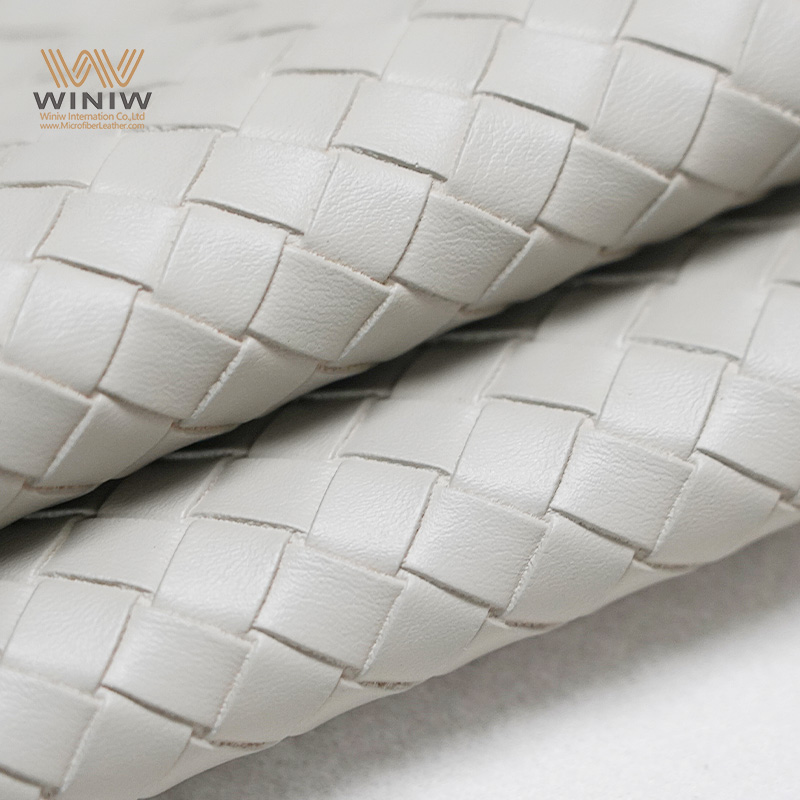
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather definition
Navigating the intricate landscape of faux leather sourcing can be daunting, particularly for B2B buyers seeking sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to genuine leather. Faux leather, a synthetic material crafted from PVC or polyurethane, offers a versatile solution for various applications, from fashion to upholstery. However, understanding the nuances of this material—such as its production processes, environmental impact, and market dynamics—is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of faux leather, covering critical aspects such as types, applications, and supplier vetting processes. We will explore the different manufacturing techniques, highlight key players in the global market, and provide insights into pricing structures that can help buyers from regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Nigeria and Brazil, navigate their sourcing decisions effectively.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and a thorough understanding of faux leather, this guide aims to empower your business to make strategic choices that align with both market demands and ethical considerations. As the demand for sustainable and animal-friendly materials continues to rise, understanding the full spectrum of faux leather will be key to staying competitive and meeting consumer expectations.
Table Of Contents
- Top 5 Faux Leather Definition Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather definition
- Understanding faux leather definition Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of faux leather definition
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather definition’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather definition
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather definition
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather definition’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather definition Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather definition With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather definition
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather definition Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather definition
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather definition
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding faux leather definition Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Soft, flexible, and resembles genuine leather | Upholstery, fashion accessories, automotive | Pros: Durable, versatile colors; Cons: May be less resistant to heat and moisture. |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Economical, water-resistant, and sturdy | Furniture coverings, luggage, clothing | Pros: Cost-effective, good for heavy use; Cons: Less breathable, can feel plastic-like. |
| Cuir végétalien | Made from sustainable materials, often plant-based | Eco-friendly fashion, accessories, upholstery | Pros: Ethical choice, biodegradable options; Cons: Availability may vary, price can be higher. |
| Naugahyde | Brand-specific, known for its durability | Automotive upholstery, commercial furniture | Pros: Highly durable, stain-resistant; Cons: Brand recognition can limit choices. |
| Cuir microfibre | Ultra-soft texture, lightweight, and durable | Clothing, accessories, upholstery | Pros: Soft feel, easy to clean; Cons: May not hold up as well under extreme conditions. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Polyurethane (PU) Faux Leather?
Polyurethane (PU) faux leather is prized for its soft texture and flexibility, closely mimicking the feel of genuine leather. It is widely used in various applications, including upholstery for furniture, fashion accessories, and automotive interiors. B2B buyers should consider PU’s versatility in color and design, making it suitable for diverse markets. However, its heat and moisture resistance can be lower than that of genuine leather, which may affect its longevity in demanding environments.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
How Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Faux Leather Compare?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a cost-effective option that offers water resistance and durability, making it a popular choice for furniture coverings, luggage, and clothing. Its affordability is attractive to B2B buyers looking to meet budget constraints, especially in emerging markets. However, PVC is less breathable than other materials and can feel plastic-like, which may not appeal to all consumers. Buyers should weigh these factors when deciding on PVC for their product lines.
