Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for different types of leather
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing high-quality leather that meets both aesthetic and functional demands poses significant challenges for B2B buyers. With a myriad of leather types available, understanding their unique properties and applications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse world of leather, exploring various types such as full grain, top grain, nubuck, and suede, along with their respective advantages and potential applications across industries.
We address critical considerations for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including Germany and Nigeria—by providing insights on supplier vetting, cost implications, and maintenance requirements. As the leather market evolves, so too do the expectations of consumers for quality, sustainability, and innovation. By equipping buyers with actionable knowledge, this guide empowers businesses to confidently navigate their sourcing strategies, ensuring they select the right leather for their specific needs.
Whether you are in fashion, automotive, or furniture industries, understanding the nuances of different leather types will enhance your product offerings and strengthen your competitive edge. Join us on this journey to master the art of sourcing leather, ensuring your selections not only meet industry standards but also resonate with the values of your target market.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Different Types Of Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for different types of leather
- Understanding different types of leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of different types of leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘different types of leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for different types of leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for different types of leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘different types of leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for different types of leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing different types of leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for different types of leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the different types of leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of different types of leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for different types of leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding different types of leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Grain Leather | Highest quality, retains natural imperfections, develops a patina | Luxury handbags, high-end furniture | Pros: Exceptional durability, unique character; Cons: Expensive, requires skilled craftsmanship. |
| Top Grain Leather | Smoother surface, corrected imperfections, more affordable than full grain | Quality bags, wallets, upholstery | Pros: Good durability, easier to work with; Cons: Less unique, reduced breathability. |
| Nubuck Leather | Soft, velvety texture, requires regular maintenance | Footwear, handbags, furniture | Pros: Luxurious feel, durable; Cons: Prone to staining, needs special care. |
| Patent Leather | Glossy finish, highly durable, water-resistant | Formal wear, accessories | Pros: Stylish appearance, easy to clean; Cons: Susceptible to scratches, requires care to maintain shine. |
| Genuine Leather | Lower quality, made from leftover hide, variable leather content | Budget-friendly products | Pros: Affordable, decent durability; Cons: Often lacks breathability and quality assurance. |
What is Full Grain Leather and Why is it Highly Valued in B2B Markets?
Full grain leather is the pinnacle of leather quality, characterized by its unaltered surface that preserves the natural grain and imperfections. This type of leather is sought after for luxury handbags and high-end furniture due to its durability and unique aesthetic, as each piece tells its own story through the patina it develops over time. B2B buyers should consider the craftsmanship required for full grain leather products, as they often come at a premium price, reflecting their long-lasting nature and exclusivity.
How Does Top Grain Leather Compare to Full Grain Leather for B2B Buyers?
Top grain leather is the second-highest quality, featuring a smoother finish achieved through sanding and buffing. While it may lack the unique character of full grain leather, its affordability and uniform appearance make it popular in quality bags and wallets. B2B buyers should weigh the balance between cost and quality, recognizing that while top grain leather offers good durability, it may not develop the same natural patina over time.
What Makes Nubuck Leather a Unique Choice for B2B Applications?
Nubuck leather, known for its soft, velvety texture, is derived from the top grain of the hide but is sanded to create a luxurious feel. It is commonly used in footwear and handbags, appealing to consumers seeking elegance. However, B2B buyers must consider its maintenance needs, as nubuck is susceptible to stains and water damage, necessitating protective treatments to maintain its appearance and longevity.
Why is Patent Leather a Popular Choice for Formal Accessories in B2B Markets?
Patent leather stands out due to its glossy finish, achieved through multiple layers of lacquer. This type of leather is highly durable and resistant to water, making it an excellent choice for formal wear and accessories. B2B buyers should note that while patent leather is easy to clean and maintain, it can be prone to scratches, requiring careful handling to preserve its polished look.
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Genuine Leather?
Genuine leather is often marketed as real leather, but it encompasses a wide range of quality levels, as it can be made from leftover hide after the top layers have been removed. This makes it a budget-friendly option, suitable for a variety of products. However, B2B buyers should be cautious, as genuine leather may lack the durability and breathability of higher-quality leathers, often leading to a shorter lifespan of the products.
Key Industrial Applications of different types of leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of different types of leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion and Apparel | High-end handbags and footwear using full grain and nubuck leather | Enhanced brand perception due to luxury appeal and durability | Quality certification, ethical sourcing, and unique designs |
| Automotive | Upholstery and interiors using top grain and split grain leather | Improved aesthetics and durability in vehicle interiors | Material quality, color matching, and resistance to wear |
| Furniture | Upholstered furniture using genuine and nubuck leather | Long-lasting products that enhance customer satisfaction | Cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and maintenance requirements |
| Industrial Goods | Tool belts and work gear made from split grain leather | Cost-effective durability for rugged applications | Strength specifications, abrasion resistance, and pricing |
| Sporting Goods | Athletic footwear and gear using patent leather and suede | Enhanced performance and style for competitive markets | Weight, flexibility, and specialized finishes for performance |
How is Full Grain Leather Used in Fashion and Apparel?
