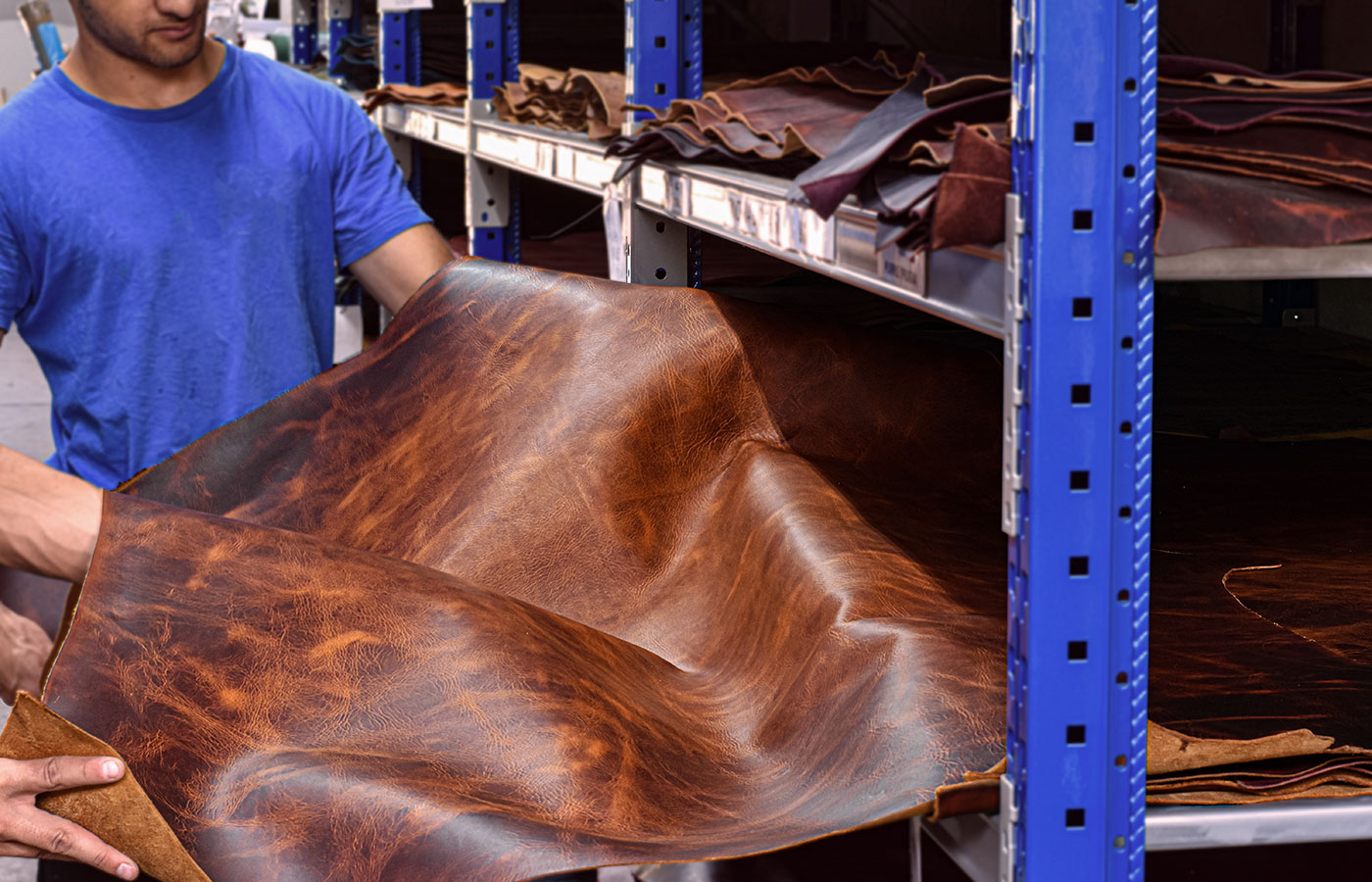
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for genuine leather vs faux leather
In the competitive landscape of global sourcing, distinguishing between genuine leather and faux leather presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With the rising demand for sustainable and ethically sourced materials, understanding the nuances of these materials is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into the key differences between genuine leather and faux leather, examining their types, applications, and the environmental impacts associated with each.
From the durability and aesthetic appeal of genuine leather to the cost-effective and cruelty-free aspects of faux leather, buyers will gain insights that extend beyond mere product selection. We will also provide critical strategies for vetting suppliers, assessing quality, and evaluating costs, ensuring you are equipped to navigate the complexities of the market effectively.
This comprehensive resource is tailored for B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. By empowering you with actionable insights and data-driven recommendations, this guide aims to enhance your sourcing strategies, enabling you to align your purchasing decisions with both business goals and consumer expectations. Discover how to leverage the unique characteristics of these materials to meet your specific needs while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 Genuine Leather Vs Faux Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for genuine leather vs faux leather
- Understanding genuine leather vs faux leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of genuine leather vs faux leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘genuine leather vs faux leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for genuine leather vs faux leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for genuine leather vs faux leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘genuine leather vs faux leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for genuine leather vs faux leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing genuine leather vs faux leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for genuine leather vs faux leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the genuine leather vs faux leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of genuine leather vs faux leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for genuine leather vs faux leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding genuine leather vs faux leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Grain Leather | Made from the top layer of hide, retaining natural grain and imperfections; highly durable. | High-end fashion, luxury goods, furniture | Pros: Long-lasting, develops character; Cons: Higher cost, requires maintenance. |
| Top Grain Leather | Second-highest quality, sanded to remove imperfections; more uniform appearance. | Handbags, wallets, automotive interiors | Pros: Durable, less expensive than full grain; Cons: Less natural feel, may not age as well. |
| Genuine Leather | Made from lower-quality hides; may include bonded leather. | Everyday consumer products, budget-friendly items | Pros: Affordable; Cons: Less durable, can wear out quickly. |
| Faux Leather | Synthetic material (PVC or polyurethane) designed to mimic leather; uniform texture. | Fashion, upholstery, accessories | Pros: Animal-friendly, often cheaper; Cons: Less durable, may have environmental concerns. |
| Vegan Leather | Made from non-animal materials, such as cork or recycled plastics; marketed as environmentally friendly. | Eco-conscious fashion, accessories | Pros: Sustainable options available; Cons: Durability varies, can have a synthetic feel. |
What Are the Characteristics of Full Grain Leather and Its B2B Suitability?
