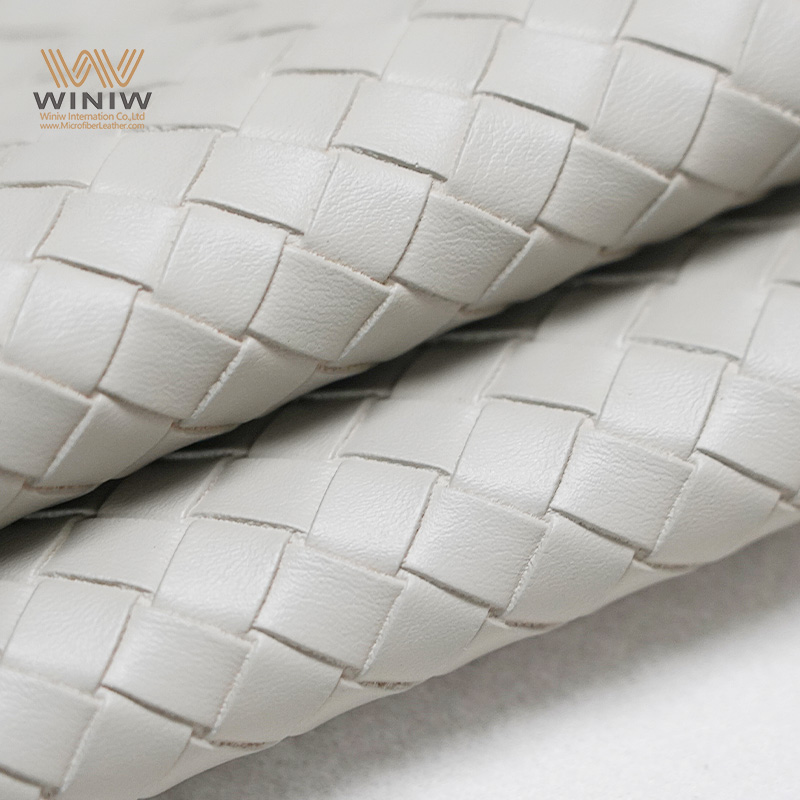
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ecological leather
In an era where sustainability is paramount, sourcing ecological leather presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers striving to balance quality, ethics, and cost. As the demand for eco-friendly materials surges across diverse industries—from fashion to automotive—understanding the nuances of ecological leather becomes crucial. This guide aims to equip international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia), with the insights needed to navigate this evolving landscape.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will explore various types of ecological leather, such as plant-based alternatives and innovative materials like Piñatex, alongside their applications in different sectors. Additionally, we will provide actionable strategies for vetting suppliers, evaluating product longevity, and estimating costs, ensuring that your sourcing decisions align with both sustainability goals and business objectives.
By arming you with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide empowers you to confidently engage with suppliers and embrace ecological leather as a viable and responsible alternative to traditional materials. In doing so, you can not only enhance your product offerings but also contribute positively to the environment and meet the growing consumer demand for sustainable solutions.
Table Of Contents
- Top 3 Ecological Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ecological leather
- Understanding ecological leather Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of ecological leather
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ecological leather’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for ecological leather
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ecological leather
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ecological leather’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ecological leather Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ecological leather With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ecological leather
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ecological leather Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ecological leather
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ecological leather
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Understanding ecological leather Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| جلد البولي يوريثان | Soft, durable, mimics natural leather; often made from bio-polyoil | Fashion accessories, upholstery | Pros: Eco-friendly, soft, easy maintenance. Cons: Less durable than PVC. |
| جلد بولي كلوريد الفينيل | Multi-layered structure, highly durable, resistant to stains | Upholstery, bags, footwear | Pros: Extremely durable, resistant to wear. Cons: Less breathable than PU. |
| Piñatex | Made from pineapple leaf fibers; sustainable and biodegradable | Fashion, accessories, furniture | Pros: Unique texture, sustainable sourcing. Cons: May require special care. |
| Recycled Leather | Made from post-consumer leather waste; reduces landfill impact | Fashion, automotive interiors | Pros: Reduces waste, retains leather’s characteristics. Cons: Quality may vary. |
| Mycelium Leather | Produced from fungi; offers a unique, natural feel | Fashion, accessories, sustainable products | Pros: Biodegradable, innovative material. Cons: Limited availability, higher cost. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of PU Leather for B2B Buyers?
PU leather, or polyurethane leather, is known for its soft texture and durability, making it an appealing alternative to traditional animal leather. It is often produced using bio-polyoil, which enhances its eco-friendliness. B2B buyers in the fashion and upholstery sectors appreciate PU leather for its luxurious feel and ease of maintenance, as it can typically be cleaned with a damp cloth. However, while PU leather is more sustainable than traditional leather, it may not have the same longevity as PVC leather, which could be a consideration for high-traffic applications.
