Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather grading
In the ever-evolving landscape of international trade, sourcing high-quality leather can be a daunting task for B2B buyers. With the diverse grades of leather available, understanding how to navigate the complexities of leather grading is essential for securing products that meet both quality standards and budget constraints. This guide delves into the intricacies of leather grading, exploring various types such as full-grain, top-grain, and bonded leather, along with their specific applications across industries—from fashion to automotive.
As buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including markets like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia) seek to make informed purchasing decisions, it becomes crucial to comprehend the nuances of leather quality. This guide will equip you with the necessary insights on supplier vetting, cost implications, and the overall impact of leather quality on product longevity and customer satisfaction. By understanding these critical factors, you can confidently select leather goods that not only enhance your offerings but also align with your business values and customer expectations.
Ultimately, this comprehensive resource aims to empower you as an international B2B buyer, providing the tools to make educated choices in a competitive marketplace. With the right knowledge of leather grading, you can ensure that your investments yield durable and aesthetically pleasing products that stand the test of time.
Table Of Contents
- Top 7 Leather Grading Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather grading
- Understanding leather grading Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of leather grading
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather grading’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather grading
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather grading
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather grading’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather grading Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather grading With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather grading
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather grading Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather grading
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather grading
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
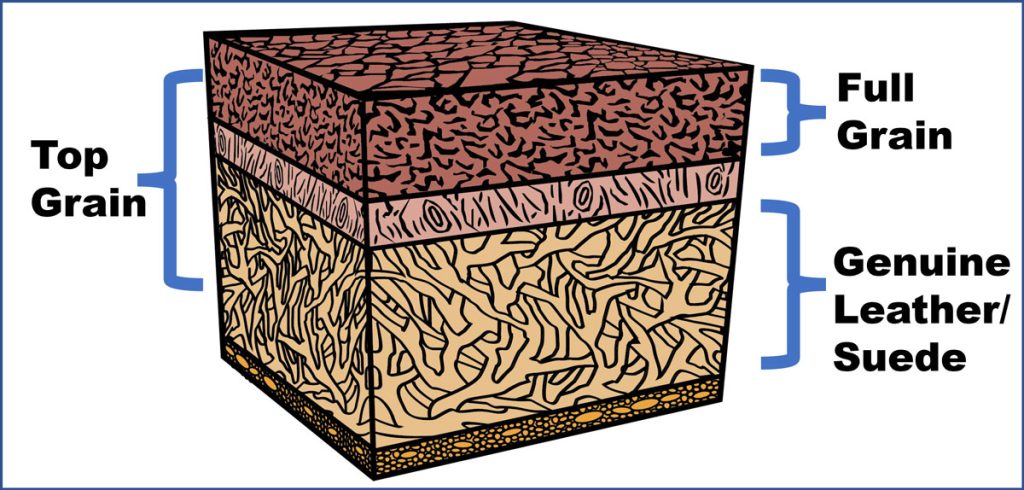
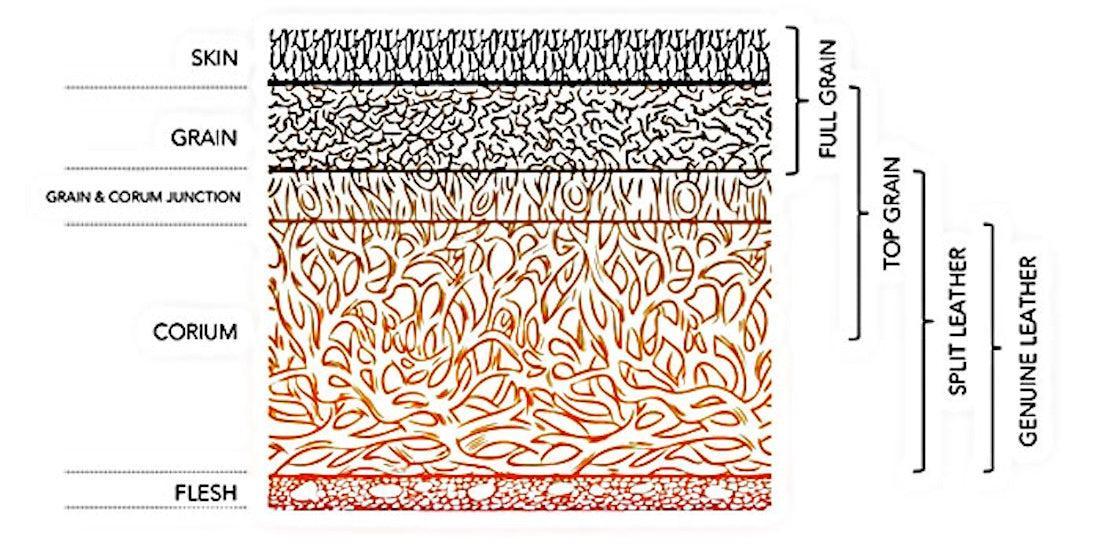
Understanding leather grading Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Grain Leather | Retains the entire natural grain, very durable | High-end furniture, luxury goods | Pros: Exceptional durability, develops patina. Cons: Higher cost. |
| Top-Grain Leather | Sanded and treated for uniformity, less porous | Fashion accessories, upholstery | Pros: Attractive appearance, easier to maintain. Cons: Less breathable than full-grain. |
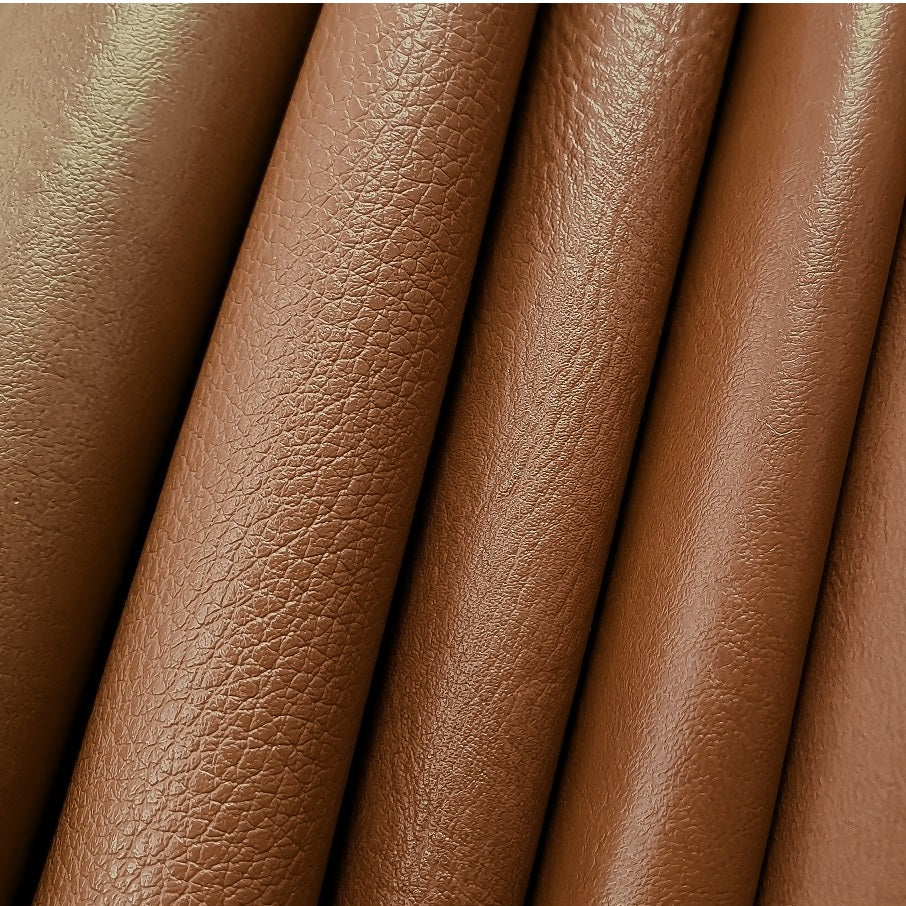
| Split-Grain Leather | Lacks natural grain, typically softer (e.g., suede) | Footwear, bags, jackets | Pros: Soft texture, cost-effective. Cons: Less durable, prone to wear. |
| Genuine Leather | Made from the lower layers of hide, heavily processed | Budget-friendly products | Pros: Affordable. Cons: Low durability, lacks natural beauty. |
| Bonded Leather | Composite of leather scraps and synthetic materials | Inexpensive furniture, accessories | Pros: Very low cost. Cons: Poor quality, prone to damage. |
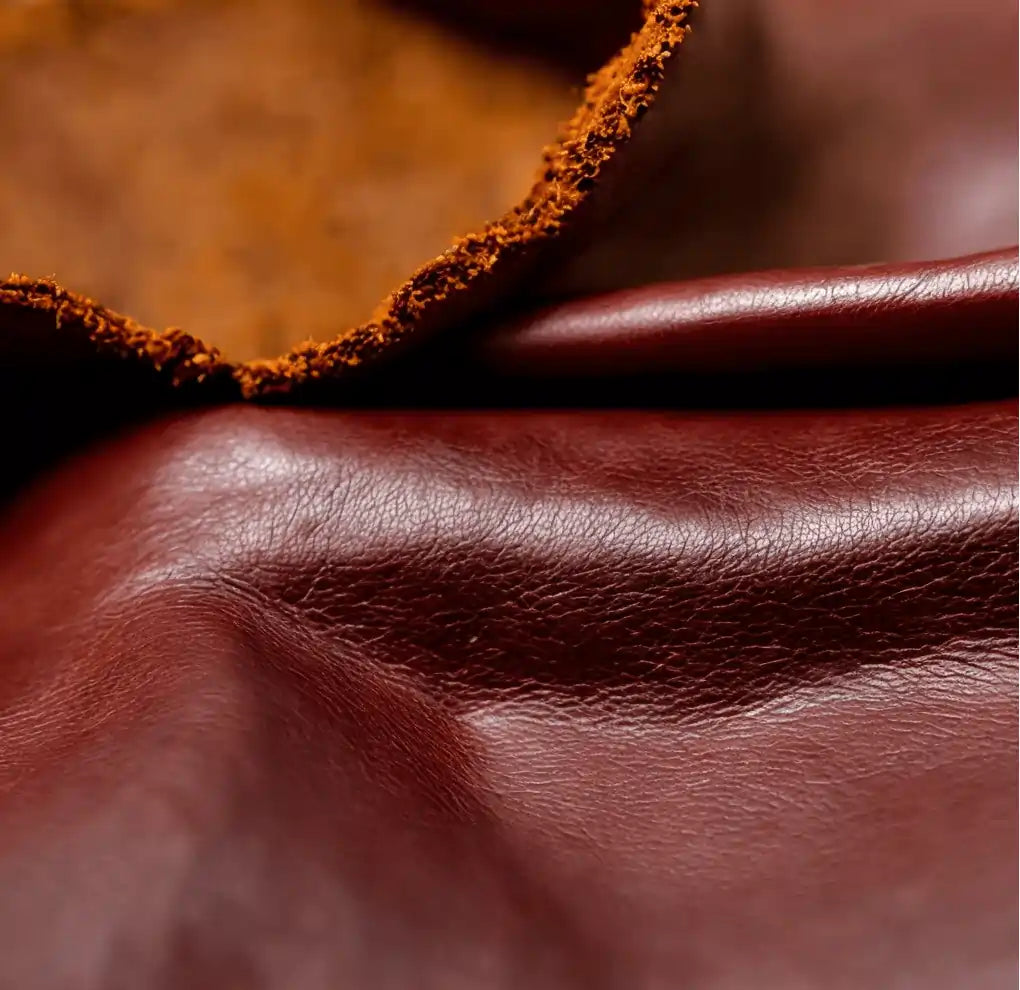
What Are the Characteristics of Full-Grain Leather and Its Suitability for B2B Buyers?
