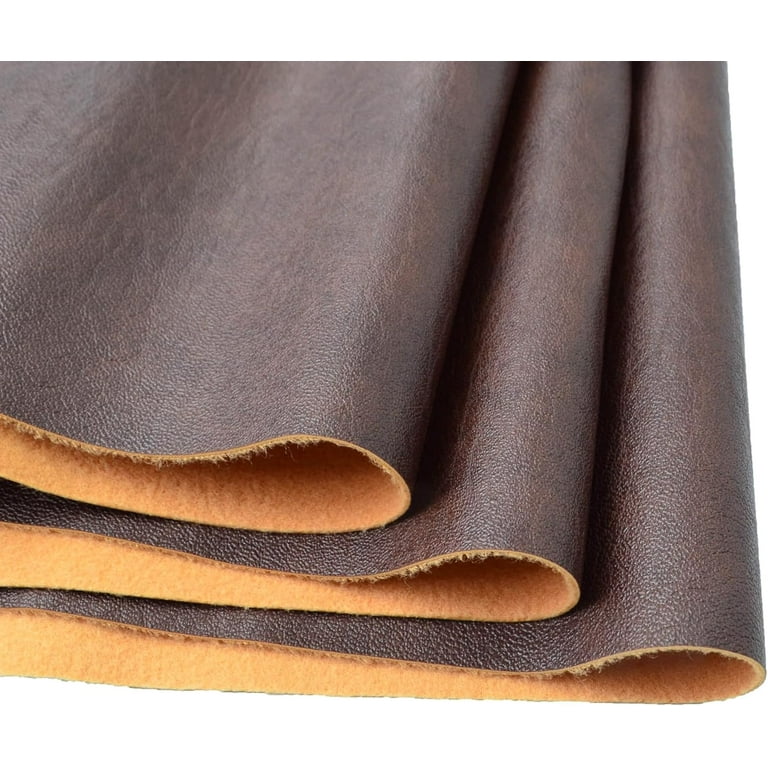
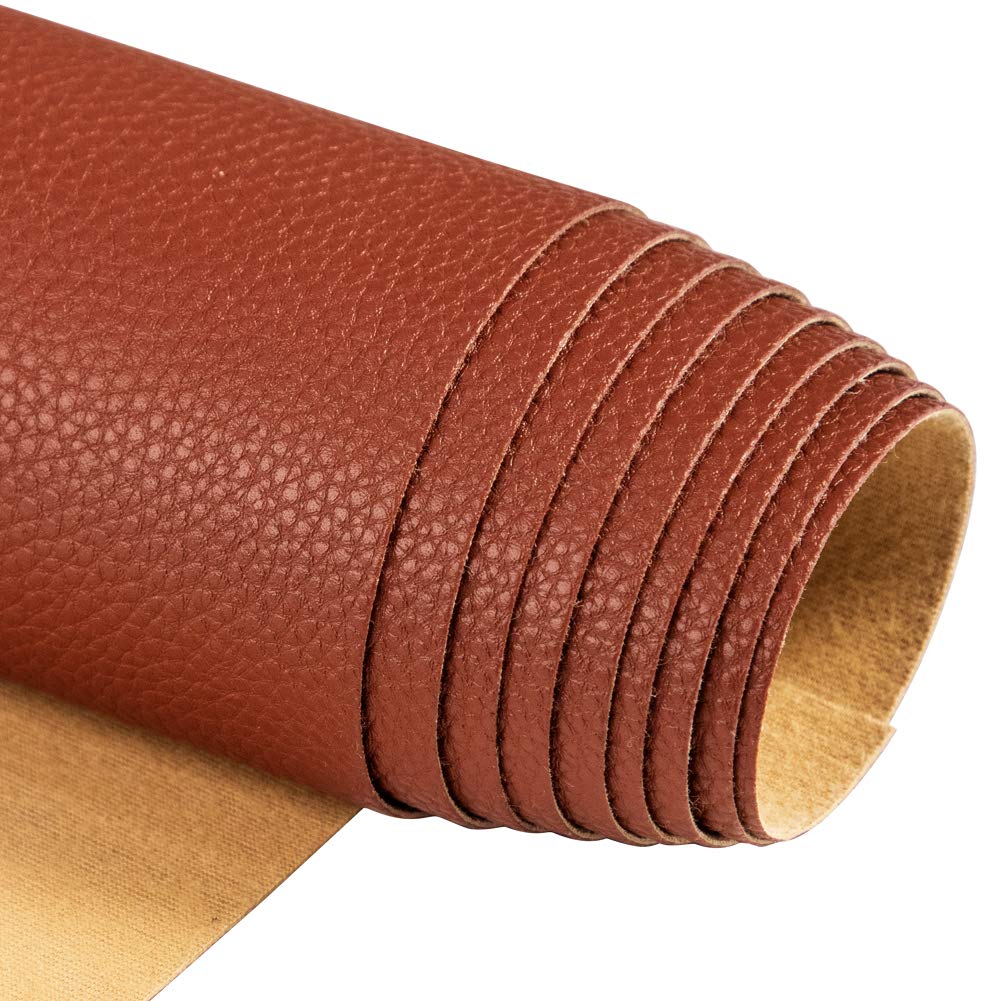
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is microfiber fabric made of
Microfiber fabric has become a pivotal material in various industries, but understanding what it is made of and its applications can pose a challenge for international B2B buyers. As sourcing high-quality microfiber materials becomes increasingly essential—whether for cleaning products, apparel, or upholstery—it’s crucial to grasp the nuances of this versatile fabric. This guide delves into the composition of microfiber, which typically consists of ultra-fine synthetic fibers like polyester and polyamide, and explores its myriad applications across sectors, including home goods, industrial uses, and fashion.