Full grain leather is a staple in the fashion industry, particularly for high-end handbags and footwear. Its unique character, derived from the natural imperfections of the hide, appeals to luxury brands aiming to offer exclusive products. Buyers from regions such as Europe and the Middle East prioritize quality and authenticity, requiring suppliers to provide detailed sourcing documentation and certifications. Additionally, the durability of full grain leather ensures longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements, which is a critical consideration for B2B buyers looking for sustainable options.
What Role Does Top Grain Leather Play in Automotive Upholstery?
In the automotive sector, top grain leather is commonly utilized for vehicle upholstery due to its smooth finish and durability. It offers a balance between luxury and practicality, making it ideal for high-end vehicles. B2B buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, must consider factors like resistance to wear and tear, color consistency, and compliance with safety regulations. Suppliers should be prepared to provide samples and technical specifications that demonstrate the leather’s performance under varying environmental conditions.
How is Genuine Leather Applied in Furniture Manufacturing?
Genuine leather is frequently used in the furniture industry for upholstered products, balancing affordability with acceptable quality. Its versatility allows for various applications, from sofas to office chairs. B2B buyers often focus on cost-effectiveness while ensuring that the leather meets durability standards. Sourcing genuine leather requires careful attention to the tanning process and potential artificial finishes that could affect longevity. Suppliers should provide comprehensive information about maintenance and care to help buyers make informed decisions.
Why is Split Grain Leather Ideal for Industrial Goods?
Split grain leather is highly regarded in the industrial sector for producing tool belts and work gear. Its affordability and durability make it a practical choice for rugged applications where wear resistance is crucial. B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets, look for suppliers who can offer bulk pricing and consistent quality. Ensuring that the leather meets specific strength and abrasion resistance standards is essential for manufacturers aiming to provide reliable products to their customers.
What Advantages Does Patent Leather Offer in Sporting Goods?
Patent leather is often used in athletic footwear and sporting gear due to its glossy finish and water-resistant properties. It enhances the aesthetic appeal of sports products while providing a durable surface that can withstand rigorous use. B2B buyers in the sporting goods sector must consider factors like weight and flexibility when sourcing materials. Suppliers should highlight their ability to meet specific performance criteria, such as breathability and moisture management, to attract discerning buyers in competitive markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘different types of leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Assurance in Leather Procurement
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in ensuring the quality of leather products sourced from various suppliers. With multiple types of leather available—such as full grain, top grain, and genuine leather—buyers may struggle to differentiate between high-quality and inferior materials. This situation is exacerbated when suppliers misrepresent the type of leather being sold, leading to potential product failures and customer dissatisfaction. For companies in sectors like fashion and furniture, where brand reputation hinges on quality, this is a significant concern.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should implement a rigorous quality assurance process during procurement. Start by developing a comprehensive checklist that includes specific characteristics of each leather type, such as grain structure, thickness, and finish. When engaging with suppliers, request samples and verify their authenticity through third-party testing, if necessary. Additionally, building long-term relationships with reputable suppliers who offer transparency in their sourcing and manufacturing processes can enhance trust. Consider visiting tanneries or production facilities to observe their practices firsthand. This proactive approach will ensure that the leather meets your standards and aligns with your brand’s quality promise.
Scenario 2: Managing Cost Constraints While Seeking Premium Leather
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are under pressure to balance cost and quality when sourcing leather. High-quality leathers, like full grain and top grain, often come at a premium price, which can strain budgets—especially for smaller businesses or startups. Compromising on quality to meet financial constraints can lead to products that do not perform well, ultimately impacting customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should explore alternative sourcing strategies that allow for cost-effective procurement of quality leather. One approach is to negotiate bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers, which can often result in reduced prices. Additionally, consider utilizing mixed materials in product lines, where premium leather is used in high-visibility areas while more affordable types like split grain or genuine leather are used in less critical components. This strategy can maintain an overall premium feel while optimizing costs. Lastly, participating in leather trade shows and industry events can provide insights into emerging suppliers and innovative products that may offer competitive pricing without sacrificing quality.