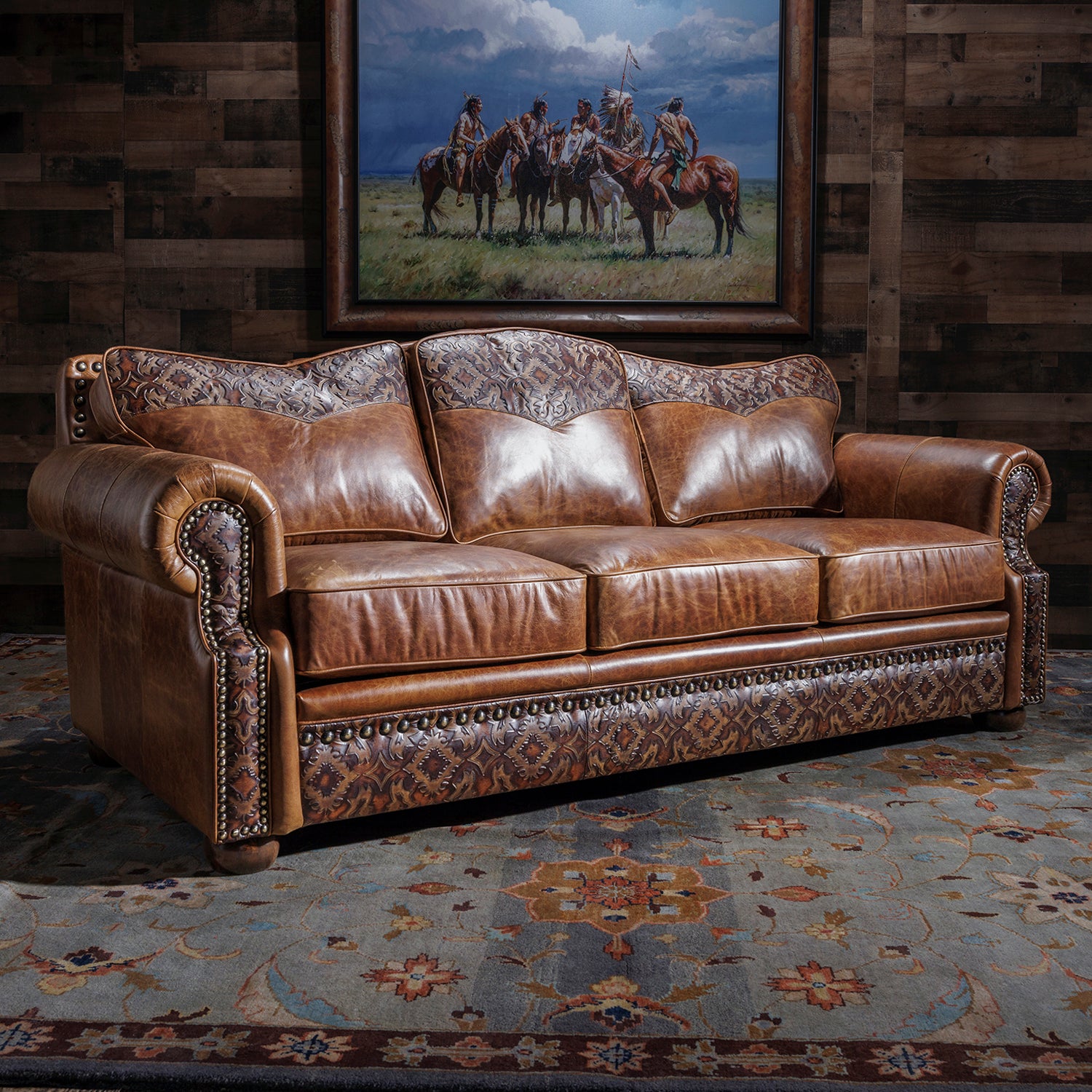
Full-grain leather is derived from the top layer of the hide, preserving its natural texture and imperfections. This type of leather is known for its exceptional durability and breathability, making it suitable for high-end applications such as luxury furniture and premium leather goods. B2B buyers should consider full-grain leather for products that require longevity and a premium aesthetic, as it develops a rich patina over time. However, the higher cost may be a barrier for some businesses.
How Does Top-Grain Leather Compare to Other Types for Business Use?
Top-grain leather is slightly processed to achieve a smoother and more uniform appearance, making it a popular choice for fashion accessories and upholstery. While it retains some durability, it is less breathable than full-grain leather due to the sealing of its pores. B2B buyers often select top-grain leather for products where aesthetics and ease of maintenance are prioritized. However, it is essential to weigh the trade-off between appearance and the potential reduction in durability.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Split-Grain Leather?
Split-grain leather, often processed into suede, is softer and more pliable but lacks the natural markings of higher-grade leathers. This type is commonly used in footwear, bags, and jackets, providing a cost-effective alternative for businesses. While it offers a luxurious feel, B2B buyers should be cautious of its lower durability and potential for wear over time. It is best suited for products that will not experience heavy use.
Illustrative image related to leather grading
Why Is Genuine Leather Considered a Low-Quality Option?
Genuine leather is made from the lower layers of the hide and undergoes extensive processing, resulting in a product that lacks the natural beauty and durability of higher-grade leathers. It is often used in budget-friendly products, appealing to cost-sensitive buyers. However, B2B purchasers should be aware of its limitations, including reduced longevity and aesthetic appeal, which may not meet the expectations of discerning customers.
What Should Buyers Know About Bonded Leather in Their Purchasing Decisions?
Bonded leather is a composite material made from leather scraps and synthetic components, often found in inexpensive furniture and accessories. While its low price point can be attractive, B2B buyers should recognize its poor quality and susceptibility to damage. It is advisable to consider bonded leather only for short-term use or low-end products, as it does not provide the durability or aesthetic qualities of genuine leather options.
Key Industrial Applications of leather grading
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of leather grading | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Upholstery and interior components | Enhances vehicle aesthetics and longevity | Source full-grain or top-grain leather for durability and comfort. |
| Fashion and Apparel | High-end clothing and accessories | Offers superior quality and brand differentiation | Ensure traceability and quality certifications of leather grades. |
| Furniture | Upholstered furniture manufacturing | Increases product lifespan and customer satisfaction | Opt for genuine or top-grain leather for durability and ease of maintenance. |
| Footwear | Production of premium shoes | Improves comfort, breathability, and overall style | Look for suppliers that provide full-grain leather for high-end footwear. |
| Sporting Goods | Manufacturing of leather sports equipment | Enhances performance and durability in athletic gear | Prioritize sourcing from reputable tanneries with a focus on quality control. |
How is Leather Grading Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, leather grading is crucial for selecting the right upholstery and interior components. High-quality full-grain or top-grain leather is preferred for its durability and aesthetic appeal, which enhances the overall vehicle experience. Buyers must ensure that they source leather that meets stringent quality standards to avoid issues such as wear and tear, which can lead to costly repairs and affect customer satisfaction.
What Role Does Leather Grading Play in Fashion and Apparel?
For the fashion and apparel industry, leather grading is essential for creating high-end clothing and accessories that stand out in a competitive market. Top-grain and full-grain leathers are favored for their luxurious feel and longevity, allowing brands to position themselves as premium offerings. International buyers should focus on suppliers who can provide detailed certifications of leather quality to ensure they receive the best materials that align with their brand identity.
Why is Leather Grading Important in Furniture Manufacturing?
In furniture manufacturing, leather grading directly impacts the quality and lifespan of upholstered products. By opting for genuine or top-grain leather, manufacturers can produce items that not only look sophisticated but also withstand daily use. Buyers should consider the sourcing of leather to include suppliers with robust quality control measures, ensuring that the leather used meets the desired standards for durability and maintenance ease.
How Does Leather Grading Affect Footwear Production?
Leather grading is pivotal in the footwear industry, where the choice of leather can significantly influence comfort, breathability, and style. High-quality full-grain leather is often used for premium shoe lines, providing a luxurious touch while ensuring durability. B2B buyers must evaluate suppliers based on their ability to consistently provide high-grade leather and consider the environmental practices of tanneries to align with sustainability goals.
What is the Significance of Leather Grading in Sporting Goods?
