Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather meaning
Navigating the global market for faux leather presents unique challenges for B2B buyers, especially when it comes to sourcing high-quality materials that meet diverse needs and ethical standards. Understanding the meaning of faux leather is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. This guide delves deep into the nuances of faux leather, offering insights into its various types, applications, and production processes. From distinguishing between polyurethane and PVC-based options to exploring innovative vegetable-based alternatives, we equip buyers with essential knowledge to identify the best products for their businesses.
In addition to product types, this comprehensive resource covers supplier vetting strategies, pricing structures, and market trends, empowering international buyers to navigate complexities with confidence. As demand for sustainable and animal-friendly materials grows, understanding the implications of faux leather’s composition and production methods becomes increasingly vital. This guide serves as a valuable tool for businesses aiming to capitalize on the expanding faux leather market, ensuring that buyers are well-prepared to select reliable suppliers and make cost-effective decisions that align with their corporate values. By leveraging the insights provided, B2B buyers can enhance their product offerings and meet the evolving expectations of their customers while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Table Of Contents
- Top 6 Faux Leather Meaning Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for faux leather meaning
- Understanding faux leather meaning Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of faux leather meaning
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather meaning’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather meaning
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather meaning
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather meaning’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather meaning Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather meaning With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather meaning
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather meaning Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather meaning
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather meaning
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding faux leather meaning Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Durable, water-resistant, cost-effective | Upholstery, automotive interiors, fashion accessories | Pros: Affordable, wide color range; Cons: Less breathable, environmental concerns. |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Softer feel, more breathable, eco-friendlier than PVC | High-end fashion, upholstery, bags | Pros: Looks and feels like real leather; Cons: Generally pricier than PVC. |
| Vegan Leather | Made from plant-based materials, biodegradable options | Eco-friendly fashion, upholstery, accessories | Pros: Sustainable, ethical; Cons: Limited durability compared to traditional faux leather. |
| Naugahyde | Historically significant, robust, and versatile | Commercial upholstery, marine applications | Pros: Highly durable, resistant to stains; Cons: Can be heavier and less flexible. |
| Microfiber Leather | Soft texture, high durability, mimics genuine leather | Apparel, upholstery, automotive interiors | Pros: Easy to clean, resistant to wear; Cons: Higher production costs. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Faux Leather?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used types of faux leather due to its cost-effectiveness and durability. It is highly resistant to water and stains, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including upholstery and automotive interiors. However, PVC faux leather is less breathable and raises environmental concerns due to its petroleum-based composition. B2B buyers should consider their target market’s demand for sustainability when choosing PVC as a material.
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Differ from Other Faux Leathers?
Polyurethane (PU) faux leather offers a softer texture and greater breathability compared to PVC. It closely resembles the look and feel of genuine leather, making it a popular choice for high-end fashion products and luxury upholstery. While PU is generally more expensive than PVC, its aesthetic appeal and comfort can justify the investment for businesses targeting premium segments. Buyers should assess the balance between cost and quality when selecting PU for their product lines.
Why Choose Vegan Leather for Sustainable Applications?
Vegan leather, often made from plant-based materials, presents a sustainable alternative to traditional faux leather. Its biodegradable options appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, making it ideal for eco-friendly fashion brands and products. However, vegan leather may have limited durability compared to synthetic options, which could affect its suitability for heavy-use applications. B2B buyers focusing on sustainability should evaluate the performance characteristics of vegan leather in relation to their product requirements.
What are the Benefits of Using Naugahyde in Commercial Applications?
Naugahyde is a historically significant faux leather known for its robustness and versatility. It is particularly favored in commercial upholstery and marine applications due to its resistance to stains and wear. While Naugahyde can be heavier and less flexible than other materials, its durability makes it a practical choice for high-traffic areas. B2B buyers should consider the specific demands of their applications when choosing Naugahyde for their projects.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
How Does Microfiber Leather Compare in Terms of Durability and Cost?
Microfiber leather is recognized for its soft texture and high durability, often mimicking the appearance of genuine leather closely. It is commonly used in apparel and automotive interiors, offering ease of cleaning and resistance to wear. However, the production costs for microfiber leather can be higher than traditional faux leather options. B2B buyers should weigh the long-term benefits of investing in microfiber against initial costs, especially when targeting quality-conscious markets.