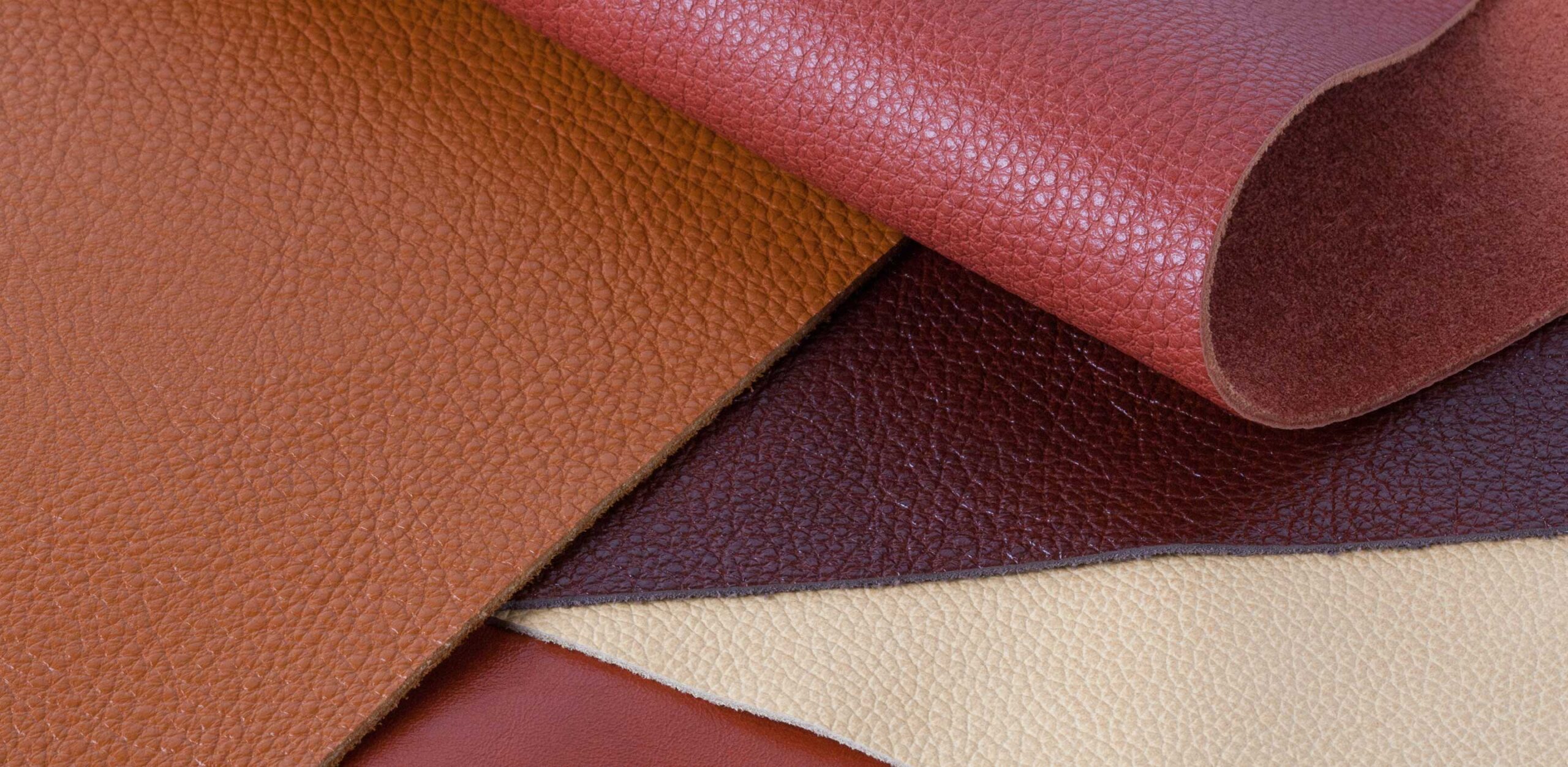

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
How Does PVC Leather Compare in Durability for Business Applications?
PVC leather, or polyvinyl chloride leather, is characterized by its multi-layered structure that provides exceptional durability and stain resistance. This makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring robust materials, such as upholstery for furniture or bags that need to withstand wear and tear. B2B buyers should note that while PVC leather is highly durable, it lacks the breathability of PU leather, which could be a factor in applications such as clothing or footwear. Understanding the environmental impact of PVC is also crucial, as it can involve more plastic components.
What Makes Piñatex an Innovative Choice for Sustainable Fashion?
Piñatex is a unique ecological leather alternative made from the fibers of pineapple leaves, making it both sustainable and biodegradable. B2B buyers in the fashion and accessories sectors may find Piñatex appealing due to its distinct texture and eco-friendly profile. However, it does require special care to maintain its appearance, which could be a consideration for brands focusing on ease of use. As sustainability continues to be a major purchasing factor, Piñatex offers a compelling option for businesses looking to differentiate themselves in the market.
How Does Recycled Leather Contribute to Sustainability in B2B Markets?
Recycled leather is produced from post-consumer leather waste, significantly reducing environmental impact by diverting materials from landfills. This type of ecological leather retains many of the desirable characteristics of traditional leather, making it suitable for fashion and automotive applications. B2B buyers should consider that while recycled leather can be a sustainable choice, the quality may vary depending on the sourcing and manufacturing processes. This variability can affect product consistency, making it essential for buyers to establish strong supplier relationships.
Why is Mycelium Leather Emerging as a Valuable Option for Innovative Businesses?
Mycelium leather, derived from fungi, represents a cutting-edge approach to sustainable materials. It offers a unique, natural feel and is fully biodegradable, appealing to eco-conscious B2B buyers in the fashion and accessories sectors. However, availability can be limited, and production costs may be higher compared to traditional materials. Businesses looking to innovate with sustainable options may find mycelium leather an exciting choice, but they should assess supply chain capabilities and market readiness for such novel products.
