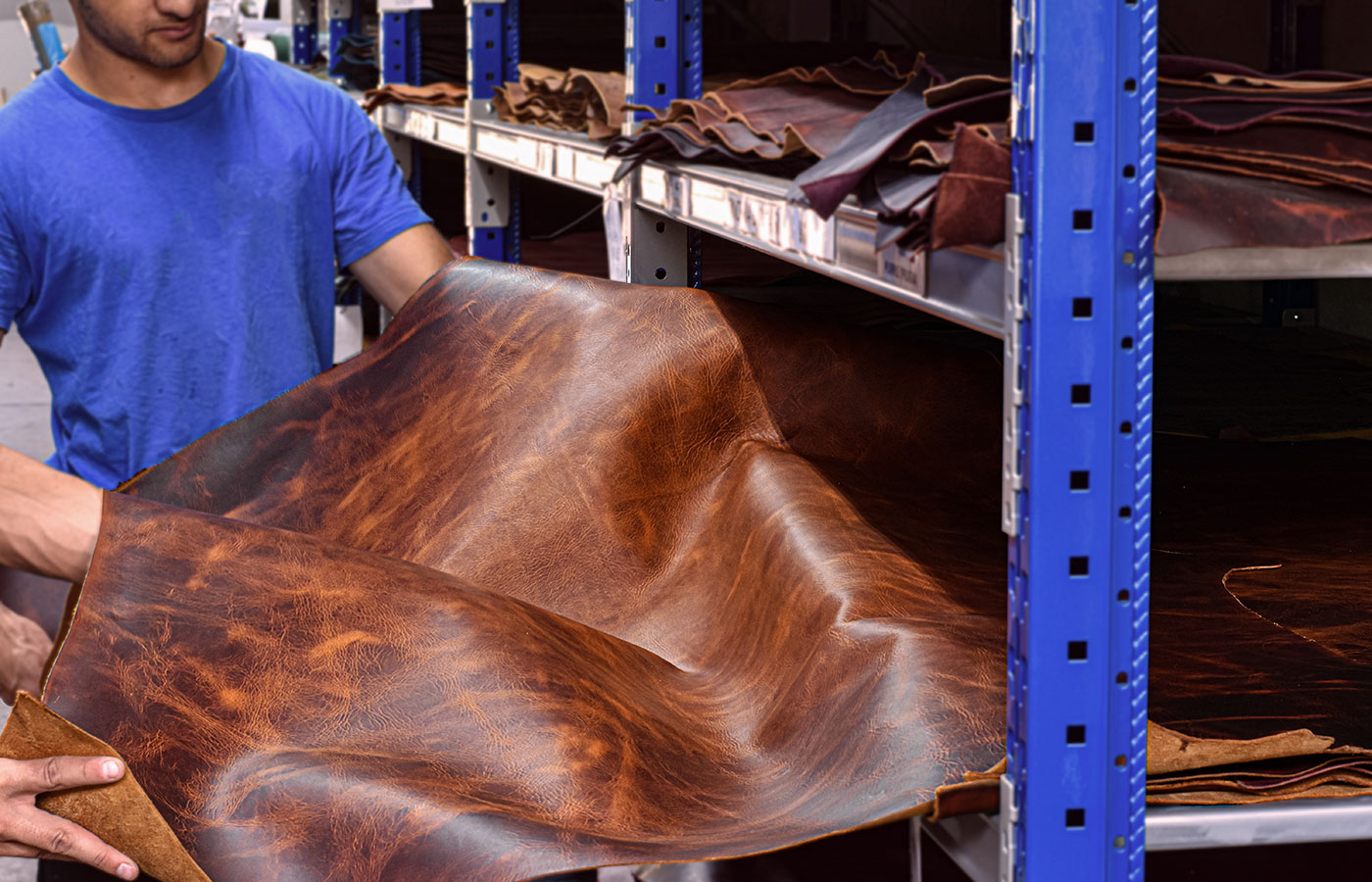
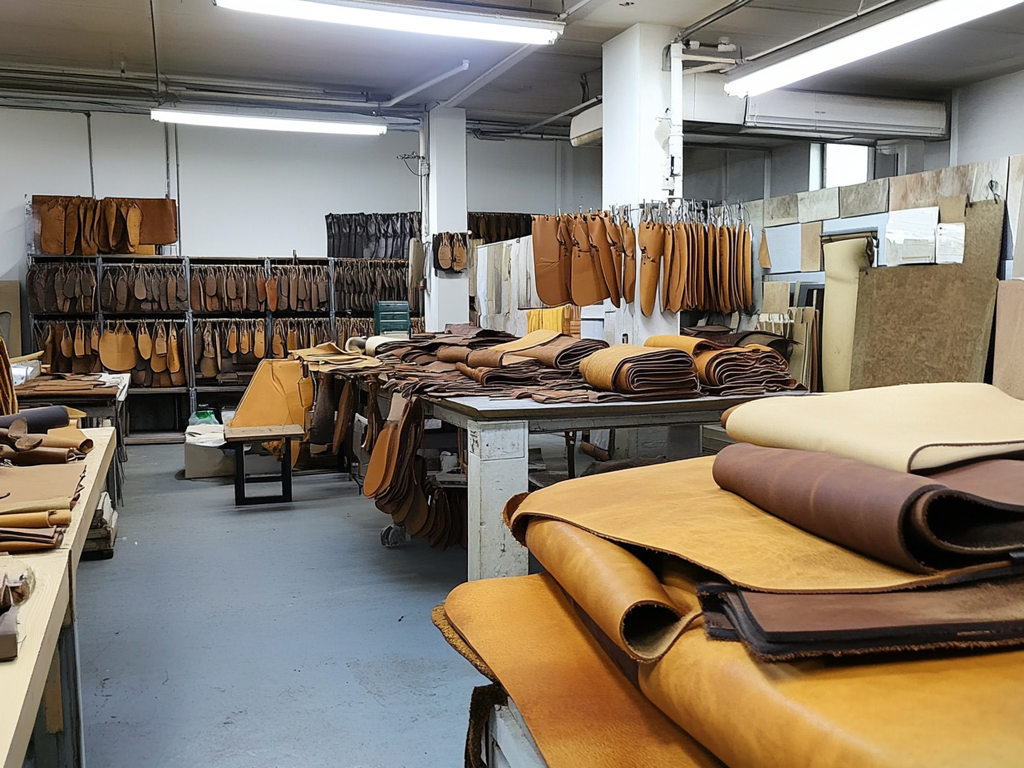
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for the leather factory
In the dynamic realm of global trade, sourcing high-quality leather products can present a formidable challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you are seeking durable leather goods for fashion, automotive, or industrial applications, navigating the complexities of supplier selection, quality assurance, and cost management is essential. This guide aims to illuminate the intricacies of the leather factory landscape, providing valuable insights into various types of leather, their applications, and critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
As the leather industry evolves, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—especially countries like Germany and Brazil—face unique hurdles, including fluctuating market prices, ethical sourcing concerns, and varying quality standards. This comprehensive resource not only outlines the essential characteristics of different leather types but also delves into effective strategies for establishing partnerships with trustworthy suppliers.