Why Choose Vegan Leather for Sustainable Practices?
Vegan leather is increasingly popular among environmentally conscious brands, as it is often made from sustainable materials, including plant-based fibers. This type of faux leather is suitable for eco-friendly fashion, accessories, and upholstery, appealing to a growing market segment focused on sustainability. While the ethical benefits are significant, B2B buyers should consider the availability and potential higher costs associated with vegan leather, which may impact their pricing strategies.
What Makes Naugahyde a Reliable Choice for B2B Buyers?
Naugahyde, a well-known brand of synthetic leather, is recognized for its exceptional durability and stain resistance, making it ideal for automotive upholstery and commercial furniture. B2B buyers can leverage its brand reputation when marketing products, ensuring a level of trust among consumers. However, the brand’s dominance may limit options, so buyers should explore alternatives that meet their specific needs while maintaining quality.
How Does Microfiber Leather Fit into the Market?
Microfiber leather is characterized by its ultra-soft texture and lightweight nature, making it a popular choice for clothing, accessories, and upholstery. Its ease of cleaning is a significant advantage for B2B buyers, especially in industries where hygiene is paramount. However, its performance in extreme conditions may not match that of other materials, so buyers should assess their target market’s requirements to ensure microfiber leather aligns with their product offerings.
Key Industrial Applications of faux leather definition
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of faux leather definition | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Upholstery for car interiors | Durable, easy to clean, and cost-effective alternative to leather | Supplier reliability, compliance with automotive standards, and color/texture options |
| Fashion and Apparel | Handbags, jackets, and footwear | Versatile design options, ethical production, and lower cost than genuine leather | Material quality, customization capabilities, and ethical sourcing practices |
| Furniture and Upholstery | Sofas and chairs | Cost-effective, stain-resistant, and easy maintenance for high-traffic areas | Durability, compliance with fire safety standards, and availability of diverse textures |
| Sports Equipment | Protective gear and sports apparel | Enhanced durability, weather resistance, and lightweight properties | Performance specifications, compliance with safety regulations, and availability in various colors |
| Home Décor | Wall coverings and decorative items | Aesthetic appeal, easy installation, and low maintenance | Material sourcing, environmental impact, and design flexibility |
How is Faux Leather Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, faux leather is primarily used for car interiors, including seats, door panels, and dashboards. Its durability and ease of cleaning make it an attractive alternative to genuine leather, particularly for vehicles in markets with high humidity or where maintenance is challenging. International buyers, especially from regions like Nigeria and Brazil, need to consider supplier reliability and compliance with automotive industry standards, ensuring that the materials can withstand wear and tear while also meeting aesthetic demands.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
What are the Benefits of Faux Leather in Fashion and Apparel?
Faux leather has gained significant traction in the fashion and apparel industry, where it is used in handbags, jackets, and footwear. This material offers designers versatile color and texture options while adhering to ethical production practices, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. For B2B buyers, especially in Europe and South America, assessing material quality and customization capabilities is crucial to meet local consumer preferences and regulatory requirements.
How Does Faux Leather Enhance Furniture and Upholstery?
In furniture and upholstery, faux leather is commonly used for sofas and chairs, providing a cost-effective solution that resists stains and is easy to maintain. This is particularly beneficial in high-traffic areas, such as homes with children or pets. Buyers from the Middle East and Africa should focus on the durability of the material and compliance with fire safety standards, as these factors can significantly impact product longevity and safety in commercial settings.
What Role Does Faux Leather Play in Sports Equipment?
Faux leather is increasingly utilized in sports equipment, including protective gear and apparel, due to its lightweight and weather-resistant properties. This makes it suitable for various sports, especially in regions with varying climates. International B2B buyers should prioritize performance specifications and compliance with safety regulations when sourcing faux leather for sports applications, ensuring that the products can withstand rigorous use while maintaining comfort and style.
How is Faux Leather Applied in Home Décor?
In the realm of home décor, faux leather is used for wall coverings and decorative items, offering aesthetic appeal and ease of installation. Its low maintenance requirements make it suitable for both residential and commercial spaces. Buyers, particularly in emerging markets, should consider the environmental impact of sourcing faux leather and seek suppliers that provide sustainable options without compromising on design flexibility.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather definition’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding Faux Leather Specifications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties in distinguishing between various types of faux leather due to the wide range of terms used in the industry, such as pleather, vegan leather, and synthetic leather. This confusion can lead to sourcing the wrong materials, resulting in products that do not meet quality standards or customer expectations. For instance, a manufacturer might expect high durability and moisture resistance from a product labeled as faux leather, only to find out it is made from a lower-quality material that does not perform as required.