Full grain leather is recognized for its premium quality, made from the outer layer of animal hides. It retains the natural grain, showcasing unique imperfections that enhance its character over time. This type is ideal for high-end fashion, luxury goods, and premium furniture. B2B buyers should consider its longevity and aesthetic appeal, making it a worthwhile investment despite its higher price point. Proper maintenance can further extend its lifespan, providing significant value in the long run.
Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
How Does Top Grain Leather Compare and Where Is It Used?
Top grain leather is slightly lower in quality than full grain but is still highly regarded. It undergoes sanding to remove imperfections, resulting in a more uniform appearance. This type is commonly used in handbags, wallets, and automotive interiors, offering a balance between durability and cost. B2B buyers appreciate its relative affordability while still delivering a quality product. However, it may not age as gracefully as full grain leather, a consideration for buyers focused on long-term value.
What Should Buyers Know About Genuine Leather?
Genuine leather is a broader category that includes lower-quality hides and can sometimes consist of bonded leather. It is typically more affordable and is widely used in everyday consumer products, making it appealing for budget-conscious buyers. However, its durability is often compromised, leading to quicker wear and tear. B2B purchasers should weigh the cost savings against the potential need for more frequent replacements, which could impact overall profitability.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Faux Leather?
Faux leather, made from synthetic materials like PVC or polyurethane, is designed to mimic the look and feel of real leather. It is often used in fashion, upholstery, and accessories due to its affordability and animal-friendly nature. However, its durability is generally inferior to genuine leather, and it may raise environmental concerns during production. B2B buyers should evaluate the intended use and lifecycle of products made from faux leather, as they may require more frequent replacements, impacting overall costs.
How Does Vegan Leather Fit Into the Market?
Vegan leather represents a growing segment of the market, crafted from non-animal materials such as cork or recycled plastics. It is marketed as an environmentally friendly alternative, appealing to eco-conscious consumers. While it offers sustainable options, the durability of vegan leather can vary significantly based on the materials used. B2B buyers should assess the specific characteristics and market demand for vegan leather products, as they can be a unique selling point in an increasingly sustainability-focused landscape.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
Key Industrial Applications of genuine leather vs faux leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of genuine leather vs faux leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion and Apparel | Leather garments (jackets, shoes, handbags) | Genuine leather offers durability and a premium aesthetic; faux leather provides cost-effectiveness and ethical appeal. | Assess material sourcing, production processes, and certifications (e.g., sustainability). |
| Automotive | Upholstery for car interiors | Genuine leather enhances luxury and resale value; faux leather is easier to maintain and can be more affordable. | Evaluate durability, environmental impact, and regional preferences for materials. |
| Furniture | Sofas and seating solutions | Genuine leather provides longevity and comfort; faux leather is lightweight and versatile for various designs. | Consider comfort standards, fire safety regulations, and maintenance requirements. |
| Accessories | Wallets, belts, and small leather goods | Genuine leather products develop character over time; faux leather offers a wide range of styles at lower prices. | Look for quality assurance, brand reputation, and availability of diverse designs. |
| Sporting Goods | Equipment and apparel (e.g., gloves, bags) | Genuine leather offers superior performance and durability; faux leather is often lighter and more affordable. | Ensure compliance with performance standards and assess the environmental impact of materials. |
How is Genuine Leather Used in the Fashion and Apparel Industry?
In the fashion and apparel sector, genuine leather is predominantly used for high-quality garments like jackets, shoes, and handbags. Its durability and luxurious feel appeal to consumers looking for long-lasting products. For B2B buyers, sourcing genuine leather involves ensuring traceability and ethical sourcing, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where consumers may demand transparency regarding animal welfare and environmental practices. Conversely, faux leather is favored for its affordability and ethical considerations, appealing to brands targeting eco-conscious consumers.
What Role Does Leather Play in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, genuine leather is a staple for premium car interiors, enhancing both comfort and the vehicle’s resale value. Buyers in this sector must consider the leather’s durability against wear and tear and its ability to withstand varying climates, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East. Faux leather, while less durable, is often chosen for its cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance, making it suitable for budget-friendly models. Sourcing decisions should also factor in regional preferences and the environmental impact of the materials used.
Why is Leather Important for Furniture Applications?
Genuine leather is highly valued in the furniture industry for creating comfortable, stylish seating solutions. It offers a unique aesthetic that improves with age, appealing to buyers looking for long-term investments. In contrast, faux leather provides a lightweight alternative that can be designed in various styles, catering to different market segments. B2B buyers need to consider compliance with comfort and safety standards, as well as the maintenance requirements of each material, particularly in regions with diverse climates.
How Do Accessories Utilize Leather Materials?
In the accessories market, genuine leather is used for items like wallets, belts, and bags, which often command higher prices due to their quality and craftsmanship. These products develop a distinctive character over time, making them desirable for consumers seeking uniqueness. Faux leather, however, offers a budget-friendly alternative with a wide variety of styles, appealing to cost-conscious buyers. When sourcing, businesses should focus on quality assurance and the reputation of suppliers, especially when targeting international markets that value authenticity and craftsmanship.
What is the Significance of Leather in Sporting Goods?