By understanding the nuances of the leather market, buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their business goals, ensuring they acquire the best products at competitive prices. From cost analysis to logistical considerations, this guide empowers you to navigate the global leather market confidently, ultimately enhancing your procurement strategy and driving business success.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 The Leather Factory Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for the leather factory
- Understanding the leather factory Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of the leather factory
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘the leather factory’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for the leather factory
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for the leather factory
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘the leather factory’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for the leather factory Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing the leather factory With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for the leather factory
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the the leather factory Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of the leather factory
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for the leather factory
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding the leather factory Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tannery | Processes raw hides into leather using various methods, such as vegetable or chrome tanning. | Supply to fashion brands, upholstery, automotive, and accessories. | Pros: High customization, quality control. Cons: Longer lead times, potential for higher costs. |
| Leather Goods Manufacturer | Produces finished leather products, including garments, bags, and accessories. | Direct sales to retailers, wholesalers, and custom orders. | Pros: Wide product range, ready-to-sell items. Cons: Less flexibility in customization, potential for inventory issues. |
| Leather Component Supplier | Provides specific leather components like straps, buckles, and patches. | Supply chain support for manufacturers of leather goods. | Pros: Specialized products, lower volume requirements. Cons: Limited product range, dependency on larger manufacturers. |
| Upcycling Leather Factory | Utilizes recycled leather materials to create new products, promoting sustainability. | Eco-friendly fashion brands, artisan markets. | Pros: Sustainable practices, unique product offerings. Cons: Variable quality, limited supply of materials. |
| Leather Finishing Plant | Focuses on the finishing processes, including dyeing, embossing, and coating. | Supply to manufacturers requiring specific finishes for leather goods. | Pros: Specialized finishing options, enhanced product aesthetics. Cons: Limited to finishing services, may require coordination with other suppliers. |
What are the characteristics of a Tannery and its B2B relevance?
Tanneries are essential in the leather supply chain, transforming raw hides into usable leather through various tanning processes. They can employ methods like vegetable tanning, which is more environmentally friendly, or chrome tanning, which is faster and produces softer leather. B2B buyers should consider the quality of the tanning process, as it directly affects the leather’s durability and appearance. When sourcing from a tannery, buyers need to assess lead times and potential costs, especially if they require customized leather solutions.
How does a Leather Goods Manufacturer operate within the B2B landscape?
Leather goods manufacturers take tanned leather and produce finished products, including jackets, bags, and accessories. These manufacturers typically cater to retailers and wholesalers, providing ready-to-sell items that meet specific market demands. Buyers should evaluate the manufacturer’s production capacity, quality control processes, and ability to accommodate custom orders. While these manufacturers offer a diverse product range, they may have less flexibility for customization compared to tanneries, leading to potential inventory challenges.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
What should buyers know about Leather Component Suppliers?
Leather component suppliers focus on providing specific parts made from leather, such as straps, buckles, and patches. They play a critical role in the supply chain for larger manufacturers of leather goods, allowing for more efficient production processes. Buyers looking for components should consider the supplier’s ability to meet volume requirements and the quality of materials used. While these suppliers offer specialized products, they may have a limited range of offerings compared to full manufacturers, which can affect overall project scope.
What makes Upcycling Leather Factories a sustainable choice for buyers?
Upcycling leather factories focus on repurposing recycled leather materials to create new products, aligning with the growing trend towards sustainability in fashion. These factories often produce unique items that appeal to eco-conscious consumers and brands. B2B buyers interested in sustainable practices should assess the quality of upcycled materials, as variability can occur. While these factories offer distinct product offerings, the supply of recycled materials may be inconsistent, impacting production capabilities.
How do Leather Finishing Plants contribute to the leather industry?
Leather finishing plants specialize in the final stages of leather production, including dyeing, embossing, and applying protective coatings. They provide essential services to manufacturers who require specific finishes to enhance the aesthetic appeal of their products. Buyers should consider the finishing plant’s expertise in various techniques and the quality of their output. While these plants offer specialized services, they may be limited to finishing, necessitating coordination with other suppliers for complete product development.
Key Industrial Applications of the leather factory
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of the leather factory | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion and Apparel | Production of high-quality leather garments | Enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty | Quality of leather, sustainability practices, and lead times |
| Automotive | Manufacturing leather interiors for vehicles | Increased luxury appeal and customer satisfaction | Compliance with automotive standards and material durability |
| Furniture | Creation of leather upholstery for furniture | Improved aesthetic value and durability | Sourcing from reputable suppliers and design customization options |
| Sporting Goods | Development of leather equipment (e.g., gloves, bags) | Performance enhancement and brand differentiation | Material performance specifications and safety standards |
| Leather Goods and Accessories | Crafting leather bags, wallets, and belts | Versatile product offerings and market competitiveness | Sourcing unique designs and customizations for target markets |
How is ‘the leather factory’ utilized in the fashion and apparel industry?
The leather factory plays a crucial role in the fashion and apparel industry by producing high-quality leather garments, such as jackets and coats. These products not only enhance a brand’s reputation but also foster customer loyalty due to their perceived value and durability. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and South America, sourcing leather from factories that prioritize sustainable practices and have a consistent supply chain is vital. This ensures that the products meet both ethical standards and consumer expectations.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
What applications does the leather factory have in the automotive sector?
In the automotive industry, leather factories are integral to manufacturing premium leather interiors for vehicles, including seats, dashboards, and steering wheels. This application significantly boosts the luxury appeal of vehicles and enhances customer satisfaction, as leather interiors are often associated with comfort and style. Buyers from the Middle East and Africa should consider compliance with automotive standards and the durability of leather materials to ensure longevity and performance in various climates.
How does the leather factory contribute to the furniture industry?
Leather factories provide high-quality upholstery materials for furniture, which enhances the aesthetic value and durability of products. This application is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in Europe who are focused on quality craftsmanship and stylish design. When sourcing leather for furniture, it is essential to partner with factories that offer customization options and have a reputation for using sustainable materials, which can influence consumer purchasing decisions.
In what ways does the leather factory serve the sporting goods sector?
The leather factory is vital for the sporting goods sector, producing leather equipment such as gloves, bags, and protective gear. These products benefit from the natural durability and comfort of leather, enhancing performance and providing a competitive edge in the market. B2B buyers in regions like Africa and Brazil should focus on sourcing leather that meets specific performance standards and safety regulations to ensure their products are both reliable and marketable.
What role does the leather factory play in the leather goods and accessories market?
In the leather goods and accessories market, factories are responsible for crafting a variety of products, including bags, wallets, and belts. This versatility allows businesses to cater to diverse consumer preferences and market demands. For international buyers, particularly in Europe, it is crucial to source unique designs and customization options that align with local trends, ensuring that the products stand out in a competitive landscape.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘the leather factory’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing High-Quality Leather on a Budget
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing high-quality leather while adhering to strict budget constraints. This challenge is particularly pronounced for businesses in regions like Africa and South America, where economic fluctuations can impact purchasing power. Buyers may find themselves facing limited options that compromise quality for price, leading to dissatisfaction with the final product and potential brand damage.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should consider establishing direct relationships with reputable leather suppliers who offer bulk purchasing options. Engaging in long-term partnerships can lead to negotiated discounts and access to exclusive product lines. It’s essential to conduct thorough research on suppliers, verifying their quality standards and ethical practices. Utilizing online platforms, trade shows, and industry networks can help buyers discover reliable sources. Additionally, consider diversifying leather types based on project needs; for example, opting for chrome-tanned leather for cost-sensitive items while reserving premium cowhide for high-end products. This approach ensures a balanced inventory that caters to different market segments without sacrificing quality.