In addition to detailing the types of microfiber available, this comprehensive resource offers insights into supplier vetting processes, pricing structures, and the environmental considerations associated with microfiber production. By equipping B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Nigeria and Vietnam—with actionable knowledge, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the properties, benefits, and potential pitfalls of microfiber will enable businesses to select the right suppliers and products that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals. As the global market for microfiber continues to evolve, staying informed is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
Table Of Contents
- Top 2 What Is Microfiber Fabric Made Of Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is microfiber fabric made of
- Understanding what is microfiber fabric made of Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of what is microfiber fabric made of
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is microfiber fabric made of’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is microfiber fabric made of
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is microfiber fabric made of
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is microfiber fabric made of’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is microfiber fabric made of Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is microfiber fabric made of With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is microfiber fabric made of
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is microfiber fabric made of Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is microfiber fabric made of
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is microfiber fabric made of
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding what is microfiber fabric made of Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat-Weave Microfibre | High durability, less absorbent | Upholstery, bags, and clothing | Pros: Durable, easy to clean. Cons: Lower absorbency compared to other types. |
| Split-Weave Microfibre | Excellent absorbency, softer feel | Cleaning cloths, towels | Pros: Highly absorbent, soft texture. Cons: May wear out faster under heavy use. |
| Brushed Microfibre | Soft, fuzzy texture, good insulation properties | Blankets, bedding, apparel | Pros: Soft, warm, aesthetically pleasing. Cons: Can pill over time. |
| Suede Microfibre | Imitates genuine suede, luxurious appearance | Fashion items, upholstery | Pros: Attractive, versatile. Cons: Requires careful maintenance to avoid stains. |
| Microfibre Blend | Combination of microfibre with other materials | Diverse applications in textiles | Pros: Tailored properties for specific uses. Cons: Quality varies based on blend ratio. |
What Are the Characteristics of Flat-Weave Microfibre and Its B2B Suitability?
Flat-weave microfibre is characterized by its durability, making it a favored choice for applications requiring strength, such as upholstery and bags. It is less absorbent than other types, which may limit its use in cleaning applications. B2B buyers should consider its longevity and ease of maintenance, particularly in environments where wear and tear are common.
How Does Split-Weave Microfibre Excel in Absorbency for Cleaning Applications?
Split-weave microfibre is renowned for its exceptional absorbency and soft texture, making it ideal for cleaning cloths and towels. Its ability to trap dirt and moisture effectively makes it a staple in both commercial and residential cleaning supplies. Buyers should evaluate the balance between absorbency and durability based on their specific cleaning needs, as this type may experience wear with heavy usage.
Why Choose Brushed Microfibre for Bedding and Apparel?
Brushed microfibre offers a soft, fuzzy texture and good insulation properties, making it popular for blankets, bedding, and apparel. Its aesthetic appeal and comfort can enhance product offerings in the textile market. However, buyers should be mindful of its tendency to pill, which may affect the longevity of products in high-traffic environments.
What Makes Suede Microfibre a Luxurious Option for Fashion and Upholstery?
Suede microfibre mimics the appearance of genuine suede while providing a versatile and luxurious option for fashion items and upholstery. Its visual appeal can attract customers looking for high-end products. However, it requires careful maintenance to avoid staining, which buyers should consider when selecting materials for their collections.
How Do Microfibre Blends Offer Tailored Solutions for Various Textile Applications?
Microfibre blends combine microfibre with other materials to create fabrics tailored for specific applications. This versatility allows manufacturers to achieve desired properties, such as improved durability or enhanced softness. Buyers should assess the blend ratios to ensure they meet performance expectations for their intended use, as the quality can vary significantly depending on the composition.