Leather is commonly used in sporting goods, such as gloves and bags, where its durability and performance characteristics are essential. Genuine leather items often provide superior grip and longevity, making them ideal for professional athletes. On the other hand, faux leather is lighter and more affordable, making it suitable for casual sports enthusiasts. B2B buyers must ensure that sourced products meet performance standards and consider the environmental implications of production, particularly in regions prioritizing sustainability.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘genuine leather vs faux leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Discrepancies in Leather Products
The Problem: For B2B buyers, especially those sourcing leather goods for retail or manufacturing, the differentiation between genuine leather and faux leather can be a significant challenge. Buyers may encounter products labeled as “genuine leather,” yet the quality can vary widely. This inconsistency can lead to customer dissatisfaction and increased return rates, impacting the buyer’s reputation and bottom line. Additionally, buyers from diverse regions like Africa or Europe may face cultural perceptions that affect their purchasing decisions, complicating the quality assessment process.
The Solution: To navigate these quality discrepancies, B2B buyers should establish clear specifications and sourcing guidelines. It’s advisable to partner with reputable suppliers who provide detailed product descriptions, including the type of leather, its source, and the tanning process. Buyers should request samples before making bulk orders, allowing for tactile and visual inspection. Additionally, consider utilizing third-party certification for leather products, which can help ensure authenticity and quality. Engaging in training for staff on how to identify genuine leather through tactile and olfactory methods can also enhance confidence in sourcing decisions.
Scenario 2: Addressing Environmental and Ethical Concerns
The Problem: Environmental sustainability is a growing concern among B2B buyers, particularly in regions where eco-friendly practices are valued. Buyers may struggle with the perception that genuine leather is less sustainable due to animal welfare concerns, while faux leather often involves synthetic materials that can be harmful to the environment. This dichotomy can lead to confusion, as businesses strive to align their product offerings with ethical consumerism trends.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should conduct thorough research into the sourcing and manufacturing processes of both genuine and faux leather products. Opting for genuine leather from suppliers who practice sustainable ranching and natural tanning methods can alleviate ethical concerns. For faux leather, seek out options made from biodegradable or recycled materials. Buyers can also consider establishing a dual-product line, offering both genuine leather and sustainably produced faux leather to cater to a wider customer base. Transparency in marketing efforts about the environmental impact of each product type will also resonate well with ethically conscious consumers.
Scenario 3: Managing Costs versus Long-Term Value
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face a common dilemma between initial costs and long-term value when deciding between genuine leather and faux leather. While faux leather products are often cheaper upfront, they may not withstand wear and tear, leading to higher replacement costs over time. Conversely, genuine leather products, while initially more expensive, can last significantly longer and even improve in appearance with age. This cost-benefit analysis can be particularly challenging for businesses with tight budgets.
The Solution: To manage this dilemma effectively, buyers should conduct a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis for both genuine and faux leather products. This analysis should account for initial purchase price, expected lifespan, maintenance costs, and potential resale value. Engage with suppliers who can provide insights into the durability and lifecycle of their products. Additionally, consider offering warranty options or maintenance services for genuine leather products to enhance their appeal. By presenting a compelling case for the long-term value of genuine leather, buyers can justify the initial investment to stakeholders and ensure a more sustainable purchasing strategy.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for genuine leather vs faux leather
What Are the Key Properties of Genuine Leather?
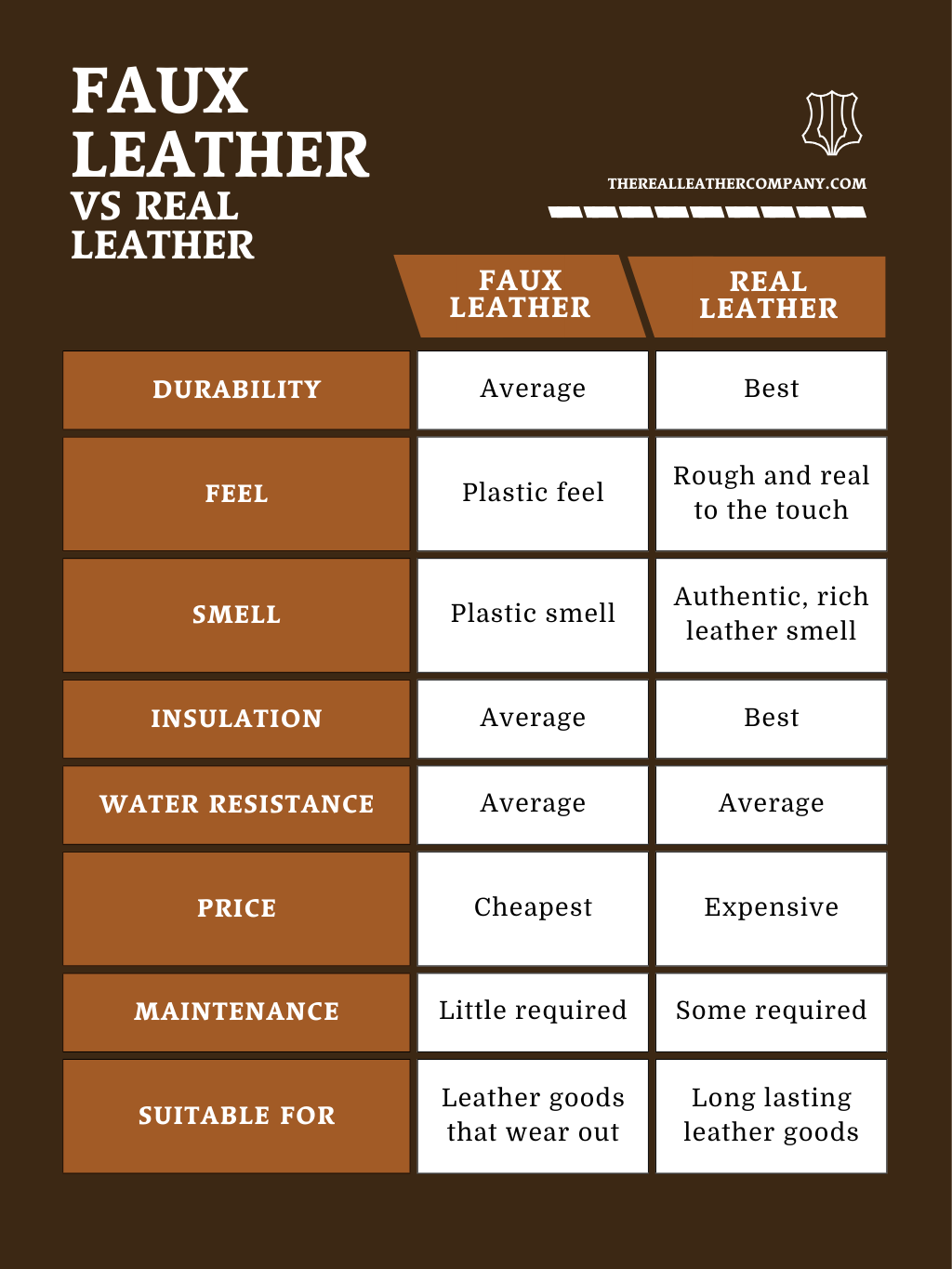
Genuine leather, primarily sourced from animal hides, exhibits unique characteristics that make it a preferred choice for high-quality products. Its temperature resilience allows it to maintain its integrity across various climates, making it suitable for diverse applications, from luxury handbags to automotive interiors. Genuine leather is also resistant to corrosion and wear, developing a patina that enhances its aesthetic appeal over time.