In the sporting goods sector, leather grading is vital for manufacturing durable and high-performance equipment. Leather used in items such as gloves, balls, and protective gear must be of superior quality to withstand rigorous use. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable tanneries that emphasize quality control, as this ensures that the leather not only meets performance standards but also enhances the overall user experience in competitive sports.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather grading’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Leather Grades in Procurement
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter confusion when navigating the different grades of leather available in the market. With terms like full-grain, top-grain, genuine, and bonded leather thrown around, it can be overwhelming for buyers, especially when sourcing for specific product applications. This confusion can lead to poor purchasing decisions, resulting in either overpaying for lower-quality leather or receiving subpar products that do not meet customer expectations. For instance, a manufacturer in South America may order what they believe to be high-quality leather, only to find that they received bonded leather, which lacks the durability and aesthetic appeal needed for their premium line of goods.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
The Solution:
To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should implement a structured procurement process that includes clear specifications and education on leather grades. First, establish a detailed requirement document that outlines the desired leather qualities for each product, including the specific grade needed. This document should be shared with suppliers to ensure they understand the expectations. Additionally, buyers should seek suppliers who provide comprehensive product descriptions and samples. Requesting physical samples allows buyers to assess the quality firsthand before making bulk purchases. Finally, consider partnering with a leather expert or consultant who can provide insights into sourcing the right grades and help navigate the complexities of the leather market.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality Across Suppliers
The Problem:
Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the inconsistency in leather quality across different suppliers. A buyer in Europe may receive leather from multiple sources, but variations in grain structure, color, and texture can lead to significant quality discrepancies. This inconsistency can compromise the overall quality of the final product, especially in industries like fashion and luxury goods where aesthetics are paramount. Such variations can result in customer dissatisfaction and increased return rates, ultimately affecting the bottom line.
The Solution:
To ensure consistent quality, buyers should establish long-term relationships with a select few trusted suppliers who are known for their reliable leather quality. Engage in regular communication with these suppliers to set quality benchmarks and expectations. Implementing quality control measures, such as periodic audits of the supplier’s production processes, can help maintain standards. Additionally, consider developing a quality assurance protocol that includes standardized testing for leather samples upon arrival, ensuring that they meet the established criteria. By fostering collaboration and transparency with suppliers, buyers can significantly reduce variability and maintain high-quality leather products.
Scenario 3: Misunderstanding Leather Care and Maintenance
The Problem:
B2B buyers often overlook the importance of leather care and maintenance when sourcing leather products. A company in Africa that produces leather goods may purchase high-quality full-grain leather but fail to educate their team on proper maintenance practices. This oversight can lead to premature wear and tear, detracting from the leather’s natural beauty and durability. Consequently, products may not perform as expected, resulting in increased returns and customer complaints.
Illustrative image related to leather grading
The Solution:
To address this issue, B2B buyers should incorporate leather care education into their operational procedures. This can involve providing training sessions for staff on how to care for and maintain the specific types of leather used in their products. Additionally, suppliers can be encouraged to provide care instructions and maintenance kits with leather purchases. Implementing a post-purchase follow-up with customers to share care tips can also enhance the customer experience and extend the life of the products. By promoting proper leather maintenance, businesses can enhance product longevity, reduce returns, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather grading
What Are the Key Properties of Full-Grain Leather for B2B Buyers?
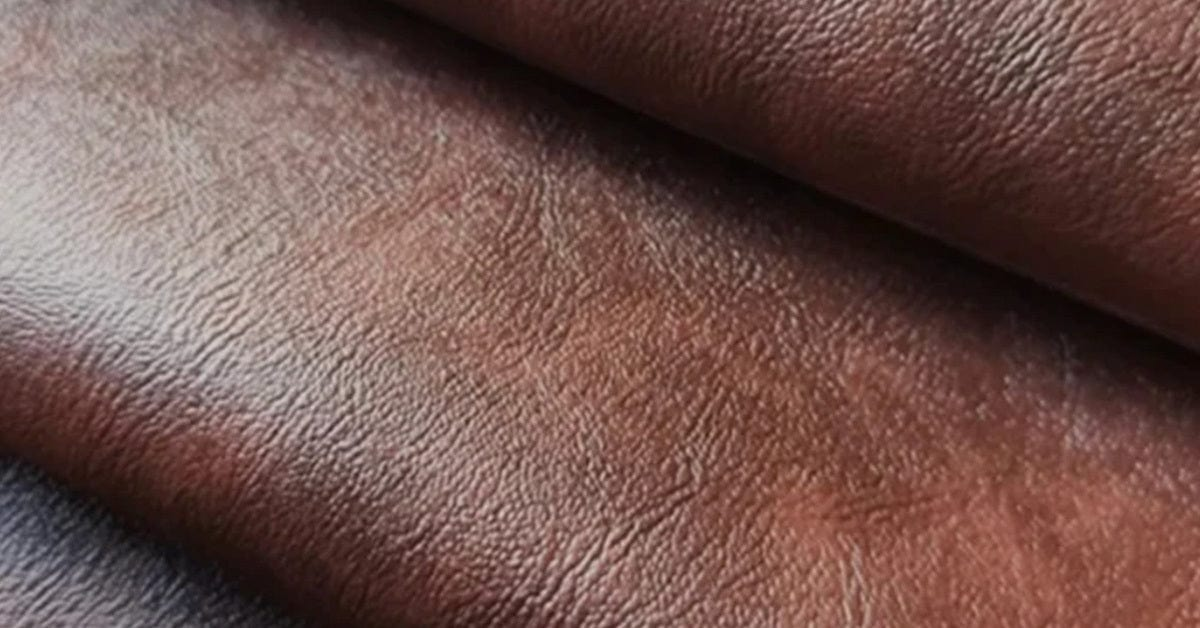
Full-grain leather is renowned for its superior quality, derived from the top layer of the hide. This material retains the natural grain and imperfections, providing a unique aesthetic and exceptional durability. It is breathable, moisture-wicking, and develops a rich patina over time, enhancing its appearance with age. Its temperature and pressure ratings are excellent, making it suitable for various applications, including high-end upholstery and luxury goods.
Pros: Full-grain leather is highly durable, resistant to wear and tear, and can last a lifetime with proper care. It is also more environmentally friendly, as it typically undergoes less chemical processing compared to lower grades.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost; full-grain leather is more expensive than other types. Additionally, its natural imperfections may not appeal to all consumers, especially in markets where uniformity is preferred.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
How Does Top-Grain Leather Compare to Other Materials?
Top-grain leather is the second-highest quality leather, created by sanding and buffing the surface of full-grain leather to remove imperfections. This process results in a more uniform appearance while still maintaining good durability and flexibility. Top-grain leather is also resistant to stains and moisture, making it easier to maintain.
Pros: It offers a balance between quality and price, providing a more polished look than full-grain leather while still being durable. Its treatment makes it suitable for various applications, including fashion accessories and furniture.
Cons: While more affordable than full-grain, top-grain leather does not develop the same rich patina over time. Additionally, the sanding process can weaken the leather slightly, making it less durable than full-grain.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
What Are the Characteristics of Split-Grain Leather?
Split-grain leather is derived from the lower layers of the hide and lacks the natural grain characteristics of higher-grade leathers. Commonly used for suede, it is soft and pliable, making it suitable for various applications, such as footwear and garments.
Pros: Split-grain leather is generally more affordable and offers a unique texture that can be appealing for specific products. Its softness makes it comfortable for wearables.
Cons: It is less durable than full-grain and top-grain leather, as it is more susceptible to wear and damage. Additionally, split-grain leather does not age as gracefully, lacking the patina development seen in higher-quality leathers.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
Why Should B2B Buyers Consider Genuine and Bonded Leather?