The Solution: To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should establish clear specifications and requirements before sourcing faux leather. This includes understanding the manufacturing processes and material compositions such as PVC or PU, as well as the specific applications for which they are intended. Engaging with suppliers who can provide detailed product specifications, including breathability, stretchability, and durability ratings, is essential. Buyers should also ask for samples and conduct tests to ensure the material meets their quality expectations. Collaborating with suppliers who have a strong reputation and transparency in their production methods can significantly reduce the risk of miscommunication and dissatisfaction.
Scenario 2: Navigating Environmental Concerns with Faux Leather
The Problem: As global awareness of environmental issues rises, B2B buyers face challenges in reconciling the benefits of faux leather with its environmental impact. Many traditional faux leathers are made from petroleum-based products, which raise concerns about sustainability and biodegradability. Companies in regions like Europe, where there is a strong push for eco-friendly products, may struggle to find reliable suppliers who offer environmentally responsible options without compromising on quality.
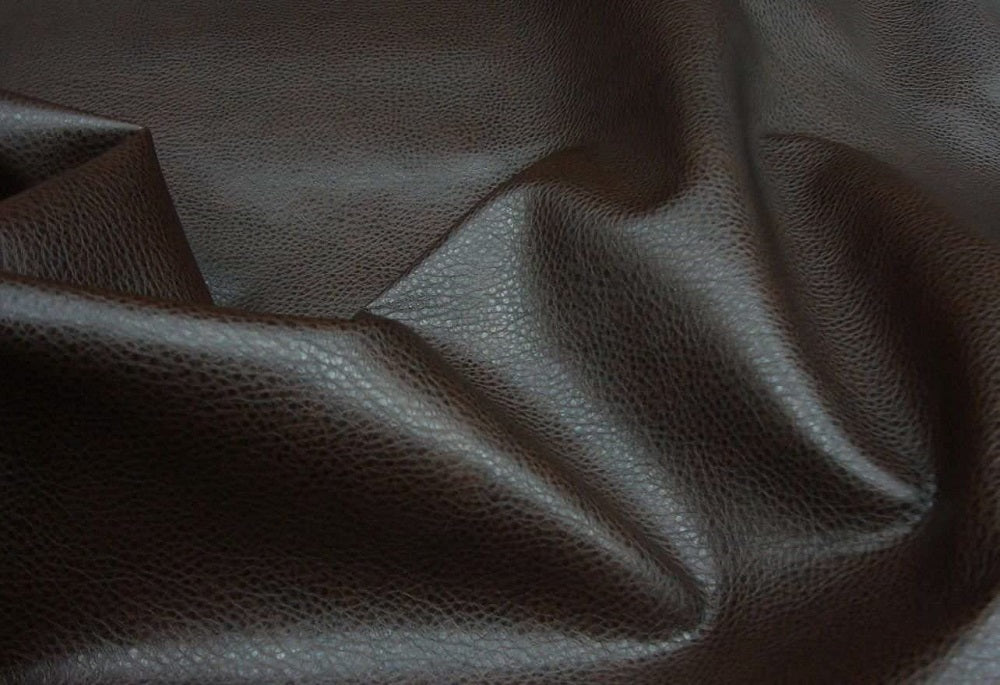

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing faux leather that is made from sustainable materials, such as vegetable-based synthetic leather, which addresses both ethical and environmental concerns. When evaluating suppliers, it is crucial to inquire about their production processes and certifications related to sustainability. Buyers can also request lifecycle assessments of the materials to better understand their environmental impact. By aligning purchasing decisions with sustainable practices, companies not only meet regulatory demands but also enhance their brand reputation among eco-conscious consumers. Additionally, forming partnerships with suppliers who prioritize innovation in sustainable materials can lead to more competitive product offerings.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Product Quality and Consistency in Faux Leather
The Problem: Quality inconsistency is a common issue in the faux leather market, especially when sourcing from different suppliers or regions. Variations in manufacturing processes can result in differences in texture, durability, and color matching, which can significantly affect the final product’s appeal. For instance, a furniture manufacturer may receive faux leather upholstery that varies in quality from batch to batch, leading to customer complaints and increased returns.
The Solution: To ensure consistency in product quality, B2B buyers should implement stringent quality control measures and establish long-term relationships with a select group of reliable suppliers. This includes conducting regular audits of supplier facilities and processes to ensure they adhere to specified quality standards. Buyers should also consider setting up a quality assurance team responsible for inspecting incoming materials before they are used in production. Additionally, developing a standardized sample approval process can help maintain consistency across different batches, ensuring that every product meets the expected quality criteria. By focusing on quality assurance, companies can minimize disruptions in production and enhance customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather definition
What Are the Key Materials Used in Faux Leather Production?
Faux leather is primarily produced using synthetic materials, with the most common being Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and Polyurethane (PU). Each of these materials has distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly influence their suitability for various applications. Understanding these materials is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Perform in Faux Leather Applications?
PVC is a widely used synthetic polymer known for its versatility and cost-effectiveness. It offers a range of properties that make it suitable for various faux leather applications, including upholstery and fashion accessories.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
Key Properties: PVC is resistant to abrasion and can withstand moderate temperatures, making it suitable for various environments. However, its breathability is low, which may affect comfort in apparel applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PVC is its affordability and availability, making it an attractive option for manufacturers. However, it is less durable than PU and can be less environmentally friendly due to its production process and non-biodegradability.