However, the sourcing and processing of genuine leather can be complex and costly. International B2B buyers must consider compliance with animal welfare standards and environmental regulations, particularly in regions where ethical sourcing is a priority. Additionally, genuine leather often comes with a higher price point, which may impact budget considerations for bulk purchases.
How Does Faux Leather Compare in Terms of Performance?
Faux leather, made from synthetic materials like polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offers a more uniform appearance and is generally less expensive than genuine leather. It is lightweight and resistant to moisture, making it a practical choice for products that require easy cleaning, such as upholstery and fashion accessories. Faux leather can also be produced in a variety of colors and textures, providing flexibility in design.
On the downside, faux leather lacks the durability and longevity of genuine leather. It tends to wear out more quickly, especially in high-friction applications, and does not develop the same character over time. For international buyers, it’s essential to assess the environmental impact of faux leather production, especially in regions with stringent sustainability regulations. Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN may also vary depending on the synthetic materials used.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
What Are the Pros and Cons of Suede Leather?
Suede, a type of genuine leather, is known for its soft texture and luxurious feel. It is often used in fashion items and high-end upholstery. Suede is breathable and comfortable, making it ideal for products that require a softer touch. However, it is less resistant to stains and moisture, which can limit its application in certain environments.
From a B2B perspective, suede’s unique properties can cater to niche markets, but its maintenance requirements can be a drawback. Buyers should consider the local climate and the end-use application when selecting suede, as it may not be suitable for humid or wet conditions. Compliance with specific leather treatment regulations is also crucial, especially in regions with strict environmental standards.
How Does Microfiber Leather Fit into the Market?
Microfiber leather, another synthetic alternative, is made from ultra-fine polyester fibers. It mimics the look and feel of genuine leather while offering superior durability and stain resistance. This material is often used in automotive interiors and high-performance applications due to its strength and ease of maintenance.
While microfiber leather is more affordable than genuine leather, it may not appeal to consumers seeking the prestige associated with natural materials. B2B buyers should evaluate the target market’s preferences, as some regions may favor traditional leather over synthetic options. Additionally, understanding the manufacturing processes and ensuring compliance with relevant standards are essential for international transactions.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for genuine leather vs faux leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genuine Leather | Luxury goods, automotive interiors, high-end fashion | Durability and develops character | Higher cost and complex sourcing | High |
| Faux Leather | Upholstery, fashion accessories, budget-friendly products | Cost-effective and easy to clean | Less durable and may wear unattractively | Low |
| Suede Leather | Fashion items, luxury upholstery | Soft texture and breathability | Susceptible to stains and moisture | Med |
| Microfiber Leather | Automotive interiors, high-performance applications | Superior durability and stain resistance | May lack prestige compared to genuine leather | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on performance characteristics, cost considerations, and compliance with regional standards.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for genuine leather vs faux leather
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Genuine Leather and Faux Leather?
Understanding the manufacturing processes for genuine leather and faux leather is essential for B2B buyers seeking quality products. The production stages for both materials include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, but they differ significantly in their techniques and materials used.
How is Genuine Leather Manufactured?
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with sourcing animal hides, primarily from cattle or buffalo. These hides undergo a series of treatments, including cleaning, soaking, and liming, to remove hair and flesh. This step is crucial for achieving the desired quality and characteristics of the leather.
-
Forming: After preparation, the hides are cut into specific shapes according to the product requirements. Techniques such as drum dyeing are employed, where the leather is placed in a rotating drum with dyes, allowing for deep penetration of color.
-
Assembly: The cut pieces of leather are sewn together using specialized stitching techniques. The quality of stitching plays a vital role in the durability of the final product. High-quality leather goods often use reinforced stitching to enhance strength.
-
Finishing: The finishing process involves applying oils, waxes, or protective coatings to enhance the leather’s appearance and durability. This may include polishing to achieve a desired sheen or texture. Genuine leather is also conditioned to maintain its suppleness.
What Are the Manufacturing Steps for Faux Leather?
-
Material Preparation: Faux leather, often referred to as synthetic leather or vegan leather, typically begins with a base of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyurethane. These materials are produced in sheets, which can then be treated to achieve various textures and finishes.
-
Forming: The synthetic material is cut into shapes, similar to genuine leather. Techniques like embossing are commonly employed to mimic the natural grain patterns of leather. This step is crucial for creating a visually appealing product.
-
Assembly: Faux leather pieces are sewn together using similar techniques as genuine leather. However, the stitching may differ in terms of thread type and strength, as synthetic materials often require different handling.
