Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what does pu leather mean
In the ever-evolving landscape of materials sourcing, understanding what PU leather means is crucial for B2B buyers seeking quality and sustainability. As industries increasingly prioritize eco-friendly alternatives, the demand for synthetic leather has surged, posing challenges in differentiating between high-quality products and those that may not meet long-term expectations. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of PU leather, exploring its composition, applications, and the critical nuances that set it apart from genuine leather.
From fashion and upholstery to automotive and beyond, PU leather’s versatility makes it a popular choice. However, it’s essential for international buyers—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe like Germany and Nigeria—to navigate the complexities of sourcing responsibly. This comprehensive resource covers various types of PU leather, supplier vetting techniques, cost considerations, and the potential environmental impacts associated with its use.
Equipped with this knowledge, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their quality standards and sustainability goals. By understanding the intricacies of PU leather, businesses can not only enhance their product offerings but also contribute positively to the global market’s shift towards more responsible consumption.
Table Of Contents
- Top 8 What Does Pu Leather Mean Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what does pu leather mean
- Understanding what does pu leather mean Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what does pu leather mean
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what does pu leather mean’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what does pu leather mean
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what does pu leather mean
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what does pu leather mean’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what does pu leather mean Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what does pu leather mean With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what does pu leather mean
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what does pu leather mean Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what does pu leather mean
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what does pu leather mean
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
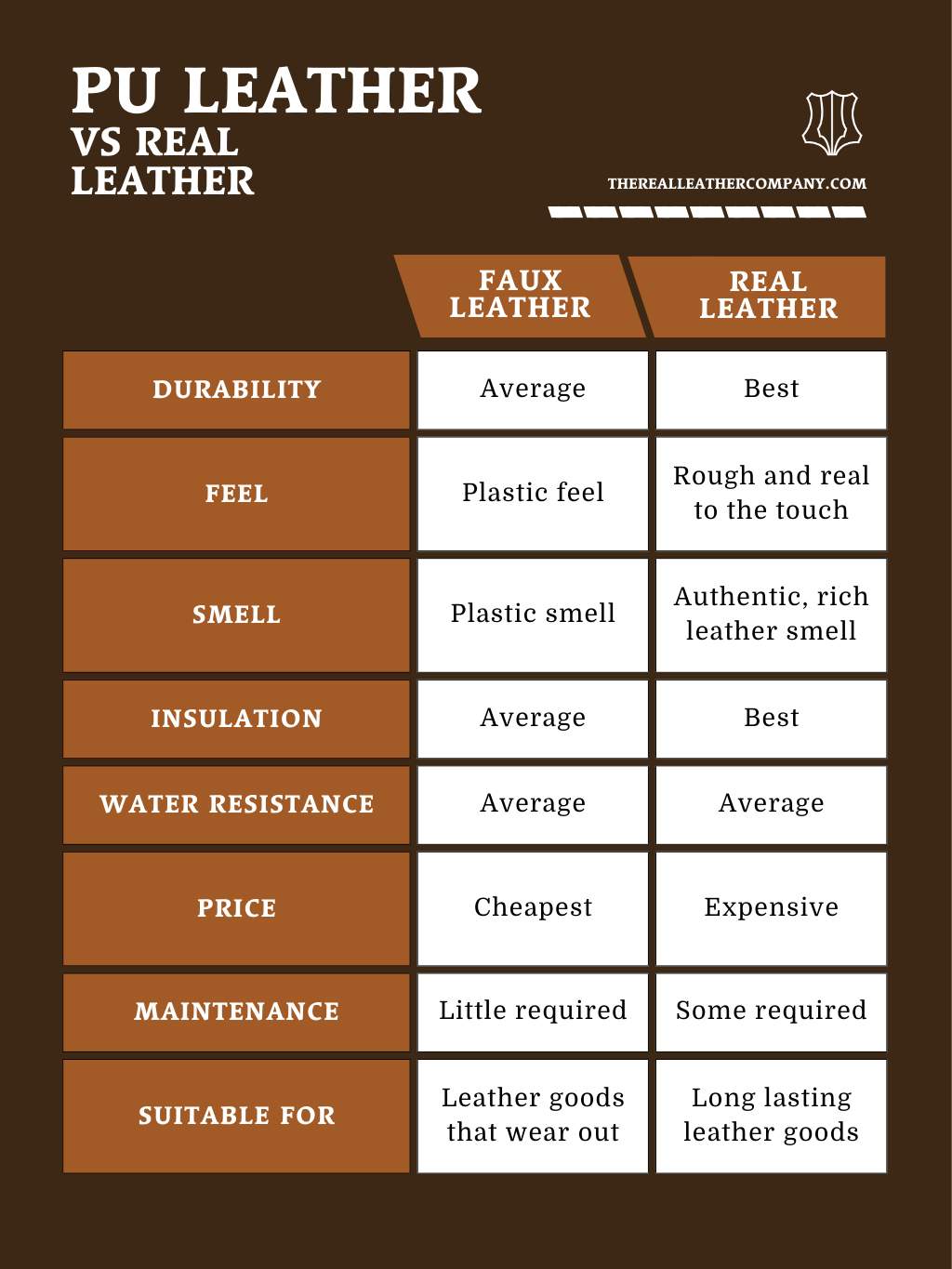
Understanding what does pu leather mean Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard PU Leather | Basic synthetic material, often with a uniform texture. | Fashion accessories, upholstery | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to clean. Cons: Low durability, prone to cracking. |
| Microfiber PU Leather | Softer feel, enhanced durability, often more breathable. | Automotive interiors, furniture | Pros: Better durability, more comfortable. Cons: Higher cost than standard PU. |
| Eco-friendly PU Leather | Made with less harmful chemicals, often recyclable. | Sustainable fashion, eco-friendly products | Pros: Reduced environmental impact, safer for users. Cons: Limited availability, potentially higher price. |
| Coated PU Leather | Fabric base with a thick polyurethane coating for added durability. | Bags, wallets, and footwear | Pros: Increased lifespan, water-resistant. Cons: Heavier, can be less flexible. |
| Printed PU Leather | Features printed designs or textures to mimic genuine leather. | Fashion items, promotional products | Pros: Customizable aesthetics, appealing visuals. Cons: May not have the same tactile feel as real leather. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard PU Leather for B2B Buyers?