Key Industrial Applications of ecological leather
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ecological leather | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | Eco-friendly handbags and footwear | Enhances brand image and attracts eco-conscious consumers | Certifications for sustainability, material sourcing transparency |
| Automotive | Interior upholstery and trim components | Reduces environmental impact while maintaining luxury feel | Durability standards, compliance with automotive regulations |
| Furniture | Upholstery for sofas and chairs | Offers a sustainable alternative that appeals to modern consumers | Fire safety regulations, comfort, and aesthetic appeal |
| Accessories | Belts, wallets, and small goods | Provides a unique selling point in competitive markets | Customization options, durability, and market trends |
| Sports Equipment | Eco-leather for sports bags and protective gear | Aligns with growing demand for sustainable sports products | Performance standards, waterproofing, and maintenance ease |
How is Ecological Leather Used in the Fashion and Apparel Industry?
In the fashion and apparel sector, ecological leather is utilized in the production of eco-friendly handbags and footwear. Brands are increasingly adopting this sustainable material to align with the values of environmentally conscious consumers. The use of ecological leather not only enhances a brand’s image but also helps in reducing the environmental footprint associated with traditional leather production. International buyers should look for suppliers that provide certifications for sustainability and transparency in material sourcing to ensure they meet ethical standards.
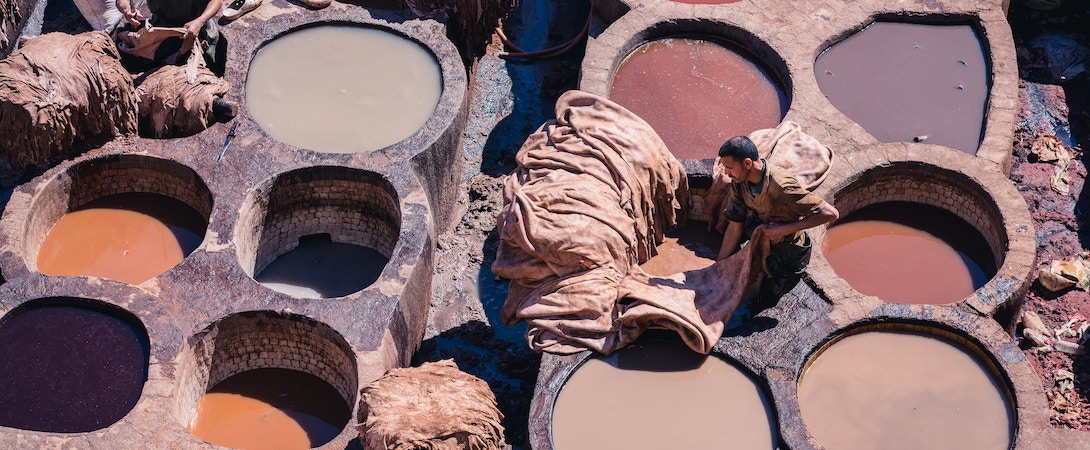

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
What are the Applications of Ecological Leather in the Automotive Sector?
The automotive industry employs ecological leather for interior upholstery and trim components, offering a luxurious feel without the associated environmental costs of animal leather. By choosing eco-leather, manufacturers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint while appealing to consumers who prioritize sustainability. Buyers in this sector must consider durability standards and ensure compliance with automotive regulations to maintain safety and quality in their products.
How is Ecological Leather Transforming the Furniture Industry?
In furniture design, ecological leather is increasingly used for upholstery in sofas and chairs. This material provides a sustainable alternative that resonates with consumers looking for eco-friendly home furnishings. The appeal of ecological leather lies in its durability and aesthetic qualities, making it a preferred choice for modern designs. Buyers should pay attention to fire safety regulations and the comfort level of the material to meet consumer expectations and legal requirements.
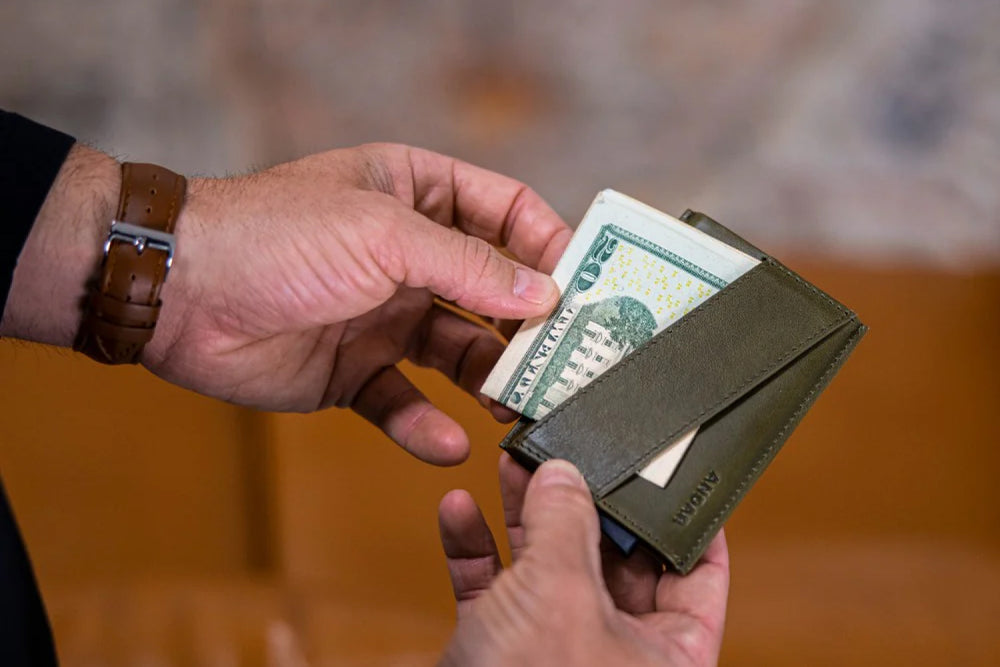
What Role Does Ecological Leather Play in Accessories?