Scenario 3: Addressing Maintenance and Longevity Concerns of Leather Products
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter issues regarding the maintenance and longevity of leather products. Different types of leather require varying levels of care, and a lack of knowledge about these requirements can lead to premature wear and tear, ultimately diminishing product value and customer satisfaction. For instance, nubuck and suede need specialized cleaning techniques, while full grain leather may develop a desirable patina over time but can also show scuffs if not cared for properly.
The Solution: To alleviate these concerns, buyers should educate their teams and end customers about proper leather care practices tailored to each type of leather used in their products. Providing detailed care instructions with each product can enhance customer experience and prolong the life of the leather. Additionally, consider investing in protective treatments for vulnerable leather types, such as nubuck and suede, to prevent stains and damage. Partnering with leather care product manufacturers to offer bundled care kits alongside your leather goods can also be a value-added service. This not only demonstrates a commitment to quality but also empowers customers to maintain their purchases effectively, leading to increased satisfaction and repeat business.

Illustrative image related to different types of leather
Strategic Material Selection Guide for different types of leather
What are the Key Properties of Full Grain Leather for B2B Applications?
Full grain leather is recognized as the highest quality leather available, retaining the natural grain and imperfections of the hide. This type of leather offers exceptional durability and breathability, making it ideal for high-end products such as luxury handbags and footwear. Its resistance to wear and tear is unmatched, as it develops a unique patina over time, enhancing its aesthetic appeal. However, the manufacturing complexity is significant, as only a small percentage of cowhide can be utilized for this type of leather, leading to higher costs. For international buyers, particularly in Europe and Africa, compliance with quality standards such as ASTM or DIN can be crucial, as full grain leather often meets stringent durability requirements.
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Top Grain Leather in B2B Sourcing?
Top grain leather is the second-highest quality and is often used in premium products. It undergoes some correction processes, which allow for a smoother and more uniform appearance. This type of leather is easier to work with compared to full grain, making it a popular choice for manufacturers looking for a balance between quality and cost. However, the protective finishes applied can reduce breathability and prevent the development of a natural patina. For B2B buyers, especially from South America and the Middle East, understanding the trade-offs between aesthetics and functionality is essential. Additionally, ensuring that suppliers adhere to recognized quality standards can help mitigate risks associated with product performance.
How Does Nubuck Leather Compare for Specific Applications in the B2B Market?
Nubuck leather, characterized by its soft, velvety texture, is made from the top grain of the hide and is often used in footwear and upholstery. While it offers a luxurious appearance, it requires careful maintenance to prevent staining and water damage. Its durability is good but not as high as full grain or top grain leather. B2B buyers should consider the specific needs of their target market when selecting nubuck, as its care requirements may not align with consumer preferences in regions like Africa, where conditions may lead to quicker wear. Compliance with local standards for leather goods can also influence the choice of nubuck in product lines.
What are the Key Considerations for Patent Leather in B2B Transactions?
Patent leather is known for its glossy finish and high durability, making it a popular choice for formal wear and accessories. Its resistance to water and stains adds to its appeal, particularly in regions with varying climates like Europe and the Middle East. However, the manufacturing process involves multiple layers of lacquer, which can complicate production and increase costs. B2B buyers must weigh the aesthetic benefits against the potential for scratches and the need for special care. Understanding local market preferences and compliance with international standards can guide purchasing decisions, ensuring that products meet consumer expectations.
| Material | Typical Use Case for different types of leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Grain Leather | Luxury handbags, high-end footwear | Exceptional durability and breathability | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Top Grain Leather | Premium bags, wallets, and apparel | Smooth appearance and easier to work with | Reduced breathability and natural patina | Medium |
| Nubuck Leather | Footwear, upholstery, luxury accessories | Luxurious feel and appearance | Requires regular maintenance, less durable | Medium |
| Patent Leather | Formal wear, handbags, accessories | Water-resistant and durable | Prone to scratches, complex production | Medium to High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for different types of leather
What Are the Main Stages of Leather Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing process of leather involves several critical stages, each requiring specific skills and techniques to ensure the final product meets quality standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to different types of leather
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Hide Processed?
The first stage of leather manufacturing begins with the selection and preparation of raw hides, which can come from various animals such as cows, goats, or sheep. The hides are initially cleaned to remove dirt, hair, and any residual flesh. This is often done through a process called fleshing, where mechanical tools are used to scrape off any remaining flesh. After cleaning, the hides undergo tanning, which stabilizes the collagen fibers and prevents decomposition. Common tanning methods include chrome tanning, which is faster and more common, and vegetable tanning, which is more environmentally friendly and results in more durable leather.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Leather?