Standard PU leather is a widely used synthetic material characterized by its affordability and ease of maintenance. It is primarily utilized in fashion accessories and upholstery due to its ability to mimic the look of genuine leather. However, it has significant drawbacks, including low durability, which can lead to cracking and peeling over time. For B2B buyers, this means considering the total cost of ownership, as products made from standard PU leather may require frequent replacements, impacting long-term budgets.
How Does Microfiber PU Leather Stand Out in Durability?
Microfiber PU leather is a more advanced form of synthetic leather, known for its softer feel and enhanced durability compared to standard PU. This type is often used in automotive interiors and high-quality furniture, where comfort and longevity are crucial. B2B buyers should note that while microfiber PU leather is generally more expensive, its increased durability and comfort can justify the investment, particularly in applications where wear and tear are prevalent.
Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Why Consider Eco-friendly PU Leather for Sustainable Business Practices?
Eco-friendly PU leather is produced using fewer harmful chemicals and may even be recyclable. This type of PU leather is increasingly popular among businesses focused on sustainability, such as those in the eco-friendly fashion sector. For B2B buyers, choosing eco-friendly options can enhance brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, though the potential for higher costs and limited availability must be taken into account.
What Are the Advantages of Coated PU Leather for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Coated PU leather features a fabric backing with a thick layer of polyurethane, providing enhanced durability and water resistance. This makes it suitable for bags, wallets, and footwear, where a longer lifespan is essential. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of increased durability against the heavier weight and reduced flexibility, as these factors can influence the usability of the final product.
How Does Printed PU Leather Offer Customization for B2B Buyers?
Printed PU leather allows for a variety of designs and textures, making it ideal for fashion items and promotional products. This type appeals to B2B buyers looking for customizable aesthetics to differentiate their products in a crowded market. However, while printed PU leather can provide visually appealing options, it may lack the tactile authenticity of genuine leather, which could be a consideration for certain high-end applications.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Key Industrial Applications of what does pu leather mean
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what does pu leather mean | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Upholstery for sofas and chairs | Cost-effective, easy to clean, and available in various designs | Ensure compliance with fire safety standards and durability requirements |
| Fashion and Accessories | Handbags and wallets | Affordable alternative to genuine leather, appealing aesthetics | Look for suppliers with certifications for non-toxicity and environmental impact |
| Automotive | Seat covers and interiors | Lightweight, versatile, and resistant to wear and tear | Assess the material’s longevity and compatibility with vehicle design |
| Footwear | Synthetic leather shoes | Lower production costs and a wide range of styles available | Evaluate the breathability and comfort level of the material |
| Sports Equipment | Protective gear and bags | Durable, water-resistant, and easy to maintain | Source from manufacturers who follow sustainable practices in production |
How is PU Leather Used in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture industry, PU leather is commonly used for upholstery on sofas, chairs, and other seating options. Its affordability and ease of maintenance make it an attractive choice for manufacturers looking to minimize costs while providing a stylish product. PU leather’s resistance to stains and spills solves the problem of frequent cleaning, which is essential in high-traffic areas. International buyers should consider sourcing PU leather that meets fire safety standards and durability requirements, ensuring longevity in various climates.
What Role Does PU Leather Play in Fashion and Accessories?
PU leather has become a staple in the fashion industry for items such as handbags, wallets, and belts. It offers a visually appealing alternative to genuine leather at a fraction of the cost. This synthetic material provides designers with the flexibility to create various styles without the ethical concerns associated with animal leather. Buyers, especially in regions like Africa and Europe, should prioritize suppliers who can provide certifications regarding the non-toxicity and environmental impact of their PU leather products.
How is PU Leather Utilized in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, PU leather is widely used for seat covers and interior trim. Its lightweight nature contributes to overall vehicle efficiency, while its durability ensures resistance to wear and tear. PU leather can also be treated for moisture resistance, making it suitable for various climates. International automotive buyers should assess the longevity of PU leather and its compatibility with specific vehicle designs, ensuring that it meets stringent automotive standards.
What is the Application of PU Leather in Footwear?