Ecological leather is also popular in the production of accessories such as belts, wallets, and small goods. This application allows brands to differentiate themselves in a competitive market by offering unique, sustainable products. Buyers should consider customization options and the durability of ecological leather to ensure that their offerings remain appealing and functional, keeping up with current market trends.
How is Ecological Leather Used in Sports Equipment?
In the sports equipment sector, ecological leather is gaining traction for use in sports bags and protective gear. This material aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products in sports and fitness, providing a competitive edge. Buyers should focus on performance standards, such as waterproofing and ease of maintenance, to ensure that the products meet the rigorous demands of athletes while also being environmentally friendly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ecological leather’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Concerns About Durability of Eco-Leather Products
The Problem: B2B buyers are often apprehensive about the durability of ecological leather, fearing that it may not withstand the rigors of everyday use as well as traditional leather. This concern is particularly pronounced in industries such as fashion and automotive, where product longevity is critical to maintaining brand reputation and customer satisfaction. Buyers might worry that choosing eco-leather could lead to increased returns or complaints from end-users, ultimately affecting their bottom line.
The Solution: To address these durability concerns, B2B buyers should focus on sourcing eco-leather products made from high-quality materials like PU (Polyurethane) rather than PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride). PU eco-leather has been shown to be more resilient and less prone to cracking, peeling, or fading compared to traditional leather. When sourcing, it’s crucial to request product samples and conduct wear-and-tear tests to evaluate the material’s performance under expected use conditions. Moreover, establishing a relationship with reputable manufacturers who provide detailed specifications and testing results can help ensure that the eco-leather products you choose will meet your durability needs.

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
Scenario 2: Misunderstanding the Environmental Impact of Eco-Leather
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are committed to sustainability but often face confusion regarding the environmental implications of various eco-leather products. For instance, some buyers may mistakenly believe that all eco-leathers are created equal, overlooking the fact that certain manufacturing processes can still be harmful to the environment. This misunderstanding can lead to unintentional choices that contradict a company’s sustainability goals, resulting in reputational damage and loss of consumer trust.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize transparency in the supply chain. Request certifications or reports that detail the environmental practices of manufacturers, such as the use of non-toxic dyes and sustainable sourcing of raw materials. Engaging in discussions with suppliers about their production methods can provide valuable insights and help ensure that the eco-leather options you select align with your sustainability objectives. Additionally, investing in training for your procurement team about the differences in eco-leather types can empower them to make informed choices that genuinely reflect environmental responsibility.
Scenario 3: Limited Availability and Sourcing Challenges
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges related to the limited availability of quality eco-leather products in certain markets. This is particularly true for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where access to sustainable materials can be restricted. The resulting scarcity may lead to higher prices or the need to compromise on quality, which can ultimately affect product offerings and competitiveness in the market.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, buyers should consider diversifying their supplier base and exploring partnerships with manufacturers in regions where eco-leather is more readily available. Attending trade shows or industry conferences focused on sustainable materials can also help establish valuable connections and open up new sourcing channels. Additionally, consider collaborating with local artisans or small-scale producers who specialize in eco-leather, as they may offer unique products that can differentiate your brand in the marketplace. By fostering a network of reliable suppliers, you can ensure a consistent supply of high-quality eco-leather while supporting sustainable practices within local economies.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ecological leather
When selecting ecological leather for various applications, understanding the different materials available is crucial for B2B buyers. Below, we analyze four common materials used in ecological leather, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international markets.

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
What Are the Key Properties of PU (Polyurethane) Eco-Leather?
Polyurethane (PU) is a popular choice for ecological leather due to its ability to mimic the texture and feel of genuine leather. It is known for its softness, flexibility, and resistance to cracking. PU can withstand a range of temperatures and is less prone to fading when exposed to UV light, making it suitable for products that may be used outdoors or in varying climates.
Pros & Cons: PU eco-leather is generally more affordable than traditional leather and offers good durability, but it may not be as resistant to heavy wear and tear compared to some other materials. It is relatively easy to clean and maintain, requiring only a damp cloth for upkeep. However, its manufacturing process can involve some synthetic components, which may not appeal to all environmentally conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: PU is ideal for applications such as bags, shoes, and upholstery. Its soft texture makes it a preferred choice for products requiring a luxurious feel.
How Does PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Compare in Terms of Durability and Cost?
PVC is another widely used material in the production of ecological leather. It is recognized for its durability and multi-layered structure, which enhances its resistance to stains and scratches. PVC is often employed in applications where high durability is paramount, such as in upholstery for commercial settings.
Illustrative image related to ecological leather
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of PVC is its robustness and lower cost compared to other eco-leathers. However, it may lack the luxurious feel of PU and can be less breathable, which may not be suitable for all applications. Additionally, the environmental impact of PVC production can be a concern for sustainability-focused buyers.