Once the hides are tanned, they are cut into various shapes and sizes based on the intended product. This forming stage can involve several techniques, including die-cutting, where specific shapes are stamped out of the leather, and hand-cutting for more intricate designs. For thicker leathers, techniques such as skiving may be employed to reduce the thickness at certain edges. This step is crucial as it directly influences the aesthetic and functional properties of the leather products.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Leather Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital at every stage of the leather manufacturing process to ensure the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers must understand the various quality checkpoints and testing methods employed by suppliers.
What Are the Key International Standards for Leather Quality?
International standards like ISO 9001 are widely recognized and ensure that organizations meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications may apply depending on the leather’s end use. These standards guide manufacturers in establishing a quality management system that can be audited for compliance.
What Are the Common Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated into the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase checks the quality of raw materials upon arrival at the facility. Hides are inspected for defects such as scars or excessive thickness.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, various tests are performed to ensure that the leather is processed correctly. This may include checking the thickness, color consistency, and tanning effectiveness.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the leather products are finished, they undergo a final inspection to ensure they meet design specifications and quality standards. This includes checking for stitching integrity, surface finish, and overall appearance.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Leather Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality of leather products. These can include:
-
Physical Testing: This involves measuring tensile strength, tear resistance, and abrasion resistance to ensure the leather can withstand typical use.
-
Chemical Testing: The pH level of the leather is checked to ensure it is within acceptable limits, preventing issues like degradation over time.
-
Visual Inspection: Trained quality inspectors visually assess the leather for any imperfections, color discrepancies, or finish issues.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can help verify their compliance with international quality standards. Audits can reveal the supplier’s commitment to quality and their adherence to established processes.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request documentation that outlines the quality control processes, including test results and compliance certificates. This information can provide insights into the reliability of the supplier’s quality assurance measures.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the leather products before shipping. This can help mitigate risks related to quality discrepancies.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate several nuances when it comes to quality control in leather manufacturing. Understanding local regulations, compliance requirements, and cultural expectations can significantly impact procurement strategies. For example, buyers in Europe may have stricter environmental regulations compared to those in other regions. Additionally, language barriers and differing business practices may affect communication regarding quality expectations.

Illustrative image related to different types of leather
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Leather Products for B2B Transactions
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms in leather production are intricate and crucial for ensuring high-quality products. B2B buyers must be proactive in understanding these processes, verifying supplier capabilities, and ensuring compliance with international standards. By focusing on these areas, businesses can secure reliable sources of quality leather that meet their specific needs and expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘different types of leather’
Introduction
Sourcing leather for your business requires careful consideration and a structured approach. This guide outlines essential steps to help B2B buyers effectively procure different types of leather, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your product needs and quality standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s crucial to clearly define your technical specifications for leather. Consider the intended use of the leather—be it for luxury handbags, footwear, or upholstery. Different applications may require specific types of leather, such as full grain for durability or patent leather for aesthetic appeal.
- Identify Quality Requirements: Determine the grade of leather needed based on the end product’s quality expectations.
- Assess Performance Needs: Evaluate factors such as breathability, durability, and maintenance requirements.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in the type of leather you require. Use industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of potential vendors.
- Look for Industry Experience: Suppliers with a proven track record in leather sourcing are likely to provide higher quality products.
- Consider Geographical Factors: Suppliers from different regions may offer unique leather types and characteristics due to local tanning processes.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with industry standards. This step is crucial to ensure that the leather is sourced ethically and meets quality benchmarks.
- Check for Environmental Standards: Look for certifications such as ISO 14001 or Leather Working Group (LWG) certifications.
- Assess Quality Assurance Practices: Ensure suppliers have robust quality control processes in place to maintain product consistency.
Step 4: Request Samples for Assessment
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request leather samples for evaluation. This allows you to assess the texture, quality, and finish of the leather firsthand.
- Evaluate Physical Characteristics: Pay attention to the softness, grain, and durability of the samples.
- Test for Performance: Conduct tests to see how the leather holds up under various conditions, such as exposure to water or wear.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations with your chosen supplier to agree on terms, pricing, and delivery timelines. A clear agreement helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures that both parties are aligned.
- Discuss Minimum Order Quantities: Clarify the minimum order quantities to ensure they meet your production needs.
- Review Payment Terms: Establish favorable payment terms that align with your cash flow requirements.
Step 6: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
Implement a quality assurance process to monitor the leather received from suppliers. This step ensures that the leather meets your predefined specifications and maintains consistent quality.
- Define Inspection Criteria: Set specific criteria for inspection upon delivery, focusing on aspects like color uniformity and defect rates.
- Plan for Feedback Loops: Establish communication channels with suppliers for ongoing feedback and issue resolution.
