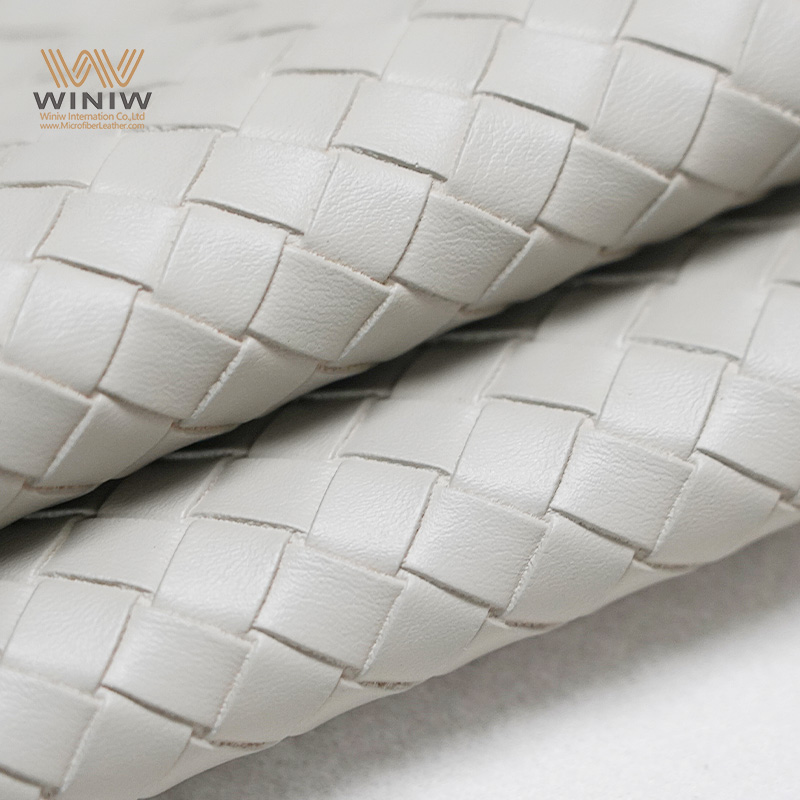
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather texture
The global market for faux leather texture is rapidly evolving, presenting both opportunities and challenges for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality materials. One of the key challenges is identifying reliable suppliers who can deliver a diverse range of textures—such as embossed, quilted, or distressed—while ensuring product consistency and competitive pricing. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets like Brazil and Vietnam.
In the following sections, we will delve into various types of faux leather textures available in the market, their numerous applications ranging from automotive interiors to upholstery for commercial spaces, and strategies for vetting suppliers effectively. Additionally, we will address pricing structures, helping buyers understand the cost implications of different materials and the factors that influence these prices.
By equipping you with actionable insights and knowledge, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business needs. Whether you are sourcing materials for furniture, fashion, or automotive industries, understanding the nuances of faux leather textures will enable you to enhance product offerings, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive your business’s success in a competitive landscape.
Table Of Contents
- Top 9 Faux Leather Texture Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather texture
- Understanding faux leather texture Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of faux leather texture
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather texture’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather texture
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather texture
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather texture’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather texture Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather texture With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather texture
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather texture Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather texture
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather texture
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding faux leather texture Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cuir PU | Soft, supple texture; resembles genuine leather closely | Furniture upholstery, automotive interiors, fashion accessories | Pros: Affordable, easy to clean, durable; Cons: Less breathable than real leather. |
| Cuir PVC | Glossy finish; highly durable; often more rigid | Marine applications, commercial furniture, outdoor furniture | Pros: Water-resistant, cost-effective; Cons: Can be less flexible than PU. |
| Embossed Faux Leather | Textured surface with patterns; mimics exotic leathers | High-end fashion items, luxury upholstery, decorative applications | Pros: Offers unique aesthetic appeal; Cons: May require higher maintenance. |
| Quilted Faux Leather | Padded texture with diamond or square patterns | Automotive interiors, luxury handbags, home decor | Pros: Adds comfort and style; Cons: Can be heavier and bulkier. |
| Distressed Faux Leather | Aged appearance; soft and flexible; rustic charm | Vintage-style furniture, fashion, and accessories | Pros: Unique character; Cons: May not appeal to all markets. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of PU Leather for B2B Buyers?
PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is known for its soft and supple texture, making it a popular choice for various applications, including furniture upholstery and automotive interiors. Its close resemblance to genuine leather allows it to be used in fashion accessories as well. When considering PU leather, B2B buyers should evaluate its durability, ease of cleaning, and affordability, which can be significantly lower than genuine leather. However, it’s essential to note that PU leather may not be as breathable, which can affect comfort in certain applications.
How Does PVC Leather Stand Out in the Faux Leather Market?
PVC leather, or polyvinyl chloride leather, features a glossy finish and is known for its high durability, making it suitable for marine applications and commercial furniture. Its rigidity offers a robust alternative for outdoor furniture, where exposure to the elements is a concern. B2B buyers looking for cost-effective solutions will find PVC leather appealing, especially due to its water-resistant properties. However, the reduced flexibility compared to PU leather may limit its use in more intricate designs.
What Makes Embossed Faux Leather Ideal for Luxury Applications?