Key Industrial Applications of faux leather meaning
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of faux leather meaning | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Upholstery for car seats and interiors | Cost-effective alternative to leather, durable, easy to clean | Ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards |
| Fashion and Apparel | Handbags, jackets, and footwear | Versatile design options, cruelty-free, lightweight | Look for suppliers offering a variety of colors and textures |
| Furniture and Home Decor | Sofas and chairs upholstery | Durable, stain-resistant, and easy maintenance | Consider sourcing from manufacturers with eco-friendly practices |
| Sports Equipment | Gear and accessories (e.g., gloves, bags) | Lightweight, weather-resistant, and customizable | Evaluate the material’s performance under various conditions |
| Electronics Accessories | Cases for smartphones and laptops | Aesthetic appeal, protection, and reduced weight | Focus on suppliers with strong quality assurance processes |
How is Faux Leather Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, faux leather is extensively utilized for upholstery in car seats and interiors. It offers a cost-effective alternative to genuine leather while maintaining a high-end appearance. For international buyers, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Africa, sourcing faux leather that meets local safety and environmental regulations is crucial. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that can provide durable materials resistant to wear and tear, ensuring longevity in high-use environments.
What are the Applications of Faux Leather in Fashion and Apparel?
Faux leather is a popular choice in the fashion industry for products such as handbags, jackets, and footwear. Its versatility allows designers to experiment with colors and textures, appealing to consumers looking for cruelty-free options. Buyers from South America and Europe should seek suppliers that offer a wide range of styles and customization options. Additionally, suppliers should demonstrate compliance with ethical sourcing practices to align with consumer expectations in these markets.
How is Faux Leather Used in Furniture and Home Decor?
In furniture manufacturing, faux leather is commonly used for upholstery on sofas and chairs. Its durability and stain resistance make it a practical choice for homes with children or pets. For B2B buyers in Europe and Africa, it’s essential to consider the environmental impact of sourcing decisions. Opting for suppliers who utilize sustainable production methods can enhance a brand’s reputation while meeting increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
What are the Benefits of Faux Leather in Sports Equipment?
Faux leather is frequently used in sports equipment, including gloves and bags, due to its lightweight and weather-resistant properties. This material provides athletes with the necessary durability without the added weight of traditional leather. Buyers in regions like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia should ensure that their suppliers can meet specific performance standards, particularly for products exposed to varying climates. Customization options can also be a significant advantage in this competitive market.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
How is Faux Leather Applied in Electronics Accessories?
In the electronics sector, faux leather is utilized for protective cases for smartphones and laptops. This application not only offers aesthetic appeal but also ensures that devices are safeguarded against damage. International buyers should focus on suppliers that implement rigorous quality assurance processes to guarantee the durability and functionality of their products. Additionally, sourcing from manufacturers who prioritize sustainable materials can enhance brand value in eco-conscious markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘faux leather meaning’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Faux Leather Composition for Quality Assurance
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with understanding the composition of faux leather products, which can vary widely in quality based on the materials used. For instance, many suppliers may use PVC or PU, but the specific formulations and manufacturing processes can greatly affect durability, feel, and environmental impact. This lack of clarity can lead to purchasing decisions that result in poor product performance, ultimately affecting customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should establish clear criteria for faux leather sourcing by requiring detailed product specifications from suppliers. This includes understanding the type of base fabric (cotton, polyester) and the type of plastic used (PVC or PU). Buyers should also ask for samples to evaluate texture and durability firsthand. Moreover, working with suppliers who adhere to quality certifications or eco-friendly practices can ensure that the faux leather not only meets performance standards but also aligns with sustainable practices, which can be a strong selling point in many markets.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
Scenario 2: Navigating Faux Leather’s Environmental Concerns
The Problem: With increasing awareness around sustainability, many buyers are concerned about the environmental implications of sourcing faux leather, particularly those made from traditional PVC. The production of these materials can release harmful chemicals, and their non-biodegradable nature raises significant ethical questions. This concern can hinder business operations, especially in regions where consumers demand more sustainable options.
The Solution: To address these environmental concerns, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers who offer eco-friendly alternatives, such as vegetable-based faux leather or recycled materials. Engaging in partnerships with suppliers who transparently share their production processes and sustainability efforts can also be beneficial. Additionally, incorporating sustainability into branding and marketing strategies can attract environmentally conscious consumers, thereby enhancing brand loyalty and market reach.
Scenario 3: Misalignment in Product Expectations and Market Needs
The Problem: Buyers may face challenges when the faux leather products they purchase do not align with market needs or customer expectations. For instance, if a retailer stocks faux leather jackets that lack breathability or moisture-wicking properties, they risk disappointing customers and incurring returns. This misalignment can stem from insufficient research or communication with suppliers regarding the intended use of the products.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should conduct thorough market research to understand customer preferences and requirements for faux leather products. Clear communication with suppliers about the intended applications—such as fashion, upholstery, or accessories—is crucial. Buyers can also create detailed product briefs outlining desired features and performance metrics. Regular feedback loops with customers can help refine product offerings, ensuring that the faux leather sourced meets or exceeds market expectations, thereby reducing the risk of returns and enhancing customer satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
Strategic Material Selection Guide for faux leather meaning
What Are the Key Materials Used in Faux Leather Production?