-
Finishing: The finishing process for faux leather involves applying coatings to enhance durability and aesthetics. This can include treatments to make the surface water-resistant or to provide additional texture. Unlike genuine leather, faux leather may not require conditioning.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Commonly Implemented in Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the leather industry to ensure that products meet international standards. Both genuine and faux leather manufacturers often follow rigorous quality control (QC) protocols.
What International Standards Apply to Leather Production?
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for manufacturers to demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: Particularly relevant in Europe, this marking indicates that products conform to health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For manufacturers dealing with leather used in industrial applications, adhering to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards can be crucial.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in Leather Manufacturing?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials for defects before production begins. For genuine leather, this includes checking hides for blemishes and ensuring they meet quality specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, random checks are conducted to ensure adherence to processes and standards. This may involve measuring the thickness of leather or checking the uniformity of synthetic materials.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the products are finished, a final inspection is carried out. This includes checking for stitching accuracy, surface quality, and overall appearance. Any defective items are typically reworked or discarded.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who implement robust QC measures. Here are actionable steps to verify quality control:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the production processes and adherence to quality standards. Buyers can request to observe the manufacturing process and assess compliance.
-
Review QC Reports: Request detailed QC reports from suppliers, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checkpoints. This documentation can help buyers understand the level of quality control exercised during production.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engage independent third-party inspection services to evaluate the quality of products before shipment. These inspections can provide an unbiased assessment of product quality and compliance with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to understand the local regulations and market expectations.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers comply with both international and local regulations governing leather production. This can vary significantly from one region to another.
-
Cultural Preferences: Different markets may have varying preferences for leather products, impacting quality standards. For example, European buyers may prioritize eco-friendly practices, while Middle Eastern markets may focus on durability and luxury.
-
Traceability and Sustainability: Increasingly, buyers are interested in sustainable sourcing and traceability in the leather supply chain. Suppliers should be prepared to provide information on the sourcing of hides and the environmental impact of their processes.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for both genuine and faux leather, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their quality expectations and market needs.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘genuine leather vs faux leather’
Introduction
In the competitive world of B2B procurement, understanding the nuances between genuine leather and faux leather is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist tailored for international buyers, focusing on key factors such as quality, sustainability, and supplier reliability. By following these steps, you can ensure that your sourcing process aligns with your business values and market expectations.
Step 1: Identify Your Product Requirements
Begin by clearly defining the specific products you need, whether it’s bags, upholstery, or accessories. Understanding the intended use will help you determine the right material. For instance, if durability and a premium feel are essential, genuine leather may be preferable. Conversely, for cost-sensitive or fashion-oriented items, faux leather might suffice.
Step 2: Research Material Characteristics
Familiarize yourself with the characteristics of both genuine and faux leather. Genuine leather is known for its unique texture and longevity, while faux leather offers a uniform appearance and lower cost. Consider the following:
– Durability: Genuine leather typically lasts longer and develops a desirable patina over time.
– Maintenance: Faux leather requires less upkeep but may wear out unattractively.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers possess relevant certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards. This step is vital for verifying the quality and ethical sourcing of materials. Look for certifications such as:
– ISO certifications for quality management.
– Environmental certifications indicating sustainable practices.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
Step 4: Request Material Samples
Always request samples of both genuine and faux leather from potential suppliers. This allows you to assess the tactile and visual qualities firsthand. Pay attention to:
– Texture: Genuine leather should feel warm and slightly uneven, while faux leather will feel uniformly smooth.
– Odor: Genuine leather has a distinctive, organic smell, whereas faux leather often emits a chemical scent.
Step 5: Assess Environmental Impact
Consider the environmental implications of your choice. Genuine leather can be more sustainable if sourced from responsible ranches, while faux leather often involves petroleum-based materials that can have a higher environmental cost. Ask suppliers about their sourcing practices and any initiatives they have in place to mitigate environmental impact.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers, ensuring that you compare similar quality levels. While pricing is crucial, also evaluate the terms of sale, including:
– Minimum order quantities: Understand the implications for your inventory.
– Payment terms: Check for flexibility, especially if you’re dealing with international transactions.
Step 7: Check Supplier Reputation and Reviews
Before finalizing your supplier, research their reputation in the industry. Look for reviews and testimonials from other buyers, especially those in your region. This insight can provide valuable context regarding their reliability and product quality. Engaging in conversations with other businesses can also yield recommendations or warnings about potential suppliers.
By following this checklist, you can navigate the complexities of sourcing genuine leather versus faux leather with confidence, ensuring that your procurement aligns with your business objectives and market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for genuine leather vs faux leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Genuine Leather and Faux Leather?
When considering the sourcing of genuine leather versus faux leather, understanding the cost structure is paramount. Each material presents distinct cost components that can influence overall pricing.
Materials: Genuine leather is sourced from animal hides, primarily cattle, which can be costly due to the raw material’s price fluctuations influenced by livestock availability and market demand. Faux leather, made from synthetic materials like PVC or polyurethane, generally has lower material costs. However, the quality of the synthetic material can vary significantly, impacting the overall cost.
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: The labor costs associated with processing genuine leather tend to be higher. Skilled artisans are often required for cutting, stitching, and finishing, especially for high-quality leather products. In contrast, faux leather production often involves automated processes, which can reduce labor costs but may compromise craftsmanship.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
Tooling and Quality Control (QC): Tooling costs can be significant for both materials, especially if custom designs are required. Quality control processes are crucial for both leather types, but the standards may differ, leading to varying costs. Genuine leather may require more rigorous QC due to its natural imperfections, while faux leather’s uniformity can simplify the QC process.
Logistics and Margin: The logistics costs for transporting genuine leather can be higher due to its weight and the need for careful handling. Conversely, faux leather is lighter and easier to ship, potentially lowering logistics costs. Margins will depend on the supplier’s pricing strategy, with genuine leather often commanding higher margins due to its perceived value.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors influence the pricing of genuine and faux leather, particularly for international B2B buyers.