Embossed faux leather features a textured surface with intricate patterns that mimic exotic leathers, making it an ideal choice for high-end fashion items and luxury upholstery. This type of faux leather not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of products but also provides a unique tactile experience. B2B buyers should consider the potential for higher maintenance requirements associated with embossed textures, as they may attract dirt and require more frequent cleaning. Nonetheless, the distinctive look can justify the investment in premium markets.
Why Choose Quilted Faux Leather for Comfort and Style?
Quilted faux leather is characterized by its padded texture, often designed in diamond or square patterns, which adds both comfort and visual interest to products. This type is frequently used in automotive interiors and luxury handbags, offering a blend of style and functionality. For B2B buyers, the decision to invest in quilted faux leather should take into account its weight and bulkiness, which may affect design choices. However, its ability to enhance comfort makes it a preferred option in many applications.
What are the Advantages of Distressed Faux Leather for Vintage Styles?
Distressed faux leather features an aged appearance that provides a rustic charm, making it a popular choice for vintage-style furniture and accessories. This type of faux leather is typically soft and flexible, appealing to buyers seeking unique character in their products. B2B buyers should assess market demand for distressed looks, as it may not appeal to all demographics. However, the distinctive aesthetic can attract niche markets, making it a valuable addition to a product line aimed at style-conscious consumers.
Key Industrial Applications of faux leather texture
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of faux leather texture | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Car seat covers and interior trim | Cost-effective, durable, and easy to maintain alternative to genuine leather | Ensure compliance with automotive standards and regulations; consider UV resistance and colorfastness. |
| Furniture Manufacturing | Upholstery for residential and commercial furniture | Provides a luxurious look at a lower cost; easy to clean and maintain | Select from a variety of textures and colors to match design specifications; verify durability for high-traffic areas. |
| Marine Industry | Upholstery for boats and marine vehicles | Water-resistant and mildew-resistant options enhance longevity | Look for UV-resistant materials; ensure compliance with marine safety standards. |
| Fashion and Accessories | Handbags, wallets, and clothing | Eco-friendly alternative to leather; wide range of design options | Source from suppliers with a focus on sustainable practices; consider market trends for color and texture preferences. |
| Home Decor and Interior Design | Wall coverings, cushions, and decorative items | Versatile design options that enhance aesthetic appeal at a lower cost | Evaluate custom design capabilities; ensure material meets fire safety regulations for indoor use. |
How is Faux Leather Texture Utilized in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, faux leather is extensively used for car seat covers and interior trim. Its cost-effectiveness compared to genuine leather makes it an attractive option for manufacturers aiming to reduce production costs while still offering a luxurious feel. Additionally, faux leather is durable and easy to clean, addressing common maintenance issues associated with natural leather. International buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that comply with automotive safety and quality standards, ensuring features like UV resistance and colorfastness to withstand various environmental conditions.
What Role Does Faux Leather Play in Furniture Manufacturing?
Faux leather is a popular choice for upholstery in both residential and commercial furniture manufacturing. It provides a sophisticated appearance at a fraction of the cost of genuine leather, making it ideal for budget-conscious businesses. The material is also easy to maintain, which is crucial for high-traffic areas like hotels and restaurants. Buyers should consider the range of textures and colors available to meet specific design requirements, as well as the durability of the fabric to ensure it can withstand daily use without significant wear.
Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
Why is Faux Leather Important in the Marine Industry?
In the marine industry, faux leather is used for upholstery in boats and other marine vehicles due to its water-resistant and mildew-resistant properties. This application addresses the challenges of maintaining upholstery in humid and wet environments, extending the lifespan of the materials used. Buyers should look for UV-resistant options to prevent fading and degradation from sun exposure, and ensure that the materials comply with marine safety standards to guarantee their suitability for use in this demanding environment.
How is Faux Leather Transforming Fashion and Accessories?
Faux leather is increasingly popular in the fashion industry for items such as handbags, wallets, and clothing. As an eco-friendly alternative to traditional leather, it appeals to consumers seeking sustainable options without sacrificing style. The wide variety of design possibilities allows brands to cater to diverse market trends. International B2B buyers should focus on sourcing from suppliers committed to sustainable practices and stay informed about current trends in colors and textures to align their offerings with consumer preferences.
How Does Faux Leather Enhance Home Decor?
In home decor, faux leather serves as an elegant solution for wall coverings, cushions, and various decorative items. Its versatility allows designers to create appealing aesthetics while keeping costs manageable. Faux leather can be customized to fit unique design themes, making it a favored choice for interior design projects. Buyers should assess the custom design capabilities of suppliers and ensure that the materials meet fire safety regulations, particularly for indoor applications, to enhance both safety and aesthetic appeal.