Key Industrial Applications of what is microfiber fabric made of
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is microfiber fabric made of | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cleaning & Janitorial | Microfiber cleaning cloths and mops | Enhanced cleaning efficiency and reduced chemical use | Evaluate durability, absorbency, and cost-effectiveness of fabric |
| Apparel & Fashion | Microfiber jackets and activewear | Lightweight, moisture-wicking, and stain-resistant garments | Ensure compliance with international textile standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Upholstery and interior linings | Durable, easy-to-clean materials that enhance aesthetics | Assess fire resistance and colorfastness for long-term performance |
| Industrial Filtration | Filtration fabrics for air and liquid filtration systems | High filtration efficiency and durability | Verify compatibility with specific filtration needs and regulations |
| Home Textiles | Microfiber bed linens and towels | Softness and high absorbency, improving customer satisfaction | Consider hypoallergenic properties and ease of maintenance |
How is Microfiber Fabric Used in Cleaning & Janitorial Applications?
In the cleaning and janitorial sector, microfiber fabric is extensively utilized for its superior cleaning capabilities. Microfiber cleaning cloths and mops can capture more dirt and bacteria than traditional materials, making them ideal for maintaining hygiene standards in commercial spaces. International buyers should focus on sourcing durable microfiber that withstands frequent washing while retaining its effectiveness. Additionally, evaluating the environmental impact of the cleaning products used alongside microfiber is crucial for sustainability.
What Role Does Microfiber Fabric Play in Apparel & Fashion?
Microfiber fabric has carved a niche in the apparel and fashion industry, particularly in the production of jackets and activewear. Its lightweight and moisture-wicking properties make it suitable for sports and outdoor activities, while its stain resistance appeals to fashion-conscious consumers. Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should ensure that the sourced microfiber meets international textile standards, including breathability and durability, to cater to diverse climates and consumer preferences.
Why is Microfiber Important in Automotive Upholstery?
In the automotive industry, microfiber is favored for upholstery and interior linings due to its durability and ease of cleaning. It provides a luxurious feel while being resistant to stains and wear, enhancing the overall aesthetics of vehicles. B2B buyers should consider sourcing microfiber with fire-resistant properties to comply with safety regulations. Additionally, colorfastness is vital to ensure that the upholstery maintains its appearance over time, especially in regions with high sun exposure.
How is Microfiber Fabric Utilized in Industrial Filtration?
Microfiber fabric serves a critical role in industrial filtration applications, where it is employed in air and liquid filtration systems. Its fine fibers allow for high filtration efficiency, capturing contaminants while maintaining airflow. Buyers in this sector should verify that the sourced microfiber meets specific filtration requirements and regulatory standards, particularly in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals where hygiene is paramount.
What are the Benefits of Microfiber in Home Textiles?
In the home textiles sector, microfiber is commonly used for bed linens and towels due to its unmatched softness and absorbency. These qualities not only enhance customer satisfaction but also contribute to a luxurious feel. Buyers should prioritize sourcing hypoallergenic microfiber to cater to health-conscious consumers. Additionally, ease of maintenance is a key consideration, as products that are machine washable and quick-drying are highly desirable in today’s market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is microfiber fabric made of’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Composition of Microfiber Fabric
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion regarding the composition of microfiber fabric, which can lead to misinformed purchasing decisions. Many suppliers may not provide clear information about the ratios of polyester, polyamide, or other synthetic fibers used in their products. This lack of clarity can result in difficulties in selecting materials that meet specific performance requirements, such as durability, absorbency, and cost-effectiveness. For instance, a company in the cleaning industry may need a microfiber that is highly absorbent for effective cleaning but might end up purchasing a product with insufficient polyamide content, leading to poor performance.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should request detailed material specifications from suppliers that include the exact composition of the microfiber. Establishing a standardized form for suppliers to fill out can facilitate this process. Additionally, conducting material testing for performance characteristics such as absorbency, tensile strength, and durability can help ensure that the microfiber meets the intended application requirements. Collaborating with textile experts or consultants can provide further insights into the optimal ratios of polyester to polyamide for various applications, enabling informed sourcing decisions.
Scenario 2: The Environmental Impact of Microfiber Fabric
The Problem: As sustainability becomes a priority for businesses, B2B buyers are increasingly concerned about the environmental implications of their material choices. Microfiber fabric, while versatile and durable, has been associated with microplastic pollution. Buyers may feel pressured to avoid microfiber due to negative perceptions about its environmental impact, yet they also recognize the fabric’s performance benefits in various applications, from cleaning to apparel. This creates a dilemma where businesses must balance performance needs with environmental responsibility.
The Solution: To address this concern, B2B buyers should seek out suppliers that prioritize sustainable manufacturing practices, such as using recycled materials or implementing processes to minimize microplastic shedding. Conducting a lifecycle analysis of the microfiber fabric can provide a clearer picture of its environmental impact compared to other materials. Additionally, engaging in partnerships with suppliers that have certifications for environmental responsibility can enhance credibility and align with corporate sustainability goals. By promoting and using responsibly sourced microfiber, businesses can leverage its benefits while mitigating negative perceptions related to environmental impact.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
Scenario 3: Quality Control Issues in Microfiber Fabric Sourcing
The Problem: Quality control can be a significant challenge when sourcing microfiber fabric, particularly for companies that require consistency across large orders. Variability in production batches can lead to discrepancies in fabric performance, color, and texture, which can ultimately affect the end product’s quality. For instance, a manufacturer of microfiber cleaning cloths may receive a shipment where the fabric’s absorbency is inconsistent, resulting in customer dissatisfaction and returns.
