Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cork and leather
In an increasingly competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing sustainable materials that not only meet quality standards but also align with ethical practices. This guide on cork and leather serves as a valuable resource for businesses looking to navigate the complexities of these two distinct yet complementary materials. With cork leather emerging as a viable eco-friendly alternative to traditional leather, understanding its properties, applications, and sourcing strategies becomes essential for informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide covers a wide array of topics, including the different types of cork and leather, their various applications across industries, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations. By delving into the unique qualities of cork leather—such as its lightweight, water-resistant, and hypoallergenic properties—buyers can better assess its suitability for products ranging from fashion accessories to furniture upholstery.
Moreover, the guide highlights the importance of ethical sourcing, particularly for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany. Understanding the environmental impact and benefits of cork production—such as its role in carbon sequestration and habitat preservation—empowers businesses to make choices that resonate with increasingly eco-conscious consumers. Ultimately, this resource equips B2B buyers with the insights needed to make strategic decisions that enhance their product offerings while fostering sustainability.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Cork And Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cork and leather
- Understanding cork and leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of cork and leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cork and leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for cork and leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cork and leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cork and leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cork and leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cork and leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cork and leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cork and leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cork and leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cork and leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding cork and leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cork Leather | Made from cork oak bark; eco-friendly; water and flame resistant | Fashion accessories, upholstery | Pros: Sustainable, lightweight, durable; Cons: Less durable than full-grain leather. |
| Full Grain Leather | Natural grain; high durability; ages beautifully | Luxury goods, high-end furniture | Pros: Long-lasting, develops a unique patina; Cons: Higher cost, requires maintenance. |
| Composite Leather | Made from leather scraps; often labeled as ‘genuine leather’ | Mass-produced goods, budget items | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Lower quality, may contain synthetic materials. |
| Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Tanned using natural materials; environmentally friendly | Eco-conscious markets, artisan goods | Pros: Safer for workers, biodegradable; Cons: Longer production time, higher price. |
| Synthetic Leather | Made from polyurethane or PVC; mimics leather appearance | Affordable fashion, automotive interiors | Pros: Cost-effective, wide variety of styles; Cons: Less breathable, environmental concerns. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Cork Leather?
Cork leather is distinguished by its eco-friendly nature, being made from the bark of cork oak trees. This material is lightweight, water-resistant, and flame-resistant, making it suitable for a variety of B2B applications, including fashion accessories and upholstery. When purchasing cork leather, businesses should consider its sustainability credentials, as it is produced without harmful chemicals and is biodegradable when backed with organic materials. However, it may not be as durable as traditional full-grain leather, which could affect long-term usage in high-wear environments.
How Does Full Grain Leather Stand Out in the Market?
Full grain leather is characterized by its natural grain and high durability, making it a preferred choice for luxury goods and high-end furniture. It develops a unique patina over time, enhancing its aesthetic appeal. B2B buyers should recognize that while full grain leather is an investment, its longevity and timeless quality can justify the higher cost. Additionally, it requires regular maintenance to preserve its appearance, which may be a consideration for businesses with varying levels of resources for upkeep.
What Should Buyers Know About Composite Leather?
Composite leather, often marketed as ‘genuine leather’, is made from leather scraps and is more affordable than full-grain options. This type is commonly used in mass-produced goods and budget items. Buyers should be aware that while composite leather offers versatility and cost savings, it typically lacks the quality and longevity of higher-grade leathers. Understanding the composition and sourcing of composite leather is essential for businesses aiming to maintain brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
Why Choose Vegetable-Tanned Leather for Eco-Conscious Markets?
Vegetable-tanned leather is tanned using natural materials, appealing to eco-conscious markets and artisan goods. This method is safer for workers and the environment, as it avoids harmful chemicals. B2B buyers should consider the longer production time and potentially higher prices associated with vegetable-tanned leather. However, its biodegradability and ethical production practices can enhance brand value, particularly in markets where sustainability is a key selling point.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Synthetic Leather?
Synthetic leather, made from materials like polyurethane or PVC, mimics the appearance of real leather and is often more affordable. It is widely used in fashion and automotive interiors due to its cost-effectiveness and variety of styles. However, buyers should be aware of the environmental concerns associated with synthetic materials, including their non-biodegradable nature. Understanding these factors can help businesses align their product offerings with consumer preferences for sustainability while balancing budgetary constraints.
Key Industrial Applications of cork and leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cork and leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion and Apparel | Sustainable handbags and accessories | Eco-friendly alternatives appeal to conscious consumers, enhancing brand image and market reach. | Ensure compliance with ethical sourcing standards and certifications. |
| Automotive | Interior trims and upholstery | Lightweight, durable materials improve vehicle efficiency and comfort. | Evaluate fire resistance and durability ratings for safety compliance. |
| Home Decor | Cork flooring and wall coverings | Natural insulation properties lead to energy savings and enhanced aesthetics. | Source from suppliers with sustainable harvesting practices to ensure quality. |
| Packaging | Wine stoppers and eco-friendly packaging solutions | Biodegradable options reduce environmental impact and cater to eco-conscious brands. | Verify the origin of cork and certifications to ensure sustainability. |
| Health and Wellness | Yoga mats and eco-friendly footwear | Non-toxic, hypoallergenic materials promote health and safety for consumers. | Check for certifications related to health safety and environmental impact. |
How Is Cork and Leather Used in Fashion and Apparel?
Cork and leather are increasingly utilized in the fashion industry, particularly for sustainable handbags, wallets, and shoes. The eco-friendly nature of cork leather appeals to environmentally conscious consumers, offering brands an opportunity to enhance their image and market reach. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who comply with ethical sourcing standards and certifications, ensuring that their products meet both quality and sustainability expectations.
