Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for polyurethane fake leather
In the competitive landscape of global sourcing, finding high-quality polyurethane fake leather can be a challenging endeavor for B2B buyers, especially when looking to balance aesthetics, cost, and sustainability. As businesses increasingly pivot towards eco-friendly materials, understanding the nuances of polyurethane leather—its types, applications, and production processes—becomes essential. This comprehensive guide aims to equip international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—specifically markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of sourcing PU leather.
The guide delves into various aspects of polyurethane fake leather, including its diverse types such as bicast and bonded leather, and explores its applications across industries like fashion, furniture, and automotive. We also discuss crucial factors for supplier vetting, ensuring that you select partners who align with your quality and sustainability standards. Additionally, insights into pricing dynamics will help you make informed decisions that benefit your bottom line.
By leveraging this guide, you will empower your purchasing strategy with actionable insights, enabling you to confidently source the best polyurethane fake leather products while addressing the growing demand for ethical and sustainable alternatives. In doing so, you can enhance your product offerings and meet the evolving preferences of your clientele.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 Polyurethane Fake Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for polyurethane fake leather
- Understanding polyurethane fake leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of polyurethane fake leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘polyurethane fake leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for polyurethane fake leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for polyurethane fake leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘polyurethane fake leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for polyurethane fake leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing polyurethane fake leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for polyurethane fake leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the polyurethane fake leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of polyurethane fake leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for polyurethane fake leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding polyurethane fake leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| PU Leather | Made from thermoplastic polymer; vegan; easy to maintain | Furniture, fashion, automotive | Pros: Cost-effective, durable, easy to clean. Cons: Can look synthetic, less breathable. |
| Bicast Leather | Genuine leather base with a polyurethane coating | Upholstery, bags, shoes | Pros: Retains some leather qualities, affordable. Cons: Limited durability compared to full leather. |
| Split Leather | Made from the fibrous part of hide; coated with PU | Upholstery, fashion accessories | Pros: Affordable, maintains some leather texture. Cons: Less durable, can wear out quickly. |
| Bonded Leather | Composed of leather scraps bonded with PU | Furniture, accessories | Pros: Eco-friendly, cost-effective. Cons: Limited lifespan, may peel or crack. |
| Vegan Leather | Fully synthetic, no animal products; varied aesthetics | Fashion, furniture, accessories | Pros: Ethical choice, wide design options. Cons: May lack durability, can feel less luxurious. |
What Are the Characteristics of PU Leather for B2B Buyers?
PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is a synthetic material made from thermoplastic polymers. It is widely used in various industries, including furniture and fashion, due to its affordability and ease of maintenance. For B2B buyers, the key considerations include its cost-effectiveness and durability, which make it suitable for high-turnover products like office furniture. However, it may not provide the same aesthetic appeal as genuine leather, which could be a drawback for luxury-oriented markets.
How Does Bicast Leather Stand Out in the Market?
Bicast leather features a genuine leather base, enhanced with a layer of polyurethane. This combination allows it to offer some of the tactile qualities of leather while remaining more affordable. It is particularly favored in upholstery and fashion accessories. B2B buyers should consider its balance between cost and quality, but they should also note that its durability may not match that of full-grain leather, making it less ideal for high-use applications.

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
What Makes Split Leather a Viable Option for Buyers?
Split leather is derived from the fibrous parts of animal hides, which are then coated with polyurethane. This type of leather offers a more economical solution while maintaining some of the textural qualities of genuine leather. It is commonly used in upholstery and fashion accessories. B2B buyers should evaluate its price point and texture, but they must also be aware that it may wear out quicker than other types of leather, potentially impacting long-term value.
Why Consider Bonded Leather for Sustainable Solutions?
Bonded leather is made from leather scraps bonded together with polyurethane. This product is often marketed as an eco-friendly option, appealing to businesses looking to reduce waste. It is suitable for furniture and various accessories. While its cost-effectiveness is a significant advantage, buyers should be mindful of its limited lifespan and potential for peeling, which could affect customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
What Are the Benefits of Vegan Leather for Ethical Markets?
Vegan leather is entirely synthetic and contains no animal products, making it an ethical choice for businesses focused on sustainability. Its versatility in design allows for a wide range of applications in fashion and furniture. B2B buyers should consider the growing demand for ethical products, but they should also be aware that vegan leather may lack the durability and luxurious feel associated with traditional leather, which could limit its appeal in premium markets.
Key Industrial Applications of polyurethane fake leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of polyurethane fake leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion and Apparel | Manufacturing of clothing items like jackets and shoes | Cost-effective, versatile design options, and vegan-friendly | Quality of finish, durability, and compliance with international standards |
| Furniture | Upholstery for office furniture and home decor | Easy maintenance, long-lasting appearance, and aesthetic appeal | Supplier reliability, customization options, and eco-friendliness |
| Automotive | Interior components such as seat covers and trims | Enhanced durability, lightweight, and easy to clean | Material specifications, compliance with safety regulations, and sourcing from sustainable manufacturers |
| Sports Equipment | Production of gear like bags and protective wear | High durability, resistance to wear, and easy cleaning | Performance specifications, weight considerations, and material sourcing transparency |
| Home Decor | Decorative items like cushions and wall coverings | Aesthetic flexibility, cost savings, and ease of care | Color and texture variety, sourcing from environmentally responsible suppliers, and compliance with safety standards |
How is Polyurethane Fake Leather Used in the Fashion and Apparel Industry?
In the fashion and apparel sector, polyurethane fake leather is widely utilized for creating stylish yet affordable clothing items, including jackets, shoes, and handbags. It offers numerous design options, allowing brands to cater to diverse consumer preferences, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where fashion trends are rapidly evolving. Buyers must ensure that the PU leather sourced meets quality standards and is durable enough to withstand regular wear, while also being mindful of environmental impacts and ethical production practices.

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
What Role Does Polyurethane Fake Leather Play in Furniture Upholstery?