Impact on Application: PVC is commonly used in products requiring high durability, such as automotive interiors and heavy-duty bags.
What Unique Benefits Does Piñatex Offer for Eco-Friendly Applications?
Piñatex is a relatively new entrant in the ecological leather market, made from pineapple leaf fibers. This innovative material is not only sustainable but also biodegradable, making it an attractive option for environmentally conscious brands.
Pros & Cons: Piñatex offers a unique aesthetic and texture that can differentiate products in the marketplace. However, it may be less durable compared to PU and PVC, making it more suitable for fashion items rather than heavy-duty applications. Its production can be more complex, which may lead to higher costs.

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
Impact on Application: Piñatex is ideal for fashion accessories, bags, and shoes, particularly in markets that prioritize sustainability and unique design.
What Should Buyers Consider When Selecting Eco-Leather Materials?
When sourcing ecological leather, international buyers must consider compliance with local and international standards, such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS. Each region may have different preferences regarding material sustainability and performance. For instance, European buyers may prioritize eco-certifications, while buyers in the Middle East may focus on durability and ease of maintenance due to climate conditions.
Summary Table of Ecological Leather Materials
| المواد | Typical Use Case for ecological leather | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PU (Polyurethane) | Bags, shoes, upholstery | Soft, luxurious feel | Less durable under heavy wear | Medium |
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | Automotive interiors, heavy-duty bags | High durability, low cost | Less breathable, environmental concerns | منخفضة |
| Piñatex | Fashion accessories, bags, shoes | Sustainable, biodegradable | Lower durability, higher cost | عالية |
| Recycled Leather | Upholstery, fashion items | Eco-friendly, unique texture | Variable quality, potential higher cost | Medium |
In conclusion, selecting the right ecological leather material involves weighing the properties, advantages, and limitations of each option. By considering the specific application requirements and regional preferences, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ecological leather
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Ecological Leather?
The production of ecological leather involves several critical stages that ensure the final product is both durable and environmentally friendly. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Are Eco-Friendly Raw Materials Sourced?
The journey of ecological leather begins with sourcing sustainable raw materials. Commonly used materials include polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and innovative alternatives like Piñatex, which is derived from pineapple leaves. Suppliers often prioritize sourcing from certified sustainable farms or recycling centers to minimize environmental impact. This initial stage also involves ensuring that all materials comply with regulations such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) in Europe, which governs the use of harmful substances.

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Create Eco-Leather?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes, which can include extrusion, casting, or coating. For instance, PU leather is typically produced by applying a PU coating over a textile substrate, providing a soft touch and durability. In contrast, PVC leather may involve a multi-layered approach, where the backing is reinforced with a foam layer for added strength. Each technique has its merits, and the choice often depends on the desired product attributes, such as texture and flexibility.
Assembly: How Are Eco-Leather Products Constructed?
After forming, the ecological leather is cut and sewn into the desired shapes and sizes, whether for bags, shoes, or upholstery. This stage often involves skilled labor to ensure precision and quality. Automated cutting machines may be employed for high-volume production, while artisanal methods are favored for bespoke items. It’s crucial for buyers to inquire about the assembly techniques used, as they can significantly affect the final product’s quality and aesthetic appeal.
Finishing: What Are the Final Touches for Eco-Leather Products?
The finishing stage involves applying protective coatings, dyes, and treatments to enhance the leather’s appearance and durability. This can include UV protection, water resistance, and anti-scratch properties. Eco-friendly finishes are increasingly popular, as they align with the sustainability ethos of ecological leather. Buyers should verify that any chemical treatments used meet international safety standards, which can vary by region.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Ecological Leather?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of ecological leather, particularly for B2B buyers who require consistency and reliability in their supply chains.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems are crucial for manufacturers of ecological leather. These standards ensure that processes are consistently monitored and improved. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking in Europe or API standards for certain applications can also be significant. Buyers should look for suppliers that hold these certifications as indicators of quality and compliance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control in ecological leather manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection verifies the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line. Buyers can request IQC reports to ensure materials meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks ensure that processes remain within control limits. This step is crucial for identifying and rectifying issues early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, a thorough inspection assesses the finished products against quality criteria. This includes checking for defects, consistency in color and texture, and adherence to specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can ensure the reliability of their suppliers through various verification methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their adherence to quality standards. These can be scheduled or surprise audits, depending on the contractual terms.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC documentation, provides insight into the manufacturer’s quality assurance processes.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control practices. This is particularly relevant for international buyers who may not have direct oversight.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding quality control nuances is vital. Regulatory requirements may differ significantly across countries, necessitating awareness of local standards and compliance expectations.
How Do Regional Standards Impact the Quality of Ecological Leather?
In Europe, stringent regulations govern the use of chemicals in leather production, while countries in the Middle East may have different environmental regulations. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers are not only compliant with their local laws but also with those of their target markets. This may involve additional certifications or adjustments in production processes to meet varying standards.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding Sustainable Practices?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point for B2B buyers. Suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices—such as using recycled materials or reducing water consumption—can enhance their appeal. Buyers should inquire about the sustainability certifications held by their suppliers, such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX, which can further validate the eco-friendliness of the products.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Ensure They Source High-Quality Ecological Leather?
