Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather designer fabric
In the dynamic landscape of the global market for leather designer fabric, B2B buyers face the pressing challenge of sourcing high-quality materials that align with both aesthetic demands and functional requirements. With a multitude of options ranging from genuine leather to innovative faux alternatives, the decision-making process can be overwhelming. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the world of leather designer fabric by exploring various types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting. By understanding the differences between materials, such as cowhide, goat leather, and synthetic options, buyers can make informed choices that enhance their product offerings.
The guide also delves into the intricacies of pricing, highlighting factors that influence cost across different regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With insights into current market trends and consumer preferences, this resource is designed to empower international B2B buyers, enabling them to navigate the complexities of sourcing leather fabrics effectively. Whether you’re looking to elevate your fashion line, enhance interior design projects, or meet specific industry standards, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make strategic purchasing decisions. By leveraging the insights provided, buyers can confidently select materials that not only satisfy their business needs but also resonate with their target markets.
Table Of Contents
- Top 4 Leather Designer Fabric Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for leather designer fabric
- Understanding leather designer fabric Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of leather designer fabric
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather designer fabric’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather designer fabric
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather designer fabric
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather designer fabric’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather designer fabric Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather designer fabric With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather designer fabric
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather designer fabric Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather designer fabric
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather designer fabric
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
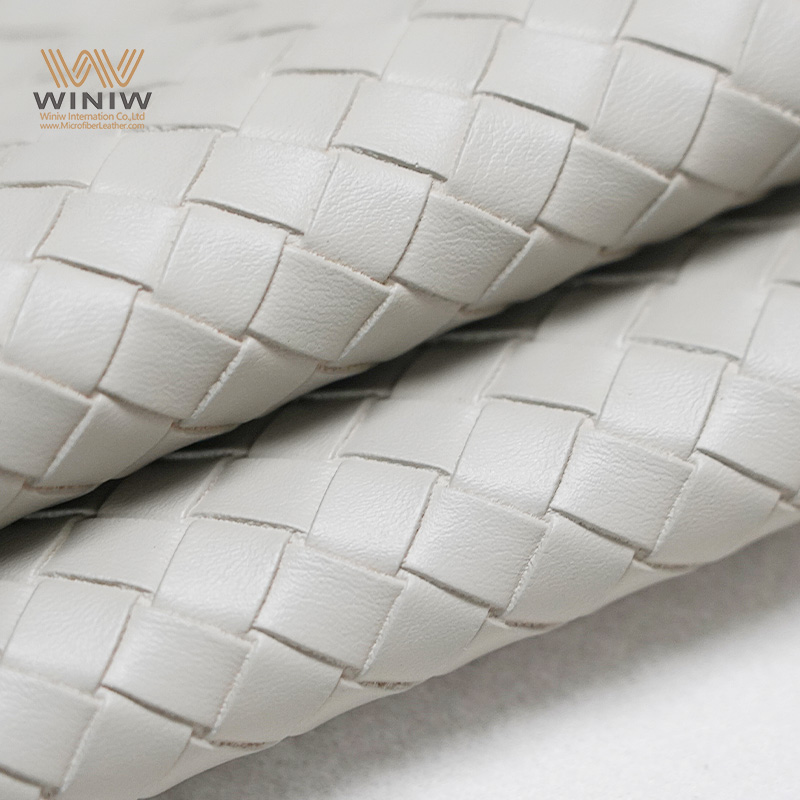
Understanding leather designer fabric Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genuine Leather | Durable, luxurious feel; natural grain patterns; breathability | High-end fashion, upholstery, accessories | Pros: Premium quality, timeless appeal. Cons: Higher cost, requires maintenance. |
| جلد صناعي | Synthetic alternative; available in various textures/colors | Fashion, furniture, automotive interiors | Pros: Cost-effective, animal-friendly. Cons: Less durable, can wear faster than genuine leather. |
| Suede | Soft, napped finish; less durable than full-grain leather | Fashion items, upholstery, luxury products | Pros: Unique texture, elegant appearance. Cons: Prone to staining, requires special care. |
| Exotic Leather | Unique textures from animals like crocodiles or snakes | Luxury handbags, bespoke fashion items | Pros: Distinctive look, high market value. Cons: Ethical concerns, higher price point. |
| Performance Leather | Treated for enhanced durability and resistance to wear | Commercial upholstery, automotive seating | Pros: Long-lasting, easy to clean. Cons: Can be more expensive, limited aesthetic variations. |
What Are the Characteristics of Genuine Leather for B2B Buyers?