Polyurethane fake leather serves as a popular upholstery material for both office and residential furniture. Its easy-to-clean nature and resistance to stains make it ideal for high-traffic areas, which is particularly beneficial for businesses in the Middle East and Europe where durability is essential. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers who can provide custom color and texture options while ensuring compliance with international quality standards, as well as considering the environmental footprint of the materials used.
How is Polyurethane Fake Leather Applied in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, polyurethane fake leather is commonly used for seat covers, interior trims, and headliners. Its lightweight nature and resistance to wear make it an attractive alternative to genuine leather, especially for manufacturers looking to enhance the comfort and aesthetics of their vehicles. Buyers should prioritize sourcing PU leather that meets safety regulations and performance specifications while also considering the supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices, which is increasingly relevant in markets like Saudi Arabia and Brazil.
What Advantages Does Polyurethane Fake Leather Offer in Sports Equipment?
Polyurethane fake leather is utilized in the sports equipment sector for producing items such as bags, protective gear, and footwear. Its durability and ease of cleaning make it an excellent choice for items subjected to rigorous use. When sourcing PU leather for sports applications, businesses should focus on the performance characteristics of the material, including its resistance to wear and tear, while also ensuring transparency in sourcing practices to align with growing consumer demand for sustainability.
How is Polyurethane Fake Leather Used in Home Decor?
In home decor, polyurethane fake leather is employed for decorative cushions, wall coverings, and various accent pieces. Its versatility allows for a wide range of aesthetic applications, appealing to consumers seeking modern and stylish home environments, particularly in emerging markets across Africa and South America. Buyers should consider the variety of colors and textures available while ensuring that the materials sourced are compliant with safety standards and reflect an eco-friendly production process.

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘polyurethane fake leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Differentiating Quality Levels of PU Leather
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges in distinguishing between high-quality and low-quality polyurethane fake leather. This is particularly problematic when sourcing materials for products that require durability and aesthetics, such as furniture or fashion items. Poor quality PU leather can result in customer dissatisfaction, returns, and damage to brand reputation. Buyers may struggle with inconsistent quality, as different manufacturers may use varying production processes or materials, leading to significant discrepancies in performance and appearance.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should establish a robust supplier evaluation process that includes clear quality criteria. Request samples from multiple suppliers to assess the look, feel, and durability of their PU leather. Conduct a water resistance test and check for smell—high-quality PU leather should not emit strong chemical odors. Additionally, consider suppliers who provide certifications or have a transparent production process, as these indicators often correlate with higher quality. Regular audits and quality checks can further ensure that the products meet your standards consistently.
Scenario 2: Environmental Concerns Regarding PU Leather Production
The Problem: Increasingly, B2B buyers are facing pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to ensure that the materials they use are environmentally friendly. While PU leather is often marketed as a vegan alternative to genuine leather, its production still involves synthetic materials and chemicals that may not be sustainable. Buyers may find it difficult to navigate these concerns, especially in markets that prioritize eco-friendliness and corporate social responsibility.
The Solution: To address environmental concerns, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing PU leather from manufacturers who are committed to sustainable practices. Look for suppliers who use recycled materials in their production or those who have adopted greener manufacturing processes that minimize waste and chemical use. Collaborate with suppliers to understand their environmental impact and inquire about their certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management. Additionally, consider integrating life cycle assessments (LCA) into your sourcing strategy to evaluate the environmental impacts of PU leather throughout its life cycle, enabling informed decisions that align with your sustainability goals.
Scenario 3: Misalignment Between Product Performance and Customer Expectations
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the mismatch between the performance of PU leather products and customer expectations. For example, customers may assume that PU leather will perform similarly to genuine leather, leading to dissatisfaction when the products crack, tear, or wear out more quickly than anticipated. This can result in negative reviews and damage to brand loyalty, especially in competitive markets.

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should establish clear product specifications and communicate these effectively to customers. Provide detailed information about the properties of PU leather, including its limitations and care instructions. Educate your sales team on the differences between PU leather and genuine leather, so they can set realistic expectations for customers. Furthermore, consider incorporating warranties or guarantees for PU leather products, which can reassure customers about their durability. By aligning product offerings with customer expectations and providing transparent information, you can enhance customer satisfaction and reduce the likelihood of returns.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for polyurethane fake leather
What Are the Common Materials Used in Polyurethane Fake Leather?
When selecting polyurethane fake leather for various applications, understanding the materials involved is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we analyze several common materials used in the production of polyurethane fake leather, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Polyurethane Coatings?
Polyurethane coatings are typically applied over a base material, which can include textiles like polyester or nylon. These coatings provide a flexible, durable surface that mimics the appearance of genuine leather. Key properties include:
- Temperature Resistance: Generally withstands temperatures from -30°C to 80°C, making it suitable for various climates.
- Chemical Resistance: Offers moderate resistance to oils and solvents, but may degrade with prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Polyester as a Base Material?
Polyester is a popular choice for the backing material in PU leather.
- Pros:
- Cost-effective and widely available.
- Offers good tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for high-traffic applications.
-
Easy to dye, allowing for a range of colors and finishes.
-
Cons:
- Less breathable than natural materials, which may affect comfort in certain applications.
- Can be prone to pilling and wear over time, particularly in high-friction areas.
How Does Nylon Compare as a Base Material for PU Leather?
Nylon is another common base for polyurethane fake leather, known for its strength and versatility.
- Pros:
- Highly durable and resistant to abrasion, making it ideal for products subjected to heavy use.
-
Excellent elasticity and flexibility, which enhances comfort in applications like clothing and upholstery.
-
Cons:
- Generally more expensive than polyester, impacting overall product cost.
- May require specialized treatments to enhance UV resistance, especially in outdoor applications.
What Are the Considerations for International Buyers in Different Regions?