Impact on Application: PVC faux leather is particularly suitable for products requiring durability, such as furniture coverings and bags. However, its limited breathability may restrict its use in apparel, especially in warmer climates.
Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding PVC use, especially in Europe, where stringent standards exist. Understanding the environmental impact of PVC is also crucial, as consumers increasingly prefer sustainable materials.
What Advantages Does Polyurethane (PU) Offer in Faux Leather Production?
Polyurethane is another popular material used in faux leather production, known for its superior flexibility and softness compared to PVC.
Key Properties: PU offers excellent abrasion resistance and can mimic the feel of genuine leather closely. It also has better breathability, making it more comfortable for wear in clothing applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PU is its high-quality finish and durability, making it suitable for high-end applications. However, it tends to be more expensive than PVC, which may affect cost-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: PU is widely used in fashion items, automotive interiors, and high-quality upholstery due to its aesthetic appeal and comfort. Its breathability makes it particularly suitable for garments and accessories.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that PU products meet relevant international standards such as ASTM or DIN, especially for automotive applications. Additionally, the growing trend towards sustainable materials is prompting manufacturers to explore bio-based PU options.
How Do Vegetable-Based Faux Leather Alternatives Compare?
In response to environmental concerns, some manufacturers are developing vegetable-based faux leather alternatives. These materials aim to provide a more sustainable option without compromising on quality.
Key Properties: Vegetable-based faux leather typically offers similar durability and aesthetic qualities as traditional synthetic options. However, their performance can vary based on the specific formulation and production process.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
Pros & Cons: The main advantage is their reduced environmental impact, appealing to eco-conscious consumers. However, they may not yet match the durability and cost-effectiveness of PVC and PU, which can limit their adoption.
Impact on Application: These materials are suitable for applications where sustainability is a key selling point, such as eco-friendly fashion and furniture. However, their relatively higher cost may deter some manufacturers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for certifications that verify the sustainability claims of vegetable-based materials. Understanding local market preferences for eco-friendly products can also provide a competitive advantage.
Summary Table of Faux Leather Materials
| Matériau | Typical Use Case for faux leather definition | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Upholstery, bags, and low-cost fashion items | Cost-effective and durable | Low breathability and environmental concerns | Low |
| Polyurethane (PU) | High-end fashion, automotive interiors, and quality upholstery | Soft feel and better breathability | Higher cost compared to PVC | Medium |
| Vegetable-Based Faux Leather | Eco-friendly fashion and furniture | Reduced environmental impact | Potentially lower durability and higher cost | Medium to High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in faux leather production, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and market conditions.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather definition
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Faux Leather?
The manufacturing process of faux leather involves several key stages, each critical to producing a high-quality product that meets the diverse needs of B2B buyers. Understanding these stages can help international buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Faux Leather Production?
The first step in faux leather manufacturing involves selecting the right base materials. Common choices include cotton and polyester, which serve as the foundation for the synthetic leather. These fabrics must be specially treated to ensure they can effectively bond with the plastic coatings applied later. In some cases, manufacturers may produce their own base textiles, but it’s more common to source them from specialized suppliers.
Once the base material is selected, manufacturers formulate the plastic that will be used to create the faux leather surface. The two primary types of plastic used are polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The choice between these plastics can affect the final product’s characteristics, such as durability, flexibility, and environmental impact.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
2. Forming: How Is Faux Leather Created?
The forming stage involves binding the prepared plastic to the base textile. This process generally requires heating the plastic to a specific temperature, allowing it to melt and adhere to the fabric. Various techniques are employed, such as coating, lamination, or extrusion, depending on the desired texture and finish of the faux leather.
For instance, in the lamination process, a thin layer of plastic is applied to the textile, ensuring a strong bond while maintaining the fabric’s breathability. The choice of technique can significantly influence the faux leather’s feel and performance, making it crucial for manufacturers to select the appropriate method based on the intended application of the final product.
3. Assembly: What Steps Are Involved in Finalizing Faux Leather Products?
Once the faux leather has been formed, it is cut into the desired shapes for various applications, such as upholstery, apparel, or accessories. This stage often involves automated cutting machines that ensure precision and consistency across large production runs. After cutting, the individual pieces are assembled into finished products, which may include stitching, gluing, or other joining methods.
Quality control during this stage is vital. Manufacturers often perform inspections to ensure that the cut pieces meet the specified dimensions and that the assembly process adheres to design specifications.
4. Finishing: What Techniques Enhance the Quality of Faux Leather?
The finishing stage adds the final touches to the faux leather. This may include applying coatings for enhanced durability, color treatments, or embossing to mimic the texture of genuine leather. Some manufacturers also conduct additional processes to improve the material’s resistance to water and stains.