Scenario 2: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Global supply chain disruptions can significantly impact the leather industry, causing delays in production and delivery. B2B buyers often face challenges in maintaining consistent inventory levels, which can lead to lost sales opportunities and strained customer relationships. This is particularly critical for businesses operating in fast-paced markets like Europe, where consumer demand can shift rapidly.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, B2B buyers should adopt a proactive inventory management strategy. This includes diversifying suppliers across different geographical locations to reduce dependency on a single source. Implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system can also help maintain optimal stock levels while minimizing holding costs. Additionally, buyers should invest in supply chain visibility tools that allow for real-time tracking of shipments and inventory levels. Regular communication with suppliers about potential disruptions can also facilitate timely adjustments to orders. By being prepared and adaptable, businesses can maintain operational continuity and customer satisfaction even during challenging times.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Quality Standards
The Problem: Navigating the complexities of quality standards and regulations in the leather industry can be daunting for B2B buyers. Many buyers may not be fully aware of the specific compliance requirements in their respective markets, leading to potential legal issues and product recalls. This is especially relevant in regions with stringent environmental and labor regulations, such as Europe.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize education on relevant quality standards and compliance requirements within their target markets. Engaging with industry associations and participating in workshops can provide valuable insights into best practices and regulatory updates. It’s also advisable to develop a comprehensive checklist of compliance criteria that must be met by suppliers. Regular audits of suppliers can help ensure adherence to these standards, fostering a culture of quality assurance. Furthermore, buyers should consider collaborating with third-party testing organizations to validate the quality of leather products before finalizing large orders. By proactively addressing compliance issues, businesses can enhance their reputation and build trust with their customers, ultimately leading to increased sales and loyalty.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for the leather factory
What are the Key Properties of Common Leather Materials for B2B Buyers?
When selecting materials for leather manufacturing, understanding the properties of each type is crucial for ensuring product performance and meeting market demands. Here, we analyze four common materials used in leather factories: cowhide, lambskin, suede, and synthetic leather.
Cowhide Leather: The Durable Choice
Cowhide leather is renowned for its durability and strength, making it a popular choice for a variety of leather products, including jackets and upholstery. It typically boasts a temperature resistance of up to 80°C and is relatively resistant to wear and tear. The primary advantage of cowhide is its longevity, which makes it suitable for high-use applications. However, it can be heavier and more expensive than other leathers, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
From an international perspective, cowhide leather must comply with various standards, such as ASTM for testing leather properties. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East often prefer cowhide for its robustness, while those in Africa and South America may seek more cost-effective alternatives.
Lambskin Leather: The Soft and Luxurious Option
Lambskin leather is known for its softness and luxurious feel, making it ideal for high-end fashion items. It offers a temperature resistance similar to cowhide but is less durable, which can be a drawback for products that require heavy use. The lightweight nature of lambskin allows for comfortable wear, but its susceptibility to scratches and stains means it may not be suitable for all applications.
For B2B buyers, particularly in Europe, lambskin is often associated with luxury brands. Compliance with environmental standards, such as those set by the European Union, is also essential, especially for buyers concerned with sustainability.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Suede Leather: The Versatile and Textured Choice
Suede leather, derived from the underside of animal hides, offers a unique texture that is both appealing and functional. It is lightweight and breathable, making it suitable for a variety of applications, from footwear to fashion accessories. However, suede is less resistant to water and stains, which can limit its use in certain environments.
International buyers should be aware of the specific care requirements for suede, as it may not perform well in humid or wet conditions. Compliance with local regulations regarding animal welfare and tanning processes is also critical, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
Synthetic Leather: The Cost-Effective Alternative
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane or PVC, provides a cost-effective alternative to traditional leather. It is highly resistant to moisture and easy to clean, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive and furniture upholstery. However, synthetic leather may lack the breathability and durability of natural leather, which can affect its long-term performance.
For B2B buyers, particularly from South America and Africa, synthetic leather can offer a more affordable solution without compromising on style. However, compliance with environmental regulations is increasingly important, as buyers seek sustainable and eco-friendly options.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Summary Table of Material Selection for Leather Factories
| Material | Typical Use Case for the leather factory | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cowhide Leather | Jackets, upholstery | High durability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Lambskin Leather | High-end fashion items | Soft and luxurious feel | Less durable, prone to scratches | Medium |
| Suede Leather | Footwear, fashion accessories | Unique texture and lightweight | Less water-resistant, requires care | Medium |
| Synthetic Leather | Automotive, furniture upholstery | Cost-effective and easy to clean | Less durable than natural leather | Low |
This guide serves as a strategic resource for international B2B buyers, helping them navigate the complexities of material selection in the leather industry. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs and market expectations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for the leather factory
What Are the Key Stages in Leather Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing process of leather goods involves several critical stages, each designed to transform raw materials into finished products that meet the needs of B2B buyers. Understanding these stages can help international buyers evaluate the capabilities of potential suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: Sourcing and Treatment
The first stage begins with sourcing high-quality hides, typically from cattle, sheep, or goats. The choice of material significantly impacts the final product’s quality and durability. After procurement, the hides undergo a preparation process that includes:

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
- Curing: This step prevents decomposition and prepares the hides for tanning. Salting is a common method, where the hides are covered with salt to draw out moisture.
- Soaking: Hides are soaked in water to remove salt and dirt, followed by a liming process to loosen hair and flesh.
- Fleshing: Any excess flesh is mechanically removed, ensuring a clean hide for tanning.
This initial phase is crucial, as the quality of the raw material directly influences the final product.
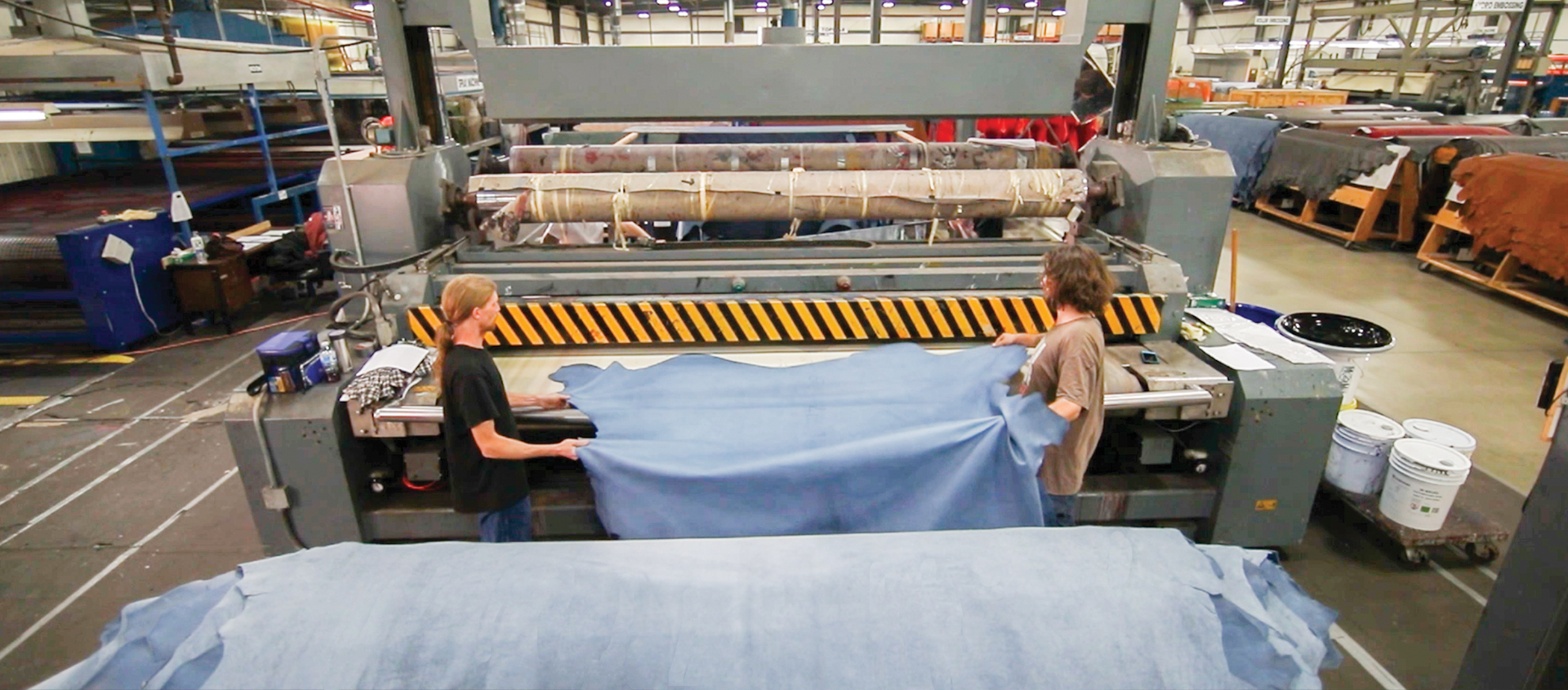
2. Forming: Tanning and Coloring Techniques
The tanning process transforms raw hides into leather. Various methods are employed, including:
- Vegetable Tanning: Utilizing tannins from plant sources, this method is eco-friendly but may take longer. It yields a sturdy leather, often used in high-quality goods.