When sourcing polyurethane fake leather, international B2B buyers must consider compliance with local regulations and standards. For instance:

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
- Africa and South America: Buyers should be aware of local environmental regulations regarding the use of synthetic materials and any import restrictions on chemicals used in production.
- Middle East: Compliance with GCC standards for textiles and materials is crucial, as is understanding the climate’s impact on material performance.
- Europe: Adherence to EU regulations, including REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals), is essential. Buyers should also consider the growing demand for sustainable materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Polyurethane Fake Leather
| Material | Typical Use Case for polyurethane fake leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester | Upholstery, fashion accessories | Cost-effective and widely available | Less breathable, prone to wear over time | Low |
| Nylon | Clothing, high-use furniture | Highly durable and resistant to abrasion | More expensive than polyester | Med |
| Polyurethane | Coating for various base materials | Flexible, mimics genuine leather appearance | Moderate chemical resistance, can degrade | Med |
| Bicast Leather | Luxury furniture, handbags | Combines real leather with PU for texture | Higher cost, may not be fully vegan | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions regarding polyurethane fake leather. Understanding the properties, advantages, and regional considerations will aid in selecting the most suitable materials for specific applications.
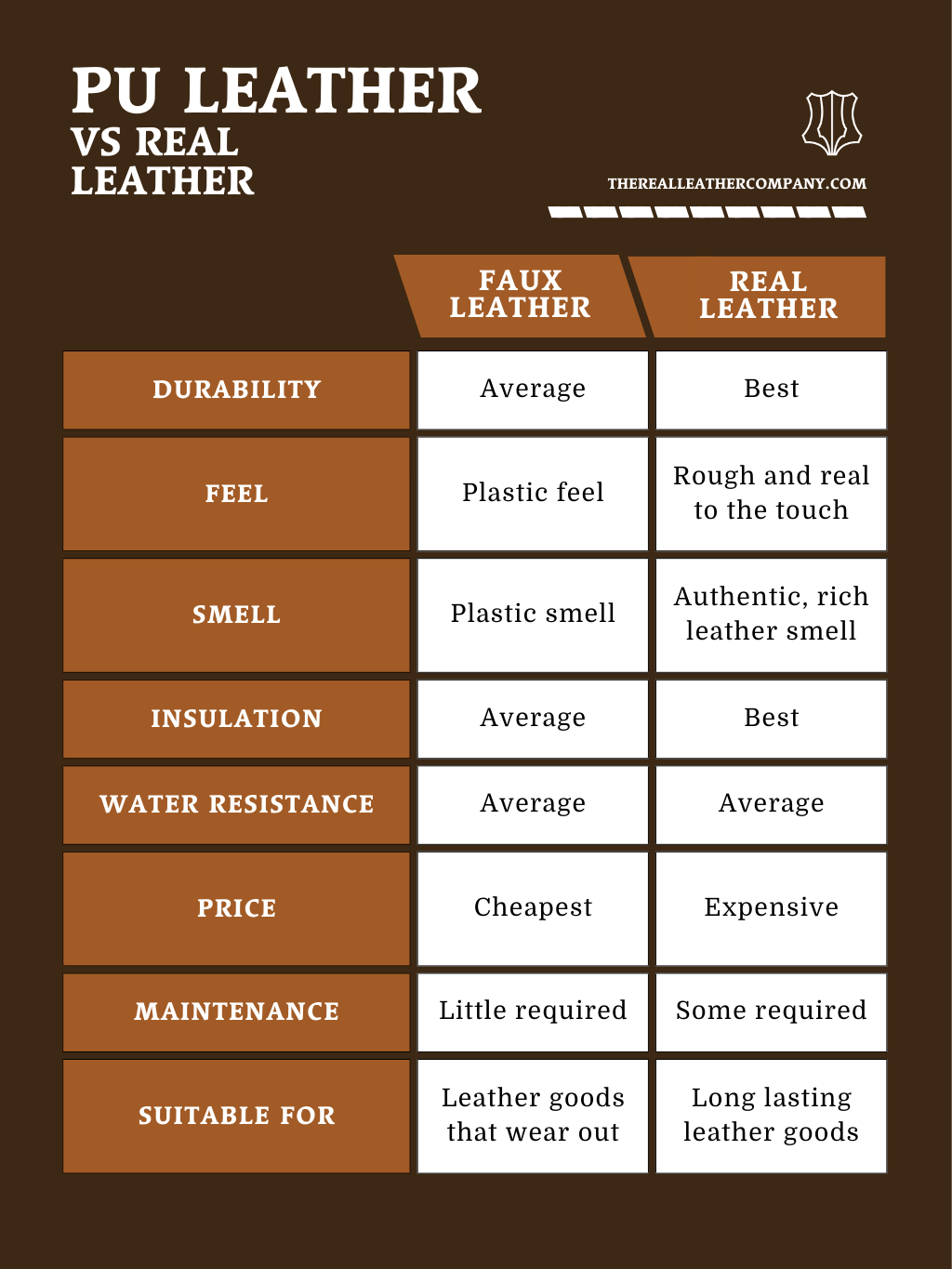
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for polyurethane fake leather
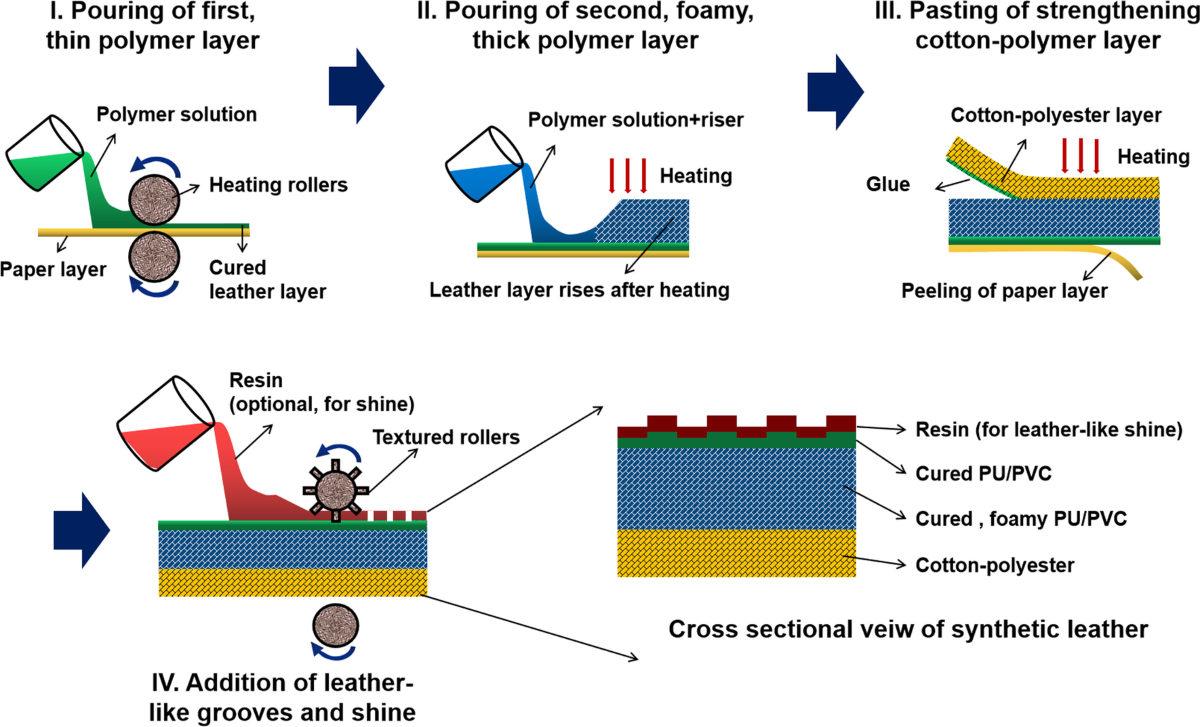
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Polyurethane Fake Leather?
The manufacturing of polyurethane (PU) fake leather involves several critical stages, each ensuring that the final product meets quality, durability, and aesthetic standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in PU Leather Production?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. PU leather is made using a thermoplastic polymer called polyurethane, which is combined with a fabric backing. Common backing materials include polyester, cotton, and nylon. The selection of these materials can significantly affect the final product’s durability, texture, and visual appeal. Suppliers often source high-quality raw materials to ensure that the PU leather can withstand wear and tear.
Forming: How Is PU Leather Coated and Textured?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves coating the fabric backing with a layer of liquid polyurethane. The application process typically employs techniques such as:
-
Roller Coating: The fabric is passed through rollers that apply a uniform layer of polyurethane. This method ensures even coverage and thickness.
-
Spray Coating: In some cases, a spray application is used for intricate designs or textures, allowing for greater control over the finish.
After coating, the material undergoes a drying process, where heat is applied to cure the polyurethane. This step is crucial for achieving the right level of flexibility and durability.

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
Assembly: What Techniques Are Used for Creating Finished Products?
The assembly phase involves cutting the coated material into desired shapes and sizes, which can then be sewn or glued together to form various products like handbags, upholstery, or footwear. Common techniques include:
-
Die Cutting: This method uses sharp dies to cut through multiple layers of material, ensuring precision in shapes.
-
Sewing: For items that require stitching, industrial sewing machines are employed to create strong seams that can withstand stress and usage.
-
Adhesive Bonding: In cases where sewing is not feasible, high-strength adhesives are used to bond layers together.
Finishing: How Is PU Leather Treated for Aesthetic Appeal and Durability?
The final stage is finishing, which enhances both the aesthetic qualities and durability of PU leather. This can include:
-
Texturing: A textured roller may imprint patterns that mimic the grain of genuine leather, providing a more authentic appearance.
-
Embossing: Designs can be embossed onto the surface for added visual appeal and differentiation.
-
Coating: A protective topcoat is applied, which can offer water resistance and UV protection, ensuring longevity.
What Are the Key Quality Control Measures in PU Leather Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of PU leather manufacturing, ensuring that the products meet international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be familiar with the quality control measures employed by manufacturers.
What International Standards Should Be Considered?
Manufacturers of PU leather often adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which sets criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer has established processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe, and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications for specific applications, may also be relevant.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control is typically integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process, with the following checkpoints being common:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, regular checks are performed to monitor the quality of the coating, assembly, and finishing processes. This helps in identifying issues before they escalate.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the required specifications. This may include visual inspections, strength tests, and assessments of colorfastness and durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Here are some effective strategies:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to verify quality control practices. Buyers should consider:
-
On-Site Visits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to observe processes firsthand and assess the working conditions, equipment, and overall operations.
-
Documentation Review: Requesting access to quality control documentation, including inspection reports and compliance certificates, can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent entities can conduct thorough evaluations at various stages of production, ensuring that the final product adheres to the agreed-upon specifications.
Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances in quality control. Different markets may have varying expectations regarding materials, certifications, and environmental standards.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Supplier Selection?
Understanding regional standards can guide buyers in selecting the right suppliers. For instance, buyers in Europe may prioritize eco-friendly materials and sustainable practices, while those in the Middle East might focus on durability and resistance to extreme conditions.
What Additional Considerations Should Be Made for Compliance?
Buyers should also consider local regulations and compliance requirements when importing PU leather products. Familiarity with these regulations can help mitigate risks associated with customs and trade barriers.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for polyurethane fake leather is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and robust quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs and market demands.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘polyurethane fake leather’
When sourcing polyurethane fake leather, understanding the material’s properties and the supplier landscape is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide provides a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital to ensure that the polyurethane fake leather meets your product requirements. Consider factors such as thickness, texture, color, and intended use (e.g., upholstery, fashion, or automotive applications). Documenting these specifications will help streamline communication with suppliers and prevent misunderstandings.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in polyurethane fake leather. Look for companies that have a proven track record in your target market. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of potential partners.