What Are the Benefits of Cork in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, cork is applied in interior trims and upholstery, where its lightweight and durable properties contribute to overall vehicle efficiency and passenger comfort. Cork’s natural insulation capabilities also help in reducing noise and improving climate control within vehicles. International buyers should assess fire resistance and durability ratings to meet safety compliance and ensure a high-quality product.
How Does Cork Enhance Home Decor Solutions?
Cork is a popular choice for flooring and wall coverings due to its aesthetic appeal and natural insulation properties. These features not only improve energy efficiency but also create a warm and inviting atmosphere in homes. Buyers should seek suppliers committed to sustainable harvesting practices, as this ensures the quality of the cork and aligns with consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
Why Is Cork Important for Sustainable Packaging?
The packaging industry is leveraging cork for applications such as wine stoppers and eco-friendly packaging solutions. Cork’s biodegradable nature significantly reduces environmental impact, catering to brands focused on sustainability. Buyers should verify the origin of cork and its certifications to ensure that they are sourcing from responsible suppliers, thus reinforcing their commitment to environmental stewardship.

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
What Role Does Cork Play in Health and Wellness Products?
In the health and wellness sector, cork is increasingly used in products like yoga mats and eco-friendly footwear. Its non-toxic and hypoallergenic properties make it an ideal choice for consumers prioritizing health and safety. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers hold relevant certifications related to health safety and environmental impact, which can enhance product credibility and appeal to health-conscious consumers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cork and leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Quality Consistency in Cork Leather Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the inconsistency in quality when sourcing cork leather. Given that cork leather is made from natural materials, variations can occur due to differences in the grade of cork, the processing methods used, or the backing materials selected. This inconsistency can lead to challenges in product quality, affecting brand reputation and customer satisfaction. Buyers may receive batches that do not meet their expectations, leading to returns and lost sales.
The Solution: To mitigate quality inconsistency, B2B buyers should establish clear quality benchmarks and work closely with suppliers who can provide certifications or documentation of their cork’s grade. It’s advisable to request samples from different batches to assess the quality before placing large orders. Additionally, forming long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers can facilitate better control over quality consistency. Engage in open dialogue about quality expectations and consider incorporating quality assurance checks during production. Implementing a standardized testing process for incoming materials can also help ensure that only the highest quality cork leather is used in final products.
Scenario 2: Addressing Environmental Concerns and Consumer Demands
The Problem: With increasing awareness of environmental issues, B2B buyers face pressure to source materials that align with sustainable practices. Cork leather is celebrated for its eco-friendly properties, yet buyers often encounter skepticism from consumers regarding the actual sustainability of their sourcing practices. This can lead to challenges in marketing and selling products made from cork leather, particularly in regions where consumers are highly informed and conscientious about their purchases.
The Solution: B2B buyers can address these environmental concerns by emphasizing the sustainable harvesting practices of cork leather. They should actively seek suppliers who utilize organic and non-toxic processes and who can provide transparency about their sourcing and production methods. Developing marketing materials that highlight the environmental benefits of cork leather—such as its biodegradability, low carbon footprint, and the positive impact of cork oak harvesting on biodiversity—can help alleviate consumer skepticism. Furthermore, engaging in certifications such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) can bolster credibility and reassure consumers that their purchases support sustainable practices.

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
Scenario 3: Navigating Cost-Effectiveness While Sourcing Cork Leather
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in balancing the cost of cork leather with the need for high-quality materials. While cork leather is generally more affordable than traditional leather, the perception of higher costs associated with eco-friendly materials can deter potential buyers. This cost concern is particularly significant for businesses operating on tight margins or those in competitive markets where price sensitivity is high.
The Solution: To navigate cost-effectiveness, B2B buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify competitive pricing while ensuring quality. Exploring partnerships with suppliers that offer bulk purchasing discounts or flexible payment terms can help reduce upfront costs. Additionally, buyers can consider diversifying their product range to include both cork leather and traditional leather options, allowing them to appeal to a broader market segment. Highlighting the long-term durability and maintenance savings of cork leather can also justify the initial investment to consumers, making it a more attractive option in the long run. Engaging in cost-benefit analyses that include environmental impact savings can further strengthen the business case for cork leather, making it a viable alternative even in price-sensitive markets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cork and leather
What Are the Key Properties of Cork Leather for B2B Applications?
Cork leather, derived from the bark of cork oak trees, boasts unique properties that make it a compelling choice for various applications. Its lightweight nature, stemming from its honeycomb structure, provides excellent thermal, electrical, and acoustic insulation. Additionally, cork leather is water-resistant, flame-resistant, and hypoallergenic, making it suitable for products such as bags, shoes, and upholstery. The durability of cork leather is notable, although it does not match the longevity of high-quality full-grain leather. For international buyers, understanding the sourcing and processing of cork leather is essential, as these factors influence product quality and compliance with environmental standards.

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Full-Grain Leather?
Full-grain leather is renowned for its durability and aesthetic appeal, often improving with age. It is suitable for high-end products such as luxury handbags, shoes, and furniture. However, the production of full-grain leather involves significant environmental concerns, particularly due to the tanning processes that can use toxic chemicals. Additionally, full-grain leather can be costly and may require ongoing maintenance to retain its quality. International buyers must consider local regulations regarding leather sourcing and animal welfare, as well as consumer preferences for sustainable materials.
How Do Synthetic Leathers Compare in Terms of Performance and Cost?
Synthetic leathers, commonly made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offer a vegan alternative to traditional leather. They are often more affordable and can be produced in a variety of textures and colors. However, synthetic leathers typically lack the breathability and durability of natural materials, which can limit their application in high-performance products. Furthermore, environmental concerns arise from the production and disposal of synthetic materials, as they can take hundreds of years to decompose. B2B buyers should evaluate the long-term sustainability of synthetic options, especially in markets with increasing demand for eco-friendly products.