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for ecological leather is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly methods, and finishing touches, buyers can better assess the quality of the products they procure. Furthermore, adhering to international quality standards and implementing rigorous quality control measures will help ensure that the ecological leather sourced meets their expectations for sustainability and performance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ecological leather’
مقدمة
Sourcing ecological leather requires a comprehensive approach to ensure that the materials meet sustainability standards and quality expectations. This guide serves as a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to navigate the complexities of procuring eco-friendly leather alternatives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the ecological leather you intend to source. Consider factors such as thickness, texture, and color, as well as the intended application (e.g., upholstery, fashion, accessories). This step is critical to ensure that you select a product that meets your specific needs and aligns with your brand’s sustainability goals.
Step 2: Research Eco-Leather Materials
Familiarize yourself with the various types of ecological leather available in the market. Common materials include PU (polyurethane), PVC (polyvinyl chloride), and innovative options like Piñatex (made from pineapple leaves). Understanding the characteristics and benefits of each material will help you make informed decisions that cater to your product requirements and sustainability criteria.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that validate their commitment to sustainability. Look for certifications such as OEKO-TEX, Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), or certifications specific to eco-leather production. These certifications provide assurance that the materials are produced in an environmentally responsible manner and that they meet health and safety standards.

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers before making a commitment. Request detailed company profiles, including their manufacturing processes, sustainability practices, and case studies. Additionally, seek references from other businesses in similar industries or regions to gauge their reliability and quality of service.
Step 5: Request Samples for Assessment
Always request samples of the ecological leather you are considering. Assess the samples for quality, texture, and durability, and ensure they meet your predefined specifications. This hands-on evaluation is essential for confirming that the product will perform well in its intended application.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your business objectives. This includes pricing, minimum order quantities, lead times, and payment terms. Clear communication during this phase is vital to establish a mutually beneficial relationship and to ensure that both parties are aligned on expectations.

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
Step 7: Monitor Supplier Performance
After finalizing your supplier, implement a system for ongoing evaluation of their performance. Regularly assess product quality, delivery timelines, and adherence to sustainability practices. Building a strong partnership with your supplier will enhance reliability and ensure that your ecological leather sourcing meets your company’s standards over time.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for ecological leather, ensuring they select high-quality, sustainable materials that align with their business values.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ecological leather Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Ecological Leather Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of ecological leather is vital for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The type of eco-leather significantly influences material costs. Options range from polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) to innovative materials like Piñatex, derived from pineapple waste. While PU is generally softer and more environmentally friendly, PVC may offer durability for specific applications. Buyers should consider the trade-offs between cost and quality when selecting materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary depending on the region where production occurs. Countries with lower labor costs may initially seem appealing; however, the skill level and experience of the workforce can greatly impact the quality of the final product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to facility operations, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead costs, which is crucial for maintaining competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for unique designs or specifications can add to the initial investment. Buyers should assess whether the tooling costs are justified by the expected return on investment, particularly for custom orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality often involves additional costs for inspections and testing. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who have robust QC processes in place, as this can prevent costly returns and rework.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the Incoterms agreed upon and the distance between the supplier and buyer. Understanding the logistics involved in sourcing ecological leather is crucial for accurate cost estimation.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market positioning. Buyers should be aware of standard industry margins and consider negotiating based on volume or long-term partnerships.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Several factors can influence the pricing of ecological leather:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often yield better unit prices, making it essential for buyers to align their purchasing strategy with their demand forecasts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to obtain accurate quotes.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet certain environmental standards or certifications (such as OEKO-TEX) may come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of such certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms can help buyers anticipate additional costs related to shipping, insurance, and customs duties. For instance, choosing DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) may simplify the purchasing process but can also increase costs.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs in Ecological Leather Sourcing?
B2B buyers can employ several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate: Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond the initial purchase price and factor in long-term costs such as maintenance, durability, and potential waste. Higher-quality eco-leather may incur a higher upfront cost but could prove more economical over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must consider currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local market conditions that could affect pricing.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for ecological leather can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed decisions. Always consider current market trends and economic conditions when assessing costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ecological leather With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Ecological Leather: What Are the Options?
As businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability, understanding the options available for eco-friendly materials becomes crucial. Ecological leather, known for its reduced environmental impact, is often compared against other alternatives like traditional leather, synthetic leather, and innovative materials. Each option has its unique characteristics, and this analysis aims to provide clarity to B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Ecological Leather | Traditional Leather | جلد صناعي |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Durable and resistant to wear; mimics genuine leather | Excellent durability and longevity; natural feel | Moderate durability; can vary based on material (e.g., PU, PVC) |
| Cost | Generally higher than synthetic options, but competitive with high-quality leather | Often the most expensive due to sourcing and processing | Typically lower cost, especially for mass-produced items |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires sourcing from certified producers; may need consumer education | Well-established supply chains; widely accepted | Easy to source; numerous manufacturers available |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean with water | Requires regular conditioning and care | Varies; some types are easy to clean, while others may degrade over time |
| Best Use Case | Fashion, accessories, and upholstery | High-end fashion, luxury goods, and durable products | Budget-conscious fashion, promotional items, and temporary uses |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Leather
Traditional leather is a premium material known for its durability and classic appeal. It offers excellent longevity and a luxurious feel, making it a preferred choice for high-end fashion and accessories. However, the environmental impact associated with cattle farming and the tanning process raises ethical concerns. Additionally, traditional leather requires significant maintenance, including conditioning and protection from moisture, which can be a drawback for businesses seeking low-maintenance solutions.