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer better pricing on higher volumes. For genuine leather, this could mean negotiating for larger orders to benefit from economies of scale. Faux leather suppliers may have more flexible MOQ policies, allowing buyers to test different products without committing to large orders.
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs for both materials. Genuine leather offers opportunities for bespoke designs, which can enhance value but also increase costs. Faux leather can be customized, but variations in quality must be accounted for, potentially impacting pricing.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
Quality and Certifications: Genuine leather often comes with certifications that can affect cost. Buyers should consider whether certifications such as sustainability or cruelty-free sourcing are important for their brand. Faux leather may have fewer certification options, but buyers should verify the quality to avoid low-cost, subpar products.
Supplier Factors and Incoterms: The choice of supplier can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers with a reputation for quality may charge more. Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they dictate who bears the costs and risks during shipping.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost Efficiency?
B2B buyers should adopt strategic approaches to maximize cost efficiency when sourcing leather products.
Negotiation Strategies: Always negotiate with suppliers to secure the best possible prices, especially when dealing with genuine leather. Use volume commitments to leverage better terms.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the upfront price. Genuine leather may have a higher initial cost but offers durability, potentially reducing replacement costs over time. Faux leather may seem cheaper initially, but its shorter lifespan can lead to higher long-term expenses.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers must be aware of additional costs such as import duties, taxes, and currency fluctuations. These factors can significantly impact the final price, so it’s crucial to factor them into budgeting.
In conclusion, the choice between genuine leather and faux leather involves a nuanced understanding of costs, pricing influencers, and strategic buying practices. By carefully evaluating these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals and market demands.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing genuine leather vs faux leather With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Genuine Leather and Faux Leather
In the evolving landscape of materials used for fashion, upholstery, and various products, both genuine leather and faux leather have established their unique niches. However, several alternative solutions are available that can fulfill similar purposes while offering distinct advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these options can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
| Comparison Aspect | Genuine Leather Vs Faux Leather | Alternative 1 Name (Recycled Materials) | Alternative 2 Name (Cork Leather) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, ages well, unique character | Varies based on material, less durable | Water-resistant, durable |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Generally lower cost | Moderate cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled craftsmanship | Readily available and easy to use | Requires specialized processing |
| Maintenance | Needs regular care to maintain quality | Low maintenance | Minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Luxury goods, long-lasting items | Fast fashion, eco-friendly products | Sustainable fashion, accessories |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Recycled Materials?
Recycled materials, such as those derived from plastic bottles or textile waste, present a sustainable alternative to traditional leather products. One of the significant advantages of recycled materials is their lower cost compared to genuine leather. Additionally, they cater to the growing demand for eco-friendly products, making them attractive to brands focused on sustainability. However, the performance can vary significantly based on the specific material used, and they may not offer the same durability or aesthetic appeal as leather. This makes them more suitable for fast fashion items rather than luxury goods.
How Does Cork Leather Compare as an Alternative?
Cork leather, made from the bark of cork oak trees, is another innovative alternative. Its water-resistant properties and natural durability make it an excellent choice for various products, including bags and footwear. Cork leather is also lightweight and easy to clean, which adds to its appeal. However, it is a niche product and may not yet have the widespread recognition or availability of traditional leather options. While it offers a unique aesthetic, it may not resonate with all consumers, particularly those seeking the classic look of genuine leather.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting between genuine leather, faux leather, and alternative materials, B2B buyers must assess their specific needs, budget constraints, and target market preferences. Genuine leather is ideal for high-end products where durability and aesthetics are paramount. Faux leather offers a cost-effective solution for brands aiming for a more sustainable image without the commitment of genuine leather. Meanwhile, alternatives like recycled materials and cork leather cater to eco-conscious consumers, providing a unique selling proposition. By understanding the characteristics and best use cases for each option, buyers can align their choices with their brand values and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for genuine leather vs faux leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Comparing Genuine Leather and Faux Leather?
When evaluating genuine leather and faux leather for B2B purchases, several technical properties are critical to making informed decisions. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Composition
- Genuine Leather: Derived from animal hides, primarily cow, lamb, or goat. It retains natural characteristics and breathability.
- Faux Leather: Typically made from synthetic materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyurethane (PU). It offers a uniform appearance but lacks the organic traits of genuine leather.
Importance: Understanding material composition helps in assessing durability, maintenance, and environmental impact, influencing buyer preferences based on ethical or sustainability considerations.
2. Grade and Tannage
- Grade: Refers to the quality of leather, which can be full-grain, top-grain, genuine, or bonded. Full-grain is the highest quality, retaining the natural grain and imperfections.
- Tannage: The process of treating animal hides to make them durable and resistant to decay. Vegetable tanning is eco-friendly, while chrome tanning is faster but can have environmental concerns.
Importance: Knowledge of grade and tanning methods is crucial for buyers to ensure they are sourcing high-quality materials that meet industry standards.
3. Durability and Wear Resistance
- Genuine Leather: Known for its longevity, it can last decades with proper care, developing a unique patina over time.
- Faux Leather: Generally less durable, with a lifespan of only a few years, often showing wear unattractively.
Importance: Durability affects long-term cost and value, making it essential for businesses to consider the lifespan of products when sourcing materials.
4. Maintenance Requirements
- Genuine Leather: Requires regular conditioning and cleaning to maintain its appearance and prevent drying or cracking.
- Faux Leather: Easier to clean with basic soap and water, but may not withstand rigorous use.
Importance: Understanding maintenance needs can influence inventory management and customer satisfaction, as products that require less upkeep may appeal more to certain markets.
5. Environmental Impact
- Genuine Leather: When sourced sustainably, it can have a lower environmental impact than faux alternatives, which often involve harmful chemicals in production.
- Faux Leather: While marketed as “vegan,” its production can contribute to pollution and waste.
Importance: As sustainability becomes a priority for consumers and businesses alike, understanding the environmental implications of materials can enhance brand reputation and compliance with regulatory standards.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Leather Industry?
