Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is sueded
In the ever-evolving landscape of fashion and upholstery, understanding what is sueded presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers seeking to procure high-quality materials. Suede, known for its luxurious texture and versatile applications, is often a preferred choice for items ranging from footwear to high-end accessories. However, the complexities surrounding sourcing this unique fabric—such as identifying reliable suppliers, differentiating between genuine and synthetic alternatives, and navigating varying price points—can hinder informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of sueded materials, covering essential topics including types of suede, applications across various industries, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations. By equipping international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—with actionable insights and authoritative knowledge, this guide aims to empower you to make strategic decisions that align with your business needs.
Understanding the nuances of suede not only enhances product quality but also enables companies to meet consumer demand for sophisticated and stylish options. As we explore the global market for sueded materials, you will gain the expertise necessary to navigate this essential fabric landscape with confidence and precision.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 What Is Sueded Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is sueded
- Understanding what is sueded Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is sueded
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is sueded’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is sueded
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is sueded
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is sueded’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is sueded Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is sueded With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is sueded
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is sueded Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is sueded
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is sueded
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what is sueded Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Suede | Soft texture, derived from animal skins, permeable | Fashion apparel, high-end accessories | Pros: Luxurious feel; Cons: Less durable and requires special care. |
| Synthetic Suede | Man-made, often more durable, water-resistant | Budget-friendly fashion, upholstery | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: May lack the premium feel of natural suede. |
| Ultrasuede | High-performance synthetic, soft, and stain-resistant | Automotive interiors, high-end fashion | Pros: Durable and easy to clean; Cons: Higher cost compared to basic synthetics. |
| Faux Suede | Imitation leather made from polyester or nylon | Cost-effective fashion, home decor | Pros: Affordable and versatile; Cons: May not replicate the softness of real suede. |
| Microfiber Suede | Soft, lightweight, and water-resistant | Upholstery, clothing, accessories | Pros: Easy to maintain; Cons: Can be less breathable than natural suede. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Traditional Suede?
Traditional suede is crafted from the underside of animal skins, typically lamb, goat, or deer. This material is renowned for its soft texture and luxurious feel, making it a popular choice in high-end fashion apparel and accessories. However, its permeability and susceptibility to stains necessitate careful handling and maintenance, often requiring professional cleaning. B2B buyers should consider the long-term care costs associated with traditional suede products, as well as the potential for wear and tear in high-use applications.
How Does Synthetic Suede Compare to Natural Options?
Synthetic suede is a man-made alternative that mimics the look and feel of traditional suede but offers enhanced durability and water resistance. It is often used in budget-friendly fashion lines and upholstery due to its lower cost. While synthetic suede can be less luxurious than its natural counterpart, it provides a practical solution for manufacturers looking to appeal to cost-conscious consumers. B2B buyers should evaluate the balance between cost and quality when considering synthetic options for their product lines.
What Makes Ultrasuede a Preferred Choice for High-End Applications?
Ultrasuede is a premium synthetic fabric that combines the softness of traditional suede with superior durability and stain resistance. This material is commonly utilized in automotive interiors and high-end fashion items, where both aesthetics and functionality are paramount. Its ease of cleaning and maintenance makes it an attractive option for B2B buyers looking for longevity in their products. However, the price point may be higher than basic synthetic suedes, warranting a careful cost-benefit analysis.
What Are the Advantages of Faux Suede in Various Applications?
Faux suede is an imitation leather typically made from polyester or nylon, designed to provide an affordable alternative to genuine suede. It is widely used in fashion and home decor, appealing to budget-conscious consumers. While faux suede offers versatility and ease of maintenance, it may not deliver the same tactile experience as real suede. B2B buyers should consider the target market’s expectations when opting for faux suede in their offerings.
How Does Microfiber Suede Enhance Product Offerings?
Microfiber suede is a lightweight, water-resistant fabric that combines the soft texture of suede with enhanced practicality. This material is often used in clothing, upholstery, and accessories, providing an easy-to-clean option that retains a luxurious appearance. While it may lack the breathability of traditional suede, its maintenance-friendly properties make it a valuable choice for B2B buyers aiming to meet consumer demands for convenience and style.
Key Industrial Applications of what is sueded
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is sueded | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Suede jackets and coats | Offers luxury appeal and comfort, attracting high-end consumers. | Quality of suede, ethical sourcing, and dye options. |
| Footwear | Suede shoes | Provides style and softness, enhancing brand prestige. | Durability, maintenance requirements, and color options. |
| Automotive | Suede seat covers | Enhances interior aesthetics and comfort, appealing to luxury markets. | Stain resistance, durability, and compatibility with existing designs. |
| Accessories | Designer handbags | Elevates product value and consumer perception, ideal for luxury brands. | Material quality, sourcing ethics, and color versatility. |
| Home Furnishings | Suede upholstery | Adds a touch of luxury and comfort to furniture, appealing to high-end consumers. | Cleaning requirements, durability, and fabric color options. |
How is Suede Used in Fashion and Apparel?