Genuine leather is prized for its durability and luxurious feel. It features natural grain patterns that add character and uniqueness to each piece. This type of leather is breathable, making it suitable for high-end fashion, upholstery, and accessories. B2B buyers should consider the long-term investment value, as genuine leather tends to age beautifully, although it requires regular maintenance to prevent damage.
How Does Faux Leather Compare in Terms of Suitability?
Faux leather, a synthetic alternative, provides a wide range of textures and colors, making it a versatile choice for various applications. It is commonly used in fashion, furniture, and automotive interiors due to its affordability and animal-friendly nature. However, buyers should keep in mind that while faux leather is cost-effective, it may not offer the same durability and longevity as genuine leather.
Why Choose Suede for Specific Applications?
Suede is characterized by its soft, napped finish, which gives it a unique texture and elegant appearance. It is often used in fashion items and luxury upholstery. However, B2B buyers should be aware that suede is less durable than full-grain leather and prone to staining, necessitating special care. This makes it ideal for products that prioritize aesthetics over heavy use.
What Makes Exotic Leather a Luxury Choice?
Exotic leather, sourced from animals such as crocodiles and snakes, offers a distinctive look that commands high market value. This type of leather is often used in luxury handbags and bespoke fashion items. While it can elevate a product’s status, ethical concerns and higher price points are significant factors for B2B buyers to consider when sourcing exotic leather products.
How Does Performance Leather Serve Commercial Needs?
Performance leather is specifically treated to enhance durability and resistance to wear, making it an excellent choice for commercial applications, such as upholstery and automotive seating. It is designed for easy cleaning and long-lasting use, catering to buyers looking for functional yet stylish options. However, the initial cost may be higher, and aesthetic variations can be limited compared to other types of leather.
Key Industrial Applications of leather designer fabric
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of leather designer fabric | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion & Apparel | High-end clothing and accessories | Enhances brand prestige and customer appeal | Quality, durability, and compliance with local regulations |
| Automotive | Interior upholstery for vehicles | Improves aesthetic value and resale potential | Material performance, color options, and compatibility with manufacturing processes |
| Furniture & Home Decor | Upholstery for luxury furniture | Adds value and durability to products | Fabric weight, texture, and fire resistance standards |
| Hospitality | Decorative elements in hotels and restaurants | Creates a luxurious atmosphere, improving guest experience | Customization options, ease of maintenance, and stain resistance |
| Sports & Leisure | Custom gear and apparel for sports teams | Provides a unique identity and enhances team branding | Sourcing of eco-friendly materials and adherence to performance standards |
How is leather designer fabric used in the fashion and apparel industry?
In the fashion and apparel sector, leather designer fabric is primarily utilized for creating high-end clothing, handbags, shoes, and accessories. Its luxurious appearance and texture can significantly enhance a brand’s prestige, appealing to consumers looking for premium products. International buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality materials that comply with local regulations regarding animal welfare and sustainability, ensuring that the final products align with consumer expectations in different markets.
What are the applications of leather designer fabric in the automotive industry?
In the automotive sector, leather designer fabric is commonly used for vehicle interiors, including seats, dashboards, and door panels. This material not only elevates the aesthetic appeal of vehicles but also contributes to higher resale values. Buyers in this industry should prioritize sourcing durable and easy-to-clean materials that can withstand wear and tear while offering a variety of colors and textures to match diverse vehicle designs.
How does leather designer fabric enhance furniture and home decor?
Leather designer fabric plays a crucial role in the furniture and home decor industry, particularly for luxury upholstery. Its durability and rich texture add significant value to furniture pieces, making them more appealing to consumers. When sourcing for this application, buyers should consider factors such as fabric weight, texture, and compliance with fire resistance standards, which are often mandatory in many regions.
Why is leather designer fabric important in the hospitality industry?
In the hospitality sector, leather designer fabric is used to create decorative elements in hotels and restaurants, such as seating, wall coverings, and decorative accents. This fabric helps establish a luxurious atmosphere, enhancing the overall guest experience and encouraging repeat business. Buyers should seek customization options that align with their brand identity and ensure the materials are easy to maintain and resistant to stains, which is vital for high-traffic environments.
What role does leather designer fabric play in sports and leisure?