Step 7: Consider Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
In today’s market, sustainability is a critical factor. Ensure that your sourcing practices align with ethical standards and consider the environmental impact of leather production.
- Evaluate Eco-Friendly Options: Look for suppliers offering sustainable leather alternatives or those committed to environmentally friendly practices.
- Promote Transparency: Choose suppliers who are transparent about their sourcing and tanning processes, which can enhance your brand’s reputation.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing different types of leather, ensuring quality products that meet market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for different types of leather Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of different types of leather is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Various factors contribute to the pricing of leather, which can significantly affect the total cost of ownership. This analysis will explore the cost components, price influencers, and practical tips for buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Different Types of Leather?
The cost structure for leather sourcing can be broken down into several components:
-
Materials: The type of leather significantly influences material costs. Full grain leather, being the most premium, commands the highest prices, while split grain and genuine leather are more affordable due to their lower quality.
-
Labor: Skilled craftsmanship is crucial, especially for high-quality leathers like full grain and nubuck. Labor costs can vary widely based on the region and the level of expertise required for processing specific leather types.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs include utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. These can vary depending on the production scale and location of the manufacturing facilities.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specialized leather products, adding to the initial costs. This is particularly relevant for buyers seeking unique designs or specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of leather products involves additional costs related to inspections and testing. High-quality leathers often require more stringent QC processes.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the leather’s origin and destination, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Buyers should factor in potential tariffs and import duties, especially when sourcing from overseas suppliers.
-
Margin: Supplier markups will vary based on the quality of leather and the overall market demand. Premium leather suppliers may have higher margins due to the perceived value of their products.
What Factors Influence Leather Pricing for B2B Buyers?
Several factors can significantly influence leather pricing:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to ensure they can secure competitive pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized leather goods may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Leather that meets specific quality standards or certifications (e.g., eco-friendly tanning) may have higher prices. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their target markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial. Different Incoterms can affect who bears the shipping costs and risks, influencing the overall pricing structure.
How Can B2B Buyers Negotiate Effectively for Leather Pricing?
To achieve cost efficiency when sourcing leather, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Consolidating orders can lead to significant savings. If possible, collaborate with other businesses to increase order volumes.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider long-term costs such as maintenance and durability. Higher-quality leathers may have a higher upfront cost but can offer better longevity and lower replacement rates.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market fluctuations in leather pricing. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations and help buyers time their purchases effectively.
-
Be Open to Alternative Materials: Exploring different types of leather or synthetic alternatives can lead to cost savings while meeting quality requirements.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term relationships can lead to better pricing, priority access to new products, and improved service.
What Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (e.g., Germany, Nigeria), understanding regional market dynamics and regulatory requirements is crucial. Currency fluctuations, geopolitical factors, and trade agreements can all impact pricing. It is advisable to maintain flexibility and adaptability in sourcing strategies to navigate these complexities effectively.

Illustrative image related to different types of leather
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis of different types of leather is vital for B2B buyers. By considering the key cost components, influencers, and practical negotiation strategies, buyers can optimize their sourcing processes and achieve better pricing outcomes. Always remember that prices can vary significantly based on the specific requirements and conditions of the leather market.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing different types of leather With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Different Types of Leather
When evaluating leather options for various applications, it is essential to consider viable alternatives that can meet similar needs. This analysis compares different types of leather with other materials and solutions that provide similar functionalities, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
| Comparison Aspect | Different Types Of Leather | Synthetic Leather | Fabric-Based Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability, unique aesthetic, develops a patina over time. | Water-resistant, consistent appearance, less breathable. | Good breathability, lightweight, but less durable. |
| Cost | Varies from high (full grain) to moderate (genuine). | Generally lower than high-quality leather. | Usually the most cost-effective option. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled craftsmanship for high-quality leather goods. | Easier to manufacture and process, can be mass-produced. | Simple to produce, widely available. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular care; specific methods for each type. | Low maintenance; easy to clean. | Easy to care for but may require replacement over time. |
| Best Use Case | Luxury items, high-end fashion, durable goods. | Everyday products, fashion items, budget-friendly options. | Casual wear, promotional items, temporary applications. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Synthetic Leather?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional leather. Its primary advantage is affordability and ease of maintenance; it does not require the same level of care as genuine leather and is resistant to water and stains. However, synthetic materials typically lack the unique aesthetic and durability of high-quality leather, and they may not develop the desirable patina over time. Additionally, concerns about environmental impact and breathability can deter some buyers from choosing synthetic options.