PU leather is increasingly used in the footwear industry for producing synthetic leather shoes. The material allows manufacturers to offer a wide range of styles and designs without the higher costs associated with genuine leather. Additionally, PU leather is lightweight and can be engineered for breathability, enhancing overall comfort. When sourcing for footwear applications, buyers should evaluate the comfort level and breathability of PU leather to ensure consumer satisfaction, especially in warmer climates.
How Does PU Leather Benefit Sports Equipment Manufacturing?
In the realm of sports equipment, PU leather is often used for protective gear, bags, and sports balls due to its durability and water resistance. The material’s ability to withstand wear and tear makes it ideal for high-impact activities. Moreover, its lightweight nature aids in the performance of athletes. Buyers in the sports sector should focus on sourcing PU leather from manufacturers who adhere to sustainable practices, as this can align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what does pu leather mean’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding PU Leather’s Quality Standards
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those new to sourcing materials, struggle to distinguish the quality of PU leather products. This can lead to purchasing items that appear appealing but lack durability and longevity. For example, a furniture manufacturer in Nigeria may order PU leather sofas only to find they crack and peel within months of use, resulting in customer dissatisfaction and costly replacements.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide detailed information about their PU leather products, including the composition and manufacturing processes. Request samples to evaluate the material’s texture and durability firsthand. Additionally, ask for certifications or third-party testing results that demonstrate the material’s quality and safety standards. Establishing a checklist of quality indicators—such as thickness, feel, and warranty terms—can also help buyers make informed decisions and avoid subpar products.
Scenario 2: Navigating Environmental Concerns with PU Leather
The Problem: Environmental impact is a critical concern for many businesses today. B2B buyers often face the challenge of sourcing PU leather products that align with sustainability goals. For instance, a fashion retailer in South America may want to promote eco-friendly products but finds that the PU leather options available are linked to harmful chemicals and non-biodegradable materials, leading to potential backlash from environmentally conscious consumers.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
The Solution: Buyers should seek suppliers that transparently disclose their production processes and materials used in PU leather. Look for brands that utilize eco-friendly manufacturing practices, such as water-based adhesives and non-toxic dyes. Engaging with suppliers who are committed to sustainability can provide options that meet both quality and environmental standards. Additionally, consider incorporating a circular economy approach by sourcing PU leather that is designed for recyclability or made from recycled materials, thus enhancing your brand’s environmental credentials.
Scenario 3: Confusion Around PU Leather Terminology and Labeling
The Problem: Confusion around terms like “genuine leather,” “synthetic leather,” and “PU leather” can lead to misunderstandings and misaligned expectations between buyers and suppliers. A buyer in Europe might assume that a product labeled as “genuine leather” is high-quality, only to discover that it is actually a low-grade PU leather, resulting in reputational damage and financial loss.
The Solution: To combat this issue, it is crucial for B2B buyers to familiarize themselves with industry terminology and the differences between various types of leather and synthetic alternatives. Establish a clear communication channel with suppliers to verify product labels and definitions. Buyers should also consider developing a glossary of terms to share with their teams and stakeholders, ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding product specifications. Conducting training sessions on material identification and sourcing strategies can further enhance understanding and reduce the risk of miscommunication in future transactions.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what does pu leather mean
What Materials Are Commonly Used in PU Leather Production?
When considering PU leather from a B2B perspective, it is essential to analyze the materials involved in its production. PU leather primarily consists of polyurethane, but the backing materials and additives also play significant roles in determining its properties and suitability for various applications. Below, we examine three common materials associated with PU leather: polyurethane, backing fabrics, and chemical additives.
How Does Polyurethane Affect PU Leather Performance?
Polyurethane (PU) is the primary component of PU leather, created through a chemical reaction between diisocyanates and polyols. This synthetic polymer is known for its versatility, allowing manufacturers to produce a material that mimics the look and feel of genuine leather.
Key Properties: PU is flexible and can be formulated to exhibit various hardness levels, making it suitable for diverse applications. It also has moderate resistance to moisture and abrasion.
Pros & Cons: While PU is generally more affordable than genuine leather, it lacks durability, often cracking and peeling with frequent use. The manufacturing process can be complex, requiring precise control over chemical reactions to achieve desired properties.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Impact on Application: PU leather is commonly used in fashion accessories, upholstery, and automotive interiors. However, its limited lifespan can affect the overall value proposition for buyers seeking long-term solutions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the environmental impact and potential toxicity of PU, especially regarding compliance with local regulations on chemical safety.
What Role Do Backing Fabrics Play in PU Leather?
Backing fabrics, typically made from polyester or cotton blends, provide structural support to PU leather. The choice of backing material can significantly influence the final product’s durability and feel.
Key Properties: Backing fabrics contribute to the tensile strength and flexibility of PU leather. They can also affect the breathability and moisture-wicking properties of the final product.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Pros & Cons: Polyester backing offers high durability and resistance to wear, while cotton blends can enhance comfort. However, the choice of backing can increase manufacturing complexity and costs, especially if high-quality materials are used.
Impact on Application: The type of backing fabric can determine the suitability of PU leather for specific applications, such as high-end fashion versus budget-friendly options.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe, particularly in Germany, may prioritize sustainable backing materials that comply with stringent environmental standards like REACH.
How Do Chemical Additives Influence PU Leather?
Chemical additives, including flame retardants, UV stabilizers, and antimicrobial agents, are often incorporated into PU leather to enhance its performance characteristics.