In the sports and leisure industry, leather designer fabric is utilized for custom gear and apparel, providing teams with a unique identity and enhancing brand recognition. The fabric’s durability and aesthetic appeal make it an ideal choice for uniforms, bags, and sports accessories. Buyers should prioritize eco-friendly materials that meet specific performance standards, ensuring that the products not only look good but also perform well under various conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘leather designer fabric’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Authenticity in Leather Designer Fabrics
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with verifying the authenticity and quality of leather designer fabrics. In markets where imitation products abound, distinguishing between genuine and faux leather can be challenging. This issue is particularly pronounced for international buyers who may have limited access to samples or direct supplier interactions. This can lead to costly mistakes, such as sourcing inferior materials that do not meet quality standards or the expectations of their clientele.
The Solution: To ensure authenticity, buyers should prioritize sourcing from established suppliers with a strong reputation for quality. It’s advisable to request detailed product specifications and certifications that verify the material’s origin and quality. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers, including video calls and factory visits if possible, can also enhance trust. Additionally, consider utilizing third-party quality assurance services to conduct inspections and verify samples before placing bulk orders. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also builds long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Scenario 2: Navigating Color and Texture Consistency
The Problem: Consistency in color and texture is a critical pain point for B2B buyers who need to ensure that the leather designer fabric matches their design specifications across different batches. Variability can occur due to differences in dye lots or manufacturing processes, leading to mismatched products that fail to meet client expectations. This inconsistency can disrupt production schedules and result in significant financial losses.
The Solution: Buyers should establish clear specifications regarding color and texture when placing orders. It is beneficial to request color samples or swatches before finalizing orders, as this allows for a visual comparison with existing products. Implementing a color-matching system based on industry standards, such as Pantone, can further ensure uniformity. Additionally, maintaining an ongoing relationship with suppliers to communicate any issues or concerns about product consistency can facilitate quick resolutions. Consider ordering in larger quantities to minimize the risk of variability from multiple batches and ensure that your supply remains consistent.
Scenario 3: Understanding Application Versatility of Leather Designer Fabrics
The Problem: B2B buyers often face uncertainty regarding the application versatility of leather designer fabrics. Whether for upholstery, fashion, or accessories, understanding the appropriate use cases for different types of leather can be complex. Buyers may inadvertently choose a fabric that is unsuitable for their intended use, resulting in product failures and negative customer feedback.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should invest time in researching the specific properties of various leather types, including durability, flexibility, and maintenance requirements. Engaging with suppliers who offer detailed product descriptions and application guidelines can be invaluable. Attending industry trade shows or workshops can also provide insights into the latest trends and innovative uses of leather fabrics. Furthermore, establishing a feedback loop with customers can help gather insights on how different fabrics perform in real-world applications, enabling better future sourcing decisions. By aligning material choices with practical applications, businesses can enhance product quality and customer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for leather designer fabric
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Leather Designer Fabric?
When selecting materials for leather designer fabric, understanding the properties of each option is crucial for ensuring optimal product performance. Here, we analyze four common materials: genuine leather, faux leather, suede, and synthetic leather. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its suitability for various applications.
Genuine Leather: What Are Its Key Properties and Considerations?
Genuine leather is renowned for its durability and luxurious feel. It can withstand high temperatures and pressure, making it suitable for upholstery and high-wear items. However, it is sensitive to moisture and requires regular maintenance to prevent drying or cracking.
Pros: Genuine leather offers exceptional durability and a classic aesthetic, making it ideal for high-end products. Its natural breathability also enhances comfort in applications like clothing and furniture.
Cons: The cost of genuine leather is relatively high compared to alternatives, which may limit its use in budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring skilled labor.
For international buyers, compliance with environmental and animal welfare standards is essential. Different regions have varying regulations regarding leather sourcing and treatment, which can impact sourcing decisions.
Faux Leather: How Does It Compare in Terms of Performance and Cost?
Faux leather, or synthetic leather, mimics the appearance of genuine leather while offering a more cost-effective solution. It is typically made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which provides good resistance to moisture and UV light.
Pros: Faux leather is more affordable and easier to clean than genuine leather. It is also vegan-friendly, appealing to a growing market segment that prioritizes ethical sourcing.
Cons: While faux leather is durable, it may not match the longevity of genuine leather, especially in high-stress applications. It can also be less breathable, which may affect comfort in clothing.
International buyers should consider the varying quality standards for faux leather. Compliance with regulations such as REACH in Europe, which restricts harmful substances in textiles, is crucial.
Suede: What Are the Unique Properties That Affect Its Use?
Suede, a type of leather with a napped finish, is known for its soft texture and luxurious appearance. It is less durable than full-grain leather and is sensitive to stains and moisture.