Faux leather, a popular alternative to genuine leather, is primarily made from synthetic materials that offer various properties suitable for different applications. Understanding the key materials used in faux leather production can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions regarding their procurement strategies.
What Are the Key Properties of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) in Faux Leather?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is one of the most commonly used materials in faux leather production. It is known for its durability and resistance to moisture and stains. PVC faux leather can withstand a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for various climates. However, it has low breathability and can feel less comfortable in warmer conditions.
Pros & Cons: PVC is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications, such as upholstery and fashion accessories. However, its environmental impact is significant, as it is not biodegradable and can release harmful chemicals during production.
Impact on Application: PVC faux leather is compatible with a variety of media, including upholstery and fashion items. However, its low breathability may limit its use in applications requiring high comfort levels.
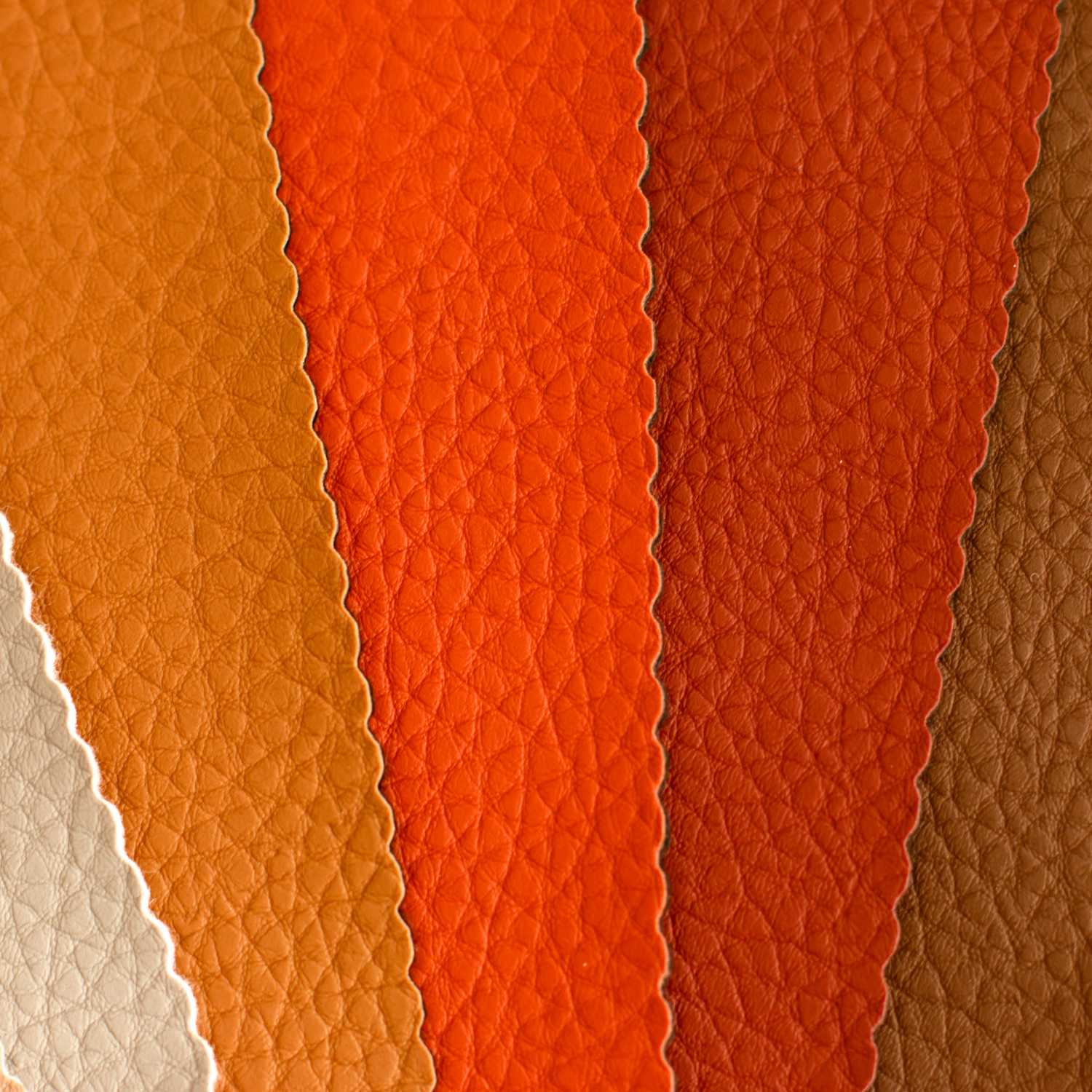
Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with local environmental regulations regarding PVC use. Standards such as ASTM and DIN may apply, and preferences for more sustainable materials are growing.