The Solution: To ensure quality consistency, B2B buyers should establish clear quality control protocols with their suppliers. This includes setting specific performance benchmarks for absorbency, durability, and thread count, along with regular sampling and testing of incoming shipments. Implementing a robust supplier audit process can help identify and address potential quality issues before they impact production. Additionally, developing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can facilitate better communication and adherence to quality standards, ultimately leading to more reliable sourcing of microfiber fabric that meets the required specifications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is microfiber fabric made of
What Materials Comprise Microfiber Fabric and Their Strategic Implications for B2B Buyers?
Microfiber fabric is predominantly composed of ultra-fine synthetic fibers, primarily polyester and polyamide (nylon). Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Key Properties of Polyester in Microfiber Fabric?
Polyester is the core component of most microfiber fabrics. It possesses high tensile strength, making it durable and resistant to wear and tear. Polyester can withstand a broad range of temperatures, typically rated for use between -40°C to 150°C, which is beneficial for various applications. Its inherent moisture-wicking properties enhance comfort in apparel and improve performance in cleaning applications.
Pros: Polyester is cost-effective and widely available, making it an ideal choice for mass production. Its durability ensures that products made from polyester microfiber can withstand repeated use without significant degradation.
Cons: While polyester is resistant to many chemicals, it can be susceptible to degradation from prolonged exposure to UV light. Additionally, its production process can be complex, requiring careful control to maintain fiber quality.
Impact on Application: Polyester’s moisture-wicking ability makes it suitable for athletic wear and cleaning products. Its compatibility with dyes allows for vibrant colors, enhancing marketability.
How Does Polyamide Enhance Microfiber Fabric Performance?
Polyamide, often blended with polyester, provides additional properties such as improved absorbency and flexibility. It has a lower density than polyester, which enhances the overall softness of the fabric. Polyamide fibers can also withstand higher temperatures, making them suitable for applications requiring heat resistance.
Pros: The combination of polyester and polyamide results in a fabric that is both durable and soft, making it comfortable for clothing and effective for cleaning applications.
Cons: Polyamide can be more expensive than polyester, which may affect overall production costs. Additionally, it is less resistant to abrasion than polyester, which could limit its use in high-friction applications.
Impact on Application: Polyamide’s absorbent nature is particularly beneficial in cleaning cloths and towels, where moisture retention is critical. This makes it a preferred choice for products requiring high absorbency.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
What are the Environmental Considerations for B2B Buyers?
The production of microfiber, particularly polyester and polyamide, raises environmental concerns. Microfiber pollution has become a significant issue, as these synthetic fibers can shed during washing, contributing to ocean pollution. B2B buyers must consider the sustainability practices of suppliers, including compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN.
Pros: Suppliers that adopt sustainable practices may improve their market appeal, especially in regions where eco-consciousness is rising.
Cons: Compliance with environmental regulations can increase production costs and complexity, which may be passed on to buyers.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
Impact on Application: Buyers should seek suppliers that provide transparency regarding their environmental impact and compliance with standards, particularly in markets sensitive to sustainability, such as Europe.
Summary Table of Microfiber Fabric Materials
| المواد | Typical Use Case for what is microfiber fabric made of | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester | Cleaning cloths, athletic wear, upholstery | High durability and moisture-wicking | Susceptible to UV degradation | منخفضة |
| Polyamide | Towels, apparel, cleaning products | Softness and high absorbency | Higher cost and lower abrasion resistance | Medium |
| Bicomponent | Specialty applications requiring strength and flexibility | Enhanced structural integrity | Complex manufacturing process | عالية |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the composition of microfiber fabric, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and environmental considerations. Understanding these materials can enhance product offerings and align with market demands across various regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is microfiber fabric made of
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Microfiber Fabric?
The manufacturing of microfiber fabric involves a series of precise stages that ensure the quality and characteristics of the final product. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
What Are the Main Stages in Microfiber Fabric Manufacturing?
-
Material Preparation
The primary materials used in microfiber production are polyester and polyamide. These polymers are sourced based on their specific properties. The first step involves the preparation of these materials, which includes selecting high-quality polymers and ensuring they meet the necessary specifications for denier and tensile strength. -
Forming
The forming stage is critical as it involves the extrusion of the fibers. Unlike traditional textiles, microfiber fibers are extruded through specialized spinnerets or long metallic tubes to achieve the desired diameter, often less than 10 micrometers. This is followed by cooling and then blending the polyester and polyamide fibers using heat, which allows them to meld together effectively. -
Assembly
After forming, the microfiber strands are woven or knitted into fabric. This process can vary depending on the intended application. For instance, cleaning cloths may require a different weave compared to apparel. The assembly process also includes cutting the fabric into specified dimensions for various products. -
Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the fabric’s properties and may include dyeing, chemical treatments for water resistance, and softening processes. These treatments ensure that the microfiber fabric meets the aesthetic and functional requirements of end-users.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Commonly Used in Microfiber Fabric Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be familiar with these QA measures.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Microfiber Fabric?