Key Properties: These additives can improve resistance to fire, UV degradation, and microbial growth, thereby extending the product’s usability in various environments.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Pros & Cons: While additives can enhance the performance of PU leather, they may also introduce potential health risks, particularly if volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are present. This can lead to regulatory challenges in certain markets.
Impact on Application: The presence of additives can make PU leather more suitable for specific applications, such as automotive interiors that require fire resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN regarding chemical safety and performance, especially in regions with strict regulations.
Summary Table of PU Leather Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for what does pu leather mean | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Fashion accessories, upholstery, automotive interiors | Affordable and versatile | Lacks durability, prone to cracking and peeling | Medium |
| Backing Fabrics | Clothing, furniture, automotive interiors | Enhances strength and flexibility | Increased manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Chemical Additives | Automotive interiors, high-performance applications | Improves resistance to fire and UV damage | Potential health risks due to VOCs | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers considering PU leather. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials can help inform purchasing decisions, ensuring compliance with local standards and aligning with market preferences.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what does pu leather mean
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of PU Leather?
The production of PU leather involves several critical stages that transform raw materials into a finished product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers seeking to evaluate the quality and consistency of PU leather products.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing PU leather is the preparation of raw materials. This typically involves sourcing polyurethane (PU) and a suitable backing fabric, which can include polyester or cotton blends. The quality of these materials significantly influences the final product’s durability and appearance. Buyers should inquire about the sourcing of these materials to ensure they meet desired standards, particularly regarding sustainability and environmental impact.
2. Forming: Coating and Texturing
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves applying a layer of polyurethane over the backing fabric. The coating is accomplished using methods such as:

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
- Roll Coating: A continuous process where the fabric is passed through rollers coated with liquid PU.
- Spray Coating: Involves spraying the PU onto the fabric, allowing for more control over thickness.
After the coating, the polyurethane layer undergoes a texturing process, where it is embossed to create a leather-like appearance. This step can significantly impact the aesthetics and tactile feel of the final product, making it essential for manufacturers to employ precise techniques.
3. Assembly
Following the coating and texturing, the next stage is assembly. This involves cutting the coated fabric into desired shapes and sizes, which are then sewn or bonded together to create the final product. The assembly process requires skilled labor to ensure that seams are durable and aesthetically pleasing. Buyers should assess the manufacturer’s capabilities and labor quality to ensure high production standards.
4. Finishing
The final stage of production is finishing, where additional treatments are applied to enhance the product’s durability and aesthetics. This may include:

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
- UV Treatment: To protect against sun damage.
- Waterproofing: To enhance moisture resistance.
- Surface Treatments: To improve scratch and stain resistance.
Finishing processes can vary widely among manufacturers, and buyers should inquire about the specific treatments used, as these can affect the longevity and performance of the PU leather products.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Commonly Implemented in PU Leather Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of PU leather manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding QA practices can help verify supplier credibility and product reliability.
International Standards and Industry Certifications
Manufacturers often adhere to various international standards to ensure quality and safety, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Relevant for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Buyers should request proof of compliance with these standards, as they reflect the manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control in PU leather production typically involves several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products to ensure they meet specifications before shipment.
Each of these checkpoints is crucial in maintaining product quality and minimizing defects, providing assurance to B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in PU Leather Quality Assurance?
To ensure that PU leather meets quality and performance standards, various testing methods are employed. Buyers should be familiar with these tests to assess the reliability of potential suppliers.
- Physical Testing: This includes assessing tensile strength, tear resistance, and elongation to evaluate the material’s durability.
- Chemical Testing: Testing for harmful substances, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals, is essential to ensure safety and compliance with environmental regulations.
- Aging Tests: Simulating the effects of prolonged use and exposure to elements can predict the longevity of the PU leather.
B2B buyers can request test reports from suppliers to verify that these tests have been conducted and that the products meet relevant standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is paramount. Here are actionable steps to ensure due diligence:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting or requesting third-party audits can provide insight into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing methods, results, and compliance with international standards can give buyers confidence in their purchases.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services before shipment can help ensure that products meet specified standards and reduce the risk of receiving defective goods.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate additional complexities in quality control, including:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality perceptions can help buyers communicate more effectively with suppliers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding product safety and environmental impact. Buyers should be aware of these differences to avoid compliance issues.
- Logistical Challenges: Ensuring quality throughout the supply chain, particularly in transportation and storage, is vital. Buyers should establish clear guidelines with suppliers regarding handling and delivery to maintain product integrity.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with PU leather, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their quality expectations and business goals.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what does pu leather mean’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, understanding the nuances of materials like PU leather is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide provides a practical checklist for international buyers seeking to navigate the complexities of sourcing PU leather products. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select high-quality materials that align with your business needs and ethical standards.
1. Understand PU Leather Characteristics
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the fundamental properties of PU leather. This synthetic material is designed to mimic the appearance and texture of genuine leather, but it has notable limitations, such as reduced durability and potential environmental concerns. Recognizing these characteristics will help you set clear expectations for your sourcing needs.
2. Define Your Product Requirements
Clearly outline the specific applications for PU leather in your product lines. Are you using it for fashion items, upholstery, or automotive interiors? Each application may demand different qualities, such as water resistance, texture, or colorfastness. This clarity will guide your supplier discussions and help you avoid misalignment.
3. Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their industry certifications and compliance with environmental standards. Look for certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Oeko-Tex Standard 100 for safety in textiles. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality and sustainability, which is increasingly important to consumers and regulatory bodies.
4. Request Material Samples
Always ask for samples of the PU leather before placing a bulk order. Assess the texture, durability, and overall appearance of the samples to ensure they meet your expectations. This step is essential to avoid costly returns or dissatisfaction after procurement.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
5. Analyze Cost vs. Quality
While price is a significant factor in procurement, it should not be the sole consideration. Compare the cost of PU leather with its quality and longevity. Cheaper options may save money upfront but could lead to higher replacement costs in the long run due to durability issues. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to make an informed decision.
6. Inquire About Manufacturing Processes
Understanding how the PU leather is produced is vital for assessing its quality and environmental impact. Ask suppliers about their manufacturing processes, including the types of chemicals used and their waste management practices. This knowledge will help you ensure that the materials align with your sustainability goals.
7. Establish Clear Communication Channels
Finally, set up effective communication with your suppliers. Ensure that you have a reliable point of contact for any queries or concerns throughout the procurement process. Clear communication can facilitate timely updates on order status, delivery timelines, and any potential issues that may arise.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing PU leather, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and values.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what does pu leather mean Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing PU Leather?
When sourcing PU leather, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The primary material, polyurethane, is generally less expensive than natural leather, but prices can fluctuate based on the quality of the polymers and backing materials used. Low-quality PU leather may cost less initially but could lead to higher long-term costs due to durability issues.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Africa and South America, manufacturing PU leather can be cheaper. However, sourcing from countries with stringent labor regulations, like Germany, might incur higher labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Factories that specialize in PU leather production may have more streamlined operations, thus reducing overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for creating molds and machines specifically for PU leather production can be significant. However, these costs are often amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that PU leather meets specified quality standards is essential. QC processes can add to the cost but are critical to avoid defects that could lead to returns or customer dissatisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs depend on the origin of the PU leather and the destination market. International buyers should consider tariffs, import duties, and transportation costs, which can significantly affect the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin based on the complexity of the product, market demand, and competition. Understanding the typical margins in the PU leather market can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
What Influences the Pricing of PU Leather Products?
Several factors can influence the pricing of PU leather products, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders. Understanding the minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help buyers optimize their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific specifications can increase costs due to the additional resources and time required. Buyers should weigh the importance of customization against potential price increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials used in the production of PU leather, including the quality of the backing fabric and the type of polyurethane, can significantly impact costs. Higher-quality materials will typically result in higher prices.
-
Quality Certifications: Products that meet specific environmental or safety standards may come at a premium. Certifications can assure buyers of the product’s safety and sustainability, which is increasingly important in many markets.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Long-term partnerships with trustworthy suppliers can lead to better pricing and favorable terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international shipping and can affect the overall cost. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who is responsible for various costs during transportation.
What Tips Should B2B Buyers Consider for Cost-Efficiency?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate: Always negotiate prices and terms with suppliers. Establishing a rapport can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the TCO, which includes shipping, tariffs, and potential replacement costs due to the durability of PU leather.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of seasonal pricing changes, as raw material costs can fluctuate throughout the year. Timing your purchase can lead to significant savings.
-