The finishing touches not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the faux leather but also contribute to its functional properties. For B2B buyers, understanding these finishing processes can be crucial when selecting products that meet specific performance requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Practices for Faux Leather?
Quality assurance is paramount in the production of faux leather, as it ensures that the final product meets international standards and buyer specifications. For B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, understanding the quality control processes can significantly influence procurement decisions.
International Standards: Which Certifications Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Faux leather manufacturers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer has processes in place to consistently produce quality products.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe or API (American Petroleum Institute) for petroleum-based products may also be relevant. These certifications assure buyers that the products meet specific safety and environmental regulations.
What Are the QC Checkpoints in the Faux Leather Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to ensuring the consistency and reliability of faux leather products. Typically, these checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, IPQC involves ongoing inspections to monitor production processes. This helps identify any deviations from quality standards early on.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At the end of the production line, FQC checks the finished products for defects, ensuring they meet the required specifications before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Buyers can take several steps to ensure quality compliance:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular supplier audits can help assess adherence to quality standards and production processes. This can be performed by the buyer’s quality assurance team or by third-party inspection firms.
-
Request Quality Reports: Buyers should request documentation demonstrating compliance with international standards and internal quality checks. This can include test results, inspection reports, and certification documents.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s production and quality control processes. This can be particularly valuable for buyers unfamiliar with the local manufacturing landscape.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges when sourcing faux leather products. Understanding regional regulations and certification requirements is vital for successful procurement.
For instance, buyers from Europe may need to ensure compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations, which govern the use of hazardous substances. Similarly, buyers in the Middle East may encounter different standards that affect product specifications and quality assurance processes.
Additionally, cultural and logistical considerations can impact the effectiveness of quality control measures. Buyers should be proactive in communicating their quality expectations and requirements, fostering transparent relationships with suppliers to ensure mutual understanding and compliance.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for faux leather is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production, relevant international standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their quality requirements and business objectives.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather definition’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to source and understand faux leather, a versatile and increasingly popular alternative to genuine leather. By following these steps, you will ensure that your procurement process is efficient, informed, and aligned with your specific business needs and ethical considerations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the qualities you require in faux leather, including composition, thickness, and intended application. This step is essential because different products may vary significantly in durability, appearance, and functionality. For example, if you need faux leather for upholstery, prioritize options with high abrasion resistance and easy maintenance.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest trends in faux leather production, including environmentally friendly alternatives like vegetable-based synthetic leather. Understanding market movements can give you a competitive edge and help you meet consumer demand for sustainable products. Look for suppliers that offer innovative materials that align with your company’s values.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough due diligence. Request detailed company profiles, product samples, and references from other clients in your industry. This vetting process helps you assess the reliability and quality of the supplier, ensuring that they can meet your specifications and delivery timelines.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your chosen suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO or REACH indicate adherence to quality and safety protocols. This step is crucial not only for the integrity of your products but also for maintaining your company’s reputation in the market.
Step 5: Assess Cost and Payment Terms
Carefully evaluate pricing structures and payment terms offered by suppliers. Consider factors such as minimum order quantities, shipping costs, and potential discounts for bulk orders. A transparent pricing model will help you manage your budget effectively while ensuring you are getting value for your investment.
Step 6: Request Samples and Conduct Quality Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the faux leather products. Conduct quality tests to assess factors such as colorfastness, durability, and texture. This step is vital to confirm that the materials meet your standards and will perform well in their intended applications.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Set up a clear communication strategy with your supplier to facilitate smooth interactions throughout the procurement process. Regular updates regarding production timelines, shipping, and any potential issues will enhance collaboration and ensure that your project stays on track. Establishing a point of contact can streamline this process significantly.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
By following this checklist, you will be well-prepared to source high-quality faux leather that meets your business requirements while navigating the complexities of international procurement.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather definition Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing of faux leather sourcing is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the components and influencers of pricing can enhance negotiation strategies and ultimately lead to more cost-effective procurement.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Faux Leather Production?
-
Materials: The primary materials for faux leather are polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), often combined with a base textile like cotton or polyester. The choice of materials significantly affects costs; for instance, PU tends to be more expensive than PVC but offers better quality and durability. Additionally, the recent trend towards vegetable-based synthetics, though environmentally friendly, can also elevate costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly depending on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs, such as China, often dominate the faux leather market. However, as production moves to regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, labor will contribute more significantly to the overall expense.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, but these efficiencies must be balanced with quality controls.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized designs or specifications. This investment can lead to lower costs per unit in the long run, particularly when ordering large volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of faux leather is essential, particularly for B2B applications where durability and performance are critical. Quality control processes can increase costs but are necessary to avoid returns and maintain customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. Buyers should consider the total cost of logistics, including shipping, customs duties, and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a markup to cover costs and ensure profitability. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
What Influences Faux Leather Pricing?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Pricing is often tiered based on order volume. Larger orders can lead to reduced per-unit costs, making it advantageous for businesses to consolidate purchases when possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specific quality certifications can raise costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials or environmentally certified products may come at a premium. Buyers should consider the implications of material choices on both cost and end-use performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and geographical location can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices but could offer greater assurance of supply and product consistency.