In the fashion industry, suede is primarily utilized for jackets and coats, providing a luxurious texture that appeals to consumers seeking high-end products. Its softness and unique napped finish enhance comfort while making a style statement. Buyers in this sector must prioritize the quality of the suede, ensuring it meets ethical sourcing standards, especially for international markets sensitive to animal welfare. Additionally, the availability of dye options is crucial for creating diverse product lines that cater to varying consumer preferences.
What Role Does Suede Play in Footwear?
Suede is a popular choice for footwear, particularly in dress shoes, due to its stylish appearance and soft feel. This fabric elevates brand prestige and attracts discerning customers who value aesthetics and comfort. However, suede’s maintenance requirements can be a challenge; buyers need to consider the durability of the material and how it will hold up against wear and environmental conditions. Color options also play a significant role, as the ability to offer various shades can enhance product appeal in competitive markets.
How is Suede Applied in Automotive Interiors?
In the automotive sector, suede is commonly used for seat covers, particularly in luxury vehicles. Its soft texture and visual appeal enhance the overall interior experience, making it a favored choice among high-end manufacturers. Buyers must consider factors such as stain resistance and durability, as well as how the suede integrates with existing vehicle designs. Given the diverse climates across regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing materials that can withstand varying conditions is essential for maintaining product quality.
Why is Suede Popular for Designer Handbags?
Suede is a favored material for designer handbags, as it adds a layer of luxury and sophistication that attracts upscale consumers. The unique texture and finish of suede enhance the perceived value of these accessories. For international buyers, ensuring the quality of the suede and its ethical sourcing is paramount, especially in markets where consumer awareness of sustainability is high. Furthermore, the versatility in color options allows brands to create distinct collections that resonate with diverse consumer tastes.
How is Suede Used in Home Furnishings?
In home furnishings, suede upholstery is sought after for its ability to add luxury and comfort to furniture pieces. This fabric appeals to consumers looking for high-end, stylish home decor. Buyers should be mindful of the cleaning requirements and durability of suede when sourcing for this application, as maintaining the fabric’s appearance is critical for customer satisfaction. Additionally, the availability of various color options can help brands cater to different interior design trends, enhancing their market competitiveness.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is sueded’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Durability Limitations of Suede
The Problem: B2B buyers often face uncertainty regarding the durability of suede fabric, especially when sourcing materials for products expected to withstand rigorous use. Suede, while luxurious and appealing, is not as resilient as traditional leather. Many businesses, particularly in regions with diverse climates like Africa or the Middle East, might struggle with how suede will perform under varying conditions, leading to concerns about returns and customer satisfaction.

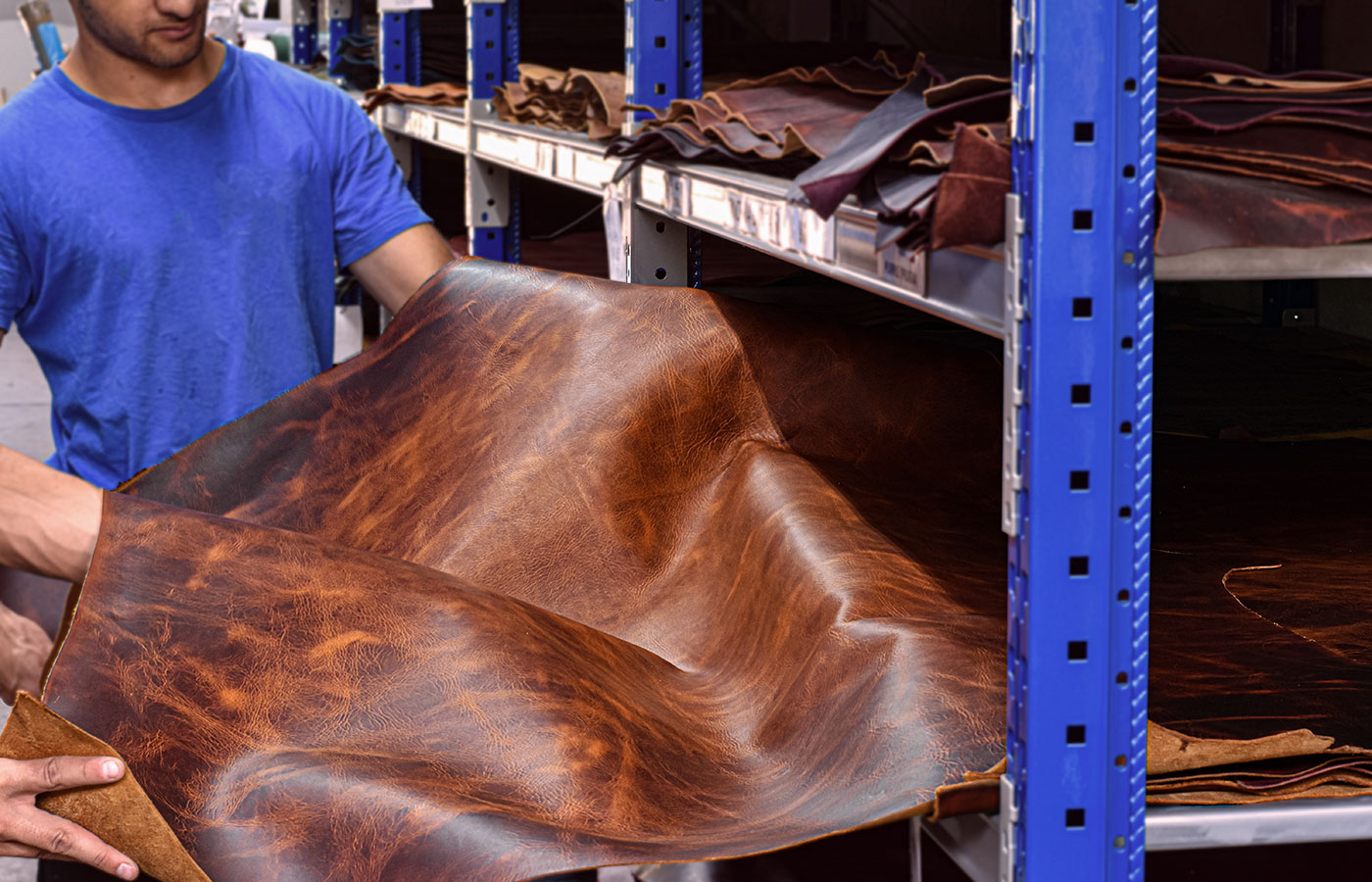
Illustrative image related to what is sueded