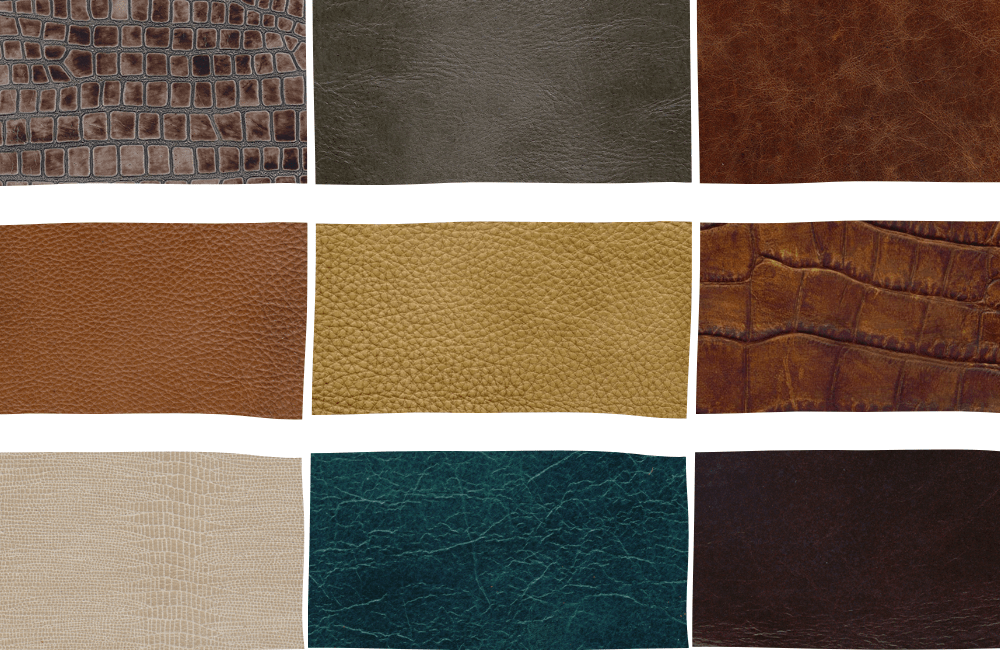

Illustrative image related to different types of leather
How Do Fabric-Based Solutions Compare to Different Types of Leather?
Fabric-based solutions, such as canvas or nylon, provide an economical and lightweight alternative to leather. These materials are often chosen for their breathability and versatility, making them suitable for casual wear and promotional items. However, they generally fall short in terms of durability and long-term aesthetic appeal compared to leather. While they can be easily produced and are often less expensive, fabric items may require more frequent replacement due to wear and tear, making them less ideal for high-end applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
In selecting the right leather type or alternative solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including budget constraints, desired product lifespan, and the intended application. High-quality leather is ideal for luxury items where durability and craftsmanship are paramount, while synthetic and fabric options may be better suited for cost-sensitive projects or high-volume production. By carefully evaluating the trade-offs of each material, businesses can align their product offerings with market demands and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for different types of leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Different Types of Leather?
When navigating the diverse landscape of leather products, understanding essential technical properties is critical for B2B buyers. Here are some key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade: This refers to the quality classification of leather based on its origin and processing. Full grain and top grain leathers are considered higher grades due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. In contrast, split grain and genuine leather, while more affordable, may lack the longevity and character of higher grades. For buyers, material grade directly influences product pricing and market positioning.
-
Thickness: The thickness of leather is typically measured in millimeters and can significantly impact the material’s durability and usage. Thicker leather (such as full grain) is more robust and suitable for high-end products, while thinner options (like suede) may be used for garments and accessories. Understanding thickness helps buyers select the right leather for specific applications, ensuring product performance aligns with consumer expectations.
-
Finish Type: Leather finishes can vary from natural to heavily treated. Full grain leather retains its natural look, while patent leather is coated for a glossy finish. The type of finish impacts durability, maintenance needs, and overall appearance. Buyers should consider the desired aesthetic and care requirements when selecting leather types for their products.
-
Breathability: This property refers to how well the leather allows air to pass through. Full grain leather is highly breathable, making it ideal for items like footwear and bags that require comfort. Conversely, heavily finished leathers may restrict airflow. Buyers need to consider breathability, especially for products that will be worn or used in warm climates.
-
Durability and Resistance: Different leather types exhibit varying levels of resistance to wear, moisture, and staining. For instance, nubuck leather, while luxurious, requires more maintenance compared to more durable options like split grain leather. Buyers should assess the intended use of the leather product to ensure it meets durability requirements.