-
Incoterms: The terms of sale (Incoterms) can affect the total landed cost. Buyers should understand whether costs include shipping, insurance, and duties, as this will influence the overall pricing strategy.
How Can Buyers Effectively Negotiate Faux Leather Prices?
Negotiation strategies should focus on understanding the total cost of ownership, which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, quality, and potential waste or returns. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should also consider local economic conditions and currency fluctuations when negotiating.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
To achieve cost-efficiency, buyers should:
- Leverage Volume: Consolidate orders to meet or exceed MOQs for better pricing.
- Request Samples: Assess quality prior to bulk purchasing, avoiding costly mistakes.
- Explore Alternative Suppliers: Diversifying supplier bases can reduce dependency and drive competitive pricing.
- Clarify Terms: Ensure all logistics and cost components are transparently discussed in contracts to avoid unexpected expenses.
Conclusion and Pricing Disclaimer
While this analysis provides a framework for understanding the cost and pricing dynamics of faux leather sourcing, actual prices can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and regional factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to ensure they achieve the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather definition With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Faux Leather: A Comparative Analysis
In the pursuit of sustainable and ethical materials, faux leather has emerged as a prominent choice for many businesses. However, it is essential to explore other viable alternatives that may better suit specific applications or align with corporate values. This analysis will compare faux leather with two notable alternatives: natural leather and recycled materials.
| Comparison Aspect | Faux Leather Definition | Natural Leather | Recycled Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good abrasion resistance, water-resistant, less durable than natural leather | Excellent durability, natural breathability, long-lasting | Variable performance depending on the source, often less durable than faux or natural leather |
| Cost | Generally lower cost compared to natural leather | Higher cost due to sourcing and processing | Cost-effective, often cheaper than faux leather, but varies widely |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to source and fabricate, available in various colors | Requires skilled labor for tanning and finishing | Dependent on availability and processing; may require additional infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean, but can be less heat resistant | Requires regular conditioning and care to maintain quality | Maintenance varies; generally easy to clean but can be less durable |
| Best Use Case | Fashion items, upholstery, and accessories where animal welfare is a concern | High-end fashion, luxury goods, and durable products | Eco-conscious products, promotional items, and budget-friendly applications |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Natural Leather?
Natural leather is renowned for its durability and timeless appeal. It offers excellent breathability and develops a unique patina over time, enhancing its aesthetic value. However, the cost of natural leather is significantly higher due to the complexities involved in sourcing and processing animal hides. Additionally, the environmental impact of leather tanning processes can be considerable, which may conflict with sustainability goals. Natural leather is best suited for high-end products where longevity and luxury are prioritized.
How Do Recycled Materials Compare to Faux Leather?
Recycled materials, including those derived from post-consumer plastics or other waste products, present an eco-friendly alternative to faux leather. They can reduce environmental waste and often come at a lower cost. However, the performance of recycled materials can be variable, depending on the source and processing techniques. While they may not always match the durability of faux leather or natural leather, they are gaining traction in eco-conscious markets. Recycled materials are ideal for businesses aiming to promote sustainability while maintaining budget constraints.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Material?
When selecting the appropriate material for products, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and environmental impact. Faux leather offers a versatile, cost-effective solution, particularly for fashion and upholstery applications, while natural leather is ideal for luxury markets where quality and longevity are paramount. Recycled materials provide an innovative approach for businesses focused on sustainability without sacrificing cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s core values and target market demands, ensuring that the chosen material enhances the overall product offering.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather definition
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Faux Leather?
Faux leather, a widely used alternative to genuine leather, possesses several critical properties that influence its application in various industries. Understanding these specifications is essential for B2B buyers who prioritize quality and performance in their sourcing decisions.
-
Material Composition
Faux leather is primarily made from either Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) or Polyurethane (PU). PVC is cost-effective and provides good durability, while PU offers a more leather-like feel and is often perceived as more environmentally friendly. Buyers must consider the material grade when sourcing faux leather, as it impacts the product’s longevity and overall quality. -
Breathability
Faux leather typically exhibits low breathability, which can affect comfort in applications such as clothing or upholstery. For products requiring higher air circulation, such as athletic wear or summer garments, selecting a more breathable option or a blend with natural fibers may be necessary. -
Moisture Resistance
One of the significant advantages of faux leather is its water-resistant properties, making it suitable for various applications, including upholstery and outerwear. Understanding the moisture-wicking capabilities can help buyers choose the right products for environments where spills and stains are a concern, particularly in regions with high humidity. -
Durability and Wear Resistance
Faux leather generally shows good resistance to abrasions and cuts, making it an ideal choice for items subjected to wear and tear, like bags and upholstery in homes with children or pets. Buyers should evaluate the durability ratings provided by manufacturers to ensure they are meeting end-user expectations. -
Heat Retention
Faux leather has high heat retention capabilities, which can be beneficial for outerwear. However, this property may not be ideal for all applications, especially in warmer climates. Buyers must assess the heat retention characteristics based on the intended use of the product. -
Environmental Considerations
As sustainability becomes a priority in procurement decisions, the environmental impact of faux leather’s production process is increasingly relevant. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s practices, especially regarding the use of PVC versus more sustainable alternatives like vegetable-based synthetic leathers.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Faux Leather Industry?
