-product characteristics.
Understanding the nuances between suede and traditional leather can inform better purchasing decisions. For instance, while suede offers softness and a casual vibe, it may require more careful maintenance. Buyers should also explore partnerships with reputable tanneries that provide sustainably sourced materials, which not only enhances product value but also caters to the growing consumer demand for ethically produced goods.
Looking ahead, the global market for suede leather is poised for growth, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As trends evolve towards personalized and unique offerings, B2B buyers should seize the opportunity to innovate within their product lines. Engage with suppliers today to capitalize on the expanding potential of suede leather, ensuring your business remains at the forefront of this dynamic industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.