جلد صناعي
Synthetic leather, which includes materials such as polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), presents a cost-effective alternative to both ecological and traditional leather. It is widely available and can be produced in various styles and finishes. While synthetic leather offers ease of cleaning and is often more affordable, its long-term durability can be questionable, particularly with lower-quality options. Furthermore, synthetic leathers made from PVC can have a significant environmental footprint due to their plastic content, which may counteract some of the sustainability goals businesses aim to achieve.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
In selecting the appropriate leather alternative, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including performance, cost, and environmental impact. Ecological leather stands out for its sustainability and low maintenance, making it an excellent choice for businesses committed to ethical practices. Traditional leather is ideal for luxury markets but may not align with sustainability goals. Meanwhile, synthetic leather offers affordability but varies in quality and durability. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on the buyer’s target market, product application, and commitment to sustainability.

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ecological leather
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Ecological Leather?
Understanding the technical specifications of ecological leather is essential for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and classification of the ecological leather based on its composition and performance. Higher-grade materials, such as PU (Polyurethane) derived from bio-polyoil, offer better durability and a more authentic leather feel compared to lower-grade options like PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride). B2B buyers should prioritize material grades that align with their brand values and target market preferences, ensuring product longevity and customer satisfaction.
2. Thickness
The thickness of ecological leather is a vital specification that impacts its durability, flexibility, and application. Typically measured in millimeters, thickness can range from 0.5mm to 2.0mm or more. Thicker materials are generally more durable and suitable for heavy-use products like upholstery, while thinner materials may be ideal for fashion accessories. Buyers must consider the intended use to select the appropriate thickness that meets performance requirements.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the thickness and other dimensions of the ecological leather. This specification is crucial during manufacturing, as strict tolerances ensure uniformity and quality in finished products. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels can help in negotiating contracts and ensuring that suppliers can meet their production standards consistently.
Illustrative image related to ecological leather
4. Color Fastness
Color fastness indicates how well the ecological leather maintains its color when exposed to various environmental conditions such as light, water, and friction. This property is essential for products that will experience high visibility or frequent handling. B2B buyers should seek materials with high color fastness ratings to ensure that their products retain their aesthetic appeal over time.
5. Weight
The weight of ecological leather can influence its application and consumer perception. Lighter materials may be preferable for fashion items, while heavier materials may be better suited for furniture or automotive applications. B2B buyers need to evaluate the weight of materials in relation to their product design and target market to ensure optimal performance and appeal.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Ecological Leather?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiation processes. Here are some common terms relevant to ecological leather:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce products that are then rebranded and sold by other companies. In the ecological leather sector, OEM partnerships can be beneficial for brands looking to offer customized products without investing heavily in manufacturing infrastructure.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and initial investment costs. Suppliers often set MOQs based on production costs and material availability.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. This process is important in the ecological leather industry as it allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals based on quality and price.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, particularly concerning shipping and delivery. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, ensuring smoother logistics for ecological leather products.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the ecological leather market, lead times can vary significantly depending on material availability and production schedules. B2B buyers should account for lead times when planning their inventory and product launches to avoid disruptions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing ecological leather, ensuring that their products meet quality standards and market demands effectively.

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ecological leather Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers Influencing Ecological Leather Sourcing?
The ecological leather market is rapidly evolving, driven by increased consumer demand for sustainable products and the urgent need to address environmental concerns. Global awareness of climate change and its impact on natural resources has prompted brands to seek alternatives to traditional leather, which is often associated with significant carbon emissions and ethical issues related to animal welfare. Key trends include the rise of plant-based materials such as Piñatex and mushroom leather, which are gaining traction as viable alternatives. Additionally, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, such as improved methods for creating biodegradable and recyclable materials, are influencing sourcing decisions.
International B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of regional preferences and market dynamics. For instance, Europe is leading in regulatory frameworks that mandate sustainability, influencing procurement strategies. Conversely, emerging markets in Africa and South America may present unique opportunities for sourcing eco-friendly materials that align with local agricultural practices. Companies are increasingly leveraging digital platforms to connect with suppliers of ecological leather, making it essential for buyers to stay updated on emerging B2B tech trends that facilitate efficient sourcing.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Ecological Leather?
The environmental impact of sourcing ecological leather is a critical consideration for B2B buyers. Traditional leather production is resource-intensive, often leading to deforestation, water pollution, and high greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, ecological leather offers a more sustainable alternative, using materials that minimize ecological footprints. This shift is not only beneficial for the planet but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for brands that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
Ethical supply chains are paramount in the ecological leather sector. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to responsible sourcing practices, ensuring fair labor conditions and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX can provide assurance of a product’s sustainability credentials. Furthermore, transparency in the supply chain fosters trust and can enhance a brand’s reputation, making it a vital factor for B2B buyers looking to differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
What Is the Evolution of Ecological Leather in the B2B Market?
The evolution of ecological leather can be traced back to the growing awareness of environmental issues in the late 20th century. Initially, alternatives to animal leather were limited and often of lower quality. However, advancements in materials science and a shift in consumer values have transformed the landscape. Brands began experimenting with various sustainable materials, leading to the development of high-quality, durable ecological leather options that closely mimic the look and feel of traditional leather.