- Tip: Focus on suppliers that have experience serving your specific industry, as they will better understand your needs and challenges.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verifying supplier certifications is crucial for ensuring product quality and compliance with international standards. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and OEKO-TEX for eco-friendly materials. These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to best practices in manufacturing and sustainability.
- Key Consideration: Ensure that the certifications are up-to-date and relevant to the specific type of polyurethane fake leather you intend to purchase.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Before making a bulk order, request samples from shortlisted suppliers to evaluate the quality of their polyurethane fake leather. Examine the samples for durability, texture, and color accuracy. Conduct tests such as water resistance and abrasion resistance to assess performance under real-world conditions.
- Important Note: Take into account the environmental impact of the materials used in the samples, as sustainability is a growing concern among consumers.
Step 5: Inquire About Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)
Understanding the supplier’s minimum order quantities is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Some suppliers may impose high MOQs, which could be a barrier for smaller businesses or those testing new product lines. Discuss flexibility in order quantities and potential for smaller trial orders.
- Action Item: Negotiate terms that align with your purchasing capacity while ensuring you can secure the best pricing.
Step 6: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have selected a potential supplier, review their pricing structure and payment terms. Consider factors such as unit price, shipping costs, and any additional fees for customizations. Aim for transparent terms that align with your financial strategy and budget constraints.

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
- Tip: Explore options for bulk discounts or favorable payment terms that can enhance your cash flow.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Effective communication is essential for a successful supplier relationship. Ensure that your chosen supplier has responsive customer support and clear channels for addressing any concerns that may arise during the order process. Establish regular check-ins to discuss updates and any potential issues proactively.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for polyurethane fake leather, ensuring that they select a supplier that meets their specific needs while adhering to quality and sustainability standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for polyurethane fake leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Polyurethane Fake Leather?
When sourcing polyurethane fake leather, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The base materials for PU leather are thermoplastic polymers, typically polyurethane, alongside a fabric backing made from nylon, cotton, or vinyl. The choice of materials can significantly impact pricing, as higher-quality polymers or sustainable options may come at a premium.
-
Labor: Manufacturing PU leather involves skilled labor for the coating, texturing, and finishing processes. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographical location, with labor-intensive regions potentially driving up the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these overheads.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds and tools used in the production of PU leather can be considerable, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider these costs when negotiating contracts for bespoke items.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the PU leather meets specified quality standards incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes are necessary to ensure product durability and compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on distance, method (air, sea, or land), and the complexity of the supply chain. International buyers must factor in tariffs and import duties, which can inflate overall costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing. Understanding the market and the competitive landscape can provide leverage in negotiations.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider When Sourcing PU Leather?
Several factors influence pricing for PU leather that B2B buyers should keep in mind:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often attract discounts, so understanding minimum order quantities (MOQs) can be vital for cost savings. Higher volumes typically lead to better pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized designs, colors, or finishes can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The quality of the polyurethane used and any environmental certifications can impact pricing. Eco-friendly materials, while beneficial for sustainability, may incur additional costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices but offer better assurance of product consistency.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for determining who bears the costs and risks during shipping. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect final pricing and logistics planning.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
To achieve cost-efficiency in sourcing PU leather, B2B buyers should adopt the following negotiation strategies:

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Buyers should consider consolidating orders to meet MOQs for better pricing. This can significantly reduce the cost per unit.
-
Explore Long-Term Contracts: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can secure more favorable pricing structures and reliability in supply.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the durability, maintenance, and potential resale value of PU leather products. A lower initial cost might lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Different regions may have varying standards, certifications, and pricing structures. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should familiarize themselves with local market dynamics to negotiate effectively.
Conclusion
Sourcing polyurethane fake leather involves a complex interplay of costs and price influencers. By understanding the cost components, recognizing the factors that affect pricing, and employing effective negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals. Always remember that prices may vary based on market conditions and supplier capabilities, so it’s essential to approach negotiations with a comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing polyurethane fake leather With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Polyurethane Fake Leather
In the search for sustainable and cost-effective materials, polyurethane fake leather (PU leather) has emerged as a popular choice in the fashion and furniture industries. However, businesses must evaluate other alternatives to ensure they select the most suitable material for their needs. This analysis will compare PU leather against two viable alternatives: natural leather and recycled polyester (rPET) fabric, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Polyurethane Fake Leather | Natural Leather | Recycled Polyester (rPET) Fabric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable, water-resistant | Highly durable, breathable | Good durability, less water-resistant |
| Cost | Lower production costs | Higher costs due to sourcing and tanning | Moderate costs, depending on sourcing |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to manufacture | Complex tanning process | Simple to produce from recycled materials |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, non-porous | Requires conditioning | Easy to clean, less maintenance than leather |
| Best Use Case | Fashion accessories, furniture | Luxury items, high-end furniture | Casual wear, eco-friendly products |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Natural Leather: Is It Worth the Investment?
Natural leather is known for its superior durability and breathability. It is often favored in high-end products and luxury markets due to its aesthetic appeal and ability to develop a unique patina over time. However, sourcing and tanning processes can be resource-intensive and costly, making natural leather a less viable option for budget-conscious businesses. Additionally, maintenance is required to keep it in optimal condition, which can increase long-term costs.
Recycled Polyester (rPET) Fabric: An Eco-Friendly Option?
Recycled polyester fabric, made from post-consumer plastic bottles, offers a sustainable alternative with lower environmental impact compared to traditional materials. It is lightweight, easy to clean, and has decent durability, making it suitable for casual wear and eco-friendly products. However, its performance in terms of water resistance and breathability may not match that of PU leather or natural leather. Cost-wise, rPET can be moderate, depending on sourcing and availability, which may be a concern for buyers looking for the most economical solution.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Material for Your Needs
When selecting the best material for your products, consider your target market, budget, and sustainability goals. Polyurethane fake leather offers an affordable and versatile option, particularly for fashion and furniture that requires easy maintenance. Conversely, natural leather excels in durability and luxury appeal but comes with higher costs and maintenance needs. Recycled polyester presents a promising eco-friendly alternative, though it may lack some of the performance characteristics of leather. By understanding these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and customer expectations.