- Chrome Tanning: A faster method that uses chromium salts, producing softer and more water-resistant leather. This method is prevalent for fashion items and accessories.
Following tanning, hides are dyed using various techniques, such as drum dyeing or spray dyeing, ensuring even color distribution. The choice of dye impacts the leather’s look, feel, and longevity.
3. Assembly: Cutting and Stitching
Once the leather is tanned and dyed, it moves to the assembly stage, where skilled artisans cut the leather into specific shapes and sizes. Advanced cutting techniques, including die cutting and laser cutting, are often utilized for precision.
- Stitching: This is a critical part of assembly, where high-quality threads and robust stitching techniques are employed to enhance durability. Methods like double stitching or reinforced seams can be used based on the product’s requirements.
Quality at this stage is vital, as any flaws can lead to product failure. Ensuring that assembly workers are skilled and experienced is essential for maintaining high standards.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
4. Finishing: Surface Treatment and Inspection
The final stage involves finishing processes that enhance the leather’s appearance and performance. Common techniques include:
- Polishing: To give the leather a refined look, polishing is often applied.
- Coating: Surface coatings may be added for protection against wear and environmental factors, such as water and stains.
Quality control checkpoints are implemented at this stage to ensure that each product meets the required specifications. This includes visual inspections and tactile evaluations.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in Leather Production?
Quality assurance is critical in the leather manufacturing process, ensuring that the end products meet international standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding these quality control processes can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
Relevant International Standards for Leather Products
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential for establishing quality management systems. These standards ensure that manufacturers adhere to consistent quality across all production stages. Other specific certifications may include:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for leather goods that require specific performance measures, especially in industrial applications.
These certifications provide buyers with confidence in the quality of the products they are sourcing.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is typically divided into three main checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet the required specifications. For leather, this may include evaluating the quality of hides for defects or inconsistencies.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor compliance with production standards. This includes checking for defects during cutting, stitching, and finishing.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a comprehensive inspection is performed to ensure that they meet all specifications and quality standards. This may involve physical tests, such as durability tests, and visual inspections for aesthetic quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure reliability and consistency. Here are several approaches:
-
Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems. Buyers should request audit reports to assess compliance with relevant standards.
-
Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline testing methods, inspection results, and any corrective actions taken. This transparency is crucial for building trust.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. These agencies can perform audits and inspections to validate claims made by the supplier.
What Are the QC Nuances for International Buyers from Different Regions?
International buyers must also be aware of regional nuances in quality control. For instance:
-
Africa: Buyers may face challenges related to infrastructure and logistics, affecting the reliability of quality control processes. Establishing strong relationships with local suppliers can help mitigate these issues.
-
South America: Understanding local regulations and quality standards is crucial, as they may differ significantly from international norms. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international standards.
-
Middle East: The market is increasingly competitive, and buyers should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate robust quality control practices to stand out in the region.
-
Europe (e.g., Germany): European buyers often have stringent quality requirements. Suppliers must be well-versed in compliance with EU regulations and standards, making thorough documentation and certification essential.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols of leather factories is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production, relevant quality standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions and secure high-quality leather products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘the leather factory’
The purpose of this guide is to provide international B2B buyers with a clear, actionable checklist for sourcing leather products from factories. With the global demand for high-quality leather goods, understanding how to effectively procure from leather factories is essential for ensuring product quality and supplier reliability.
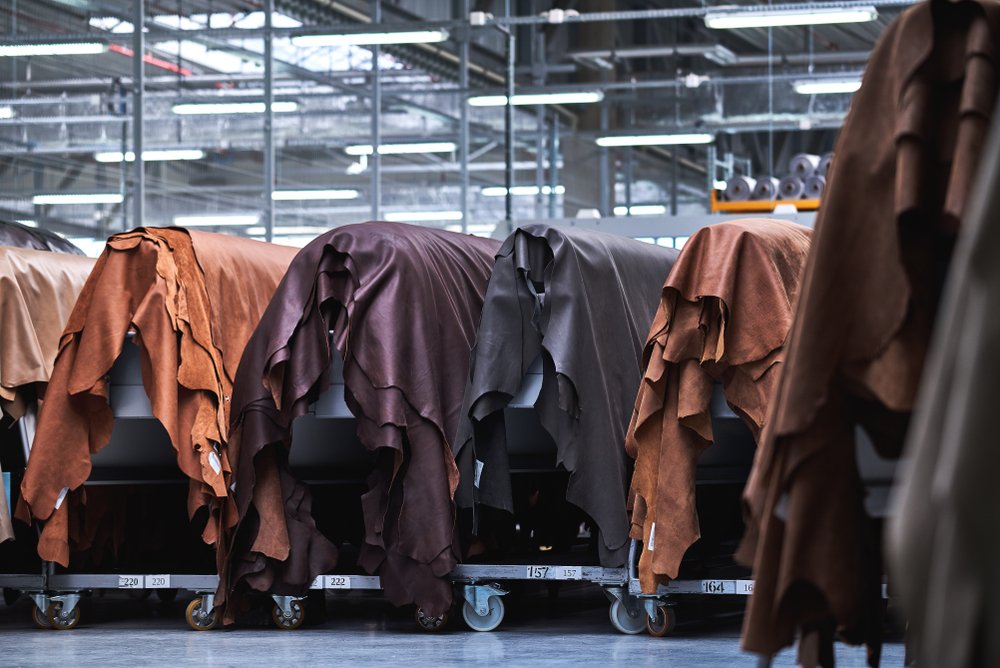

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Step 1: Define Your Product Requirements
Clearly outline the specifications of the leather products you need. This includes the type of leather (e.g., cowhide, lambskin), product categories (jackets, accessories), and any specific design features. A detailed product requirement helps suppliers understand your needs and prevents miscommunication later in the sourcing process.
- Considerations:
- What is the intended use of the leather products?
- Are there specific aesthetic or functional features that must be included?
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable leather factories. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the industry and positive reviews from other buyers. Utilize platforms like Alibaba, industry-specific trade shows, and local directories to compile a list of potential suppliers.
- Actions:
- Verify the supplier’s business registration and history.
- Check for reviews or testimonials from previous clients.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the manufacturing capabilities of each supplier. It’s important to ensure they have the necessary equipment, technology, and workforce to meet your production needs. A factory’s capacity can directly influence delivery times and product quality.
- Key points to examine:
- Production capacity and lead times.
- Quality control measures in place.
Step 4: Request Samples
Always request product samples before finalizing orders. Samples allow you to evaluate the quality of the leather and craftsmanship. This step is crucial for ensuring that the products meet your standards and are suitable for your target market.
- What to look for in samples:
- Texture, weight, and finish of the leather.
- Overall construction quality and attention to detail.
Step 5: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the supplier complies with industry standards and regulations. Certifications related to environmental practices, labor conditions, and product quality are important indicators of a reliable supplier. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues and damage to your brand reputation.
- Important certifications to check:
- ISO certifications for quality management.