Genuine leather refers to the lowest quality leather, made from the leftover layers of the hide after higher grades are processed. Bonded leather is a composite material made from leather scraps and synthetic materials. Both are often used in budget-friendly products.
Pros: The primary advantage is cost; both types are significantly cheaper than full-grain and top-grain leathers, making them accessible for mass production.
Cons: They lack durability and quality, often showing signs of wear quickly. Genuine leather offers minimal aesthetic appeal, while bonded leather is not considered true leather and may not meet the expectations of discerning customers.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
Considerations for International B2B Buyers
When sourcing leather materials, international buyers should be aware of compliance with local and international standards, such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe may have varying preferences based on cultural perceptions of leather quality. Additionally, understanding the environmental regulations surrounding leather production is crucial, especially in regions with strict sustainability practices.
| Material | Typical Use Case for leather grading | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Grain Leather | Luxury goods, high-end upholstery | Exceptional durability and aesthetic appeal | Higher cost, natural imperfections | High |
| Top-Grain Leather | Fashion accessories, furniture | Good balance of quality and price | Less durable than full-grain, lacks patina | Medium |
| Split-Grain Leather | Footwear, garments | Soft texture and comfort | Less durable, does not age well | Low |
| Genuine Leather | Budget-friendly products | Very affordable | Low durability, minimal aesthetic appeal | Low |
| Bonded Leather | Inexpensive furniture, accessories | Cost-effective for mass production | Not true leather, poor longevity | Low |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather grading
What Are the Main Stages of the Leather Manufacturing Process?
The leather manufacturing process consists of several key stages that transform raw hides into finished leather products. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers who wish to assess the quality of leather they are sourcing.
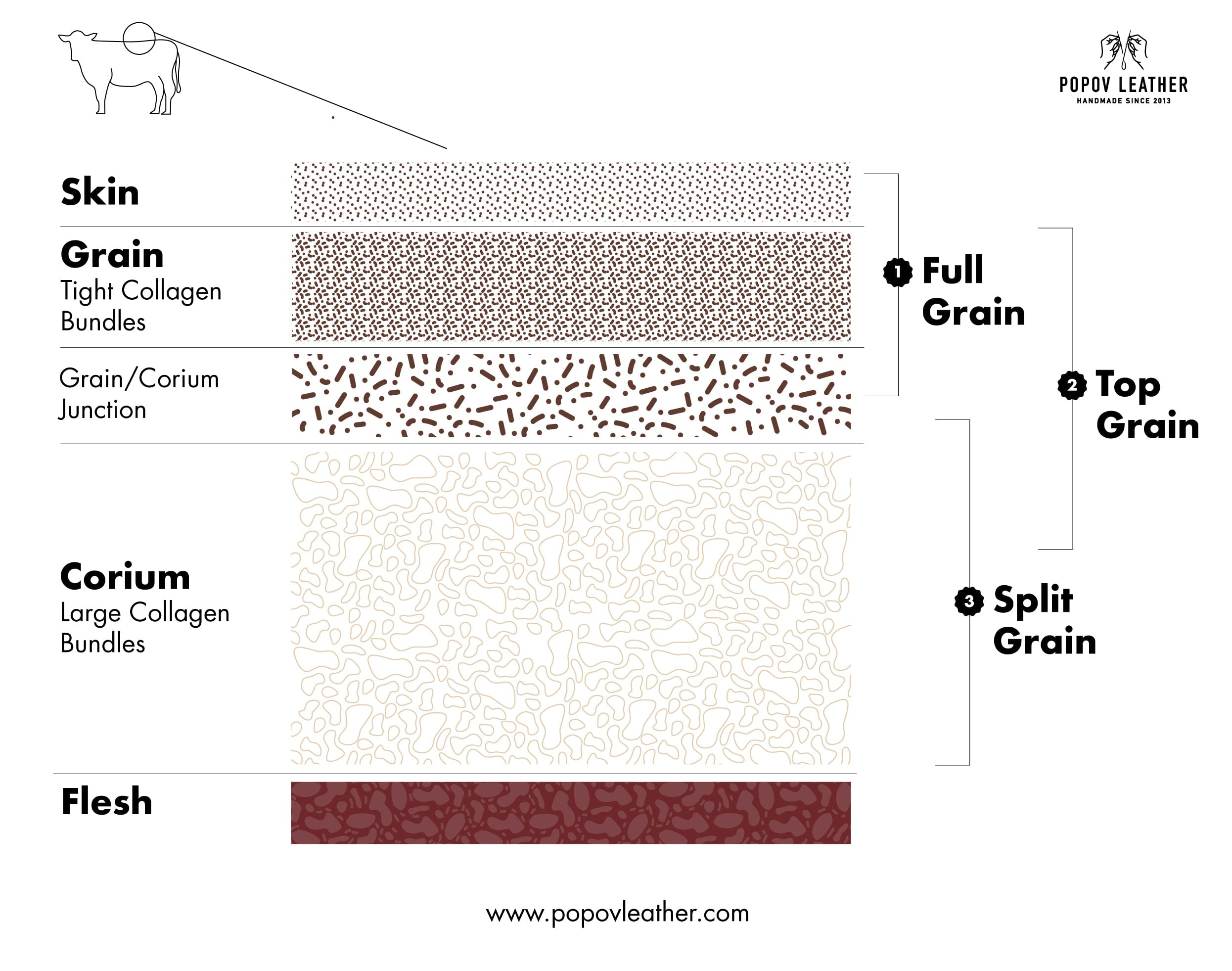
Material Preparation: How Are Hides Processed?
The initial stage in leather manufacturing involves the careful selection and preparation of raw hides. Typically sourced from cattle, these hides undergo a process known as curing, which prevents decay. This can be achieved through salting or drying methods. Once cured, hides are soaked in water to restore their original moisture content before being cleaned and inspected for quality.
During preparation, the hides are split into layers. The uppermost layer, known as the grain layer, is used for high-quality leather products, while the lower layer can be processed into split leather or suede. This stage is critical as it determines the final grade of the leather.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Leather?
After preparation, the forming stage begins. This involves cutting the hides into specific shapes and sizes required for various products. Advanced cutting techniques, such as die-cutting and laser cutting, ensure precision and minimize waste.
Once cut, the leather pieces may undergo a process called embossing to create patterns or textures. This can enhance both aesthetics and functionality, especially for products like handbags and shoes.
Assembly: How Are Leather Goods Constructed?
The assembly stage is where the leather pieces are stitched together to form the final product. Skilled artisans often perform this task, ensuring that the seams are both strong and visually appealing. Various stitching techniques, such as saddle stitching or machine stitching, are employed based on the product’s design and intended use.
In addition to stitching, components like zippers, buckles, and linings are added during this stage. Quality control measures are essential here to ensure that each piece meets the desired specifications and standards.