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for polyurethane fake leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Polyurethane Fake Leather?
When evaluating polyurethane (PU) fake leather for commercial purposes, understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality classification of the PU leather based on its composition and manufacturing process. Higher grades usually indicate better durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is essential to ensure the product meets specific usage requirements, particularly in high-traffic environments like furniture or automotive applications.
2. Thickness
Thickness is a critical specification that affects the durability and feel of PU leather. Common thickness ranges from 0.8 mm to 2.0 mm. Thicker materials tend to be more robust and longer-lasting, making them suitable for upholstery, while thinner variants are often used for fashion items. Buyers should consider the intended application when selecting the appropriate thickness.
3. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the material’s ability to withstand pulling forces without breaking. It is typically expressed in megapascals (MPa). A higher tensile strength indicates a more durable material that can endure stress and wear. For B2B buyers, particularly in industries such as fashion or automotive, understanding tensile strength is vital to ensure longevity and reliability in their products.
4. Water Resistance
Water resistance indicates how well the PU leather can repel moisture. This property is crucial for applications in environments exposed to spills or humidity. Materials with high water resistance are easier to clean and maintain, making them ideal for furniture and automotive interiors. B2B buyers should prioritize this property based on the end-use conditions of the product.
Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
5. Flame Retardance
Flame retardance is a property that indicates how well the PU leather can resist burning when exposed to flames. This is particularly important for applications in public spaces or industries that require compliance with safety regulations. Understanding flame retardance standards can help buyers make choices that align with safety protocols.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the PU Leather Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B sector. Here are some common terms related to polyurethane fake leather:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components or products that are then marketed and sold by another company. In the context of PU leather, OEMs often supply materials to brands that incorporate them into finished goods. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers secure favorable pricing and quality assurance.

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is a critical consideration for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and initial investment. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategies more effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. In the PU leather industry, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from different manufacturers, ensuring they get the best value for their purchase.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international shipping terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions involving PU leather, as they clarify costs, risks, and logistics responsibilities.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. In the context of PU leather, lead times can vary significantly based on production schedules and shipping logistics. B2B buyers need to factor lead times into their planning to ensure timely delivery for their projects.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can make more informed purchasing decisions that align with your business needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the polyurethane fake leather Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in Polyurethane Fake Leather?
The polyurethane fake leather market is witnessing significant growth, driven by a confluence of factors. The increasing demand for cost-effective and cruelty-free alternatives to genuine leather is a primary driver, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These regions are experiencing a rise in consumer awareness regarding sustainability and ethical sourcing, prompting manufacturers to pivot towards synthetic materials like PU leather.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. Innovations in manufacturing processes, such as the use of recycled materials and advancements in polymer technology, are enhancing the quality and appeal of PU leather. Automation and digital sourcing platforms are becoming prevalent, allowing international B2B buyers to streamline procurement processes, compare suppliers, and ensure transparency in the supply chain. The rise of e-commerce is also facilitating access to global markets, enabling buyers from diverse regions to source PU leather products efficiently.
Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
Another noteworthy trend is the shift towards customization. Buyers are increasingly looking for personalized solutions that cater to their specific market needs. Manufacturers that offer a variety of colors, textures, and finishes in PU leather are likely to gain a competitive edge. This trend is particularly relevant for fashion, furniture, and automotive industries, where aesthetic appeal is crucial.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Polyurethane Fake Leather?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the sourcing of polyurethane fake leather. While PU leather is often marketed as a more environmentally friendly alternative to genuine leather, it is essential for B2B buyers to be aware of the environmental impacts associated with its production. The manufacturing process of PU leather can involve harmful chemicals and energy consumption, raising concerns about its overall sustainability.
To address these challenges, many manufacturers are adopting ethical supply chain practices. This includes sourcing materials from suppliers who adhere to environmentally responsible practices and obtaining certifications that validate their sustainability claims. Buyers should look for products labeled with “green” certifications, such as Global Recycled Standard (GRS) or OEKO-TEX, which signify that the material meets stringent environmental and safety criteria.
Moreover, investing in PU leather that incorporates recycled content or is produced using eco-friendly methods can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with sourcing. By prioritizing sustainable and ethical sourcing, international B2B buyers can not only comply with regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation among increasingly eco-conscious consumers.

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
What Is the Historical Context of Polyurethane Fake Leather in the B2B Market?
The evolution of polyurethane fake leather dates back to the mid-20th century when the need for affordable and versatile alternatives to genuine leather became apparent. Initially, synthetic materials were primarily used in industrial applications, but as consumer preferences shifted, manufacturers began exploring the fashion and furniture sectors.
In the 1980s and 1990s, advancements in polymer technology significantly improved the aesthetics and durability of PU leather, leading to its widespread acceptance in the marketplace. As global awareness of animal rights and environmental issues grew in the 21st century, PU leather gained further traction as a vegan-friendly option. Today, it stands as a prominent choice for various applications, from upholstery to fashion, reflecting the changing dynamics of consumer demand and market trends.
Understanding this historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it highlights the ongoing innovation and market responsiveness that characterize the polyurethane fake leather sector. By recognizing the journey of PU leather, buyers can better appreciate its potential and make informed sourcing decisions aligned with contemporary trends.