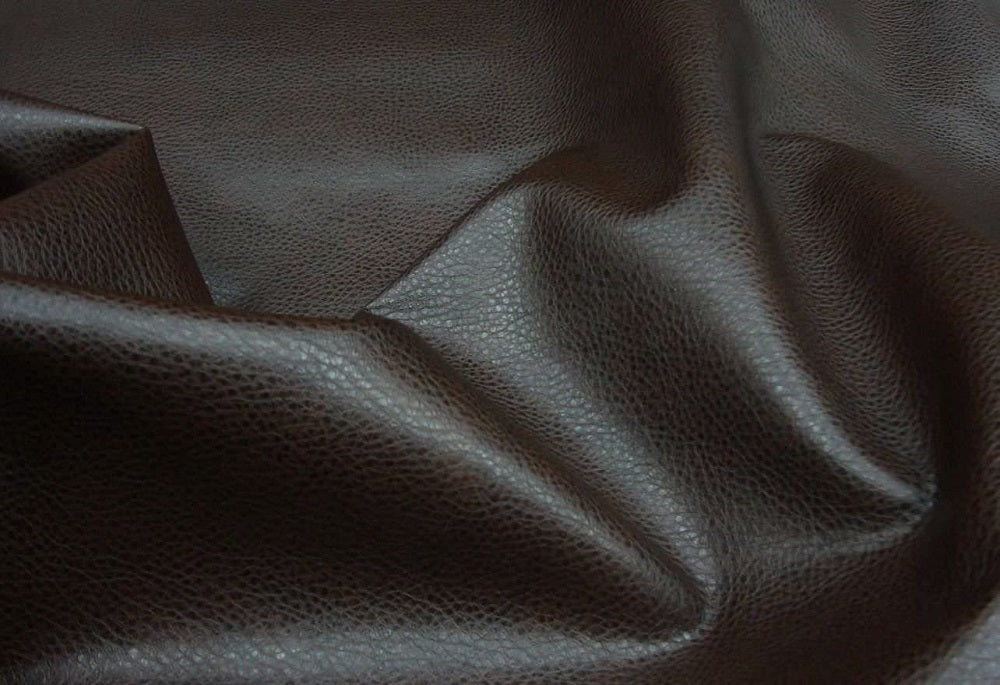

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather texture’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Matching Faux Leather Textures to Design Specifications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when trying to match faux leather textures to specific design requirements. For instance, an interior designer working on a luxury hotel project may need a faux leather that mimics the look and feel of high-end materials like genuine leather or suede. If the texture is too shiny or not soft enough, it could compromise the overall aesthetic of the space. Additionally, inconsistencies in texture and color across different batches can lead to delays and increased costs as buyers scramble to find matching materials.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable manufacturers that offer a wide range of faux leather options, including various textures and finishes. It’s beneficial to request physical samples before making bulk orders. When specifying faux leather, clearly communicate the desired texture and appearance in detail, referencing specific product lines known for their quality. Using a color matching system can also help ensure consistency across different batches. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers about production methods and material characteristics will further assist in selecting the right faux leather for any project.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over Durability and Maintenance of Faux Leather
The Problem: Another common pain point is the concern regarding the durability and maintenance of faux leather materials, especially in high-traffic environments such as restaurants or commercial spaces. B2B buyers may worry that faux leather will wear out quickly, become stained, or lose its aesthetic appeal over time. For instance, a furniture buyer for a café might find that the faux leather used on chairs scuffs easily or is difficult to clean, leading to dissatisfaction from customers and increased replacement costs.
The Solution: To address durability concerns, buyers should opt for high-quality faux leather products specifically designed for commercial use. Look for materials labeled as “contract grade,” which are tested for durability and resistance to stains and wear. Buyers should also inquire about the cleaning and maintenance recommendations from the manufacturer. Establishing a regular maintenance schedule, using appropriate cleaning agents, and training staff on proper care can significantly extend the life of faux leather products. Additionally, selecting faux leather with protective coatings can help resist stains and enhance durability, making it a more viable option for high-traffic areas.
Scenario 3: Misunderstanding Faux Leather’s Environmental Impact
The Problem: As sustainability becomes a crucial consideration for many businesses, some B2B buyers struggle with the perception that faux leather is not an environmentally friendly option. They may encounter resistance from clients or stakeholders who prioritize eco-friendly materials, leading to a dilemma about whether to use faux leather or traditional leather. For example, a buyer in the fashion industry may find it challenging to justify faux leather products when there is a growing demand for sustainable and ethically sourced materials.
Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
The Solution: Buyers can turn this challenge into an opportunity by educating themselves and their clients about the environmental benefits of modern faux leather options. Many contemporary faux leathers are made from recycled materials and are more sustainable than traditional leather production methods, which often involve harmful chemicals and significant water usage. When sourcing faux leather, prioritize suppliers who are transparent about their manufacturing processes and sustainability practices. Providing clients with information on the lifecycle of the material, including its recyclability and reduced carbon footprint compared to genuine leather, can help shift perceptions and position faux leather as a responsible choice for eco-conscious projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather texture
What Are the Key Materials Used for Faux Leather Textures?
When selecting faux leather textures for various applications, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of different materials is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials used in faux leather production: Polyurethane (PU), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Microfiber, and Eco-Leather. Each material has unique characteristics that impact product performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications.
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Leather Perform in Various Applications?
Polyurethane leather, commonly referred to as PU leather, is a synthetic material that mimics the look and feel of genuine leather. It is known for its softness and flexibility, making it ideal for upholstery in furniture and automotive applications. Key properties include excellent abrasion resistance and a temperature tolerance range of -20°C to 80°C.
Pros: PU leather is durable, easy to clean, and offers a luxurious appearance at a lower cost than genuine leather. It is also water-resistant and does not crack easily over time.
Cons: The primary limitation is its susceptibility to heat; prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to degradation. Additionally, while PU leather is more environmentally friendly than PVC, it is still made from synthetic materials.