Research Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on suppliers and their pricing strategies. Comparing multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Understand Market Dynamics: Being aware of market trends and consumer preferences can help in making strategic sourcing decisions that align with current demand.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Pricing for PU leather can vary widely based on numerous factors, including regional economic conditions, supplier capabilities, and market demand. Buyers should conduct due diligence and seek multiple quotes to ensure they obtain competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
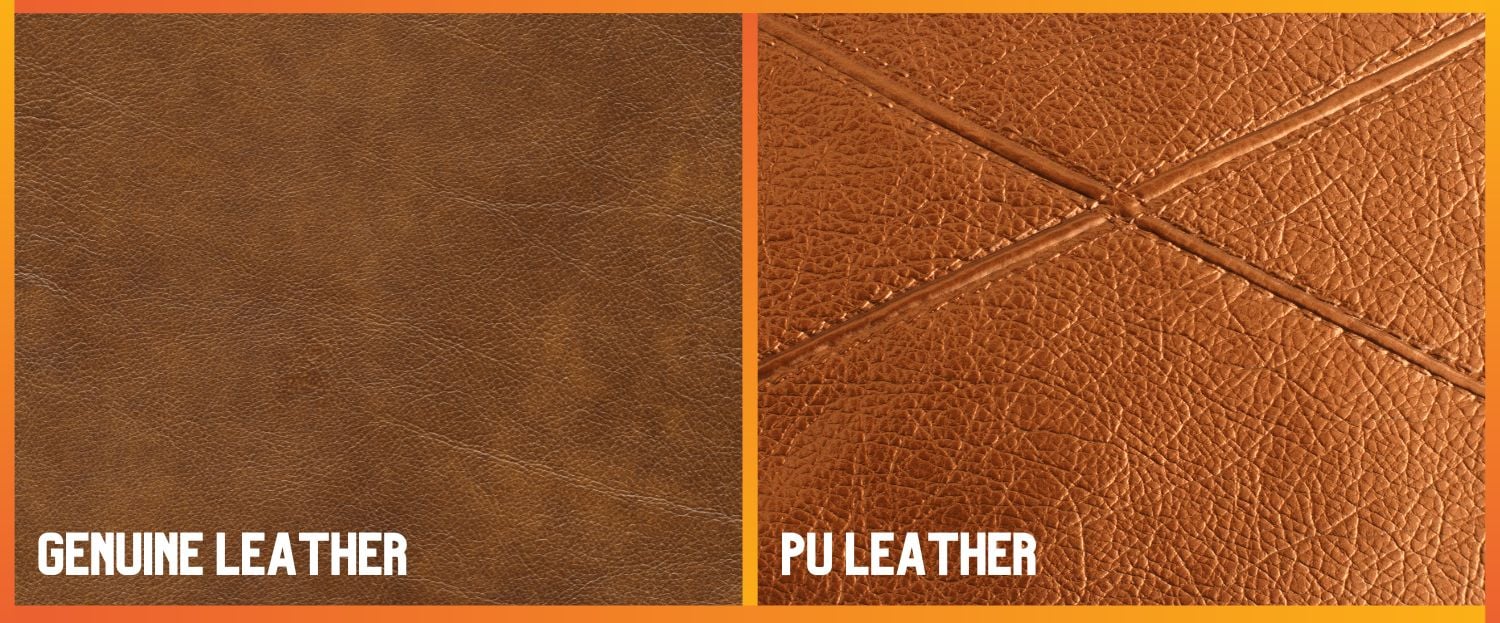
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what does pu leather mean With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Synthetic Leather Solutions
As the demand for leather alternatives continues to rise, it is essential for B2B buyers to explore various options beyond PU leather. While PU leather is a popular choice due to its affordability and aesthetic appeal, it has notable drawbacks, including durability issues and environmental concerns. This analysis will compare PU leather with two viable alternatives: vegetable-tanned leather and high-quality faux leather. Understanding these options can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their business values and customer expectations.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | What Does PU Leather Mean | Vegetable-Tanned Leather | High-Quality Faux Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate durability; prone to cracking and peeling | High durability; ages beautifully | Good durability; varies by quality |
| Cost | Generally low-cost | Higher initial investment | Mid-range pricing |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to source and manufacture | Requires skilled craftsmanship | Widely available and easy to produce |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; wipes clean | Requires conditioning and care | Low maintenance; typically wipes clean |
| Best Use Case | Fast fashion, temporary products | High-end fashion, bespoke items | Versatile applications across fashion and accessories |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What is Vegetable-Tanned Leather and Why Choose It?
Vegetable-tanned leather is derived from natural plant-based tannins, making it an eco-friendly choice with a rich history. Its superior durability allows it to withstand wear and tear, developing a unique patina over time. While the initial cost is higher compared to PU leather, this investment pays off as the lifespan can exceed several decades with proper care. This option is ideal for high-end fashion products, luxury accessories, and bespoke items where quality and craftsmanship are paramount. The downside is that it requires more care and maintenance to keep the leather in optimal condition.
Understanding High-Quality Faux Leather as an Alternative
High-quality faux leather, often made from advanced synthetic materials like polyurethane or PVC, offers a more durable and aesthetically appealing alternative to PU leather. It can mimic the look and feel of genuine leather closely, making it suitable for various applications, from apparel to upholstery. The cost is typically higher than PU leather but remains more affordable than genuine leather. While it usually requires less maintenance than vegetable-tanned leather, the quality can vary significantly between manufacturers. Buyers should ensure they source from reputable suppliers to avoid subpar products that may not meet their durability expectations.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting an alternative to PU leather, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including the intended use, budget constraints, and long-term sustainability goals. Vegetable-tanned leather is an excellent choice for those prioritizing quality and environmental responsibility, while high-quality faux leather serves as a versatile solution that can cater to diverse applications. Understanding the nuances of each option will empower buyers to make decisions that not only enhance their product offerings but also align with their brand values and customer preferences.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what does pu leather mean
What Are the Key Technical Properties of PU Leather?
Understanding the technical properties of PU leather is crucial for B2B buyers, as these specifications impact product selection, quality assessment, and long-term value. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Composition
PU leather is primarily composed of polyurethane, a synthetic polymer. It is typically layered over a backing material made of fabric or non-woven materials. This composition affects the product’s appearance and durability. For B2B buyers, knowing the material grade helps in assessing the quality and suitability for specific applications, such as fashion, upholstery, or automotive interiors.
2. Durability and Lifespan
The durability of PU leather ranges between 6 to 24 months under regular use. This relatively short lifespan is a critical consideration for buyers, as it dictates replacement frequency and overall cost-effectiveness. Understanding the expected durability allows businesses to plan inventory and manage customer expectations regarding product longevity.
3. Water Resistance
PU leather generally offers some degree of water resistance, which can vary based on the manufacturing process. This property is vital for applications where moisture exposure is a concern, such as in outdoor furniture or fashion items. Buyers should inquire about specific water resistance ratings to ensure the product meets their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
4. Chemical Resistance
PU leather’s resistance to various chemicals can be a significant factor in its usability across different industries. Some PU leathers are treated with additional coatings for enhanced resistance to stains and solvents. For B2B buyers, understanding the chemical resistance properties can inform decisions for industries like automotive, where exposure to oils and cleaning agents is common.