Navigating the faux leather market requires familiarity with specific jargon and trade terms that streamline communication and ensure clarity in transactions.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components or products that are used in another company’s end products. In the faux leather industry, OEMs may supply raw materials or finished goods to brands that incorporate them into their offerings. Understanding OEM relationships can be crucial for buyers looking to establish reliable supply chains. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure they are not overcommitting to purchases that exceed their immediate needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that potential buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. It helps buyers compare prices, quality, and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for understanding shipping, risk management, and cost allocation during faux leather procurement. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for buyers to manage production schedules and inventory levels effectively, particularly in industries where timely delivery is critical. -
Grade
In the context of faux leather, grade refers to the quality classification based on factors such as thickness, durability, and finish. Buyers must assess the grade to ensure that the faux leather meets the performance requirements of their specific applications.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives while ensuring product quality and supplier reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather definition Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Faux Leather Sector?
The faux leather market is experiencing significant growth, driven by a combination of consumer preferences for cruelty-free products and the rising demand for sustainable materials. Globally, the faux leather market is projected to expand at a CAGR of over 10% through the next five years, particularly as emerging economies in Africa, South America, and the Middle East enhance their industrial capabilities. International B2B buyers are increasingly sourcing faux leather due to its cost-effectiveness compared to genuine leather, making it a popular choice for various applications, including upholstery, fashion, and automotive industries.
Key technological trends include the adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing and digital textile printing, which allow for greater customization and reduced waste. This is particularly relevant for buyers in regions like Nigeria and Brazil, where local production capabilities are evolving. Additionally, the rise of online B2B platforms is facilitating easier access to suppliers and manufacturers, enabling buyers to compare products and prices efficiently.
Another noteworthy dynamic is the increasing focus on product differentiation. Manufacturers are exploring innovative textures and finishes, mimicking the luxurious look and feel of genuine leather while offering unique colors and patterns. This trend is particularly appealing in European markets, where fashion and design considerations are paramount.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Faux Leather Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the faux leather sector. Traditional faux leather is primarily made from petroleum-based plastics, raising environmental concerns due to non-biodegradability and the emission of harmful chemicals during production. In response, many manufacturers are shifting towards more sustainable alternatives, such as plant-based or recycled materials, which are gaining traction globally.
Ethical sourcing is also paramount. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains, seeking partners who adhere to environmental standards and labor practices. Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and OEKO-TEX Standard 100 are becoming essential for brands aiming to enhance their credibility and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, the importance of establishing ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. As consumers demand transparency, sourcing faux leather from manufacturers who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices can significantly enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Faux Leather Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The history of faux leather dates back to the early 20th century, with the introduction of materials like Naugahyde, developed by U.S. Rubber Company in the 1920s. Initially used for handbags, faux leather rapidly gained popularity across various industries due to its affordability and versatility. By the 1950s, the market expanded, with numerous manufacturers entering the space, driven by advancements in synthetic materials.
However, the environmental movement of the 1970s brought scrutiny to the synthetic leather industry, leading to a decline in public perception. In recent years, this landscape has shifted again, with increased awareness and demand for sustainable products prompting innovation in the production of faux leather. As manufacturers pivot towards eco-friendly materials, B2B buyers must stay informed about these developments to align with market trends and consumer expectations.
By understanding the evolution of faux leather, international buyers can better navigate the complexities of sourcing while ensuring they remain competitive in an increasingly conscientious market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather definition
-
How do I identify high-quality faux leather for my business needs?
To identify high-quality faux leather, consider factors such as the material composition (PVC vs. PU), texture, and durability. Request samples from suppliers to assess the feel and appearance, ensuring it meets your standards. Additionally, inquire about the manufacturing processes and certifications that indicate compliance with environmental and safety standards. Conducting a thorough vetting of suppliers, including checking reviews and references, will also help ensure you’re sourcing quality products. -
What is the best faux leather option for upholstery projects?
For upholstery projects, polyurethane (PU) faux leather is often the best choice due to its durability, aesthetic appeal, and soft texture. PU offers better breathability and is generally more resistant to wear and tear compared to PVC options. When selecting a supplier, ensure they provide a range of colors and finishes that match your design requirements. Always request samples to evaluate how the material will perform in real-world conditions. -
How do I determine the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for faux leather?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for faux leather can vary significantly among suppliers based on their production capacity and business model. Typically, MOQs can range from a few yards to several hundred. To determine the right MOQ for your needs, communicate directly with potential suppliers, explaining your project scope and requirements. This dialogue can sometimes lead to flexibility in MOQs, especially for first-time orders or long-term partnerships. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing faux leather internationally?