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
Impact on Application: PU leather is suitable for a variety of applications, including residential and commercial upholstery, automotive interiors, and fashion accessories.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with REACH regulations, while those in South America may need to consider local environmental standards.
What Advantages Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Leather Offer?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) leather is another popular synthetic option, often used in commercial and industrial applications. It boasts high durability and resistance to water, stains, and mildew, with a temperature tolerance of -30°C to 70°C.

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
Pros: PVC leather is cost-effective and offers a wide range of colors and textures. It is particularly resistant to chemicals and can be treated to enhance its durability.
Cons: However, PVC leather can be less breathable than PU leather, which may not be suitable for all applications, especially in warmer climates. It is also less flexible, which may limit its use in certain designs.
Impact on Application: PVC leather is commonly used in automotive interiors, marine upholstery, and commercial furniture. Its durability makes it a preferred choice for high-traffic areas.

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
International Considerations: Compliance with ASTM and DIN standards is essential for buyers in Europe, while Middle Eastern countries may have specific regulations regarding chemical content.
How Does Microfiber Leather Compare in Terms of Performance?
Microfiber leather is a synthetic fabric made from ultra-fine polyester fibers. It is known for its soft texture and high durability, with temperature ratings similar to PU leather.
Pros: Microfiber leather is lightweight, breathable, and easy to clean. It is also resistant to stains and fading, making it suitable for various applications.
Cons: While it offers a luxurious feel, microfiber leather can be more expensive than PU and PVC options. Additionally, its production process may involve more complex manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: Microfiber leather is ideal for high-end furniture, automotive interiors, and fashion items where a premium look is desired.

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
International Considerations: Buyers should verify compliance with international textile standards, especially in Europe, where sustainability is increasingly prioritized.
What Is Eco-Leather and Its Role in Sustainable Sourcing?
Eco-leather is a term used for faux leather made from recycled materials or produced with environmentally friendly processes. It typically combines synthetic and natural fibers, offering a unique texture and appearance.
Pros: Eco-leather is a sustainable alternative that appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. It often features a unique texture and can be produced in various colors and patterns.
Cons: The main drawback is the potential variability in quality, as eco-leather can vary significantly based on the manufacturing process. It may also be more expensive than traditional faux leather options.

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
Impact on Application: Eco-leather is suitable for fashion, upholstery, and accessories, particularly in markets focused on sustainability.
International Considerations: Buyers should look for certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX, especially in Europe and North America.
Summary Table of Faux Leather Materials
| Matériau | Typical Use Case for faux leather texture | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Upholstery, automotive interiors | Soft, luxurious feel | Heat sensitivity | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Commercial furniture, automotive interiors | High durability, cost-effective | Less breathable | Low |
| Microfibre | High-end furniture, fashion items | Lightweight and breathable | Higher cost | Haut |
| Eco-Leather | Fashion, upholstery, accessories | Sustainable and environmentally friendly | Variable quality | Medium to High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials available for faux leather textures, equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather texture
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Faux Leather Texture?
The manufacturing of faux leather involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers who are sourcing materials for various applications such as upholstery, automotive interiors, and fashion.
Material Preparation: What Is Involved?
The first stage of faux leather manufacturing begins with material preparation. This typically involves the selection of a substrate, which can be made from polyester, cotton, or other synthetic fibers. The choice of substrate impacts the durability, feel, and overall quality of the faux leather.

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
Once the substrate is chosen, it undergoes a treatment process to enhance its properties. This may include applying a primer layer that improves adhesion for subsequent coatings. Additionally, a protective layer may be added to increase resistance to water, stains, and UV damage, making the material suitable for various environments.
How Is Faux Leather Formed?
The forming stage is where the texture and appearance of faux leather are created. This is primarily achieved through two techniques: coating and lamination.
-
Coating: In this method, a polymer, typically polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), is applied to the substrate. The coating process can involve various technologies, including spraying, rolling, or dipping. The thickness and texture of the coating can be adjusted to achieve different finishes such as matte, glossy, or embossed.
-
Lamination: This technique involves bonding multiple layers of materials together. A layer of foam or a similar material can be added to provide cushioning, enhancing comfort in applications like automotive seating. The lamination process also allows for the introduction of various textures, such as pebbled or crocodile patterns, giving buyers a range of aesthetic options.
What Are the Finishing Techniques Used?
Finishing is the final stage of faux leather production, where additional treatments are applied to enhance the material’s look and functionality. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Embossing: This process creates a three-dimensional texture on the surface of the faux leather, mimicking the grain of genuine leather. It is achieved by pressing the material against heated molds.
-
Printing: Digital or screen printing techniques can be employed to add patterns or colors to the faux leather. This allows for endless customization options, catering to diverse market preferences.
-
Sealing: A protective sealant may be applied to enhance durability, making the faux leather resistant to wear and tear. This is particularly important for applications in high-traffic areas.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Faux Leather Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the faux leather manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be aware of the various QA processes and certifications that govern faux leather production.