5. Environmental Impact
PU leather is often criticized for its environmental implications, particularly due to its non-biodegradable nature and the presence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production. For businesses focusing on sustainability, it’s essential to evaluate the environmental certifications of PU leather products and consider alternatives that align with eco-friendly practices.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to PU Leather?
Navigating the terminology in the PU leather industry is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products based on the specifications provided by another company. In the context of PU leather, an OEM might produce leather goods for a brand that specifies design and quality standards. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking to maintain brand integrity.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and initial investment. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategy and manage cash flow effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to request price quotes for specific products. In the PU leather market, an RFQ can help buyers compare costs, specifications, and lead times. Crafting a clear RFQ ensures that suppliers understand the requirements, leading to more accurate responses.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics. For B2B transactions involving PU leather, understanding Incoterms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for clarifying risk and cost allocation during shipping.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes for an order to be fulfilled and delivered. For buyers in the PU leather sector, understanding lead times is essential for inventory planning and ensuring timely product availability, especially in industries with seasonal demands.
6. Sustainability Certifications
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, sustainability certifications (like OEKO-TEX or GOTS) have become vital in the PU leather industry. These certifications provide assurance regarding the environmental impact and safety of the materials used, influencing purchasing decisions for eco-conscious businesses.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what does pu leather mean Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for PU Leather in B2B Sourcing?
The PU leather market is witnessing significant growth, driven by several global factors. The rising demand for cost-effective and versatile materials in sectors such as fashion, automotive, and furniture is pushing suppliers to expand their offerings. Notably, emerging markets in Africa and South America are becoming key players in PU leather sourcing due to their burgeoning manufacturing capabilities and increasing consumer demand for affordable alternatives to genuine leather. In Europe, particularly in Germany, there is a growing focus on innovation and quality, prompting suppliers to adopt advanced technologies in the production process to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal.
Current trends indicate a shift towards digitalization in sourcing practices. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging e-commerce platforms and digital marketplaces to streamline procurement processes, find reliable suppliers, and conduct price comparisons. Additionally, the integration of AI and data analytics is helping companies forecast demand more accurately, optimizing inventory management and reducing costs. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for international buyers looking to navigate the complexities of the PU leather market and secure advantageous sourcing agreements.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in PU Leather Procurement?
The environmental impact of PU leather production is a critical consideration for B2B buyers. As a petroleum-based product, PU leather has a significant carbon footprint and is non-biodegradable, raising concerns about its long-term sustainability. In response, there is a growing emphasis on ethical sourcing practices within the industry. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who prioritize transparency in their supply chains and adhere to stringent environmental standards.
Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and OEKO-TEX Standard 100 are becoming essential for brands aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. These certifications ensure that materials are sourced responsibly and processed without harmful chemicals. Buyers can enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty by prioritizing suppliers with green certifications. Furthermore, the demand for eco-friendly alternatives is prompting innovations in the market, including the development of bio-based PU leathers, which could potentially mitigate some of the negative environmental impacts associated with traditional PU leather.
What Is the Historical Context of PU Leather’s Development?
PU leather emerged in the mid-20th century as a synthetic alternative to genuine leather, primarily driven by the need for affordability and mass production. Initially developed for industrial applications, its versatility was recognized in the 1960s, leading to its adoption in consumer goods. Over the decades, advancements in technology have refined PU leather’s quality, making it more appealing for various applications, from fashion to automotive interiors.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
Despite its initial promise, PU leather faces criticism for its environmental footprint and durability issues. As awareness of sustainability grows, the market is now witnessing a transition towards more responsible sourcing practices and the exploration of innovative materials. Understanding this evolution can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing PU leather, balancing cost with quality and environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what does pu leather mean
-
What is PU leather and how is it made?
PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is a synthetic material designed to mimic the appearance and feel of genuine leather. It is created by applying a layer of polyurethane over a fabric backing, which can be made from various materials. This process includes coating the fabric and embossing it to create a leather-like texture. While PU leather is cost-effective and versatile, it lacks the durability and longevity of real leather, making it essential for buyers to consider their needs when sourcing materials. -
Is PU leather considered a sustainable option for businesses?
While PU leather is often marketed as a vegan alternative to real leather, its sustainability is questionable. The production involves petroleum-based processes that can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) harmful to health and the environment. Additionally, PU leather is non-biodegradable, contributing to waste. Businesses looking to align with sustainable practices may want to explore vegetable-tanned leather or other eco-friendly materials, which offer greater longevity and environmental benefits. -
What are the key differences between PU leather and genuine leather?
PU leather is a synthetic product, while genuine leather is derived from animal hides. The durability of genuine leather typically far exceeds that of PU leather, which can crack and peel over time. Genuine leather also develops a unique patina, enhancing its aesthetic appeal, whereas PU leather maintains a uniform appearance. For B2B buyers, understanding these differences is crucial for making informed procurement decisions that align with their quality standards. -
How do I vet suppliers of PU leather products?
To effectively vet suppliers, conduct thorough research on their manufacturing practices and material sourcing. Request certifications that indicate environmental compliance and safety standards, such as ISO or OEKO-TEX certifications. Additionally, ask for samples to assess the quality of their PU leather. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who are transparent about their processes can mitigate risks associated with quality and sustainability. -
What customization options are available for PU leather products?