-
Aging Characteristics: The way leather ages can significantly affect its appeal. Full grain leather develops a unique patina, enhancing its character over time, while other types may show wear more quickly. Understanding aging characteristics allows buyers to select products that align with their brand’s identity and customer expectations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Leather Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the leather industry, OEM relationships can help brands offer unique products without investing in their production facilities.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is crucial for B2B buyers to understand, as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. A higher MOQ may lead to better pricing but could also increase upfront investment.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent by buyers to suppliers requesting pricing information for specified products. In the leather industry, an RFQ helps buyers compare prices and negotiate terms with multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive pricing.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and costs involved in the delivery of leather goods.
-
Tanning Process: This term refers to the method used to convert raw animal hides into leather. Different tanning processes (e.g., chrome vs. vegetable tanning) affect the leather’s characteristics, including flexibility, durability, and environmental impact. Buyers should be aware of the tanning process to ensure it aligns with their sustainability goals.
-
Lead Time: Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving it. In the leather industry, understanding lead times is crucial for inventory planning and aligning product launches with market demand. Efficient lead time management can enhance customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their supply chain, and enhance their product offerings in the competitive leather market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the different types of leather Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Leather Sector?
The leather market is evolving rapidly, influenced by a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern technology. As of 2024, the global leather market is projected to grow significantly, driven by rising demand in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key trends include the increasing adoption of e-commerce platforms for leather goods, allowing international buyers easier access to diverse products. Additionally, the incorporation of digital technologies such as AI in inventory management and customer service is enhancing the efficiency of sourcing processes.
Another notable trend is the growing preference for high-quality leather types such as full grain and top grain leather. B2B buyers are increasingly recognizing the value of durability and longevity in leather products, which translates to higher customer satisfaction and reduced return rates. In Europe, for instance, there is a noticeable shift towards premium leather goods as consumers seek products that combine quality with aesthetic appeal. Furthermore, the rise of direct-to-consumer brands is altering traditional distribution channels, offering buyers more competitive pricing and unique product offerings.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Leather Sourcing Decisions in B2B?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the leather industry, compelling B2B buyers to prioritize ethical sourcing practices. The environmental impact of leather production, particularly in terms of water usage and chemical waste, has led to increased scrutiny from consumers and regulators alike. As a result, many companies are seeking suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, including the use of vegetable-tanned leathers and recycled materials.
Ethical supply chains are now more important than ever. B2B buyers are looking for ‘green’ certifications, such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification, which assesses the environmental performance of tanneries. Additionally, buyers are increasingly interested in suppliers that can demonstrate transparency in their sourcing processes, showcasing how they mitigate environmental impacts. This focus on sustainability not only meets consumer demand for responsible products but also enhances brand reputation and loyalty.
How Has the Leather Sector Evolved Over Time?
The leather industry has a rich history dating back thousands of years, initially driven by necessity for clothing and shelter. Over time, it has transformed into a sophisticated market characterized by diverse product offerings, from luxury handbags to durable work gear. The evolution of tanning techniques, especially the introduction of chrome tanning in the 19th century, significantly improved leather’s durability and versatility.
In recent decades, the market has shifted towards more specialized leather types, catering to changing consumer preferences and lifestyle trends. Today’s international B2B buyers are not just seeking basic leather goods; they are looking for high-quality, ethically sourced products that align with contemporary values. This evolution reflects a broader trend where craftsmanship meets innovation, creating opportunities for businesses to thrive in a competitive global landscape.
By understanding these dynamics, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with market trends and consumer expectations, ensuring long-term success in the leather sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of different types of leather
-
How do I select the right type of leather for my products?
Choosing the right type of leather depends on your product’s intended use and target market. Full grain leather is ideal for high-end goods due to its durability and unique character, while top grain leather offers a balance of quality and affordability. For fashion items, consider nubuck or patent leather for their luxurious appearance. If your products require resilience, split grain or genuine leather might be more suitable. Assessing your customers’ preferences and the desired aesthetics will guide you in making the best selection. -
What is the best leather type for luxury handbags?
Full grain leather is widely regarded as the best choice for luxury handbags due to its premium quality, durability, and ability to develop a unique patina over time. Top grain leather is also popular, providing a smooth finish while being slightly more affordable. Nubuck leather adds a soft texture, making it an attractive option for a luxe feel, though it requires more maintenance. Ultimately, the choice should align with your brand’s image and your customers’ expectations of quality. -
How can I verify the quality of leather from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of leather, request samples from potential suppliers and conduct a thorough inspection. Look for indicators of quality, such as grain consistency, thickness, and smell. Verify certifications and ask for documentation related to tanning processes and animal welfare standards. Engaging in factory visits can also provide insights into the supplier’s production methods and quality control practices. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can also lead to more transparency regarding their products. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for different types of leather?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely among suppliers based on leather type and production capabilities. Generally, full grain and top grain leathers may have higher MOQs due to their premium nature, often ranging from 100 to 500 square feet. In contrast, split grain and genuine leather may have lower MOQs, sometimes starting at as little as 50 square feet. Always confirm MOQs with suppliers before placing orders, as they can also be negotiable based on your business needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing leather internationally?