- Environmental certifications like the Leather Working Group (LWG).
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Establish clear terms and conditions before entering into a contract. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and return policies. Transparent negotiations help build a strong relationship with the supplier and mitigate potential disputes.
- Considerations:
- What payment methods are acceptable?
- Are there penalties for late deliveries or quality issues?
Step 7: Maintain Communication and Monitor Production
Establish ongoing communication with the supplier during production. Regular updates can help address any issues that arise and ensure the project remains on track. Monitoring production also allows you to verify that quality standards are maintained throughout the process.
- Actions:
- Schedule regular check-ins via email or video calls.
- Request progress photos or reports during production.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing process, ensuring they procure high-quality leather products while building sustainable relationships with suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for the leather factory Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Factory Sourcing?
In sourcing from a leather factory, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement strategy. The primary components influencing costs include:
-
Materials: The choice of leather—whether premium cowhide, lambskin, or synthetic alternatives—plays a significant role in determining the base cost. Leather quality, sourcing location, and availability can cause fluctuations in pricing.
-
Labor: Skilled craftsmanship is crucial in leather production. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region and the level of expertise required. For instance, factories in Europe may incur higher labor costs compared to those in regions with lower wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient factories often have optimized processes that can lower overhead costs, benefiting buyers.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds and tools can be substantial, especially for custom designs. These costs are often amortized over larger production runs, making them more manageable for bulk orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality can add costs, particularly if multiple inspections or testing certifications are required. Factories with established QC processes might charge a premium but can save buyers from future quality issues.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs depend on the distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms agreed upon. Import duties and tariffs may also influence the final cost, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Factories typically apply a markup on their costs to achieve profit margins. Understanding these margins can help buyers assess pricing fairness.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Leather Factory Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing in leather sourcing, particularly for international B2B buyers:

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger orders can lead to better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their budget while ensuring they meet production requirements.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products often incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges during production.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products meeting specific quality standards or certifications (like ISO or environmental certifications) may cost more, but they can add significant value in terms of marketability and compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and timely delivery may charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms can help buyers anticipate additional costs associated with shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) impact overall pricing significantly.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Leather Prices?
For B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic negotiation can lead to cost savings:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct market research to understand prevailing prices for similar leather products. This knowledge will empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with the product, such as maintenance, durability, and potential resale value.
-
Transparent Communication: Establish clear communication with suppliers regarding expectations, timelines, and quality. Building a strong relationship can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Flexibility in Specifications: Be open to alternative materials or designs that can reduce costs without compromising quality. This flexibility can lead to innovative solutions that benefit both parties.
-
Long-Term Partnerships: Developing long-term relationships with suppliers can yield better pricing over time, as suppliers may offer discounts to loyal customers or provide priority during high-demand periods.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is essential to note that pricing can vary based on numerous factors, including market conditions, regional economic factors, and specific buyer requirements. Always confirm current prices directly with suppliers before making procurement decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing the leather factory With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Leather Production and Supply
In the ever-evolving landscape of leather production and supply, international B2B buyers often seek alternatives to traditional leather factories. These alternatives can range from synthetic leather manufacturers to specialized leather suppliers, each presenting unique advantages and drawbacks. The following analysis compares ‘The Leather Factory’ with other viable solutions, providing insights into their performance, cost, and suitability for specific needs.
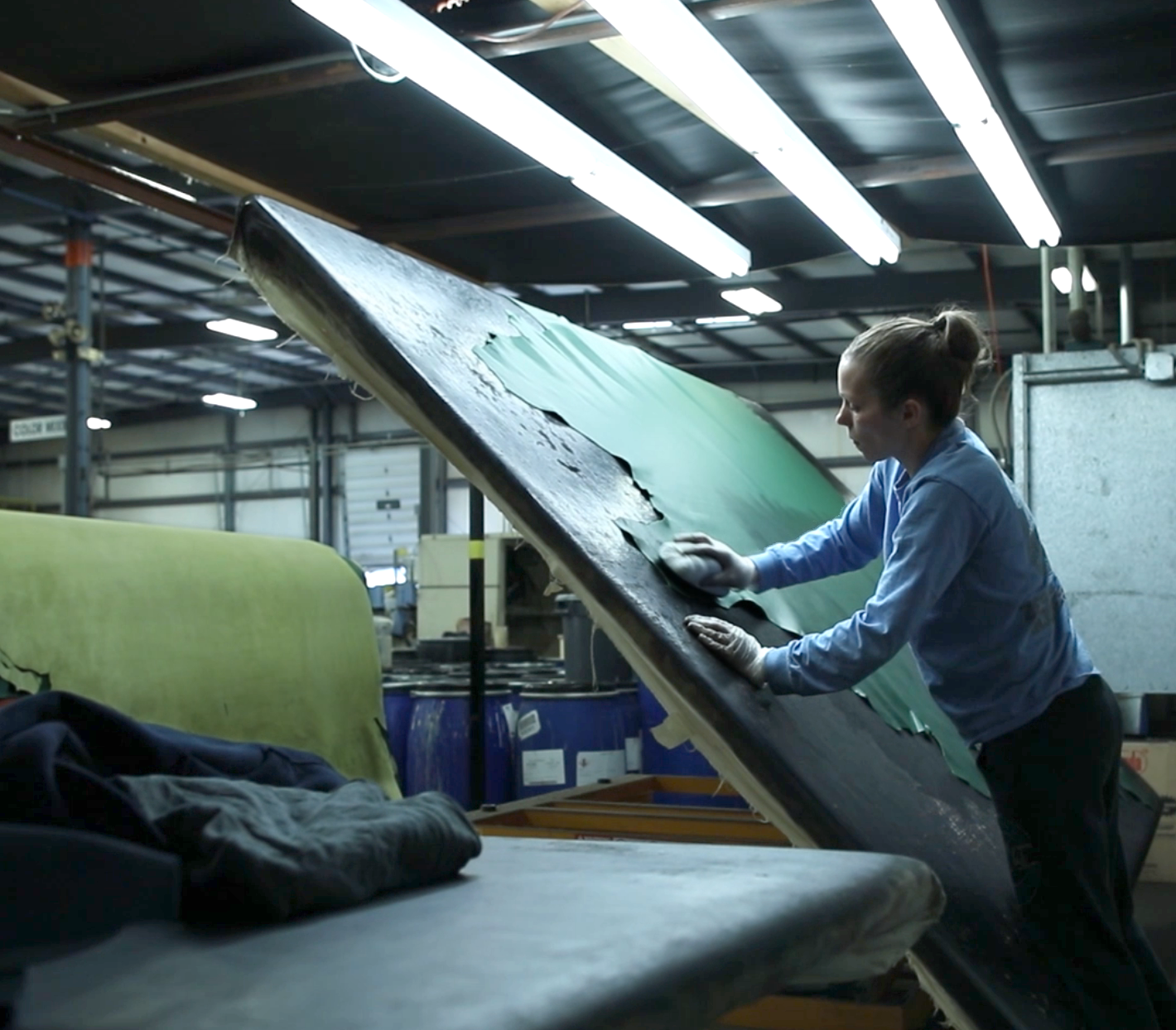

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
| Comparison Aspect | The Leather Factory | Alternative 1: Synthetic Leather Manufacturers | Alternative 2: Tandy Leather (Raw Materials Supplier) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality leather products, tailored for durability and style | Varies; can mimic leather aesthetics, often less durable | Offers raw materials for customization and craftsmanship |
| Cost | Higher production costs due to quality materials and craftsmanship | Generally lower costs; less expensive raw materials | Competitive pricing for bulk purchases, but additional costs for crafting |
| Ease of Implementation | Established supply chain, often requiring minimum order quantities | Easier integration for mass production, with standardization | Requires skilled labor for crafting; may need additional tools |
| Maintenance | Requires careful maintenance to ensure longevity | Low maintenance; easy to clean and maintain | Maintenance depends on the final product crafted from raw materials |
| Best Use Case | Premium fashion items, bespoke leather goods | Mass-market products, cost-effective fashion | Custom leather goods, craft projects, and artisanal products |
Exploring Synthetic Leather Manufacturers as an Alternative
Synthetic leather manufacturers produce alternatives that mimic the look and feel of genuine leather at a lower cost. This option is particularly appealing for mass-market brands looking to reduce production costs while maintaining a stylish appearance. The benefits of synthetic leather include its ease of maintenance and resistance to wear and tear. However, the downsides include potential lower durability and a perception of inferior quality among consumers who prefer authentic leather.