The Solution: To effectively address durability concerns, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality suede from reputable suppliers who can provide detailed information about the fabric’s treatment and care. When specifying products, it’s crucial to consider the intended use—selecting suede for items like jackets or bags that won’t be exposed to harsh conditions can enhance longevity. Additionally, look for suede that has been treated with protective coatings to improve stain resistance and water repellency. Implementing a thorough quality check process upon receipt of goods can also ensure that the suede meets durability expectations.
Scenario 2: Managing Maintenance and Cleaning Challenges of Suede
The Problem: One of the significant pain points for B2B buyers is the maintenance requirements of suede products. Suede is notoriously difficult to clean, as traditional washing methods can damage the fabric, leading to potential financial losses and customer dissatisfaction. Businesses that offer suede items, such as apparel or accessories, may receive complaints about stains or wear, creating a burden on customer service teams.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance challenges, B2B buyers should educate their customers on proper suede care. This can include providing care kits that contain a suede brush and specialized cleaning solutions designed for the fabric. Additionally, consider including detailed care instructions with every suede product sold. For businesses engaged in the production of suede items, partnering with professional cleaning services can provide customers with a reliable option for maintaining their products. Offering a cleaning service as part of the purchase can also enhance customer loyalty and differentiate your brand in a competitive market.
Scenario 3: Navigating the Cost Differences Between Genuine and Synthetic Suede
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter confusion regarding the cost-benefit ratio of genuine versus synthetic suede. With varying price points—genuine suede costing significantly more than synthetic alternatives—buyers may struggle to justify costs to their stakeholders or clients, especially in regions where budget constraints are a significant factor.
The Solution: To navigate these cost differences effectively, buyers should conduct a comprehensive analysis of their target market’s preferences and willingness to pay for quality. When sourcing suede, consider offering a range of products that include both genuine and synthetic options. Highlight the unique qualities of genuine suede, such as its luxurious feel and breathability, compared to the lower maintenance of synthetic alternatives. Providing samples can allow buyers to experience the differences firsthand, facilitating informed decisions. Furthermore, clear communication about the value proposition of each type will enable buyers to make choices that align with their brand identity and customer expectations, ultimately leading to better sales outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is sueded
What Are the Key Materials Used in Suede Production?
When selecting materials for suede production, it is essential to consider the various options available, each with unique properties, advantages, and disadvantages. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the production of suede: natural suede, synthetic suede, Ultrasuede, and Alcantara. This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
What Are the Key Properties of Natural Suede?
Natural suede is derived from the underside of animal hides, primarily lamb, goat, and calf. It is characterized by its soft, napped finish and luxurious feel. The key properties of natural suede include low breathability and moisture-wicking abilities, which make it less suitable for humid environments. However, its high heat retention makes it ideal for cooler climates.