How Does Polyurethane (PU) Compare as a Faux Leather Material?
Polyurethane (PU) is another popular material used in faux leather, known for its soft texture and flexibility. PU faux leather is more breathable than PVC, making it suitable for apparel and accessories that require comfort.
Pros & Cons: While PU is more expensive than PVC, it offers better durability and a more premium feel, making it ideal for high-end fashion items. However, manufacturing PU can be more complex and energy-intensive, which may affect pricing.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
Impact on Application: PU faux leather is often used in high-fashion garments, bags, and footwear, where aesthetics and comfort are paramount. Its compatibility with various dyeing processes allows for a wide range of colors and designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and South America may find PU more acceptable due to its lower environmental impact compared to PVC. Compliance with EU regulations regarding chemical safety and sustainability should be a priority.
What Role Do Vegetable-Based Alternatives Play in Faux Leather Production?
Vegetable-based faux leather materials are emerging as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional synthetic options. These materials are often derived from plant sources and aim to reduce the environmental footprint associated with conventional faux leather.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of vegetable-based materials is their biodegradability, which addresses significant environmental concerns. However, they may not yet match the durability and versatility of PVC or PU, leading to limited applications.
Impact on Application: Vegetable-based faux leather is suitable for eco-conscious brands looking to appeal to environmentally aware consumers. However, their current performance may restrict their use in high-stress applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as Europe, may prefer vegetable-based options. Understanding local market trends towards sustainability can guide purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Faux Leather Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for faux leather meaning | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Upholstery, fashion accessories | Cost-effective and durable | Low breathability and environmental concerns | Low |
| Polyurethane (PU) | High-end fashion, bags, footwear | Soft texture and breathability | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | Med |
| Vegetable-based | Eco-friendly fashion and accessories | Biodegradable and sustainable | Limited durability and application | High |
This strategic analysis of materials used in faux leather production provides B2B buyers with essential insights for making informed procurement decisions, especially in the context of varying regional preferences and compliance requirements.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for faux leather meaning
What Are the Main Stages of Faux Leather Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of faux leather involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets both aesthetic and functional requirements. Understanding these processes can aid B2B buyers in evaluating the quality and suitability of faux leather products for their specific needs.
How Is Material Prepared in Faux Leather Production?
The first step in the faux leather manufacturing process is material preparation. Typically, manufacturers begin by selecting a base fabric, which is often made of cotton or polyester. These base fabrics are chosen for their porous nature, which allows for effective bonding with synthetic materials.
After selecting the base fabric, it undergoes a treatment process to enhance its durability and texture. This may involve processes such as coating or finishing to ensure the fabric can withstand the binding process with synthetic materials like PVC or PU.
What Techniques Are Used to Form Faux Leather?
Once the base material is prepared, the next stage involves the formulation of synthetic materials. PVC is created from combining salt and petroleum constituents, while PU involves a more complex reaction between isocyanates and polyols. These materials are then processed to create flexible polymers suitable for faux leather.
The binding process is crucial; it typically involves melting the plastic and applying it to the base fabric. Techniques such as calendering or coating are commonly used to ensure a uniform application. The result is a material that mimics the look and feel of genuine leather while being more cost-effective and animal-friendly.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
How Is Faux Leather Assembled and Finished?
After the forming process, the faux leather is cut into desired shapes and sizes for various applications, from upholstery to fashion accessories. The finishing stage may include additional treatments such as embossing to create textures or applying protective coatings to enhance durability and resistance to wear.
Finishing techniques also play a role in the aesthetic appeal of faux leather. Manufacturers can add dyes and finishes that allow for a wide range of colors and designs, giving B2B buyers a variety of options tailored to their market demands.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards for Faux Leather?
Quality assurance (QA) in faux leather production is paramount, especially for international B2B buyers who must ensure that the products meet their specific requirements and regulations.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Most manufacturers adhere to international quality standards, with ISO 9001 being one of the most recognized. This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent product quality.
Additionally, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) may be relevant for products sold within the European Union, ensuring compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. In some industries, especially those involving medical or safety equipment, API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications might also be applicable.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in faux leather manufacturing typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they enter production. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s procedures for evaluating the quality of base fabrics and synthetic materials.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring is conducted to ensure that each stage meets established standards. This can include checks on the thickness of the synthetic layer and the bonding quality between materials.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet quality specifications. This may include assessments of durability, colorfastness, and resistance to abrasion.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers need to implement strategies to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. Here are several actionable steps:
What Are Effective Methods for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a critical method for assessing a manufacturer’s quality assurance processes. Buyers can request audits to review production methods, quality control checkpoints, and compliance with international standards.