Pros: Suede provides a unique aesthetic that is highly desirable in fashion and interior design. Its softness makes it comfortable for clothing and accessories.
Cons: The main limitation of suede is its vulnerability to damage from water and stains, requiring special care and cleaning. This can increase maintenance costs for end-users.
For B2B buyers, understanding the market demand for suede in various regions is important. In humid climates, for example, the demand for suede may be lower due to its sensitivity to moisture.
Synthetic Leather: What Are Its Advantages and Disadvantages?
Synthetic leather, often made from a blend of materials, offers a versatile alternative to traditional leather. It can be engineered for specific applications, providing varying levels of durability and flexibility.
Pros: Synthetic leather can be produced in a wide range of colors and textures, making it highly customizable. It is also generally more affordable than genuine leather.
Cons: The environmental impact of synthetic leather production can be significant, particularly if not made from recycled materials. Additionally, some synthetic leathers may not perform as well under extreme conditions.
International buyers should be aware of the growing trend towards sustainable materials. Certifications such as Global Recycled Standard (GRS) can enhance marketability and compliance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Leather Designer Fabric
| المواد | Typical Use Case for leather designer fabric | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genuine Leather | High-end upholstery and fashion accessories | Exceptional durability and luxury | High cost and complex manufacturing | عالية |
| جلد صناعي | Affordable fashion items and upholstery | Cost-effective and easy to maintain | Less durable than genuine leather | Medium |
| Suede | Fashion apparel and luxury items | Unique aesthetic and softness | Vulnerable to stains and moisture | Medium |
| جلد صناعي | Versatile applications across industries | Customizable and affordable | Environmental concerns in production | منخفضة |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in leather designer fabric. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their market needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for leather designer fabric
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Leather Designer Fabric?
The manufacturing process for leather designer fabric is intricate, combining traditional craftsmanship with modern technology. This process can be broken down into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation
– The initial stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials. For genuine leather, this includes sourcing hides from animals like cows, goats, or exotic species. For faux leather, synthetic materials such as polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are chosen.
– The hides undergo a cleaning process to remove impurities and are then treated with preservatives to prevent decay. For faux leather, the synthetic base is prepared by blending polymers to achieve desired characteristics like durability and texture. -
Forming
– In this stage, the prepared materials are cut into specific shapes and sizes according to design specifications. Precision cutting machines are often employed to ensure accuracy.
– For leather, this might involve techniques such as die-cutting, where steel dies are used to create patterns. For faux leather, the material is typically rolled out and cut to size using automated systems. -
Assembly
– After forming, the pieces are stitched or bonded together. This can involve hand-sewing for high-end products or machine stitching for larger production runs.
– Adhesives are commonly used in faux leather applications to bond layers, ensuring a strong hold without the need for stitching. For leather, reinforced stitching is vital to enhance durability, particularly in items like bags or garments. -
Finishing
– The final stage includes applying treatments to enhance the fabric’s appearance and performance. This can involve dyeing, embossing, or applying protective coatings.
– Finishing touches such as polishing or buffing are also performed to achieve the desired aesthetic. Quality control checks are integral at this stage to ensure that the final product meets the specified standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Important for Leather Designer Fabric?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the production of leather designer fabric, ensuring that products meet both customer expectations and international standards. Two primary frameworks are often referenced in the industry: ISO 9001 and specific industry certifications like CE and API.
-
ISO 9001 Standards
– ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS). It emphasizes a process-oriented approach to enhance customer satisfaction through effective system implementation.
– Manufacturers of leather designer fabric should be ISO 9001 certified, indicating that they have robust processes for maintaining quality at every stage of production. -
Industry-Specific Certifications
– Certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) indicate compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, while API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply to synthetic materials derived from petrochemicals.
– These certifications assure B2B buyers that the products meet specific regulatory requirements relevant to their markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Leather Fabric Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is woven into the fabric of the manufacturing process, with several checkpoints established to ensure product integrity. Key QC checkpoints include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– IQC focuses on inspecting raw materials upon receipt. This includes evaluating the leather hides or synthetic materials for defects such as tears, discolorations, or inconsistencies.
– A comprehensive IQC process is crucial as it sets the foundation for quality throughout the production cycle. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– During the forming and assembly stages, IPQC checks are implemented to monitor adherence to design specifications and production processes.
– Regular inspections help identify defects early, enabling corrective actions before the final product is completed. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– FQC involves a thorough examination of the finished products. This includes checking for visual defects, measuring dimensions, and testing durability.