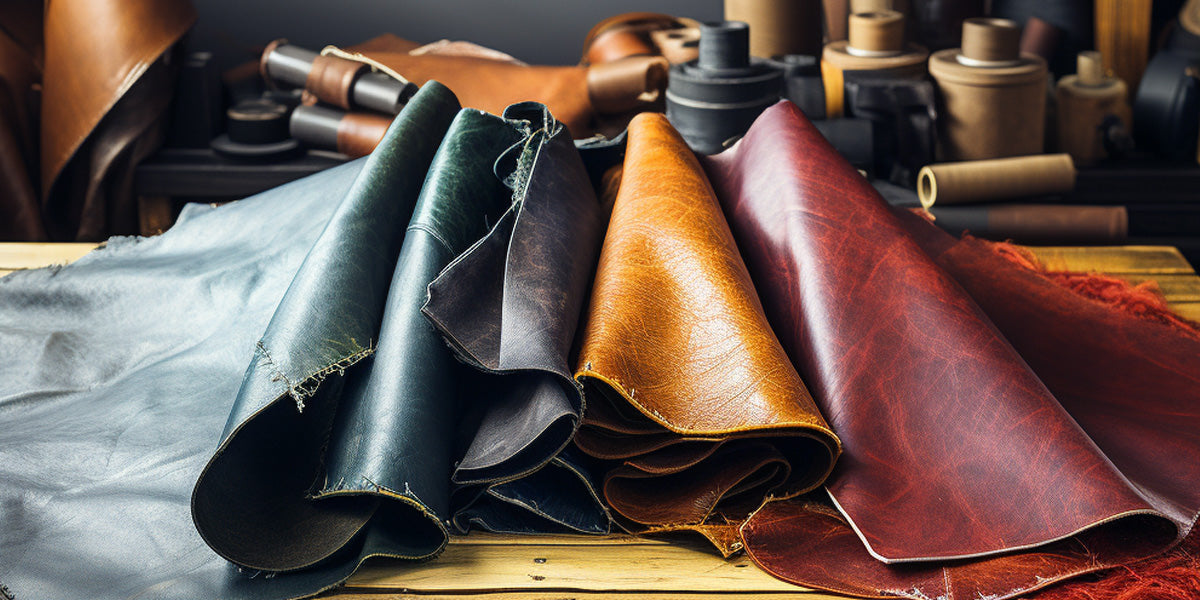

Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of polyurethane fake leather
-
How do I determine the quality of polyurethane fake leather for my products?
To assess the quality of polyurethane fake leather, request samples from potential suppliers and evaluate them based on texture, durability, and appearance. Look for consistent grain patterns and a smooth finish. It’s also essential to inquire about the production methods, as eco-friendly practices often indicate higher quality. Additionally, checking for certifications related to sustainability and safety can further ensure the material meets your standards. -
What is the best type of PU leather for furniture manufacturing?
The best type of PU leather for furniture manufacturing is often a high-grade variant that balances durability and aesthetics. Look for PU leather that is specifically designed for upholstery, as it typically offers enhanced resistance to wear and tear. Consider options like bicast leather, which combines genuine leather with a PU coating for added strength and style. Always assess color options and textures that align with your design needs. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities for polyurethane fake leather can vary significantly by supplier and region. Typically, MOQs range from 500 to 2,000 square meters, depending on the manufacturer’s production capabilities. It’s advisable to communicate your specific requirements and negotiate MOQs that suit your purchasing strategy, especially if you’re a smaller business or just starting. -
How can I vet suppliers of PU leather to ensure reliability?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation through online reviews and industry forums. Request references from previous clients and assess their response times and willingness to communicate. Verify certifications for quality and sustainability standards. Conducting a factory visit, if possible, can also provide insights into their manufacturing processes and working conditions. -
What payment terms are commonly offered in B2B PU leather transactions?
Payment terms in B2B transactions for PU leather often include options like a 30% deposit with the order and the remaining 70% before shipment. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 payment terms, allowing more time to settle the balance after receipt. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, credit terms) and ensure terms are documented in the contract to avoid disputes. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for PU leather products?
Quality assurance can be ensured by establishing a clear set of specifications and standards before production begins. Request detailed product samples and conduct tests for durability, colorfastness, and resistance to wear. Many suppliers will offer inspection services or third-party quality checks, which can be beneficial. Regular communication during the production process is also crucial to address any issues proactively. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing PU leather?
When importing PU leather, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and potential tariffs that may apply based on the origin of the material. Work with a logistics partner experienced in international trade to streamline the process. Ensure all documentation, such as bills of lading and certificates of origin, is in order to facilitate smooth customs clearance. -
Can I customize PU leather products to fit my brand’s needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for PU leather products, including colors, textures, and patterns. When approaching suppliers, clearly communicate your design requirements and any specific branding elements you wish to incorporate. Discuss lead times for custom orders, as these may vary depending on the complexity of the design and the supplier’s production capabilities.
Top 6 Polyurethane Fake Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Manuel Dreesmann – PU Leather Alternatives
Domain: manuel-dreesmann.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: PU leather is a synthetic material made from polyurethane, often used as a cheaper alternative to genuine leather. It is less durable, can wear out more quickly, and may not have the same aesthetic appeal as real leather. The text suggests avoiding PU leather due to these drawbacks.