Finishing: What Processes Enhance Leather Quality?
Finishing is the final stage of leather manufacturing, where the product is treated to enhance its appearance and durability. Techniques such as dyeing, polishing, and applying protective coatings are employed to achieve the desired look and feel.
The finishing process also plays a significant role in determining the leather’s resistance to water, stains, and wear. High-quality finishing can significantly extend the lifespan of leather goods, making it a crucial aspect for B2B buyers to consider when sourcing products.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Leather Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the leather industry, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. This process involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing stages.
What International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with relevant international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. This standard emphasizes a quality management system that ensures consistent quality in products and services. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) indicate compliance with European safety standards.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these standards is crucial for ensuring that the leather goods they source are both compliant and of high quality.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the leather manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials upon arrival at the facility. Hides are inspected for defects, thickness, and other quality indicators.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor adherence to specifications. This ensures that any issues can be addressed promptly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the products are completed, a final inspection is performed to verify that they meet the required quality standards. This includes checking for defects in stitching, finishing, and overall appearance.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Leather Quality?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality of leather products, including:
- Tensile Strength Testing: Measures the leather’s resistance to tearing and stretching.
- Water Resistance Testing: Evaluates how well the leather withstands exposure to moisture.
- Colorfastness Testing: Assesses the leather’s ability to retain color when exposed to light and rubbing.
These tests are essential for ensuring that leather goods can withstand the rigors of daily use.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures, B2B buyers should consider the following steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with quality standards. This includes reviewing their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and certifications.
-
Request Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality reports that outline testing results and quality assurance processes. This transparency can help build trust and ensure that products meet expectations.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can occur at various stages of the manufacturing process, offering an added layer of assurance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate specific nuances when sourcing leather goods. Different countries may have varying regulations and standards, which can impact quality assurance practices.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
For example, buyers from Europe may require compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations, which govern the use of chemicals in leather production. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for ensuring compliance and maintaining high-quality standards.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in leather grading are intricate and multifaceted. For B2B buyers, especially those in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, a thorough understanding of these processes can lead to better sourcing decisions and long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers. By focusing on quality at every stage of production, buyers can ensure that they receive leather goods that not only meet but exceed their expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather grading’
Introduction
This guide provides a structured approach for B2B buyers looking to procure leather with a focus on grading. Understanding leather grades is essential for ensuring that the materials meet quality standards and expectations for durability, aesthetics, and performance. By following this checklist, buyers can make informed decisions and build lasting relationships with suppliers.
Step 1: Understand Leather Grades
Before sourcing leather, familiarize yourself with the various grades available—full-grain, top-grain, split-grain, genuine leather, and bonded leather. Each grade has unique characteristics that affect durability and use. Knowing the differences helps you select the right type of leather for your specific applications, ensuring that you meet your customers’ expectations.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the leather you intend to procure. Consider factors such as thickness, texture, color, and intended use (e.g., upholstery, fashion accessories). This specificity will guide your supplier discussions and help you avoid misunderstandings regarding what you need.
- Example Specifications:
- Thickness range (e.g., 1.2mm for upholstery)
- Desired finish (e.g., natural, pigmented, or corrected grain)
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly assess potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your quality and delivery needs. Request detailed company profiles, including their production processes, quality control measures, and past client references. A supplier’s experience in your specific industry can be a strong indicator of their reliability.
- Key Questions to Ask:
- What quality certifications do you hold?
- Can you provide examples of past projects similar to mine?
Step 4: Request Samples
Always request samples of the leather grades you are considering. This allows you to evaluate the material’s texture, durability, and overall appearance firsthand. Pay attention to how the leather feels, its color consistency, and any natural markings that may be present, as these can indicate the quality of the leather.
Step 5: Inquire About Sustainability Practices
As global demand for ethical sourcing grows, inquire about your suppliers’ sustainability practices. Understand their sourcing methods and whether they use environmentally friendly tanning processes. This not only aligns with consumer preferences but also reduces the risk of reputational damage associated with unethical sourcing.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirm that your chosen supplier holds relevant certifications that reflect their commitment to quality and sustainability. Certifications such as ISO or Leather Working Group (LWG) can provide assurance that the supplier adheres to industry best practices.
- Important Certifications to Look For:
- ISO 9001 for quality management
- LWG certification for sustainable leather production
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Maintain open lines of communication with your supplier throughout the sourcing process. Establishing a good rapport and clarity in communication helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures that both parties are aligned on expectations, timelines, and quality standards. Regular updates can help you stay informed about production progress and any potential issues that may arise.
By following this checklist, you can navigate the complexities of leather grading and sourcing with confidence, ensuring that you procure high-quality materials that meet your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather grading Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Grading Sourcing?
When sourcing leather for grading, it’s crucial to understand the various cost components that contribute to the final price. These include:

Illustrative image related to leather grading
-
Materials: The type of leather significantly affects costs. Full-grain leather, being the highest quality, commands a premium price compared to lower grades like bonded leather. Suppliers may also charge differently based on the source of the hide, whether it’s cow, goat, or exotic leathers.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for tanning and processing leather, impacting overall costs. Regions with high labor costs will see increased prices, while those with a skilled but lower-cost workforce might offer more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to equipment, facility maintenance, and utilities. For example, advanced tanning technologies may require higher initial investments, influencing the pricing structure.
-
Tooling: The cost of machinery and tools used in the production of leather goods can vary widely. Custom tooling for unique designs or specifications will add to the cost, making it essential for buyers to consider their design requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the leather meets specific grading standards necessitates rigorous QC processes, which can increase labor and overhead costs. Buyers should inquire about a supplier’s QC practices to understand their implications on pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the origin of the leather and the destination market. International shipping, customs duties, and storage fees can add significant expenses, particularly for buyers in regions like Africa and South America.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin will also influence the final price. It’s important for buyers to understand the typical margins within the industry to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Leather Grading Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing structure in leather grading sourcing:
-
Volume/MOQ: Buying in bulk often results in lower per-unit costs. Suppliers typically offer discounts for larger orders, so negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom requests for specific leather types or treatments can increase costs. Buyers should balance their needs for customization with budget constraints, considering whether standard options could suffice.
-
Quality and Certifications: Certifications, such as environmental compliance or ethical sourcing, may add to the cost but can also enhance the product’s marketability. Buyers should evaluate the importance of these certifications in relation to their target market.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can also affect pricing. Suppliers with a strong track record may charge more but offer better quality and reliability, which can justify the higher price.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (Incoterms) is crucial as it affects cost allocation between the buyer and seller. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can shift financial responsibilities and impact overall pricing.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Leather Sourcing?
To optimize cost-efficiency when sourcing leather, particularly for international B2B buyers, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always enter negotiations with a clear understanding of market prices and your requirements. Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better deals and terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with leather products, including maintenance and durability. Investing in higher-quality leather, like full-grain, may lead to lower TCO despite higher upfront costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local taxes that can affect overall costs. Buyers from regions like the Middle East or South America should account for these factors when budgeting.