Payment terms can differ significantly based on supplier policies and the buyer’s location. Common practices include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50% of the total order) with the remaining balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or deferred payments based on established trust. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect both parties and ensure clarity on currency, payment methods, and timelines to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I ensure the leather is sourced sustainably and ethically?
To source leather sustainably, inquire about the supplier’s sourcing practices and their commitment to ethical standards. Look for certifications such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification, which indicates adherence to environmental and social responsibility. Request information on animal welfare practices and the environmental impact of tanning processes. Building relationships with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance your brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing leather?
When importing leather, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, costs, and customs regulations in your country. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments but may take longer. Familiarize yourself with import duties, tariffs, and any necessary documentation to prevent delays. Working with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the process and ensure compliance with international trade regulations. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I implement when sourcing leather?
Implementing quality assurance measures is crucial for maintaining product standards. Establish clear specifications with your suppliers, including acceptable tolerances for defects and detailed descriptions of the leather’s characteristics. Conduct regular inspections during production and upon receipt of goods. Consider third-party quality audits to ensure compliance with your standards. A robust QA process will help mitigate risks associated with leather defects and ensure customer satisfaction.
Top 5 Different Types Of Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. LeatherNeo – Premium Full Grain & Top-Grain Leather
Domain: leatherneo.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: 1. Full Grain Leather: Top layer of the hide, contains the entire grain, authentic appearance, no buffing or sanding, premium price, develops a unique patina with use, strong, long-lasting, water-resistant, used in furniture, footwear, and saddlery. 2. Top-Grain Leather: Second layer of the hide, buffed or sanded to remove flaws, more supple and comfortable, artificial grain added, improved appear…
2. RubnRestore – Leather Types Explained
Domain: rubnrestore.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Different types of leather include:
1. Full Grain Leather: Finest quality, fully intact hide, may be absorbent or have a pigmented finish.
2. Top Grain Leather: Second best grade, sanded or buffed for a uniform appearance, repels liquids and resists stains.
3. Aniline & Semi-Aniline Leather: Full or top grain, dyed to accentuate fiber variations, prone to stains and fading.
4. Pull-up Leather:…
3. Billy Tannery – Types of Leather
Domain: billytannery.co.uk
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Types of Leather: 1. Full Grain Leather – Highest quality, retains natural state, durable, unique marks, improves with age. 2. Top Grain Leather – Sanded for uniform look, softer finish, less durable. 3. Genuine Leather – Corrected-grain, thinner, weaker, used for cheaper goods. 4. Split Leather – Uses corium section, fragile, low life expectancy. 5. Bonded Leather – Made from scraps mixed with bi…
4. Overland – Leather Types
Domain: overland.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Leather Types: Cowhide, Bison, Deerskin, Goatskin, Lambskin, Calfskin. Cowhide: Strong, thick, durable, water- and dirt-resistant. Bison: Strong, durable, distinctive pebbled grain. Deerskin: Soft, lightweight, contours to form. Goatskin: Soft, lightweight, durable, smooth. Lambskin: Softest, lightweight, flattering drape. Calfskin: Strong, durable, supple, smooth. Leather Grades: Full-Grain Leath…
5. Leather Honey – Leather Care Essentials
Domain: leatherhoney.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Sale Leather Conditioner . from $27.99 $68.95 Sale Leather Cleaner from $18.99 $33.99 Sale Leather Care Kit . $43.99 $70.99
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for different types of leather
In the evolving landscape of leather sourcing, understanding the nuances between various types of leather—such as full grain, top grain, and nubuck—is crucial for international B2B buyers. Each type presents unique characteristics and applications, influencing decisions based on quality, durability, and cost. For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing not only ensures access to high-quality materials but also supports sustainable practices that resonate with today’s conscious consumers.
Investing time in evaluating suppliers and understanding the properties of different leathers can lead to significant long-term benefits. Establishing relationships with reputable manufacturers guarantees consistency in quality and supply, which is essential for meeting market demands. As the leather industry continues to innovate, staying informed about emerging trends and sustainable practices will empower businesses to make informed sourcing decisions.
Looking ahead, now is the time for B2B buyers to leverage these insights and refine their procurement strategies. By prioritizing quality and sustainability, businesses can enhance their product offerings and strengthen their market position. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore diverse leather options, and elevate your brand’s reputation in the global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.