For microfiber fabric production, several international quality standards are applicable:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Relevant for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for industrial applications, API standards ensure the quality and safety of materials used in oil and gas industries.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Microfiber Fabric Production?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers must provide certificates of conformity to ensure that the materials meet specified quality standards. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring is essential. This includes checking for uniformity in fiber diameter, tensile strength, and ensuring that the extrusion process adheres to the required specifications. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
Once the fabric is produced, it undergoes final inspections. This step includes checking for defects in the fabric, color consistency, and ensuring it meets the specified requirements for application.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Microfiber Fabric Quality?
B2B buyers should be aware of the testing methods that validate the quality of microfiber fabric. Common tests include:

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
- Tensile Strength Testing: Measures the fabric’s resistance to breaking under tension.
- Abrasion Resistance Testing: Evaluates how well the fabric can withstand wear and tear.
- Water Absorption Testing: Assesses the fabric’s moisture-wicking properties.
- Colorfastness Testing: Determines how well the fabric retains its color when exposed to washing and light.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following verification methods:
-
Supplier Audits
Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards firsthand. -
Requesting Quality Reports
Suppliers should provide regular quality control reports that detail testing outcomes and compliance with relevant standards. This transparency can help build trust. -
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and the products produced.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Understanding regional nuances in quality control and certification can be crucial for international buyers:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific quality standards. For example, while ISO 9001 is recognized globally, certain local certifications may also be necessary for market entry in regions like Africa and South America.
-
Cultural Expectations: Buyers from diverse regions may have varying expectations regarding product quality, packaging, and delivery timelines. It is essential to communicate these expectations clearly with suppliers.
-
Logistics and Compliance: International logistics can complicate quality assurance. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust logistics systems in place to maintain product integrity during transport.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for microfiber fabric is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on supplier verification, compliance with international standards, and quality control checkpoints, businesses can ensure they source high-quality microfiber products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is microfiber fabric made of’
To aid B2B buyers in sourcing microfiber fabric effectively, this guide outlines essential steps to ensure you procure high-quality materials that meet your specific needs. Microfiber fabric, known for its versatility and unique properties, requires careful consideration during the sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical requirements for microfiber fabric is crucial. Specify the desired composition, typically a blend of polyester and polyamide, and consider factors such as thread count, moisture-wicking capabilities, and breathability. These specifications will guide you in selecting suppliers that can meet your unique product needs.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct comprehensive research to identify potential suppliers of microfiber fabric. Utilize trade directories, industry-specific websites, and trade shows to find manufacturers. Focus on suppliers with a strong reputation in the market, particularly those who specialize in synthetic textiles, as they are likely to have the expertise necessary for high-quality production.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing a supplier, it’s essential to verify their certifications. Look for compliance with international standards such as ISO or OEKO-TEX, which indicate the safety and quality of the fabric. Certifications ensure that the supplier adheres to environmental regulations and ethical manufacturing practices, which is particularly important for buyers concerned about sustainability.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples of microfiber fabric before making bulk purchases. Testing samples will allow you to assess the fabric’s softness, durability, and performance characteristics such as absorbency and stain resistance. This hands-on evaluation will help you determine if the fabric meets your quality standards and product specifications.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in negotiations to establish favorable pricing and payment terms. Understand the market rates for microfiber fabric to ensure you are receiving a competitive offer. Discuss lead times, minimum order quantities, and shipping costs to avoid unexpected expenses later in the process.
Step 6: Assess Production Capabilities
Evaluate the production capabilities of your potential suppliers. Inquire about their manufacturing processes, capacity, and technology used in producing microfiber fabric. A supplier with advanced technology and sufficient capacity can better meet your demands, especially during peak order times.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
Implement a quality assurance process to monitor the fabric’s quality throughout production. Work with your supplier to define quality control measures, including inspection standards and testing methods. This ensures that the microfiber fabric delivered meets your specifications and reduces the risk of defects.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for microfiber fabric, ensuring they select high-quality materials that align with their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is microfiber fabric made of Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Microfiber Fabric?