What Are the Specific Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing cork and leather materials, international buyers must navigate various compliance and quality standards. For instance, European buyers may adhere to DIN standards, while those in the United States may follow ASTM guidelines. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should also consider local regulations regarding sustainable sourcing and ethical production. Additionally, understanding the preferences of regional markets is crucial; for example, European consumers often prioritize eco-friendly products, while Middle Eastern markets may focus on luxury and durability.
Summary Table of Material Comparisons
| Material | Typical Use Case for cork and leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cork Leather | Eco-friendly bags, shoes, upholstery | Lightweight, water-resistant, biodegradable | Not as durable as full-grain leather | Medium |
| Full-Grain Leather | Luxury handbags, high-end furniture | Exceptional durability and aesthetic appeal | High cost, environmental concerns in tanning | High |
| Synthetic Leather | Affordable fashion items, upholstery | Cost-effective, variety of textures/colors | Less durable, environmental concerns | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in diverse international markets, enabling informed decisions when sourcing cork and leather products. By evaluating the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, businesses can better align their offerings with market demands and sustainability goals.

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cork and leather
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Cork and Leather?
The manufacturing processes for cork and leather are distinct yet share some similarities in terms of attention to detail and quality. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing materials for high-end products.
Material Preparation: How Are Cork and Leather Sourced and Processed?
For cork leather, the journey begins with the harvesting of cork from cork oak trees, primarily found in the Mediterranean region. The process is sustainable, as the bark is hand-harvested every nine years without harming the tree. Once harvested, the cork is air-dried for six months to remove moisture. This drying phase is critical, as it prepares the cork for subsequent processing. After drying, the cork undergoes steaming and boiling, which enhances its elasticity. The final step in material preparation involves cutting the cork into thin sheets, ready for backing.
In contrast, leather manufacturing typically starts with the sourcing of animal hides, which can vary significantly in quality. The hides are then tanned using either chrome or vegetable tanning methods. Chrome tanning is faster and cheaper but can pose environmental hazards, while vegetable tanning is slower but more environmentally friendly. The tanning process transforms the raw hide into a durable material, ready for further processing.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Cork and Leather Products?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into usable forms. For cork leather, the sheets are often bonded to a fabric backing, typically cotton, using the natural adhesive suberin found in cork. This eliminates the need for synthetic glues, making the process more eco-friendly. The sheets can then be cut and sewn into various products, from wallets to bags.
Leather, on the other hand, is often cut into patterns and stitched to create finished products. Techniques like embossing or dyeing may be employed to enhance aesthetic appeal. For both materials, precision cutting and sewing are essential to ensure product quality and durability.
How Is the Assembly Process Managed for Cork and Leather Products?
Assembly for cork leather products typically involves stitching the cut pieces together, ensuring that seams are strong and aesthetically pleasing. Quality control during this stage is vital, as imperfections can lead to product failures. Leather products follow a similar assembly process, though additional steps such as lining or adding hardware may be included.
Both materials benefit from skilled artisans who ensure that the final products meet the desired specifications. This human element is especially important in luxury markets, where craftsmanship is often a key selling point.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Applied to Cork and Leather?
Finishing techniques play a crucial role in enhancing the durability and appearance of both cork and leather products. For cork leather, a protective coating may be applied to enhance water resistance and durability. This step can significantly extend the product’s lifespan and maintain its appearance over time.

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
For leather, finishing processes may include polishing, dyeing, or applying protective sprays. These treatments can not only improve aesthetics but also add functional qualities, such as stain resistance. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific finishing techniques used by suppliers to ensure that products meet their standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be familiar with the relevant standards, such as ISO 9001 for general quality management systems and CE marking for products sold within the European Economic Area.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing Cork and Leather?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential in maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. For cork, this could include checking for blemishes or inconsistencies, while for leather, it may involve assessing hide quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks should be conducted at various stages to ensure that products are being made to specifications. This might include verifying dimensions during cutting or inspecting seams during assembly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final stage involves a comprehensive inspection of the finished products. B2B buyers should look for suppliers who conduct thorough FQC checks to ensure that all products meet quality standards before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Control for Cork and Leather?
Several testing methods can be employed to ensure the quality of cork and leather products:
-
Physical Testing: This may include assessments of tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and water resistance to determine the durability of the materials.
-
Chemical Testing: For leather, tests may be conducted to check for the presence of harmful substances, especially if chrome tanning was used.
-
Environmental Testing: Given the eco-friendly nature of cork leather, B2B buyers may also want to verify that suppliers adhere to sustainability practices during production.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control practices. This can be achieved through:
-
Supplier Audits: Regular audits can provide insights into a supplier’s quality management systems and manufacturing processes. Buyers should schedule periodic visits to assess the facilities and practices firsthand.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can offer transparency into the supplier’s quality assurance processes. This should include information on testing methods and results.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of product quality before shipment. This is particularly useful for international buyers who may not be able to visit suppliers in person.
What Are the Unique QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification when sourcing cork and leather products from different regions:

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
-
Regional Standards: Different countries may have varying standards for materials and manufacturing processes. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations, particularly in markets like Europe, where CE marking is essential.
-
Cultural Practices: Understanding local manufacturing practices and cultural attitudes towards quality can help buyers assess the reliability of suppliers. In some regions, craftsmanship is highly valued, which can enhance product quality.