What International Standards Are Relevant?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are crucial for manufacturers to adhere to as they provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards ensures that the manufacturer consistently delivers products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for safety standards and API (American Petroleum Institute) for specific applications may also apply. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers hold these certifications to ensure product reliability and safety.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Common?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins. This step is vital in preventing defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the manufacturing process. This includes checking the thickness of coatings, adhesion quality, and texture consistency.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production is complete, a final inspection is conducted to ensure the faux leather meets all specifications. This includes testing for colorfastness, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with standards. Here are some actionable steps buyers can take:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This allows buyers to assess compliance with international standards and identify potential risks.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed QA reports that outline their quality control processes, including any certifications they hold. This documentation can provide assurance regarding the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These services can conduct pre-shipment inspections to ensure products meet specified standards before they are shipped.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing faux leather from international suppliers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural differences in business practices and communication can aid in building strong relationships with suppliers. Clear communication regarding quality expectations is essential.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: The distance and logistics involved in international shipping can impact product quality. Buyers should consider factors such as shipping times and conditions to ensure products arrive in optimal condition.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in faux leather production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs and standards. This knowledge not only aids in supplier selection but also enhances the overall quality of the final products they offer to their customers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather texture’
To successfully procure faux leather texture for your business needs, it is essential to follow a systematic approach. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist that will help you navigate the sourcing process effectively, ensuring that you find the right materials that meet your specifications and budget.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your requirements regarding the faux leather texture. Consider the specific applications, such as upholstery for furniture or automotive interiors, as these will dictate the necessary durability and aesthetic qualities. Additionally, identify the desired textures—ranging from smooth to embossed or distressed—as this will help in narrowing down your choices.
Step 2: Research Available Materials and Textures
Understanding the various types of faux leather materials available is crucial. Faux leather can be made from different polymers, such as polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), each with unique properties. Investigate different textures like pebbled, crocodile, or quilted patterns, as these can significantly impact the final product’s look and feel. Make a list of preferred textures to guide your discussions with potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough due diligence. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers that have a proven track record in delivering high-quality faux leather materials, and ensure they have the capacity to meet your order volume and timelines.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assurance
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of their faux leather products. Evaluate the samples for texture, durability, and color accuracy against your specifications. This step is critical as it allows you to assess the material’s quality firsthand and determine if it meets your project’s needs.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
After evaluating the quality of materials, compare pricing structures among suppliers. Look for transparent pricing models that include details on bulk discounts, shipping costs, and payment terms. Be mindful of any hidden fees that could affect your overall budget. This comparison will help you identify the best value for your investment.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your chosen supplier complies with international standards and regulations related to faux leather production. Certifications such as ISO or compliance with environmental regulations can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and sustainability. This is especially important for B2B buyers in regions with strict regulatory environments.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Contract
Once you have selected a supplier, draft a contract that outlines all terms and conditions, including delivery schedules, payment terms, and quality assurance measures. A well-defined contract protects both parties and ensures that expectations are met throughout the procurement process. Include clauses for dispute resolution and penalties for non-compliance to safeguard your investment.
By following this structured checklist, you can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing faux leather texture, ensuring that you select the best materials that align with your business needs and standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather texture Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Faux Leather Textures?
When sourcing faux leather textures, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary components of cost include:
-
Materials: The base material, typically polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), significantly influences pricing. PU leather is often more expensive due to its superior quality and durability. The choice of texture, such as embossed or quilted, can also affect material costs.
-
Labor: The manufacturing process for faux leather involves skilled labor to ensure quality and consistency. Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the region; for instance, labor in Southeast Asia may be more cost-effective than in Europe.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, such as utilities and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overheads.
-
Tooling: Custom designs or specific textures may require specialized tooling, adding to the initial investment. Buyers should consider these costs when requesting unique designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the final product meets specified standards involves rigorous quality control processes. This is particularly important for buyers in regulated markets.
-
Logistics: Shipping faux leather internationally entails freight costs, insurance, and tariffs. These costs can vary based on the shipping method and destination, particularly for regions with different trade agreements.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market competition and perceived value.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Faux Leather Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of faux leather textures, making it essential for buyers to understand their implications:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to better pricing due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom textures or colors may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with certifications (e.g., eco-friendly, fire-retardant) will typically cost more. Buyers should evaluate the importance of these certifications in their specific application.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while emerging suppliers might offer competitive rates to build their client base.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is crucial. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping costs, risk, and liability, impacting the overall pricing structure.
What Are the Best Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Strategies for Buyers?
To maximize value when sourcing faux leather, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Don’t hesitate to negotiate on volume discounts and payment terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes shipping, handling, and potential waste. Opting for higher-quality materials may reduce replacement costs in the long run.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of fluctuations in currency exchange rates and how they can affect pricing. Additionally, local tariffs and import duties can significantly impact the final cost.
-
Conduct Market Research: Regularly analyze the market for trends in faux leather pricing and availability. Staying informed can provide leverage during negotiations.
Conclusion
The faux leather market offers diverse options, but understanding the cost structure and price influencers is vital for international B2B buyers. By leveraging negotiation strategies and being aware of the total cost of ownership, buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their budget and quality requirements. Keep in mind that prices may vary widely based on region, supplier, and market conditions, so always seek up-to-date and indicative pricing before finalizing any deals.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather texture With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Faux Leather Texture?