-
Research Market Trends: Keeping abreast of market trends in leather pricing can provide leverage in negotiations and help buyers identify the best times to purchase.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures mentioned are indicative and can vary significantly based on specific supplier relationships, market conditions, and regional factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather grading With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Leather Grading in Material Assessment
When evaluating leather products, leather grading is a crucial process that helps buyers understand the quality and durability of leather goods. However, there are alternative methods and materials that can serve similar purposes in assessing quality and functionality, especially in the context of B2B procurement. This section explores these alternatives to provide a comprehensive understanding for international buyers.
Comparison of Leather Grading with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Leather Grading | Synthetic Leather | Textile-Based Alternatives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability, develops patina | Generally durable, varies by quality | Moderate durability, can be designed for specific uses |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Generally lower cost | Varies widely based on material |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires expertise in grading | Easy to produce and source | Moderate; requires knowledge of fabric types |
| Maintenance | Requires specific care | Easy to clean, low maintenance | Varies; some require special care |
| Best Use Case | High-end products, luxury items | Affordable fashion, furniture | Everyday wear, casual items |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Synthetic Leather
Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), is a popular alternative to natural leather. Its main advantages include cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance. Synthetic leather is less expensive than high-grade leather, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. However, while it can mimic the look and feel of leather, it often lacks the same level of durability and aesthetic appeal. Over time, synthetic leather may show wear and tear more quickly than high-quality natural leather, which develops a unique patina as it ages.
Textile-Based Alternatives
Textile-based materials, such as cotton, polyester, or blends, offer a diverse range of options for various applications. These materials can be designed for specific functionalities, such as moisture-wicking or stretchability. The cost of textiles can vary significantly, providing options for both low-budget and premium products. However, textile alternatives typically do not match the durability or luxurious feel of high-quality leather. Moreover, some textiles may require special care to maintain their appearance and functionality, which could complicate their long-term use in B2B settings.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When deciding between leather grading and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements and the intended application of the materials. If durability, aesthetic appeal, and long-term investment are priorities, high-quality leather grading is likely the best choice. However, for projects with tighter budgets or where maintenance is a concern, synthetic leather or textile alternatives may be more suitable. Ultimately, understanding the unique characteristics and performance metrics of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather grading
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Leather Grading?
When engaging in the leather market, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Leather is categorized into various grades based on its quality and processing methods. The primary grades include full-grain, top-grain, split-grain, genuine leather, and bonded leather. Each grade has distinct characteristics affecting durability, appearance, and cost. For B2B buyers, recognizing these differences is vital for ensuring product quality aligns with customer expectations and intended use. -
Thickness
The thickness of leather, typically measured in millimeters (mm), plays a significant role in its application. Full-grain leather can range from 1.2mm to 3.2mm or more, depending on the end product (e.g., upholstery vs. belts). For manufacturers, understanding thickness allows for better design choices and material sourcing, ultimately impacting product durability and performance. -
Grain Structure
The grain structure refers to the natural pattern on the leather surface. Full-grain leather retains its original texture, which is essential for high-end products that develop a rich patina over time. In contrast, split-grain leather lacks the natural grain, affecting its aesthetic appeal and market value. B2B buyers should consider grain structure when selecting materials that will resonate with their target audience. -
Durability and Wear Resistance
Durability is a critical property in leather grading, often influenced by the leather’s grade and thickness. Full-grain leather, for instance, is renowned for its ability to withstand wear and tear, making it ideal for high-traffic applications. Understanding durability helps B2B buyers select leather that will meet the longevity requirements of their products, reducing the need for replacements and enhancing customer satisfaction. -
Moisture Resistance
The ability of leather to resist moisture varies significantly among grades. Full-grain and top-grain leathers can repel water to an extent, while genuine and bonded leathers may not offer the same level of protection. For businesses in humid climates or those producing goods exposed to moisture, selecting the right leather type is essential to prevent damage and maintain product integrity.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Leather Grading?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the leather market. Here are some common terms to know:

Illustrative image related to leather grading
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the leather industry, OEMs often provide components like leather upholstery for furniture or automotive manufacturers. Understanding OEM relationships can help B2B buyers identify potential suppliers and streamline procurement processes. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In leather procurement, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their demand to avoid overstocking or stockouts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. In the leather industry, an RFQ can help buyers gather competitive quotes for different grades and types of leather, aiding in informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers, as they define who bears the risk and costs associated with shipping leather products, influencing overall pricing and logistics planning. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. In leather procurement, lead times can vary based on the supplier, material availability, and shipping methods. B2B buyers should consider lead times when planning production schedules to ensure timely delivery of finished products.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of leather grading with greater confidence, ensuring they make well-informed purchasing decisions that align with their business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather grading Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Leather Grading?
The leather grading sector is experiencing significant shifts driven by globalization, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe engage with this market, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Key drivers include the rising demand for high-quality leather goods, particularly in luxury markets, and the increasing interest in leather alternatives due to sustainability concerns. Moreover, innovations in leather processing technologies, such as digital tanning methods and enhanced quality control systems, are emerging, allowing for more consistent grading and better product offerings.
Emerging sourcing trends highlight a growing reliance on digital platforms for procurement. Many buyers are now leveraging e-commerce and B2B marketplaces to access a wider range of suppliers, facilitating more competitive pricing and streamlined purchasing processes. Additionally, the trend toward direct sourcing from tanneries is gaining traction, enabling businesses to ensure quality and traceability while reducing costs associated with intermediaries. As these dynamics evolve, buyers must remain agile and informed to capitalize on new opportunities in the leather grading market.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Leather Grading in B2B?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount in the leather grading sector, influencing buyer decisions and brand reputations. The environmental impact of leather production is significant, from water usage to chemical runoff, prompting many companies to seek more sustainable practices. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt eco-friendly tanning methods and utilize sustainable raw materials. Certifications such as the Leather Working Group (LWG) and Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) are gaining importance, as they provide assurance of responsible sourcing and processing.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
Ethical supply chains are crucial not only for environmental reasons but also for social responsibility. Consumers are more aware of the implications of their purchases, leading to a demand for transparency in sourcing practices. Buyers are encouraged to establish relationships with suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and maintain high animal welfare standards. By investing in ethically sourced leather, businesses can enhance their marketability and align with the values of a growing segment of conscientious consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Leather Grading Relevant to B2B?
The evolution of leather grading can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where leather was a prized commodity due to its durability and versatility. Initially, grading was rudimentary, relying on the physical characteristics of hides. Over time, with advancements in tanning techniques and processing technologies, a more systematic approach to grading emerged. By the 19th century, the establishment of standardized grades—such as full-grain and top-grain—allowed for better classification and quality assurance.
Today, leather grading has evolved into a complex system that not only considers the physical attributes of the hide but also incorporates technological innovations and sustainability factors. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers, as understanding the nuances of leather grading is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The shift toward higher quality and ethically sourced leather continues to shape the market, providing opportunities for businesses that prioritize quality and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather grading
-
How do I ensure I’m sourcing high-quality leather?