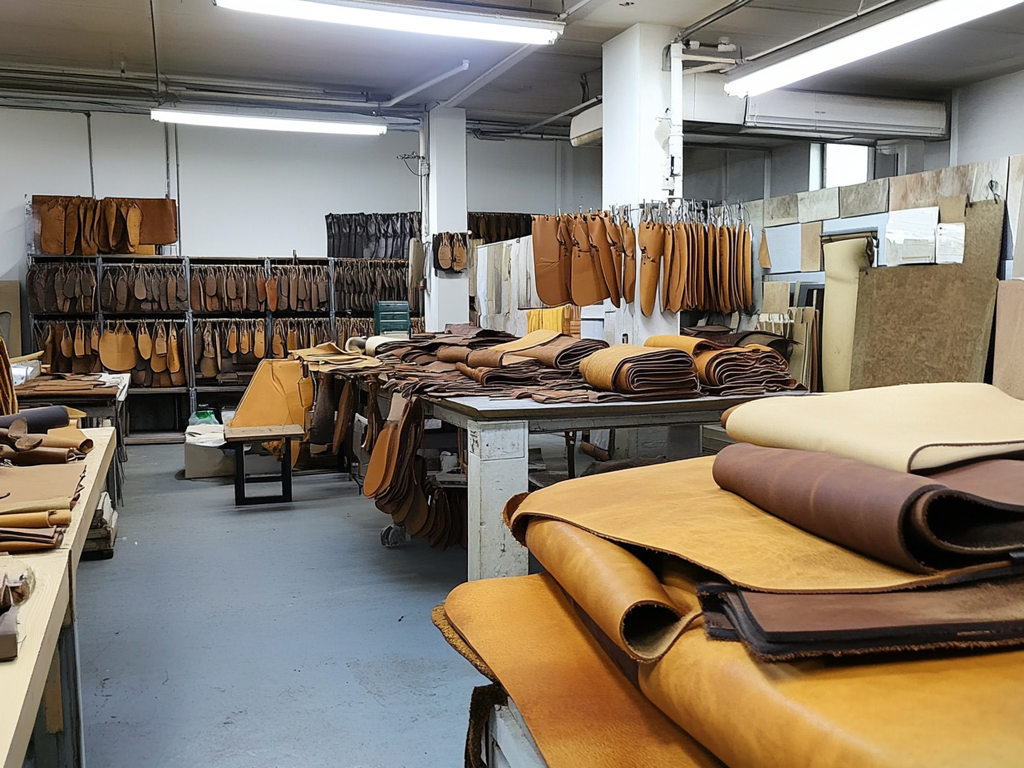
Illustrative image related to what is sueded
Pros: Natural suede offers unmatched softness and comfort, making it a popular choice for high-end apparel and accessories. Its aesthetic appeal is a significant advantage for luxury brands.
Cons: The primary drawbacks include its susceptibility to staining and water damage, necessitating professional cleaning. Additionally, natural suede can be more expensive, with costs typically ranging from $30 to $40 per yard.
How Does Synthetic Suede Compare?
Synthetic suede, often made from polyester or polyurethane, mimics the appearance and feel of natural suede but offers enhanced durability and ease of maintenance. Its key properties include higher resistance to water and stains compared to natural suede, making it suitable for a broader range of applications.
Pros: Synthetic suede is generally more affordable, costing between $8 and $12 per yard. Its durability and ease of cleaning make it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking for cost-effective solutions.
Cons: While synthetic suede can replicate the look of natural suede, it may lack the same luxurious feel, which can be a disadvantage in high-end markets. Additionally, some synthetic materials may not be as environmentally friendly.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
What Are the Advantages of Ultrasuede?
Ultrasuede is a premium synthetic material known for its softness and durability. It is made from polyester fibers and is designed to mimic the texture of natural suede while offering superior stain resistance and ease of cleaning.
Pros: Ultrasuede is highly durable and can withstand heavy use, making it ideal for applications in upholstery and fashion. Its stain-resistant properties reduce maintenance costs, and it is often machine washable.
Cons: The cost of Ultrasuede can be higher than standard synthetic options, which may deter budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, while it is durable, it may not provide the same luxurious feel as natural suede.
Why Choose Alcantara for Suede Applications?
Alcantara is another synthetic alternative to suede, made from a blend of polyester and polyurethane. It is renowned for its soft texture and is often used in luxury automotive interiors and high-end fashion.
Pros: Alcantara offers excellent durability and is resistant to fading and staining. Its luxurious feel makes it a popular choice for premium products, enhancing brand image.
Cons: The primary limitation of Alcantara is its higher price point, which can be a barrier for some manufacturers. Additionally, while it is durable, it may not appeal to consumers seeking authentic leather products.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Suede
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is sueded | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Suede | High-end apparel and accessories | Unmatched softness and comfort | Susceptible to stains and water | High |
| Synthetic Suede | Cost-effective apparel and accessories | Affordable and easy to maintain | Lacks the luxurious feel of natural suede | Low |
| Ultrasuede | Upholstery and fashion | Highly durable and stain-resistant | Higher cost compared to standard synthetic | Med |
| Alcantara | Luxury automotive interiors and fashion | Luxurious feel and durability | Higher price point | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in suede production, facilitating informed decision-making based on application needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is sueded
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Suede?
The manufacturing process of suede involves several critical stages that transform raw animal hides into the luxurious fabric known for its softness and appeal. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers identify quality suppliers and make informed purchasing decisions.
Material Preparation: How Are Hides Processed for Suede Production?
The manufacturing journey begins with the selection of animal hides, predominantly lamb skin, although calf, goat, and deer hides are also used. After the animals are slaughtered, the hides undergo a thorough cleaning and drying process. Once dried, a natural chemical, lime, is applied to remove hair follicles. This initial step is crucial, as it prepares the hide for the tanning process, which is essential for converting raw hides into leather.