In the quest for high-quality materials that mimic the look and feel of genuine leather, faux leather has emerged as a popular choice among B2B buyers. However, it is essential to consider alternative solutions that also provide durability, aesthetic appeal, and cost-effectiveness. This analysis will compare faux leather texture with two notable alternatives: genuine leather and high-performance synthetic materials like PVC and PU leather. By examining key aspects such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Faux Leather Texture | Genuine Leather | High-Performance Synthetic Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, water-resistant, and flexible | Highly durable but can crack or fade | Excellent durability and flexibility |
| Cost | Significantly lower (up to 75% less) | High initial investment | Moderate cost, often mid-range |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to cut and sew, widely available | Requires specialized tools and skills | Easy to work with, versatile |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean; resistant to stains and mildew | Requires conditioning and care | Easy to clean; often water-resistant |
| Best Use Case | Furniture, automotive, and fashion items | High-end furniture and luxury goods | Commercial applications, outdoor use |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Genuine Leather
Genuine leather is renowned for its superior quality and timeless appeal. It offers an unmatched aesthetic that many consumers desire, particularly in high-end applications. However, genuine leather comes with a higher price tag and requires ongoing maintenance, such as conditioning to prevent cracking and fading. Additionally, it is less water-resistant than faux leather, making it susceptible to damage if not properly cared for. Buyers looking for luxury and durability may opt for genuine leather, but they must be prepared for the associated costs and upkeep.
High-Performance Synthetic Materials (PVC and PU Leather)
High-performance synthetic materials, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and PU (polyurethane) leather, are engineered to deliver exceptional durability while maintaining a leather-like appearance. These materials are often more affordable than genuine leather but can be slightly higher in cost than faux leather. They are easy to implement in various applications, from upholstery to automotive interiors, and are available in a broad range of styles and colors. Maintenance is straightforward, as these materials are typically water-resistant and easy to clean. However, some may lack the authentic feel that genuine leather offers, which could be a consideration for certain buyers.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right material for your specific applications, B2B buyers should evaluate their priorities carefully. If cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance are paramount, faux leather remains an excellent choice. However, for those seeking luxury and authenticity, genuine leather may justify the higher investment. Conversely, high-performance synthetic materials present a balanced option, combining durability and versatility, making them suitable for various commercial applications. Ultimately, understanding the unique characteristics of each alternative will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather texture
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Faux Leather Texture?
When sourcing faux leather for various applications, understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Faux leather is typically categorized into grades based on quality and durability. Common grades include standard, premium, and luxury. Premium and luxury grades often feature enhanced characteristics such as greater softness, durability, and resistance to wear. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the faux leather meets the demands of specific applications, whether for automotive interiors or high-end upholstery. -
Thickness
The thickness of faux leather can significantly affect its usability and aesthetic appeal. Generally measured in millimeters, thickness can range from ultra-thin (0.5mm) to thicker options (2mm or more). Thicker materials are often more durable and better suited for high-use environments, while thinner options may be preferred for fashion applications. Buyers should consider the end-use requirements when selecting thickness to ensure optimal performance. -
Surface Texture
Faux leather is available in a variety of textures, including smooth, embossed, and distressed finishes. The surface texture not only impacts the look and feel of the material but also its functionality. For instance, embossed textures can enhance grip and durability, making them ideal for automotive and furniture applications. Buyers should evaluate the desired aesthetic and functional properties when choosing a texture. -
UV Resistance
Exposure to sunlight can degrade materials over time, making UV resistance a critical property for faux leather used in outdoor applications. Materials treated for UV resistance can prevent fading and deterioration, ensuring longevity. This property is especially important for B2B buyers in regions with high sun exposure, as it affects both product lifespan and maintenance costs. -
Water and Stain Resistance
Many faux leather materials come with inherent water and stain resistance, making them easy to clean and maintain. This property is particularly beneficial in commercial settings, such as restaurants and healthcare facilities, where hygiene and appearance are paramount. B2B buyers should prioritize materials with these features to reduce long-term maintenance efforts and costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Faux Leather Industry?
Understanding industry jargon can greatly facilitate communication and negotiation processes. Here are several common terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of faux leather, it often pertains to manufacturers who supply materials for automotive or furniture industries under the branding of another company. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers navigate sourcing and branding strategies effectively. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand as it directly affects inventory management and cost. B2B buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their project needs to avoid overstocking or underordering. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where a buyer requests pricing and other terms from suppliers for specific products. Issuing an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better decision-making based on budget and requirements. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand their obligations and rights in international trade, minimizing risks associated with shipping faux leather products. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes for an order to be fulfilled, from the moment it is placed until it is received. Understanding lead times is essential for effective project planning and inventory management. B2B buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating contracts to ensure timely delivery of materials.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their purchasing strategies, ensuring they procure high-quality faux leather that meets their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather texture Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Faux Leather Texture Sector?
The global faux leather market is witnessing significant growth, driven by rising consumer demand for affordable, stylish, and sustainable alternatives to genuine leather. Key trends indicate a shift toward innovative materials, such as polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which offer enhanced durability and a wide range of textures, including distressed, embossed, and quilted patterns. International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly interested in these materials for applications across automotive interiors, furniture upholstery, and fashion accessories.

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
Emerging technologies in production, such as digital printing and advanced coating techniques, are enabling manufacturers to create customized designs and textures that cater to diverse market preferences. This flexibility is particularly appealing to B2B buyers looking to differentiate their products in competitive markets. Moreover, the rise of e-commerce platforms is facilitating easier access to a broader range of suppliers, allowing businesses to source faux leather at competitive prices while maintaining quality standards.