Many suppliers offer customization for PU leather products, including colors, textures, and embossing patterns. Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) for custom items can vary by supplier, so it’s essential to clarify these details upfront. Customization can enhance brand identity and meet specific customer demands, making it a valuable aspect for B2B buyers in competitive markets. -
What are typical payment terms in international B2B transactions for PU leather?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier and region, but common practices include upfront deposits (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or acceptance of goods. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or other financing options to reduce risk. It’s crucial for buyers to negotiate terms that align with their cash flow and operational needs while ensuring that both parties are protected. -
How long does PU leather typically last, and what factors affect its lifespan?
The lifespan of PU leather usually ranges from 6 months to 2 years, depending on usage and care. Factors such as exposure to sunlight, moisture, and abrasive surfaces can accelerate wear and tear. For B2B buyers, it’s essential to communicate care instructions clearly to end-users to maximize the product’s lifespan and minimize returns or complaints. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing PU leather?
When sourcing PU leather internationally, consider shipping costs, import regulations, and lead times. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience with international shipping and can provide insights on customs duties and taxes. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can streamline the supply chain, ensuring timely delivery and reducing the risk of delays that could impact your business operations.
Top 8 What Does Pu Leather Mean Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Manuel Dreesmann – PU Leather Alternatives
Domain: manuel-dreesmann.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: PU leather is a synthetic material made from polyurethane, often used as a cheaper alternative to genuine leather. It is less durable, less breathable, and can wear out more quickly than real leather. The text suggests avoiding PU leather due to its lower quality and potential environmental impact.
2. HowStuffWorks – PU Leather
Domain: home.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: PU (Polyurethane) leather is an artificial leather made from polyurethane, a type of plastic. It is 100% vegan, offering a more affordable alternative to genuine leather. Key features include: water resistance, easier maintenance, and a variety of color options. However, it lacks the authentic appearance and texture of real leather, does not age well, and can suffer from flexibility issues leading…
3. Prestige Leather Care – PU Leather Solutions
Domain: prestigeleathercare.co.uk
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: PU leather is an artificial type of leather made from polyurethane, a thermoplastic polymer. It is also known by various names including bicast leather, split leather, reconstituted leather, bonded leather, and corrected grain leather. PU leather can be cleaned with a suitable leather cleaner and brush. It is considered vegan only if it is 100% PU; otherwise, it may contain real leather. PU leathe…
4. Rahui – Polyurethane Leather
Domain: rahui.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, Rahui – Polyurethane Leather, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Senreve – PU Leather Handbags
Domain: senreve.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is an artificial leather made of thermoplastic polymer. It is 100% vegan and does not absorb water, making it more durable and easier to clean than real leather. PU leather can take on a variety of colors and decorations. However, it has a plastic shine, can smell strongly of plastic, does not develop a patina, and is not as puncture-resistant or tear-resistant…
6. Carl Friedrik – PU Leather Accessories
Domain: carlfriedrik.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: PU leather, also known as artificial or imitation leather, is a synthetic material made from polyurethane, which is a type of plastic. It is created by applying a PU resin coating to natural fabrics like nylon, cotton, or vinyl. 100% PU leather is vegan-friendly, while PU leather made with split leather is not. The manufacturing process is automated and involves high pressure and temperature to bo…
7. Fibrenew – PU Leather Solutions
Domain: fibrenew.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: PU leather (polyurethane leather) is a synthetic material that mimics the feel of semi-aniline leather, made from plastic and applied to a fabric base, typically polyester. It is cheaper to produce than real leather and has no imperfections. Bonded leather, often marketed as genuine leather, is made from leftover animal hide bits combined with a fabric base and topped with a layer of polyurethane….
8. Vintage Leather – PU Leather
Domain: vintageleather.store
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: PU leather, also known as polyurethane leather, is a synthetic leather made from thermoplastic polymer, specifically polyurethane. It is manufactured by coating a layer of polyurethane onto a base fabric such as nylon, cotton, or vinyl. PU leather is cost-effective, durable, and easy to maintain, making it suitable for various applications including fashion, upholstery, and automotive interiors. I…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what does pu leather mean
What Key Insights Should B2B Buyers Consider About PU Leather?
In conclusion, understanding PU leather is essential for international B2B buyers navigating the complex landscape of material sourcing. While PU leather offers a cost-effective alternative to genuine leather, its significant drawbacks—such as durability issues, potential toxicity, and environmental impact—should not be overlooked. Strategic sourcing requires a holistic view, weighing both immediate cost savings and long-term value. Opting for high-quality materials, such as vegetable-tanned leather, can enhance product longevity and align with sustainability goals.
As buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to establish strong supplier relationships, it is imperative to prioritize transparency and ethical sourcing. Understanding the materials you choose not only influences your product quality but also impacts your brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
Looking ahead, the demand for sustainable and ethically produced materials will only grow. Embrace this shift by integrating responsible sourcing practices into your procurement strategies. By doing so, you not only meet consumer expectations but also contribute to a more sustainable future for the industry. Take proactive steps today to ensure your sourcing decisions reflect the values and quality that your customers deserve.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to what does pu leather mean
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.