-
Sustainability Certifications: As environmental concerns become more prominent, certifications related to sustainability and ethical practices can influence buying decisions. Buyers should look for certifications that verify eco-friendly practices, especially for cork products.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for cork and leather, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their product offerings and build sustainable partnerships with suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cork and leather’
In the competitive landscape of B2B sourcing, acquiring high-quality cork and leather products requires a strategic approach. This guide provides a clear checklist to ensure that international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can effectively navigate the procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, outline your specific requirements for cork and leather products. This includes determining the intended application, desired grades of cork or leather, and any environmental standards you wish to uphold.
– Considerations: Think about product durability, aesthetics, and functionality to ensure the materials meet your business needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in cork and leather. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of manufacturers and distributors.
– Action Items: Look for suppliers with a proven track record and positive reviews. Pay attention to their production capabilities and experience in exporting to your region.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that your shortlisted suppliers hold relevant certifications that demonstrate compliance with international quality and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Oeko-Tex for textile safety are particularly important.
– Why It Matters: Certification ensures that suppliers adhere to sustainable practices and produce high-quality materials, aligning with the ethical expectations of modern consumers.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before making a bulk order, request samples of cork and leather products from potential suppliers. This step allows you to assess the quality, texture, and durability firsthand.
– Evaluation Criteria: Examine the samples for uniformity, finish, and any potential defects. Consider how well the materials meet your technical specifications and aesthetic requirements.
Step 5: Discuss Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions regarding pricing, payment terms, and minimum order quantities. Transparency in pricing is crucial for budgeting and financial planning.
– Negotiation Tips: Be clear about your expectations and inquire about bulk purchase discounts. Ensure that the terms are favorable for both parties to foster a long-term relationship.
Step 6: Conduct a Site Visit or Virtual Audit
If feasible, arrange for a site visit or a virtual audit of the supplier’s facilities. This provides deeper insight into their production processes, labor practices, and quality control measures.
– Key Observations: Assess the working conditions and the technology used in production. This step can significantly influence your decision by ensuring ethical practices are upheld.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Contract
Once you select a supplier, draft a comprehensive contract that outlines all terms of the agreement, including product specifications, delivery timelines, and penalties for non-compliance.
– Important Inclusions: Ensure that the contract addresses quality assurance processes and dispute resolution mechanisms to protect your interests throughout the partnership.

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for cork and leather, ensuring they select the right suppliers who meet their quality, ethical, and logistical requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cork and leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Cork and Leather Sourcing?
When evaluating the cost structure for cork and leather sourcing, several critical components must be considered. These include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials varies significantly. For cork, quality and sourcing location (e.g., Portugal, China, India) affect pricing. High-quality cork can command a premium, while leather prices fluctuate based on the type (e.g., full-grain, genuine) and the treatment processes involved (e.g., chrome vs. vegetable tanning).
-
Labor: Labor costs differ across regions, influenced by local wage standards and the skills required for harvesting cork or tanning leather. In areas where traditional methods are employed, labor may be more expensive, but this can also translate into higher quality products.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with facilities, equipment, and utilities. Cork processing requires specific machinery and skilled labor, while leather tanning involves additional complexities due to environmental regulations and safety standards.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be significant, particularly for custom designs. For cork and leather goods, the tooling costs may include molds for specific shapes or dies for intricate patterns.
-
Quality Control (QC): QC processes are vital in ensuring that the final products meet the required specifications and certifications. This adds an additional layer of cost but is essential for maintaining product integrity, especially when exporting to markets with strict regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the distance from suppliers to buyers, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Freight rates can fluctuate based on fuel prices and shipping routes, which can impact overall pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin on top of their costs, which can vary widely based on competition, brand positioning, and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Cork and Leather Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing for cork and leather products:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order quantities can lead to discounts, as suppliers often have lower per-unit costs with larger runs. Buyers should consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) when negotiating prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of bespoke designs against potential cost increases.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific quality standards or certifications (e.g., eco-friendly, organic) may command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these certifications based on their market requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms will affect the overall cost of sourcing. For example, terms like DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) include shipping and duties in the price, while FOB (Free on Board) requires buyers to manage shipping logistics, which can affect final costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Cork and Leather Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of cork and leather pricing is essential for cost efficiency. Here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the unit price, consider the entire lifecycle cost of the product, including shipping, storage, and potential returns. This holistic view can uncover better deals.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: When feasible, consolidate orders to achieve better pricing. Engage with suppliers about potential bulk purchase agreements or long-term contracts.
-
Research Market Rates: Stay informed about current market trends and prices for cork and leather. This knowledge will empower buyers during negotiations and help identify fair pricing.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships can lead to more favorable pricing and terms over time. Suppliers may be more willing to negotiate with trusted partners.
-
Be Cautious of Indicative Prices: Always request detailed quotes that break down costs to avoid surprises. Indicative prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so obtaining a firm quote is critical.
By understanding these cost components and pricing influencers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals and market demands.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cork and leather With Other Solutions
In the quest for sustainable and high-performance materials, cork and leather often emerge as frontrunners. However, various alternatives are available that may better suit specific business needs. This section explores viable alternatives to cork and leather, providing a comprehensive comparison to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
| Comparison Aspect | Cork and Leather | Synthetic Leather | Recycled Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, water-resistant, hypoallergenic; retains shape well | Good durability, but can be less breathable | Varies widely, depending on the source materials |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on quality | Generally lower than genuine leather | Varies; often lower, but quality can be inconsistent |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor for production | Easily mass-produced | May require additional processing |
| Maintenance | Low; easy to clean and resistant to dust | Moderate; may require conditioning | Varies; some may need special care |
| Best Use Case | Eco-conscious brands, luxury goods | Fast fashion, affordable goods | Sustainable brands focused on recycling |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Synthetic Leather?