Evaluating Tandy Leather as a Supplier of Raw Materials
Tandy Leather provides high-quality raw leather materials, catering to artisans and businesses that prefer a hands-on approach to leather crafting. This alternative is ideal for companies looking to create bespoke leather products, allowing for customization in design and material selection. While Tandy offers competitive pricing, it requires skilled labor for crafting, which can increase overall costs if the workforce is not readily available. The flexibility and creativity offered by Tandy Leather make it an attractive option for specialized projects.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Leather Solution for Your Business
When selecting the right leather solution for your business, consider factors such as your target market, budget constraints, and production capabilities. If premium quality and brand prestige are critical, ‘The Leather Factory’ may be the best choice despite its higher costs. Alternatively, if you aim to produce cost-effective, stylish products, synthetic leather could be more suitable. For businesses looking to engage in craftsmanship and customization, Tandy Leather offers the raw materials necessary for unique creations. Ultimately, aligning your choice with your business strategy will ensure the most effective use of resources and maximize customer satisfaction.
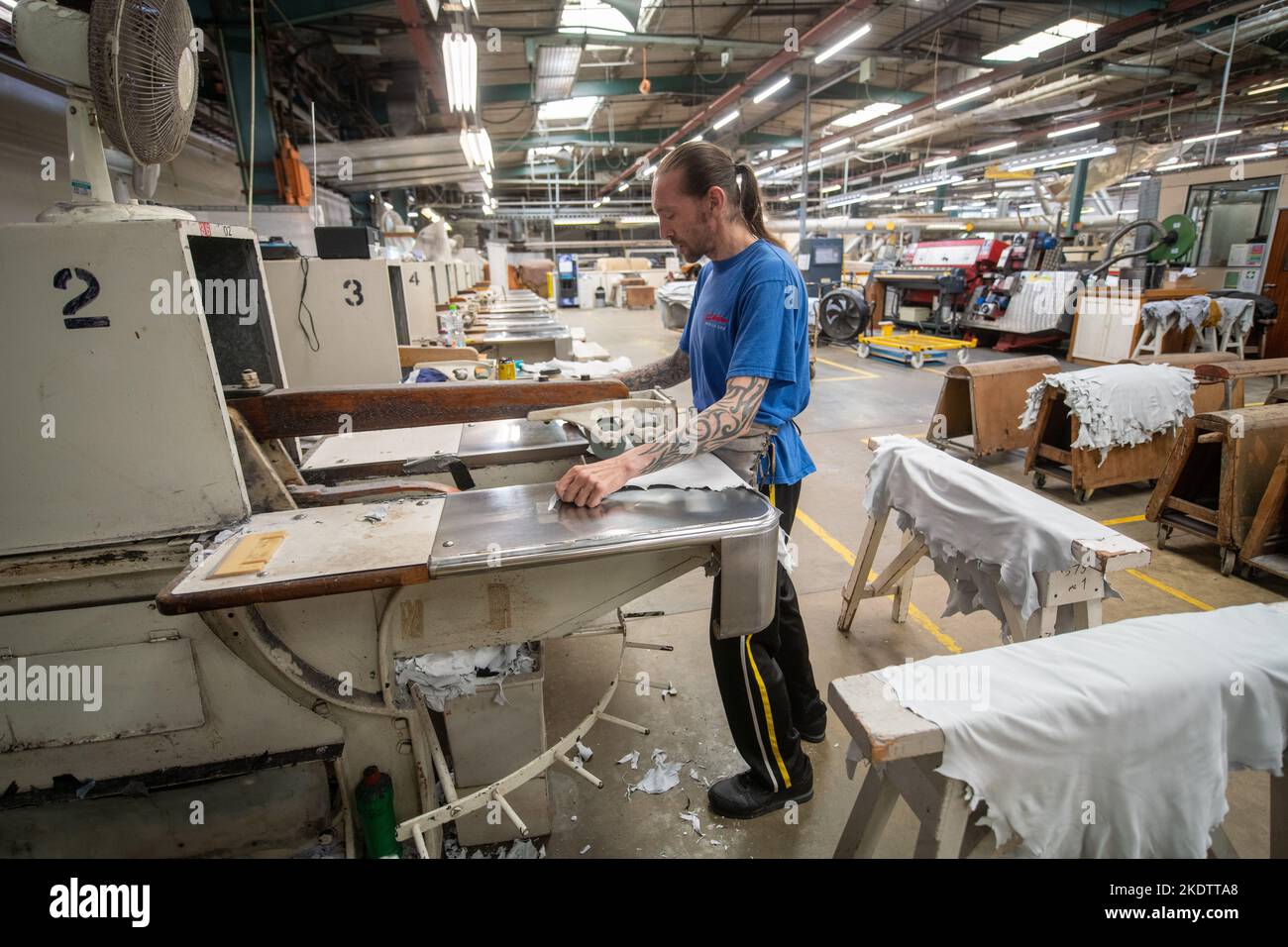

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for the leather factory
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Leather for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical properties of leather is crucial for B2B buyers, as these specifications directly impact product quality, durability, and overall performance. Here are several critical specifications that international buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the quality classification of leather, which can include full-grain, top-grain, corrected grain, and genuine leather.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade leathers like full-grain offer superior durability and aesthetic appeal, making them suitable for high-end products. Understanding the grade helps buyers ensure they meet market demands and customer expectations. -
Thickness (Gauge)
– Definition: Thickness is measured in ounces or millimeters and indicates the leather’s weight and robustness.
– B2B Importance: Thicker leather typically indicates greater durability and resistance to wear, which is essential for products like jackets and upholstery. Buyers must specify thickness requirements to align with product functionality and market positioning. -
Tannage Type
– Definition: The tanning process preserves the leather and can be vegetable-tanned or chrome-tanned, among other methods.
– B2B Importance: The tanning type affects the leather’s characteristics, such as flexibility, color retention, and eco-friendliness. Buyers focusing on sustainability may prefer vegetable-tanned leather, while others may prioritize the quick production times associated with chrome tanning. -
Finish and Coating
– Definition: This refers to the final treatment applied to the leather surface, affecting its appearance and performance.
– B2B Importance: Different finishes can enhance water resistance, UV protection, or aesthetic qualities. Buyers should specify the desired finish to ensure the leather meets their product requirements and customer preferences. -
Colorfastness
– Definition: Colorfastness measures the leather’s resistance to fading when exposed to light, water, or friction.
– B2B Importance: For products exposed to the elements or frequent handling, high colorfastness is essential to maintain product integrity and appearance. Buyers must evaluate colorfastness to ensure the leather meets their long-term performance expectations.
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand in the Leather Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some key trade terms relevant to leather procurement:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or products that are used in another company’s end product.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify potential suppliers that can meet specific production requirements, ensuring product quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is critical for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational capacities and sales forecasts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other terms for specific products.