When sourcing microfiber fabric, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary raw materials for microfiber are polyester and polyamide. The price of these synthetic fibers fluctuates based on global oil prices, as they are petroleum derivatives. Buyers should monitor these trends to anticipate cost changes.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the manufacturing location. For instance, labor is generally less expensive in countries like Vietnam and China compared to Europe or North America. This can impact the overall pricing of microfiber fabric.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with machinery, utilities, and facility maintenance. Manufacturers with advanced technology may have higher initial costs but can achieve economies of scale, leading to lower prices in the long run.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific fabric designs or patterns can add to the upfront costs. However, this investment can yield unique products that may command higher prices in the market.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the microfiber meets industry standards. This is particularly important for buyers looking for certifications that guarantee the fabric’s quality and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the Incoterms agreed upon. For international shipments, factors like distance, customs duties, and insurance can significantly influence the total landed cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the margin structure can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
What Influences the Pricing of Microfiber Fabric?
Several factors can influence the pricing of microfiber fabric:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volume orders often lead to lower per-unit prices. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers optimize their costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized microfiber fabrics, such as those with specific colors or patterns, may incur additional costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Fabrics with higher quality standards or eco-certifications may be priced higher. Buyers should assess whether the added cost aligns with their product needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to their track record.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and logistics. Different terms can lead to variations in pricing based on who bears the shipping costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers?
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial price, consider the TCO, which includes shipping, duties, and potential returns. This holistic view can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Market Research: Familiarize yourself with market rates for microfiber fabric. Having this data can strengthen your position during negotiations.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate with long-term partners.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Don’t hesitate to seek quotes from multiple suppliers. This can provide leverage during negotiations and help identify the best pricing.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should be mindful of exchange rates and local economic conditions that might affect pricing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for microfiber fabric can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. The information provided here serves as a guideline and should be verified through direct communication with suppliers for accurate pricing.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is microfiber fabric made of With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Microfiber Fabric: A Comparative Analysis
In the textile industry, microfiber fabric, composed mainly of ultra-fine synthetic fibers such as polyester and polyamide, has carved a niche due to its unique properties and applications. However, several alternative materials also offer viable solutions for various uses, particularly in cleaning, apparel, and home textiles. This section provides a detailed comparison of microfiber fabric against two alternatives: cotton and bamboo fabric.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | What Is Microfiber Fabric Made Of | Cotton Fabric | Bamboo Fabric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High absorbency, soft, durable | Good absorbency, soft, breathable | Excellent moisture-wicking, antimicrobial properties |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high | Moderate to high |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to manufacture and process | Established production processes | Requires specific processing techniques |
| Maintenance | Machine washable, quick-drying | Machine washable, prone to wrinkling | Machine washable, requires care to maintain softness |
| Best Use Case | Cleaning, apparel, upholstery | Apparel, home textiles, sheets | Eco-friendly apparel, home textiles |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Cotton Fabric
Cotton is one of the most widely used natural fibers, known for its softness and breathability. It offers good absorbency, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including clothing and home textiles. However, cotton can be more expensive than microfiber, especially when sourced organically. Additionally, it tends to wrinkle and may require ironing to maintain a polished appearance. For B2B buyers focused on sustainability, organic cotton options are available, though they come at a premium.
Bamboo Fabric
Bamboo fabric is gaining traction due to its eco-friendly properties and natural antimicrobial benefits. It excels in moisture-wicking and is softer than cotton, making it comfortable against the skin. However, the manufacturing process can be more complex and may require specific techniques to transform bamboo into a usable textile. While the cost is comparable to cotton, its environmental benefits may appeal to businesses looking to enhance their sustainability profile. However, the market for bamboo fabric is still developing, which could affect availability and consistency in supply.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a fabric for your business needs, consider the specific application and target market. Microfiber fabric stands out for its performance in cleaning and durability, making it ideal for industries that prioritize functionality. Cotton offers a classic choice for apparel and home textiles, appealing to consumers who value tradition and comfort. Bamboo fabric presents an innovative alternative for businesses aiming for sustainability, although it may require careful sourcing and production management. Ultimately, understanding the unique benefits and limitations of each fabric will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is microfiber fabric made of
Microfiber fabric is a versatile synthetic textile known for its unique properties and applications across various industries. Understanding its essential technical specifications and trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing materials for diverse applications from cleaning products to apparel.
What Are the Critical Specifications of Microfiber Fabric?
1. Fabric Composition
Microfiber is primarily composed of ultra-fine synthetic fibers, typically polyester and polyamide (nylon). The combination of these materials provides a balance of durability and absorbency, making microfiber suitable for cleaning, apparel, and home goods. For B2B buyers, understanding fabric composition is essential for quality assurance and performance expectations in end products.
2. Denier Count
Denier is a unit of measure that indicates the fiber thickness in a fabric. Microfiber typically ranges from 0.2 to 0.7 denier, making it one of the finest fibers available. A lower denier count correlates with softer, more flexible fabric, which is vital for applications like clothing and upholstery. Buyers should consider denier specifications to meet performance and tactile requirements in their products.