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), presents a cost-effective alternative to natural leather. One of its primary advantages is affordability, allowing brands to offer competitive pricing while still achieving a leather-like aesthetic. Additionally, synthetic leather is easier to produce at scale, making it a popular choice in the fast fashion industry. However, it lacks breathability and can retain odors, which may deter consumers seeking high-quality products. Furthermore, the environmental impact of synthetic leathers, particularly those derived from fossil fuels, raises concerns regarding their sustainability.
How Do Recycled Materials Compare?
Recycled materials, such as those derived from post-consumer plastics or old textiles, offer an eco-friendly alternative to both cork and leather. Their primary advantage lies in their sustainability; utilizing waste materials reduces landfill impact and conserves resources. However, the performance of recycled materials can vary significantly based on the source, leading to inconsistencies in quality and durability. While they can be cost-effective, the requirement for additional processing may increase production costs. Brands aiming for a strong sustainability message may find recycled materials to be an attractive option, provided they can ensure quality control.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When evaluating alternatives to cork and leather, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. For brands targeting eco-conscious consumers, cork leather may provide the right balance of durability and environmental benefits. Conversely, those prioritizing cost-effectiveness and scalability might lean towards synthetic leather. Lastly, businesses committed to sustainability and recycling initiatives could explore recycled materials as a viable option. Ultimately, the choice should align with the brand’s values, target audience, and market positioning.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cork and leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cork and Leather?
Understanding the essential technical properties of cork and leather is crucial for B2B buyers, as these specifications directly influence product quality, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of cork or leather based on quality and characteristics. For cork, there are typically seven grades, with higher grades being smoother and free of blemishes. In leather, grades range from full-grain (the highest quality) to bonded leather (lower quality). Buyers should prioritize high-grade materials for premium products, as they ensure better performance and longevity, which can significantly impact customer satisfaction and brand reputation.

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the allowable variation in dimensions or properties of the material during manufacturing. For instance, cork sheets may have a specified tolerance in thickness, impacting their application in various products. Understanding tolerances is vital for ensuring that components fit together correctly in the final product, reducing waste and the risk of defects. This is especially important in industries like fashion and automotive, where precision is essential.
3. Water Resistance
Water resistance is a key property of both cork and leather, influencing their suitability for various applications. Cork leather is naturally water-resistant due to its cellular structure, while treated leather can also offer varying levels of water resistance. Buyers should assess this property based on the intended use of the product, as it can determine durability and maintenance requirements, especially in regions with high humidity or exposure to moisture.
4. Biodegradability
Biodegradability is an increasingly important property for environmentally conscious buyers. Cork leather, made from natural materials, is biodegradable, making it an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic leathers. This property is critical for brands aiming to enhance their sustainability credentials. Buyers should consider the lifecycle impact of their materials, as consumers are increasingly favoring products that align with sustainable practices.
5. Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance measures how well a material can withstand wear from friction. Cork leather exhibits a high friction coefficient, making it durable in high-wear applications like bags and wallets. Evaluating abrasion resistance is essential for buyers, especially in the fashion and accessories industry, as it affects the longevity and aesthetic appeal of the final product.
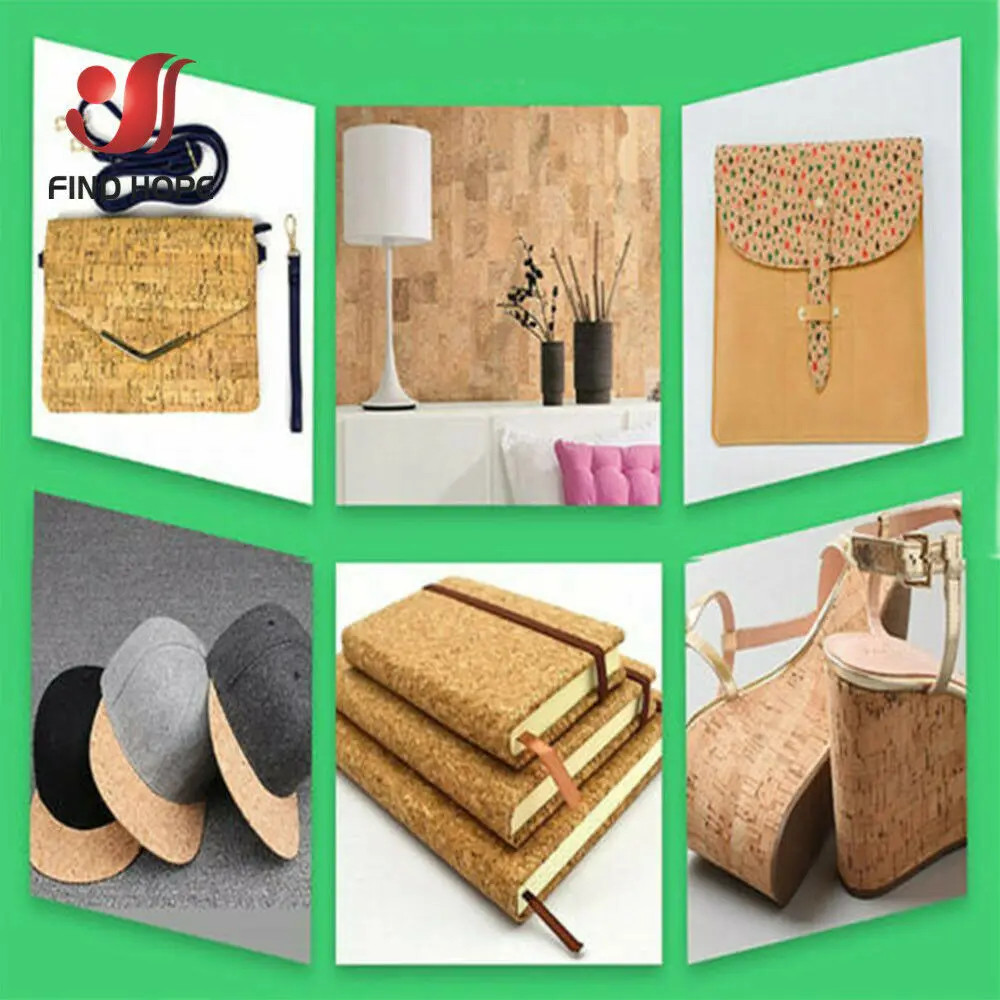

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Cork and Leather Industry?