– Importance: An RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive pricing and favorable terms for their procurement strategy. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms helps buyers assess costs and responsibilities related to shipping, insurance, and customs clearance, ultimately aiding in risk management and budgeting. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Knowing lead times is essential for inventory planning and ensuring timely product availability. Buyers should discuss lead times with suppliers to align production schedules and customer demands.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, streamline procurement processes, and enhance their product offerings in the competitive leather market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the the leather factory Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Leather Factory Sector?
The leather industry is experiencing significant transformation driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. International buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly Germany and Brazil, must navigate a landscape characterized by competitive pricing and innovative sourcing strategies. Key drivers include the rise of e-commerce, which facilitates direct access to suppliers and enhances supply chain transparency. Digital platforms are increasingly being used to streamline procurement processes, enabling buyers to compare prices, lead times, and product quality more effectively.
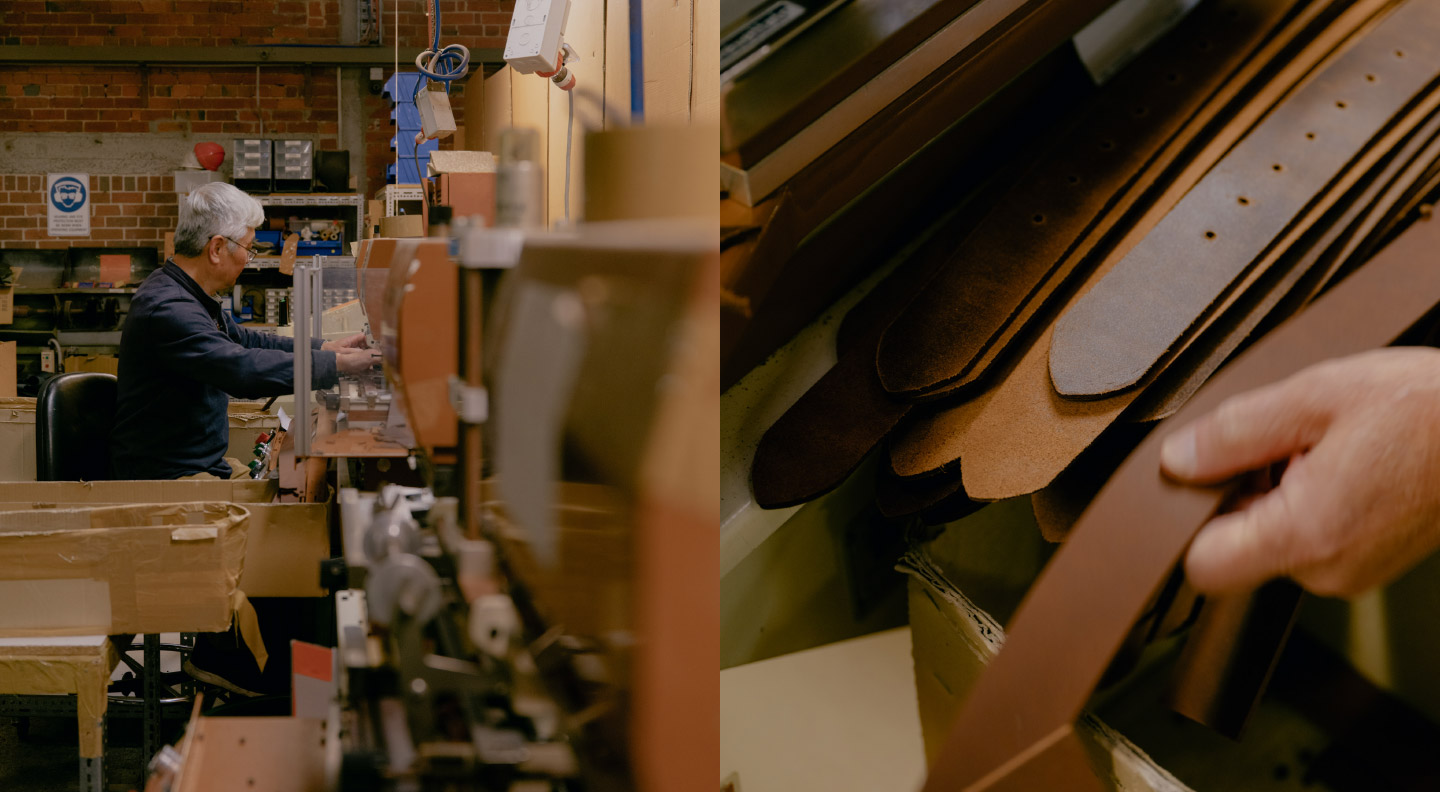

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Emerging trends, such as the adoption of artificial intelligence and automation in manufacturing, are reshaping production efficiencies. These technologies allow factories to reduce waste and optimize labor costs while enhancing the speed of product delivery. Furthermore, the leather market is witnessing a shift towards customization and personalization, driven by consumer demand for unique products. B2B buyers should be aware of these trends to leverage partnerships with manufacturers that embrace technology and innovation.
Another critical factor is the impact of international trade policies and tariffs, which can significantly affect pricing and sourcing strategies. Buyers must stay informed about regulations that may influence supply chain dynamics, particularly in light of recent geopolitical tensions and trade agreements.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Leather Industry?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it has become a crucial component of the leather supply chain. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally responsible practices. This includes sourcing leather from tanneries that utilize eco-friendly processes, such as vegetable tanning, which reduces harmful chemical usage.
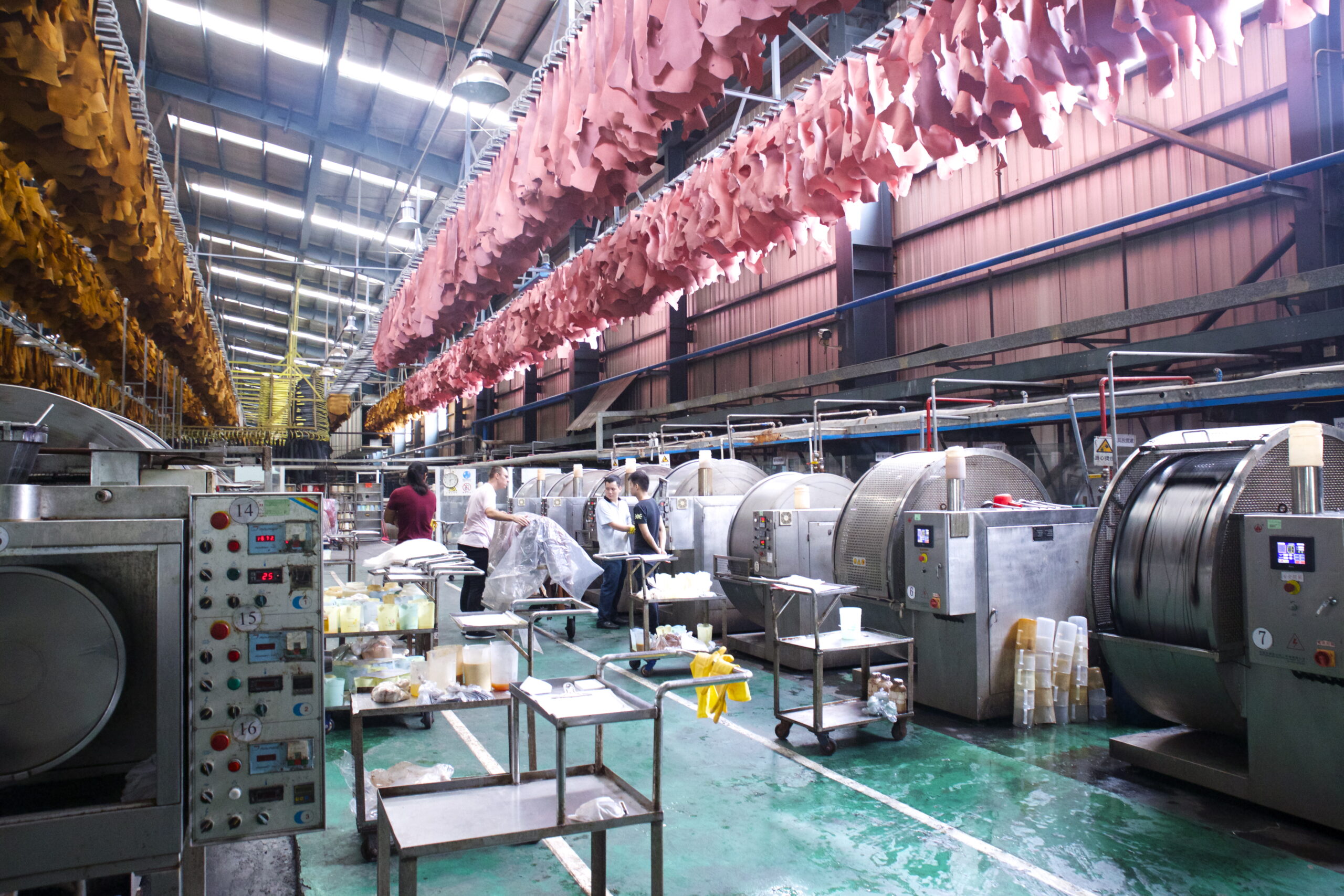

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
The importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated, as consumers are becoming more conscious of the environmental and social impacts of their purchases. Buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers with certifications like the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification, which ensures that tanneries adhere to strict environmental and social standards. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also foster consumer trust.