In addition to technical properties, familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms:

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In leather, this often involves companies that create custom leather goods for brands.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This is vital for B2B buyers to know as it affects inventory costs and cash flow.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A document used to solicit price offers from suppliers. This is a critical step in the procurement process, ensuring competitive pricing and clear expectations.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standard trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. Understanding these terms helps in risk management and logistics planning.
5. Grain
Refers to the surface texture of leather, including full-grain, top-grain, and corrected grain. The grain affects the aesthetic and functional properties of the leather.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting between genuine and faux leather products, ultimately leading to better purchasing outcomes and customer satisfaction.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the genuine leather vs faux leather Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends in the Genuine Leather vs Faux Leather Sector?
The global leather market is experiencing dynamic shifts fueled by changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and economic factors. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of these trends to make informed sourcing decisions. One significant driver is the rising demand for sustainable products. Consumers increasingly prefer materials that align with their values, which has led to the emergence of eco-friendly alternatives and the so-called “vegan leather.”
Moreover, advancements in manufacturing technologies have improved the quality of faux leather, making it a more viable competitor to genuine leather. This includes innovations in durability and texture, which allow faux leather to mimic the appearance and feel of real leather more closely than ever before. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated e-commerce growth, prompting B2B buyers to seek flexible, online sourcing options, including direct-from-manufacturer deals and digital marketplaces.
As the global market evolves, buyers must also consider regional economic factors. For example, in the Middle East, luxury goods, including high-quality leather products, continue to see robust demand, while African markets may prioritize affordability and durability. Understanding these nuances will be essential for successful procurement strategies.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Leather Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone in the leather industry, impacting how B2B buyers approach sourcing. Genuine leather, when sourced from sustainable ranches and responsibly tanned, can have a lower environmental footprint than synthetic options, which often rely on non-biodegradable materials like PVC and polyurethane. This environmental perspective is crucial as buyers increasingly seek products that do not contribute to pollution or waste.
Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to partner with suppliers who provide transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) and Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) are becoming important benchmarks for evaluating the sustainability of leather products. These certifications ensure that the leather is sourced responsibly, adhering to environmental standards and ethical labor practices.
The importance of these practices cannot be overstated, as consumers are more likely to support brands that prioritize sustainability. For B2B buyers, aligning with suppliers that share these values can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty, ultimately leading to increased sales and market share.
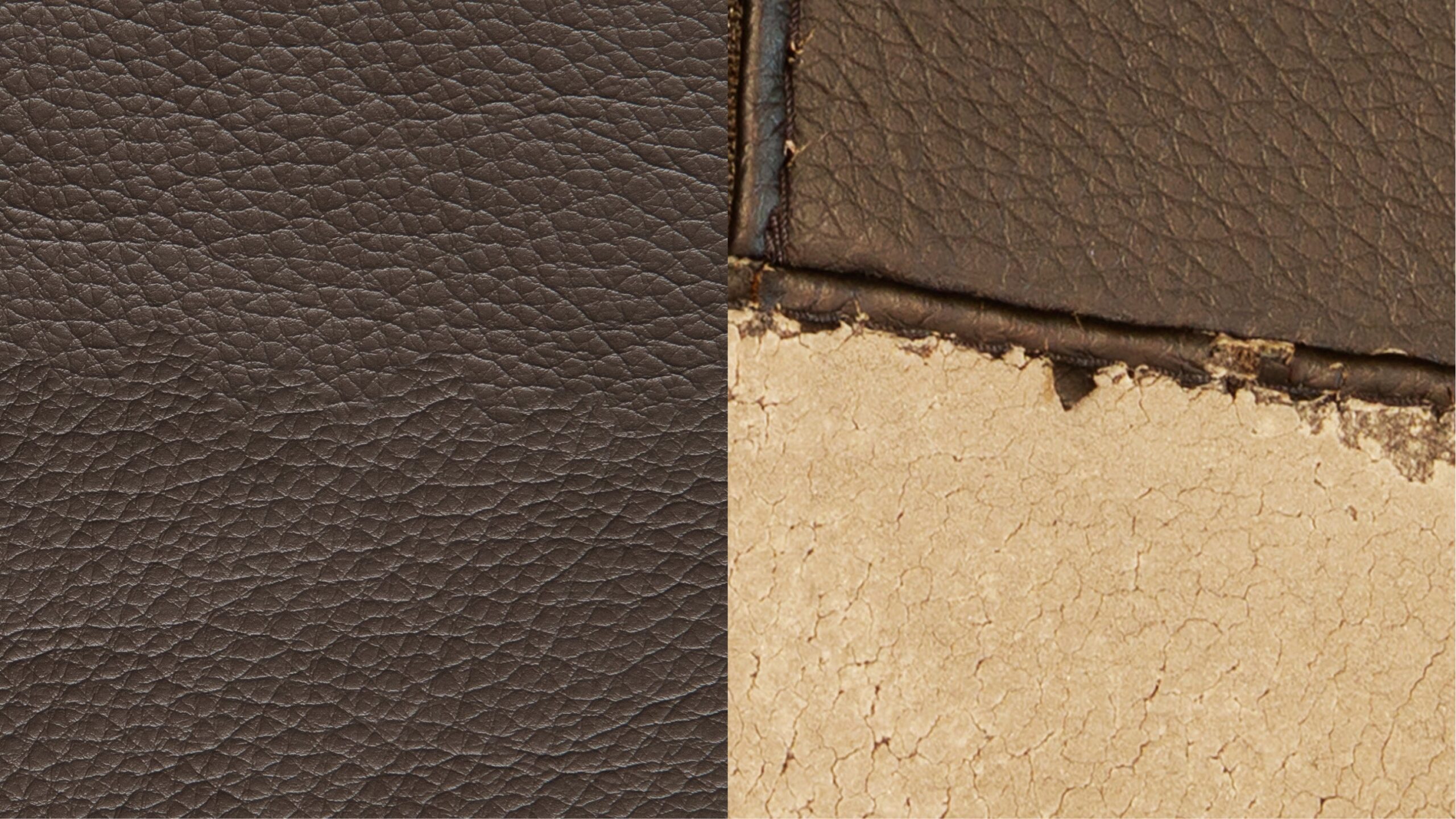
How Has the Leather Industry Evolved Over Time?