Navigating the cork and leather supply chain requires familiarity with industry-specific terminology. Here are some common trade terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the cork and leather industry, OEMs can be crucial for sourcing high-quality materials or components that meet specific design requirements. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they receive reliable products that adhere to their quality standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the cork and leather sector, MOQs can vary widely based on material type, production methods, and supplier capabilities. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to plan their inventory and purchasing strategies effectively, ensuring they balance cost efficiency with demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In the context of cork and leather, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing, terms, and conditions from multiple suppliers. This process is vital for making informed purchasing decisions and securing the best value for materials.
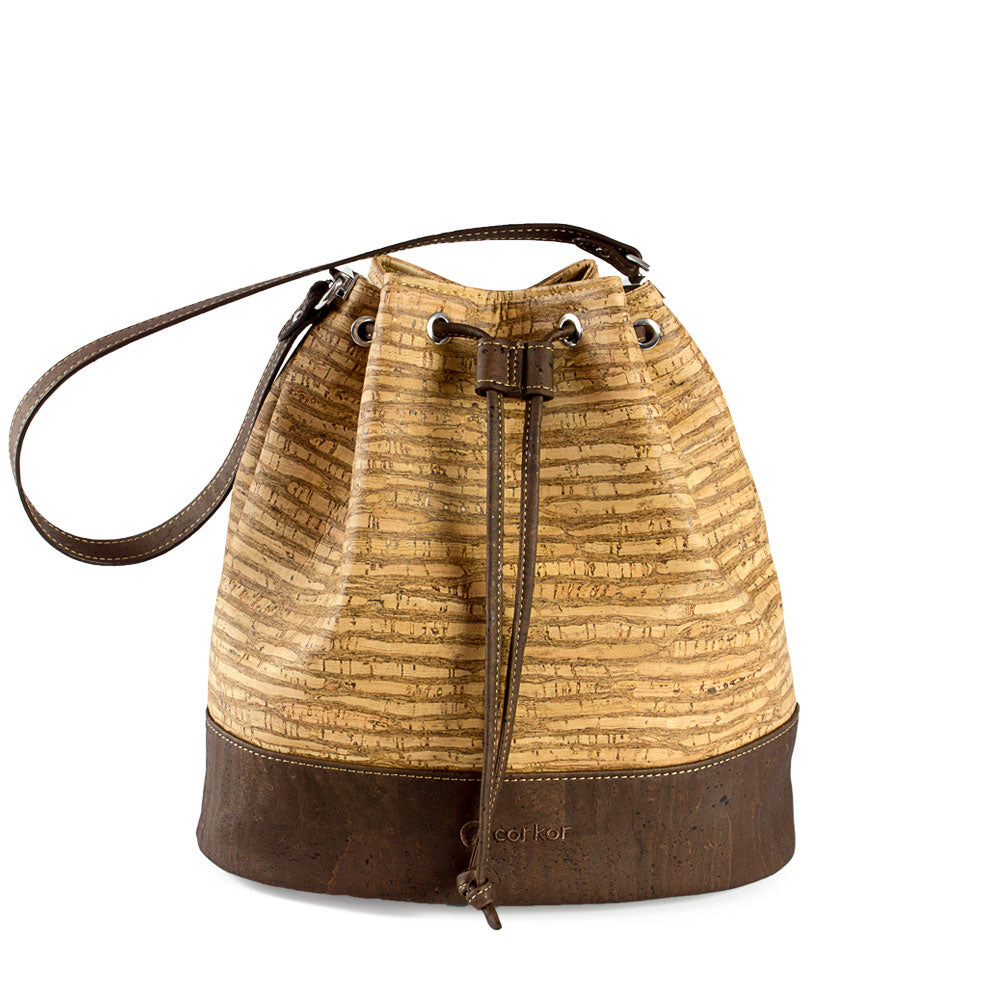

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping costs, insurance responsibilities, and delivery timelines in the cork and leather trade. Proper knowledge of these terms can help buyers negotiate better shipping agreements and avoid unexpected costs.
5. Tanning Process
In leather production, the tanning process involves treating animal hides to prevent decomposition. There are several methods, including chrome tanning and vegetable tanning. Buyers should be aware of the tanning process used, as it affects the leather’s quality, durability, and environmental impact, guiding them in sourcing ethically produced materials.
Understanding these properties and terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions in the cork and leather marketplace, enhancing their product offerings and overall business success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cork and leather Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Cork and Leather Sector?
The cork and leather sector is witnessing significant transformations driven by a blend of environmental awareness, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. The global demand for sustainable and ethically sourced materials is on the rise, particularly among B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key trends include the increasing popularity of cork leather as a viable alternative to traditional leather, primarily due to its eco-friendly properties and unique characteristics. The cork industry, predominantly based in the Mediterranean region, is expanding its production capabilities to meet this growing demand, with countries like Portugal, Spain, and Italy leading the way.
Technological innovations are reshaping sourcing practices, with digital platforms facilitating direct connections between producers and buyers. Blockchain technology is emerging as a tool for ensuring transparency in the supply chain, enabling companies to trace the origins of their materials. This is particularly important for international buyers who prioritize ethical sourcing. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce is allowing manufacturers to reach a broader audience, enabling B2B buyers to explore and source cork and leather products more efficiently.