Tanning: What Techniques Are Used to Transform Hides into Suede?
The tanning process involves treating the hides with tannins, which render them inert and prevent decomposition. Tannins can be derived from various natural sources, including tree barks and leaves. After tanning, the leather is further processed to achieve the desired suede characteristics. Techniques such as splitting and thinning the leather are employed to create the soft, napped texture that distinguishes suede from other leather types.
Finishing: How Is Suede Treated to Enhance Durability and Appearance?
Once the leather has been transformed into suede, it undergoes additional treatments to enhance its durability and aesthetic appeal. Manufacturers apply a mixture of salts, oils, and sometimes synthetic chemicals to ensure the suede retains its softness while becoming more resilient to wear and tear. A final texturing process is also implemented to achieve the signature fuzzy finish that makes suede desirable for various applications.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
What Are the Quality Assurance Protocols for Suede Production?
Quality assurance is paramount in the suede manufacturing process to ensure that the end product meets international standards and buyer expectations. Adhering to these protocols minimizes defects and enhances customer satisfaction.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Suede Manufacturing?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a crucial role in establishing quality management systems that ensure consistent product quality. ISO 9001 provides a framework for manufacturers to improve their processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and comply with regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking may apply, particularly for products intended for the European market, ensuring that they meet health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Suede Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early. The primary QC stages include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase focuses on inspecting the raw hides before they enter the production process. Suppliers should provide documentation proving the quality of their hides, including origin and treatment processes.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC monitors the tanning and finishing stages to ensure adherence to predefined quality standards. This may involve visual inspections and measurements to check for consistency in thickness and texture.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, the finished suede products undergo rigorous testing for defects, color consistency, and overall appearance. Any items failing to meet quality standards are rejected or sent back for rework.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is critical. Here are actionable steps to ensure compliance with quality standards:
What Methods Can Be Used for Supplier Audits?
B2B buyers should conduct supplier audits to evaluate their quality control processes. This includes reviewing their compliance with ISO standards, examining their QC documentation, and observing their manufacturing practices firsthand. Audits can be performed by the buyer or through third-party inspection services, which provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities.
How Can Buyers Leverage Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services is an effective way to verify supplier quality. These services conduct thorough checks at various manufacturing stages and provide detailed reports on compliance with quality standards. Buyers can request these reports as part of their supplier evaluation process, ensuring transparency and accountability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in Suede Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance for suede typically includes several testing methods to assess durability, colorfastness, and overall performance. Common tests include:
- Abrasion Resistance Test: Evaluates the wear resistance of suede when subjected to friction.
- Water Resistance Test: Assesses how well the suede withstands moisture exposure.
- Colorfastness Test: Measures the ability of the suede to retain its color after exposure to light and washing.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing suede products from international suppliers, buyers must be aware of specific nuances in quality certification. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, where compliance with CE marking is often required. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are knowledgeable about these requirements and have the necessary certifications to facilitate smooth import processes.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for suede is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to ensure high-quality products. By focusing on material preparation, tanning, finishing, and rigorous quality control measures, buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing suede in a competitive global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is sueded’
The following checklist is designed to guide B2B buyers in procuring suede materials effectively. Understanding the nuances of suede can help ensure that you select high-quality products that meet your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clarify what type of suede you require. Consider factors such as thickness, texture, and color, as well as whether you need natural or synthetic suede. Specifying these details upfront will help you communicate your needs clearly and avoid misunderstandings later in the sourcing process.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers who specialize in suede. Look for manufacturers with a solid track record in the industry, preferably with experience serving similar markets. Utilize online resources, trade directories, and industry publications to compile a list of potential candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management or other industry-specific certifications. This will help guarantee that the suede meets international quality standards and is produced in an environmentally sustainable manner. Ask for documentation and verify their compliance with industry regulations.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Before placing bulk orders, request samples of the suede from shortlisted suppliers. Evaluate these samples for factors such as texture, durability, and color consistency. This step is crucial to ensure that the suede meets your specifications and is suitable for your intended applications, whether for clothing, accessories, or upholstery.
Illustrative image related to what is sueded
Step 5: Understand Pricing Structures and Terms
Discuss pricing with potential suppliers, including any volume discounts or additional costs associated with shipping or customs. Compare the pricing of natural suede against synthetic alternatives to understand the cost-benefit ratio. Make sure to clarify payment terms, delivery timelines, and any guarantees or warranties associated with the products.
Step 6: Assess Production Capabilities and Lead Times
Inquire about the supplier’s production capabilities and typical lead times for orders. Understanding their capacity to fulfill your order on time is essential, especially if you have specific deadlines or seasonal demands. Ensure that the supplier can scale production if your needs increase in the future.
Step 7: Negotiate Contracts and Terms of Service
Once you have chosen a supplier, negotiate contracts that clearly outline the terms of service, including delivery schedules, payment terms, and return policies. Pay attention to clauses related to quality assurance and dispute resolution to safeguard your interests. A well-structured agreement will help prevent conflicts and ensure a smoother business relationship.