Payment terms for international faux leather sourcing can vary widely but often include options like a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining 70% before shipment. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or escrow services for added security. Always clarify payment methods accepted, including wire transfers or credit terms, and ensure you have a written agreement outlining the terms to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing faux leather?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing faux leather, it’s essential to establish clear specifications regarding the material’s properties, dimensions, and performance standards. Conduct factory audits or inspections prior to shipment and request third-party testing reports to confirm compliance with industry standards. Additionally, implementing a robust return policy and warranty terms can provide further assurance and protect your investment. -
What are the common uses of faux leather in various industries?
Faux leather is widely used across multiple industries, including fashion, automotive, furniture, and accessories. In fashion, it serves as a popular material for bags, shoes, and outerwear. In the automotive sector, it’s used for seat covers and interiors. For furniture, faux leather is favored for sofas, chairs, and cushions due to its durability and ease of cleaning. Understanding these applications can help you identify market opportunities and tailor your product offerings accordingly. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing faux leather?
When importing faux leather, consider logistical aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with importing textiles to navigate tariffs and documentation requirements. Additionally, plan for potential delays in shipping, especially during peak seasons. Establishing clear communication with your supplier about production timelines and shipping schedules will help ensure a smoother procurement process. -
How do environmental concerns impact the faux leather market?
Environmental concerns are increasingly influencing the faux leather market, particularly regarding the use of PVC and its non-biodegradable properties. As consumers and businesses seek more sustainable options, suppliers are beginning to explore vegetable-based synthetic leathers and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. Keeping abreast of these trends can help your business align with consumer preferences and enhance your brand’s sustainability credentials, potentially opening new market opportunities.
Top 5 Faux Leather Definition Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sewport – Faux Leather
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is a petroleum-based alternative to genuine leather. It is soft to the touch, water-resistant, and highly resistant to stains, making it easy to clean. While less durable than real leather, it is resistant to abrasions and cuts, ideal for upholstery in homes with children or pets. Faux leather can be produced in various colors, including unconventiona…
2. Mitchell Faux Leathers – Synthetic Leather Solutions
Domain: mitchellfauxleathers.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, comes in three primary types: polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC – Vinyl), and silicone. PU is softer, more flexible, and breathable, making it suitable for high-wear products like clothing and upholstery. Vinyl is less breathable but ideal for moisture-repelling products. Silicone is versatile and environmentally friendly, produced through a …
3. LeatherCult – Faux Leather Solutions
Domain: leathercult.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as PU leather, is a synthetic material made to look and feel like real leather. It is constructed primarily from two types: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and Polyurethane (PU). Faux leather is cheaper than genuine leather and easier to maintain. It is commonly used in clothing, upholstery, and accessories. Faux leather jackets are available in various styles for both men and wo…
4. The Real Leather Company – Faux Leather Solutions
Domain: therealleathercompany.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Faux leather is a manufactured alternative to genuine leather, known for its affordability and durability. It is made from petroleum-based products and does not decompose. Common types include: 1. Polyurethane (PU) Leather – soft, flexible, and durable, used in fashion and upholstery. 2. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Leather – moisture-resistant, affordable, used in furniture and car interiors. 3. Micr…
5. Buffalo Jackson – Faux Leather Products
Domain: buffalojackson.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is made from a fabric base such as polyester, which is then treated with wax, dye, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or polyurethane to create an imitation leather finish. It is designed to look like real leather but has a uniform surface texture and feels cold and even compared to genuine leather. Faux leather does not last as long as real leather and does n…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather definition
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers Considering Faux Leather?
In summary, faux leather represents a versatile and cost-effective alternative to genuine leather, appealing to various industries from fashion to upholstery. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the properties and applications of faux leather is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions. Its affordability and wide range of colors and finishes offer unique branding opportunities, while ethical concerns regarding animal welfare and environmental sustainability drive demand for innovative alternatives.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Faux Leather Procurement?
Strategic sourcing can significantly enhance your procurement processes by identifying reliable suppliers, ensuring quality control, and optimizing costs. With China being the leading producer, establishing strong relationships with manufacturers can facilitate better pricing and supply chain reliability. Additionally, as the market for eco-friendly alternatives grows, staying ahead of industry trends can position your business as a leader in sustainable practices.
What’s Next for International Buyers in the Faux Leather Market?
As the faux leather market continues to evolve, now is the time for B2B buyers to explore new opportunities. Engage with suppliers who prioritize sustainable production methods and innovative materials. By leveraging strategic sourcing, you can not only meet consumer demands but also contribute to a more sustainable future. Take the next step in your sourcing journey—connect with manufacturers today to explore the possibilities that faux leather can bring to your product line.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to faux leather definition
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.