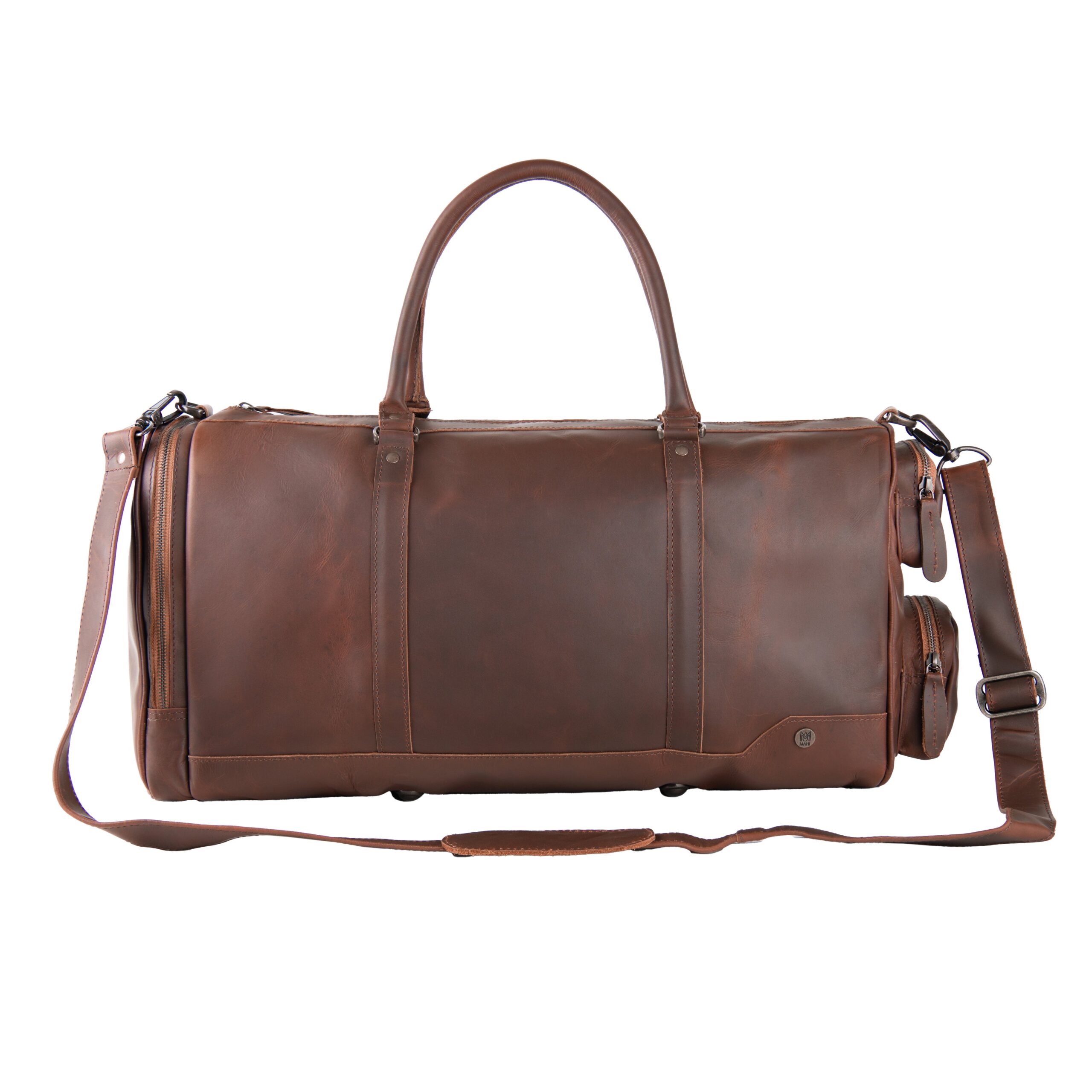

Illustrative image related to cork and leather
Market dynamics are also influenced by regional preferences. For instance, European buyers are increasingly inclined towards sustainable products, while Middle Eastern and African markets are exploring the potential of cork leather in various applications, including fashion and interior design. As competition intensifies, companies that can effectively communicate their sustainability credentials and innovative product offerings are likely to gain a competitive edge.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Cork and Leather Industry?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the cork and leather industry, with increasing pressure on companies to adopt ethical sourcing practices. The environmental impact of traditional leather production has led to a significant shift towards alternatives like cork leather, which is derived from the bark of cork oaks. This process not only preserves the trees but also promotes biodiversity in cork forests, which play a crucial role in carbon sequestration. For international B2B buyers, understanding the environmental credentials of their suppliers is essential, as consumers are becoming more discerning about the origins and ethical implications of their purchases.
Ethical supply chains are no longer optional; they are a necessity. Certifications such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) are becoming increasingly important for buyers looking to validate the sustainability of their products. Cork leather, often backed with organic materials, aligns well with these standards, offering a biodegradable alternative to synthetic leathers and traditional animal hides. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide transparent information regarding their sourcing practices and certifications, as this will not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the growing demand for sustainable products in the marketplace.
What Is the Historical Context of Cork and Leather Relevant for Today’s B2B Buyers?
The historical significance of cork and leather extends beyond their functional uses; they are deeply intertwined with cultural practices and economic systems. Cork has been harvested for over 5,000 years, initially for sealing containers and later for its applications in footwear and various other products. The establishment of protective laws in Portugal as early as 1209 reflects the long-standing value placed on cork forests, which are now recognized for their ecological importance.
The leather industry has evolved in parallel, facing scrutiny for its environmental and ethical implications. The rise of synthetic alternatives and changing consumer preferences have prompted a renewed interest in sustainable materials like cork leather. This evolution is crucial for B2B buyers to understand, as it underscores the importance of sourcing materials that not only meet current market demands but also align with ethical practices. As the cork and leather sectors continue to evolve, the integration of historical insights with modern sustainability efforts presents a unique opportunity for international buyers to capitalize on emerging trends while fostering responsible consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cork and leather
-
How do I choose the right supplier for cork and leather products?