Audits can be conducted by the buyers themselves or through third-party organizations specializing in quality assessments. In regions like Africa and South America, where regulatory frameworks may differ, third-party inspections can provide an added layer of assurance.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
How Can Buyers Utilize Quality Reports?
Quality reports, often generated after inspections or audits, are valuable tools for B2B buyers. These documents should detail the results of quality assessments, including any non-conformities or areas for improvement. Buyers should request these reports regularly to stay informed about their supplier’s commitment to quality.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Testing methods for faux leather can vary but often include:
- Tensile Strength Tests: Evaluating the material’s ability to withstand pulling forces.
- Abrasion Resistance Tests: Determining how well the material can resist wear over time.
- Colorfastness Tests: Assessing whether dyes used in the faux leather will bleed or fade when exposed to light or moisture.
These testing methods provide insights into the durability and performance of faux leather products, enabling buyers to make informed decisions.
What Are the Unique Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as the Middle East, Europe, and Africa, understanding local regulations and market expectations is crucial.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have varying standards for material safety and environmental impact. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations regarding synthetic materials, especially in markets like the EU, where regulations can be stringent.
What Are the Challenges of Sourcing Faux Leather Globally?
Sourcing faux leather from different countries may present challenges, such as variations in quality and compliance with international standards. B2B buyers should consider establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers who demonstrate consistent quality and compliance with international standards.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in faux leather production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality products that meet their market needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘faux leather meaning’
When sourcing faux leather, understanding its characteristics, production processes, and market dynamics is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide offers a structured checklist to assist B2B buyers in procuring faux leather effectively.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
Step 1: Understand the Material Composition
Before sourcing faux leather, familiarize yourself with its composition, which typically includes PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or PU (polyurethane). Knowing the differences helps in determining the durability and suitability for your intended applications. For instance, PU is often more breathable and softer, making it ideal for garments, while PVC is more robust and suitable for upholstery.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Identify the specific attributes you need from faux leather, such as thickness, texture, color, and finish. This is crucial for ensuring that the material meets your product requirements. Consider the end-use applications, like upholstery for furniture or fashion accessories, as these will dictate the necessary specifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers to ensure reliability and quality. Request detailed company profiles, production capabilities, and certifications relevant to your industry. Look for suppliers with experience in your target markets, such as Africa, South America, or the Middle East, as they may better understand local preferences and regulations.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Before finalizing a supplier, obtain samples of the faux leather. This will allow you to assess its texture, appearance, and durability firsthand. Pay attention to details such as colorfastness, pilling resistance, and overall finish, as these factors can significantly impact the final product’s quality.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Environmental Standards
Given the environmental concerns surrounding synthetic materials, it’s important to ensure that your suppliers comply with relevant environmental regulations. Inquire about their manufacturing processes and whether they utilize eco-friendly materials or practices, such as vegetable-based alternatives to PVC. This not only enhances your brand’s sustainability image but may also meet the increasing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, minimum order quantities, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Clear communication on these aspects can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process. Additionally, consider discussing return policies and warranty options for defective materials.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Building a lasting relationship with your chosen supplier can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products. Regular communication and feedback can help both parties align on expectations and foster collaboration on future projects. Consider setting up periodic reviews to discuss performance and explore opportunities for innovation.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they make well-informed decisions when sourcing faux leather, ultimately enhancing their product offerings and competitive edge in the market.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for faux leather meaning Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Faux Leather?
When sourcing faux leather, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in faux leather production are PVC and PU, which are derived from petroleum products. The price of these materials can fluctuate based on global oil prices. Additionally, the base fabric, typically polyester or cotton, adds to the material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as certain parts of Asia, manufacturers can offer more competitive pricing. However, labor costs in regions like Europe may be higher, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs, allowing suppliers to pass savings onto buyers.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom designs. This cost is often amortized over large production runs, making it essential for buyers to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) when evaluating tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is vital in maintaining brand reputation. QC processes may add to costs but are necessary for compliance with international standards, particularly for buyers in markets with stringent regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs depend on distance, shipping method, and Incoterms. Buyers should factor in logistics, as these can significantly affect total costs, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Faux Leather Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of faux leather, which B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs. Negotiating favorable MOQs can be beneficial for cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their specifications to ensure accurate pricing and avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certified products (e.g., eco-friendly options) may come at a premium. Buyers should assess the trade-off between price and quality based on their end-use requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly impact the final price. Understanding the implications of these terms on shipping responsibilities and costs is essential for accurate budgeting.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers of Faux Leather?
Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms. Here are some strategies for B2B buyers:

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
-
Leverage Volume: Use your purchasing power to negotiate discounts for larger orders. Presenting forecasts for future orders can also incentivize suppliers to offer better rates.
-
Be Clear About Specifications: Ensure that your requirements are explicit to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to additional costs.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront costs but also the long-term implications of sourcing faux leather, including maintenance, durability, and potential waste disposal costs.
-
Research Market Prices: Stay informed about market trends and pricing benchmarks to strengthen your negotiating position. Knowledge of competitor pricing can provide leverage during discussions.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms. Long-term partnerships often yield better pricing and service over time.
What Pricing Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, pricing nuances are crucial. Currency fluctuations can impact costs, so consider negotiating in a stable currency. Additionally, be aware of import tariffs and taxes that may apply to faux leather products in your country. Understanding local market demand can also help you gauge whether pricing is competitive or inflated.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and other external factors. Always consult multiple suppliers to obtain the best pricing and terms for your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing faux leather meaning With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Faux Leather: What Are Your Options?
When considering the use of faux leather, B2B buyers should evaluate various alternatives that offer similar functionality. This analysis provides a comparison of faux leather against other viable solutions, helping businesses make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and specific use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Faux Leather Meaning | Alternative 1 Name: Genuine Leather | Alternative 2 Name: Textile-Based Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Water-resistant, soft to touch, low breathability | Highly durable, natural breathability | Moderate durability, customizable textures |
| Cost | Generally low-cost compared to genuine leather | Higher initial investment | Mid-range cost, varies by material |
| Ease of Implementation | Widely available, easy to source | Requires specialized manufacturing | Easy to source, but varies by supplier |
| Maintenance | Spot clean or professional cleaning required | Requires regular conditioning and care | Machine washable, but may require special treatment |
| Best Use Case | Fashion items, upholstery, and accessories | Luxury goods, high-end fashion | Casual wear, eco-friendly products |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Genuine Leather: Is It Worth the Investment?
Genuine leather, often considered the gold standard in textiles, offers unparalleled durability and a classic aesthetic. Its natural breathability makes it suitable for high-end fashion items and durable upholstery. However, the cost can be significantly higher than faux leather, which may not be feasible for all businesses. Additionally, genuine leather requires ongoing care to maintain its appearance, which can add to long-term costs.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
Textile-Based Leather: An Eco-Friendly Option?
Textile-based leather, often made from recycled materials or sustainably sourced fibers, presents a compelling alternative for environmentally conscious buyers. This material can be designed to mimic the look and feel of leather while being more affordable and easier to care for. However, its durability can be variable, and while it may not have the same prestige as genuine leather, it appeals to a growing market that prioritizes sustainability.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting between faux leather and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific use cases, target market, and budget constraints. Faux leather is an excellent choice for cost-sensitive applications where aesthetics and ease of care are paramount. In contrast, genuine leather may be preferable for high-end products where durability and brand prestige are critical. Meanwhile, textile-based leather serves as a practical solution for those looking to align with eco-friendly practices. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and disadvantages of each option will empower buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their business goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for faux leather meaning
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Faux Leather for B2B Buyers?
When assessing faux leather for procurement, understanding its technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Composition
Faux leather is primarily made from two types of synthetic materials: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and Polyurethane (PU). PVC is cost-effective but less flexible, while PU offers a softer touch and better breathability. For B2B buyers, knowing the composition helps in determining the product’s suitability for specific applications, such as upholstery or fashion items.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
2. Breathability
Breathability refers to the fabric’s ability to allow air and moisture to pass through. Faux leather typically has low breathability, which can affect comfort in clothing and upholstery. For buyers, selecting a breathable material is crucial in applications like apparel, where moisture management enhances user comfort and product longevity.
3. Durability and Resistance
Faux leather is generally resistant to abrasions and stains, making it suitable for high-traffic areas. However, it is less durable than genuine leather. Understanding durability ratings helps B2B buyers gauge the lifespan of the material in various applications, from automotive interiors to furniture.
4. Heat Retention and Insulation
Faux leather exhibits high heat retention properties, making it ideal for outerwear. This characteristic is important for industries that prioritize thermal insulation in their products, such as fashion and outdoor gear. Buyers should consider this when selecting materials for seasonal collections.