– Techniques such as tensile strength testing, colorfastness tests, and surface texture assessments are employed to ensure that the leather designer fabric meets required standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is essential. Here are actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Audits
– Regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. Buyers should look for transparency in operations and adherence to quality standards.
– Audits can be conducted by the buyer’s internal teams or third-party organizations specializing in quality assessments. -
Request Quality Control Reports
– Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their QC processes, including inspection results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These documents should outline methods used and any corrective actions taken for defects.
– Consistent reporting indicates a supplier’s commitment to quality and accountability. -
Third-Party Inspections
– Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality management practices. These inspections can be scheduled before shipment to ensure compliance with agreed-upon standards.
– This step is particularly valuable for international buyers, as it mitigates risks associated with cross-border transactions.
What Are the Common Testing Methods for Leather Designer Fabric?
Testing methods for leather designer fabric are essential to validate performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Common testing methods include:
-
Tensile Strength Testing
– This test measures the fabric’s ability to withstand pulling forces without breaking, ensuring that the leather or faux material can endure everyday use. -
Colorfastness Testing
– This involves exposing the fabric to various conditions such as light, water, and rubbing to evaluate how well the color holds up. High-quality leather fabrics should maintain their color over time. -
Abrasion Resistance Testing
– Abrasion tests assess how well the fabric can withstand wear and tear. This is particularly important for items like upholstery or garments that experience friction. -
Environmental Testing
– Evaluating the fabric’s performance under different environmental conditions (humidity, temperature) ensures that it meets the specific needs of the target market.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing leather designer fabric, ensuring they partner with suppliers who uphold the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘leather designer fabric’
مقدمة
Sourcing leather designer fabric is a critical process for B2B buyers seeking high-quality materials for their products. This guide provides a practical checklist to ensure you effectively navigate the procurement process, minimizing risks and maximizing value. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select the best suppliers and materials to meet your business needs.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin sourcing, clearly outline your technical requirements for leather designer fabric. This includes specifications like fabric type (genuine leather vs. faux leather), thickness, texture, and color. Having a well-defined set of criteria will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that the products you receive meet your quality expectations.
2. Conduct Market Research
Take the time to research the market landscape for leather designer fabrics. Identify key suppliers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding market trends and competitor offerings can provide insights into pricing, material availability, and innovative designs, enabling you to make informed sourcing decisions.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to assess their capabilities. Look for references from other businesses in your industry or region to gauge their reliability and quality. This step is crucial to ensuring that you partner with a reputable supplier who can deliver on your specifications.
4. Request Samples
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of their leather designer fabric. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the quality, feel, and durability of the materials firsthand. Pay attention to color consistency, texture, and any finishing details, as these factors can significantly affect the final product’s appearance and performance.
5. Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers adhere to industry standards and regulations. Verify their compliance with environmental regulations and labor practices, as well as any certifications relevant to your market (e.g., ISO, REACH). This step not only safeguards your brand’s reputation but also mitigates risks associated with unethical sourcing practices.
6. Negotiate Terms and Conditions
After selecting a supplier, engage in discussions to negotiate favorable terms and conditions. This includes pricing, minimum order quantities, lead times, and payment terms. Clearly outline expectations to avoid misunderstandings later. A well-negotiated agreement can lead to a more beneficial long-term relationship.
7. Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a robust quality control process to monitor the materials received from your supplier. Define inspection criteria and procedures to ensure that the leather designer fabric meets your established specifications. This step is vital for maintaining product quality and consistency, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for leather designer fabric, ensuring that they acquire high-quality materials while building strong relationships with reliable suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for leather designer fabric Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Leather Designer Fabric Sourcing?
When sourcing leather designer fabric, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of leather (genuine vs. faux), thickness, and finish significantly influence material costs. For instance, premium grades of cowhide or exotic leathers like crocodile can command higher prices compared to standard faux leather.
-
Labor: The production process for leather fabrics often involves skilled labor, particularly in cutting, stitching, and finishing. Labor costs can vary based on the region and the complexity of the design.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can mitigate overhead expenses, impacting overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom designs may require specific tooling or molds, which adds to the initial investment. This cost is typically amortized over the volume of products produced.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing strict quality control measures ensures that the leather meets the required standards. This process adds to the cost but is essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can significantly affect overall costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin varies based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Pricing Influencers Impact Leather Designer Fabric Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of leather designer fabrics, and being aware of these can aid in effective sourcing:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically qualify for volume discounts. Buyers should assess their needs against potential savings when negotiating.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom colors, patterns, or finishes can increase costs. Buyers should determine if these custom features are essential or if standard options suffice.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Fabrics that meet specific quality standards or certifications (e.g., eco-friendly, cruelty-free) may carry a premium price. Buyers should balance quality with budgetary constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their quality assurance and service levels.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) dictate responsibilities and costs, which can alter the total price.