Choosing the right supplier involves thorough research and vetting. Start by verifying their certifications and compliance with international standards, especially in terms of sustainability and ethical practices. Request samples to assess product quality and durability. Additionally, consider their production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your demands. Engage in discussions to gauge their responsiveness and customer service. A reliable supplier should also provide clear communication regarding payment terms and logistics, essential for successful international trade. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cork and leather products?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific products. Typically, cork and leather suppliers may set MOQs to ensure cost efficiency in production. For custom designs or specialized products, MOQs might be higher. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers upfront to negotiate MOQs that align with your business needs. Some suppliers may also offer flexibility for initial orders, especially for new clients, which can help you test the market without significant upfront investment. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing cork and leather?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance payable upon delivery or prior to shipping. Some suppliers may offer letter of credit options, which can provide added security for both parties. It’s crucial to clarify payment terms in advance to avoid misunderstandings. Always consider the currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees, especially when dealing with international suppliers, to ensure your financial planning remains intact. -
How can I ensure the quality of cork and leather products?
To ensure product quality, request certifications that confirm adherence to international standards, such as ISO or environmental certifications. Conduct audits or factory visits if feasible, and establish a clear quality assurance process that includes detailed specifications for materials and finishes. Implementing a pre-shipment inspection can also be beneficial, allowing you to verify quality before products leave the supplier’s facility. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can further enhance quality control, as they may prioritize your orders and feedback. -
What are the environmental benefits of cork and leather?
Cork is celebrated for its sustainability, as harvesting does not harm the trees and actually promotes their longevity. Cork forests play a vital role in CO2 absorption and support biodiversity. Conversely, while traditional leather production often raises environmental concerns, sourcing from suppliers that utilize vegetable tanning processes can mitigate some negative impacts. As a B2B buyer, prioritizing eco-friendly suppliers can enhance your brand’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. -
How is cork leather made, and what are its unique properties?
Cork leather is produced from the bark of cork oaks, harvested every nine years without harming the trees. The process involves drying, boiling, and flattening the cork, followed by bonding it to a backing material, typically organic. Unique properties of cork leather include its water resistance, durability, and hypoallergenic nature. Its lightweight structure, combined with excellent thermal and acoustic insulation, makes it an attractive alternative to traditional leather for various applications in fashion and home goods. -
What customization options are available for cork and leather products?
Customization options for cork and leather products can include variations in color, texture, and backing materials. Many suppliers offer the ability to create bespoke designs tailored to your brand’s specifications, such as embossing logos or custom shapes. Discuss your customization needs early in the procurement process to understand the feasibility and any associated costs. Establishing a clear design brief and timeline will help streamline the process and ensure that the final products meet your expectations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing cork and leather?
When importing cork and leather products, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties applicable in your country. Collaborate with suppliers to determine the best logistics partners who can handle international shipping efficiently. Ensure all documentation is prepared to facilitate smooth customs clearance, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Timely communication with your logistics provider can help avoid delays and ensure that your products arrive as scheduled.
Top 3 Cork And Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Buckleguy – Cork Fabric
Domain: buckleguy.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Cork Fabric by Buckleguy is available in 13 colors and patterns, sold by the foot or linear yard. Sourced from a 3rd generation Italian factory, it emphasizes sustainable harvesting practices. This cork leather is suitable for accessories, bags, totes, shoes, upholstery, keychains, and crafts, and is a vegan alternative to leather. Pricing ranges from $4.00 to $73.39 depending on the pattern and q…
2. MBCork – Wholesale Cork Fabrics & Accessories
Domain: mbcork.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Wholesale Portugal Cork Fabric | Cork Leather | Cork Fabric To Sew. Offers a variety of cork fabrics including Cork Fabric Samples, Cork Colored Fabric, Cork Printed Fabric, and Cork Fabric for bags. Features products like coin purses, wallets, crossbody bags, handbags, and backpacks. Jewelry options include cork bracelets, necklaces, earrings, rings, keychains, and watches. Accessories such as be…
3. Carl Friedrik – Sustainable Cork Leather
Domain: carlfriedrik.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Cork leather is a sustainable vegan option derived from the bark of the cork oak tree (Quercus suber), primarily found in Portugal. It is harvested every nine years without harming the tree, which can live up to 300 years. The production process involves drying the bark for six months, steaming, boiling, and cutting it into thin sheets, often backed with cotton or polyurethane (PU). Benefits inclu…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cork and leather
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing of Cork and Leather?
The strategic sourcing of cork and leather presents a unique opportunity for B2B buyers to align with sustainable practices while addressing market demands. Cork leather, derived from the bark of cork oaks, offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional leather, combining durability with a low environmental impact. It is essential for buyers to evaluate the quality and sourcing of materials, as the sustainability narrative can significantly influence consumer preferences, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East where ethical considerations are paramount.
How Can International Buyers Capitalize on Cork and Leather Trends?
As global markets evolve, the demand for sustainable materials is on the rise. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider integrating cork leather into their product offerings, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Collaborating with reputable suppliers who adhere to ethical harvesting and production practices will enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What’s Next for the Cork and Leather Market?
Looking ahead, the cork and leather sector is poised for growth, driven by increasing awareness of sustainability and the need for innovative materials. International buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with cork producers and leather manufacturers who prioritize environmental stewardship. Engaging in this market not only supports sustainable practices but also positions businesses at the forefront of a transformative industry. Embrace the opportunity to make a positive impact while meeting consumer needs—start sourcing strategically today!
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.