By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions when sourcing suede, ensuring that your business receives high-quality materials that align with your specifications and market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is sueded Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Suede Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of suede sourcing is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The primary components of the cost structure include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice between genuine suede and synthetic alternatives significantly impacts costs. Genuine suede typically ranges from $30 to $40 per yard, while synthetic options like Ultrasuede can be found for $8 to $12 per yard. The quality of the animal hide, the tanning process, and any additional treatments will also influence material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the country of production. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing but could compromise on craftsmanship. Conversely, countries with higher labor standards may yield better quality but at an increased cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, equipment maintenance, and utilities. High overhead costs can arise from advanced machinery used for suede processing, which can enhance the quality of the final product.
-
Tooling: If the production involves specific tools for cutting and finishing suede, these costs must be factored in. Custom tooling can lead to significant upfront costs but may be necessary for high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of suede is critical, particularly for luxury markets. The QC process can add to the overall cost but is essential for maintaining product standards and minimizing returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on the origin of the suede, the destination market, and the chosen Incoterms. International shipping adds complexity and costs, especially for bulk orders.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add their profit margin to the overall cost, which can vary based on market demand and competition.
What Influences the Pricing of Suede?
Several factors can influence the pricing of suede, including order volume, specifications, material quality, supplier relationships, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs, making it essential for buyers to negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their business needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or unique specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Premium materials or certified environmentally-friendly processes typically come at a higher price point. Buyers should assess the trade-off between cost and quality.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a solid reputation may charge more due to perceived value and reliability. Buyers should vet suppliers carefully to ensure they are getting the best quality for their investment.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of various Incoterms is crucial. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect total costs based on who bears the transportation risk and responsibility.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Suede Sourcing Costs?
B2B buyers should adopt a strategic approach to sourcing suede to enhance cost-efficiency and value. Here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate: Always negotiate terms and pricing with suppliers. Building long-term relationships can lead to better rates and priority in production schedules.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but all associated costs, including maintenance, shipping, and potential returns.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying price sensitivities. For example, buyers in Europe may prioritize sustainability, while buyers in Africa might focus on cost. Tailoring your approach based on regional preferences can lead to better deals.
-
Stay Updated on Market Trends: Understanding global trends in suede production, such as shifts towards sustainable practices or synthetic alternatives, can provide insights that lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned are indicative and can vary based on multiple factors including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and engage directly with suppliers for the most accurate and relevant pricing information.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is sueded With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Suede Fabric: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of textiles, suede fabric is recognized for its soft texture and luxurious appeal. However, as global markets expand, B2B buyers are increasingly evaluating alternatives that may offer comparable aesthetics with enhanced durability or cost-effectiveness. This section provides a detailed comparison of suede fabric against two prominent alternatives: synthetic suede and leather.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is Sueded | Synthetic Suede | Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Soft, luxurious feel; less durable | Similar texture; more durable | Highly durable; water-resistant |
| Cost | $30-40 per yard | $8-12 per yard | $50-100+ per yard |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized care and cleaning | Easy to clean; machine washable | Requires special care; may need conditioning |
| Maintenance | Professional cleaning recommended | Low maintenance; machine washable | Moderate maintenance; needs conditioning |
| Best Use Case | High-end fashion, luxury items | Everyday wear, versatile applications | Heavy-duty items, outdoor gear |
What is Synthetic Suede? Pros and Cons
Synthetic suede, often marketed under names like Ultrasuede or Alcantara, mimics the texture and appearance of traditional suede while providing enhanced durability and ease of care. One of the primary advantages of synthetic suede is its affordability, costing significantly less than genuine suede. Additionally, synthetic options are machine washable, making them appealing for everyday applications. However, while they can replicate the look of suede, some buyers may find that they lack the same luxurious feel and breathability.
How Does Traditional Leather Compare? Pros and Cons
Leather is a time-honored alternative to suede that offers unparalleled durability and water resistance. It is ideal for products that require longevity, such as footwear and outerwear, making it a staple in many industries. The primary disadvantage of leather is its higher cost compared to both suede and synthetic alternatives, often requiring a more significant investment. Furthermore, leather requires regular maintenance, including conditioning to prevent cracking and drying. Despite these challenges, its classic appeal and robustness make it a preferred choice for many high-end applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting between suede and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements and the intended use of the fabric. If the goal is to create luxury items where touch and aesthetic are paramount, genuine suede may still hold its ground despite the higher maintenance. However, for businesses focused on high-volume production with a need for cost efficiency and durability, synthetic suede or leather could provide practical solutions. Understanding the nuances of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their brand values and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is sueded
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Suede Fabric?
When sourcing suede for B2B applications, understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications:
1. Material Composition
Suede is primarily made from the underside of animal hides, with lambskin being the most common source. This composition affects the fabric’s softness and texture, making it highly desirable for luxury applications. B2B buyers must consider the source of the suede, as it can influence product quality and marketability.
2. Breathability
Suede has low breathability, which means it does not allow air to pass through easily. This characteristic is vital for applications such as clothing and footwear, where comfort is paramount. Buyers should assess the intended use of the suede to ensure it meets the necessary comfort and functionality standards.