Additionally, the trend towards circular economy practices is gaining traction within the leather sector. This involves reusing and recycling leather products, thus minimizing waste and extending the lifecycle of materials. B2B buyers should consider partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize sustainability, as this aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and promote responsible consumption.
What Is the Historical Context of the Leather Factory Sector?
The leather industry has a rich history, dating back thousands of years, but its evolution into the modern factory system began during the Industrial Revolution. Initially, leather production was a labor-intensive process reliant on skilled artisans. However, technological advancements led to mass production techniques, allowing factories to produce leather goods at scale.
The late 20th century saw significant changes in the industry, particularly with the advent of global trade and the rise of synthetic alternatives. While traditional leather remains popular, the market has faced challenges from cheaper, mass-produced synthetic materials, particularly from countries like China, which have reshaped competitive dynamics.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Understanding this historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it provides insight into the market’s evolution and highlights the importance of adapting to current trends. By recognizing the shifts in consumer preferences and the emergence of ethical sourcing practices, buyers can make informed decisions that align with both market demands and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of the leather factory
-
1. How do I choose the right leather supplier for my business needs?
When selecting a leather supplier, evaluate their product quality, certifications, and manufacturing processes. Request samples to assess the leather’s texture, durability, and finish. It’s also essential to check their reputation through reviews and references. Consider their ability to meet your specific requirements, such as customization options and minimum order quantities (MOQs). A supplier with experience in international trade and knowledge of your target market can further enhance the reliability of your sourcing decision. -
2. What is the best way to ensure leather quality from a factory?
To ensure leather quality, implement a robust quality assurance (QA) process. Start by requesting detailed product specifications and certifications from the factory. Schedule factory visits if possible, or utilize third-party inspection services to verify quality standards. Establish clear communication regarding your quality expectations and conduct regular audits. Additionally, reviewing previous customer testimonials can provide insights into the factory’s quality consistency. -
3. What are common payment terms for B2B leather transactions?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and are often negotiated during the contract phase. Common terms include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days) based on your relationship and order history. Always clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, letters of credit, or PayPal, to avoid complications. -
4. How can I customize leather products to meet my brand specifications?
Most leather factories offer customization options, including selecting leather types, colors, and finishes. To initiate the customization process, provide detailed design specifications, including sketches or prototypes. Collaborate with the factory’s design team to refine your ideas and ensure feasibility. Discuss MOQs for customized orders, as they may differ from standard products. Regular communication during the production process is crucial to ensure your vision is accurately realized. -
5. What are the logistics considerations for importing leather products?
Logistics for importing leather products involve understanding customs regulations, tariffs, and shipping costs. Choose a reliable freight forwarder with experience in handling leather goods to navigate these complexities. Ensure all documentation, such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, is accurate to avoid delays. Additionally, consider the lead time for production and shipping to align with your inventory needs and market demands. -
6. How do I verify the ethical sourcing of leather from a factory?
To verify the ethical sourcing of leather, inquire about the factory’s sourcing practices and supplier relationships. Look for certifications such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification, which ensures sustainable and ethical practices. Request information about animal welfare standards and environmental impact assessments. Engaging in direct communication with the factory and visiting their operations can also provide transparency regarding their ethical commitments. -
7. What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for leather goods?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly between factories and product types. Generally, MOQs for leather goods range from 50 to 500 units, depending on the complexity of the item and the factory’s production capabilities. For customized products, MOQs may be higher due to the additional setup costs. Always discuss MOQs upfront to ensure they align with your business needs and budget. -
8. How do I handle issues with defective leather products from a supplier?
In the event of receiving defective leather products, promptly contact the supplier to report the issue, providing detailed documentation, including photos and descriptions. Review the supplier’s return and exchange policy, which should outline the process for addressing defects. Maintain open communication to negotiate solutions, whether through replacements, repairs, or refunds. Establishing a solid relationship with the supplier can facilitate smoother resolutions for any quality concerns.
Top 4 The Leather Factory Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Leather Factory – Leather Jackets
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: The Leather Factory is an eBay store specializing in leather products, particularly jackets. Key details include: 92.4% positive feedback, 3.5K items sold, and 790 followers. Featured products include various styles of leather jackets for men and women, such as motorcycle jackets, vintage cafe racer jackets, and trench coats, with prices ranging from $34.99 to $119.99. Specific items mentioned inc…
2. Leather Factory Shop – Handmade Leather Jackets
Domain: leatherfactoryshop.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Leather Factory Shop offers premium handmade leather jackets, including men’s and women’s collections. Key product categories include Men Biker, Blazers, Bomber, Hooded, and Vests, as well as Women’s Biker and Bomber jackets. The seasonal leather jacket collection features vintage motorcycling styles, iconic designs, and autumn/winter outerwear made from premium cowhide and lambskin leather. The M…
3. Facebook – Premium Quality Leather Jackets
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Premium Quality Leather Jackets, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. The Little Leather Factory – Luxury Leather & Vegan Products
Domain: thelittleleatherfactory.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: The Little Leather Factory is a manufacturer of traditional leather and vegan leather products, specializing in luxury designer items. They offer beautiful hand-made products with low minimum quantities and quick reorder times. The company provides assistance in the design process, helping clients transform sketches into prototypes and manage production runs. They use high-quality sustainable mate…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for the leather factory
The leather industry stands at a pivotal crossroads, presenting immense opportunities for international B2B buyers. Strategic sourcing plays a crucial role in navigating this landscape, offering a pathway to quality materials, competitive pricing, and sustainable practices. By focusing on reliable suppliers and innovative products, businesses can secure a competitive edge while meeting the growing demand for premium leather goods.
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that embrace quality craftsmanship and ethical sourcing. As the market evolves, leveraging technology and supply chain efficiencies will be essential in mitigating risks associated with fluctuating costs and global competition.
Looking ahead, the potential for growth in the leather sector is substantial, particularly for those willing to adapt and invest in emerging trends such as eco-friendly materials and custom designs. Engaging with forward-thinking suppliers will not only enhance product offerings but also foster long-term relationships that drive success. Now is the time for B2B buyers to explore these avenues and position themselves strategically for the future of the leather market.

Illustrative image related to the leather factory
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.