What Buyer Tips Should Be Considered for Cost-Efficiency?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engaging in negotiations can yield better pricing. Buyers should be prepared with market knowledge and supplier comparisons to leverage discussions effectively.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider all costs associated with the fabric, including shipping, duties, and potential wastage. A lower purchase price might not always equate to overall savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Currency fluctuations can impact costs. Buyers should consider hedging strategies or fixed-price agreements to mitigate exchange rate risks.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into upcoming trends or materials.
الخاتمة
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for B2B buyers sourcing leather designer fabrics. By considering the key cost components, influencers, and strategic buyer tips, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their budget and quality requirements. Always keep in mind that prices are indicative and can vary based on market conditions and specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing leather designer fabric With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Leather Designer Fabric
In the realm of textile solutions, particularly for upholstery and fashion, leather designer fabric stands out for its luxurious appeal and durability. However, various alternatives can serve similar purposes, each with unique characteristics that might align better with specific business needs. This section explores viable alternatives, comparing them based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use case scenarios.
| Comparison Aspect | أقمشة مصممة جلدية مصممة | Faux Leather Fabric | Performance Fabrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability, luxurious feel | Moderate durability, less breathable | Excellent stain resistance, durable |
| Cost | Higher price point | Generally more affordable | Variable, can be high for premium brands |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized tools for sewing and bonding | Easy to cut and sew, versatile | Usually straightforward, but may need special care |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning | Easy to clean, water-resistant | Low maintenance, often machine washable |
| Best Use Case | High-end furniture, luxury fashion | Casual wear, accessories | Commercial upholstery, outdoor furniture |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Faux Leather Fabric?
Faux leather fabric, also known as synthetic leather, offers a cost-effective and ethical alternative to genuine leather. It is made from materials like polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), providing a similar aesthetic to leather without the associated costs and ethical concerns of animal products. The primary advantages include ease of maintenance, as it can be wiped clean with a damp cloth, and its resistance to water and stains. However, faux leather generally lacks the durability and breathability of genuine leather, making it less suitable for high-end applications.
How Do Performance Fabrics Compare to Leather Designer Fabric?
Performance fabrics are engineered materials designed to withstand the rigors of everyday use while maintaining their aesthetic appeal. They are often water-resistant, stain-resistant, and easy to clean, making them ideal for commercial applications such as office furniture, restaurants, and outdoor settings. The primary advantage of performance fabrics lies in their durability and low maintenance, which can translate into lower lifecycle costs. However, they may not offer the same luxurious feel and visual richness that leather designer fabric provides, which could be a significant consideration for high-end markets.
When Should a B2B Buyer Choose Leather Designer Fabric Over Alternatives?
Selecting the right fabric solution depends on various factors, including the intended application, budget constraints, and desired aesthetic. For businesses targeting luxury markets, leather designer fabric remains the gold standard, offering unmatched durability and a prestigious look. In contrast, faux leather might be a better fit for brands focusing on affordability and sustainability without compromising on style. Performance fabrics, while lacking the luxurious touch, provide an excellent option for high-traffic environments where durability and ease of maintenance are paramount.
In conclusion, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific needs against the characteristics of leather designer fabric and its alternatives. By considering performance, cost, and maintenance requirements, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their brand identity and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for leather designer fabric
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Leather Designer Fabric?
When sourcing leather designer fabric, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring product quality and suitability for specific applications. Here are several essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade indicates the quality and type of leather used in production. This classification often ranges from full-grain, which retains the natural grain and is the most durable, to bonded leather, which is made from leftover scraps. For B2B buyers, selecting the right grade is vital, as it affects durability, aesthetics, and the final cost of the product.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and physical properties of the fabric during manufacturing. This specification is particularly important in industries such as fashion and automotive, where precise measurements are critical. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers ensure that the fabric will meet their design specifications and manufacturing processes without compromising quality.
3. Colorfastness
Colorfastness is the resistance of fabric to fading or running when exposed to light or washing. This property is especially significant for leather used in upholstery or fashion, where color integrity is essential for branding and product longevity. Buyers should inquire about colorfastness ratings to ensure the material will maintain its appearance throughout its lifecycle.