2. Naugahyde – PU Leather & Faux Leather Upholstery
Domain: decorativefabricsdirect.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: PU Leather & Faux Leather | Vinyl Upholstery Fabric
– Terms: Free Shipping Coupon Code: SHIPFREE for Most $199 Orders
– Fabric Types: Faux Leather, Vinyl (PVC), Urethane, Polycarbonate, Genuine Leather, Bonded Leather
– Uses: Furniture, Automotive, Marine, Commercial Projects
– Brands: Naugahyde, Omnova Boltaflex, Nassimi, Spradling
– Features: Durable, easy to clean, available in rich colors, low…
3. Carl Friedrik – PU Leather Collection
Domain: carlfriedrik.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: PU leather, also known as artificial or imitation leather, is made from polyurethane, a synthetic plastic. It is created by applying a PU resin coating to natural fabrics like nylon, cotton, or vinyl, mimicking the look and feel of animal leather. 100% PU leather is vegan-friendly, while PU applied to split leather is not. Benefits include being softer, lighter, UV resistant, easy to clean, afford…
4. HowStuffWorks – PU Leather Guide
Domain: home.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: PU (Polyurethane) leather is an artificial leather made from polyurethane, a type of plastic. It is 100% vegan and does not contain animal skin. There are two types of PU leather: full-synthetic (totally vegan) and semi-synthetic (which has a natural leather base). PU leather is water-resistant, easy to clean, and available in a wide variety of colors. However, it lacks the authentic appearance an…
5. Rahui – PU Leather Solutions
Domain: rahui.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, Rahui – PU Leather Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Yorkshire Fabric Shop – PU Leather & Faux Leather
Domain: yorkshirefabricshop.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: PU leather and faux leather are both alternatives to genuine leather. PU leather, or synthetic leather, is made from polyurethane, a plastic that mimics the feel and appearance of leather without using animal products. Faux leather, derived from the French term for fake leather, is a man-made material designed to resemble genuine leather, often made with a polyester base and can include finishes l…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for polyurethane fake leather
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of polyurethane fake leather presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the diverse applications and advantages of PU leather—such as cost-effectiveness, ease of maintenance, and versatility—positions businesses to meet consumer demand while optimizing operational costs. The growing preference for sustainable and vegan-friendly materials further enhances the appeal of PU leather, aligning with evolving market trends.
As sourcing strategies continue to evolve, engaging with reputable suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly production methods will be crucial. Buyers should consider not only price but also the quality and environmental impact of PU leather products. By fostering strong relationships with manufacturers and staying informed about market developments, businesses can navigate the complexities of the polyurethane leather supply chain effectively.
Looking ahead, now is the time for international buyers to explore innovative sourcing solutions that leverage the benefits of PU leather. Embrace the potential for growth and differentiation in your product offerings by integrating high-quality polyurethane fake leather into your supply chain. Take action today to secure your competitive advantage in this dynamic market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
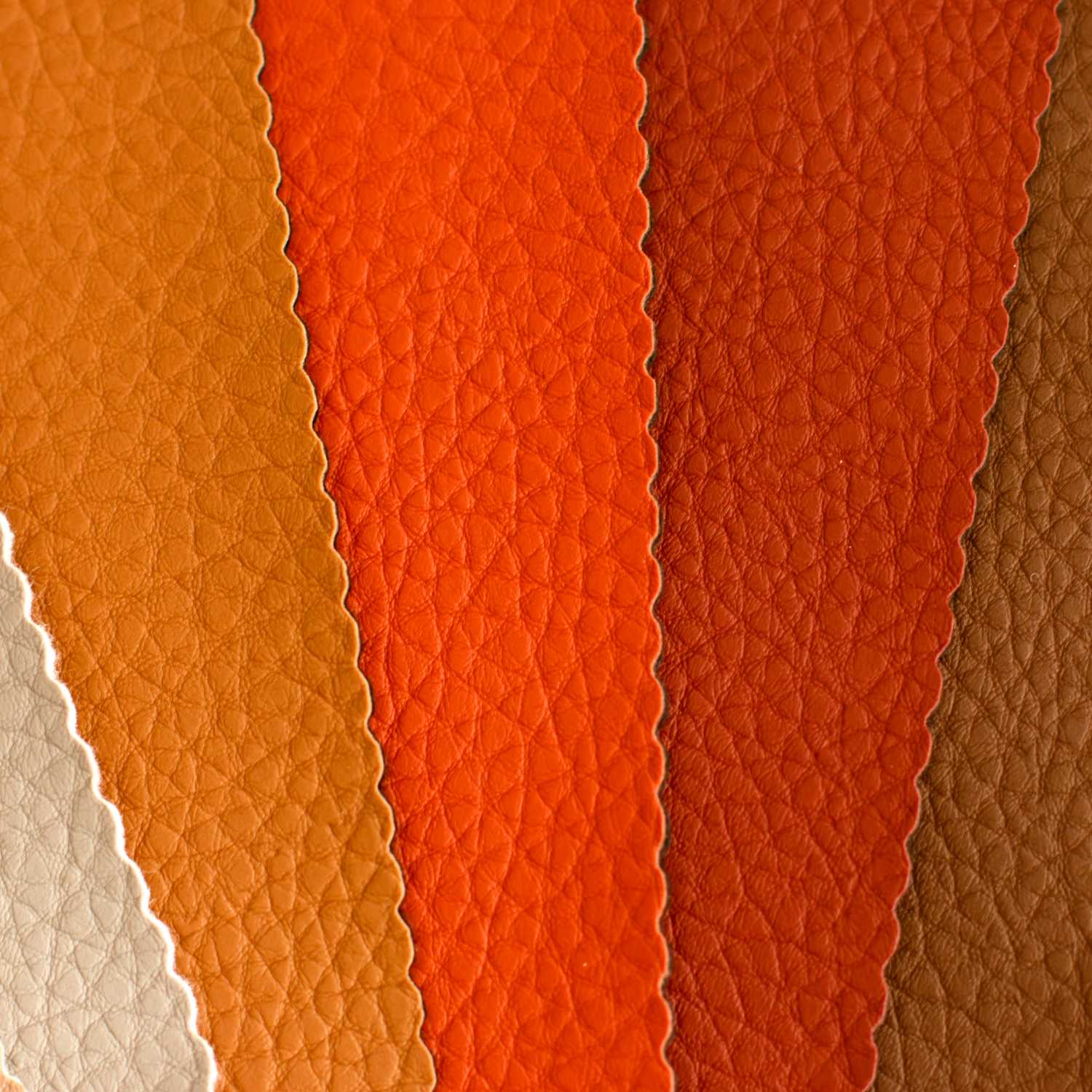
Illustrative image related to polyurethane fake leather
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.