To source high-quality leather, begin by understanding the grading system. Look for full-grain or top-grain leather, which are the most durable and aesthetically pleasing options. Always request samples to assess the texture, smell, and overall quality. Additionally, verify the supplier’s certifications and reputation in the market, as this indicates their commitment to quality. Engaging with suppliers who provide transparent information about their sourcing and tanning processes is crucial for ensuring you receive genuine products. -
What is the best type of leather for luxury goods?
Full-grain leather is the best choice for luxury goods due to its superior durability, breathability, and natural aesthetics. It retains the hide’s original grain, showcasing its unique character and developing a rich patina over time. While top-grain leather is also a good option, it may lack some of the natural imperfections that contribute to the charm of full-grain leather. When sourcing for luxury items, prioritize suppliers who specialize in high-end leather goods to ensure the best quality. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting leather suppliers?
When vetting leather suppliers, consider their experience, reputation, and production capabilities. Check for industry certifications such as ISO or LWG, which ensure adherence to quality and environmental standards. Request references or testimonials from previous clients and inquire about their sourcing practices. Additionally, assess their ability to meet your customization needs, minimum order quantities (MOQ), and delivery timelines, as these factors can significantly impact your supply chain efficiency. -
What customization options are typically available for leather products?
Many leather suppliers offer a range of customization options, including leather type, color, texture, and stitching styles. You can also request specific finishes, embossing, or debossing to enhance brand identity. When discussing customization, ensure the supplier has the capability to produce prototypes, allowing you to evaluate the final product before committing to larger orders. Be clear about your requirements and timelines to avoid any production delays. -
How can I effectively manage logistics when importing leather?
To manage logistics effectively when importing leather, work with a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling leather shipments. Ensure that you understand the customs regulations for the countries involved, as compliance is crucial to avoid delays. Plan for potential lead times, including production and shipping, and maintain clear communication with your suppliers regarding delivery schedules. Implement inventory management systems to track stock levels and anticipate replenishment needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing leather?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include a deposit upon order confirmation (typically 30-50%) with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or extended payment terms for established relationships. Always clarify payment options and negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs. Additionally, consider the payment security measures in place to protect against fraud. -
How do I assess the quality of leather samples?
To assess the quality of leather samples, examine the texture, grain, and smell. High-quality leather should feel supple and have a natural scent, while lower grades often feel plastic-like and have synthetic odors. Look for consistent color and minimal imperfections. Conduct the “fire test” by briefly holding a flame to the leather; genuine leather will singe and smell like burnt hair, whereas synthetic materials will melt. Evaluate the sample’s thickness and weight to ensure it meets your product requirements. -
What are the common issues to watch out for in leather products?
Common issues to watch for in leather products include cracks, peeling, and discoloration, which often indicate low-quality leather or poor treatment. Inspect for consistent stitching and alignment, as these are signs of good craftsmanship. Be aware of the supplier’s return policy and warranty options, which can provide recourse if defects arise. Educating yourself on proper leather care can also mitigate long-term issues, ensuring your products maintain their quality over time.
Top 7 Leather Grading Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Popov Leather – Leather Quality Chart
Domain: popovleather.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Leather Quality Chart: Decoding the World of Leather Grades – Popov Leather®
1. **Leather Grades**:
– **Top Grain Leather**: Includes Full Grain and Corrected Grain leather.
– **Full Grain Leather**:
– Common Uses: Higher-end products.
– Characteristics: Marbling, variations in grain and coloring, visible scars and imperfections, breathes well, durable, develops a patina.
– …
2. Leather Edge Paint – Leather Grades Explained
Domain: blog.leatheredgepaint.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: 5 Leather Grades: 1. Full Grain Leather: Complete grain intact, most durable and resistant to wear, lasts longer, includes vegetable tanned and distressed leather. 2. Top Grain Leather: Second highest quality, split layer with imperfections removed, thinner and more workable, common in high-end products, sanded surface with finish applied, less breathable but stain-resistant. 3. Split Grain Leathe…
3. Billy Tannery – Leather Grades Explained
Domain: billytannery.co.uk
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: This company, Billy Tannery – Leather Grades Explained, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Weaver Leather Supply – Leather Grades Explained
Domain: weaverleathersupply.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Leather grades are categorized as A, B, or C based on the amount of damage or defects present. Grade A allows for 1-2 small defects in prime areas and 3-4 in non-prime areas. Grade B can have 3-4 defects in prime areas, 6-12 inches of damage or waste, and some small holes in non-prime areas. Grade C allows for more than 12 inches of damage or waste and color variation. Weaver Leather Supply uses a…
5. SATRA – Leather Grading Accreditation
Domain: satra.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: SATRA leather grading accreditation involves a five-point grading system for leather usability, established over 16 years. Each skin is visually inspected and assigned a grade from A to F, representing a spread of five percentage points of usability. The ideal standard is a skin marked to show unusable areas, agreed upon by both supplier and user. SATRA trains quality inspection personnel, ensurin…
6. Steel Horse Leather – Grades of Leather
Domain: steelhorseleather.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Grades Of Leather – A Comprehensive Guide To Leather Qualities. Key product categories include: Leather Bags, Leather Duffle Bags (for Men and Women, Handmade, Large, Vintage), Leather Backpacks (Men’s, Women’s, Vintage, Camera), Leather Messenger Bags (Laptop, Shoulder, Vintage, for Men and Women), Leather Briefcases (Business, for Women, Black, Vintage), Leather Laptop Bags (including 17″), Leat…
7. Dalgado – Understanding Leather Grades
Domain: dalgado.de
Introduction: The leather industry is complex and often misleading. To understand leather quality, one must learn about leather grades. Cowhide is cut into layers: the grain layer (top) and the dermal layer (bottom). The grain layer has tighter collagen fibers, making it more durable. Leather grades are ranked as follows: full-grain leather (most durable and authentic), top-grain leather (sanded and buffed for …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather grading
As the leather industry continues to evolve, understanding leather grading remains crucial for international B2B buyers. Recognizing the differences between full-grain, top-grain, split-grain, genuine, and bonded leather not only influences product quality but also impacts long-term value and customer satisfaction. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can ensure they acquire high-quality leather that meets their specific needs, whether for luxury goods, durable upholstery, or fashion accessories.
With the rise of sustainable practices and consumer demand for transparency, sourcing partners who prioritize quality and ethical production will be vital. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage their purchasing power to foster relationships with reputable tanneries and suppliers. This not only supports local economies but also guarantees access to superior materials that enhance product offerings.
Illustrative image related to leather grading
Looking ahead, the leather market is poised for growth, driven by innovation and sustainability. Now is the time for businesses to invest in quality leather sourcing strategies that align with market trends and consumer preferences. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your product line and build a reputation for excellence in the leather industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to leather grading
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.