4. Weight
The weight of leather fabric, typically measured in ounces per square yard, impacts its usability for various applications. Heavier weights are often preferred for items requiring durability, such as bags and jackets, while lighter weights may be suited for garments. Understanding the weight helps buyers select materials that align with their product requirements.
5. Finish
The finish of leather can vary widely, from matte to glossy, and can significantly affect the fabric’s look and feel. Different finishes also contribute to water resistance and overall durability. Buyers should consider the desired aesthetic and functionality when selecting leather finishes.
6. Stretch and Recovery
Stretch refers to the ability of the leather to expand and contract, while recovery indicates how well it returns to its original shape. This property is particularly relevant in fashion applications where movement is essential. Understanding the stretch and recovery characteristics can guide buyers in selecting fabrics that provide comfort and longevity in their designs.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies in the Leather Fabric Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations between buyers and suppliers. Here are some key terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the leather industry, this could involve a supplier creating leather products that are branded under a different company’s name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers navigate partnerships and sourcing strategies effectively.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it influences inventory management and cost-efficiency. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchases according to demand and production schedules.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This process allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple sources, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. Using RFQs can lead to better negotiations and pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including the shipping and delivery processes. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in global sourcing to mitigate risks and clarify obligations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its fulfillment. In the leather industry, understanding lead times is essential for production planning and inventory management. Buyers should consider lead times when placing orders to ensure timely delivery of their products.
By comprehending these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing leather designer fabric, ultimately enhancing their product offerings and business success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the leather designer fabric Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Leather Designer Fabric Market?
The leather designer fabric market is witnessing transformative changes driven by globalization, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The demand for luxury and designer-inspired faux leather fabrics is on the rise, fueled by the growing interest in sustainable and ethical fashion. This trend is particularly significant in markets like Brazil and Vietnam, where local craftsmanship is gaining recognition on the global stage.
Technological innovations, such as digital printing and automated cutting technologies, are enhancing the customization capabilities for designers, allowing for unique patterns and textures that appeal to contemporary consumers. Moreover, the integration of e-commerce platforms has simplified sourcing processes, enabling buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and products from different regions with ease. The rise of social media and influencer marketing is also reshaping how businesses connect with their target audiences, leading to greater demand for unique and high-quality leather materials.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Leather Designer Fabric Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal factor in the leather designer fabric sector, with growing awareness of environmental impacts influencing purchasing decisions. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt ethical sourcing practices, which not only mitigate ecological damage but also enhance brand reputation. The use of ‘green’ certifications and eco-friendly materials is becoming a standard expectation rather than an exception.
Materials such as recycled faux leather and naturally tanned leather are gaining traction. These options not only reduce waste but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Suppliers who invest in sustainable practices can differentiate themselves in a crowded market, offering products that align with the values of modern buyers. Additionally, transparency in supply chains is paramount; buyers are keen to understand the sourcing processes and the ethical standards maintained by their suppliers.
What Is the Historical Context of Leather Designer Fabrics for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of leather designer fabrics has its roots in traditional craftsmanship, where artisans meticulously crafted leather goods for luxury markets. Over the decades, the industry has shifted from purely natural leathers to include synthetic alternatives that mimic the look and feel of genuine leather while offering greater versatility and ease of maintenance. This transition has been particularly notable in response to rising ethical concerns regarding animal welfare and environmental sustainability.
In recent years, the introduction of advanced technologies has revolutionized the production processes, enabling greater efficiency and customization. As a result, today’s buyers have access to a diverse array of materials that cater to various aesthetic preferences and functional requirements, making the leather designer fabric market more dynamic than ever. Understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to navigate the complexities of sourcing in this evolving landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of leather designer fabric
-
1. How do I choose the right leather designer fabric for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate leather designer fabric involves understanding your target market and the specific applications of the fabric. Consider factors such as durability, texture, and aesthetic appeal. For upholstery, ensure the fabric meets performance standards for wear and tear, while for fashion, prioritize trends and color palettes. Additionally, review the supplier’s swatch samples to assess quality firsthand. Collaborating with a supplier that offers customization options can also enhance your product offerings to meet unique customer demands. -
2. What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of leather designer fabric?
When evaluating suppliers, prioritize their industry reputation, product quality, and compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients and assess their customer service responsiveness. It’s also vital to evaluate their production capabilities, including lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs). Conducting factory visits, if possible, will give you insight into their operational practices. Lastly, ensure they have robust quality assurance processes in place to maintain high standards throughout production. -