3. Moisture Resistance
Suede is known for its low moisture-wicking abilities and high permeability. It tends to absorb water, making it unsuitable for outdoor use in wet conditions. Understanding this property is essential for manufacturers to prevent returns and dissatisfaction among end consumers.
4. Durability and Maintenance
While suede is softer and more comfortable than standard leather, it is less durable and prone to staining. Professional cleaning is often recommended to maintain its appearance. B2B buyers should factor in maintenance costs and durability when selecting suede for their products, especially in high-usage applications.
5. Thickness and Weight
Typically thinner than traditional leather, suede is lighter and more flexible. This property allows for more delicate designs but can impact the overall durability of the final product. Buyers need to balance the aesthetic appeal with practical considerations regarding wear and tear.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
6. Cost per Yard
The cost of genuine suede generally ranges from $30 to $40 per yard, while synthetic alternatives can be significantly cheaper, costing between $8 to $12 per yard. Cost considerations are crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when budgeting for production and pricing strategies.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Associated with Suede?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for navigating the suede market. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products for other brands under the latter’s label. In the context of suede, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify potential suppliers who can meet specific quality and design standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important in the suede market, where minimum order requirements can affect inventory costs and production planning for B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific quantities of goods. For suede sourcing, an RFQ helps buyers gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better negotiation and decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to mitigate risks related to shipping, insurance, and delivery.
5. Tanning
Tanning is the process of treating animal hides to convert them into leather. Knowledge of tanning methods is essential for buyers looking to understand the quality and durability of the suede they intend to purchase.
6. Synthetic Suede
Synthetic suede, often referred to as Ultrasuede or Alcantara, is a manufactured alternative designed to mimic the look and feel of genuine suede. Buyers should evaluate the advantages and limitations of synthetic options, especially in terms of cost and durability, compared to genuine suede.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions when sourcing suede, ensuring they meet both market demands and product quality standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is sueded Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing the Suede Sector?
The suede market is experiencing significant growth driven by a combination of fashion trends, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. As international B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the understanding of these dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing. One of the primary global drivers is the increasing demand for luxury fashion products, where suede is prized for its softness and aesthetic appeal. This trend is particularly evident in markets like Saudi Arabia, where high-end fashion is integral to consumer behavior.
Emerging B2B technologies are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. Digital platforms facilitate direct connections between suppliers and buyers, enhancing transparency and efficiency in procurement processes. Additionally, advancements in synthetic suede production offer alternatives that are often more cost-effective and durable, appealing to budget-conscious manufacturers while maintaining aesthetic quality.
Current market dynamics indicate a robust competition between natural and synthetic suede. While traditional suede holds a strong position due to its luxury status, the rise of eco-friendly synthetic alternatives presents an interesting challenge. International buyers must navigate these options carefully, considering factors such as price, quality, and consumer trends to make informed sourcing decisions.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Suede Procurement?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the suede sector, particularly regarding environmental impact and ethical sourcing practices. The tanning process of natural suede can involve harmful chemicals, which raises concerns about pollution and ecological degradation. Consequently, international buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and utilize eco-friendly materials.
Ethical supply chains are essential in addressing the growing demand for transparency among consumers. Certifications such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and the Leather Working Group (LWG) promote responsible sourcing and production methods, ensuring that suede is obtained from ethically managed farms and processed in environmentally friendly facilities. By opting for certified suppliers, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the expectations of socially conscious consumers.
Moreover, with the advent of synthetic alternatives like Ultrasuede and Alcantara, there are opportunities to source materials that minimize environmental impact without compromising on quality. These materials often require less energy and water in production, making them attractive options for businesses looking to adopt greener practices.
What Is the Historical Context of Suede Production Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The history of suede dates back to the Romantic period in France, where it gained popularity among the nobility for its luxurious feel and softness, particularly in glove production. The term “suede” itself originates from the French phrase “gants de Suede,” meaning “gloves of Sweden.” Over time, artisans recognized the broader applications of suede, expanding its use into jackets, footwear, and accessories.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is critical. Suede’s transformation from a niche product to a staple in luxury fashion reflects changing consumer preferences and market dynamics. This historical context underscores the importance of quality and craftsmanship, aspects that modern manufacturers must consider when sourcing suede. The legacy of suede as a luxury material continues to influence its market positioning, offering insights into consumer behavior and expectations that can guide purchasing strategies today.
By leveraging these insights into market dynamics, sustainability practices, and historical context, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with both current trends and long-term business goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is sueded
-
How do I determine the quality of suede fabric when sourcing?
To assess the quality of suede fabric, consider factors such as the source of the animal skin, the tanning process, and the finishing techniques used. High-quality suede typically comes from lambskin or calfskin, which offers a softer feel. Request samples to evaluate the texture, durability, and color consistency. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance processes and certifications, which can provide insights into their manufacturing standards. -
What are the best applications for suede in fashion and accessories?