Additionally, the demand for vegan and cruelty-free products is influencing sourcing decisions. Suppliers that can demonstrate transparency in their manufacturing processes and offer unique texture options are more likely to capture the attention of international buyers. As the market evolves, staying attuned to these dynamics will be crucial for B2B buyers seeking to capitalize on the growing faux leather sector.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing for B2B Buyers in the Faux Leather Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone in the faux leather industry, as environmental concerns drive demand for eco-friendly materials. Faux leather, particularly PU leather, is often touted for its lower environmental impact compared to traditional leather, as it does not involve animal cruelty and can be manufactured using fewer resources. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to assess the environmental footprint of their suppliers, focusing on materials that are recyclable or made from sustainable sources.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with buyers increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and have transparent supply chains. Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 provide assurance that products meet specific environmental and social criteria. By choosing suppliers with such certifications, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a growing segment of consumers who value sustainability.

Illustrative image related to faux leather texture
Furthermore, sustainable faux leather options often boast attributes like water resistance, stain resistance, and mildew resistance, making them suitable for various applications, from automotive interiors to outdoor furniture. As the demand for sustainable products continues to rise, B2B buyers who integrate these considerations into their sourcing strategies will not only meet consumer expectations but also contribute positively to the environment.
What Is the Evolution of Faux Leather and Its Relevance for Today’s B2B Buyers?
The evolution of faux leather dates back to the early 20th century when synthetic alternatives emerged as cost-effective substitutes for genuine leather. The introduction of materials like Naugahyde in the 1920s marked a significant milestone, offering durability and ease of maintenance for upholstery applications. Over the decades, advances in technology have led to the development of various types of faux leather, including PU and PVC, which have further enhanced the material’s appeal.
Today, faux leather is not only recognized for its practicality but also for its aesthetic versatility. With options that mimic the textures of exotic leathers, such as crocodile and ostrich, faux leather is increasingly favored in luxury markets, providing B2B buyers with opportunities to offer high-end products without the associated costs. This evolution highlights the material’s adaptability to changing consumer preferences and market demands, making it a vital component in the portfolios of B2B buyers across multiple industries.
By understanding the historical context and ongoing innovations in faux leather, B2B buyers can better navigate the market, ensuring they make informed sourcing decisions that align with current trends and consumer expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather texture
-
How do I choose the right faux leather texture for my project?
Selecting the appropriate faux leather texture depends on the intended use, aesthetic preferences, and durability requirements. Consider factors such as the environment (indoors vs. outdoors), the type of application (upholstery, automotive, fashion), and the desired look (smooth, embossed, or patterned). Additionally, request samples from suppliers to evaluate the textures firsthand. This hands-on assessment can help determine the best fit for your specific project, ensuring that the chosen material meets both functional and visual criteria. -
What are the key benefits of using faux leather over genuine leather?
Faux leather offers numerous advantages, particularly for B2B buyers. It is significantly more cost-effective, often up to 75% less than genuine leather. This makes it an attractive option for large-scale projects. Faux leather is also easier to maintain, as it is resistant to stains, water, and mildew. Furthermore, it is a vegan alternative, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Its availability in various textures and colors provides flexibility in design, making it suitable for diverse applications, from upholstery to fashion. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for faux leather?
Minimum order quantities for faux leather can vary significantly based on the supplier and specific product lines. Typically, MOQs range from 50 to 500 yards, depending on the material and customization options. For international B2B buyers, it is advisable to discuss your project needs with suppliers to negotiate suitable quantities, especially if you are exploring multiple textures or colors. Establishing a relationship with reliable suppliers can also lead to more favorable terms over time. -
How can I ensure the quality of faux leather before making a bulk purchase?
To guarantee the quality of faux leather, start by requesting samples from potential suppliers. Evaluate the material’s texture, durability, and finish. Additionally, inquire about the manufacturing process, certifications, and quality assurance measures they employ. Consider conducting a factory visit or third-party inspection, especially for larger orders, to verify compliance with international standards. A robust vetting process helps mitigate risks associated with product quality and ensures that the material meets your specifications. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing faux leather internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms based on the buyer’s relationship and order history. It is crucial to clarify payment methods (bank transfer, letters of credit, etc.) and currency preferences early in the negotiation process. Familiarizing yourself with international trade regulations and potential currency fluctuations can also help in budgeting for your purchase. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for faux leather imports?
When importing faux leather, logistics planning is essential. Collaborate with your supplier to determine the best shipping method (air, sea, or land) based on your timeline and budget. Familiarize yourself with customs regulations and duties in your destination country to avoid unexpected costs. Engaging a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the shipping process and ensure compliance with all import/export requirements. Tracking shipments and maintaining communication with your supplier can help resolve any issues that arise during transit. -
Can I customize faux leather textures and colors to suit my brand?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for faux leather, including specific textures, colors, and patterns. When discussing your requirements, provide detailed specifications and, if possible, visual references to ensure accurate production. Keep in mind that custom orders may have higher MOQs and longer lead times. Establishing a clear agreement on samples and prototypes is essential to verify that the final product aligns with your expectations before committing to a larger order. -
What are the common applications for faux leather in various industries?