3. What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for leather designer fabric?
MOQs can vary widely based on the supplier and the type of leather fabric. Typically, MOQs range from 10 to 50 yards for standard materials, while custom-designed fabrics may have higher requirements. It’s advisable to confirm these details upfront to avoid unexpected costs. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for repeat orders or long-term partnerships, so negotiating terms that suit your business needs is essential. -
4. How can I ensure the quality of leather designer fabric before making a bulk purchase?
To ensure quality, request samples from suppliers before committing to a bulk order. Evaluate these samples for texture, durability, and color accuracy. Additionally, inquire about the fabric’s specifications, including weight, finish, and care instructions. Implementing a quality assurance protocol that includes regular inspections during the production process can also help mitigate risks associated with bulk purchases. -
5. What are the payment terms typically offered by suppliers of leather designer fabric?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50%) and the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established businesses, while others may require full payment in advance for first-time orders. It’s crucial to clarify these terms and ensure they align with your cash flow management practices before proceeding with an order. -
6. How do I handle international shipping logistics for leather designer fabric?
Managing international shipping logistics involves coordinating with your supplier to understand shipping options, costs, and delivery times. Partner with a reliable freight forwarder who specializes in fabric shipments to navigate customs regulations and documentation. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary paperwork, such as invoices and certificates of origin. Additionally, consider insurance options to protect your investment during transit. -
7. What customization options are typically available for leather designer fabric?
Many suppliers offer customization options, such as color matching, texture variations, and pattern designs. You may also inquire about the possibility of branding or embossing the fabric for a unique touch. Discuss your specific requirements with the supplier to understand their capabilities and limitations. Custom orders may require longer lead times, so plan accordingly to meet your production schedules. -
8. How can I stay updated on trends in leather designer fabric for my target market?
To keep abreast of trends, regularly review industry publications, attend trade shows, and participate in online forums related to fabric design and fashion. Engaging with designers and other industry professionals can provide valuable insights into emerging styles and consumer preferences. Following influential brands and designers on social media can also help you identify trends that resonate with your target market, enabling you to adapt your offerings accordingly.
Top 4 Leather Designer Fabric Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. American Leather – Fabric Swatches
Domain: americanleather.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
مقدمة: Explore a wide selection of fabrics and order swatches from American Leather. The fabrics are designed to complement various furniture styles, offering rich textures and saturated colors. Key brands include Sunbrella, Ultrasuede, and Crypton. The collection features various colors (e.g., Beige, Black, Blue, Brown, etc.), performance brands (e.g., Crypton, InsideOut, Sunbrella), and fabric types (e…
2. Mood Fabrics – Genuine Leather by the Yard
Domain: moodfabrics.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
مقدمة: Buy Leather Fabric by the Yard | Genuine Leather Material
3. Designers Guild – Faux Leather & Suede Collections
Domain: designersguild.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
مقدمة: This company, Designers Guild – Faux Leather & Suede Collections, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Ceys Leather Fabric – Luxury LV Leather
Domain: ceysleatherfabric.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
مقدمة: High quality LV leather fabric, designer leather, luxury leather, leather fabric. Price: $5.00 (originally $9.00). Rating: 4.45 based on 11 reviews. Available sizes: A4 Sample (20cm*30cm), Half Yard, 1 Yard, 2 Yard, 3 Yard, 4 Yard, 5 Yard, 10 Yard. Width: 140cm (55″). Free shipping on orders over $180; $20 shipping fee for orders below $180. 30-day return or refund guarantee. Contact via Instagram…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for leather designer fabric
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Leather Designer Fabric Procurement?
In the dynamic landscape of leather designer fabric sourcing, strategic partnerships and informed decisions are crucial for international B2B buyers. Key takeaways highlight the importance of understanding market trends, material quality, and supplier reliability. By leveraging high-quality materials, such as luxury faux leather and genuine leather options, businesses can not only enhance their product offerings but also meet diverse consumer demands across regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Investing in strategic sourcing not only minimizes risks but also fosters sustainable practices that resonate with today’s environmentally conscious consumers. As the demand for unique and high-performance fabrics continues to rise, buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer a wide range of options, including innovative designs and textures, to stay competitive.
Looking ahead, the leather designer fabric market presents significant opportunities for growth. B2B buyers are encouraged to explore new partnerships and stay informed about emerging trends to capitalize on this potential. Embrace the future of sourcing by prioritizing collaboration and quality in your procurement strategy, ensuring your business stands out in a competitive marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.