Today, ecological leather is not just a niche market but a fundamental component of sustainable fashion and manufacturing. B2B buyers are increasingly recognizing the commercial viability of ecological leather, as brands strive to meet consumer demand for ethical and environmentally-friendly products. This evolution presents a significant opportunity for international buyers to engage with innovative suppliers who are pushing the boundaries of sustainable material development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ecological leather
-
How do I choose the right ecological leather supplier for my business?
When selecting an ecological leather supplier, consider their sustainability certifications, production methods, and material sourcing. It’s crucial to assess their transparency in operations and commitment to environmental standards. Request samples to evaluate the quality of their products, and check customer reviews or case studies for insights into their reliability. Additionally, ensure they can meet your specific needs regarding customization, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and lead times. -
What is the best type of ecological leather for high-end fashion products?
For high-end fashion products, Polyurethane (PU) leather is often the best choice due to its luxurious feel and durability. PU leather closely mimics the texture and appearance of genuine leather, making it ideal for premium items. It’s also more environmentally friendly than traditional leather, as it doesn’t involve harmful tanning processes. However, if you are looking for a unique alternative, consider Piñatex, which is made from pineapple fibers and offers a distinctive look while maintaining sustainability. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for ecological leather?
Minimum order quantities for ecological leather can vary significantly by supplier and material type. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 500 meters, depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and the specific materials requested. It’s advisable to communicate your needs clearly and negotiate with suppliers to find a mutually beneficial arrangement, especially if you are a smaller business or just starting. -
How can I ensure the quality of ecological leather products I receive?
To ensure the quality of ecological leather products, establish clear quality assurance (QA) standards with your supplier before placing an order. Request detailed product specifications, including material composition and durability tests. Conduct pre-shipment inspections or ask for third-party quality checks to verify that the products meet your standards. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also help in maintaining consistent quality over time. -
What payment terms are typically offered by ecological leather suppliers?
Payment terms for ecological leather suppliers can vary widely, but common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining 70% before shipment. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 payment terms, depending on your business relationship and order size. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and ensure that both parties are clear about payment schedules to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for ecological leather imports?
When importing ecological leather, work closely with your supplier to understand their shipping options and timelines. Consider using a freight forwarder to manage logistics and customs clearance, ensuring compliance with international trade regulations. It’s essential to factor in shipping costs, delivery times, and potential tariffs or duties that may apply to your shipments. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can streamline the process and mitigate risks. -
What sustainability certifications should I look for in ecological leather?
When sourcing ecological leather, look for certifications that validate the sustainability of the materials and processes used. Key certifications include Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), OEKO-TEX Standard 100, and the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification. These certifications indicate compliance with environmentally friendly practices and ethical labor standards, enhancing your brand’s credibility and appeal to eco-conscious consumers. -
Can ecological leather be customized to suit my brand’s needs?
Yes, many ecological leather suppliers offer customization options to align with your brand’s identity. Customizations can include specific colors, textures, and finishes, as well as printing or embossing your logo. Be sure to discuss your requirements early in the sourcing process and ask for samples to ensure that the final product meets your expectations. Collaborating closely with the supplier can yield unique and personalized products that resonate with your target audience.
Top 3 Ecological Leather Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Leather Edge Paint – Eco-Leather Solutions
Domain: blog.leatheredgepaint.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
مقدمة: Eco-leather is real leather tanned with low environmental impact processes, meeting the UNI 11427:2011 standard. It retains characteristics of traditional Chrome Tanned or Vegetable Tanned leathers. Faux leather, also known as synthetic or vegan leather, is made from synthetic materials without animal origin, and lacks specific environmental regulations in production. Faux leather can be coated fa…
2. Y Studio – Eco Leather Tray
Domain: ystudiostyle.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
مقدمة: Eco Leather Tray: Made from high-quality eco leather, functional and stylish for home or office.
3. Alternative Leathers – Desserto® Cactus Leather
Domain: alternativeleathers.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
مقدمة: {“products”:[{“name”:”Desserto® Cactus Leather”,”price”:”From $17.00″,”description”:”Unique and environmentally friendly material used by brands such as Fossil, Adidas, and Mercedes, developed in Mexico.”},{“name”:”Piñatex® Original Pineapple Leather”,”price”:”From $24.00″,”description”:”Sustainable alternative developed in the 1990s, used by trusted brands worldwide.”},{“name”:”Vegea® Grape Leath…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ecological leather
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Ecological Leather Supply Chain?
As the demand for sustainable materials continues to rise, ecological leather presents a compelling opportunity for B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By strategically sourcing eco-friendly leather alternatives like PU, PVC, and innovative options such as Piñatex, businesses can not only meet consumer preferences but also align with global sustainability goals. The durability and ease of maintenance of these materials further enhance their appeal, ensuring long-lasting value in your product offerings.
Strategic sourcing in ecological leather is not merely about procurement; it involves fostering partnerships with suppliers who prioritize ethical production and transparency. This approach not only mitigates supply chain risks but also enhances brand reputation, crucial in today’s environmentally conscious market.
Looking forward, businesses must stay ahead by continually exploring advancements in eco-leather technologies and sustainable practices. This commitment not only positions your company as a leader in sustainable fashion but also meets the evolving needs of consumers who are increasingly demanding responsible choices. Seize the opportunity to integrate ecological leather into your product lines, and take a proactive step toward a sustainable future in your industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to ecological leather
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.