Suede is commonly used in high-end fashion items such as jackets, shoes, handbags, and gloves due to its soft texture and luxurious appearance. For apparel, it is particularly suited for cool-weather outerwear. However, due to its susceptibility to staining and water damage, suede is best used in items that are not exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Understanding the target market’s preferences can help in selecting appropriate applications for suede products. -
What should I consider when evaluating suede suppliers for international trade?
When vetting suede suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, production capacity, and adherence to ethical sourcing practices. Check for certifications related to environmental standards and animal welfare, as these are increasingly important to consumers. Additionally, assess their ability to provide customization options and their responsiveness to inquiries, which can indicate their level of professionalism and reliability in fulfilling orders. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for suede fabric?
Minimum order quantities for suede fabric can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of suede. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 200 yards for natural suede, while synthetic alternatives may have lower MOQs. When negotiating, discuss your specific needs and explore possibilities for smaller orders, especially if you are a new business or testing a new product line. -
What payment terms are common in B2B transactions for suede sourcing?
Standard payment terms for suede sourcing often include a deposit of 30-50% upfront, with the balance due upon completion of production or prior to shipping. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms, allowing payment within 30 to 90 days after delivery. Always clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure that they align with your cash flow needs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for my suede orders?
To guarantee quality assurance, establish clear specifications for the suede fabric, including color, texture, and finish. Request samples before placing bulk orders and consider conducting third-party inspections during production. Implementing a quality control checklist that suppliers must adhere to can also help maintain standards. Regular communication and feedback loops with suppliers will foster a collaborative approach to quality management. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing suede?
When importing suede, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight offers cost savings but longer transit times. Familiarize yourself with the import duties and tariffs specific to suede in your country, and ensure your supplier provides the necessary documentation for customs clearance. Planning ahead will help minimize delays and extra costs. -
Are there sustainable alternatives to traditional suede that I should consider?
Yes, there are several sustainable alternatives to traditional suede, such as synthetic suede made from recycled materials or eco-friendly processes. Products like Ultrasuede and Alcantara offer similar aesthetics and tactile qualities while being more durable and easier to maintain. When sourcing, inquire about the sustainability practices of suppliers and the environmental impact of their production methods to align with growing consumer preferences for eco-conscious products.
Top 5 What Is Sueded Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sewport – Suede Fabric
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“Fabric Name”: “Suede Fabric”, “Also Known As”: [“Fuzzy leather”, “Napped leather”, “Ultrasuede”], “Fabric Composition”: “The underside of animal skins or a similar synthetic material”, “Breathability”: “Low”, “Moisture-wicking”: “Low”, “Heat Retention”: “High”, “Stretchability”: “Low”, “Prone to Pilling/Bubbling”: “Low”, “Country of Origin”: “Sweden”, “Biggest Exporting Country”: “China”, “Recom…
2. JCrew – Sueded T-shirts
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Sueded T-shirts are marketed as having a soft feel, different from regular cotton shirts. They are often made from brushed cotton, which gives them a suede-like texture. Some users have noted that while they are soft, they do not feel exactly like real suede. Brands like JCrew and Lucky Brand offer these types of shirts, and they are described as being noticeably softer than standard cotton.
3. Collins Dictionary – Sueded Materials
Domain: collinsdictionary.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Sueded is an adjective in American English that describes something made to resemble suede. Examples include materials like sueded vinyl, which is noted for being lightweight, waterproof, and easy to carry.
4. LinkedIn – Microfiber Suede
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Microfiber suede is a chemical microfiber leather fabric made from 50% polyurethane and 50% polyamide. It is produced through a process that involves creating microfiber nonwoven fabric, impregnating it with resin, and then applying a mechanical finishing process called sueding. This fabric has several advantages including a high-grade and tasteful appearance, comfort due to its fine surface fiber…
5. Merriam-Webster – Suede Definition
Domain: merriam-webster.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Suede is defined as leather with a napped surface or a fabric finished with a nap to simulate suede. The term ‘suede’ can also be used as a verb, meaning to give a suede finish or nap to a fabric or leather. The first known use of the noun ‘suede’ was in 1883, and the verb form was first used in 1921. The word originates from the French term ‘gants de Suède,’ meaning ‘Swedish gloves.’
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is sueded
As the global market for suede continues to evolve, understanding its unique properties and applications is crucial for B2B buyers. Suede, with its luxurious feel and versatile use in high-end fashion and accessories, remains a sought-after material. However, the challenges of sourcing genuine suede—such as its maintenance needs and vulnerability to environmental factors—underscore the importance of strategic sourcing. By considering both natural and synthetic alternatives, businesses can balance cost, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
Engaging with reputable suppliers, particularly from key production regions like China and Europe, can enhance product offerings while ensuring quality and sustainability. As demand grows in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, now is the time for international buyers to seize opportunities in the suede market.
In conclusion, as you navigate the complexities of sourcing suede, prioritize strategic partnerships and innovative solutions. Embrace the potential of this timeless fabric to elevate your product lines, while staying attuned to market trends and consumer preferences. Let’s move forward together to harness the full potential of suede in your business strategy.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to what is sueded
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.