3. Thread Count
Thread count refers to the number of threads woven into a square inch of fabric. Microfiber can have thread counts ranging from 200 to 1,800. Higher thread counts generally indicate denser, more durable fabric, which can enhance the longevity of products like bed linens and upholstery. B2B buyers should evaluate thread count to ensure they are selecting materials that meet their durability and comfort standards.
4. Moisture-Wicking and Absorbency
Microfiber fabrics possess high moisture-wicking abilities, allowing them to draw moisture away from the body while remaining dry to the touch. This property is particularly valuable in athletic wear and cleaning products. Understanding moisture management is key for buyers in industries such as sportswear and home textiles, where performance and hygiene are critical.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
5. Pilling Resistance
Pilling refers to the formation of small balls of fiber on the surface of the fabric. Microfiber has a medium tendency to pill, which can affect the aesthetic and functional performance of products. Buyers should consider pilling resistance when selecting fabrics for items that undergo frequent use, such as upholstery and clothing.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Microfiber Fabric Industry?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce products or components that are used in another company’s end product. In the microfiber industry, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable manufacturers that can meet specific product requirements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory levels and pricing strategies. Understanding MOQ helps in negotiating contracts and managing supply chain dynamics effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. For microfiber fabric sourcing, submitting an RFQ helps buyers obtain detailed pricing, lead times, and terms, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping, delivery, and cost responsibilities, ensuring smooth international trade practices.
5. Textile Standards and Certifications
These refer to the industry-specific guidelines and certifications that ensure fabric quality, safety, and environmental compliance. Buyers should be aware of relevant textile standards (like Oeko-Tex or GOTS) to ensure their products meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing microfiber fabric, ultimately leading to better product quality and supply chain efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is microfiber fabric made of Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends for Microfiber Fabric?
The microfiber fabric market has seen robust growth driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including cleaning, apparel, and automotive industries. Global drivers include the rising awareness of hygiene, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has led to an uptick in the use of microfiber in cleaning products and protective gear. Furthermore, the trend towards lightweight and moisture-wicking materials in athletic wear is propelling the demand for microfiber apparel.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as advanced weaving techniques and smart textiles, are enhancing the performance characteristics of microfiber, making it more appealing to international buyers. In regions like Africa and South America, manufacturers are increasingly looking to source microfiber products that combine durability with cost-effectiveness, often favoring suppliers who can offer competitive pricing without compromising quality. Additionally, the Middle East and Europe are witnessing a growing preference for multifunctional textiles that can serve various purposes, from home furnishings to industrial applications.
As global supply chains become more interconnected, international B2B buyers must navigate the complexities of sourcing, including tariffs, shipping logistics, and quality assurance. It is essential for businesses to establish strong relationships with reliable suppliers, particularly those based in China, which remains the leading producer of microfiber fabrics. The ability to adapt to these market dynamics will be crucial for companies aiming to capitalize on the growing microfiber sector.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Microfiber Fabric Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a focal point in the microfiber fabric sector, as awareness grows regarding the environmental impact of synthetic textiles. Although microfiber is known for its durability and versatility, it is not without its drawbacks; the shedding of microfibers during washing contributes to ocean pollution. For international B2B buyers, this has led to an increasing emphasis on sourcing materials that are environmentally friendly and produced under ethical labor conditions.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers who are committed to sustainable practices, such as those using recycled materials or those that have adopted processes to reduce microfiber shedding. Certifications like OEKO-TEX or Global Recycle Standard (GRS) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing. By aligning with suppliers that meet these standards, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Furthermore, as regulations regarding textile waste and sustainability tighten globally, sourcing from ethical and sustainable suppliers will not only mitigate risk but also position companies favorably in a competitive market. Understanding the implications of sustainability in microfiber sourcing is critical for B2B buyers aiming to foster long-term relationships and maintain a positive corporate image.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Microfiber Fabric Relevant to B2B Buyers?
Microfiber fabric’s journey began in the early 1950s when textile manufacturers first experimented with ultra-fine fibers. The breakthrough came in the 1960s with the Japanese company Toray’s mass production of microfiber, which set the stage for its widespread adoption. Initially popular in cleaning products, microfiber’s versatility led to its incorporation into apparel and home textiles throughout the 1990s, particularly in Europe.
As the demand for microfiber grew, so did innovations in its production, including advancements in fiber blending techniques and weaving methods. This evolution has allowed manufacturers to create high-performance fabrics suitable for various applications, from industrial use to fashion.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is essential. It not only highlights the innovation potential within the microfiber fabric sector but also emphasizes the need for continuous adaptation to market trends and consumer preferences. By staying informed about the history and advancements in microfiber technology, buyers can make strategic sourcing decisions that align with current market demands.