5. Environmental Considerations
With growing environmental concerns, the production of faux leather raises questions about biodegradability and chemical emissions. Recent advancements include vegetable-based faux leathers, which present a more sustainable option. B2B buyers should evaluate environmental impact to align with corporate social responsibility goals and market demands for eco-friendly products.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Faux Leather?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the faux leather market. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of faux leather, an OEM may create custom synthetic leather products for brands. B2B buyers should consider OEM partnerships to enhance product offerings without investing in manufacturing capabilities.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This is a critical factor for buyers, as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Understanding MOQs can help businesses negotiate better terms and ensure they meet production needs without excessive surplus.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by buyers to suppliers requesting pricing and other relevant information for a specific quantity of goods. In the faux leather industry, an RFQ can help buyers compare options and negotiate favorable terms, ensuring cost-effectiveness.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to manage shipping costs, delivery timelines, and risk allocation effectively.
5. Cutting and Preparing
This term refers to the processes involved in shaping faux leather into desired patterns or sizes before it is manufactured into final products. For buyers, understanding this process is crucial for lead time expectations and quality assurance in production.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the faux leather market more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the faux leather meaning Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Faux Leather Market?
The faux leather market is experiencing significant growth driven by a variety of factors, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. A notable driver is the increasing demand for sustainable and cruelty-free products, as consumers become more environmentally conscious and seek alternatives to genuine leather. The rise of veganism and a shift towards ethical consumerism are influencing purchasing decisions, making faux leather an attractive option for businesses looking to cater to these trends.
Technological advancements in manufacturing processes are also reshaping the market. Innovations in polyurethane (PU) and vegetable-based synthetic leathers are enhancing product quality and performance, making faux leather more competitive with traditional leather. Additionally, the proliferation of e-commerce platforms facilitates global trade, allowing international B2B buyers easy access to diverse faux leather suppliers and products. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for companies in regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam, where demand for stylish yet affordable materials is on the rise.
Furthermore, the global faux leather market is projected to grow as developing countries industrialize and urbanize, increasing the demand for cost-effective and durable materials across various sectors, including fashion, automotive, and furniture. As a result, international buyers are encouraged to stay informed about sourcing trends and market dynamics to leverage the best opportunities.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Relationships in Faux Leather?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point in the faux leather industry, significantly impacting B2B relationships and sourcing strategies. The environmental impact of traditional synthetic leather production, particularly those involving polyvinyl chloride (PVC), has prompted a shift towards more sustainable alternatives. These include biodegradable materials and vegetable-based leathers, which are gaining traction among manufacturers and consumers alike.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
B2B buyers are now prioritizing ethical sourcing and supply chain transparency. By selecting suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing consumer demand for responsible products. Certifications such as OEKO-TEX, GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard), and other ‘green’ labels are becoming essential for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, ethical sourcing can lead to long-term partnerships with suppliers who share similar values, fostering trust and collaboration. Companies that actively promote their sustainable practices can differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace, attracting environmentally-conscious clients and ultimately driving sales. As the faux leather market evolves, aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability principles will be crucial for B2B buyers looking to remain competitive.
What Is the Historical Context of Faux Leather Development for Today’s B2B Buyers?
The evolution of faux leather dates back to the early 20th century, with significant milestones that have shaped its current market presence. Initially developed as a wartime substitute for genuine leather, the first synthetic leather, Naugahyde, was introduced in the 1920s. This marked the beginning of a new era where faux leather became a viable alternative to traditional leather, particularly as consumer preferences shifted towards more affordable and accessible materials.
Over the decades, the production processes have evolved, transitioning from basic PVC formulations to more advanced PU and environmentally-friendly alternatives. The 1970s ushered in growing environmental concerns, leading to increased scrutiny of synthetic materials and a demand for better alternatives. In recent years, manufacturers have made strides in creating biodegradable and plant-based synthetic leathers, addressing both ethical concerns and environmental impact.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential for navigating the current landscape of faux leather products. It highlights the industry’s adaptability and responsiveness to consumer needs and environmental challenges, offering valuable insights into potential sourcing strategies and market opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of faux leather meaning
-
How do I ensure the quality of faux leather products when sourcing?
To ensure the quality of faux leather products, start by requesting samples from potential suppliers. Evaluate the texture, durability, and color consistency of the samples. It’s also crucial to inquire about the manufacturing processes and materials used, such as whether the faux leather is made from PVC or PU. Look for suppliers who provide certifications for quality standards, such as ISO, and consider visiting factories if possible to assess their production capabilities firsthand. -
What is the best type of faux leather for upholstery applications?
For upholstery applications, polyurethane (PU) faux leather is often preferred due to its superior durability, aesthetic appeal, and breathability compared to PVC. PU faux leather is more flexible and can withstand wear and tear better, making it suitable for items like sofas and chairs. When sourcing, ensure that the supplier can provide samples to assess the texture and resilience, especially if the upholstery will be subjected to heavy use. -
How can I customize faux leather products for my brand?