The leather industry has a rich history dating back thousands of years, evolving from traditional methods of animal hide processing to modern, technology-driven production techniques. Initially, leather was primarily a byproduct of the meat industry, with tanners using rudimentary methods to process animal skins.
As demand grew, particularly in luxury markets, the industry adapted, introducing more sophisticated tanning processes and expanding into a variety of products, from apparel to furniture. The late 20th century saw the rise of synthetic alternatives, driven by technological advancements and a growing consumer base concerned with animal rights.
Today, the market is at a crossroads, with genuine leather and faux leather coexisting. Each has its unique advantages and challenges, shaping sourcing strategies for B2B buyers. Understanding the historical context of these materials can provide valuable insights for navigating current market dynamics and anticipating future trends.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of genuine leather vs faux leather
-
How do I determine the quality of genuine leather when sourcing?
To assess the quality of genuine leather, look for indicators such as the grain, smell, and texture. High-quality leather often has natural imperfections and a rich, organic scent. Request samples from suppliers to evaluate their products firsthand. Additionally, inquire about the tanning process and the source of the hides, as sustainable and ethical practices often correlate with better quality. Certifications or third-party inspections can also provide assurance of quality and authenticity. -
What is the best faux leather option for budget-conscious businesses?
For businesses prioritizing cost without sacrificing quality, polyurethane (PU) faux leather is often the best choice. It offers a more realistic appearance and feel compared to PVC, making it suitable for various applications like upholstery and accessories. When sourcing, seek suppliers that specialize in high-quality PU materials to ensure durability and aesthetic appeal. Also, consider ordering samples to compare different options before committing to a larger order. -
How can I ensure ethical sourcing of leather products?
To ensure ethical sourcing, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for those that provide transparency about their supply chain and have certifications related to environmental sustainability and animal welfare. Establish relationships with suppliers who prioritize ethical practices, such as using hides from animals raised for food. Additionally, consider third-party audits or certifications that verify ethical sourcing, which can enhance your brand’s reputation in the market. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing leather?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and type of leather. For genuine leather, MOQs typically range from 100 to 500 square meters, while faux leather may have lower MOQs due to its synthetic nature. It’s crucial to communicate your specific needs to suppliers and negotiate MOQs that suit your business model. Some suppliers may be flexible, especially for first-time orders or long-term partnerships. -
What payment terms are standard in the leather sourcing industry?
Payment terms in the leather sourcing industry can vary widely, but common practices include a deposit of 30-50% upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or before shipment. Letters of credit and escrow services are also popular for larger transactions, providing security for both parties. When negotiating, ensure that payment terms align with your cash flow and financial strategies. Establishing clear terms in the contract can prevent misunderstandings and build trust with your suppliers. -
How do I vet suppliers for quality assurance in leather products?
Vetting suppliers involves several steps: first, verify their business credentials and reputation through references and reviews. Request product samples to evaluate quality firsthand. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including testing for durability and compliance with international standards. Consider conducting factory visits or audits, if feasible, to assess production practices and working conditions, ensuring they meet your quality and ethical standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing leather?
When importing leather, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and duty fees. Evaluate whether air or sea freight aligns with your timeline and budget, as air freight is faster but more expensive. Familiarize yourself with the import regulations in your country, including any restrictions on animal products. Collaborating with a logistics provider experienced in international trade can streamline the process and help navigate potential challenges. -
How can I customize leather products for my brand?
Customization options for leather products can range from choosing specific colors and textures to adding logos or unique designs. Work closely with your supplier to discuss available customization services, including embossing, stitching, or hardware options. Provide clear specifications and prototypes to ensure your vision is accurately translated into the final product. Establishing a strong partnership with your supplier can also facilitate ongoing customization needs as your brand evolves.
Top 2 Genuine Leather Vs Faux Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Buffalo Jackson – Authentic Leather Goods
Domain: buffalojackson.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Real leather is made from animal hides (buffalo or cattle), while faux leather is made from PVC or polyurethane. Real leather has a natural surface with imperfections, feels warm and stretches when pressed, and has a distinctive leathery smell. Faux leather has a uniform surface, feels cold and does not stretch, and has a plasticky smell. Real leather is more durable and develops character over ti…
2. Reddit – Pure Leather vs. Vegan Leather
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Pure leather is real leather, known for its durability and longevity, often lasting years with proper care. It is considered more environmentally friendly in the long run compared to vegan leather, which is typically made from plastic. Vegan leather may be easier to care for as it can be wiped clean, but it generally breaks down quicker than pure leather. Some users have reported issues with faux …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for genuine leather vs faux leather
As the global market continues to evolve, B2B buyers must carefully evaluate the strategic sourcing of genuine leather versus faux leather. Genuine leather stands out for its durability, unique aesthetics, and potential for sustainable sourcing when managed responsibly. Its longevity often translates to better value over time, making it a wise investment for businesses focused on quality and brand reputation. Conversely, faux leather appeals to buyers looking for cost-effectiveness and ethical considerations, particularly in regions where animal welfare is a concern. However, the environmental impact of synthetic materials must be factored into the decision-making process, as faux leather typically has a shorter lifespan and may lead to increased waste.
Moving forward, international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider their market’s specific demands and consumer preferences when sourcing leather products. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices can enhance your brand’s credibility and align with growing global trends toward eco-friendly materials. By making informed choices, businesses can not only satisfy customer expectations but also position themselves as leaders in responsible sourcing. Embrace the opportunity to explore innovative leather solutions that meet your strategic goals today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to genuine leather vs faux leather