Faux leather is versatile and widely used across numerous industries. In the furniture sector, it is favored for residential and commercial upholstery due to its durability and ease of maintenance. The automotive industry utilizes faux leather for seat covers and interiors, while the fashion industry incorporates it in clothing and accessories. Additionally, faux leather is popular in marine applications for boat upholstery and outdoor furniture. Understanding these applications can help B2B buyers identify potential markets for their faux leather products.
Top 9 Faux Leather Texture Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Freepik – Faux Leather Images
Domain: freepik.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Faux leather images available for free download on Freepik. The collection includes various textures such as distressed, rough, rustic, solid color, abstract, quilted, and embossed patterns. The images can be used for automotive interiors, car seat covers, upholstery, and more. The site offers tools for image generation, editing, and mockups, along with a range of file types and licenses.
2. Sallie Tomato – Faux Leather Collection
Domain: sallietomato.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux Leather collection by Sallie Tomato includes 66 products available in various colors and textures. Key features include:
– Colors: Beige (5), Black (10), Blue (6), Brown (10), Green (6), Grey (6), Navy (4), Orange (1), Pink (4), Purple (2), Red (6), Teal (1), White (2), Yellow (2).
– Textures: Alligator (4), Basket Weave (6), Crocodile (4), Legacy (15), Limited Edition (6), Lite (4), Ostrich …
3. Spoonflower – Faux-Leather Fabric & Home Decor
Domain: spoonflower.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Faux-leather Fabric, Wallpaper and Home Decor available in various designs and styles. Products include fabric by the yard or meter, wallpaper, and home decor items such as curtains, bedding, pillows, and dining accessories. Categories include Activewear & Swimwear, Apparel, Bottom Weight, Costume, Craft, Dresses, Quilting, Top Weight, Upholstery, and Wide Format. Wallpaper options include Peel an…
4. Naugahyde – PU Leather & Faux Leather
Domain: decorativefabricsdirect.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: PU Leather & Faux Leather | Vinyl Upholstery Fabric
– Terms: Free Shipping Coupon Code: SHIPFREE for most $199 orders.
– Available Uses: Furniture, Automotive, Marine.
– Brands: Naugahyde, Omnova Boltaflex, Nassimi, Spradling.
– Types: Vinyl (PVC), Urethane, Polycarbonate.
– Color Options: Black, Gray, Blue, Turquoise, Aqua, Brown, Beige, Green, Orange, Coral, Purple, Red, Pink, White, Yellow, Gol…
5. Poliigon – Leather Fabric Textures
Domain: poliigon.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Leather Fabric Textures – Seamless, high-resolution leather fabric textures for achieving a luxurious and sophisticated look in architectural visualizations, product designs, or any project that requires leather materials. Categories include 82 different leather fabric textures such as Cowhide Leather Texture, Wild Buffalo Leather Texture, Suede Leather Texture, Faux Leather Texture, and various o…
6. Adobe Stock – Faux Leather Assets
Domain: stock.adobe.com
Registered: 1986 (39 years)
Introduction: Faux Leather Images – Browse 50,827 Stock Photos, Vectors, and Video | Adobe Stock. Includes 1211 videos related to faux leather. Offers options for free trials to access images and videos. Various asset types available: Images, Videos, Audio, Templates, 3D. Options for premium content. License terms and support available.
7. The Felt Pod – Textured Faux-Leather Fabric Sheets
Domain: thefeltpod.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Textured Faux-Leather Fabric Sheets
– Soft fabric faux leather
– Realistic pebbled texture
– Available in a variety of colors including classic khaki and trendy wintergreen
– Ideal for crafting purses, backpacks, hair accessories, home décor, etc.
– Cut to size for easy handling
– Price per sheet: $3.95 – $4.40 depending on color
– Ships within 1-2 business days
– Large inventory on hand
– High-qu…
8. Sewport – Faux Leather
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is a petroleum-based alternative to genuine leather. It is soft to the touch, water-resistant, and highly resistant to stains, making it easy to clean. While less durable than real leather, it is resistant to abrasions and cuts, ideal for upholstery in homes with children or pets. Faux leather can be produced in various colors, including unconventiona…
9. Pinterest – Leather Textures
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Leather textures including cream, beige, brown, dark, gray, and white variations. Types include seamless, tufted, smooth, and embossed textures. Related interests include leather samples, fabric textures, and Photoshop resources. Specific products mentioned are BOSS LEATHER SAMPLES, high-resolution luxury leather textures, and various fabric samples for upholstery and design.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather texture
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of faux leather textures presents a significant opportunity for B2B buyers across diverse markets. By leveraging the affordability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal of faux leather, businesses can meet consumer demands for sustainable and stylish products. The availability of various textures—such as quilted, embossed, and distressed—enables companies to cater to different industries, including automotive, furniture, and fashion, while ensuring compliance with regional preferences and standards.
As international markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for faux leather is expected to grow. This growth underscores the importance of establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality materials at competitive prices. By embracing strategic sourcing practices, businesses can not only enhance their product offerings but also contribute to sustainable practices by opting for animal-friendly alternatives.
Looking ahead, now is the time for B2B buyers to capitalize on the expanding faux leather market. By exploring innovative designs and applications, companies can differentiate themselves and drive growth in their respective sectors. Engage with suppliers today to secure the materials that will shape the future of your product lines.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.