Customization options for faux leather products typically include color, texture, and branding elements such as embossed logos or unique patterns. When engaging with suppliers, clearly communicate your design requirements and inquire about their capabilities for custom orders. Many manufacturers offer minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized products, so ensure that your order aligns with their requirements to avoid delays. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for faux leather?
Minimum order quantities for faux leather can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific product. Generally, MOQs range from 500 to 1,000 yards for fabrics and may be lower for finished goods. It’s essential to clarify these details upfront during your negotiations to ensure that the supplier can meet your needs without incurring excessive costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing faux leather internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining 70% before shipment. Some suppliers may offer more flexible terms, such as letters of credit or payment upon delivery. Always negotiate payment terms that are favorable to your cash flow and ensure that the supplier is reputable to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How do I vet potential suppliers for faux leather products?
Vetting suppliers involves researching their reputation, production capabilities, and compliance with international quality standards. Request references from other buyers and check for certifications that validate their manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider using third-party inspection services to verify the quality of products before shipment. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers can also provide insights into their reliability and customer service. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing faux leather?
When importing faux leather, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply in your country. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in handling textile imports to ensure smooth transit and delivery. Additionally, factor in lead times for production and shipping when planning your inventory to avoid stock shortages. -
How can I stay updated on trends in faux leather and its market?
To stay informed about trends in faux leather, subscribe to industry publications, attend trade shows, and join relevant online forums or associations. Networking with other professionals in the textile and fashion industries can provide valuable insights into emerging trends and innovations. Additionally, following key manufacturers and brands on social media can offer a glimpse into the latest designs and consumer preferences.
Top 6 Faux Leather Meaning Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sewport – Faux Leather Solutions
Domain: sewport.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is a petroleum-based alternative to genuine leather. It is soft to the touch, water-resistant, and highly resistant to stains, making it easy to clean. While less durable than real leather, it resists abrasions and cuts, making it suitable for upholstery in homes with children or pets. Faux leather can be produced in various colors and is popular for …
2. Eco-Leather – Sustainable Tanning Solutions
Domain: blog.leatheredgepaint.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Eco-leather is real leather tanned with low environmental impact processes, meeting the UNI 11427:2011 standard. It retains characteristics of traditional Chrome Tanned or Vegetable Tanned leathers. Faux leather, also known as synthetic or vegan leather, is made from synthetic materials without animal origin and lacks specific environmental regulations. Faux leather can be coated fabric or fully s…
3. Reddit – Pure Leather vs. Vegan Leather
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Pure leather is real leather, known for its durability and longevity, often lasting many years with proper care. It is considered more environmentally friendly in the long run compared to vegan leather, which is typically made from plastic. Vegan leather may be easier to care for as it can be wiped clean, but it generally breaks down faster than real leather. Some users have reported that vegan le…
4. Leather Honey – Leather Care Essentials
Domain: leatherhoney.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Sale Leather Conditioner . from $27.99 $68.95
Sale Leather Cleaner from $18.99 $33.99
Sale Leather Care Kit . $43.99 $70.99
Sale Leather Care Wipes (10 Pack) . $13.99 $17.99
5. Sailrite – Real Leather vs. Faux Leather
Domain: sailrite.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Real Leather vs. Faux Leather: Key Factors to Consider\n1. Look & Feel: Real leather offers a unique, natural texture with imperfections; faux leather has a uniform appearance.\n2. Durability & Longevity: Real leather is extremely durable; faux leather is generally less durable but can be waterproof.\n3. Cost: Real leather is more expensive; faux leather is more affordable and sold by the yard.\n4…
6. Buffalo Jackson – Faux Leather Essentials
Domain: buffalojackson.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is made from a fabric base such as polyester, which is then treated with wax, dye, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or polyurethane to create an imitation leather finish and texture. It is designed to look like real leather but has a uniform surface and feels cold and unnaturally even. Faux leather does not last as long as real leather and does not wear out …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for faux leather meaning
Faux leather offers a compelling alternative to genuine leather, providing versatility and a range of applications across various industries, from fashion to upholstery. For international B2B buyers, understanding the properties and production methods of faux leather is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Key takeaways include the importance of assessing quality, sustainability, and the ethical implications of sourcing materials, especially as consumer preferences shift toward environmentally friendly options.
Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in securing reliable suppliers and ensuring product consistency. By leveraging the growing global demand for faux leather—particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East—businesses can tap into lucrative opportunities while aligning with modern ethical standards.
As you consider your sourcing strategy, explore partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize innovation and sustainability in faux leather production. The future of faux leather is bright, with advancements in biodegradable materials and plant-based alternatives on the horizon. Seize this opportunity to enhance your product offerings and meet the evolving expectations of your customers. Embrace the change, and position your business at the forefront of the faux leather market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to faux leather meaning
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.