Illustrative image related to what is microfiber fabric made of
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is microfiber fabric made of
-
1. How is microfiber fabric produced and what materials are used?
Microfiber fabric is primarily made from ultra-fine synthetic fibers, typically polyester and polyamide (nylon). The production process involves extruding these fibers through metallic tubes to achieve their fine diameter, which can be as small as 0.2 deniers. This unique structure allows for high durability and moisture-wicking properties. The fibers are then woven into fabric sheets, which can be dyed or treated for specific qualities. Understanding the production process helps buyers ensure that they are sourcing high-quality microfiber for their needs. -
2. What are the primary applications of microfiber fabric in B2B sectors?
Microfiber fabric is versatile and widely used across various industries, including cleaning products, apparel, upholstery, and home textiles. In the cleaning sector, its absorbency and electrostatic properties make it ideal for cloths and mops. In fashion, its softness and durability are favored for jackets and skirts. Additionally, microfiber is utilized in industrial filtration and insulation due to its high fiber density. B2B buyers should consider these applications when sourcing microfiber for their specific market needs. -
3. What should I consider when vetting microfiber suppliers?
When vetting suppliers for microfiber fabric, focus on their production capabilities, quality certifications, and sustainability practices. Evaluate their experience in the textile industry and their ability to provide samples for quality assessment. Additionally, inquire about their compliance with international standards and regulations, especially concerning environmental impact. A supplier with a solid reputation and transparent practices can ensure reliable sourcing for your business. -
4. What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for microfiber fabric?
Minimum order quantities for microfiber fabric can vary significantly by supplier and order type. Generally, MOQs may range from 500 to 1,000 meters for bulk orders. However, some suppliers may accommodate smaller orders for samples or specific projects. It is essential to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your business needs, particularly if you are entering new markets or testing products. -
5. How can I customize microfiber fabric for my brand?
Customization options for microfiber fabric include variations in color, texture, and weight, as well as the addition of branding elements such as logos or patterns. Many suppliers offer bespoke services to meet specific design requirements. When discussing customization, provide clear specifications and any relevant samples to ensure that the final product aligns with your brand vision. Lead times for customized orders may vary, so plan accordingly to meet your market timelines. -
6. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing microfiber fabric internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of microfiber fabric can vary by supplier and region. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or net payment terms (30-90 days). It is crucial to establish clear payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using escrow services for larger transactions to protect both parties. Understanding local customs and regulations can also influence payment processes, particularly in regions like Africa and South America. -
7. How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for microfiber fabric?
To ensure quality assurance for microfiber fabric, establish clear quality standards and testing protocols with your supplier. Request samples for initial evaluation, and consider third-party inspections before shipment to verify that the fabric meets your specifications. Regular communication with your supplier can help address any quality issues promptly. Implementing a quality control checklist tailored to your specific needs will further enhance product consistency and reliability. -
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing microfiber fabric?
Logistics for importing microfiber fabric involve several key factors, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with textile imports to facilitate smoother logistics. Ensure that all documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is in order to avoid customs delays. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs and duties when calculating total costs. Understanding local logistics networks in your target markets can also help optimize distribution efficiency.
Top 2 What Is Microfiber Fabric Made Of Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Microfiber Cleaning Products
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
مقدمة: Microfiber is made of extremely thin fibers of polyester, polypropylene, or polyamide, which are 1/100th the thickness of an average human hair. In cleaning products, these fibers are split, creating a cross-section that resembles an asterisk. This structure allows microfiber to trap dust, dirt, and liquids more effectively, making it ideal for cleaning surfaces like glasses without leaving smudge…
2. Linens Now – Polyester & Microfiber Fabrics
Domain: linensnow.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
مقدمة: Polyester is a resilient synthetic fiber that dries quickly, is easy to wash, resistant to wrinkles, and has good colorfastness. Microfiber refers to ultrafine filament fibers, often made from polyester, and is known for its smooth and soft hand feel. Microfiber fabrics use GSM (grams per square meter) to indicate weight, rather than thread count. Examples of products include Cosmic Comfort™ Birth…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is microfiber fabric made of
Microfiber fabric, composed primarily of polyester and polyamide, offers a myriad of benefits that make it an appealing choice for various industries, from cleaning and homewares to apparel and industrial applications. Its unique properties, such as high absorbency, softness, and durability, ensure that it meets the demands of diverse markets. As international B2B buyers explore sourcing options, understanding the production processes and the environmental implications of microfiber is crucial for making informed decisions.
Strategic sourcing of microfiber presents a significant opportunity for companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By partnering with reputable suppliers, businesses can leverage the cost-effectiveness and versatility of microfiber while contributing to sustainable practices in textile production.
Looking ahead, the market for microfiber fabric is poised for growth, driven by increasing demand for high-performance materials and eco-friendly solutions. As buyers, it is essential to engage with suppliers who prioritize innovation and sustainability. Embrace the potential of microfiber fabric in your sourcing strategy to enhance product offerings and meet evolving consumer expectations. Start exploring partnerships today to capitalize on this dynamic textile market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.